Genome-Wide Identification, Exogenous Hormone Response, Gene Structure, and Conserved Motif Analysis of the GRF Gene Family in Cerasus humilis
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Identification and Characterization of ChGRF Genes
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of the ChGRF
2.4. Collinearity and Evolutionary Gene Analysis
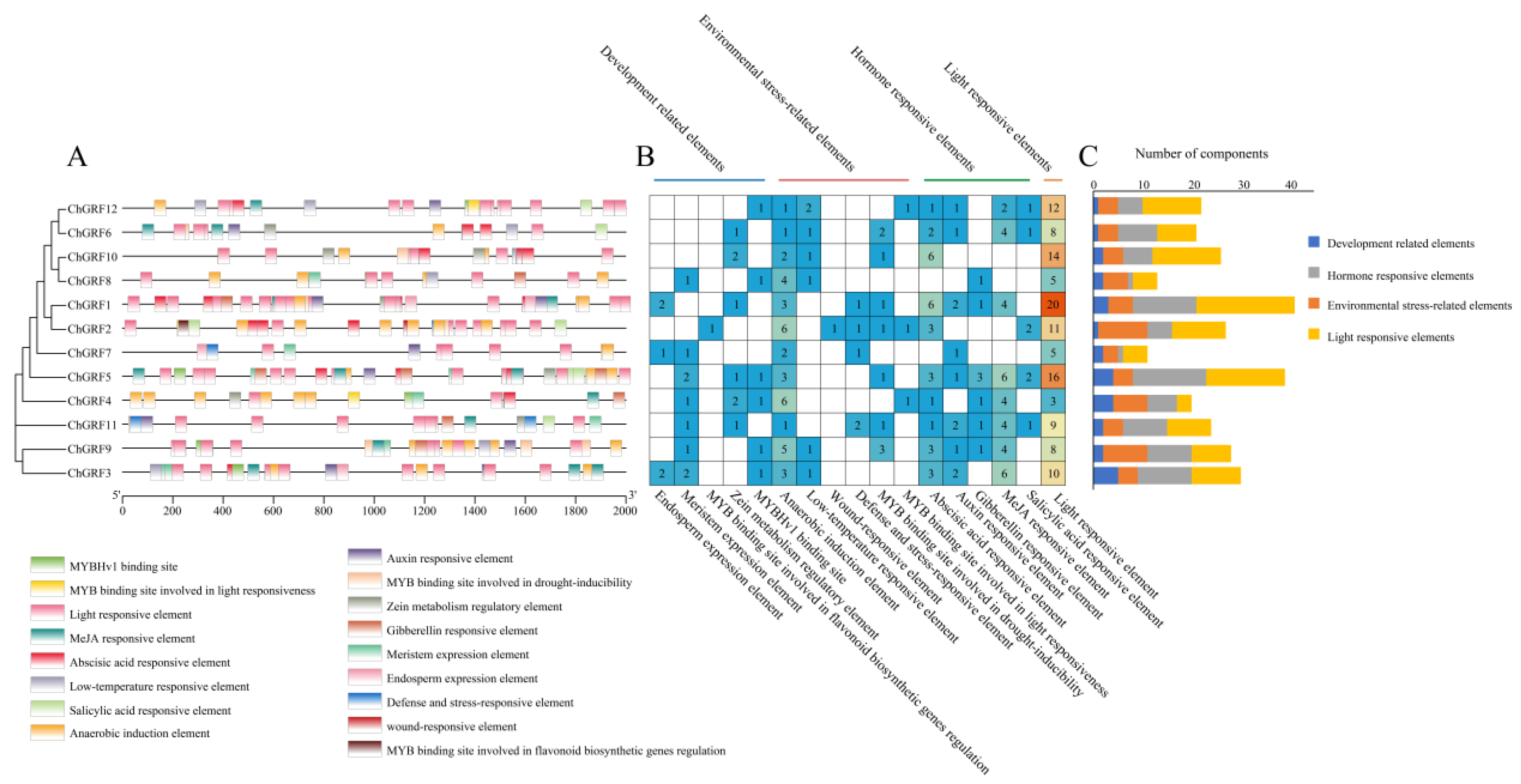
2.5. Gene Structure and Motifs of ChGRF
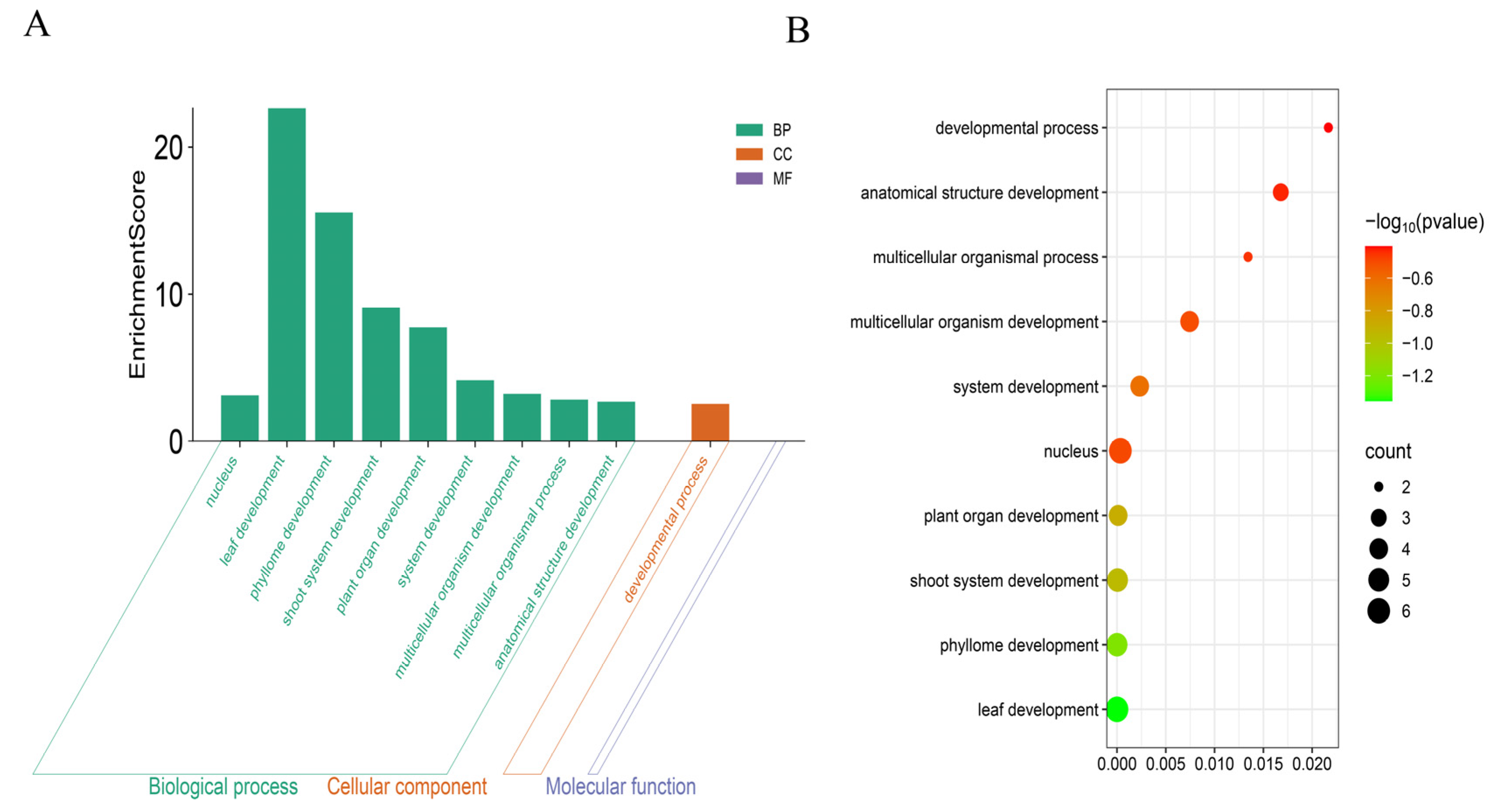
2.6. Cis-Element Analysis and GO Analysis of the ChGRF Promoter
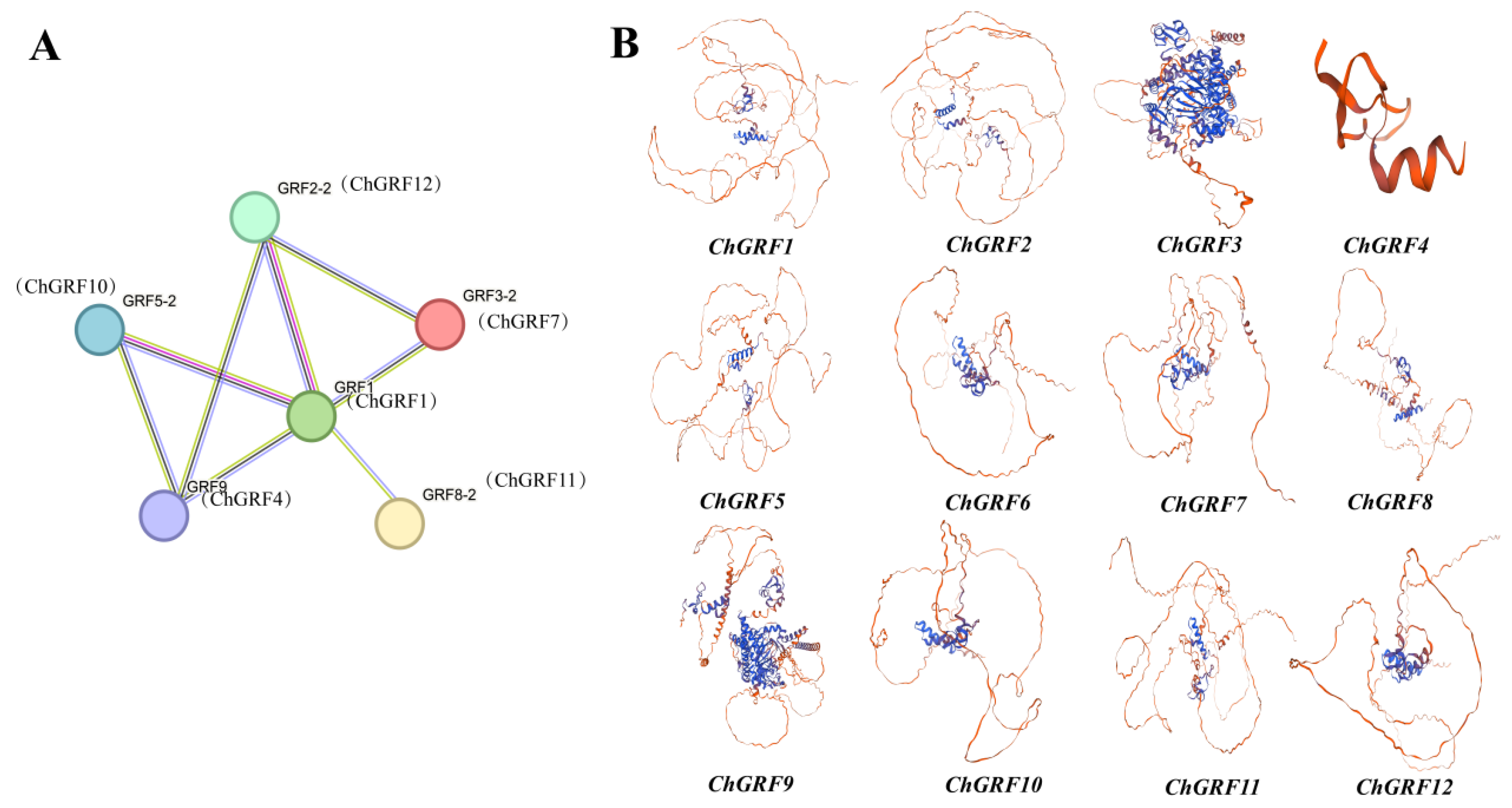
2.7. Protein–Protein Interaction Network Analysis
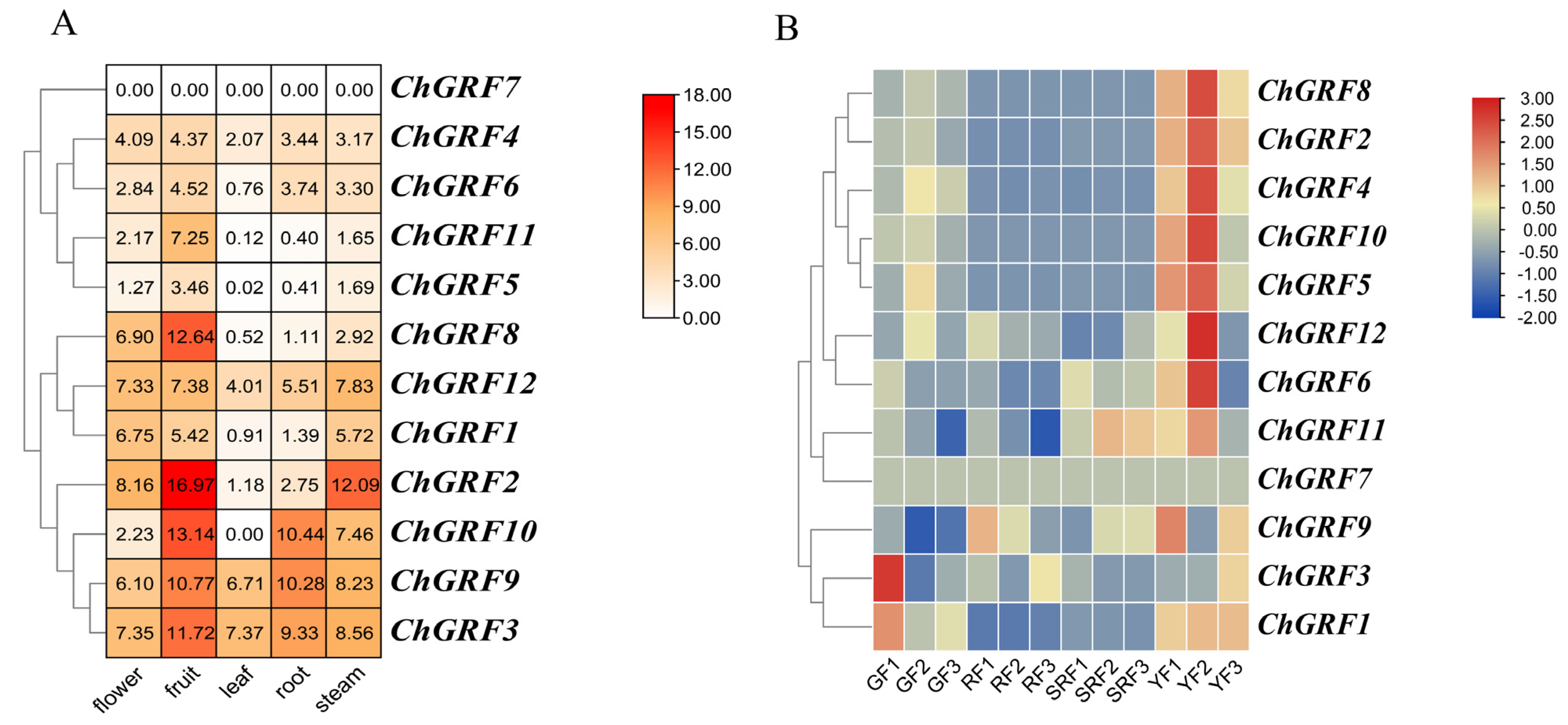
2.8. Expression Analysis of ChGRF Genes in Different Tissues and Developmental Stages
2.9. RNA Extraction Andq qRT-PCR Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of GRF Genes
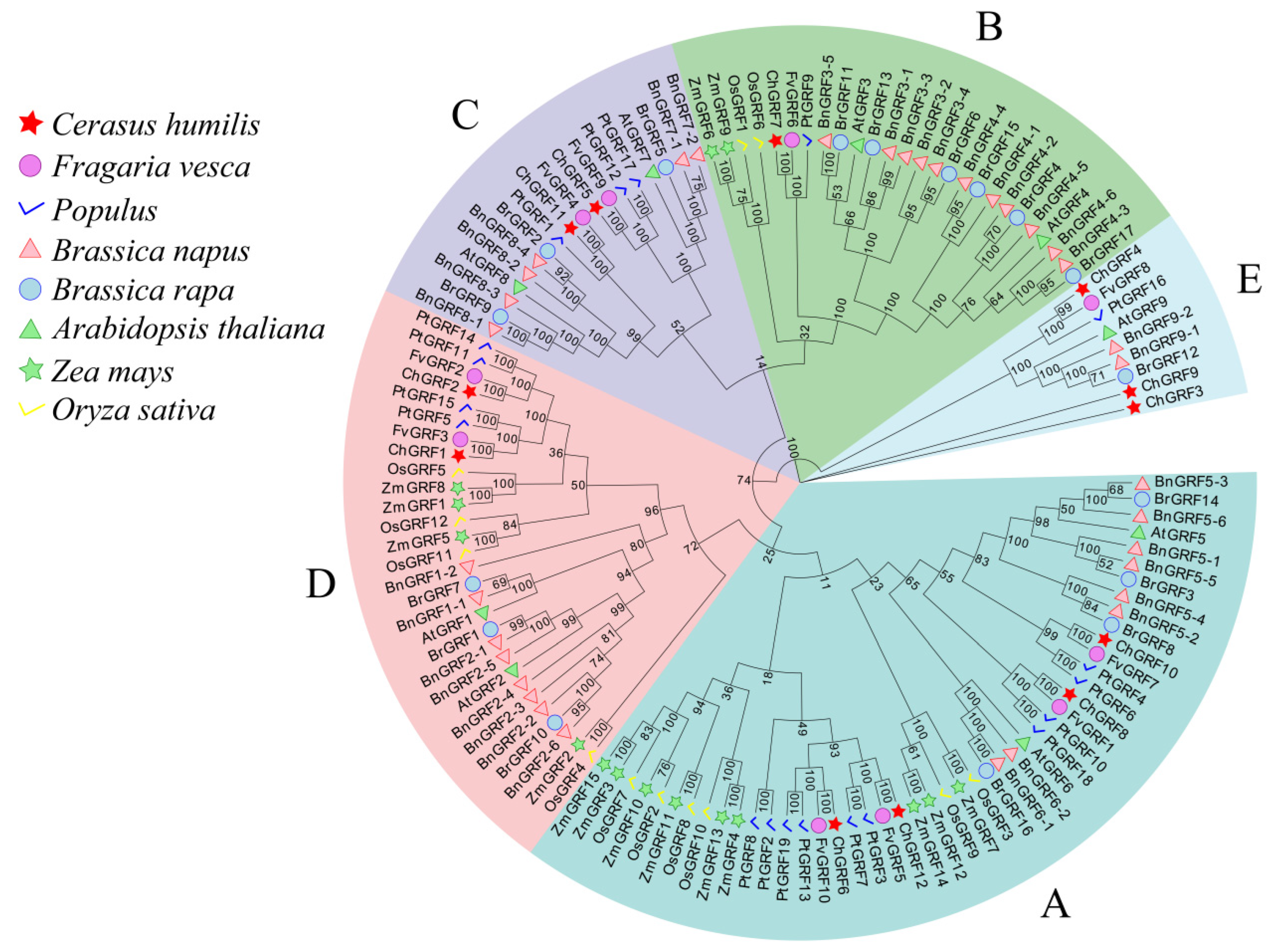
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
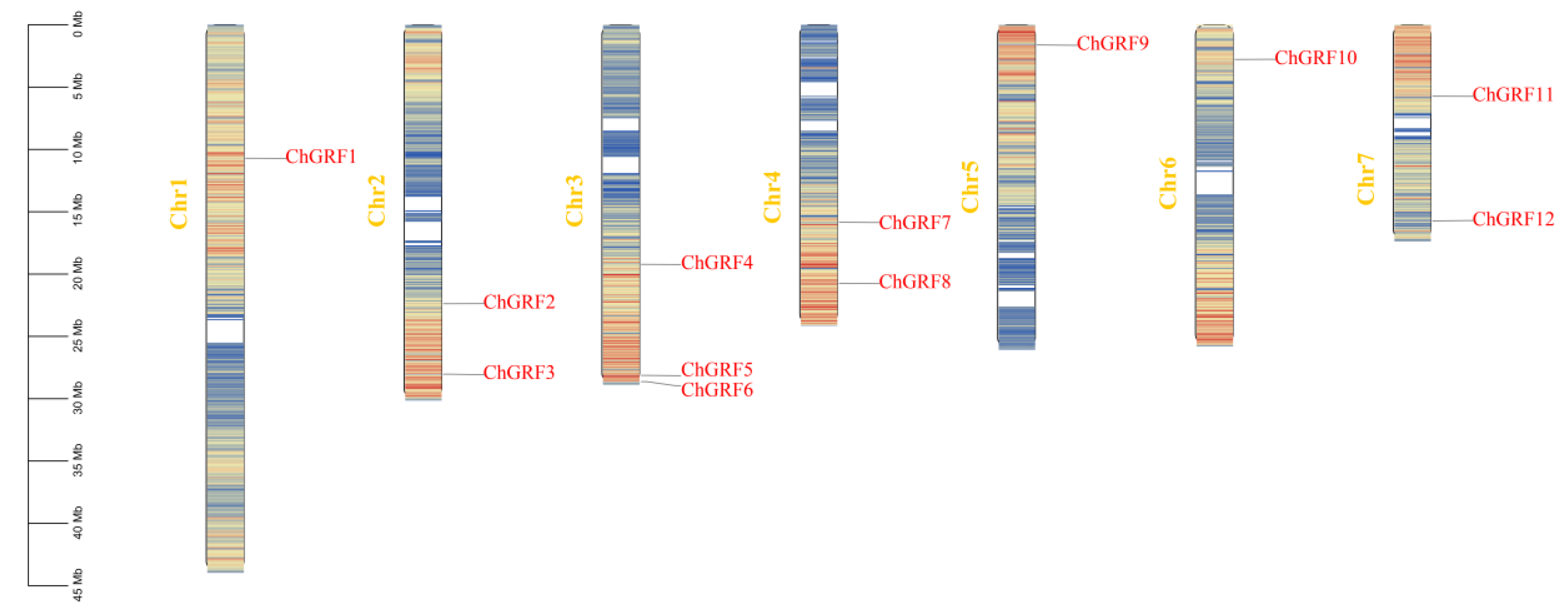
3.3. Chromosome Localization Analysis
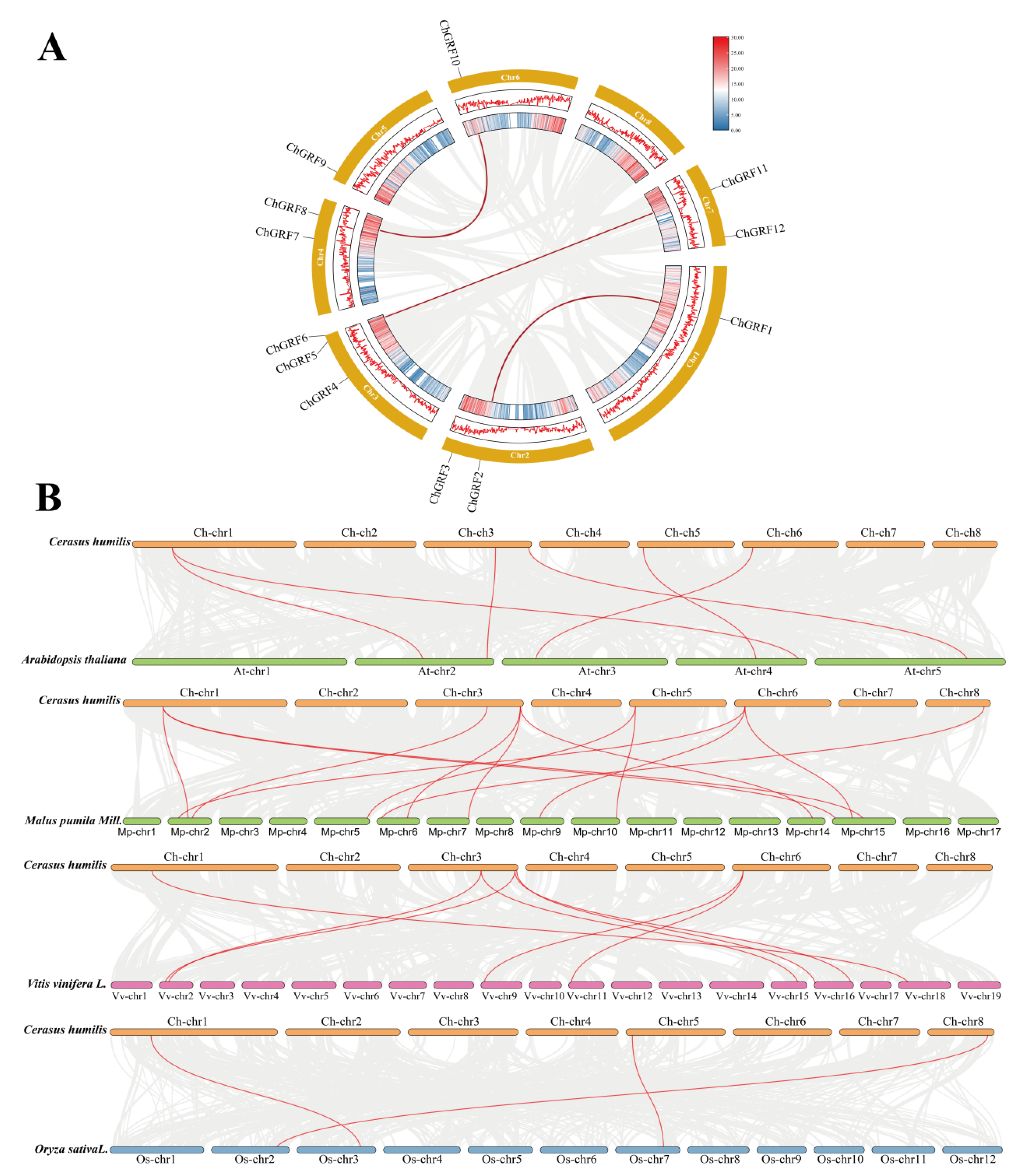
3.4. Collinearity and Evolutionary Analysis
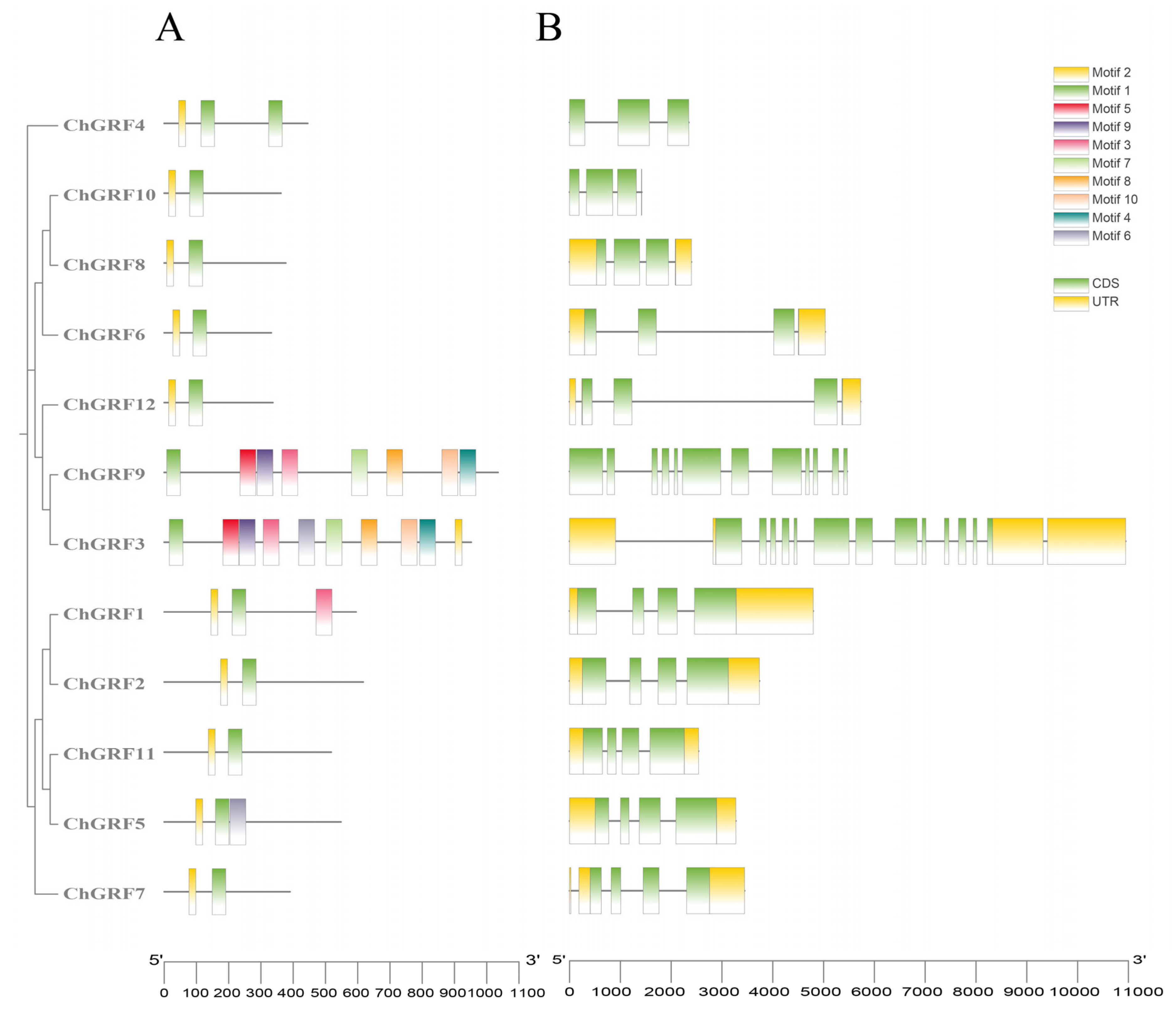
3.5. Analysis of the GRF Gene Structure and Conserved Motifs
3.6. Cis-Elements of ChGRF Genes and Their Functional Analysis
3.7. GO Analysis of the ChGRF Gene Family
3.8. Protein–Protein Interaction Network Analysis and Homology Modeling
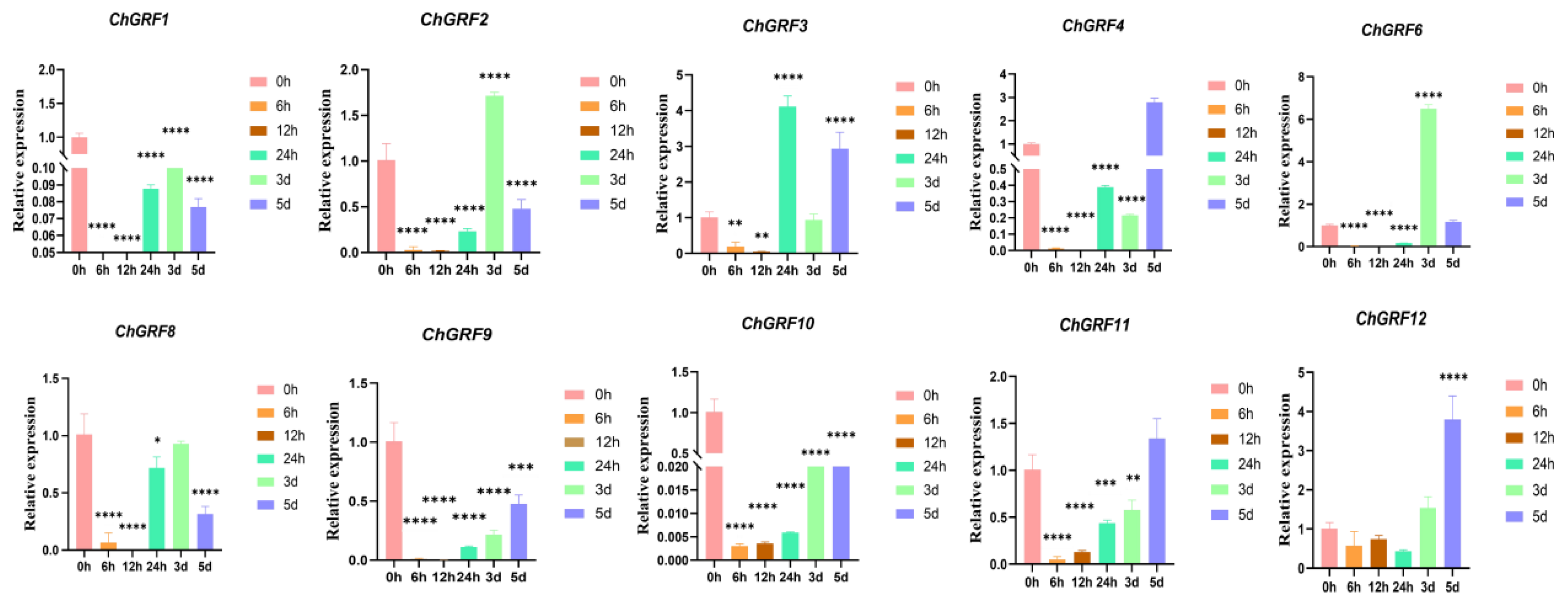
3.9. Analysis of ChGRF Gene Expression
3.10. RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoe Kim, J.; Tsukaya, H. Regulation of plant growth and development by the GROWTH-REGULATING FACTOR and GRF-INTERACTING FACTOR duo. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 6093–6107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, M.; Bian, H.; Zha, Y.; Li, F.; Sun, Y.; Bai, B.; Chen, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhu, M.; Han, N. miR396a-Mediated Basic Helix–Loop–Helix Transcription Factor bHLH74 Repression Acts as a Regulator for Root Growth in Arabidopsis Seedlings. Plant Cell Physiol. 2014, 55, 1343–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debernardi, J.M.; Mecchia, M.A.; Vercruyssen, L.; Smaczniak, C.; Kaufmann, K.; Inze, D.; Rodriguez, R.E.; Palatnik, J.F. Post-transcriptional control of GRF transcription factors by microRNA miR396 and GIF co-activator affects leaf size and longevity. Plant J. 2014, 79, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Guo, S.; Xu, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Xu, S.; Zhang, C.; Chong, K. OsmiR396d-Regulated OsGRFs Function in Floral Organogenesis in Rice through Binding to Their Targets OsJMJ706 and OsCR4. Plant Physiol. 2014, 165, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidbakhshfard, M.A.; Proost, S.; Fujikura, U.; Mueller-Roeber, B. Growth-Regulating Factors (GRFs): A Small Transcription Factor Family with Important Functions in Plant Biology. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 998–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatun, K.; Robin, A.H.K.; Park, J.-I.; Nath, U.K.; Kim, C.K.; Lim, K.-B.; Nou, I.S.; Chung, M.-Y. Molecular Characterization and Expression Profiling of Tomato GRF Transcription Factor Family Genes in Response to Abiotic Stresses and Phytohormones. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongsu Choi, J.H.K.H.K. Whole Genome Analysis of the OsGRF Gene Family Encoding Plant-Specific Putative Transcription Activators in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Physiol 2004, 45, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Qiu, N.; Ding, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Gao, J. Genome-wide identification and analysis of the growth-regulating factor family in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis). BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Knaap, E.; Kim, J.H.; Kende, H. A Novel Gibberellin-Induced Gene from Rice and Its Potential Regulatory Role in Stem Growth. Plant Physiol. 2000, 122, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiguchi, G.; Kim, G.T.; Tsukaya, H. The transcription factor AtGRF5 and the transcription coactivator AN3 regulate cell proliferation in leaf primordia of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2005, 43, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; He, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, F.; Yu, D. Molecular Mechanism of microRNA396 Mediating Pistil Development in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2013, 164, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-J.; Lee, B.H.; Jung, J.-H.; Park, S.K.; Song, J.T.; Kim, J.H. GROWTH-REGULATING FACTOR and GRF-INTERACTING FACTOR Specify Meristematic Cells of Gynoecia and Anthers. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Gao, F.; Xie, K.; Zeng, X.; Cao, Y.; Zeng, J.; He, Z.; Ren, Y.; Li, W.; Deng, Q.; et al. The OsmiR396c-OsGRF4-OsGIF1 regulatory module determines grain size and yield in rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 2134–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, R.; Tong, H.; Shi, B.; Liu, Y.; Fang, S.; Liu, D.; Xiao, Y.; Hu, B.; Liu, L.; Wang, H.; et al. Control of grain size and rice yield by GL2-mediated brassinosteroid responses. Nat. Plants 2015, 2, 15195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Jin, J.; Xie, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Q.; Luo, Z.; Yang, J. Genome-wide identification and analysis of the growth-regulating factor family in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum). Gene 2018, 639, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.-Z.; Huang, J.; Zhou, X.-Q.; Hao, Y.; Chen, J.-L.; Zhou, Y.-Z.; Ahmad, S.; Lan, S.; Liu, Z.-J.; Peng, D.-H. Comprehensive Analysis for GRF Transcription Factors in Sacred Lotus (Nelumbo nucifera). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Yuan, R.-Y.; Feng, C.-Y.; Li, S.-S.; Wang, L.-S. Analysis of Polyphenols Composition and Antioxidant Activity Assessment of Chinese Dwarf Cherry (Cerasus humilis (Bge.) Sok.). Nat. Prod. Commun. 2019, 14, 1934578X19856509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Mu, X.; Du, J.; Gao, Y.G.; Bai, D.; Jia, L.; Zhang, J.; Ren, H.; Xue, X. Flavonoid content and radical scavenging activity in fruits of Chinese dwarf cherry (Cerasus humilis) genotypes. J. For. Res. 2017, 29, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yi, S.; Mu, X.; Zhang, J.; Du, J. Chromosome-Level Genome Assembly of Cerasus humilis Using PacBio and Hi-C Technologies. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Huang, Z.; Ma, R.; Ramakrishnan, M.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yrjälä, K. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of LBD transcription factor genes in Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Ren, W.; Ma, L.; Wu, J.; Zhang, X.; Wu, W.; Kong, L.; He, J.; Ma, W.; Liu, X. Identification of the lateral organ boundary domain gene family and its preservation by exogenous salicylic acid in Cerasus humilis. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2024, 30, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Fu, G.; Jiang, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, D.; Luo, Z.; et al. Chromosome-scale Cerasus humilis genome assembly reveals gene family evolution and possible genomic basis of calcium accumulation in fruits. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 299, 111012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Bai, Y.; Shen, C.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, D.; Guilfoyle, T.J.; Chen, M.; Qi, Y. Auxin-related gene families in abiotic stress response in Sorghum bicolor. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2010, 10, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, U.; Mundhe, S.; Kumar, Y.; Jogaiah, S.; Upadhyay, A.; Gupta, V.S.; Kadoo, N.Y. Gibberellic Acid Induces Unique Molecular Responses in ‘Thompson Seedless’ Grapes as Revealed by Non-targeted Metabolomics. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2020, 40, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Tang, Z.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, K.; Liu, H.; Zhang, S.; Wu, J. Mining and evolution analysis of lateral organ boundaries domain (LBD) genes in Chinese white pear (Pyrus bretschneideri). BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artimo, P.; Jonnalagedda, M.; Arnold, K.; Baratin, D.; Csardi, G.; de Castro, E.; Duvaud, S.; Flegel, V.; Fortier, A.; Gasteiger, E.; et al. ExPASy: SIB bioinformatics resource portal. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W597–W603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol Biol Evol 2016, 33, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; DeBarry, J.D.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lee, T.h.; Jin, H.; Marler, B.; Guo, H.; et al. MCScanX: A toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.A.; Frith, M.; Grant, C.E.; Clementi, L.; Ren, J.; Li, W.W.; Noble, W.S. MEME SUITE: Tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W202–W208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, P.; Qin, C.; He, L.; Kong, L.; Ren, W.; Liu, X.; Ma, W. Genome-wide identification of the NAC transcription factors family and regulation of metabolites under salt stress in Isatis indigotica. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 240, 124436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LiLi, Z.; Xie, Q.; Yan, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, Q. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of the Abiotic-Stress-Responsive GRF Gene Family in Diploid Woodland Strawberry (Fragaria vesca). Plants 2021, 10, 1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, M.; Conery, J.S. The evolutionary fate and consequences of duplicate genes. Science 2000, 290, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Sun, J.; Jiang, Z.; Ren, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Ma, W.; Xu, J. Identification and expression analysis of YABBY family genes in Platycodon grandiflorus. Plant Signal. Behav. 2023, 18, 2163069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Ren, W.; Liu, X.; He, L.; Qin, C.; Wang, P.; Kong, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, W. Identification and characterization of Dof genes in Cerasus humilis. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, H.; Ma, H.; Dong, A.; Huang, H. Arabidopsis GenesAS1,AS2, andJAGNegatively Regulate Boundary-Specifying Genes to Promote Sepal and Petal Development. Plant Physiol. 2008, 146, 323–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, T.P.; Sá, M.E.; Malagutti, E.S.; Pinto, M.S.; Ferreira, A.F.A.; Monteiro, L.N.H.; Silva, A.C.C. Effects of gibberellic acid concentration and fruit maturation stage on seed germination and vigor of pitahaya seedlings. Braz J Biol. 2022, 3, e260650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Yang, B.; Ge, M.; Zhang, Z. Effects of gibberellin applications before flowering on the phenotype, ripening, and flavonoid compounds of Syrah grape berries. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 6100–6111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, R.E.; Mecchia, M.A.; Debernardi, J.M.; Schommer, C.; Weigel, D.; Palatnik, J.F. Control of cell proliferation in Arabidopsis thaliana by microRNA miR396. Development 2010, 137, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Hou, Z.; Liao, J.; Qin, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Su, W.; Cai, Z.; Fang, Y.; Aslam, M.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of LBD Transcription Factor Genes in Passion Fruit (Passiflora edulis). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwakawa, H.; Ueno, Y.; Semiarti, E.; Onouchi, H.; Kojima, S.; Tsukaya, H.; Hasebe, M.; Soma, T.; Ikezaki, M.; Machida, C.; et al. The ASYMMETRIC LEAVES2 gene of Arabidopsis thaliana, required for formation of a symmetric flat leaf lamina, encodes a member of a novel family of proteins characterized by cysteine repeats and a leucine zipper. Plant Cell Physiol. 2002, 43, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derelli Tufekci, E. Genome-wide identification and analysis of Lateral Organ Boundaries Domain (LBD) transcription factor gene family in melon (Cucumis melo L.). PeerJ 2023, 11, e16020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim JH, K.H. A transcriptional coactivator, AtGIF1, is involved in regulating leaf growth and morphology in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Guo, L.-X.; Jin, L.-F.; Liu, Y.-Z.; Liu, T.; Fan, Y.-H.; Peng, S.-A. Identification and transcript profiles of citrus growth-regulating factor genes involved in the regulation of leaf and fruit development. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2016, 43, 1059–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yao, W.; Zhao, K.; Liu, L.; Fan, G.; Zhou, B.; Jiang, T. Genome-wide search and structural and functional analyses for late embryogenesis-abundant (LEA) gene family in poplar. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tu, Z.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Q.; Li, H. Genome-wide identification of GROWTH-REGULATING FACTORs in Liriodendron chinense and functional characterization of LcGRF2 in leaf size regulation. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 206, 108204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, I.F.; Curran, A.; Woolsey, R.; Quilici, D.; Cushman, J.C.; Mittler, R.; Harmon, A.; Harper, J.F. Proteomic profiling of tandem affinity purified 14-3-3 protein complexes inArabidopsis thaliana. Proteomics 2009, 9, 2967–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuma, Y.; Liu, Q.; Dubouzet, J.G.; Abe, H.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. DNA-Binding Specificity of the ERF/AP2 Domain of Arabidopsis DREBs, Transcription Factors Involved in Dehydration- and Cold-Inducible Gene Expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 290, 998–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, T.; Nelson, D.; Saleem, A.; Bibi, M.; Joshi, N.; Fahad, S.; Saud, S.; Adnan, M.; Rasheed Khan, M.N.; Hassan, S.; et al. Genetic Engineering for Crop Biofortification. In Crop Biofortification; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2025; pp. 263–294. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; He, Y.; He, W.; Su, H.; Wang, Y.; Hong, G.; Xu, P. Structural and functional insights into the LBD family involved in abiotic stress and flavonoid synthases in Camellia sinensis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, L.; Ma, L.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, X.; Ma, J.; Pan, M.; Wu, W.; Liu, W.; Ren, W.; Ma, W. Genome-Wide Identification, Exogenous Hormone Response, Gene Structure, and Conserved Motif Analysis of the GRF Gene Family in Cerasus humilis. Biology 2025, 14, 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14070763
Kong L, Ma L, Jiang S, Zhang X, Ma J, Pan M, Wu W, Liu W, Ren W, Ma W. Genome-Wide Identification, Exogenous Hormone Response, Gene Structure, and Conserved Motif Analysis of the GRF Gene Family in Cerasus humilis. Biology. 2025; 14(7):763. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14070763
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Lingyang, Lengleng Ma, Shan Jiang, Xinyi Zhang, Junbai Ma, Meitong Pan, Wei Wu, Weili Liu, Weichao Ren, and Wei Ma. 2025. "Genome-Wide Identification, Exogenous Hormone Response, Gene Structure, and Conserved Motif Analysis of the GRF Gene Family in Cerasus humilis" Biology 14, no. 7: 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14070763
APA StyleKong, L., Ma, L., Jiang, S., Zhang, X., Ma, J., Pan, M., Wu, W., Liu, W., Ren, W., & Ma, W. (2025). Genome-Wide Identification, Exogenous Hormone Response, Gene Structure, and Conserved Motif Analysis of the GRF Gene Family in Cerasus humilis. Biology, 14(7), 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14070763





