Distribution and Variation Characteristics of Branched Glycerol Dialkyl Glycerol Tetraethers (BrGDGTs) in Sediment Cores Along the Nearshore-to-Offshore Gradient of the East China Sea and Their Correlation with Microbial Community Diversity
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sample Collection
2.2. Analysis of the Total Organic Carbon (TOC) and Its Stable Isotope Ratios
2.3. Lipid Extraction and IPL/CL Separation
2.4. Proxy Calculations
2.5. DNA Extraction, 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing, and Data Analyses
3. Results
3.1. TON, TN Content and δ13C
3.2. Distributions of IPL- and CL-brGDGTs
3.3. Microbial Community Composition
4. Discussion
4.1. Source Identification of IPL- and CL-brGDGTs
4.1.1. IPL-brGDGTs Primarily Produced In Situ
4.1.2. CL-brGDGTs Significantly Impacted by the Autochthonous Contribution
4.2. The Relationship Between Bacterial Community Diversity and Variations in BrGDGT Distribution
4.2.1. The Potential Biological Producers of BrGDGTs
4.2.2. Influence of Bacterial Community Diversity on the Distribution of BrGDGTs
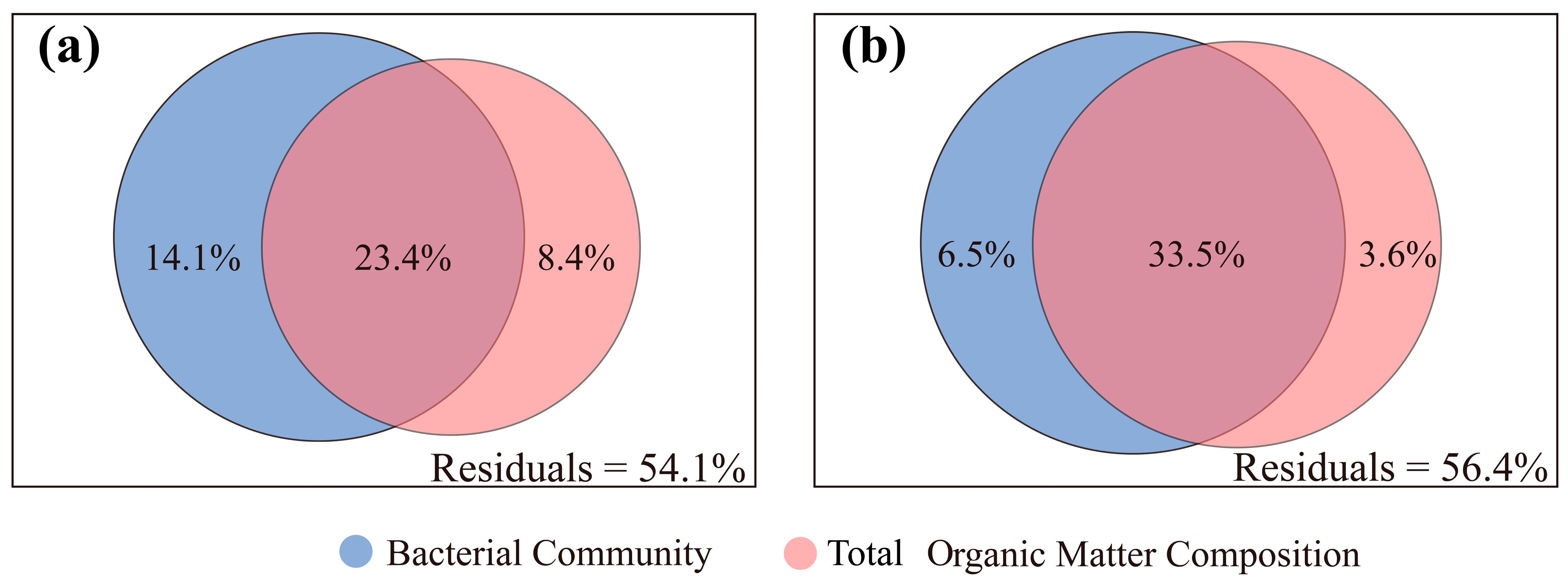
4.3. Assessment of the Effects of Bacterial Community and the Composition of TOM on brGDGT Distribution
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| brGDGTs | Branched glycerol dialkyl glycerol tetraethers |
| IPL-brGDGTs | Intact polar lipid-derived brGDGT |
| CL-brGDGTs | Core brGDGTs |
| ECS | East China Sea |
| VPA | Variance partitioning analysis |
| IPLs | Intact polar lipids |
| CLs | core lipids |
| SPM | suspended particulate matter |
| SST | sea surface temperature (SST) |
| YDW | Yangtze River Diluted Water |
| ZFCC | Zhejiang-Fujian Coastal Current |
| TWC | Taiwan Warm Current |
| YRZ | Yangtze River Estuary |
| NKBC | Nearshore Kuroshio Branch Current |
| TOC | total organic carbon |
| TN | total nitrogen |
| TOM | total organic matter |
| SDs | standard deviations |
| MeOH | methanol |
| DCM | dichloromethane |
| TLE | Total lipid extract |
| OTUs | Operational taxonomic units |
| Partial RDA | Partial redundancy analysis |
| BWT | Bottom water temperature |
References
- Sinninghe Damsté, J.S.; Hopmans, E.C.; Pancost, R.D.; Schouten, S.; Geenevasen, J.A.J. Newly discovered non-isoprenoid glycerol dialkyl glycerol tetraether lipids in sediments. Chem. Commun. 2000, 2000, 1683–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jonge, C.; Hopmans, E.C.; Stadnitskaia, A.; Rijpstra, W.I.C.; Hofland, R.; Tegelaar, E.; Sinninghe Damsté, J.S. Identification of novel penta- and hexamethylated branched glycerol dialkyl glycerol tetraethers in peat using HPLC–MS2, GC–MS and GC–SMB-MS. Org. Geochem. 2013, 54, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Schwab, V.F.; Ueberschaar, N.; Roth, V.N.; Lange, M.; Xu, Y.; Gleixner, G.; Pohnert, G. Identification of novel 7-methyl and cyclopentanyl branched glycerol dialkyl glycerol tetraethers in lake sediments. Org. Geochem. 2016, 102, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schouten, S.; Hopmans, E.C.; Sinninghe Damsté, J.S. The organic geochemistry of glycerol dialkyl glycerol tetraether lipids: A review. Org. Geochem. 2013, 54, 19–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, D.C.; Davis, W.M.; Nickels, J.S.; King, J.D.; Bobbie, R.J. Determination of the sedimentary microbial biomass by extractible lipid phosphate. Oecologia 1979, 40, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, H.R.; Fallon, R.D.; Patton, J.S. The effect of organic matter and oxygen on the degradation of bacterial membrane lipids in marine sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1986, 50, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturt, H.F.; Summons, R.E.; Smith, K.; Elvert, M.; Hinrichs, K.U. Intact polar membrane lipids in prokaryotes and sediments deciphered by high-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization multistage mass spectrometry-new biomarkers for biogeochemistry and microbial ecology. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 18, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipp, J.S.; Hinrichs, K.U. Structural diversity and fate of intact polar lipids in marine sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 6816–6833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Lipp, J.S.; Wegener, G.; Ferdelman, T.G.; Hinrichs, K.U. Turnover of microbial lipids in the deep biosphere and growth of benthic archaeal populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 6010–6014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tierney, J.E.; Schouten, S.; Pitcher, A.; Hopmans, E.C.; Sinninghe Damsté, J.S. Core and intact polar glycerol dialkyl glycerol tetraethers (GDGTs) in Sand Pond, Warwick, Rhode Island (USA): Insights into the origin of lacustrine GDGTs. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 77, 561–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zell, C.; Kim, J.H.; Hollander, D.; Lorenzoni, L.; Baker, P.; Silva, C.G.; Nittrouer, C.; Sinninghe Damsté, J.S. Sources and distributions of branched and isoprenoid tetraether lipids on the Amazon shelf and fan: Implications for the use of GDGT-based proxies in marine sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 139, 293–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raberg, J.H.; Flores, E.; Crump, S.E.; de Wet, G.; Dildar, N.; Miller, G.H.; Geirsdóttir, Á.; Sepúlveda, J. Intact Polar brGDGTs in Arctic Lake Catchments: Implications for Lipid Sources and Paleoclimate Applications. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2022, 127, e2022JG006969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Super, J.R.; Chin, K.; Pagani, M.; Li, H.; Tabor, C.; Harwood, D.M.; Hull, P.M. Late Cretaceous climate in the Canadian Arctic: Multi-proxy constraints from Devon Island. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2018, 504, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weijers, J.W.H.; Schouten, S.; van den Donker, J.C.; Hopmans, E.C.; Sinninghe Damsté, J.S. Environmental controls on bacterial tetraether membrane lipid distribution in soils. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2007, 71, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jonge, C.; Hopmans, E.C.; Zell, C.I.; Kim, J.H.; Schouten, S.; Sinninghe Damsté, J.S. Occurrence and abundance of 6-methyl branched glycerol dialkyl glycerol tetraethers in soils: Implications for palaeoclimate reconstruction. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 141, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weijers, J.W.H.; Schouten, S.; Hopmans, E.C.; Geenevasen, J.A.J.; David, O.R.P.; Coleman, J.M.; Pancost, R.D.; Sinninghe Damsté, J.S. Membrane lipids of mesophilic anaerobic bacteria thriving in peats have typical archaeal traits. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopmans, E.C.; Weijers, J.W.H.; Schefuß, E.; Herfort, L.; Sinninghe Damsté, J.S.; Schouten, S. A novel proxy for terrestrial organic matter in sediments based on branched and isoprenoid tetraether lipids. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2004, 224, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weijers, J.W.; Schefuss, E.; Schouten, S.; Sinninghe Damsté, J.S. Coupled thermal and hydrological evolution of tropical Africa over the last deglaciation. Science 2007, 315, 1701–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schouten, S.; Eldrett, J.; Greenwood, D.R.; Harding, I.; Baas, M.; Sinninghe Damsté, J.S. Onset of long-term cooling of Greenland near the Eocene-Oligocene boundary as revealed by branched tetraether lipids. Geology 2008, 36, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearing Crampton-Flood, E.; Peterse, F.; Munsterman, D.; Sinninghe Damsté, J.S. Using tetraether lipids archived in North Sea Basin sediments to extract North Western European Pliocene continental air temperatures. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2018, 490, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Xu, Y.; Lin, J.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, C. Global scale production of brGDGTs by benthic marine bacteria: Implication for developing ocean bottom environmental proxies. Glob. Planet. Change 2022, 211, 103783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Yuan, H.; Song, J.; Li, X.; Duan, L.; Wang, Y. BrGDGTs sources in eastern China marginal seas and their constraints on seawater temperature reconstruction. Chem. Geol. 2025, 676, 122624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Lian, E.; Yang, S.; Ge, H.; Jin, X.; He, J.; Jia, G. The distribution of intact polar lipid-derived branched tetraethers along a freshwater-seawater pH gradient in coastal East China Sea. Chem. Geol. 2022, 596, 120808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Xu, Y.; Canfield, D.E.; Wenzhöfer, F.; Zhang, C.; Glud, R.N. Strong linkage between benthic oxygen uptake and bacterial tetraether lipids in deep-sea trench regions. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dearing Crampton-Flood, E.; Peterse, F.; Sinninghe Damsté, J.S. Production of branched tetraethers in the marine realm: Svalbard fjord sediments revisited. Org. Geochem. 2019, 138, 103907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Yang, H.; Dong, C.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Pei, H.; Dang, X.; Lu, J.; Zhao, S.; Xie, S. Rapid response of fossil tetraether lipids in lake sediments to seasonal environmental variables in a shallow lake in central China: Implications for the use of tetraether-based proxies. Org. Geochem. 2019, 128, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weijers, J.W.H.; Panoto, E.; van Bleiswijk, J.; Schouten, S.; Balk, M.; Stams, A.J.M.; Rijpstra, W.I.C.; Sinninghe Damsté, J.S. Constraints on the Biological Source(s) of the Orphan Branched Tetraether Membrane Lipids. Geomicrobiol. J. 2009, 26, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinninghe Damsté, J.S.; Rijpstra, W.I.C.; Foesel, B.U.; Huber, K.J.; Overmann, J.; Nakagawa, S.; Kim, J.J.; Dunfield, P.F.; Dedysh, S.N.; Villanueva, L. An overview of the occurrence of ether- and ester-linked iso-diabolic acid membrane lipids in microbial cultures of the Acidobacteria: Implications for brGDGT paleoproxies for temperature and pH. Org. Geochem. 2018, 124, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zheng, F.; Yang, H.; Yang, W.; Wu, R.; Liu, X.; Liang, H.; Chen, H.; Pei, H.; Zhang, C.; et al. The production of diverse brGDGTs by an Acidobacterium providing a physiological basis for paleoclimate proxies. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2022, 337, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halamka, T.A.; Raberg, J.H.; McFarlin, J.M.; Younkin, A.D.; Mulligan, C.; Liu, X.L.; Kopf, S.H. Production of diverse brGDGTs by Acidobacterium Solibacter usitatus in response to temperature, pH, and O(2) provides a culturing perspective on brGDGT proxies and biosynthesis. Geobiology 2023, 21, 102–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahonero-Canavesi, D.X.; Villanueva, L.; Bale, N.J.; Bosviel, J.; Koenen, M.; Hopmans, E.C.; Sinninghe Damsté, J.S. Changes in the Distribution of Membrane Lipids during Growth of Thermotoga maritima at Different Temperatures: Indications for the Potential Mechanism of Biosynthesis of Ether-Bound Diabolic Acid (Membrane-Spanning) Lipids. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 88, e0176321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.; Chen, H.; Yang, H.; Chen, Y.; Yang, W.; Feng, X.; Pei, H.; Welander, P.V. Identification of a protein responsible for the synthesis of archaeal membrane-spanning GDGT lipids. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukhchtaber, D.C.; von Meijenfeldt, F.A.B.; Sahonero Canavesi, D.X.; Dorhout, D.; Bale, N.J.; Hopmans, E.C.; Villanueva, L. Discovering Hidden Archaeal and Bacterial Lipid Producers in a Euxinic Marine System. Environ. Microbiol. 2025, 27, e70054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Xiao, W.; Zheng, F.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Tian, J.; Zhang, C. Enhanced production of highly methylated brGDGTs linked to anaerobic bacteria from sediments of the Mariana Trench. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1233560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, S.; Xiao, W.; Zheng, F.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, C. Potential influence of bacterial community structure on the distribution of brGDGTs in surface sediments from Yangtze River Estuary to East China Sea. Chem. Geol. 2024, 647, 121934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, Y.; Sinninghe Damsté, J.S.; Zopfi, J.; De Jonge, C.; Gilli, A.; Schubert, C.J.; Lepori, F.; Lehmann, M.F.; Niemann, H. Redox-dependent niche differentiation provides evidence for multiple bacterial sources of glycerol tetraether lipids in lakes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 10926–10931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jonge, C.; Radujković, D.; Sigurdsson, B.D.; Weedon, J.T.; Janssens, I.; Peterse, F. Lipid biomarker temperature proxy responds to abrupt shift in the bacterial community composition in geothermally heated soils. Org. Geochem. 2019, 137, 103897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Ma, T.; Liu, N.; Zhang, X.; Hu, H.; Ma, W.; Wang, Z.; Feng, X.; Peterse, F. Soil pH and aridity influence distributions of branched tetraether lipids in grassland soils along an aridity transect. Org. Geochem. 2022, 164, 104347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halamka, T.A.; McFarlin, J.M.; Younkin, A.D.; Depoy, J.; Dildar, N.; Kopf, A. Oxygen limitation can trigger the production of branched GDGTs in culture. Geochem. Perspect. Lett. 2021, 19, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raberg, J.H.; Miller, G.H.; Geirsdóttir, Á.; Sepúlveda, J. Near-universal trends in brGDGT lipid distributions in nature. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabm7625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajallooeian, F.; Deng, L.; Lever, M.A.; De Jonge, C. Seasonal temperature dependency of aquatic branched glycerol dialkyl glycerol tetraethers: A mesocosm approach. Org. Geochem. 2024, 189, 104742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Weijers, J.W.H.; Wagner, T.; Pan, J.M.; Chen, J.F.; Pancost, R.D. Sources and distributions of tetraether lipids in surface sediments across a large river-dominated continental margin. Org. Geochem. 2011, 42, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Song, J.; Li, X.; Yuan, H. Glycerol dialkyl glycerol tetraethers signature in sediments of the East China Sea and its implication on marine and continental climate and environment records. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 103, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Li, T.; Russell, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, F.; et al. Source Identification of brGDGTs in the Surface Sediments of the East China Sea. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 9, 796539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, Z.; Jia, G. Cyclisation degree of tetramethylated brGDGTs in marine environments and its implication for source identification. Glob. Planet. Change 2020, 184, 103043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xiao, W.; Wu, J.; Han, L.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Y. Source, composition, and distributional pattern of branched tetraethers in sediments of northern Chinese marginal seas. Org. Geochem. 2021, 157, 104244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.; Wang, Z.; Xiong, W.; Zhang, Y.; Dou, Y.; Huang, L.; Mi, B.; Wang, Z.; Cong, J. Glycerol dialkyl glycerol tetraethers in surficial marine sediments across shelf-to-basin depth transects in the East China Sea: Their sources and potential as sea water temperature proxies. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2024, 636, 111992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, B.; Yao, P.; Bianchi, T.S.; Lipp, J.S.; Elvert, M.; Yu, Z.; Yu, Z.; Hinrichs, K.U. Size-fractionated distribution of glycerol dialkyl glycerol tetraether core lipids in surface sediments of a large-river delta-front estuary. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Duan, X.; Jin, X.; Lian, E.; Yin, P.; Li, L.; Jia, G. Sedimentary core brGDGTs in the East China Sea are mainly produced in situ as evidenced by their similar distributions with brGDGTs derived from intact polar lipids. Org. Geochem. 2020, 149, 104095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y. Recent sediment accumulation and carbon burial in the East China Sea. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2006, 20, GB3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.l.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Belkin, I.M. Temporal variation in the sediment load of the Yangtze river and the influences of human activities. J. Hydrol. 2002, 263, 56–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.P.; Xu, K.H.; Li, A.C.; Milliman, J.D.; Velozzi, D.M.; Xiao, S.B.; Yang, Z.S. Flux and fate of Yangtze River sediment delivered to the East China Sea. Geomorphology 2007, 85, 208–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Yang, Z.; Fan, D.; Pan, Y. Seasonal variation of sedimentation in the Changjiang Estuary mud area. J. Geogr. Sci. 2003, 13, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Gao, G.; Yan, J. Three dimensional simulation of tide and tidal current characteristics in the East China Sea. Oceanol. Acta 2001, 24, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Lei, K.; Guo, Z.; Wang, H. Effect of a Winter Storm on Sediment Transport and Resuspension in the Distal Mud Area, the East China Sea. J. Coast. Res. 2007, 23, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Dong, C.; He, Y. Wave climatological analysis in the East China Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2016, 120, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Hou, Y.; Li, S.; Du, M.; Chen, J.; Lu, J. A comparative study of storm surge and wave setup in the East China Sea between two severe weather events. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2020, 235, 106583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milliman, J.D.; Huang-ting, S.; Zuo-sheng, Y.; Mead, R.H. Transport and deposition of river sediment in the Changjiang estuary and adjacent continental shelf. Cont. Shelf Res. 1985, 4, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Yin, B.; Liu, Z.; Feng, X. Numerical study of the ocean circulation on the East China Sea shelf and a Kuroshio bottom branch northeast of Taiwan in summer. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2011, 116, C05015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Yin, B.; Liu, Z.; Bai, T.; Qi, J.; Chen, H. Numerical study on the pattern and origins of Kuroshio branches in the bottom water of southern East China Sea in summer. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2012, 117, C02014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, E.; Yang, S.; Wu, H.; Yang, C.; Li, C.; Liu, J.T. Kuroshio subsurface water feeds the wintertime Taiwan Warm Current on the inner East China Sea shelf. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2016, 121, 4790–4803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, Z.; Sun, Y. Terrestrial and marine biomarker estimates of organic matter sources and distributions in surface sediments from the East China Sea shelf. Cont. Shelf Res. 2011, 31, 1106–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Jia, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Yu, Q.; Zou, X. Anthropogenic perturbations to the fate of terrestrial organic matter in a river-dominated marginal sea. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2022, 333, 242–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitcher, A.; Hopmans, E.C.; Schouten, S.; Sinninghe Damsté, J.S. Separation of core and intact polar archaeal tetraether lipids using silica columns: Insights into living and fossil biomass contributions. Org. Geochem. 2009, 40, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huguet, C.; Hopmans, E.C.; Febo-Ayala, W.; Thompson, D.H.; Sinninghe Damsté, J.S.; Schouten, S. An improved method to determine the absolute abundance of glycerol dibiphytanyl glycerol tetraether lipids. Org. Geochem. 2006, 37, 1036–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopmans, E.C.; Schouten, S.; Sinninghe Damsté, J.S. The effect of improved chromatography on GDGT-based palaeoproxies. Org. Geochem. 2016, 93, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinninghe Damsté, J.S. Spatial heterogeneity of sources of branched tetraethers in shelf systems: The geochemistry of tetraethers in the Berau River delta (Kalimantan, Indonesia). Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2016, 186, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, W.; Hyde, E.R.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Ackermann, G.; Humphrey, G.; Parada, A.; Gilbert, J.A.; Jansson, J.K.; Caporaso, J.G.; Fuhrman, J.A.; et al. Improved Bacterial 16S rRNA Gene (V4 and V4-5) and Fungal Internal Transcribed Spacer Marker Gene Primers for Microbial Community Surveys. mSystems 2016, 1, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stackebrandt, E.; Goebel, B.M. Taxonomic Note: A Place for DNA-DNA Reassociation and 16S rRNA Sequence Analysis in the Present Species Definition in Bacteriology. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1994, 44, 846–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greay, T.L.; Gofton, A.W.; Zahedi, A.; Paparini, A.; Linge, K.L.; Joll, C.A.; Ryan, U.M. Evaluation of 16S next-generation sequencing of hypervariable region 4 in wastewater samples: An unsuitable approach for bacterial enteric pathogen identification. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 670, 1111–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastian, M.; Heymann, S.; Jacomy, M. Gephi: An Open Source Software for Exploring and Manipulating Networks. Proc. Int. AAAI Conf. Web Soc. Media 2009, 3, 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barberán, A.; Bates, S.T.; Casamayor, E.O.; Fierer, N. Using network analysis to explore co-occurrence patterns in soil microbial communities. ISME J. 2012, 6, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borcard, D.; Gillet, F.; Legendre, P. Numerical Ecology with R; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; Volume 17. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, J.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Peres-Neto, P.R. Generalizing hierarchical and variation partitioning in multiple regression and canonical analyses using the rdacca. hp R package. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2022, 13, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Shi, X.; Yu, Z.; Lin, T.; Wang, H.; Ma, D.; Guo, Z.; Yang, Z. Distribution of sedimentary organic matter in estuarine–inner shelf regions of the East China Sea: Implications for hydrodynamic forces and anthropogenic impact. Mar. Chem. 2012, 142–144, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Wang, Q.; Duan, X.; Zhang, D.; Li, X. Sources of organic carbon in surface sediments of Hangzhou Bay and Zhejiang coastal area: Implication from total organic carbon, lignin and algal pigments. J. Mar. Syst. 2025, 249, 104062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zheng, F.; Chen, S.; Liu, H.; Phelps, T.J.; Zhang, C. Branched GDGT production at elevated temperatures in anaerobic soil microcosm incubations. Org. Geochem. 2018, 117, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, X.H. Sediment Depth-Dependent Spatial Variations of Bacterial Communities in Mud Deposits of the Eastern China Marginal Seas. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Xiong, H. Hydrochemical processes controlling arsenic and selenium in the Changjiang River (Yangtze River) system. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 377, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, D. Changes in pH, CEC and Exchangeable Acidity of Some Forest Soils in Southern China During the Last 32–35 Years. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1998, 108, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S.; Shi, X.; Wang, G.; Zhou, L.; Hu, B.; Hu, L.; Yang, G.; Liu, Y.; Yao, Z.; Liu, S. Sediment accumulation and budget in the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Mar. Geol. 2017, 390, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Pancost, R.D.; Dang, X.; Zhou, X.; Evershed, R.P.; Xiao, G.; Tang, C.; Gao, L.; Guo, Z.; Xie, S. Correlations between microbial tetraether lipids and environmental variables in Chinese soils: Optimizing the paleo-reconstructions in semi-arid and arid regions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 126, 49–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naafs, B.D.A.; Gallego-Sala, A.V.; Inglis, G.N.; Pancost, R.D. Refining the global branched glycerol dialkyl glycerol tetraether (brGDGT) soil temperature calibration. Org. Geochem. 2017, 106, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zheng, Z.; Zong, Y.; Man, M.; Tian, L. Distributions of soil branched glycerol dialkyl glycerol tetraethers from different climate regions of China. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, W.; Zhao, H.; Cao, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Cai, Z.; Wu, S.; Liu, Z.; Liu, W. Biomarker-based quantitative constraints on maximal soil-derived brGDGTs in modern lake sediments. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2023, 602, 117947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Parlanti, E.; Anquetil, C.; Morelle, J.; Laverman, A.M.; Thibault, A.; Bou, E.; Huguet, A. Environmental controls on the distribution of brGDGTs and brGMGTs across the Seine River basin (NW France): Implications for bacterial tetraethers as a proxy for riverine runoff. Biogeosciences 2024, 21, 2227–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huguet, A.; Meador, T.; Laggoun-Défarge, F.; Könneke, M.; Wu, W.; Derenne, S.; Hinrichs, K.U. Production rates of bacterial tetraether lipids and fatty acids in peatland under varying oxygen concentrations. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2017, 203, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blewett, J.; Elling, F.J.; Naafs, B.D.A.; Kattein, L.; Evans, T.W.; Lauretano, V.; Gallego-Sala, A.V.; Pancost, R.D.; Pearson, A. Metabolic and ecological controls on the stable carbon isotopic composition of archaeal (isoGDGT and BDGT) and bacterial (brGDGT) lipids in wetlands and lignites. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2022, 320, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mühlenbruch, M.; Grossart, H.P.; Eigemann, F.; Voss, M. Mini-review: Phytoplankton-derived polysaccharides in the marine environment and their interactions with heterotrophic bacteria. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 2671–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, J.; Zhou, S.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Kogure, K.; Zhang, X.H. Diversity of culturable heterotrophic bacteria from the Mariana Trench and their ability to degrade macromolecules. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2020, 2, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martikainen, P.J. Heterotrophic nitrification–An eternal mystery in the nitrogen cycle. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 168, 108611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zell, C.; Kim, J.H.; Dorhout, D.; Baas, M.; Sinninghe Damsté, J.S. Sources and distributions of branched tetraether lipids and crenarchaeol along the Portuguese continental margin: Implications for the BIT index. Cont. Shelf Res. 2015, 96, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccopieri, M.; Carreira, R.S.; Wagener, A.L.R.; Hefter, J.; Mollenhauer, G. Branched GDGTs as Proxies in Surface Sediments From the South-Eastern Brazilian Continental Margin. Front. Earth Sci. 2019, 7, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Hu, L.; Yang, H.; Xu, Y. Ubiquitous production of branched glycerol dialkyl glycerol tetraethers (brGDGTs) in global marine environments: A new source indicator for brGDGTs. Biogeosciences 2016, 13, 5883–5894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, J.; Huang, D.; Wu, Y.; Liang, J. Oxygen depletion off the Changjiang (Yangtze River) Estuary. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2002, 45, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Hanada, S.; Imachi, H.; Ohashi, A.; Harada, H.; Kamagata, Y. Anaerolinea thermolimosa sp. nov., Levilinea saccharolytica gen. nov., sp. nov. and Leptolinea tardivitalis gen. nov., sp. nov., novel filamentous anaerobes, and description of the new classes Anaerolineae classis nov. and Caldilineae classis nov. in the bacterial phylum Chloroflexi. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Wu, W.; Liang, W.; Wang, Y.; Hou, J.; Chen, Y.; Elvert, M.; Hinrichs, K.U.; Wang, F. Anaerobic degradation of organic carbon supports uncultured microbial populations in estuarine sediments. Microbiome 2023, 11, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Jiang, S.; Tian, L.; Wei, L.; Jin, J.; Ibánhez, J.S.P.; Chang, Y.; Wei, X.; Wu, Y. Benthic microbial biogeography along the continental shelf shaped by substrates from the Changjiang River plume. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2022, 41, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Du, P.; Li, H.; Zhou, K.; Shou, L.; Chen, J.; Meng, L. Prokaryotic community assembly patterns and nitrogen metabolic potential in oxygen minimum zone of Yangtze Estuary water column. Environ. Res. 2024, 252, 119011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenig, J.C.; Groissmeier, K.D.; Manefield, M.J. Tolerance of anaerobic bacteria to chlorinated solvents. Microbes Environ. 2014, 29, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raven, M.R.; Keil, R.G.; Webb, S.M. Microbial sulfate reduction and organic sulfur formation in sinking marine particles. Science 2021, 371, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimek, D.; Herold, M.; Calusinska, M. Comparative genomic analysis of Planctomycetota potential for polysaccharide degradation identifies biotechnologically relevant microbes. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenferink, W.B.; van Alen, T.A.; Jetten, M.S.M.; Op den Camp, H.J.M.; van Kessel, M.A.H.J.; Lücker, S. Genomic analysis of the class Phycisphaerae reveals a versatile group of complex carbon-degrading bacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2024, 117, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spring, S.; Bunk, B.; Spröer, C.; Rohde, M.; Klenk, H.P. Genome biology of a novel lineage of planctomycetes widespread in anoxic aquatic environments. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 2438–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Liang, S.; Wang, X.; Pan, X. Distribution and Dynamics of Dissolved Organic Matter in the Changjiang Estuary and Adjacent Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2021, 126, e2020JG006161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Dai, J.; Song, J.; Ma, J.; Li, X.; Yuan, H.; Duan, L.; Wang, Q. Antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in microorganisms and their indications for the nitrogen/sulfur cycle in the East China Sea sediments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 488, 137280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xie, P.; Dai, J.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yang, X. Variation in Structure and Functional Diversity of Surface Bacterioplankton Communities in the Eastern East China Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Li, P.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Sheng, Q.; Sun, Z.; Qin, Q.; Ren, X.; et al. A pathway for chitin oxidation in marine bacteria. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Li, L.; Zhai, W.; Xu, B.; Yin, X.; He, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, T.; Tang, X. Distribution of arsenic and its biotransformation genes in sediments from the East China Sea. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 253, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Santos, I.R.; Yu, H.; Wang, F.; Burnett, W.C.; Bianchi, T.S.; Dong, J.; Lian, E.; Zhao, B.; Mayer, L.; et al. A global assessment of the mixed layer in coastal sediments and implications for carbon storage. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Bianchi, T.S.; Allison, M.A.; Dimova, N.T.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Diao, S.; Jiang, X.; Zhen, Y.; Yao, P.; et al. Using multi-radiotracer techniques to better understand sedimentary dynamics of reworked muds in the Changjiang River estuary and inner shelf of East China Sea. Mar. Geol. 2015, 370, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Chen, K.; Yang, G.; Fan, D.; Li, T. Sulfur and iron diagenesis in temperate unsteady sediments of the East China Sea inner shelf and a comparison with tropical mobile mud belts (MMBs). J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2016, 121, 2811–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xie, W.; Zhang, C.; Yin, K. Linking Bacterial Communities to Optical-Derived Properties of Porewater DOM in Sediments in the Coastal East China Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 919368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
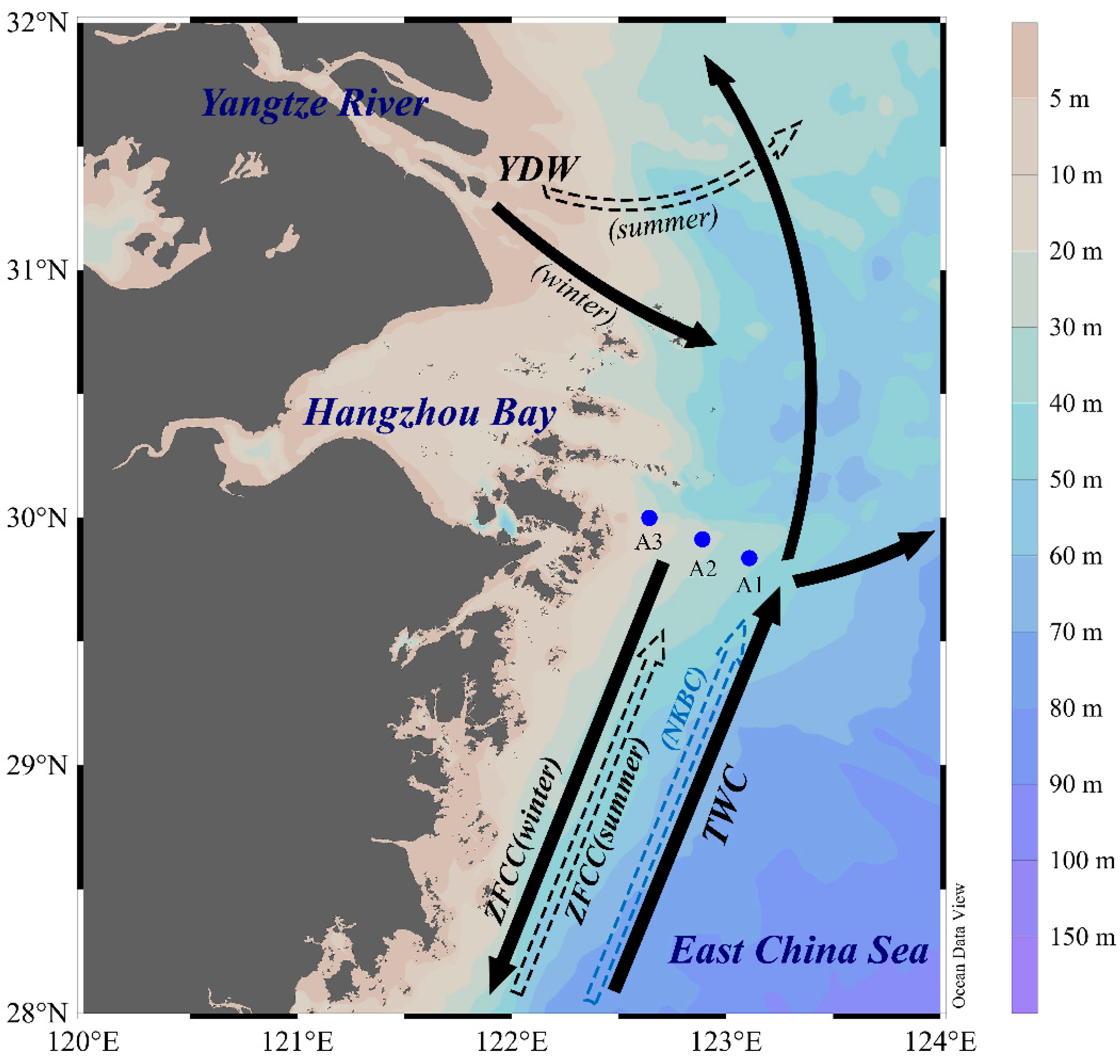

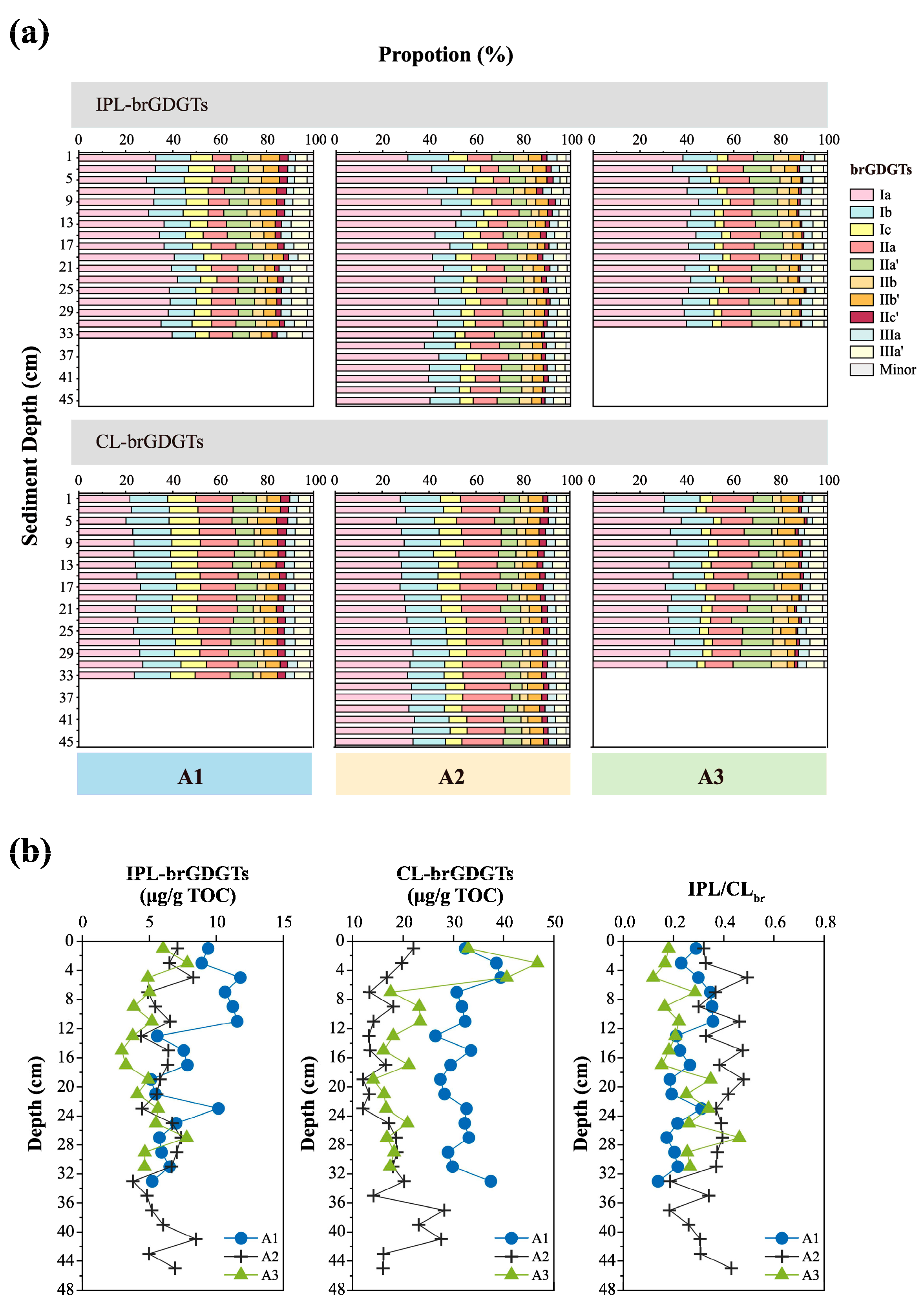



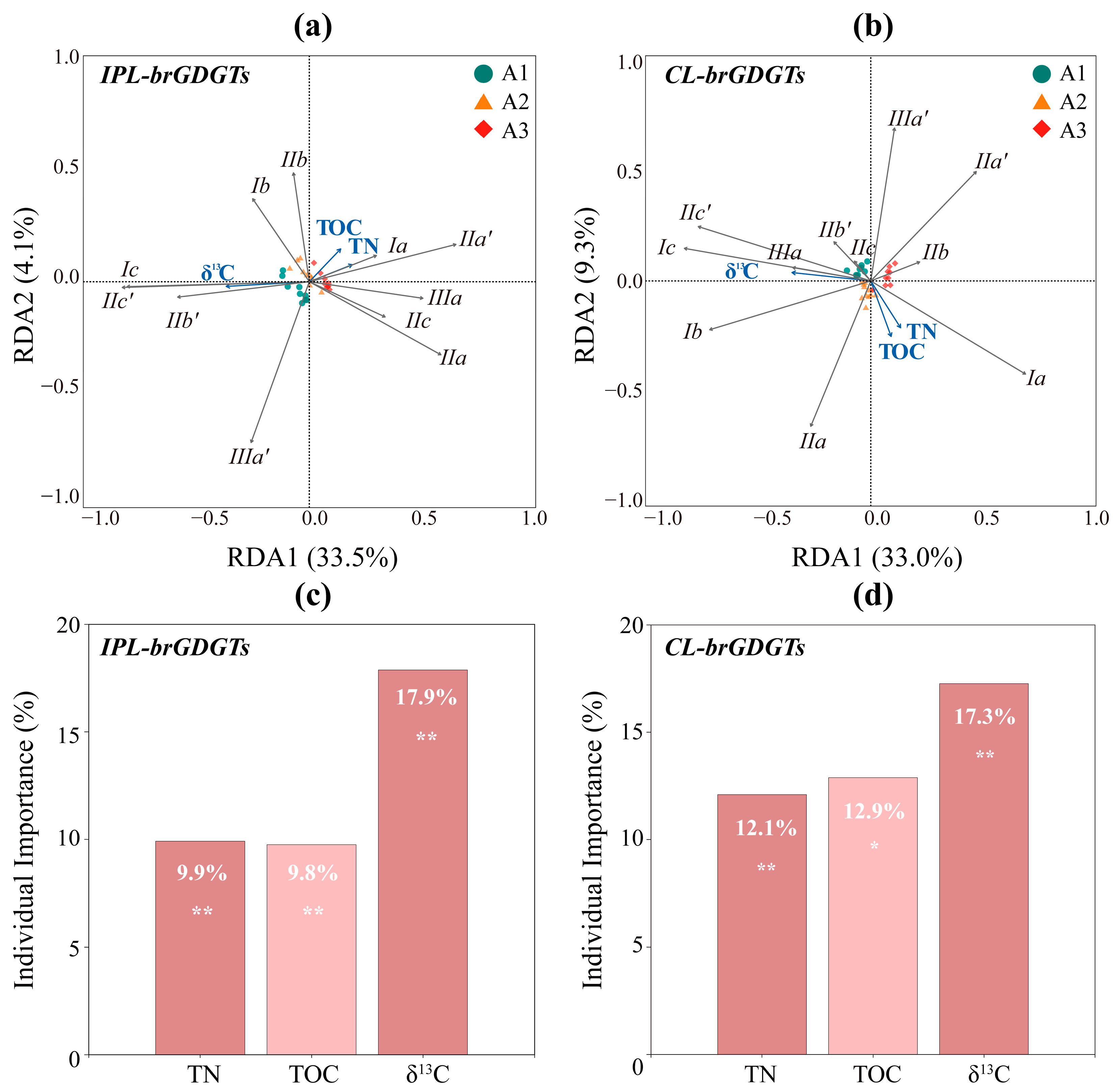
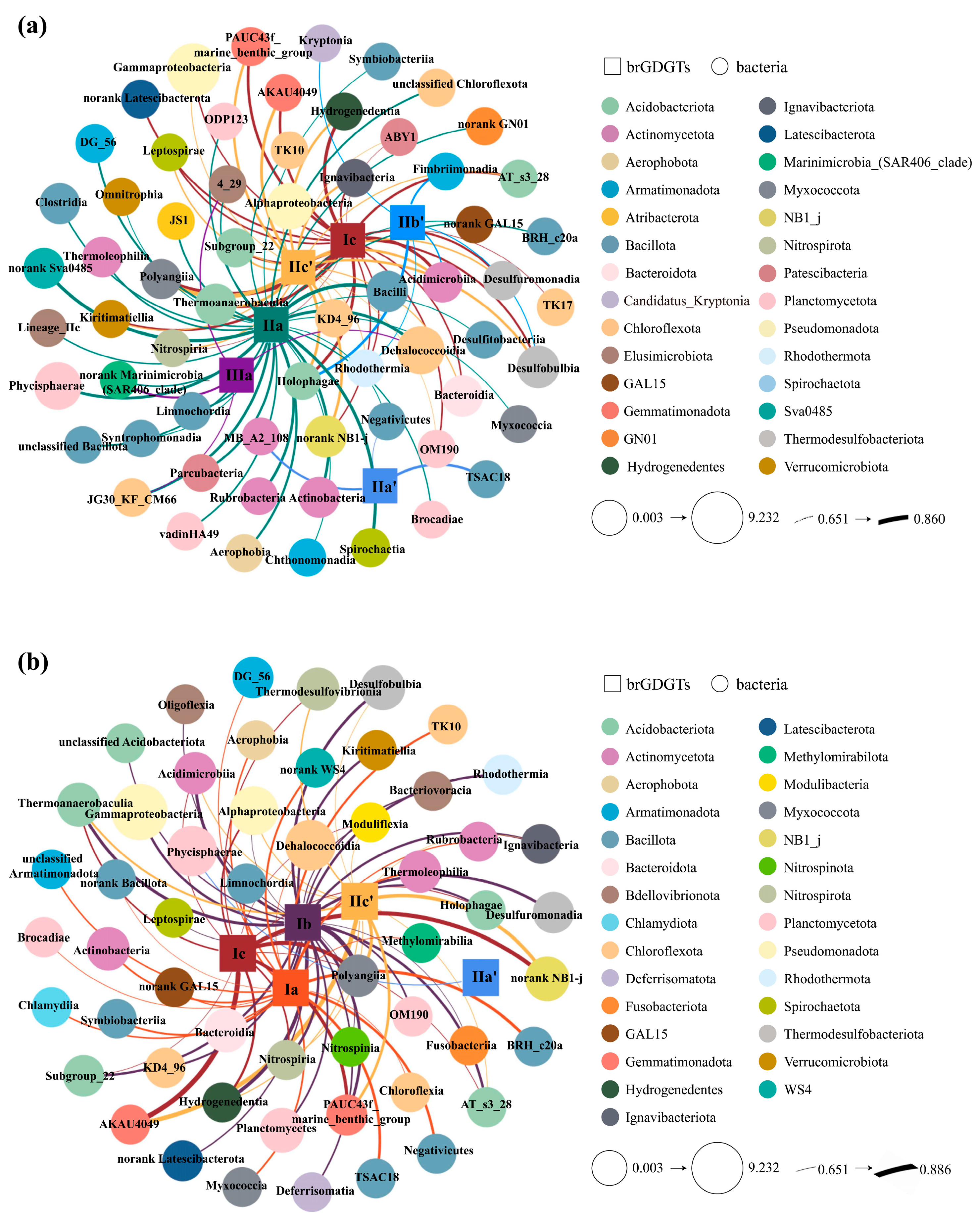
| Site | Longitude (°E) | Latitude (°N) | Water Depth (m) | Length (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 123.11 | 29.84 | 67.3 | 34 |
| A2 | 122.89 | 29.91 | 55.5 | 46 |
| A3 | 122.64 | 30.00 | 36.9 | 31 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, T.; Liu, C.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Ji, F. Distribution and Variation Characteristics of Branched Glycerol Dialkyl Glycerol Tetraethers (BrGDGTs) in Sediment Cores Along the Nearshore-to-Offshore Gradient of the East China Sea and Their Correlation with Microbial Community Diversity. Biology 2025, 14, 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081077
Zeng T, Liu C, Yang Q, Zhao J, Ji F. Distribution and Variation Characteristics of Branched Glycerol Dialkyl Glycerol Tetraethers (BrGDGTs) in Sediment Cores Along the Nearshore-to-Offshore Gradient of the East China Sea and Their Correlation with Microbial Community Diversity. Biology. 2025; 14(8):1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081077
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Ting, Cheng Liu, Qunhui Yang, Jingyuan Zhao, and Fuwu Ji. 2025. "Distribution and Variation Characteristics of Branched Glycerol Dialkyl Glycerol Tetraethers (BrGDGTs) in Sediment Cores Along the Nearshore-to-Offshore Gradient of the East China Sea and Their Correlation with Microbial Community Diversity" Biology 14, no. 8: 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081077
APA StyleZeng, T., Liu, C., Yang, Q., Zhao, J., & Ji, F. (2025). Distribution and Variation Characteristics of Branched Glycerol Dialkyl Glycerol Tetraethers (BrGDGTs) in Sediment Cores Along the Nearshore-to-Offshore Gradient of the East China Sea and Their Correlation with Microbial Community Diversity. Biology, 14(8), 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081077






