Cannabinoid Modulation of Excitability and Short-Term Neuronal Dynamics in the Dorsal and Ventral Hippocampus
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals and Hippocampal Slice Preparation
2.2. Electrophysiology and Data Analysis
2.3. Immunoblotting
2.4. Drugs
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
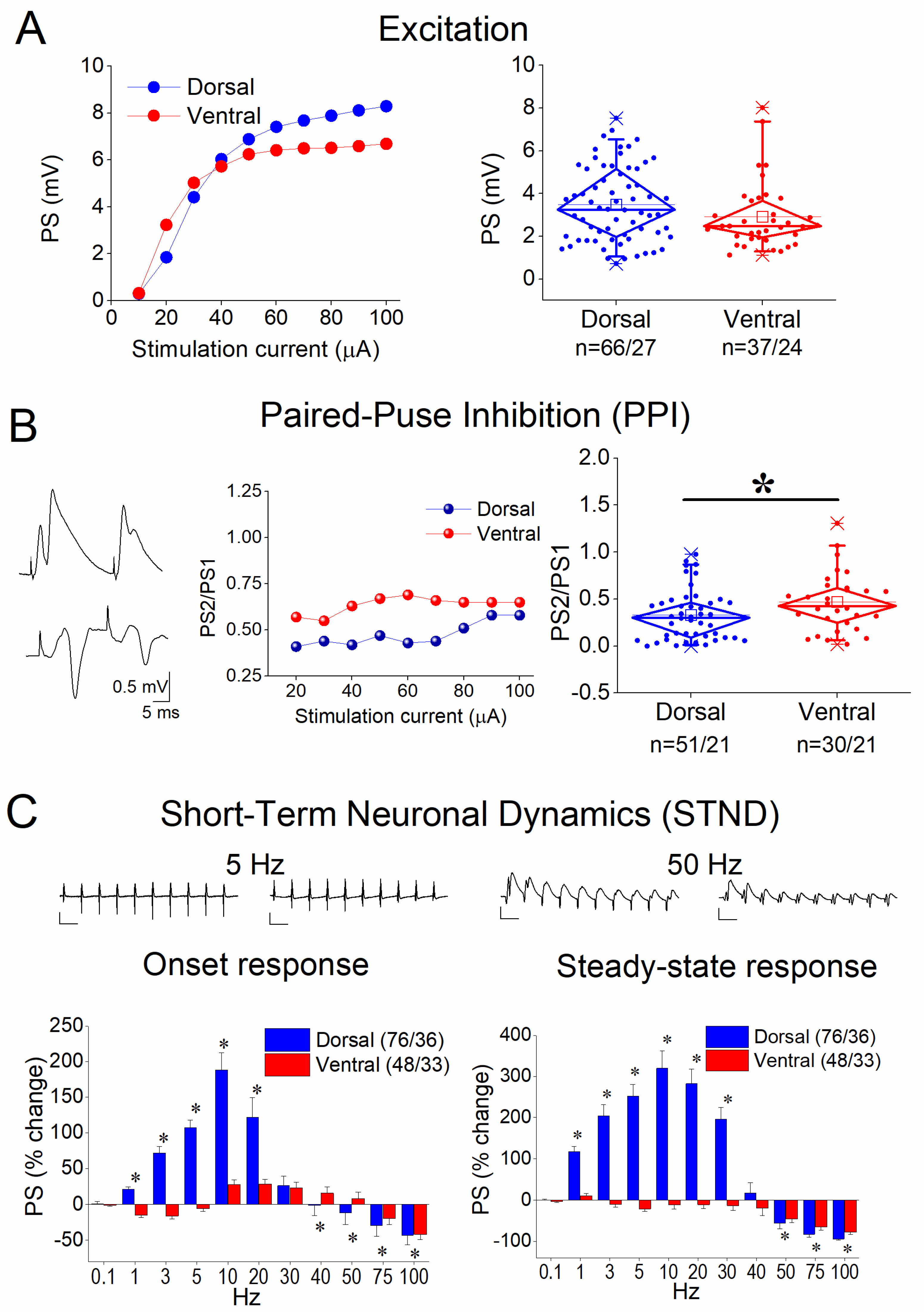
3.1. Basal Excitation, Paired-Pulse Inhibition (PPI), and Short-Term Neuronal Dynamics (STND) in the Dorsal and Ventral Hippocampus
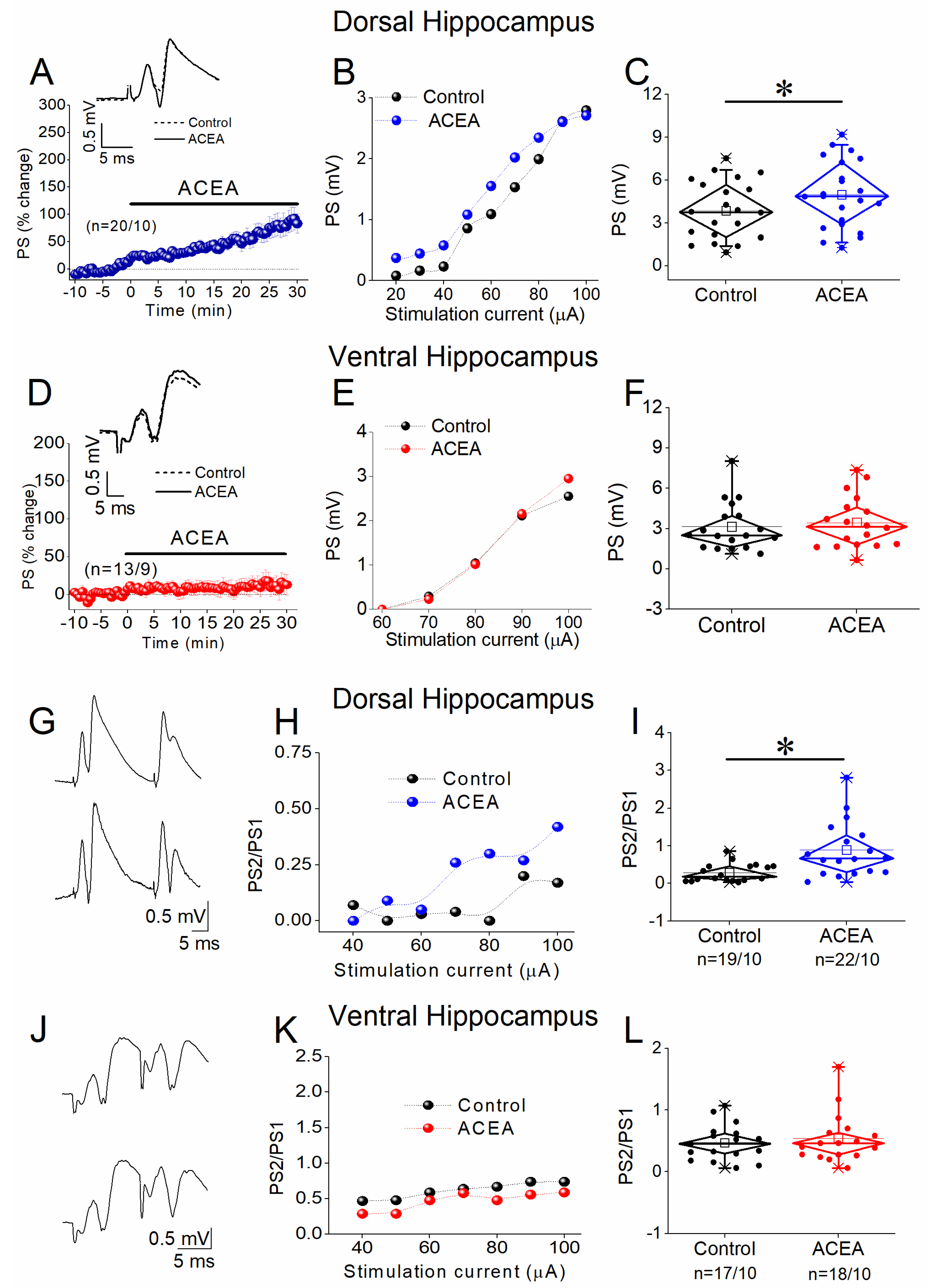
3.2. ACEA Enhances Network Excitation and Reduces PPI in the Dorsal but Not the Ventral Hippocampus
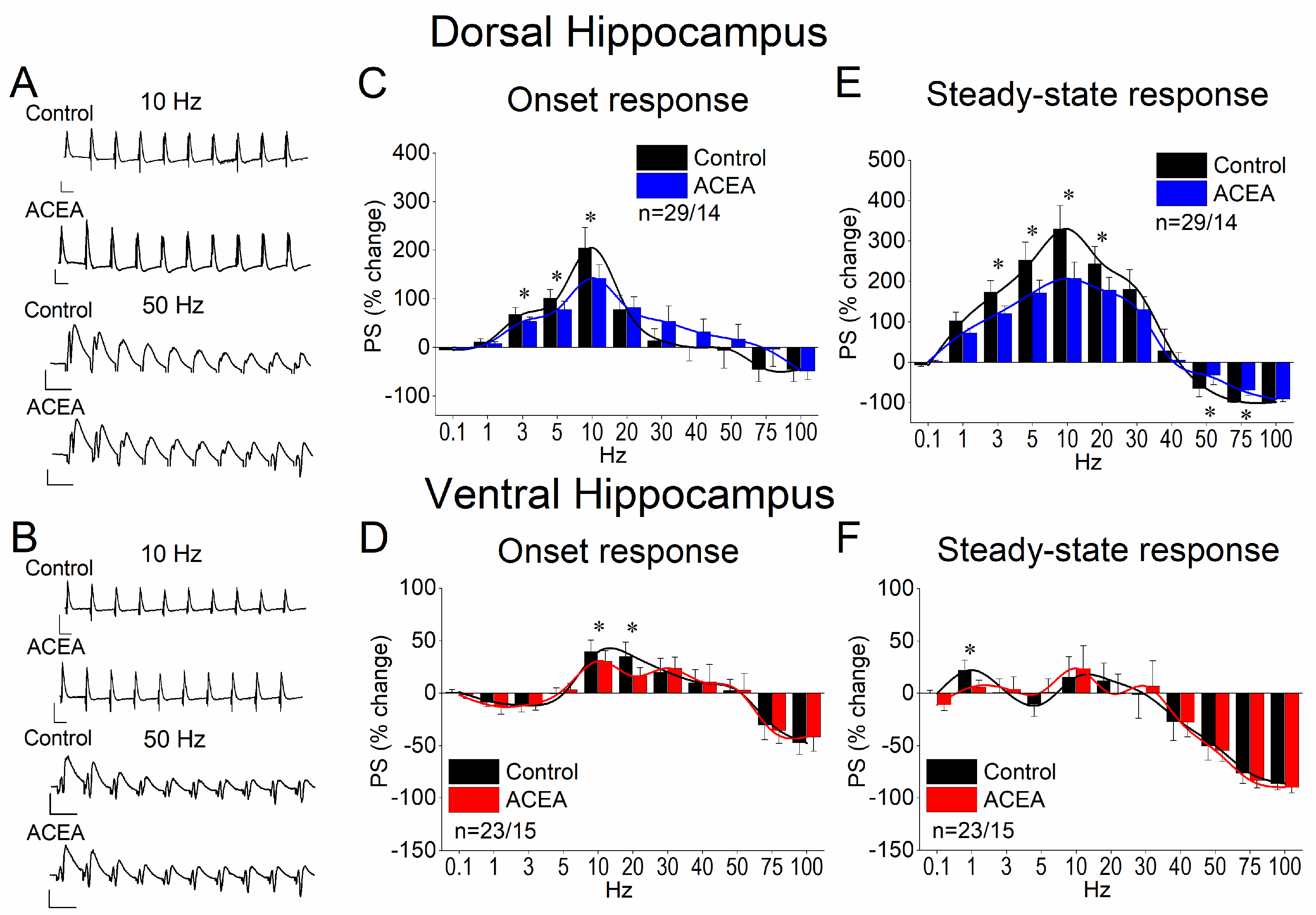
3.3. ACEA Modulates STND More in the Dorsal Than in the Ventral Hippocampus
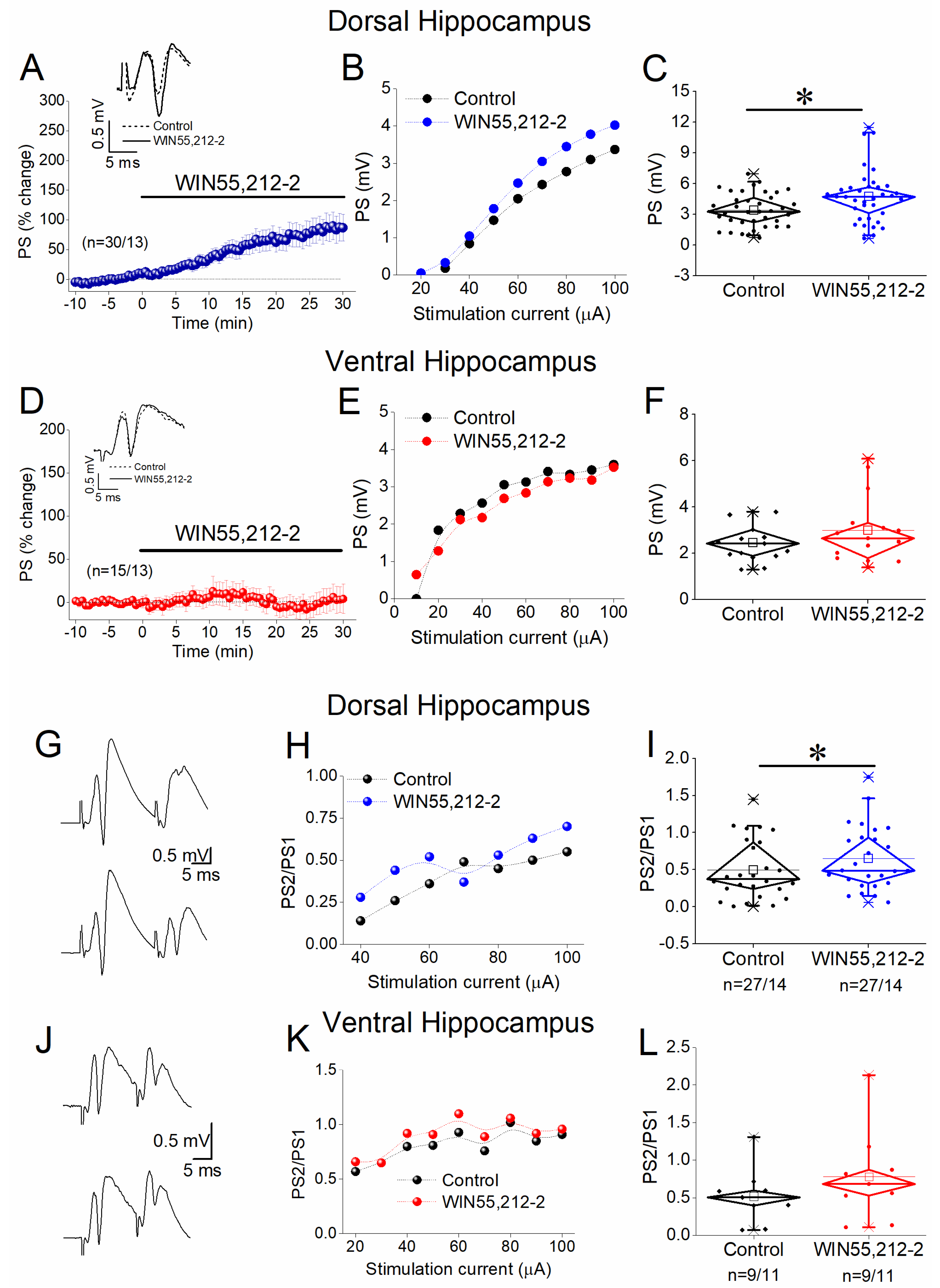
3.4. WIN55,212-2 Enhances Network Excitation and Reduces PPI in the Dorsal but Not the Ventral Hippocampus
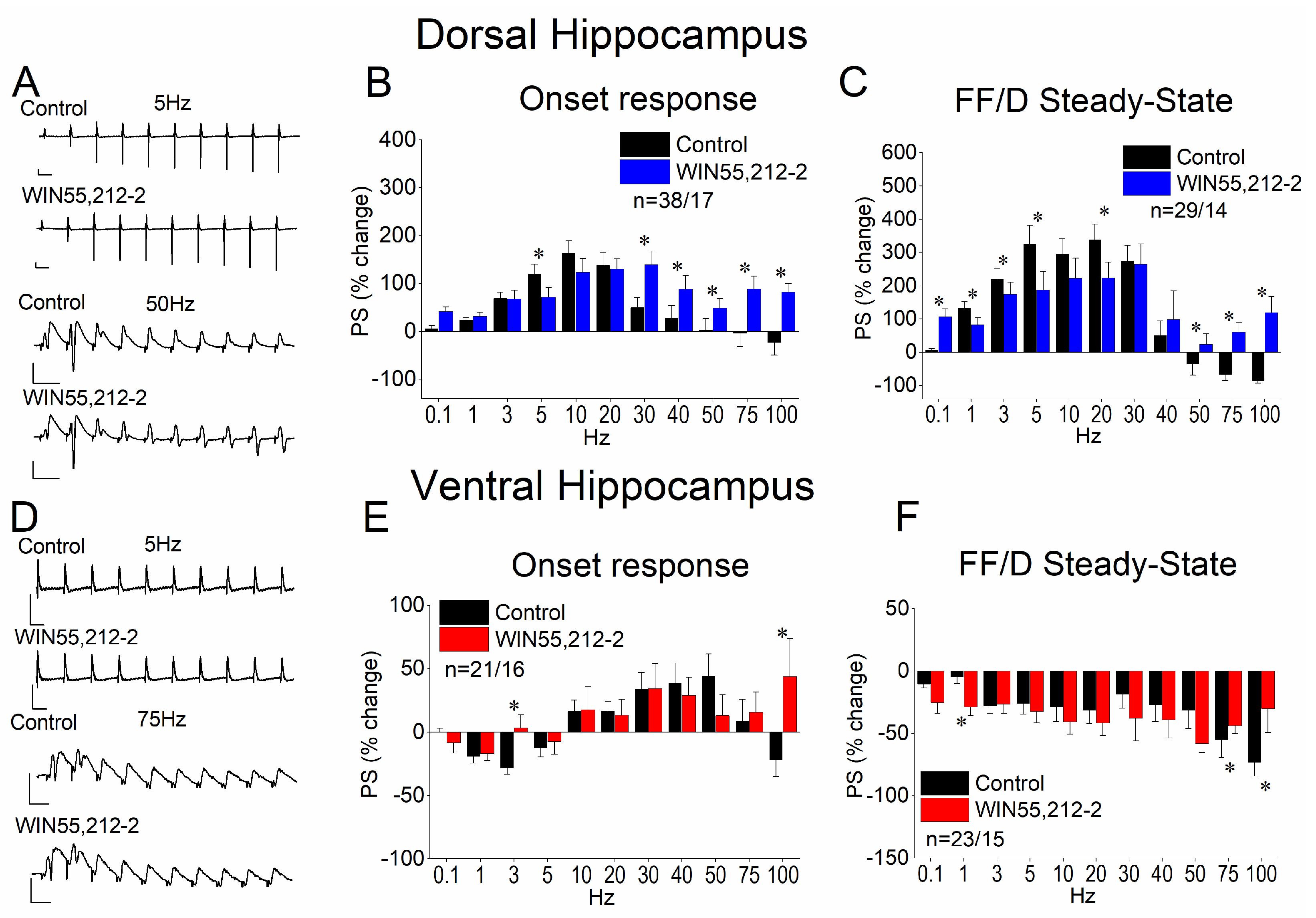
3.5. WIN55,212-2 Regulates STND More in the Dorsal Than in the Ventral Hippocampus
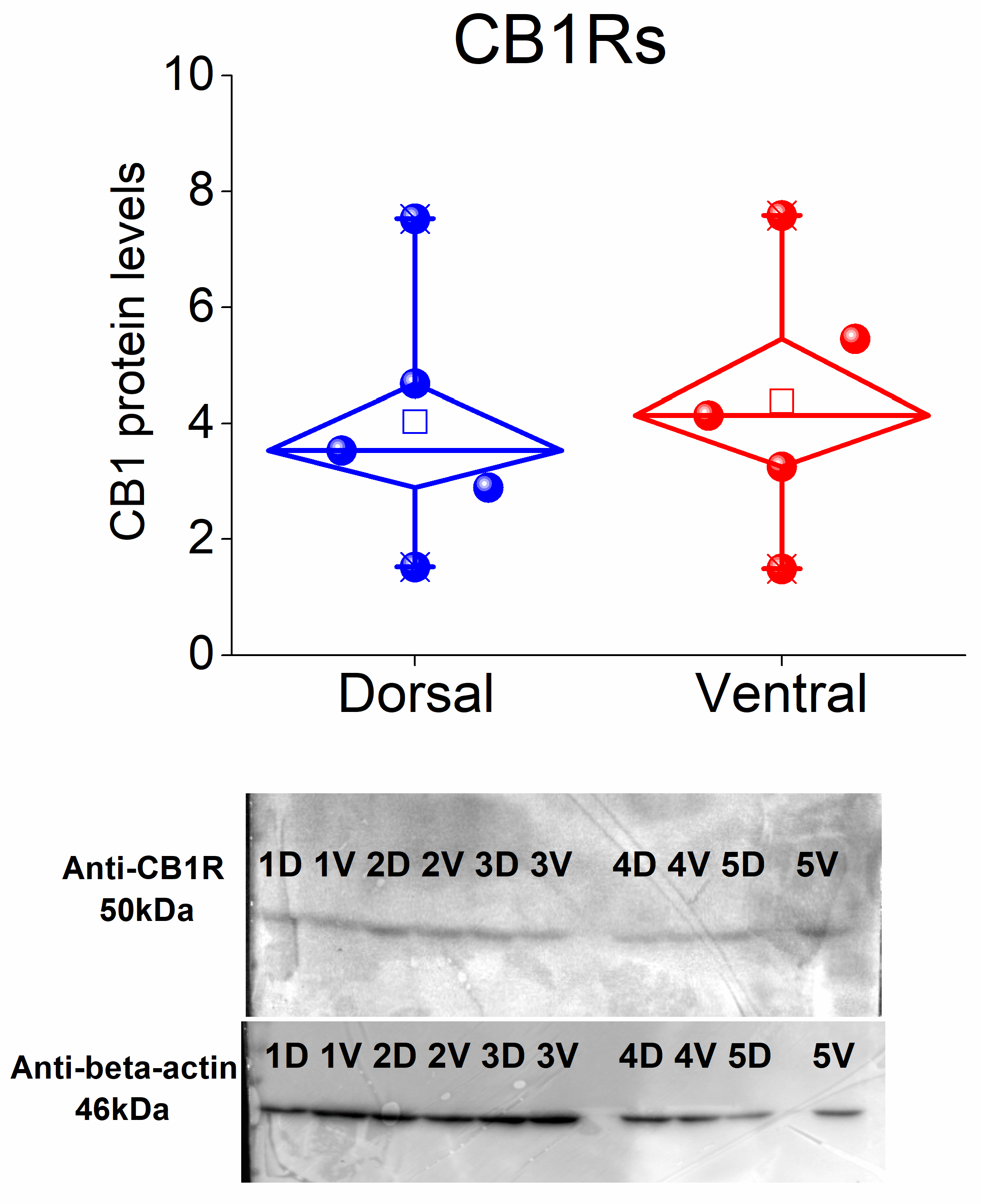
3.6. CB1 Receptors Are Similarly Expressed in the Dorsal and Ventral CA1 Hippocampal Regions
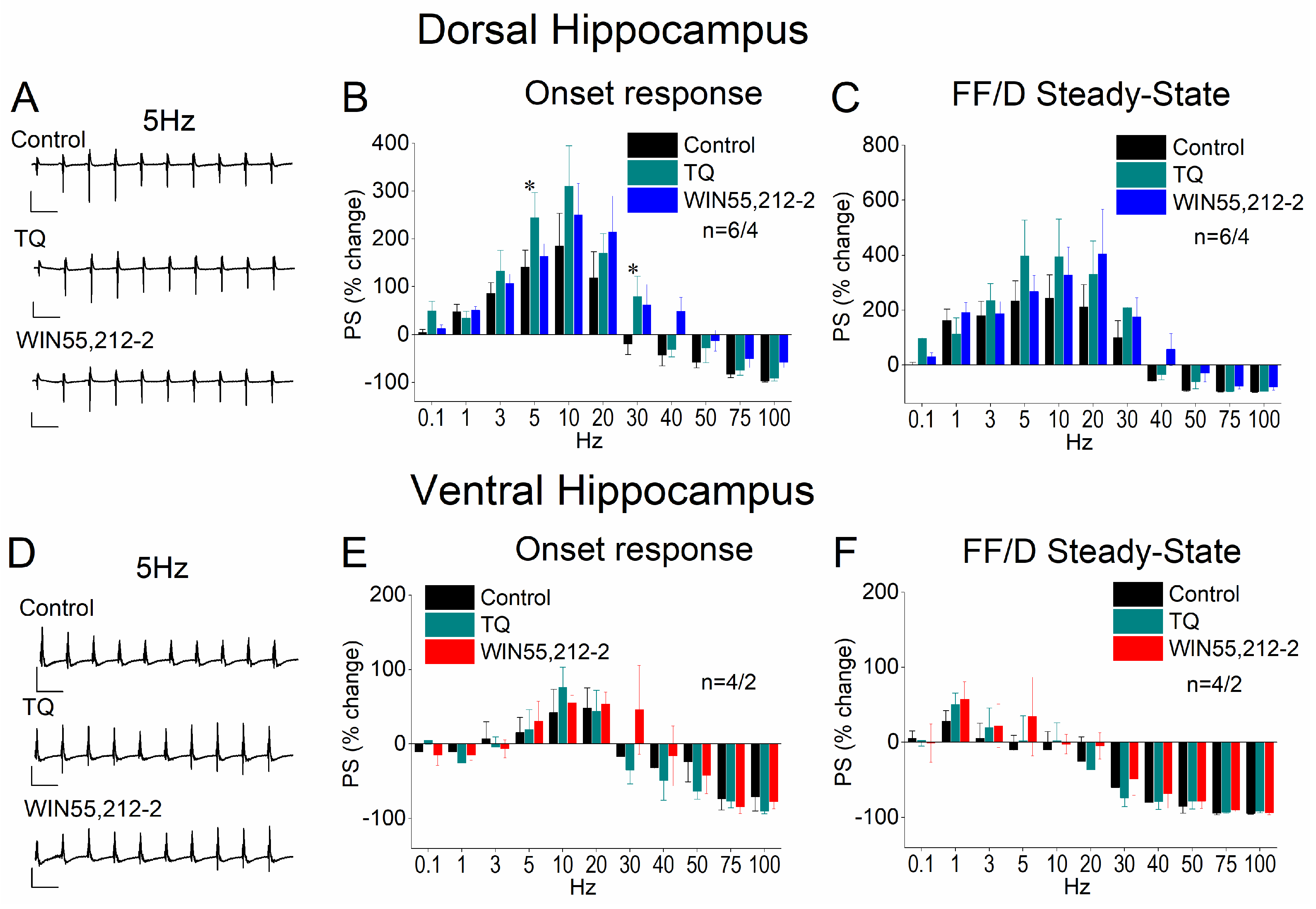
3.7. Blockade of GIRK Channels Occludes the Effects of WIN55,212-2 on STND
4. Discussion
Implications for Functional Specialization Along the Hippocampus
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CB | Cannabinoid |
| PS | Population spike |
| PPI | Paired-pulse inhibition |
| STND | Short-term neuronal dynamics |
| E/I | Excitation/inhibition |
| GIRK | Inwardly rectifying potassium |
References
- Mechoulam, R.; Parker, L.A. The endocannabinoid system and the brain. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2013, 64, 21–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leweke, F.M.; Piomelli, D.; Pahlisch, F.; Muhl, D.; Gerth, C.W.; Hoyer, C.; Klosterkötter, J.; Hellmich, M.; Koethe, D. Cannabidiol enhances anandamide signaling and alleviates psychotic symptoms of schizophrenia. Transl. Psychiatry 2012, 2, e94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witkin, J.M.; Tzavara, E.T.; Nomikos, G.G. A role for cannabinoid CB1 receptors in mood and anxiety disorders. Behav. Pharmacol. 2005, 16, 315–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.C.; Mackie, K. An Introduction to the Endogenous Cannabinoid System. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 79, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristino, L.; Bisogno, T.; Di Marzo, V. Cannabinoids and the expanded endocannabinoid system in neurological disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 16, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlett, A.C.; Barth, F.; Bonner, T.I.; Cabral, G.; Casellas, P.; Devane, W.A.; Felder, C.C.; Herkenham, M.; Mackie, K.; Martin, B.R.; et al. International Union of Pharmacology. XXVII. Classification of cannabinoid receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2002, 54, 161–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.C.; Mackie, K. Review of the Endocannabinoid System. Biol. Psychiatry. Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2021, 6, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kano, M.; Ohno-Shosaku, T.; Hashimotodani, Y.; Uchigashima, M.; Watanabe, M. Endocannabinoid-mediated control of synaptic transmission. Physiol. Rev. 2009, 89, 309–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiègue, S.; Mary, S.; Marchand, J.; Dussossoy, D.; Carrière, D.; Carayon, P.; Bouaboula, M.; Shire, D.; Le Fur, G.; Casellas, P. Expression of central and peripheral cannabinoid receptors in human immune tissues and leukocyte subpopulations. Eur. J. Biochem. 1995, 232, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stempel, A.V.; Stumpf, A.; Zhang, H.Y.; Özdoğan, T.; Pannasch, U.; Theis, A.K.; Otte, D.M.; Wojtalla, A.; Rácz, I.; Ponomarenko, A.; et al. Cannabinoid Type 2 Receptors Mediate a Cell Type-Specific Plasticity in the Hippocampus. Neuron 2016, 90, 795–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarfarin, M.; Ghadiri, T.; Dadkhah, M.; Sahab-Negah, S. The interaction between cannabinoids and long-term synaptic plasticity: A survey on memory formation and underlying mechanisms. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2024, 42, e4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herkenham, M.; Lynn, A.B.; Little, M.D.; Johnson, M.R.; Melvin, L.S.; de Costa, B.R.; Rice, K.C. Cannabinoid receptor localization in brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 1932–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackie, K. Distribution of cannabinoid receptors in the central and peripheral nervous system. In Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 299–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, E.L.; Gallopin, T.; Férézou, I.; Cauli, B.; Rossier, J.; Schweitzer, P.; Lambolez, B. Functional CB1 receptors are broadly expressed in neocortical GABAergic and glutamatergic neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 2007, 97, 2580–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, P.E.; Younts, T.J.; Chavez, A.E.; Hashimotodani, Y. Endocannabinoid signaling and synaptic function. Neuron 2012, 76, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno-Shosaku, T.; Kano, M. Endocannabinoid-mediated retrograde modulation of synaptic transmission. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2014, 29, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monory, K.; Massa, F.; Egertova, M.; Eder, M.; Blaudzun, H.; Westenbroek, R.; Kelsch, W.; Jacob, W.; Marsch, R.; Ekker, M.; et al. The endocannabinoid system controls key epileptogenic circuits in the hippocampus. Neuron 2006, 51, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busquets-Garcia, A.; Bains, J.; Marsicano, G. CB(1) Receptor Signaling in the Brain: Extracting Specificity from Ubiquity. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018, 43, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kim, J. CB2 Cannabinoid Receptor Knockout in Mice Impairs Contextual Long-Term Memory and Enhances Spatial Working Memory. Neural Plast 2016, 2016, 9817089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, C. Fine-tuning of synaptic upscaling at excitatory synapses by endocannabinoid signaling is mediated via the CB1 receptor. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katona, I.; Rancz, E.A.; Acsady, L.; Ledent, C.; Mackie, K.; Hajos, N.; Freund, T.F. Distribution of CB1 cannabinoid receptors in the amygdala and their role in the control of GABAergic transmission. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 9506–9518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, Y.; Fukaya, M.; Maejima, T.; Yoshida, T.; Miura, E.; Watanabe, M.; Ohno-Shosaku, T.; Kano, M. The CB1 cannabinoid receptor is the major cannabinoid receptor at excitatory presynaptic sites in the hippocampus and cerebellum. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 2991–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talani, G.; Licheri, V.; Biggio, F.; Locci, V.; Mostallino, M.C.; Secci, P.P.; Melis, V.; Dazzi, L.; Carta, G.; Banni, S.; et al. Enhanced Glutamatergic Synaptic Plasticity in the Hippocampal CA1 Field of Food-Restricted Rats: Involvement of CB1 Receptors. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016, 41, 1308–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monory, K.; Blaudzun, H.; Massa, F.; Kaiser, N.; Lemberger, T.; Schutz, G.; Wotjak, C.T.; Lutz, B.; Marsicano, G. Genetic dissection of behavioural and autonomic effects of Delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol in mice. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monory, K.; Polack, M.; Remus, A.; Lutz, B.; Korte, M. Cannabinoid CB1 receptor calibrates excitatory synaptic balance in the mouse hippocampus. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 3842–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarante, F.F.; Vila-Verde, C.; Detoni, V.L.; Ferreira-Junior, N.C.; Guimarães, F.S.; Campos, A.C. Cannabinoid Modulation of the Stressed Hippocampus. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroto, I.B.; Costas-Insua, C.; Berthoux, C.; Moreno, E.; Ruiz-Calvo, A.; Montero-Fernández, C.; Macías-Camero, A.; Martín, R.; García-Font, N.; Sánchez-Prieto, J.; et al. Control of a hippocampal recurrent excitatory circuit by cannabinoid receptor-interacting protein Gap43. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robledo-Menendez, A.; Vella, M.; Grandes, P.; Soria-Gomez, E. Cannabinoid control of hippocampal functions: The where matters. FEBS J. 2022, 289, 2162–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, L.E.; Thorpe, A.J.; Lichtman, A.H. Hippocampal CB(1) receptors mediate the memory impairing effects of Delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2009, 34, 2072–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, L.; Van Cleemput, J.; Ji, S.P.; Bai, G.; Zhang, X. Cannabinoids promote embryonic and adult hippocampus neurogenesis and produce anxiolytic- and antidepressant-like effects. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 3104–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, R.; Rushlow, W.; Laviolette, S.R. Phytocannabinoids modulate emotional memory processing through interactions with the ventral hippocampus and mesolimbic dopamine system: Implications for neuropsychiatric pathology. Psychopharmacology 2018, 235, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannerman, D.M.; Sprengel, R.; Sanderson, D.J.; McHugh, S.B.; Rawlins, J.N.; Monyer, H.; Seeburg, P.H. Hippocampal synaptic plasticity, spatial memory and anxiety. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 15, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.V.; Sahay, A.; Duman, R.S.; Hen, R. Functional differentiation of adult-born neurons along the septotemporal axis of the dentate gyrus. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a018978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papatheodoropoulos, C. Electrophysiological evidence for long-axis intrinsic diversification of the hippocampus. Front. Biosci. 2018, 23, 109–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouvaros, S.; Papatheodoropoulos, C. Major dorsoventral differences in the modulation of the local CA1 hippocampal network by NMDA, mGlu5, adenosine A2A and cannabinoid CB1 receptors. Neuroscience 2016, 317, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitler, T.A.; Alger, B.E. Postsynaptic spike firing reduces synaptic GABAA responses in hippocampal pyramidal cells. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 1992, 12, 4122–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.I.; Nicoll, R.A. Endogenous cannabinoids mediate retrograde signalling at hippocampal synapses. Nature 2001, 410, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno-Shosaku, T.; Maejima, T.; Kano, M. Endogenous cannabinoids mediate retrograde signals from depolarized postsynaptic neurons to presynaptic terminals. Neuron 2001, 29, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreitzer, A.C.; Regehr, W.G. Cerebellar depolarization-induced suppression of inhibition is mediated by endogenous cannabinoids. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2001, 21, Rc174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llano, I.; Leresche, N.; Marty, A. Calcium entry increases the sensitivity of cerebellar Purkinje cells to applied GABA and decreases inhibitory synaptic currents. Neuron 1991, 6, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimotodani, Y.; Ohno-Shosaku, T.; Kano, M. Ca2+-assisted receptor-driven endocannabinoid release: Mechanisms that associate presynaptic and postsynaptic activities. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2007, 17, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackie, K.; Lai, Y.; Westenbroek, R.; Mitchell, R. Cannabinoids activate an inwardly rectifying potassium conductance and inhibit Q-type calcium currents in AtT20 cells transfected with rat brain cannabinoid receptor. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 6552–6561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacci, A.; Huguenard, J.R.; Prince, D.A. Long-lasting self-inhibition of neocortical interneurons mediated by endocannabinoids. Nature 2004, 431, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maroso, M.; Szabo, G.G.; Kim, H.K.; Alexander, A.; Bui, A.D.; Lee, S.-H.; Lutz, B.; Soltesz, I. Cannabinoid Control of Learning and Memory through HCN Channels. Neuron 2016, 89, 1059–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigel, E.; Baur, R.; Rácz, I.; Marazzi, J.; Smart, T.G.; Zimmer, A.; Gertsch, J. The major central endocannabinoid directly acts at GABA(A) receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 18150–18155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirai, H.; Konno, K.; Yamasaki, M.; Watanabe, M.; Sakaba, T.; Hashimotodani, Y. Distinct release properties of glutamate/GABA co-transmission serve as a frequency-dependent filtering of supramammillary inputs. eLife 2024, 13, RP99711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsoumpa, A.; Papatheodoropoulos, C. Short-term dynamics of input and output of CA1 network greatly differ between the dorsal and ventral rat hippocampus. BMC Neurosci. 2019, 20, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Feng, Z.; Guo, Z.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Z.; Wei, X. Novel Stimulation Paradigms with Temporally-Varying Parameters to Reduce Synchronous Activity at the Onset of High Frequency Stimulation in Rat Hippocampus. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, A.L.; Durand, D.M. High frequency stimulation can block axonal conduction. Exp. Neurol. 2009, 220, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leontiadis, L.J.; Felemegkas, P.; Trompoukis, G.; Tsotsokou, G.; Miliou, A.; Karagianni, E.; Rigas, P.; Papatheodoropoulos, C. Septotemporal variation of information processing in the hippocampus of Fmr1 KO rat. Dev. Neurosci. 2024, 46, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miliou, A.; Papaleonidopoulos, V.; Trompoukis, G.; Papatheodoropoulos, C. Septotemporal variation in beta-adrenergic modulation of short-term dynamics in the hippocampus. IBRO Neurosci. Rep. 2021, 11, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginder, D.E.; Wright, H.R.; McLaughlin, R.J. The stoned age: Sex differences in the effects of adolescent cannabinoid exposure on prefrontal cortex structure and function in animal models. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2022, 161, 121–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, S.; Bisogno, T.; Wenger, T.; Manzanares, J.; Milone, A.; Berrendero, F.; Di Marzo, V.; Ramos, J.A.; Fernández-Ruiz, J.J. Sex steroid influence on cannabinoid CB1 receptor mRNA and endocannabinoid levels in the anterior pituitary gland. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 270, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsotsokou, G.; Fassea, M.; Papatheodoropoulos, C. Muscarinic Modulation of Network Excitability and Short-Term Dynamics in the Dorsal and Ventral Hippocampus. MicroPubl. Biol. 2024, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrides, T.; Georgopoulos, P.; Kostopoulos, G.; Papatheodoropoulos, C. The GABAA receptor-mediated recurrent inhibition in ventral compared with dorsal CA1 hippocampal region is weaker, decays faster and lasts less. Exp. Brain Res. 2007, 177, 370–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggio, N.; Segal, M. Differential modulation of long-term depression by acute stress in the rat dorsal and ventral hippocampus. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 8633–8638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milior, G.; Castro, M.A.; Sciarria, L.P.; Garofalo, S.; Branchi, I.; Ragozzino, D.; Limatola, C.; Maggi, L. Electrophysiological Properties of CA1 Pyramidal Neurons along the Longitudinal Axis of the Mouse Hippocampus. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steindel, F.; Lerner, R.; Haring, M.; Ruehle, S.; Marsicano, G.; Lutz, B.; Monory, K. Neuron-type specific cannabinoid-mediated G protein signalling in mouse hippocampus. J. Neurochem. 2013, 124, 795–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, P.; Arrabal, S.; Cifuentes, M.; Grondona, J.M.; Pérez-Martín, M.; Rubio, L.; Vargas, A.; Serrano, A.; Pavón, F.J.; Suárez, J.; et al. Localization of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor and the 2-AG synthesizing (DAGLα) and degrading (MAGL, FAAH) enzymes in cells expressing the Ca2+-binding proteins calbindin, calretinin, and parvalbumin in the adult rat hippocampus. Front. Neuroanat. 2014, 8, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelkey, K.A.; Chittajallu, R.; Craig, M.T.; Tricoire, L.; Wester, J.C.; McBain, C.J. Hippocampal GABAergic Inhibitory Interneurons. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 1619–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, H.K.; Piroli, G.G.; Walsh, K.B. A real time screening assay for cannabinoid CB1 receptor-mediated signaling. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2018, 94, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Ikeda, S.R. Endocannabinoids modulate N-type calcium channels and G-protein-coupled inwardly rectifying potassium channels via CB1 cannabinoid receptors heterologously expressed in mammalian neurons. Mol. Pharmacol. 2004, 65, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAllister, S.D.; Griffin, G.; Satin, L.S.; Abood, M.E. Cannabinoid receptors can activate and inhibit G protein-coupled inwardly rectifying potassium channels in a xenopus oocyte expression system. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999, 291, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Thathiah, A. Regulation of neuronal communication by G protein-coupled receptors. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 1607–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Belmonte, A.; Aguado, C.; Alfaro-Ruíz, R.; Luján, R. G protein-gated inwardly rectifying K+ (GIRK/Kir3) channels: Molecular, cellular, and subcellular diversity. Histol. Histopathol. 2024, 40, 597–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kano, H.; Toyama, Y.; Imai, S.; Iwahashi, Y.; Mase, Y.; Yokogawa, M.; Osawa, M.; Shimada, I. Structural mechanism underlying G protein family-specific regulation of G protein-gated inwardly rectifying potassium channel. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.S.; Johnston, D. A1 adenosine receptor-mediated GIRK channels contribute to the resting conductance of CA1 neurons in the dorsal hippocampus. J. Neurophysiol. 2015, 113, 2511–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, R.; Johnston, D. Dendritic GIRK Channels Gate the Integration Window, Plateau Potentials, and Induction of Synaptic Plasticity in Dorsal But Not Ventral CA1 Neurons. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 3940–3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Kesner, R.P. Encoding versus retrieval of spatial memory: Double dissociation between the dentate gyrus and the perforant path inputs into CA3 in the dorsal hippocampus. Hippocampus 2004, 14, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichenbaum, H.; Cohen, N.J. Can we reconcile the declarative memory and spatial navigation views on hippocampal function? Neuron 2014, 83, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegener, N.; Kuhnert, S.; Thüns, A.; Roese, R.; Koch, M. Effects of acute systemic and intra-cerebral stimulation of cannabinoid receptors on sensorimotor gating, locomotion and spatial memory in rats. Psychopharmacology 2008, 198, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampson, R.E.; Deadwyler, S.A. Cannabinoids reveal the necessity of hippocampal neural encoding for short-term memory in rats. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 8932–8942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.; Kesner, R.P. Time-dependent relationship between the dorsal hippocampus and the prefrontal cortex in spatial memory. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 1517–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Liu, R.; Sun, Y.X.; Wang, H.L.; Wang, H.; Wang, T.; Ma, Y.N.; Li, X.X.; Wang, Q.; Su, Y.A.; et al. Dorsal CA3 overactivation mediates witnessing stress-induced recognition memory deficits in adolescent male mice. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2024, 49, 1666–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devaraju, P.; Yu, J.; Eddins, D.; Mellado-Lagarde, M.M.; Earls, L.R.; Westmoreland, J.J.; Quarato, G.; Green, D.R.; Zakharenko, S.S. Haploinsufficiency of the 22q11.2 microdeletion gene Mrpl40 disrupts short-term synaptic plasticity and working memory through dysregulation of mitochondrial calcium. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 1313–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pals, M.; Stewart, T.C.; Akyürek, E.G.; Borst, J.P. A functional spiking-neuron model of activity-silent working memory in humans based on calcium-mediated short-term synaptic plasticity. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2020, 16, e1007936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanselow, M.S.; Dong, H.W. Are the dorsal and ventral hippocampus functionally distinct structures? Neuron 2010, 65, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannerman, D.M.; Rawlins, J.N.; McHugh, S.B.; Deacon, R.M.; Yee, B.K.; Bast, T.; Zhang, W.N.; Pothuizen, H.H.; Feldon, J. Regional dissociations within the hippocampus–memory and anxiety. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2004, 28, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakoyiannis, I.; Ducourneau, E.G.; Parkes, S.L.; Ferreira, G. Pathway specific interventions reveal the multiple roles of ventral hippocampus projections in cognitive functions. Rev. Neurosci. 2023, 34, 825–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerquetella, C.; Gontier, C.; Forro, T.; Pfister, J.P.; Ciocchi, S. Scaling of Ventral Hippocampal Activity during Anxiety. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2025, 45, e1128242025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, M.P.; Boi, M.; Lai, Y.; Trucas, M.; Fernández-Teruel, A.; Corda, M.G.; Giorgi, O.; Quartu, M. Acute stress induces different changes on the expression of CB1 receptors in the hippocampus of two lines of male rats differing in their response to stressors. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2024, 245, 173901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, T.; Guidali, C.; Vigano, D.; Realini, N.; Valenti, M.; Massi, P.; Parolaro, D. CB1 receptor stimulation in specific brain areas differently modulate anxiety-related behaviour. Neuropharmacology 2008, 54, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roohbakhsh, A.; Keshavarz, S.; Hasanein, P.; Rezvani, M.E.; Moghaddam, A.H. Role of endocannabinoid system in the ventral hippocampus of rats in the modulation of anxiety-like behaviours. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2009, 105, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsotsokou, G.; Sotiropoulou, I.-M.; Stampolitis, K.; Oikonomou, G.D.; Avdi, A.-P.; Papatheodoropoulos, C. Cannabinoid Modulation of Excitability and Short-Term Neuronal Dynamics in the Dorsal and Ventral Hippocampus. Biology 2025, 14, 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14060642
Tsotsokou G, Sotiropoulou I-M, Stampolitis K, Oikonomou GD, Avdi A-P, Papatheodoropoulos C. Cannabinoid Modulation of Excitability and Short-Term Neuronal Dynamics in the Dorsal and Ventral Hippocampus. Biology. 2025; 14(6):642. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14060642
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsotsokou, Giota, Ioanna-Maria Sotiropoulou, Klearchos Stampolitis, George D. Oikonomou, Aikaterini-Paraskevi Avdi, and Costas Papatheodoropoulos. 2025. "Cannabinoid Modulation of Excitability and Short-Term Neuronal Dynamics in the Dorsal and Ventral Hippocampus" Biology 14, no. 6: 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14060642
APA StyleTsotsokou, G., Sotiropoulou, I.-M., Stampolitis, K., Oikonomou, G. D., Avdi, A.-P., & Papatheodoropoulos, C. (2025). Cannabinoid Modulation of Excitability and Short-Term Neuronal Dynamics in the Dorsal and Ventral Hippocampus. Biology, 14(6), 642. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14060642






