The Nuclear Ribosomal Transcription Units of Two Echinostomes and Their Taxonomic Implications for the Family Echinostomatidae
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Trematodes Collection and Species Identifcation
2.2. Primers and Amplifcation
2.3. Sequence Analysis and Annotation of the Ribosomal Transcription Units
2.4. Ribosomal Phylogenetic Analyses and Tree Reconstruction
3. Results
3.1. Species Identifcation of E. miyagawai and P. bilobus
3.2. Ribosomal Transcription Unit Features of the E. miyagawai and P. bilobus
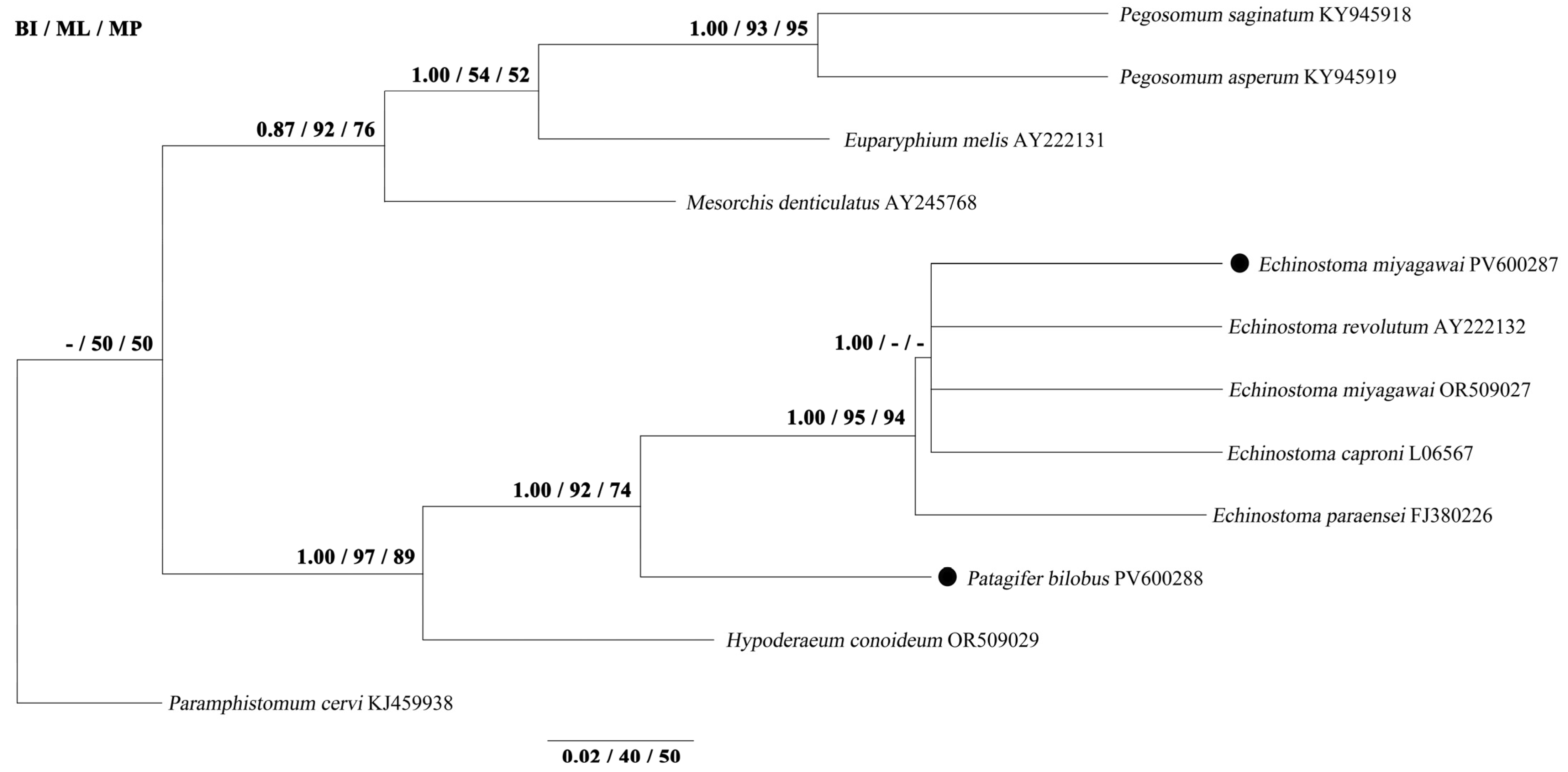
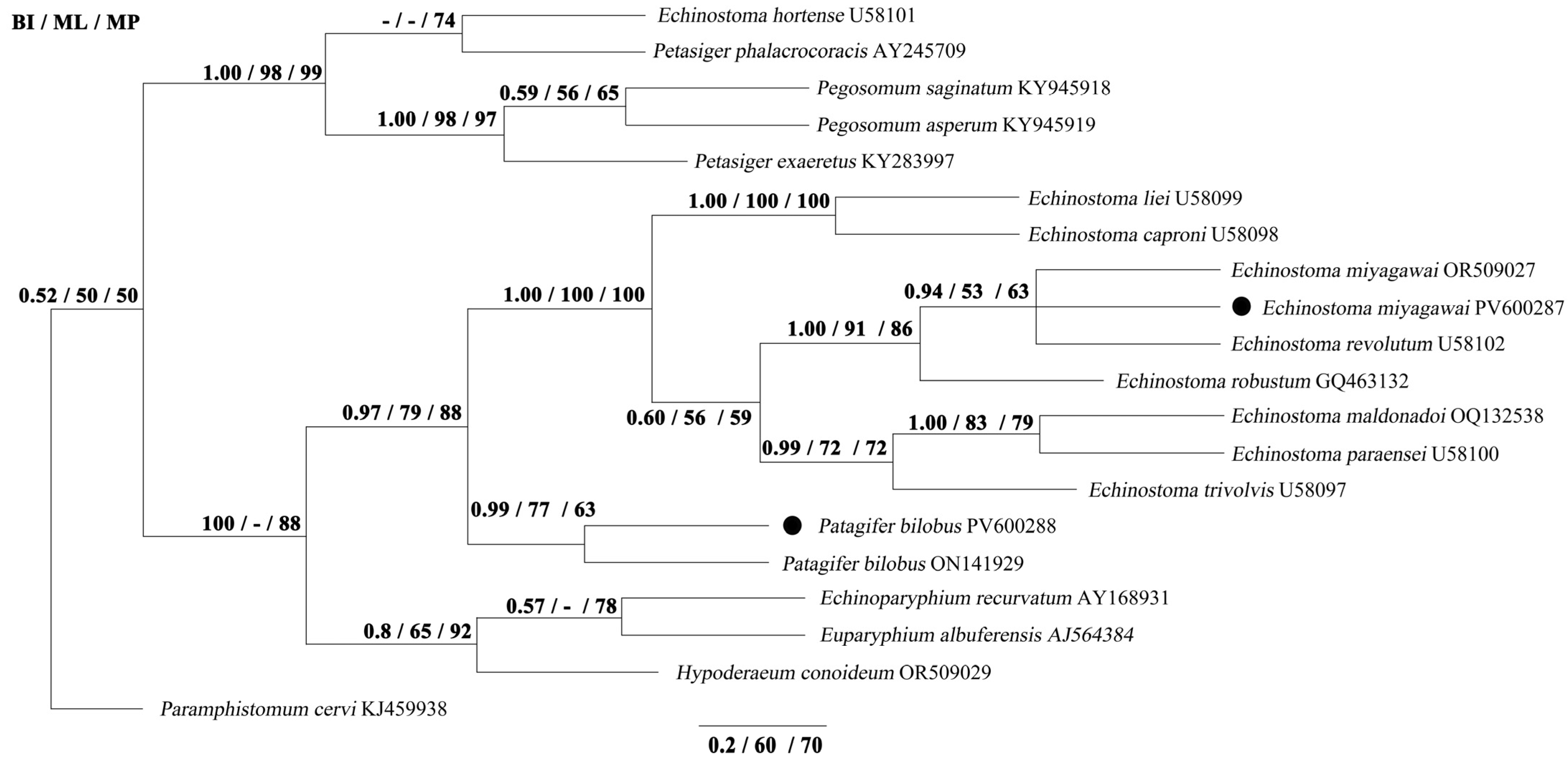
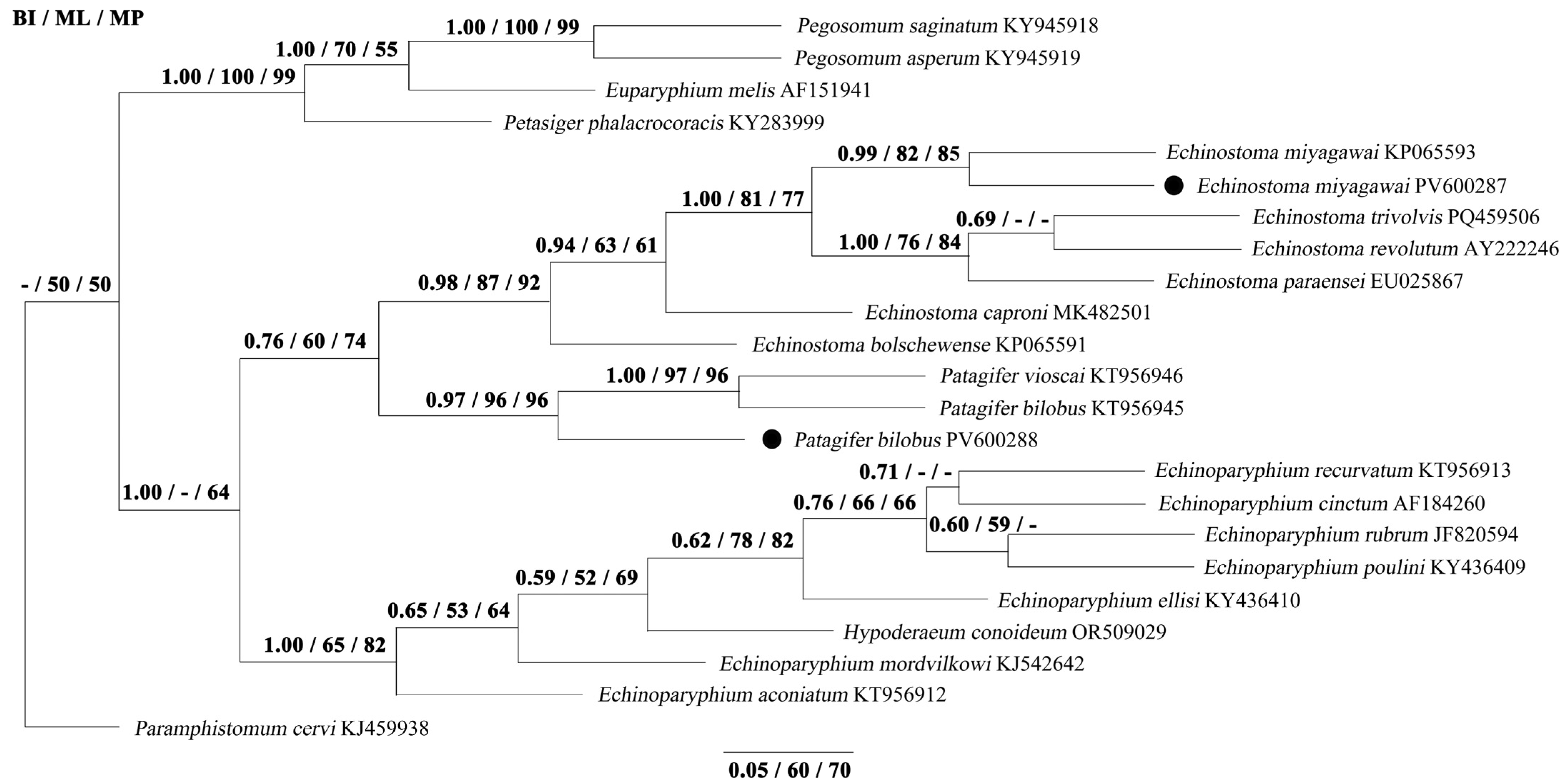
3.3. Phylogenetic Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Toledo, R.; Álvarez-Izquierdo, M.; Esteban, J.G.; Muñoz-Antoli, C. Neglected food-borne trematodiases: Echinostomiasis and gastrodiscoidiasis. Parasitology 2022, 149, 1319–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.Y.; Jung, B.K. Foodborne intestinal fukes: A brief review of epidemiology and geographical distribution. Acta Trop. 2020, 201, 105210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledo, R.; Alvárez-Izquierdo, M.; Muñoz-Antoli, C.; Esteban, J.G. Intestinal Trematode Infections. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1154, 181–213. [Google Scholar]
- Toledo, R.; Conciancic, P.; Fiallos, E.; Esteban, J.G.; Muñoz-Antoli, C. Echinostomes and Other Intestinal Trematode Infections. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2024, 1454, 285–322. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, J.Y.; Jung, B.K. General overview of the current status of human foodborne trematodiasis. Parasitology 2022, 149, 1262–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izrailskaia, A.V.; Besprozvannykh, V.V.; Tatonova, Y.V. Echinostoma chankensis nom. nov., other Echinostoma spp. And Isthmiophora hortensis in East Asia: Morphology, molecular data and phylogeny within Echinostomatidae. Parasitology 2021, 148, 1366–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, L.T.K.; Saijuntha, W.; Lawton, S.P.; Le, T.H. Mitophylogenomics of the zoonotic fluke Echinostoma malayanum confirms it as a member of the genus Artyfechinostomum Lane, 1915 and illustrates the complexity of Echinostomatidae systematics. Parasitol. Res. 2022, 121, 899–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasincová, V. The life cycle of Echinostoma bolschewense (Kotova, 1939) (Trematoda: Echinostomatidae). Folia Parasitol. 1991, 38, 143–154. [Google Scholar]
- Fried, B.; Huffman, J.E. The Biology of the intestinal trematode Echinostoma caproni. Adv. Parasitol. 1996, 38, 311–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, J.A.; Blair, D. Relative merits of nuclear ribosomal internal transcribed spacers and mitochondrial CO1 and ND1 genes for distinguishing among Echinostoma species (Trematoda). Parasitology 1998, 116, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laidemitt, M.R.; Brant, S.V.; Mutuku, M.W.; Mkoji, J.M.; Loker, E.S. The diverse echinostomes from East Africa: With a focus on species that use Biomphalaria and Bulinus as intermediate hosts. Acta Trop. 2019, 193, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besprozvannykh, V.V. Structure and life cycles of trematodes Euparyphium melis and Euparyphium amurensis sp. n (Echinostomatidae) in the Primorsky region. Zool. Zhurnal. 2001, 80, 5–11. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.; Shin, H.; Lee, Y.H.; Hong, S.J.; Kim, S.R.; Kim, Y.K.; Son, Y.J.; Song, J.G.; Chai, J.Y.; Jung, B.K. Rare Case of Echinostoma cinetorchis Infection, South Korea. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2024, 30, 1726–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, P.R.; Jung, Y.; Park, Y.K.; Hwang, M.K. Austropeplea ollula (Pulmonata: Lymnaeidae): A new molluscan intermediate host of a human intestinal fluke, Echinostoma cinetorchis (Trematoda: Echinostomatidae) in Korea. Korean J. Parasitol. 2001, 39, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, P.R.; Jung, Y.; Park, Y.K.; Hwang, M.G.; Soh, C.T. Corbicula fluminea (Bivalvia: Corbiculidae): A possible second molluscan intermediate host of Echinostoma cinetorchis (Trematoda: Echinostomatidae) in Korea. Korean J. Parasitol. 2001, 39, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.Y.; Kang, S.Y.; Ryang, Y.S. Helminthes infections in the small intestine of stray dogs in ejungbu city, Kyunggi Do, Korea. Kisaengchunghak Chapchi 1981, 19, 55–59. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, X.D.; Li, C.P.; Yang, B.H.; Zhu, Y.X.; Tian, Y.; Shen, J.; Zhao, J.H. Investigation on the zoonotic trematode species and their natural infection status in Huainan areas of China. Nutr. Hosp. 2017, 34, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.A.T.; Madsen, H.; Dao, T.H.; Hoberg, E.; Dalsgaard, A.; Murrell, K.D. Evaluation of the role of rats as reservoir hosts for fishborne zoonotic trematodes in two endemic northern Vietnam fish farms. Parasitol. Res. 2012, 111, 1045–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anh, N.T.L.; Madsen, H.; Dalsgaard, A.; Phuong, N.T.; Thanh, D.T.H.; Murrell, K.D. Poultry as reservoir hosts for fishborne zoonotic trematodes in Vietnamese fish farms. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 169, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledo, R.; Muñoz-Antolí, C.; Esteban, J.G. The life-cycle of Echinostoma friedi n. sp. (Trematoda: Echinostomatidae) in Spain and a discussion on the relationships within the ‘revolutum’ group based on cercarial chaetotaxy. Syst. Parasitol. 2000, 45, 199–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faltýnková, A.; Georgieva, S.; Soldánová, M.; Kostadinova, A. A re-assessment of species diversity within the ‘revolutum’ group of Echinostoma Rudolphi, 1809 (Digenea: Echinostomatidae) in Europe. Syst. Parasitol. 2015, 90, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.T.; Chang, Q.C.; Su, X.; Fu, X.; Yue, D.M.; Gao, Y.; Wang, C.R. Complete Mitochondrial Genome of Echinostoma hortense (Digenea: Echinostomatidae). Korean J. Parasitol. 2016, 54, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, W.M.; Na, B.K.; Cho, S.H. Echinostoma hortense and heterophyid metacercariae encysted in yellowfin goby, Acanthogobius flavimanus, from Shinan-gun and Muan-gun (Jeollanam-do), Korea. Korean J. Parasitol. 2009, 47, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okanishi, H.; Matsumoto, J.; Nogami, S.; Kagawa, Y.; Watari, T. Echinostoma hortense infection with enteritis diagnosed by upper gastrointestinal endoscopy in a dog. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2013, 75, 991–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, L.; Wang, B.; Zhang, H. Clonorchis sinensis and Echinostoma hortense detected by endoscopy and molecular characterization: Two case reports and update on diagnosis. Front. Med. 2025, 11, 1515539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.Y.; Hong, S.; Sohn, W.M.; Lee, S.H.; Seo, B.S. Studies on intestinal tematodes in Korea: XVI. Infection status of loaches with the metacercariae of Echinostoma hortense. Kisaengchunghak Chapchi 1985, 23, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, Y.K.; Ryang, Y.S.; Chung, P.R.; Lee, K.T. Echinostoma hortense metacercariae naturally encysted in Odontobutis obscura interrupta (a freshwater fish) and experimental infection to rats. Kisaengchunghak Chapchi 1985, 23, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, J.Y.; Shin, E.H.; Lee, S.H.; Rim, H.J. Foodborne intestinal flukes in Southeast Asia. Korean J. Parasitol. 2009, 47, 69–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.S.; Oh, D.S.; Ahn, K.S.; Cho, S.H.; Lee, W.J.; Na, B.K.; Sohn, W.M. Zoonotic Intestinal Trematodes in Stray Cats (Felis catus) from Riverside Areas of the Republic of Korea. Korean J. Parasitol. 2015, 53, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, B.S.; Cho, S.Y.; Hong, S.T.; Hong, S.J.; Lee, S.H. Studies on parasitic helminths of Korea 5. survey on intestinal trematodes of house rats. Kisaengchunghak Chapchi 1981, 19, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantrawatpan, C.; Saijuntha, W. Multiplex PCR development for the differential detection of four medically important echinostomes (Trematoda: Echinostomatidae) in Thailand. Acta Trop. 2020, 204, 105304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umathevy, T. The life-history of Echinostoma ilocanum. Med. J. Malaya. 1965, 20, 58. [Google Scholar]
- Sohn, W.M.; Kim, H.J.; Yong, T.S.; Eom, K.S.; Jeong, H.G.; Kim, J.K.; Kang, A.R.; Kim, M.R.; Park, J.M.; Ji, S.H.; et al. Echinostoma ilocanum infection in Oddar Meanchey Province, Cambodia. Korean J. Parasitol. 2011, 49, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, J.E.; Fried, B. Echinostoma and echinostomiasis. Adv. Parasitol. 1990, 29, 215–269. [Google Scholar]
- Kuris, A.M.; Warren, J. Echinostome cercarial penetration and metacercarial encystment as mortality factors for a second intermediate host, Biomphalaria glabrata. J. Parasitol. 1980, 66, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, B.; Donovick, R.A.; Emili, S. Infectivity, growth and development of Echinostoma liei (Trematoda) in the domestic chick. Int. J. Parasitol. 1988, 18, 413–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousif, F.; Haroun, N. Intramolluscan development of Echinostoma liei (Trematoda:Echinostomatidae) in its snail host Biomphalaria alexandrina. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 1986, 16, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jeyarassasingam, U.; Heyneman, D.; Lim, H.K.; Mansour, N. Life cycle of a new echinostome from Egypt, Echinostoma liei sp.nov. (Trematoda: Echinostomatidae). Parasitology 1972, 65, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, W.M.; Na, B.K.; Lee, D.; Eom, K.S.; Yong, T.S.; Chai, J.Y.; Min, D.Y. Echinostoma macrorchis metacercariae in Cipangopaludina chinensis malleata from Xiengkhuang Province, Lao PDR and morphologies of adults from experimental animals. Korean J. Parasitol. 2019, 57, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butboonchoo, P.; Wongsawad, C.; Wongsawad, P.; Chai, J.Y. Morphology and molecular identification of Echinostoma revolutum and Echinostoma macrorchis in freshwater snails and experimental hamsters in upper Northern Thailand. Korean J. Parasitol. 2020, 58, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, W.M.; Na, B.K. Echinostoma macrorchis (Digenea: Echinostomatidae): Metacercariae in Cipangopaludina chinensis malleata snails and adults from experimental rats in Korea. Korean J. Parasitol. 2017, 55, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, W.M.; Chai, J.Y.; Na, B.K.; Yong, T.S.; Eom, K.S.; Park, H.; Min, D.Y.; Rim, H.J. Echinostoma macrorchis in Lao PDR: Metacercariae in Cipangopaludina snails and adults from experimentally infected animals. Korean J. Parasitol. 2013, 51, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M.; Itagaki, T. Survey on wild rodents for endoparasites in Iwate Prefecture, Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2003, 65, 1151–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokohata, Y.; Abe, H.; Jiang, Y.P.; Kamiya, M. Gastrointestinal helminth fauna of Japanese moles, Mogera spp. Jpn. J. Vet. Res. 1989, 37, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Valadão, M.C.; Alves, P.V.; López-Hernández, D.; Assis, J.C.A.; Coelho, P.R.S.; Geiger, S.M.; Pinto, H.A. A new cryptic species of Echinostoma (Trematoda: Echinostomatidae) closely related to Echinostoma paraensei found in Brazil. Parasitology 2023, 150, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.; Jung, B.K.; Chang, T.; Sohn, W.M.; Sinuon, M.; Chai, J.Y. Echinostoma mekongi n. sp. (Digenea: Echinostomatidae) from Riparian people along the Mekong River in Cambodia. Korean J. Parasitol. 2020, 58, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiroonpan, P.; Chontananarth, T.; Chai, J.Y.; Purivirojkul, W. The high diversity of trematode metacercariae that parasitize freshwater gastropods in Bangkok, Thailand, and their infective situations, morphologies, and phylogenetic relationships. Parasitology 2022, 10, 1–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomchoei, N.; Backeljau, T.; Segers, B.; Wongsawad, C.; Butboonchoo, P.; Nantarat, N. Morphological and molecular characterization of larval trematodes infecting the assassin snail genus Anentome in Thailand. J. Helminthol. 2022, 96, e52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qiu, Y.Y.; Zeng, M.H.; Diao, P.W.; Chang, Q.C.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.R. The complete mitochondrial genome of Echinostoma miyagawai: Comparisons with closely related species and phylogenetic implications. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 75, 103961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, K.S.; Rim, H.J.; Jang, D.H. A study on the parasitic helminths of domestic duck (Anas Platyrhynchos Var. Domestica Linnaeus) in Korea. Kisaengchunghak Chapchi 1984, 22, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.Y.; Jung, B.K.; Chang, T.; Shin, H.; Cho, J.; Ryu, J.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Park, K.; Jeong, M.H.; Hoang, E.H.; et al. Echinostoma miyagawai Ishii, 1932 (Echinostomatidae) from ducks in Aceh Province, indonesia with special reference to its synonymy with Echinostoma robustum Yamaguti, 1935. Korean J. Parasitol. 2021, 59, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, L.T.K.; Quyen, D.V.; Saijuntha, W.; Doan, H.T.T.; Le, T.H.; Lawton, S.P. Mitogenomics of the zoonotic parasite Echinostoma miyagawai and insights into the evolution of tandem repeat regions within the mitochondrial non-coding control region. Parasitology 2024, 151, 1543–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagataki, M.; Tantrawatpan, C.; Agatsuma, T.; Sugiura, T.; Duenngai, K.; Sithithaworn, P.; Andrews, R.H.; Petney, T.N.; Saijuntha, W. Mitochondrial DNA sequences of 37 collar-spined echinostomes (Digenea: Echinostomatidae) in Thailand and Lao PDR reveals presence of two species: Echinostoma revolutum and E. miyagawai. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2015, 35, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostadinova, A.; Gibson, D.I.; Biserkov, V.; Chipev, N. Re-validation of Echinostoma miyagawai Ishii, 1932 (Digenea: Echinostomatidae) on the basis of the experimental completion of its life-cycle. Syst. Parasitol. 2000, 45, 81–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostadinova, A.; Gibson, D.I.; Biserkov, V.; Ivanova, R. A quantitative approach to the evaluation of the morphological variability of two echinostomes, Echinostoma miyagawai Ishii, 1932 and E. revolutum (Frölich, 1802), from Europe. Syst. Parasitol. 2000, 45, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rząd, I.; Sitko, J.; Dzika, E.; Zalewski, K.; Śmietana, P.; Busse, P. Geographic and ecologic aspects of the community structure of trematodes of mallards (Anas Platyrhynchos) in northern poland and the Czech Republic. J. Wildl. Dis. 2020, 56, 576–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgieva, S.; Faltýnková, A.; Brown, R.; Blasco-Costa, I.; Soldánová, M.; Sitko, J.; Scholz, T.; Kostadinova, A. Echinostoma ‘revolutum’ (Digenea: Echinostomatidae) species complex revisited: Species delimitation based on novel molecular and morphological data gathered in Europe. Parasit. Vectors. 2014, 7, 520. [Google Scholar]
- Pantoja, C.; Faltýnková, A.; O’Dwyer, K.; Jouet, D.; Skírnisson, K.; Kudlai, O. Diversity of echinostomes (Digenea: Echinostomatidae) in their snail hosts at high latitudes. Parasite 2021, 28, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svinin, A.O.; Chikhlyaev, I.V.; Bashinskiy, I.W.; Osipov, V.V.; Neymark, L.A.; Lvanov, A.Y.; Stoyko, T.G.; Chernigova, P.I.; Ibrogimova, P.K.; Litvinchuk, S.N.; et al. Diversity of trematodes from the amphibian anomaly P hotspot: Role of planorbid snails. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0281740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgieva, S.; Blasco-Costa, I.; Kostadinova, A. Molecular characterisation of four echinostomes (Digenea: Echinostomatidae) from birds in New Zealand, with descriptions of Echinostoma novaezealandense n. sp. and Echinoparyphium poulini n. sp. Syst. Parasitol. 2017, 94, 477–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lie, K.J.; Basch, P.F. The life history of Echinostoma paraensei sp. n. (Trematoda: Echinostomatidae). J. Parasitol. 1967, 53, 1192–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadão, M.C.; López-Hernández, D.; Alves, P.V.; Pinto, H.A. A new species of Echinostoma (Trematoda: Echinostomatidae) from the ‘revolutum’ group found in Brazil: Refuting the occurrence of Echinostoma miyagawai (=E. robustum) in the Americas. Parasitology 2022, 149, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buddhachat, K.; Chontananarth, T. Is species identification of Echinostoma revolutum using mitochondrial DNA barcoding feasible with high-resolution melting analysis? Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 1799–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anucherngchai, S.; Chontananarth, T. Echinostoma revolutum: Development of a high performance DNA-specific primer to demonstrate the epidemiological situations of their intermediate hosts. Acta Trop. 2019, 189, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, R.K.; Zhao, Q.; Abuzeid, A.M.I.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.Q.; Sun, Y.X.; He, L.; Li, X.; Liu, J.M.; Li, G.Q. Mitochondrial genome sequence of Echinostoma revolutum from Red-Crowned Crane (Grus japonensis). Korean J. Parasitol. 2020, 58, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantima, K.; Chai, J.Y.; Wongsawad, C. Echinostoma revolutum: Freshwater snails as the second intermediate hosts in Chiang Mai, Thailand. Korean J. Parasitol. 2013, 51, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enabulele, E.E.; Lawton, S.P.; Walker, A.J.; Kirk, R.S. Molecular epidemiological analyses reveal extensive connectivity between Echinostoma revolutum (sensu stricto) populations across Eurasia and species richness of zoonotic echinostomatids in England. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0270672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.Y.; Sohn, W.M.; Na, B.K.; Nguyen, V.D. Echinostoma revolutum: Metacercariae in Filopaludina snails from Nam Dinh Province, Vietnam, and adults from experimental hamsters. Korean J. Parasitol. 2011, 49, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Sohn, W.M.; Chai, J.Y. Echinostoma revolutum and Echinoparyphium recurvatum recovered from house rats in Yangyang-gun, Kangwon-do. Kisaengchunghak Chapchi 1990, 28, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, N.E. Storage and incubation of Echinostoma revolutum eggs recovered from wild Branta canadensis, and their infectivity to Lymnaea tomentosa snails. J. Helminthol. 2005, 79, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorensen, R.E.; Minchella, D.J. Parasite influences on host life history: Echinostoma revolutum parasitism of Lymnaea elodes snails. Oecologia 1998, 115, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanta, U.K.; Watanabe, T.; Anisuzzaman; Ohari, Y.; Itagaki, T. Characterization of Echinostoma revolutum and Echinostoma robustum from ducks in Bangladesh based on morphology, nuclear ribosomal ITS2 and mitochondrial nad1 sequences. Parasitol. Int. 2019, 69, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detwiler, J.T.; Bos, D.H.; Minchella, D.J. Revealing the secret lives of cryptic species: Examining the phylogenetic relationships of echinostome parasites in North America. Mol. Phylogenet Evol. 2010, 55, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iakovleva, G.A.; Lebedeva, D.I.; Ieshko, E.P. Trematodes fauna of waterfowl birds in Karelia. Parazitologiia 2012, 46, 98–110. [Google Scholar]
- Orlofske, S.A.; Belden, L.K.; Hopkins, W.A. Effects of Echinostoma trivolvis metacercariae infection during development and metamorphosis of the wood frog (Lithobates sylvaticus). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2017, 203, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, M.S.; Fried, B. The expulsion of Echinostoma trivolvis and retention of Echinostoma caproni in the ICR mouse: Pathological effects. Int. J. Parasitol. 1991, 21, 255–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, B.; Mueller, T.J.; Frazer, B.A. Observations on Echinostoma revolutum and Echinostoma trivolvis in single and concurrent infections in domestic chicks. Int. J. Parasitol. 1997, 27, 1319–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodinka, C.; Detwiler, J.T. Host species, host size, and miracidial dose influence the infection success of Echinostoma trivolvis lineage C larvae. J. Parasitol. 2024, 110, 725–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nollen, P.M. Mating behaviour of Echinostoma caproni and E. trivolvis in concurrent infections in hamsters. Int. J. Parasitol. 1997, 27, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, B.; Pane, P.L.; Reddy, A. Experimental infection of Rana pipiens tadpoles with Echinostoma trivolvis cercariae. Parasitol. Res. 1997, 83, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucha, K.H.; Huffman, J.E.; Fried, B. Mallard ducklings (Anas platyrhynchos) experimentally infected with Echinostoma trivolvis (Digenea). J. Parasitol. 1990, 76, 590–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Digiani, M.C. Digeneans and cestodes parasitic in the white-faced ibis Plegadis chihi (Aves: Threskiornithidae) from Argentina. Folia Parasitol. 2000, 47, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, S.; Lee, D.; Park, H.; Oh, M.; Jeon, H.K.; Lee, Y.; Na, K.J.; Kim, Y.; Lee, H.; Eom, K.S. Three echinostome species from wild birds in the Republic of Korea. Korean J. Parasitol. 2014, 52, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad-Alla, M.E.; Abdien, H.M.; Dessouki, A.A. Prevalence of bacteria and parasites in White Ibis in Egypt. Vet. Ital. 2010, 46, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, N.A.; Shalaby, I.M.; Ghobashy, M.A.; Taeleb, A.A.; Elkhawass, E.A. Filling the void: Morphological and molecular phylogenetic analyses of helminths assemblage from the Egyptian egret Bubulcus ibis. Parasitol. Int. 2025, 104, 102972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkach, V.V.; Kudlai, O.; Kostadinova, A. Molecular phylogeny and systematics of the Echinostomatoidea Looss, 1899 (Platyhelminthes: Digenea). Int. J. Parasitol. 2016, 46, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faltýnková, A.; Gibson, D.I.; Kostadinova, A. A revision of Patagifer dietz, 1909 (Digenea: Echinostomatidae) and a key to its species. Syst. Parasitol. 2008, 70, 159–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sereno-Uribe, A.L.; González-García, M.T.; Ortega-Olivares, M.P.; López-Jiménez, A.; García-Varela, M.; Andrade-Gómez, L. First record of Patagifer bilobus (Rudolphi, 1819) Dietz, 1909 (Digenea: Echinostomatidae), with a morphological and molecular characterization from two threskiornithid species in Mexico. Parasitol. Res. 2022, 121, 1921–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Outa, J.O.; Bhika, P.; Avenant-Oldewage, A. Gastropod invasions in anthropogenically impacted impoundments in South Africa: Tracing their origins and exploring field evidence of parasite spillback and amplification. Int. J. Parasitol. 2024, 54, 279–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gacad, J.L.J.; Tanabe-Hosoi, S.; Yurlova, N.I.; Urabe, M. The complete mitogenome of Echinoparyphium aconiatum (Digenea: Echinostomatidae) and a comparison with other digenean species. Parasitol. Int. 2023, 92, 102682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Wang, X.X.; Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, C.R. Characterization of the complete nuclear ribosomal DNA sequences of Eurytrema pancreaticum. J. Helminthol. 2018, 92, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, J.O.; Watase, G.J.; Warsinger-Pepe, N.; Tamashita, Y.M. Mechanisms of rDNA Copy Number Maintenance. Trends Genet. 2019, 35, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, Y.; Ma, X.X.; Lv, Q.B.; Hu, Y.; Qiu, H.Y.; Chang, Q.C.; Wang, C.R. Comparative analyses of complete ribosomal DNA sequences of Clonorchis sinensis and Metorchis orientalis: IGS sequences may provide a novel genetic marker for intraspecific variation. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 78, 104125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.H.; Pham, L.T.K.; Quyen, V.D.; Nguyen, K.T.; Doan, H.T.T.; Saijuntha, W.; Blair, D. The ribosomal transcription units of five echinostomes and their taxonomic implications for the suborder Echinostomata (Trematoda: Platyhelminthes). Parasitol. Res. 2024, 123, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.T.; Doan, H.T.T.; Pham, L.T.K.; Roan, D.T.; Agatsuma, T.; Doanh, P.N.; Le, T.H. Nuclear ribosomal transcription units in Asian Paragonimus species (Paragonimidae: Platyhelminthes): Genetic characteristics, polymorphism, and implications for intersuperfamilial phylogeny. Parasitol. Res. 2024, 123, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledo, R.; Esteban, J.G. An update on human echinostomiasis. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 110, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.B. Modern Parasitology: Release 1; People’s Military Medical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2002; pp. 694–698. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Yu, H.X. The discovery of Echinostoma miyagawai in goose in Heilongjiang province. Chin. Vet. Sci. 1993, 7, 44. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dronen, N.O.; Blend, C.K. Petagifer lamothei n. sp. (Digenea: Echinostomatidae: Nephrostominae) from the white ibis Eudocimus albus (Threskiornithidae) from Texas, USA. Rev. Mex. De Biodivers. 2008, 79, 23–32. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.T. Fauna of China: Invertebrates, Volume 3: Phylum Platyhelminthes, Class Trematoda, Order Echinostomatida (Part I); Science Press: Beijing, China, 1985; p. 81. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Chang, Q.C.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, S.Q.; Lou, Y.; Duan, H.; Guo, D.H.; Wang, C.R.; Zhu, X.Q. Characterization of the complete nuclear ribosomal DNA sequences of Paramphistomum cervi. Sci. World J. 2014, 2024, 751907. [Google Scholar]
- Burland, T.G. DNASTAR’s Lasergene sequence analysis software. Methods Mol. Biol. 2000, 132, 71–91. [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz, S.; Choudhuri, J.V.; Ohlebusch, E.; Schleiermacher, C.; Stoye, J.; Giegerich, R. REPuter: The manifold applications of repeat analysis on a genomic scale. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 4633–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Masatoshi, N.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilgenbusch, J.C.; Swofford, D. Inferring evolutionary trees with PAUP*. In Current Protocols in Bioinformatics; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; Chapter 6, Unit 6.4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaver, P.C. Experimental studies on Echinostoma revolutum (Froelich), a fluke from birds and mammals. Illin Biol. Monogr. 1937, 15, 1–96. [Google Scholar]
- Bashkirova, E.I. Family Echinostomatidae dietz, 1909. In Trematodes and Animals and Man; Skrjabin, K.I., Ed.; USSR Academy of Sciences: Moscow, Russia, 1947; pp. 310–391. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Skrjabin, K.I.; Bashkirova, E.I. Family Echinostomatidae dietz, 1909. In Trematodes and Animals and Man; Skrjabin, K.I., Ed.; Izdatelstvo Akademii Nauk SSSR: Moscow Leningrad, Russia, 1956; pp. 51–930. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kanev, I. Life-cycle, delimitation and redescription of Echinostoma revolutum (Froelich, 1802) (Trematoda: Echinostomatidae). Syst. Parasitol. 1994, 28, 125–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, B.; Graczyk, T.K. Recent advances in the biology of Echinostoma species in the ‘revolutum’ group. Adv. Parasitol. 2004, 58, 139–195. [Google Scholar]
- Toledo, R.; Esteban, J.G.; Fried, B. Recent advances in the biology of echinostomes. Adv. Parasitol. 2009, 69, 147–204. [Google Scholar]
- Heneberg, P. Taxonomic comments on the validity of Echinostoma miyagawai Ischii, 1932 (Trematoda: Echinostomatidae). Parasitol. Int. 2020, 74, 101931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machida, M. Patagifer bilobus (Echinostomatidae:Trematoda) from white ibis, Threskiornis melanocephala. Bull. Natl. Sci. Mus. Tokyo 1968, 11, 157–160. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, S.P.; Shrivastava, O.N. On the validity of some species of the genus Patagifer (Trematoda: Echinostomatidae). Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. Sect. B 1970, 72, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, C.B. The fauna of India and adjacent countries. In Platyhelminthes Vol. 1 (Suppl.) Trematoda—Digenea; Zoological Survey of India: Calcutta, India, 1982; p. 163. [Google Scholar]
- Le, T.H.; Nguyen, K.T.; Pham, L.T.K.; Doan, H.T.T.; Roan, D.T.; Le, X.T.K.; Agatsuma, T.; Blair, D. Mitogenomic and nuclear ribosomal transcription unit datasets support the synonymy of Paragonimus iloktsuenensis and P. ohirai (Paragonimidae: Platyhelminthes). Parasitol. Res. 2023, 122, 1531–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ma, X.X.; Lv, Q.B.; Hu, Y.; Chang, Q.C.; Wang, C.R. Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genome sequence of Tracheophilus cymbius (Digenea), the first representative from the family Cyclocoelidae. J. Helminthol. 2019, 94, e101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanevičiūtė, G.; Stunžėnas, V.; Petkevičiūtė, R. Phylogenetic relationships of some species of the family Echinostomatidae odner, 1910 (Trematoda), inferred from nuclear rdna sequences and karyological analysis. Comp. Cytogenet. 2015, 9, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Species and Nominator | Collar-spines | Intermediate Host | Geographical Distribution | Definitive Host | Literature Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Echinostoma bolschewense (Kotova, 1939) Nasincova, 1991 | 37 | Viviparus contectus Millet, 1813 | Russia | Mesocricetus auratus Waterhouse, 1839; Gallus gallus Linnaeus, 1758 | [8] |
| Echinostoma caproni Richard, 1964 | 37 | Biomphalaria spp.; Bulinus spp.; Helisoma duryi Wetherby, 1879; Lymnaea natalensis Krauss, 1848; Physa acuta Draparnaud, 1805; Planorbarius corneus Linnaeus, 1758 | Madagascar; Egypt; Kenya | Mice; hamsters; rats; chicks; pigeons; finches; Crocidura olivieri Lesson, 1827; Falco newtoni Gurney, 1863 | [9,10,11] |
| Echinostoma chankense Besprozvannykh, 2001 | 27 | Anisus centrifugops Prozorova & Starobogatov, 1997; Helicorbis sujfunensis Starobogatov, 1957; Amuropaludina praerosa Gerstfeldt, 1859; Lymnaea auricularia Linnaeus,1758 | Russia | Rattus norvegicus Linnaeus, 1766 | [6,12] |
| Echinostoma cinetorchis Ando & Ozaki, 1923 | 37 | Gyraulus convexiusculus Macleay, 1873; Hippeutis cantori Benson, 1850; Segmentina spp., Hemisphaerula spp., Radix auricularia coreana Adams, 1866; Austropeplea ollula Gould, 1859 Fossaria truncatula Müller, 1774; Corbicula fluminea Müller, 1774; | Korea; China; Vietnam | Humans; dogs; ducks; Rattus argentiventer Robinson & Kloss, 1916; Bandicota indica Bechstein, 1800 | [13,14,15,16,17,18,19] |
| Echinostoma friedi Toledo et al., 2000 | 37 | Lymnaea peregra Müller, 1774 Lymnaea corvus Gmelin, 1791; Gyraulus chinensis Dunker, 1848; Physella acuta Draparnaud, 1805 | Spain | Albino rats; golden hamsters; chickens; R. norvegicus | [20,21] |
| Echinostoma hortense Asada,1926 | 27–28 | Acanthogobius flavimanus Temminck & Schlegel, 1845; Misgurnus anguillicaudatus, Cantor 1842; Odontobutis interrupta, Iwata & Jeon, 1985; Misgurnus mizolepis Nichols, 1925; Moroco oxycephalus Bleeker, 1865; Coreoperca kawamebari Temminck & Schlegel, 1843; Squalidus coreanus Berg, 1906 | China; Korea; Japan | Dogs; humans; R. norvegicus; Felis catus Linnaeus, 1758; Rattus rattus Linnaeus, 1758 | [22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30] |
| Echinostoma ilocanum Garrison, 1908 | 49–51 | G. convexiusculus | Thailand; Cambodia | Rats; humans | [31,32,33] |
| Echinostoma liei Jeyarasasingam et al., 1972 | 37 | Biomphalaria glabrata Orbigny, 1835; Biomphalaria alexandrina Ehrenberg, 1831 | Egypt | Domestic chicks; hamsters; M. auratus | [34,35,36,37,38] |
| Echinostoma macrorchis Ando and Ozaki, 1923 | 40–45 | Cipangopaludina chinensis malleata Reeve, 1863; Filopaludina martensi Martens, 1860; Filopaludina doliaris Gould, 1844; Filopaludina sumatrensis polygramma Martens, 1860; Bithynia siamensis Lea, 1856; Bithynia pulchella Adams, 1853; Anentome helena Busch, 1847 | LAO; Korea; Thailand; Japan | Mice; rats; hamsters; Mogera tokudae Kuroda, 1940; Mogera wogura Temminck, 1844; Apodemus speciosus Temminck, 1835; | [39,40,41,42,43,44] |
| Echinostoma maldonadoi Kostadinova, 2000 | 33–39 | Stenophysa marmorata Guilding, 1828 | Brazil | Meriones unguiculatus Milne-Edwards, 1867 | [45] |
| Echinostoma mekongi Cho et al., 2020 | 37 | F. martensi; A. helena; F. sumatrensis polygramma | Cambodia; Thailand | Humans; M. auratus | [46,47,48] |
| Echinostoma miyagawai Ishii, 1932 | 37 | Planorbis planorbis Linnaeus, 1758; Anisus vortex Linnaeus, 1758; Lymnaea truncatula Müller, 1774; Lymnaea stagnalis Linnaeus, 1758; Lymnaea palustris Müller, 1774 | Japan; China; Korean; Czech; Thailand; Bulgaria; Poland; LAO; Indonesia | Pigeons, ducks, humans, Aythya fuligula Linnaeus, 1758; Anas platyrhynchos Linnaeus, 1758 | [21,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56] |
| Echinostoma nasincovae Georgieva et al., 2014 | 37 | P. corneus | Czech; Russia; Ireland | G. gallus; M. auratus; Anas platyrhyn Linnaeus, 1758 | [21,57,58,59] |
| Echinostoma novaezealandense Georgieva et al., 2017 | 37 | - | New Zealand | A. platyrhynchos; Cygnus atratus Latham, 1790; Branta canadensis Linnaeus, 1758 | [60] |
| Echinostoma paraensei Lie & Basch, 1967 | 37 | B. glabrata; P. acuta | Brazil | Hamsters; mice; rats; R. norvegicus; Nectomys squamipes Brants, 1827 | [45,61] |
| Echinostoma paraulum Dietz, 1909 | 37 | L. stagnalis | Austria; Russia; Germany | A. fuligula | [21,57] |
| Echinostoma pseudorobustum Dietz, 1909 | 37 | - | Brazil | G. gallus | [62] |
| Echinostoma revolutum (Froelich, 1802) Dietz, 1909 | 37 | Ampullaceana balthica Linnaeus, 1758; B. Siamensis; F. martensi; C. Bithynia funiculata Leach, 1818; Clea helena Philippi, 1847; Eyriesia eyriesi Morelet, 1865; F. doliaris; F. sumatrensis polygramma; Indoplanorbis exustus Deshayes, 1833; L. Auricularia; L. stagnalis; Lymnaea tomentosa Pfeiffer, 1855 Lymnaea elodes Say, 1821; Radix auricularia Linnaeus, 1758; Stagnicola palustris Müller, 1774 | Germany; LAO; Thailand; Korea; China; Czech; England; Poland; Scotland; Canada; Vietnam; America; Finland; Cambodia | Ducks; humans; rats; hamsters; A. fuligula G. Gallus; B. canadensis; Grus japonensis Müller, 1776; | [21,53,57,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72] |
| Echinostoma robustum Yamaguti, 1935 | 37 | P. acuta; L. elodes | China; Brazil; Bangladesh; Russia; America | Ducks; G. gallus; A. platyrhynchos | [73,74,75] |
| Echinostoma trivolvis Cort, 1914 | 37 | Lithobates sylvaticus LeConte, 1825; Physa gyrina Say, 1821; Helisoma trivolvis Say, 1817; Ladislavella elodes Say, 1821; Rana spp. tadpoles | America | Mice; chicks; hamsters; A. platyrhynchos; Ondatra zibethicus Linnaeus, 1766 | [76,77,78,79,80,81] |
| Patagifer bilobus (Rudolphi, 1819) Dietz, 1909 | 48–64 | - | Mexico; Ukraine; America; Korea; Egypt; Argentina; Lithuania; China | Plegadis chihi Vieillot, 1817 Nipponia nippon Temminck, 1835; Eudocimus albus Linnaeus, 1758; Bubulcus ibis Linnaeus, 1758; Plegadis falcinellus Linnaeus, 1766; Platalea minor Temminck & Schlegel, 1849; G. japonensis | [82,83,84,85,86,87,88] |
| Patagifer vioscai Lumsden, 1962 | 53 | Pseudosuccinea columella Say, 1817 | America; South Africa | E. albus | [86,87,89] |
| Biological Classification | Echinostoma spp. | Patagifer spp. |
|---|---|---|
| Phylum | Platyhelminthes | Platyhelminthes |
| Class | Trematoda | Trematoda |
| Subclass | Digenea | Digenea |
| Order | Plagiorchiida | Plagiorchiida |
| Suborder | Echinostomata | Echinostomata |
| Superfamily | Echinostomatoidea | Echinostomatoidea |
| Family | Echinostomatidae | Echinostomatidae |
| Gens | Echinostoma | Patagifer |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, Y.; Li, Y.; Gao, Z.-Y.; Jiang, B.-T. The Nuclear Ribosomal Transcription Units of Two Echinostomes and Their Taxonomic Implications for the Family Echinostomatidae. Biology 2025, 14, 1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081101
Cao Y, Li Y, Gao Z-Y, Jiang B-T. The Nuclear Ribosomal Transcription Units of Two Echinostomes and Their Taxonomic Implications for the Family Echinostomatidae. Biology. 2025; 14(8):1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081101
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Yu, Ye Li, Zhong-Yan Gao, and Bo-Tao Jiang. 2025. "The Nuclear Ribosomal Transcription Units of Two Echinostomes and Their Taxonomic Implications for the Family Echinostomatidae" Biology 14, no. 8: 1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081101
APA StyleCao, Y., Li, Y., Gao, Z.-Y., & Jiang, B.-T. (2025). The Nuclear Ribosomal Transcription Units of Two Echinostomes and Their Taxonomic Implications for the Family Echinostomatidae. Biology, 14(8), 1101. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081101






