Responses of Macrobenthic Communities to Heavy Metal Contamination in Sediments and Seawater: A Case Study in Temperate Bay, South Korea
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling Collection
2.3. Sample Analysis
2.3.1. Heavy Metal Analysis
2.3.2. Nutrient and Oxygen Demand Analysis
2.3.3. Suspended Solids and Organic Matter Analysis
2.3.4. Particle Size Analysis
2.3.5. Macrobenthic Identification
2.3.6. Quality Control
2.4. Data Analysis
2.4.1. Dominance and Diversity Indices
2.4.2. Analysis of Community Structure
2.4.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Environment Data Characteristics
3.2. Macrobenthic Composition and Community Structure
3.3. Results of Diversity Indices
3.4. Relationship Between Macrobenthos and Environmental Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Heavy Metal Characteristics and Sources in Asan Bay
| Study Area | As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Pb | Zn | Hg | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asan Bay | 0.13–0.89 (0.33) | 0.13–0.44 (0.27) | 0.05–0.68 (0.25) | 0.36–4.30 (1.76) | 0.16–1.94 (0.60) | 0.76–6.46 (2.86) | 0–0.01 (0.002) | This study |
| Jindo Island | 0.040–0.200 (0.090) | 0.004–0.070 (0.040) | 0.020–0.160 (0.080) | 0.120–0.500 (0.270) | 0.010–0.070 (0.030) | 0.120–0.570 (0.340) | NA | [37] |
| Jeju Island | 0.020–0.050 (0.030) | 0.001–0.050 (0.020) | 0.010–0.120 (0.040) | 0–0.170 (0.100) | 0.009–0.030 (0.020) | 0.090–0.450 (0.260) | NA | [37] |
| Gyeonggi Bay, Korea | NA | 0.037–0.073 (0.048) | NA | 0.460–1.020 (0.610) | 0.010–0.035 (0.020) | 0.140–1.190 (0.360) | NA | [31] |
| Masan Bay, Korea | NA | 0.007–0.027 (0.015) | NA | 0.420–1.010 (0.660) | 0.003–0.053 (0.012) | 0.250–3.700 (1.420) | NA | [38] |
| Korea marine seawater quality standard | 3.4 | 1.6 | 2.8 | 1.2 | 1.6 | 11 | 1.0 | [39] |
| Study Area | As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Pb | Zn | Hg | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asan Bay | 0.13–0.64 (0.35) | 0.47–0.98 (0.71) | 2.03–22.82 (11.39) | 5.01–13.54 (9.02) | 12.47–33.20 (21.71) | 18.48–65.07 (46.12) | 0–0.01 (0.003) | This study |
| East Sea of Korea | 1.91–6.14 (3.35) | 0.04–0.33 (0.124) | 8.71–66.98 (43.7) | 1.83–32.56 (16.6) | 9.79–32.27 (20.48) | 11.27–109.31 (65.9) | 0.01–0.06 (0.022) | [40] |
| South Sea of Korea | NA | NA | 6.80–165 (67.8) | 4.7–100.4 (21.9) | 11.5–91.4 (31.6) | 22–312 (109) | NA | [41] |
| Dangdong Bay, Korea | 0.30–0.70 (0.48) | 1.40–3.30 (2.56) | NA | 13.90–22.50 (17.17) | 35.80–60.00 (50.06) | 67.90–84.90 (76.10) | NA | [22] |
| Threshold Effect Level | 14.50 | 0.75 | 116 | 20.6 | 44.00 | 64.40 | 0.11 | [39] |
| Probable Effect Level | 75.5 | 2.72 | 181 | 64.4 | 119 | 157 | 0.62 | [39] |
4.2. Macrobenthic Community in Asan Bay
4.3. Influence of Heavy Metals on Macrobenthic Community
4.4. Management Recommendations for Protecting the Bay
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barbier, E.B.; Hacker, S.D.; Kennedy, C.; Koch, E.W.; Stier, A.C.; Silliman, B.R. The Value of Estuarine and Coastal Ecosystem Services. Ecol. Monogr. 2011, 81, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, F.; Yu, H.; Li, Y. From Shoreline to Sea: Evaluating Development Suitability Through Coastal Zoning and a Case Study from Shenzhen, China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.T.; Rahman, M.M.; Bhuiyan, T.; Jolly, Y.N.; Akter, S.; Yu, J.; Arai, T.; Paray, B.A.; Hossain, M.B. Holistic Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination in Coastal Zones under Diverse Anthropogenic Pressures in a Developing Nation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 116288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elayaperumal, V.; Hermes, R.; Brown, D. An Ecosystem Based Approach to the Assessment and Governance of the Bay of Bengal Large Marine Ecosystem. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2019, 163, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, T.; Wang, J.; Fang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Huang, L.; Chen, Y. Assessing Ecological Risks Caused by Human Activities in Rapid Urbanization Coastal Areas: Towards an Integrated Approach to Determining Key Areas of Terrestrial-Oceanic Ecosystems Preservation and Restoration. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 135153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekovski, I.; Newton, A.; Dennison, W.C. Megacities in the Coastal Zone: Using a Driver-Pressure-State-Impact-Response Framework to Address Complex Environmental Problems. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 96, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, M.; Day, J.W.; Ramachandran, R.; Wolanski, E. A Synthesis: What Is the Future for Coasts, Estuaries, Deltas and Other Transitional Habitats in 2050 and Beyond? In Coasts and Estuaries; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 1–28. ISBN 978-0-12-814003-1. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Dong, J.; Gao, L.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X. Macrobenthos Functional Trait Responses to Heavy Metal Pollution Gradients in a Temperate Lagoon. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 253, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edo, G.I.; Samuel, P.O.; Oloni, G.O.; Ezekiel, G.O.; Ikpekoro, V.O.; Obasohan, P.; Ongulu, J.; Otunuya, C.F.; Opiti, A.R.; Ajakaye, R.S.; et al. Environmental Persistence, Bioaccumulation, and Ecotoxicology of Heavy Metals. Chem. Ecol. 2024, 40, 322–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E.; Ilahi, I. Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology of Hazardous Heavy Metals: Environmental Persistence, Toxicity, and Bioaccumulation. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 6730305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinna, M.; Marini, G.; Rosati, I.; Neto, J.M.; Patrício, J.; Marques, J.C.; Basset, A. The Usefulness of Large Body-Size Macroinvertebrates in the Rapid Ecological Assessment of Mediterranean Lagoons. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 29, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.J.K.; John, A.; Aqilah, N.S.; Abdullah, R.; Salihah, N.T.; Basir, K.H.; Marsal, C.J. Macrobenthic Community towards Sustainable Aquatic Ecosystem: A Systematic Review along the Coastal Waters of Malaysia. Geol. Ecol. Landsc. 2024, 8, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari Noghabi, N.; Shojaei, M.G.; Farahani, M.M.; Weigt, M. Stable Isotopes Reveal the Food Sources of Benthic Macroinvertebrates in the Arid Mangrove Ecosystem of the Persian Gulf. Estuaries Coasts 2022, 45, 2241–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, V.; Jha, D.K.; Kumar, P.S.; Santhanakumar, J.; Venkatnarayanan, S.; Prince Prakash Jebakumar, J.; Dharani, G. Effect of Multiple Stressors on the Functional Traits of Sub-Tidal Macrobenthic Fauna: A Case Study of the Southeast Coast of India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 175, 113355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Huang, Y.; Wang, W.; Mou, J.; Lin, J.; Zhang, S.; Lin, L.; Sun, J.; Gao, Z.; Lin, H.; et al. Multiple Environmental Gradients Shape the Functional Structure of Macrobenthic Communities across the Pacific Arctic Shelf. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 953, 176055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adesakin, T.A.; Erhomosele, E.I.; Ogunrinola, O.F.; Oloyede, O.O.; Adedeji, A.A.; Odufuwa, P.T.; Aimienoho, A.; Aduwo, A.I.; Adewumi, E.A. Using Benthic Macroinvertebrates as Bioindicators to Evaluate the Impact of Anthropogenic Stressors on Water Quality and Sediment Properties of a West African Lagoon. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah Al, M.; Akhtar, A.; Kamal, A.H.M.; AftabUddin, S.; Islam, M.S.; Sharifuzzaman, S. Assessment of Benthic Macroinvertebrates as Potential Bioindicators of Anthropogenic Disturbance in Southeast Bangladesh Coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 184, 114217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zou, X.; Feng, Z.; Hao, Z.; Gao, J. Distribution and Transport of Heavy Metals in Estuarine–Inner Shelf Regions of the East China Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.-Y.; Zhao, L.; Sun, X.; Hu, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.-T.; Zhang, P.-D.; Zhang, X. Response of Macrobenthic Communities to Heavy Metal Pollution in Laoshan Bay, China: A Trait-Based Method. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 167, 112292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piló, D.; Ben-Hamadou, R.; Pereira, F.; Carriço, A.; Pereira, P.; Corzo, A.; Gaspar, M.B.; Carvalho, S. How Functional Traits of Estuarine Macrobenthic Assemblages Respond to Metal Contamination? Ecol. Indic. 2016, 71, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Song, J.; Li, X. Evaluation of Potential Relationships between Benthic Community Structure and Toxic Metals in Laizhou Bay. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 87, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Ma, C.-W.; Kim, K.-B. Comparing the Environmental Impacts of Pollution from Two Types of Industrial Zones on the Coast. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1433536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.A.; Johnston, E.L.; Poore, A.G.B. Contamination of Marine Biogenic Habitats and Effects upon Associated Epifauna. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 56, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukunaga, A.; Anderson, M.; Webster-Brown, J.; Ford, R. Individual and Combined Effects of Heavy Metals on Estuarine Infaunal Communities. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2010, 402, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fichet, D.; Boucher, G.; Radenac, G.; Miramand, P. Concentration and Mobilisation of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn by Meiofauna Populations Living in Harbour Sediment: Their Role in the Heavy Metal Flux from Sediment to Food Web. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 243–244, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-B.; Jung, Y.-J.; Oh, J.-K.; Kang, H.; Son, D.-S.; Ma, C.-W. Macrobenthic Community and Benthic Health Assessment of Central Area in Asan Bay. J. Fish. Mar. Sci. Educ. 2021, 33, 903–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute of Fisheries Science. National Institute of Fisheries Science Notification of Marine Environmental Process Test Standards 2010; National Institute of Fisheries Science: Busan, Republic of Korea, 2010; Available online: https://www.nifs.go.kr/board/actionBoard0052List.do?BBS_CL_CD=ALL (accessed on 19 November 2023).
- Xu, Z.; Chen, Y. Aggregated Intensity of Dominant Species of Zooplankton in Autumn in the East China Sea and Yellow Sea. Chin. J. Ecol. 1989, 4, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, Z.; Singh, V.P. The Relative Impact of Toxic Heavy Metals (THMs) (Arsenic (As), Cadmium (Cd), Chromium (Cr)(VI), Mercury (Hg), and Lead (Pb)) on the Total Environment: An Overview. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, D.; Maiti, S.K. Sources, Bioaccumulation, Health Risks and Remediation of Potentially Toxic Metal(Loid)s (As, Cd, Cr, Pb and Hg): An Epitomised Review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Choi, M.; Jang, D.; Joe, D.; Park, K.; Lee, H.; Woo, J.; Kim, T.; Park, J. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Dissolved Heavy Metals in Gyeonggi Bay, Korea. Ocean Sci. J. 2020, 55, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Zeng, Y.-Y.; Liu, L.-M.; Yin, L.; Xu, K.-P.; Chen, W.-F.; Li, S.-C.; Zhou, X.-F. Pollution Status and Assessment of Seven Heavy Metals in the Seawater and Sediments of Hangzhou Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 209, 117261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Liu, C.; Tan, X.; You, X.; Dai, C.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Li, N. Heavy Metal Transport Driven by Seawater-Freshwater Interface Dynamics: The Role of Colloid Mobilization and Aquifer Pore Structure Change. Water Res. 2022, 217, 118370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, T.-J.; Jeong, M.-H.; Jeon, J.-M.; Son, B.-S. A Study on the Concentration of Fine Particles and Heavy Metals in Iron Works. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 18, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, H.; Sun, R.; Cui, M.; Sun, N.; Zhang, S. Evaluation and Analysis of Heavy Metals in Iron and Steel Industrial Area. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 24, 10997–11010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, X.; Yutong, Z.; Shenggao, L. Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution and Human Health Risk in Urban Soils of Steel Industrial City (Anshan), Liaoning, Northeast China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 120, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Ma, C.; Kim, K. Differences in Subtidal Macrobenthic Community Structures and Influencing Factors Between Jindo and Jeju Islands in South Korea. Ecol. Evol. 2025, 15, e70990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Choi, M.; Jang, D.; Joe, D.; Park, K. Distribution and Sources of Dissolved and Particulate Heavy Metals (Mn, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Cd, Pb) in Masan Bay, Korea. Ocean Sci. J. 2020, 55, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries. Korea Marine Seawater Quality Standard. 2018. Available online: https://www.mof.go.kr/en/index.do (accessed on 19 November 2023).
- Liang, J.; Ma, C.-W.; Son, D.-S. Using the Heavy Metal and Biotic Indices to Assess Ecological Quality in the Central Area of the East Sea, South Korea. Water 2024, 16, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Choi, M.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Jang, D.J. Regional Background Concentrations of Heavy Metals (Cr, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Pb) in Coastal Sediments of the South Sea of Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 482–483, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Ma, C.-W.; Kim, K.-B.; Son, D.-S. Can the Ecological Quality of Several Bays in South Korea Be Accurately Assessed Using Multiple Benthic Biotic Indices? J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Huang, H.-R.; Ma, C.-W.; Son, D.-S.; Kim, S.-K. Using the Heavy Metal Indices and Benthic Indices to Assess the Ecological Quality in the Tidal Flats of Garolim Bay, South Korea. Water 2024, 16, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Huang, H.-R.; Shu, M.-Y.; Ma, C.-W. Assessing the Impact of Land-Based Anthropogenic Activities on the Macrobenthic Community in the Intertidal Zones of Anmyeon Island, South Korea. Land 2025, 14, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauran, A.; Lavesque, N.; Blanchet, H.; Bujan, V.; Gouillieux, B.; Humbert, S.; Lamarque, B.; Latry, L.; De Montaudouin, X. Long-Term Impact of Dredging and Beach Nourishment Works on Benthic Communities. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2025, 313, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OSPAR Commission. Literature Review on the Impacts of Dredged Sediment Disposal at Sea; OSPAR Commission: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, J.S.; Kvitek, R.G.; Slattery, P.N. Walrus Feeding Disturbance: Scavenging Habits and Recolonization of the Bering Sea Benthos. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1985, 91, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deheyn, D.; Jangoux, M.; Warnau, M. Alteration of Bioluminescence in Amphipholis Squamata (Ophiuroidea: Echinodermata) by Heavy Metals Contamination: A Field Study. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 247, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiard, J.-C.; Geffard, A.; Amiard-Triquet, C.; Crouzet, C. Relationship between the Lability of Sediment-Bound Metals (Cd, Cu, Zn) and Their Bioaccumulation in Benthic Invertebrates. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 72, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Feng, J. Assessment of the Transfer of Heavy Metals in Seawater, Sediment, Biota Samples and Determination the Baseline Tissue Concentrations of Metals in Marine Organisms. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 28764–28776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanasekaran, S.; Amal Raj, S. Heavy Metal Bioaccumulation in Sediment and Benthic Biota. In Heavy Metals—Recent Advances; A. Almayyahi, B., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2023; ISBN 978-1-83768-514-1. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Yu, Z.; Zeng, G.; Jiang, M.; Yang, Z.; Cui, F.; Zhu, M.; Shen, L.; Hu, L. Effects of Sediment Geochemical Properties on Heavy Metal Bioavailability. Environ. Int. 2014, 73, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser-Davis, R.A.; Wosnick, N. Climate Change Implications for Metal and Metalloid Dynamics in Aquatic Ecosystems and Its Context within the Decade of Ocean Sciences. Water 2022, 14, 2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorny, J.; Billon, G.; Noiriel, C.; Dumoulin, D.; Lesven, L.; Madé, B. Chromium Behavior in Aquatic Environments: A Review. Environ. Rev. 2016, 24, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oana, P.M. Chromium Impact on Marine Ecosystem. Bull. Univ. Agric. Sci. Vet. Med. CLUJ-NAPOCA 2006, 63, 379–387. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.; Singh, S.P.; Parakh, S.K.; Tong, Y.W. Health Hazards of Hexavalent Chromium (Cr (VI)) and Its Microbial Reduction. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 4923–4938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, N.; Sharma, P.; Verma, S. Microbial Remediation of Hexavalent Chromium from the Contaminated Soils. In Microbes and Microbial Biotechnology for Green Remediation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 527–546. ISBN 978-0-323-90452-0. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, V.; Singh, N.; Verma, M.; Kamal, R.; Tiwari, R.; Sanjay Chivate, M.; Rai, S.N.; Kumar, A.; Singh, A.; Singh, M.P.; et al. Hexavalent-Chromium-Induced Oxidative Stress and the Protective Role of Antioxidants against Cellular Toxicity. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, F.C.; Bourg, A.C.M. Aqueous Geochemistry of Chromium: A Review. Water Res. 1991, 25, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, C.K.; Al-Mutairi, K.A. Depuration Kinetics of Potentially Toxic Metals (Hg, Co and Cr) in Perna Viridis: Implications for Biomonitoring, Environmental Management, and Planetary Health. J. Fish. 2024, 13, 131202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Khim, J.S.; Kang, S.-G.; Kang, D.; Lee, C.; Koh, C. The Impact of Heavy Metal Pollution Gradients in Sediments on Benthic Macrofauna at Population and Community Levels. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2622–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauvin, J.-C. Effects of Heavy Metal Contamination on the Macrobenthic Fauna in Estuaries: The Case of the Seine Estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 57, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S. Assessment of Coastal Zone Issues in the Republic of Korea. Coast. Manag. 1991, 19, 391–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.O.; Olsen, S.B. The Status and Prospects for Coastal Management in Korea. Coast. Manag. 2003, 31, 99–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

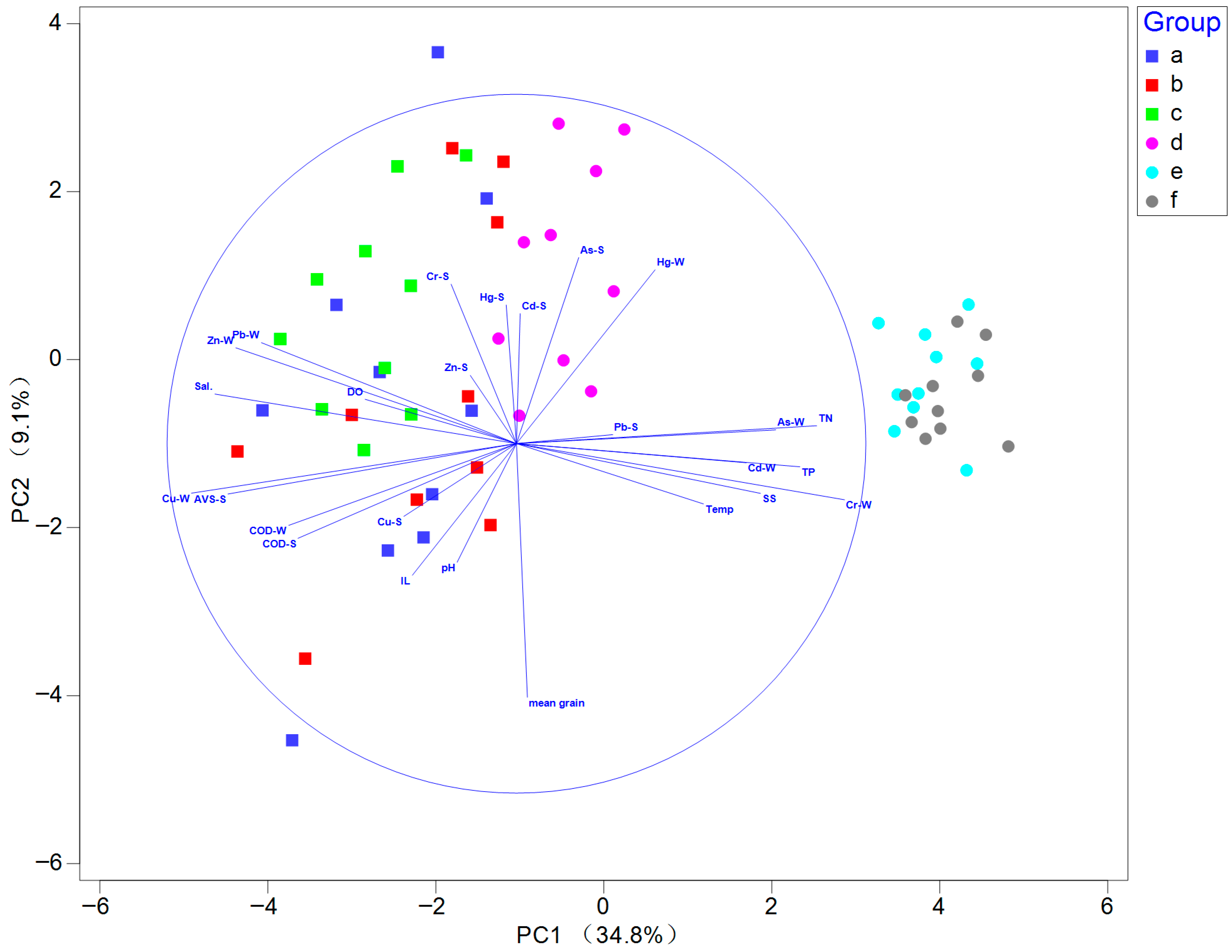

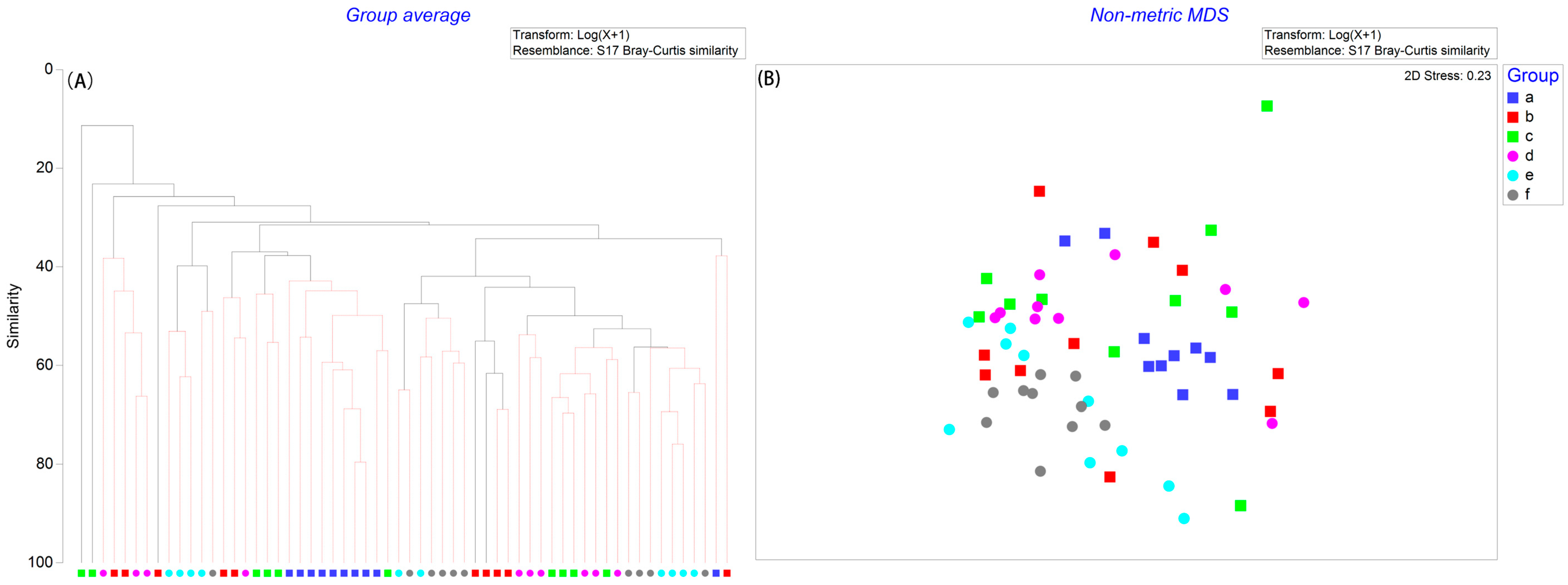
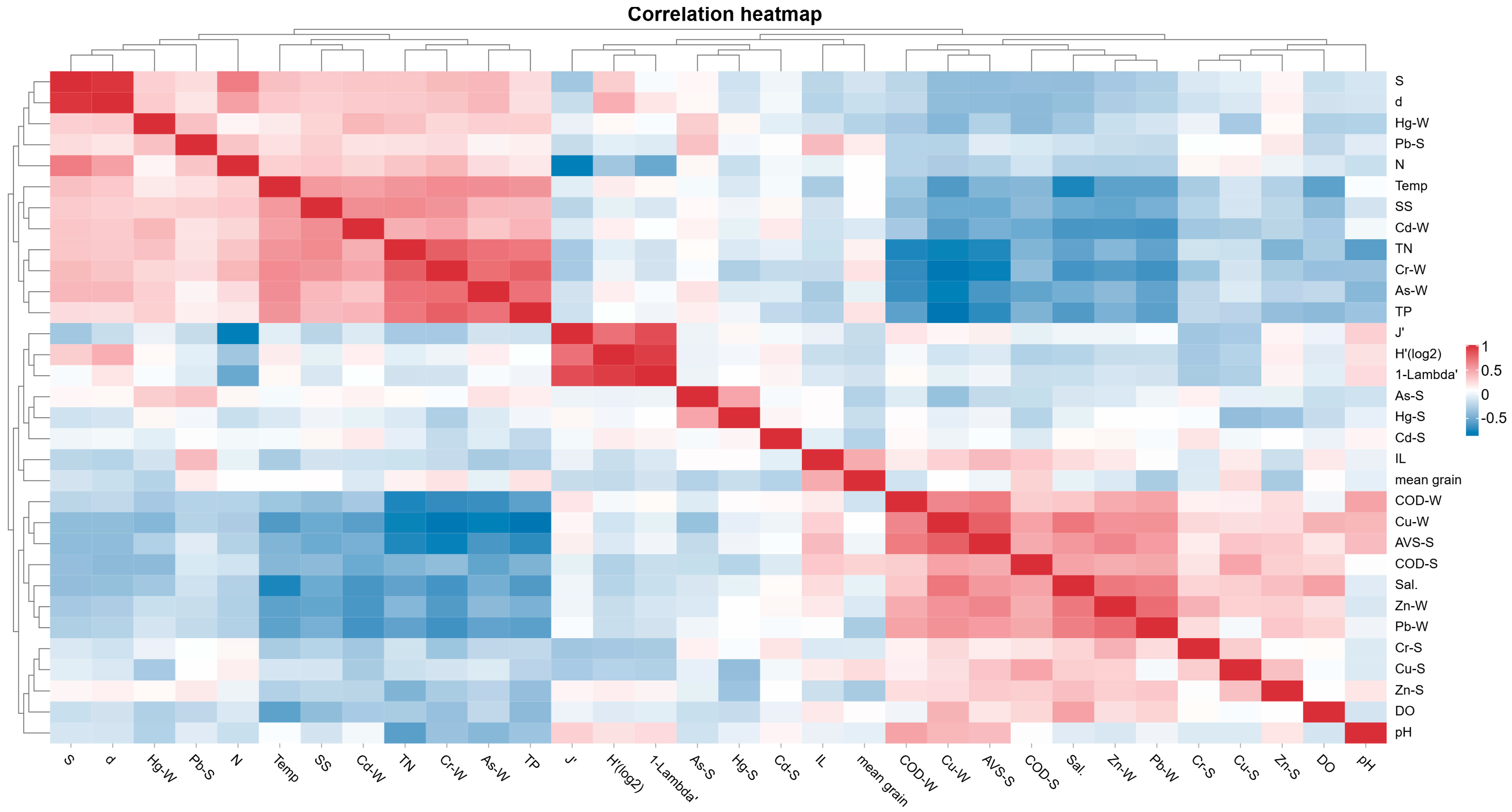
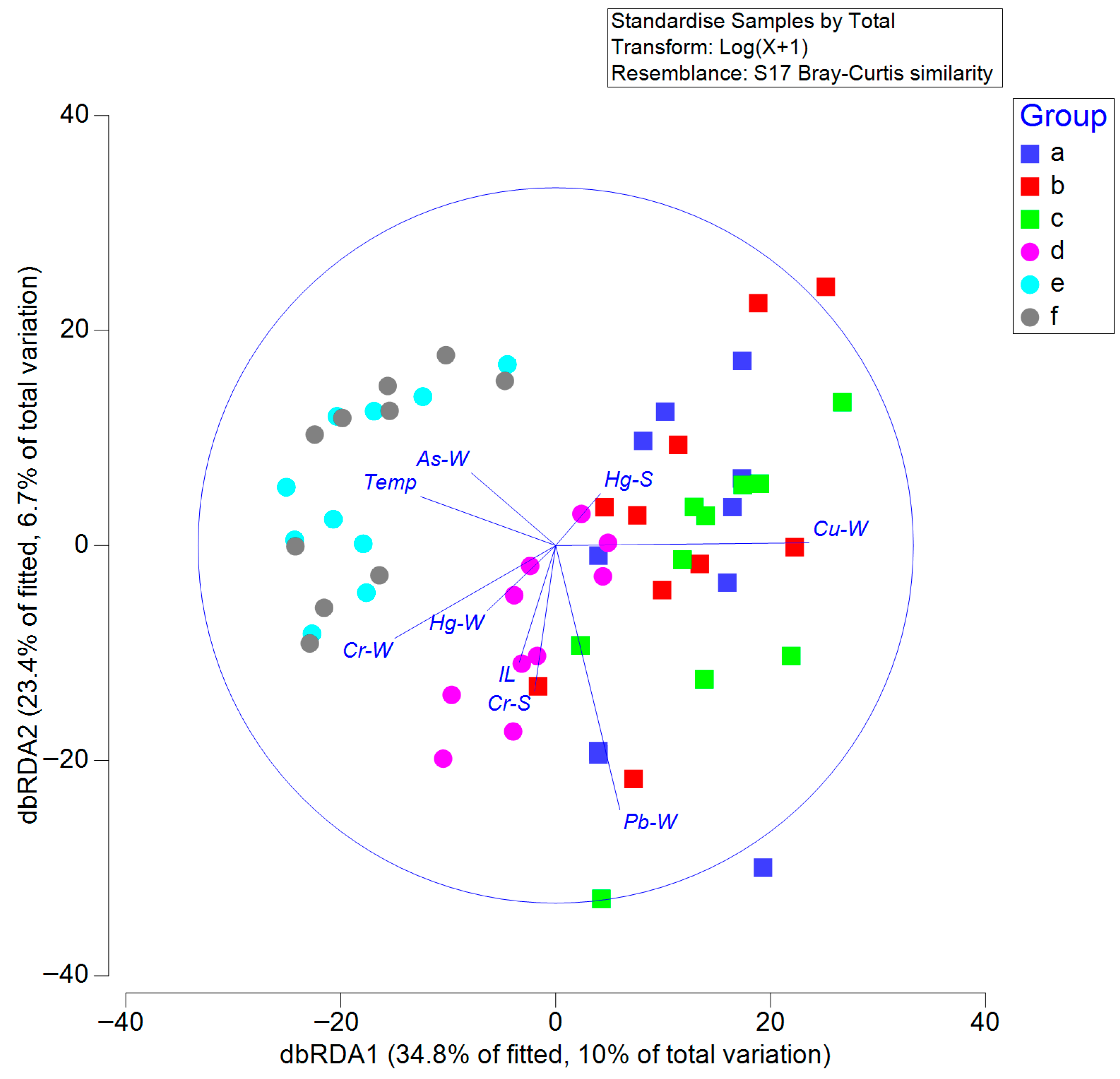

| Environment Data | Range (Min–Max) | Mean ± SD | CV |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seawater temperature, °C | 1.30–26.20 | 18.18 ± 8.56 | 0.47 |
| Salinity, PSU | 27.65–30.50 | 29.26 ± 0.94 | 0.03 |
| pH | 7.77–8.14 | 8.01 ± 0.09 | 0.01 |
| DO, mg/L | 6.92–12.95 | 8.36 ± 1.67 | 0.20 |
| COD, mg/L | 1.20–2.43 | 1.55 ± 0.31 | 0.20 |
| Total Nitrogen, mg/L | 0.44–1.42 | 0.91 ± 0.33 | 0.36 |
| Total Phosphorus, mg/L | 0.03–0.09 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 0.25 |
| Suspended Solids, mg/L | 10.40–36.60 | 19.99 ± 5.49 | 0.27 |
| As, μg/L | 0.13–0.89 | 0.33 ± 0.17 | 0.51 |
| Cd, μg/L | 0.13–0.44 | 0.27 ± 0.08 | 0.29 |
| Cr, μg/L | 0.05–0.68 | 0.25 ± 0.20 | 0.80 |
| Cu, μg/L | 0.36–4.30 | 1.76 ± 1.17 | 0.67 |
| Pb, μg/L | 0.16–1.94 | 0.60 ± 0.35 | 0.59 |
| Zn, μg/L | 0.76–6.46 | 2.86 ± 1.55 | 0.54 |
| Hg, μg/L | 0–0.01 | 0.002 ± 0 | 0.66 |
| Environment Data | Range (Min–Max) | Mean ± SD | CV |
|---|---|---|---|
| AVS, mg/g | 0.02–0.12 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 0.35 |
| COD, mg/kg | 2.37–14.00 | 5.54 ± 2.51 | 0.45 |
| IL, % | 1.55–8.14 | 3.92 ± 1.67 | 0.43 |
| Mean grain size, | 2.30–8.10 | 5.01 ± 1.77 | 0.35 |
| As, mg/kg | 0.13–0.64 | 0.35 ± 0.12 | 0.35 |
| Cd, mg/kg | 0.47–0.98 | 0.71 ± 0.11 | 0.15 |
| Cr, mg/kg | 2.03–22.82 | 11.39 ± 4.31 | 0.38 |
| Cu, mg/kg | 5.01–13.54 | 9.02 ± 2.04 | 0.23 |
| Pb, mg/kg | 12.47–33.20 | 21.71 ± 4.83 | 0.22 |
| Zn, mg/kg | 18.48–65.07 | 46.12 ± 10.37 | 0.22 |
| Hg, mg/kg | 0–0.01 | 0.003 ± 0 | 0.38 |
| Taxa | Specie | Dominant Value |
|---|---|---|
| Echinodermata | Amphiodia craterodmeta | 0.20 |
| Annelida | Heteromastus filiformis | 0.17 |
| Annelida | Ampharete finmarchica | 0.10 |
| Arthropoda | Corophium sp. | 0.03 |
| Environment Data | Pseudo -F | P | Proportion of Variation Explained |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seawater temperature, °C | 3.17 | 0.002 | 0.05 |
| As in seawater, μg/L | 4.04 | 0.001 | 0.07 |
| Cr in seawater, μg/L | 5.33 | 0.001 | 0.07 |
| Cu in seawater, μg/L | 5.35 | 0.001 | 0.08 |
| Pb in seawater, μg/L | 4.20 | 0.001 | 0.07 |
| Hg in seawater, μg/L | 2.41 | 0.006 | 0.04 |
| Ignition loss, % | 0.69 | 0.780 | 0.01 |
| Cr in sediment, mg/kg | 1.25 | 0.205 | 0.02 |
| Hg in sediment, mg/kg | 1.63 | 0.067 | 0.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, J.; Choi, S.-H.; Ma, C.-W. Responses of Macrobenthic Communities to Heavy Metal Contamination in Sediments and Seawater: A Case Study in Temperate Bay, South Korea. Biology 2025, 14, 1276. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091276
Liang J, Choi S-H, Ma C-W. Responses of Macrobenthic Communities to Heavy Metal Contamination in Sediments and Seawater: A Case Study in Temperate Bay, South Korea. Biology. 2025; 14(9):1276. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091276
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Jian, Se-Hyun Choi, and Chae-Woo Ma. 2025. "Responses of Macrobenthic Communities to Heavy Metal Contamination in Sediments and Seawater: A Case Study in Temperate Bay, South Korea" Biology 14, no. 9: 1276. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091276
APA StyleLiang, J., Choi, S.-H., & Ma, C.-W. (2025). Responses of Macrobenthic Communities to Heavy Metal Contamination in Sediments and Seawater: A Case Study in Temperate Bay, South Korea. Biology, 14(9), 1276. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091276








