Spatiotemporal Distribution of Phytoplankton Functional Groups in Baihua Reservoir: Implications for Ecosystem Management
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
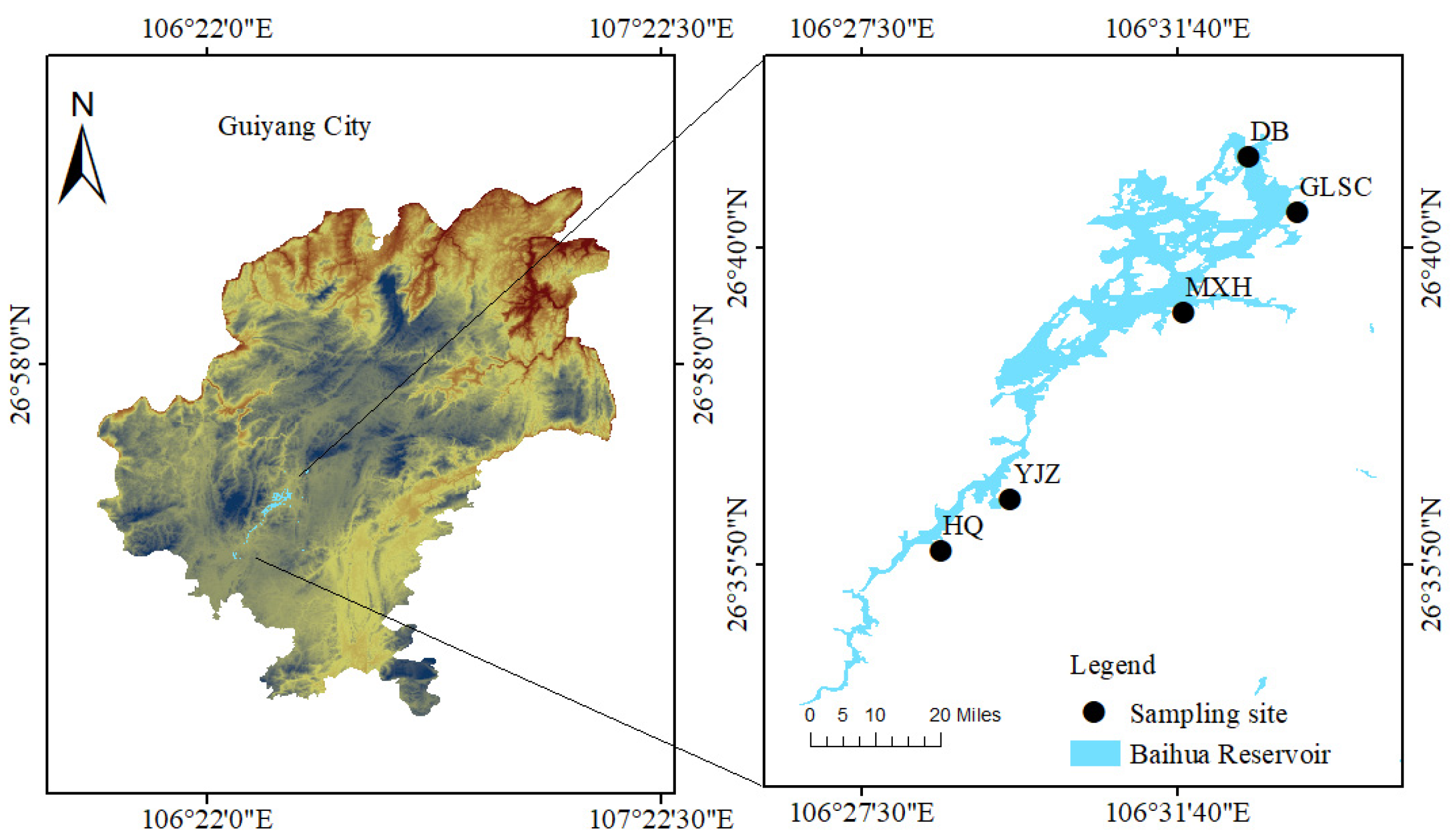
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Samples Collection and Analysis
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
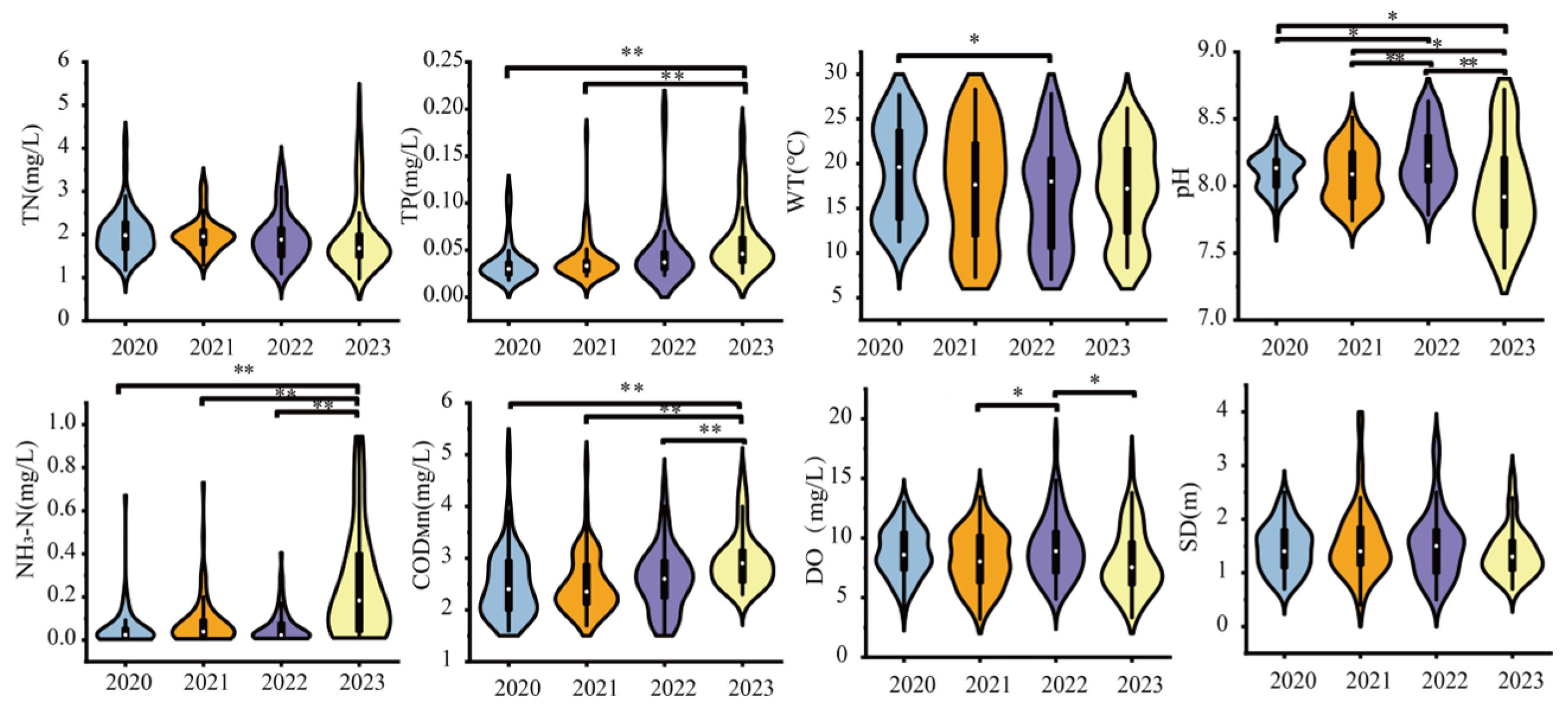
3.1. Variations in Environmental Factors
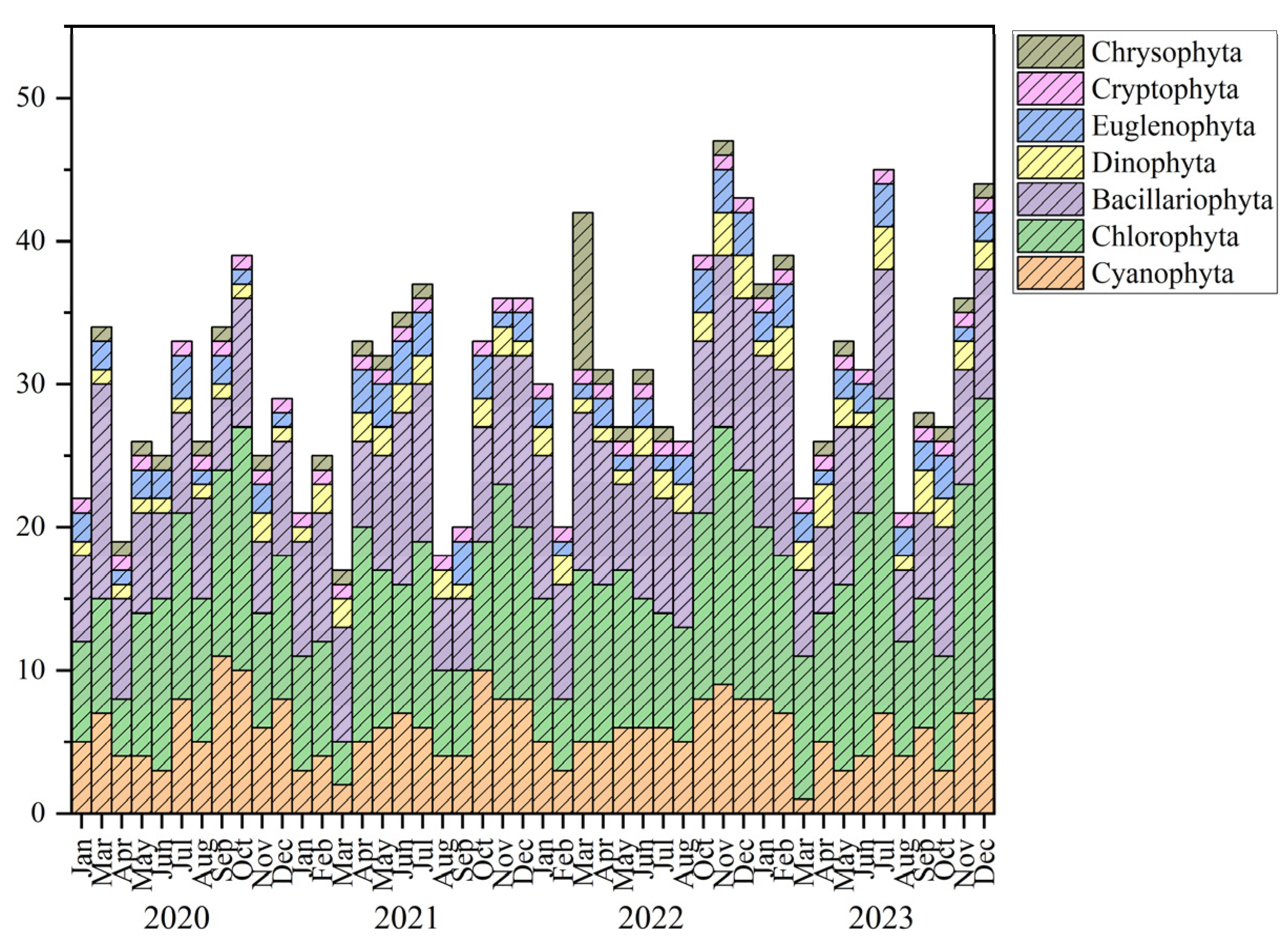
3.2. Phytoplankton Community Structure
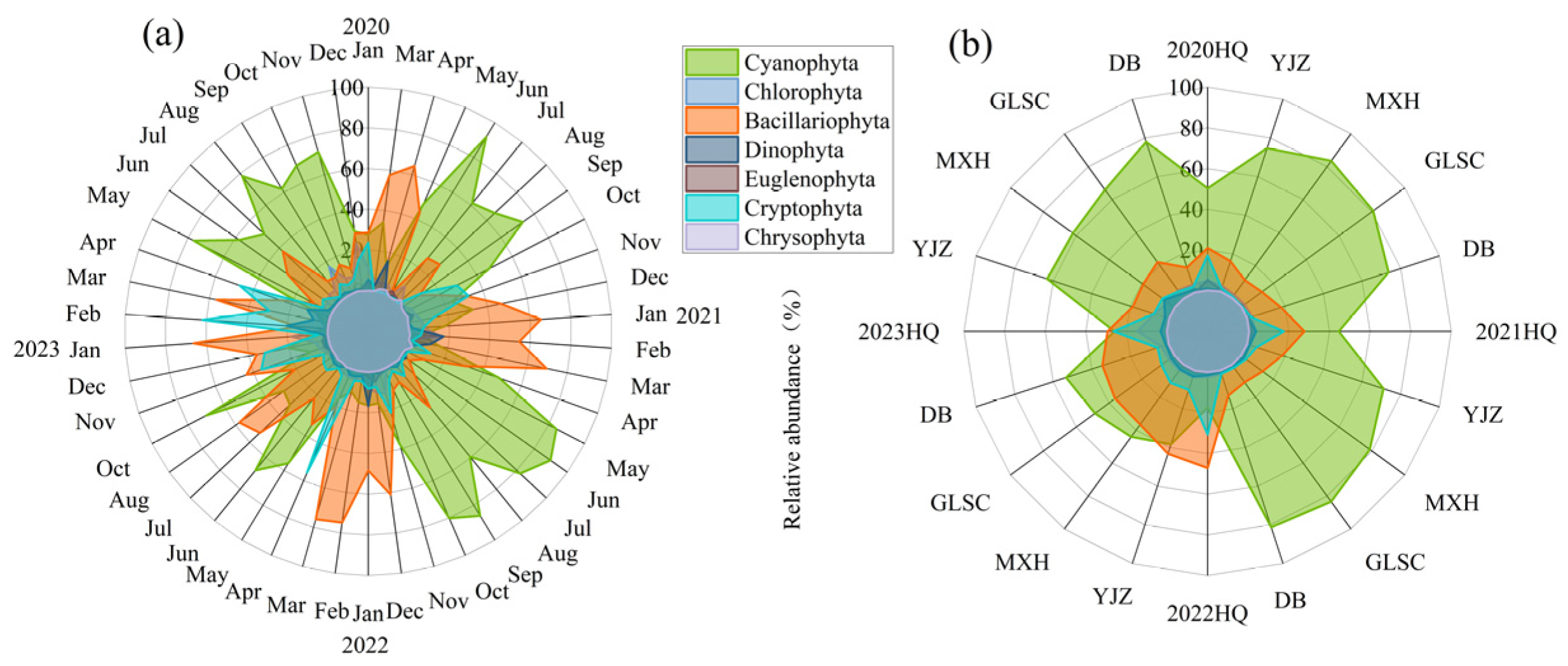
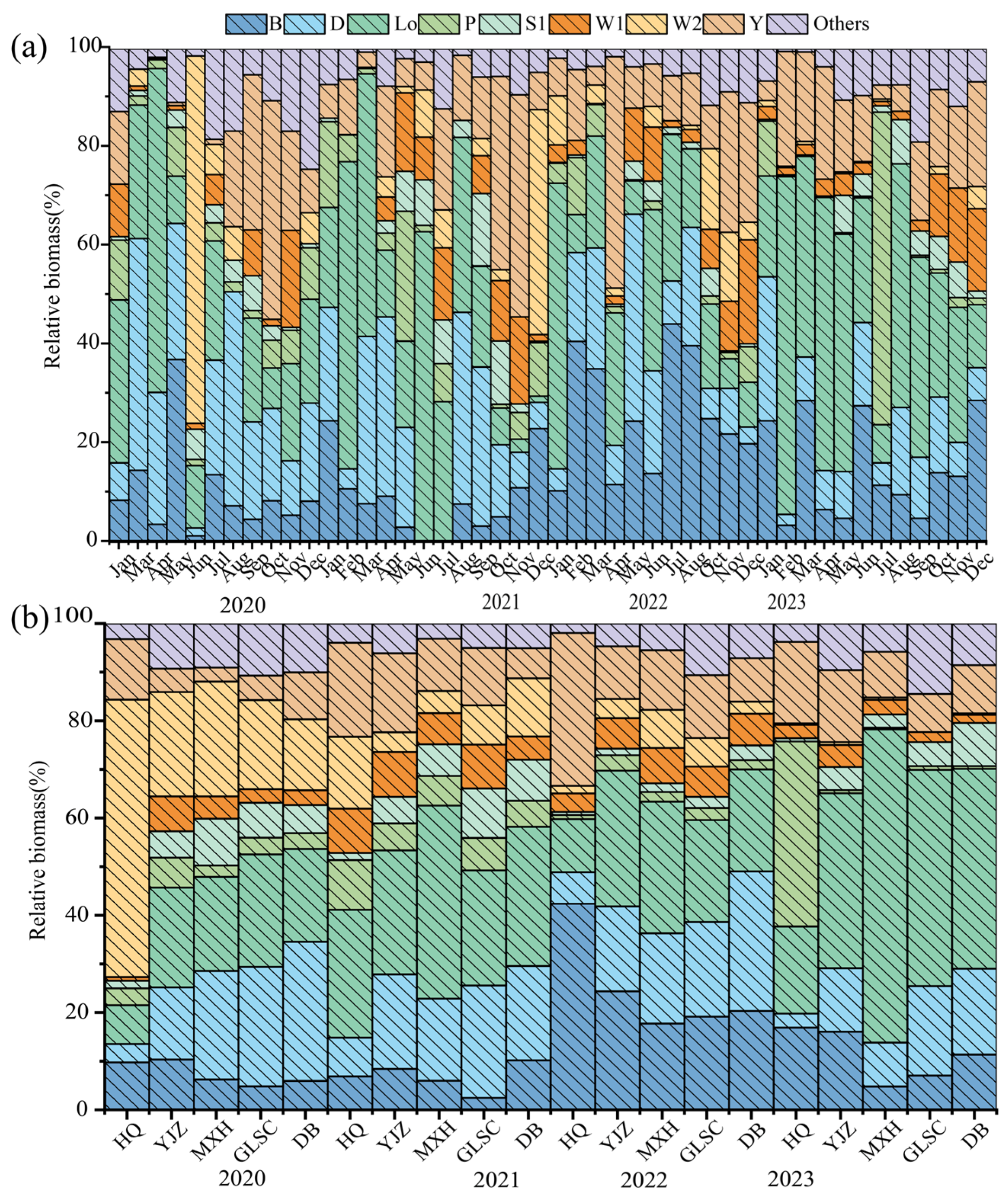
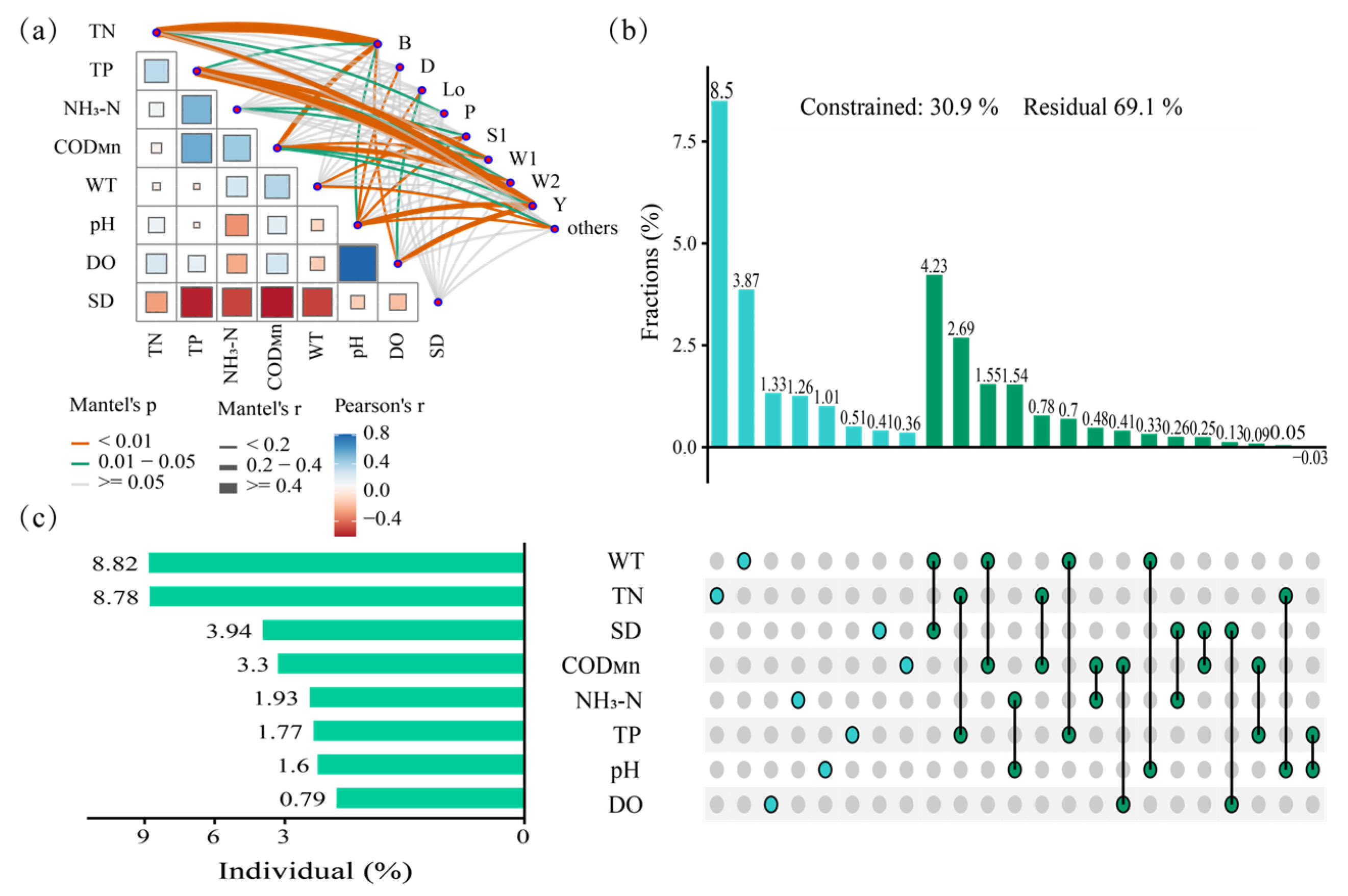
3.3. Composition and Succession Characteristics of Functional Groups
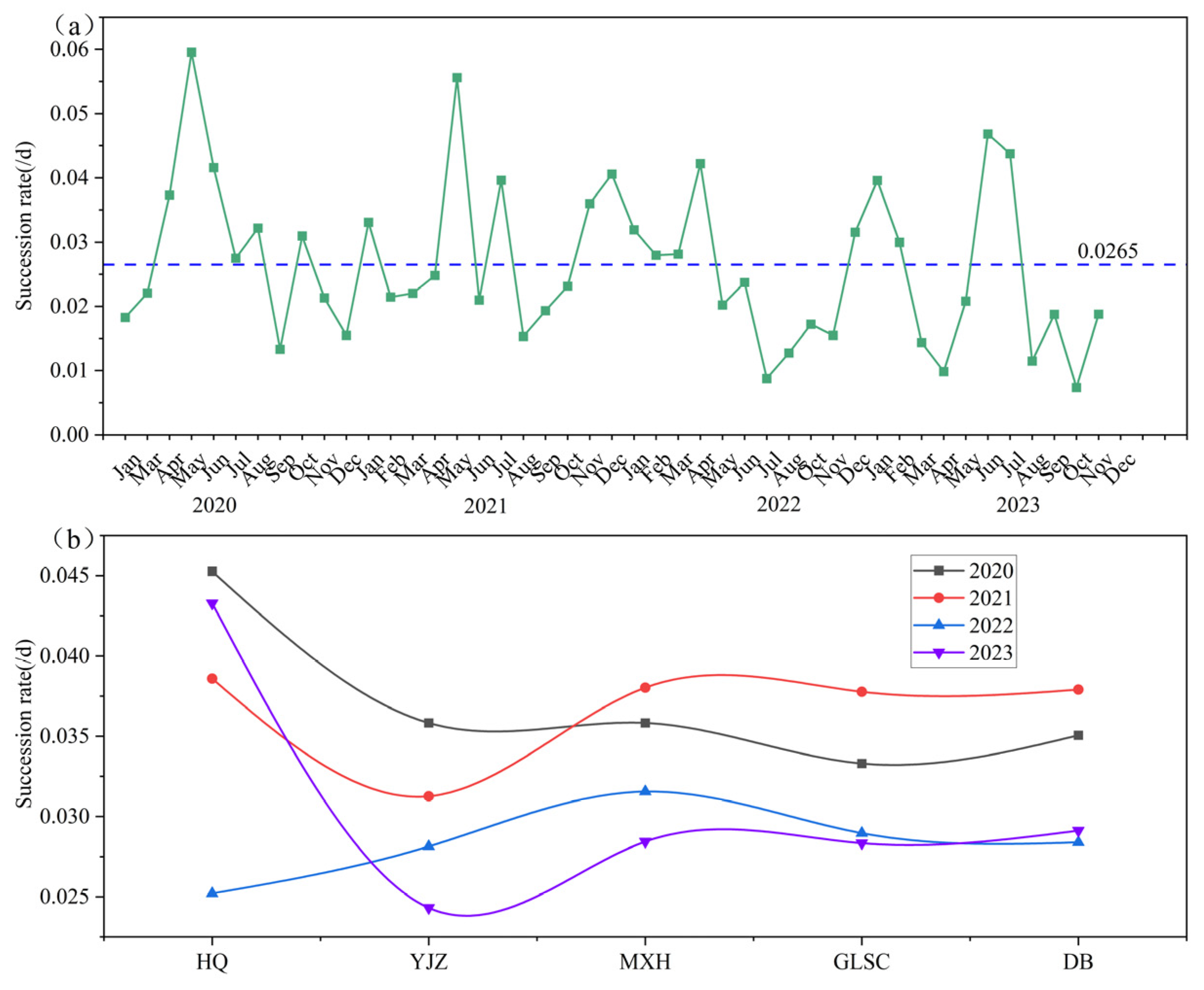
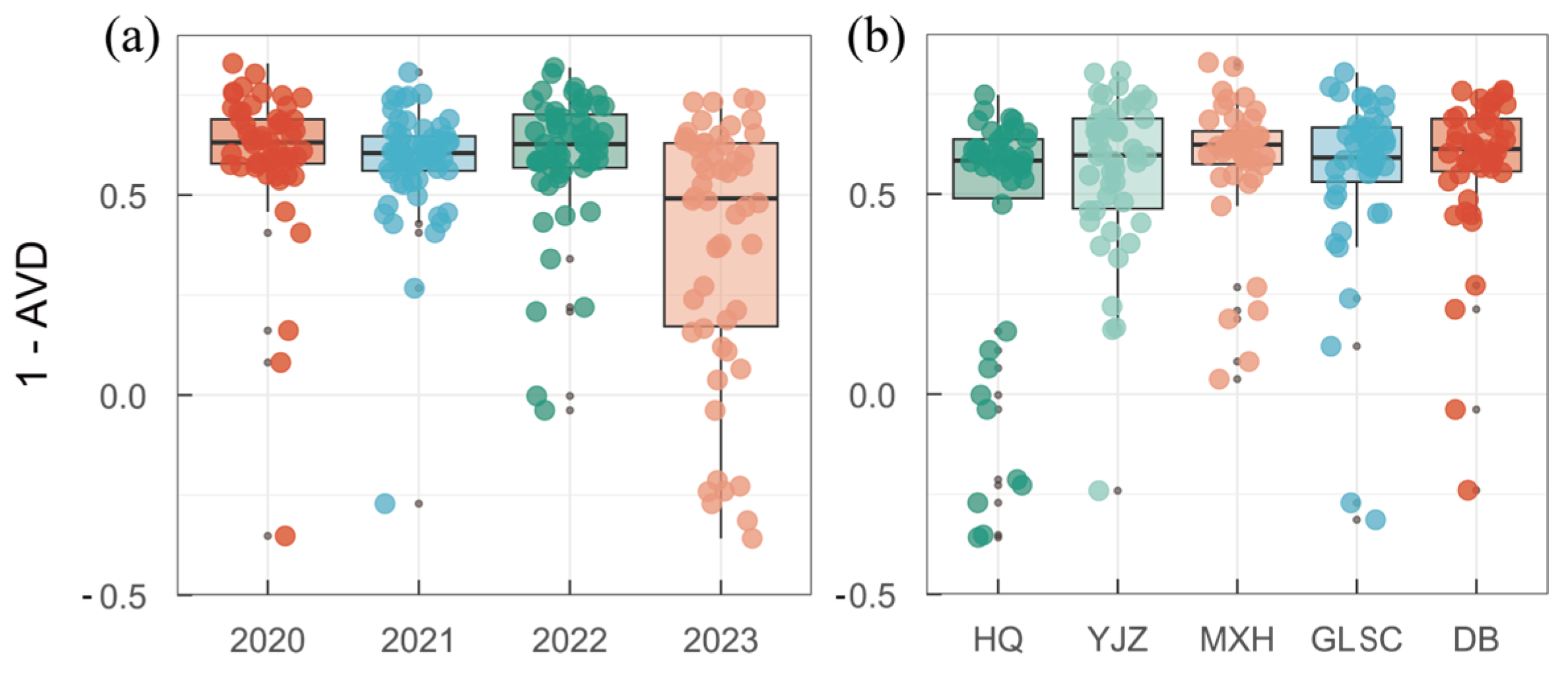
3.4. Spatiotemporal Succession Rate of Functional Groups
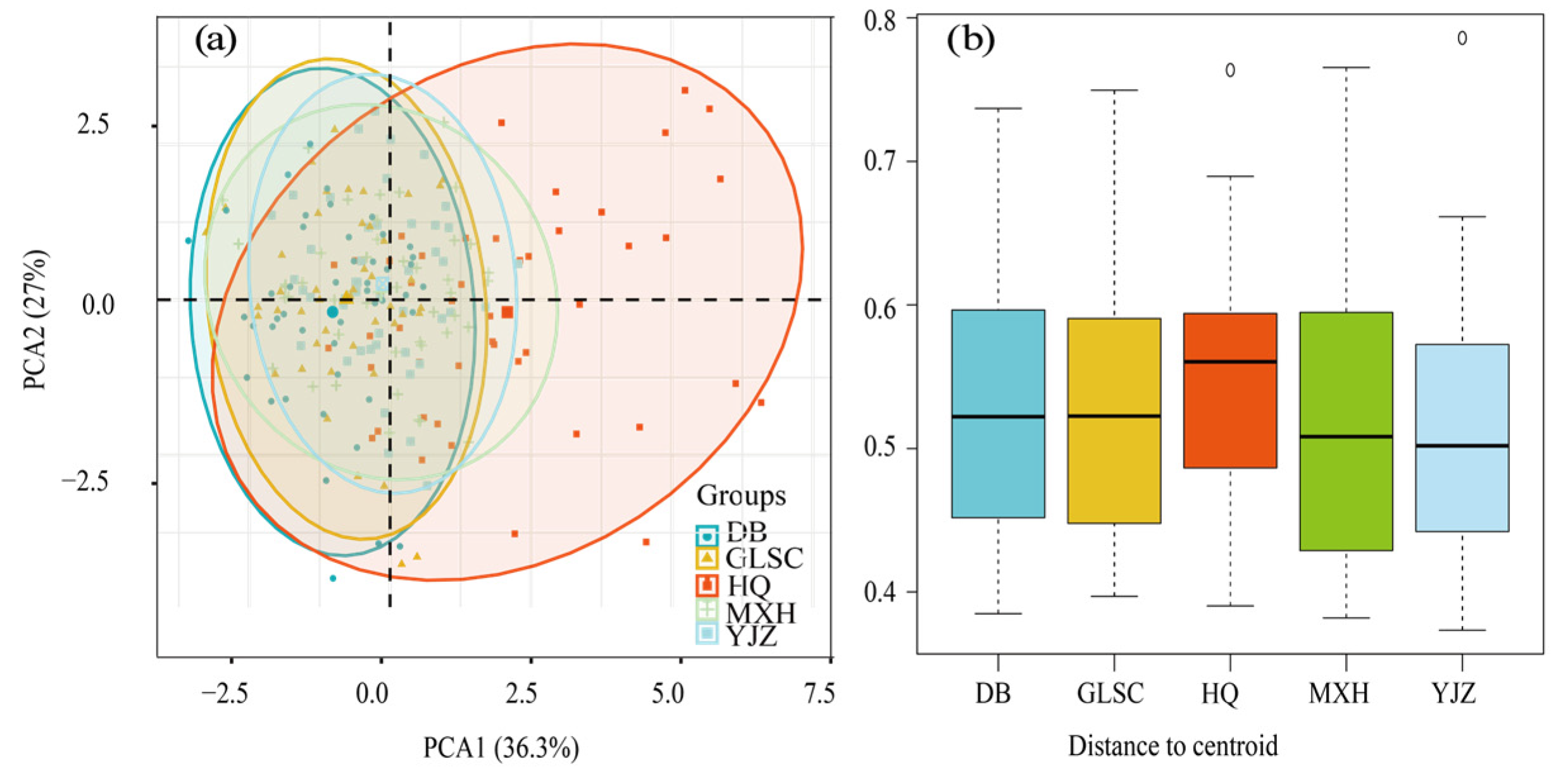
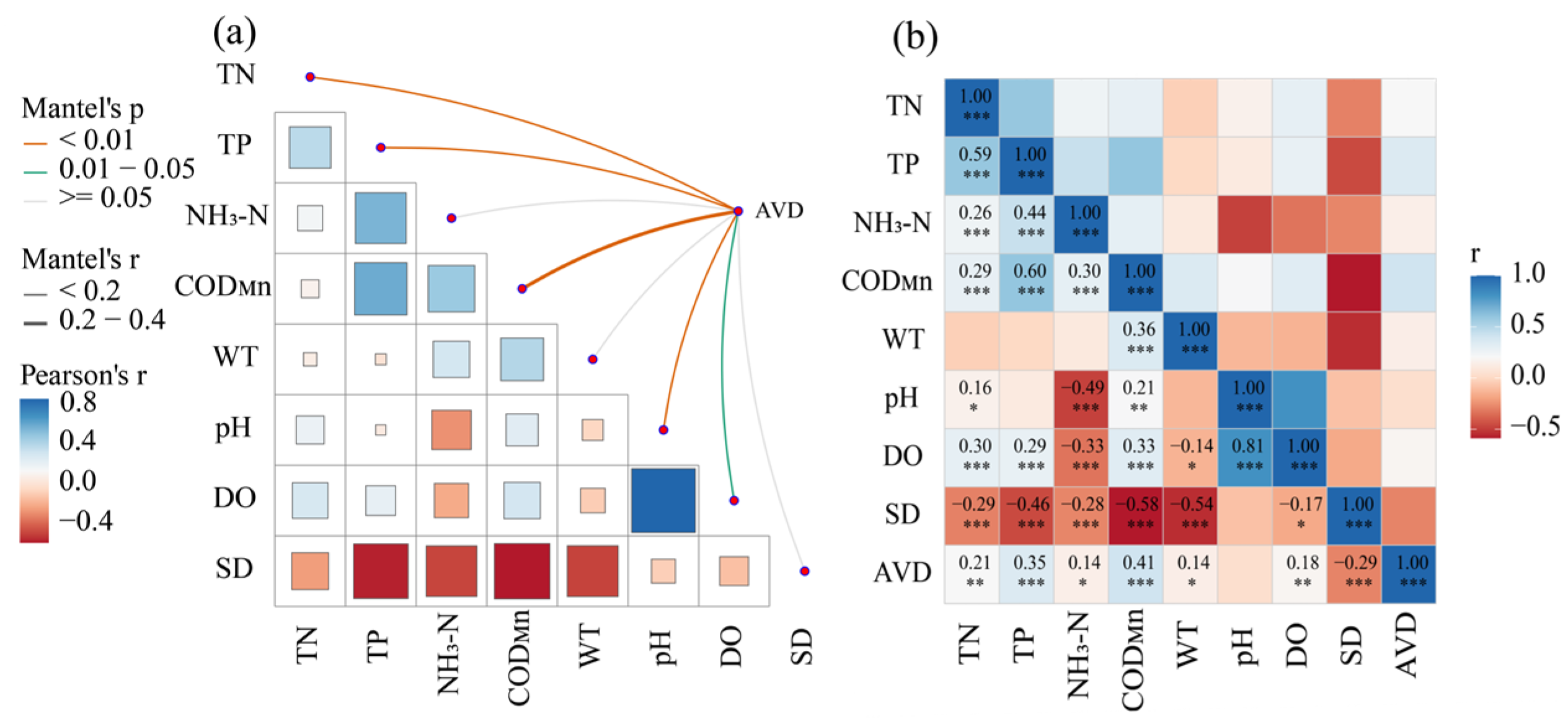
3.5. Functional Group Community Stability Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatiotemporal Succession Characteristics of Functional Groups
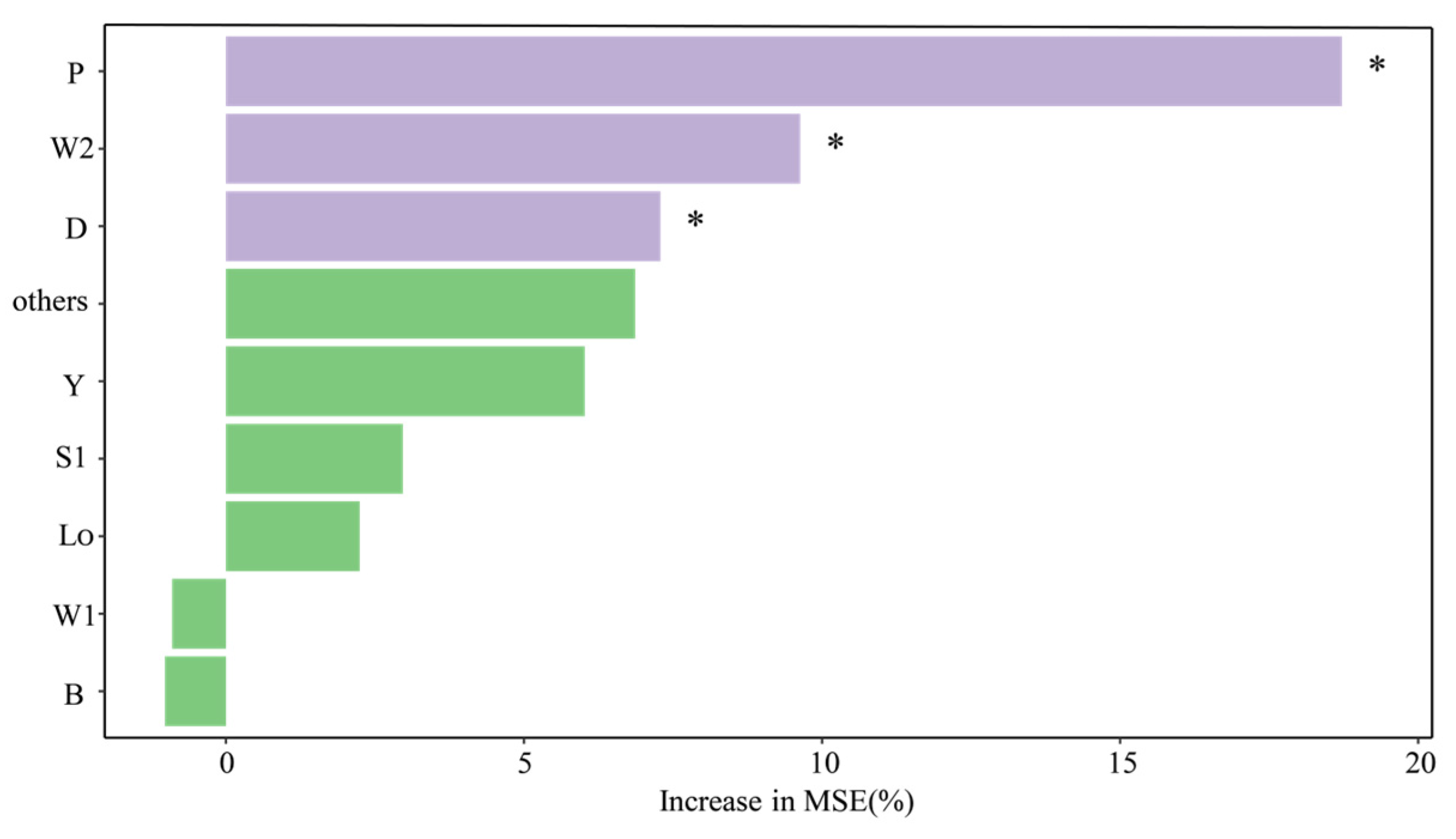
4.2. Main Environmental Factors Driving the Succession of Functional Groups
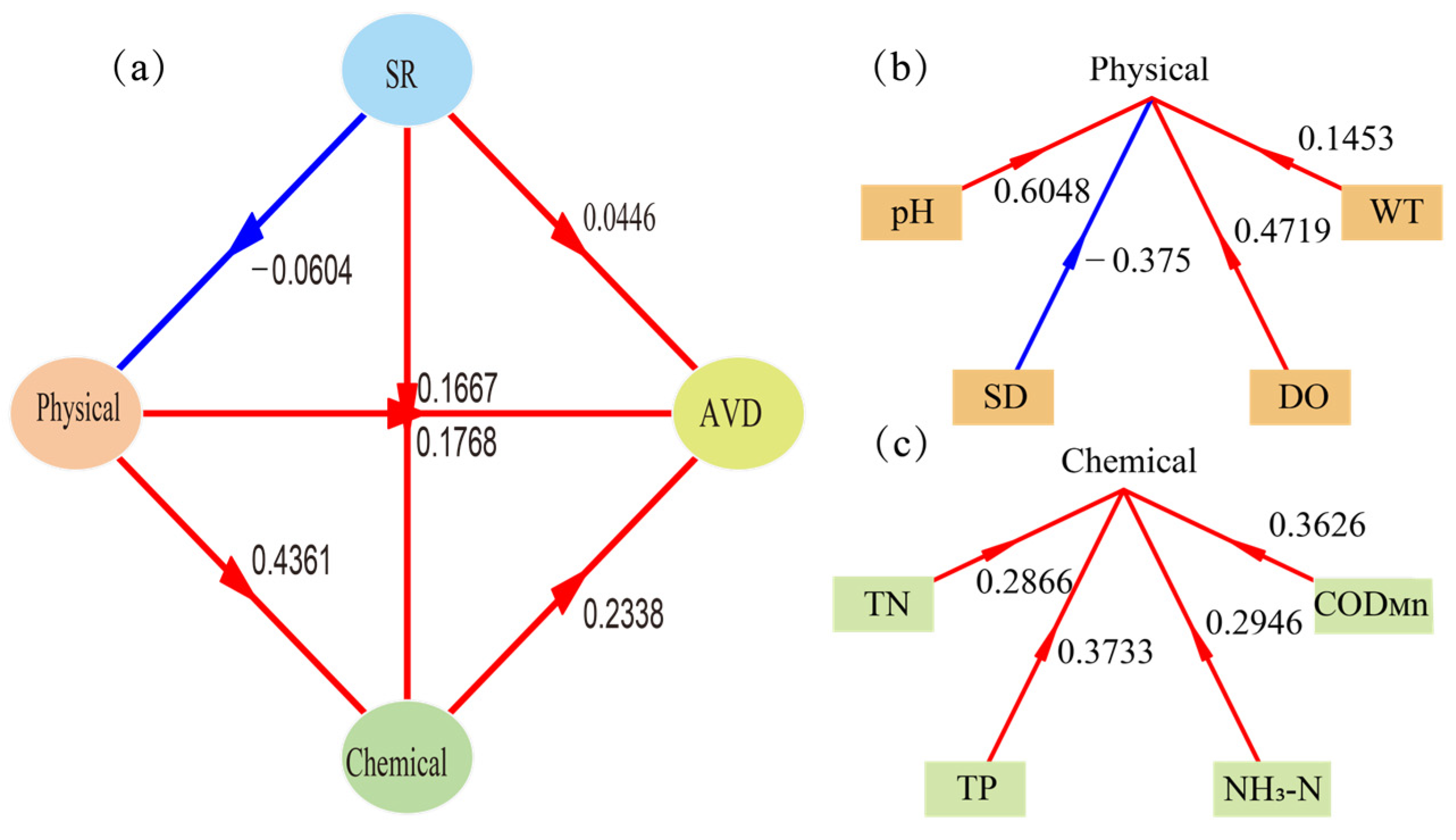
4.3. Stability Characteristics and Driving Factors of Functional Groups
4.4. Implications for Ecosystem Management of Baihua Reservoir
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, G.; Pan, B.; Li, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhu, P.; Zhang, L.; He, H. Phytoplankton in the heavy sediment-laden Weihe River and its tributaries from the northern foot of the Qinling Mountains: Community structure and environmental drivers. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 8359–8370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Yuan, L.; Peng, D. Relationship between phytoplankton and environmental factors in landscape water supplemented with reclaimed water. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 58, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.S.; Huszar, V.; Kruk, C.; Naselli-Flores, L.; Melo, S. Towards a functional classification of the freshwater phytoplankton. J. Plankton Res. 2002, 24, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.R.A.; Cardoso, M.M.L.; Selmeczy, G.B.; Padisák, J.; Becker, V. Phytoplankton functional responses induced by extreme hydrological events in a tropical reservoir. Hydrobiologia 2024, 851, 849–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padisák, J.; Crossetti, L.O.; Naselli-Flores, L. Use and misuse in the application of the phytoplankton functional classification: A critical review with updates. Hydrobiologia 2009, 621, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.G.; Hong, S.; Kim, D.; Joo, G. Drivers shaping episodic and gradual changes in phytoplankton community succession: Taxonomic versus functional groups. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 734, 138940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanov, R.E.; Kirillov, V.V. Analysis of the seasonal dynamics of river phytoplankton based on succession rate indices for key event identification. Hydrobiologia 2012, 695, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, V.; Wissel, C. Babel; or the Ecological Stability Discussions: An Inventory and Analysis of Terminology and a Guide for Avoiding Confusion. Oecologia 1997, 109, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parparov, A.; Gal, G. Quantifying Ecological Stability: From Community to the Lake Ecosystem. Ecosystems 2017, 20, 1015–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, L.; Xu, X.; Huang, H. Plankton Community Stability and its Relationship with Phytoplankton Species Richness in Lake Nansihu; China. Water 2016, 8, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Li, C.; Dai, D.; Yao, S.; Li, S.; Zhou, Q. Seasonal succession of phytoplankton functional groups in Lake Fuxian and its driving factors. Ann. Limnol. 2019, 55, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.; Xiong, F.; Lu, Y.; Xin, W.; Wang, H.; Feng, G.; Kong, C.; Fang, L.; Gao, X.; Chen, Y. Water quality and habitat drive phytoplankton taxonomic and functional group patterns in the Yangtze River. Ecol. Process. 2024, 13, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Xu, L.; Xu, D. Seasonal succession of phytoplankton functional groups in a reservoir in central China. Fundam Appl. Limnol. 2018, 192, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sthapit, E.; Ochs, C.A.; Zimba, P.V. Spatial and temporal variation in phytoplankton structure in a southeastern U.S. reservoir determined by HPLC and light microscopy. Hydrobiologia 2008, 600, 215–228. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Han, M.; Li, L.; Xiao, J.; Liu, Y. Responses of phytoplankton functional groups to environmental factors in the Maixi River; southwest China. J. Limnol. 2018, 77, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, X.; Li, Q.; Sha, J.; Wang, Y. Practices and recommendations on the Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water (GB 3838–2002). In Proceedings of the 2009 Annual Conference of the Chinese Society for Environmental Sciences, Wuhan, China, 4–5 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Olenina, I.; Hajdu, S.; Edler, L.; Andersson, A.; Wasmund, N.; Busch, S.; Göbel, J.; Gromisz, S.; Huseby, S.; Huttunen, M.; et al. Biovolumes and size-classes of phytoplankton in the Baltic Sea. Balt. Sea Environ. Proc. 2006, 106, 144. [Google Scholar]
- Mcnaughton, S.J. Relationships among Functional Properties of Californian Grassland. Nature 1967, 216, 168–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, N.J.; Goldman, C.R. Succession rates in lake phytoplankton communities. Int. Ver. Theor. Angew. Limnol. Verhandlungen 1975, 19, 808–811. [Google Scholar]
- Zanon, F.M.; Pineda, A.; Lansac-Tôha, F.M.; Rodrigues, L.C. Impact of a run-of-river dam in an Amazonian large river on the spatial and temporal patterns of phytoplankton beta diversity. Biol. Conserv. 2024, 295, 110656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Ma, W.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Pan, M.; Ding, C. Succession characteristics of phytoplankton functional groups and water quality responsiveness evaluation in an artificial constructed wetland-reservoir ecosystem. Env Pollut. Bioavail. 2022, 34, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Sun, J.; Wang, J.; Lucas-Borja, M.E.; Pandey, A.; Wang, T.; Huang, Z. Tree species richness and functional composition drive soil nitrification through ammonia-oxidizing archaea in subtropical forests. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 187, 109211. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Xu, H.; Shi, J.; Wang, Z.; Lv, J.; Li, L.; Wang, X. Soil microbial composition; diversity; and network stability in intercropping versus monoculture responded differently to drought. Agr. Ecosyste Environ. 2024, 365, 108915. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, S.; Feng, B.; Jian, S.; Wang, G.S.; Ge, Z.; Yang, Z.L. Elevation Matters More than Season in Shaping the Heterogeneity of Soil and Root Associated Ectomycorrhizal Fungal Community. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e01950-21. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Qin, X.; Wang, G.; Teng, M.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, F.; Du, H.; Wang, L.; Xu, Y. Oxygen influences spatial heterogeneity and microbial succession dynamics during Baijiu stacking process. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 403, 130854. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, M.; Yang, N.; Zhao, J.; Shaaban, M.; Hu, R. Crop straw incorporation mediates the impacts of soil aggregate size on greenhouse gas emissions. Geoderma 2021, 401, 115342. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, F.; Wang, X.; Li, K.; Zhang, L. Water quality assessment using phytoplankton functional groups in the middle-lower Changjiang River; China. Limnologica 2023, 99, 126056. [Google Scholar]
- Varol, M. Phytoplankton functional groups in a monomictic reservoir: Seasonal succession; ecological preferences; and relationships with environmental variables. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 20439–20453. [Google Scholar]
- Petar, Ž.; Marija, G.U.; Koraljka, K.B.; Anđelka, P.; Judit, P. Morpho-functional classifications of phytoplankton assemblages of two deep karstic lakes. Hydrobiologia 2014, 740, 147–166. [Google Scholar]
- Abirhire, O.; North, R.L.; Hunter, K.; Vandergucht, D.M.; Sereda, J.; Hudson, J.J. Environmental factors influencing phytoplankton communities in Lake Diefenbaker; Saskatchewan; Canada. J. Great Lakes Res. 2015, 41, 118–128. [Google Scholar]
- Çelik, K.; Ongun Sevindik, T. The phytoplankton functional group concept provides a reliable basis for ecological status estimation in the Çaygören Reservoir (Turkey). Doga Turk. J. Botany 2015, 39, 588–598. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Chen, L.; Chen, F.; Gao, T.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Li, C. Maixi River estuary to the Baihua Reservoir in the Maotiao River catchment: Phytoplankton community and environmental factors. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2013, 31, 290–299. [Google Scholar]
- Long, S.; Hamilton, P.B.; Yang, Y.; Wang, S.; Huang, W.; Chen, C.; Tao, R. Differential bioaccumulation of mercury by zoo-plankton taxa in a mercury-contaminated reservoir Guizhou China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 239, 147–160. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.; Hou, Z.; Li, Z.; Chu, Z.; Yang, P.; Zheng, B. Succession of phytoplankton functional groups and their driving factors in a subtropical plateau lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar]
- Salmaso, N. Seasonal variation in the composition and rate of change of the phytoplankton community in a deep subalpine lake (Lake Garda; Northern Italy). An application of nonmetric multidimensional scaling and cluster analysis. Hydrobiologia 1996, 337, 49–68. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández Fariñas, T.; Bacher, C.; Soudant, D.; Belin, C.; Barillé, L. Assessing phytoplankton realized niches using a French national phytoplankton monitoring network. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 159, 15–27. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, C.; Pei, H.; Hu, W.; Hao, D.; Doblin, M.A.; Ren, Y.; Wei, J.; Feng, Y. Variation of phytoplankton functional groups modulated by hydraulic controls in Hongze Lake; China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 18163–18175. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Lv, H.; Yang, J.; Liu, L.; Yu, X.; Chen, H. Decline in water level boosts cyanobacteria dominance in subtropical reservoirs. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 557–558, 445–452. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, V.; Caputo, L.; Ordóñez, J.; Marcé, R.; Armengol, J.; Crossetti, L.O.; Huszar, V.L.M. Driving factors of the phytoplank-ton functional groups in a deep Mediterranean reservoir. Water Res. 2010, 44, 3345–3354. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, R.W.; Guelda, D.L.; Bukaveckas, P.A. Phytoplankton growth in the Ohio, Cumberland and Tennessee Rivers, USA: Inter-site differences in light and nutrient limitation. Aquat. Ecol. 2004, 38, 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Jianming, D.; Yogjiu, C.; Yuwei, C.; Lu, Z. Structure of phytoplankton community and its relationship with environment factors in Lake Honghu. J. Lake Sci. 2010, 22, 70–78. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, N.; Yin, H.B.; Deng, J.; Gao, F.; Hu, W.; Gao, J.F. Spring community structure of phytoplankton from Lake Chaohu and its relationship to environmental factors. J. Lake Sci. 2010, 22, 950–956. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, A.N.; Barton, A.D. Effects of dispersal and temperature variability on phytoplankton realized temperature niches. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 14, e10882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, D.H.; Kang, J. Associating the spatial properties of a watershed with downstream Chl-a concentration using spatial analysis and generalized additive models. Water Res. 2019, 154, 387–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, S.; Zhu, Q.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Chen, L.; Wu, S. One-century sedimentary record of heavy metal pollution in western Taihu Lake; China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothenberger, M.; Burkholder, J.; Wentworth, T. Use of long-term data and multivariate ordination techniques to identify environmental factors governing estuarine phytoplankton species dynamics. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 2107–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalewajko, C.; Murphy, T.P. Effects of temperature; and availability of nitrogen and phosphorus on the abundance of Anabaena and Microcystis in Lake Biwa; Japan: An experimental approach. Limnology 2001, 2, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Li, M.; Pan, B.; Zhao, G.; Gao, L. Disentangling the drivers of phytoplankton community composition in a heavily sediment-laden transcontinental river. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 302, 113939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Li, Q.; Chen, W.; Wang, X.; Zhou, S.; Han, M.; Brancelj, A. The key environmental factors driving the succession of phytoplankton functional groups in Hongfeng Reservoir; southwest China. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2022, 40, 1472–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Tian, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yu, M.; Hou, Z.; He, K.; Xu, H.; Cui, B.; Jiang, Y. Relationship between dissolved organic matter and phytoplankton community dynamics in a human-impacted subtropical river. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 289, 125144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Functional Group | Habitat Characteristics | Representative Species | Tolerance | Susceptibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Oligotrophic, clean, deep water | Rhizosolenia | Low nutrients | Elevated pH |
| B * | Mesotrophic trophic, small-to-medium, or large shallow-water bodies | Cyclotella sp. | Low light | Elevated pH, water stratification |
| C | Eutrophic, small- and medium-sized reservoirs | Asterionella sp. | Low light | Water stratification |
| D * | Rich in nutrients, cloudy | Synedra sp., Nitzschia sp. | Scouring | Nutrient deficiency |
| E | Oligotrophic or heterotrophic type, small water bodies, shallow water | Dinobryon divergens | Low nutrients | CO2 deficiency |
| F | Mesotrophic-to-eutrophic, clean, and strong water mixing | Oocystis sp., Kirchneriella sp. | Low nutrients | CO2 deficiency |
| G | Eutrophic, stagnant water bodies | Eudorina sp., Pandorina sp | High light | Nutrient salt deficiency |
| H1 | Eutrophic, stratified, low nitrogen content | A nabaena sp., Aphanizomenon sp. | Low carbon/nitrogen content | Water mixing, low light, low phosphorus |
| J | High nutrient, mixed, shallow water | Scenedesmus sp., Crucigenia sp., Tetraedron sp. | High light | |
| K | Eutrophic, shallow water | Aphanocapsa sp. | Strong water mixing | |
| LM | eutrophic to hypereutrophic, small- and medium-sized water bodies | Dactylococcopsis sp., Ceratium sp. | Extremely low carbon content | Water mixing, low light |
| LO * | Mesotrophic-to-eutrophic, medium-to-large water bodies, can be deep or shallow | Merismopedia sp., Chroococcus sp., Peridinium sp. | Nutrient stratification | Prolonged/deep mixing |
| MP | Frequent agitation, turbidity, shallow water | Oscillatoria sp., Navicula sp., Achnanthes sp. | Mixing disturbance | |
| N | Continuous or semi-continuous mixed bodies of water | Cosmarium sp. | Low nutrients | Water stratification, elevated pH |
| P * | It is similar to functional group N, but the trophic status of the water body is higher | Melosira sp., Fragilaria sp., Closterium sp. | Low light, low carbon content | Water stratification, silicon deficiency |
| S1 * | The mixture is cloudy and has low transparency | Pseudanabaena limnetica, Rhabdogloea, Limnothrix sp. | Extremely low light | Scouring |
| S2 | Warm, highly alkaline, shallow water | Spirulina | Low light | Scouring |
| SN | Warm, blended | Cylindrospermum raciborskii, Raphidiopsis | Low light, low nutrients | Scouring |
| T | Mix water bodies continuously | Mougeotia, Quadrigula chodatii | Low light | Nutrient deficiency |
| TC | Eutrophication, still or flowing water, with upright plants | Lyngbya sp. | Scouring | |
| W1 * | Organic pollution, shallow water | Euglena sp. Euglena oxyuris | High biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) | Grazing pressure |
| W2 * | Mesotrophic nutrition, shallow water | Trachelomonas sp. | ||
| X1 | Super nutritious, shallow water | Chlorella sp., Ankistrodesmus sp. | Water stratification | Nutrient deficiency, filter feeding |
| X2 | Mesotrophic-to-eutrophic, shallow water | Chlamydomonas sp. | Water stratification | Water mixing, filter feeding |
| X3 | Oligotrophic, mixed, shallow water | Schroederia sp. | Harsh environmental conditions | Water mixing, grazing pressure |
| Y * | Still-water environment | Cryptomonas sp. Gymnodinium sp. | Low light | Predation |
| Z | Oligotrophic | Synechococcus | Low nutrients | Low light, grazing pressure |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, S.; Peng, Y.; Xiao, J.; Li, Q. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Phytoplankton Functional Groups in Baihua Reservoir: Implications for Ecosystem Management. Biology 2025, 14, 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040333
Yuan Z, Chen Y, Zhou S, Peng Y, Xiao J, Li Q. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Phytoplankton Functional Groups in Baihua Reservoir: Implications for Ecosystem Management. Biology. 2025; 14(4):333. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040333
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Zhongxiu, Yan Chen, Si Zhou, Yugui Peng, Jing Xiao, and Qiuhua Li. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Distribution of Phytoplankton Functional Groups in Baihua Reservoir: Implications for Ecosystem Management" Biology 14, no. 4: 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040333
APA StyleYuan, Z., Chen, Y., Zhou, S., Peng, Y., Xiao, J., & Li, Q. (2025). Spatiotemporal Distribution of Phytoplankton Functional Groups in Baihua Reservoir: Implications for Ecosystem Management. Biology, 14(4), 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040333






