Generation of Current Good Manufacturing Practices-Grade Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Using Automated Bioreactors
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
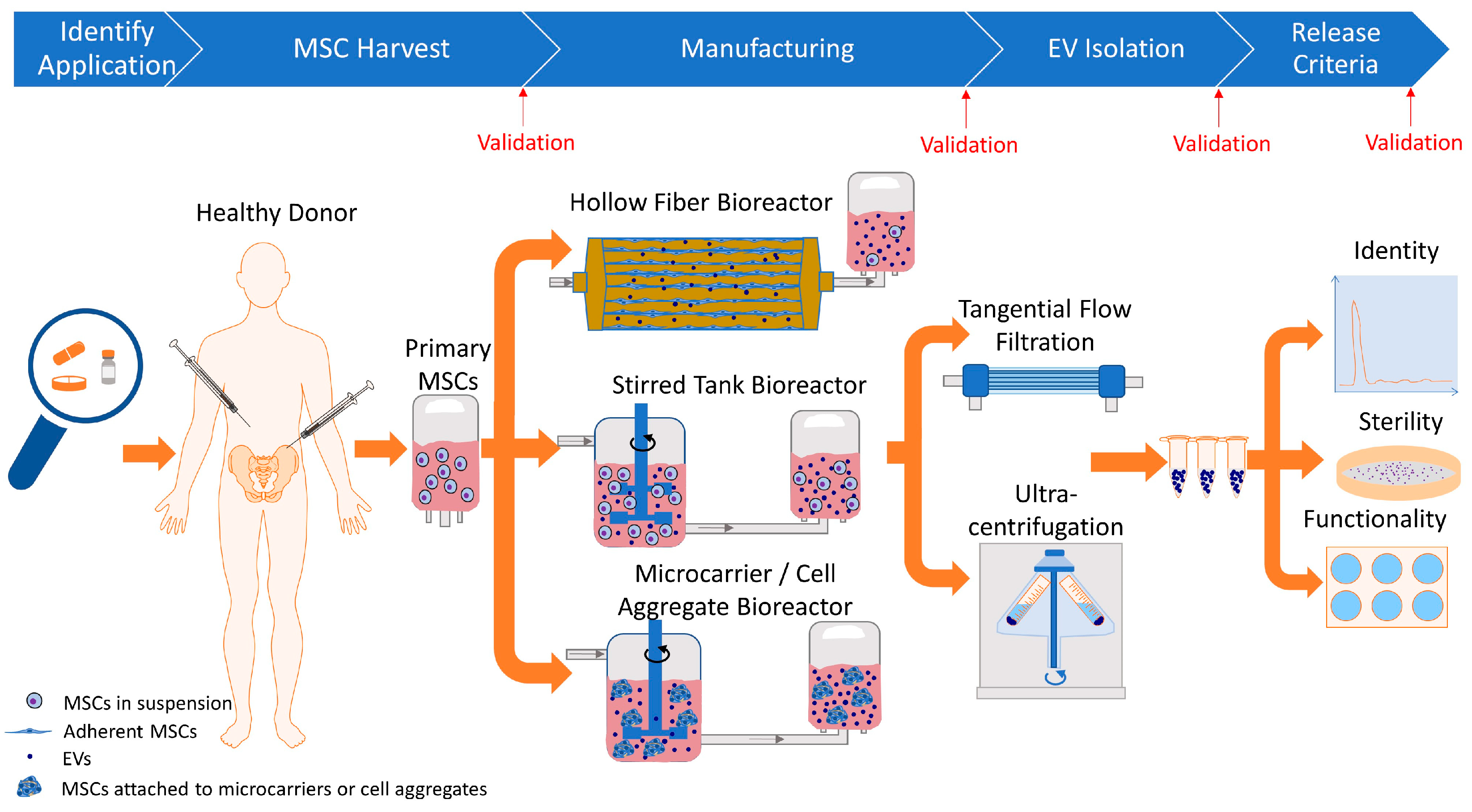
2. Cell Culture Bioreactors for Manufacturing cGMP-Grade MSC-Derived EVs
3. Factors Affecting cGMP EV Manufacturing from MSC Cultures
4. Isolating cGMP-Grade EVs from Conditioned Media
4.1. cGMP-Grade EV Isolation Techniques
4.2. Scalability
4.3. Process Validation
4.4. Serum Usage in EV Manufacturing
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| cGMP | Current Good Manufacturing Practices |
| EVs | Extracellular vesicles |
| MSCs | Mesenchymal stromal cells |
| TGFβ1 | Transforming growth factor beta 1 |
| IL-10 | Interleukin-10 |
| HGF | Hepatocyte growth factor |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal fluid |
| SVF | Stromal vascular fraction |
| BBB | Blood–brain barrier |
References
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; He, X.; Li, Q.; Lai, H.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Z.; Li, Y.; Huang, S. EV-origin: Enumerating the tissue-cellular origin of circulating extracellular vesicles using exLR profile. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 2851–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, Y.J.; Koh, B.I.; Kim, H.; Joo, H.J.; Jin, H.K.; Jeon, J.; Choi, C.; Lee, D.H.; Chung, J.H.; Cho, C.H.; et al. Stromal vascular fraction from adipose tissue forms profound vascular network through the dynamic reassembly of blood endothelial cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 1141–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, S.S.; Maijub, J.G.; Krishnan, L.; Ramakrishnan, V.M.; Clayton, L.R.; Williams, S.K.; Hoying, J.B.; Boyd, N.L. Generation of a functional liver tissue mimic using adipose stromal vascular fraction cell-derived vasculatures. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, V.M.; Boyd, N.L. The Adipose Stromal Vascular Fraction as a Complex Cellular Source for Tissue Engineering Applications. Tissue Eng. Part. B Rev. 2018, 24, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Koh, Y.J.; Moon, H.R.; Ryoo, H.G.; Cho, C.H.; Kim, I.; Koh, G.Y. Adipose tissue is an extramedullary reservoir for functional hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. Blood 2010, 115, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Graaf, M.T.; de Jongste, A.H.; Kraan, J.; Boonstra, J.G.; Sillevis Smitt, P.A.; Gratama, J.W. Flow cytometric characterization of cerebrospinal fluid cells. Cytometry B Clin. Cytom. 2011, 80, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalu, M.M.; McIntyre, L.; Pugliese, C.; Fergusson, D.; Winston, B.W.; Marshall, J.C.; Granton, J.; Stewart, D.J. Safety of cell therapy with mesenchymal stromal cells (SafeCell): A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karussis, D.; Karageorgiou, C.; Vaknin-Dembinsky, A.; Gowda-Kurkalli, B.; Gomori, J.M.; Kassis, I.; Bulte, J.W.; Petrou, P.; Ben-Hur, T.; Abramsky, O.; et al. Safety and immunological effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in patients with multiple sclerosis and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Arch. Neurol. 2010, 67, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittenger, M.F.; Discher, D.E.; Peault, B.M.; Phinney, D.G.; Hare, J.M.; Caplan, A.I. Mesenchymal stem cell perspective: Cell biology to clinical progress. NPJ Regen. Med. 2019, 4, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renesme, L.; Cobey, K.D.; Lalu, M.M.; Bubela, T.; Chinnadurai, R.; De Vos, J.; Dunbar, R.; Fergusson, D.; Freund, D.; Galipeau, J.; et al. Delphi-driven consensus definition for mesenchymal stromal cells and clinical reporting guidelines for mesenchymal stromal cell–based therapeutics. Cytotherapy 2025, 27, 146–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nicola, M.; Carlo-Stella, C.; Magni, M.; Milanesi, M.; Longoni, P.D.; Matteucci, P.; Grisanti, S.; Gianni, A.M. Human bone marrow stromal cells suppress T-lymphocyte proliferation induced by cellular or nonspecific mitogenic stimuli. Blood 2002, 99, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djouad, F.; Charbonnier, L.M.; Bouffi, C.; Louis-Plence, P.; Bony, C.; Apparailly, F.; Cantos, C.; Jorgensen, C.; Noël, D. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit the differentiation of dendritic cells through an interleukin-6-dependent mechanism. Stem. Cells 2007, 25, 2025–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, R.C.; Tan, T.T.; Sim, W.K.; Zhang, B.; Lim, S.K. A roadmap from research to clinical testing of mesenchymal stromal cell exosomes in the treatment of psoriasis. Cytotherapy 2023, 25, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenner, F.; Wagner, A.; Gerner, I.; Ludewig, E.; Trujanovic, R.; Rohde, E.; von Rechenberg, B.; Gimona, M.; Traweger, A. Evaluation of the Potential of Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles to Improve Rotator Cuff Healing: A Pilot Ovine Study. Am. J. Sports Med. 2023, 51, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Rhim, W.K.; Seo, H.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, C.G.; Han, D.K. Comparative Analysis of MSC-Derived Exosomes Depending on Cell Culture Media for Regenerative Bioactivity. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2021, 18, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breslin, S.; O’Driscoll, L. Three-dimensional cell culture: The missing link in drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2013, 18, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, K.; Grover, H.; Han, L.H.; Mou, Y.; Pegoraro, A.F.; Fredberg, J.; Chen, Z. Modeling Physiological Events in 2D vs. 3D Cell Culture. Physiology 2017, 32, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagies, S.; Schlimpert, M.; Neumann, S.; Waldin, A.; Kammerer, B.; Borner, C.; Peintner, L. Cells grown in three-dimensional spheroids mirror in vivo metabolic response of epithelial cells. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda, E.T.; Nerem, R.M.; Ahsan, T. Differentiation patterns of embryonic stem cells in two- versus three-dimensional culture. Cells Tissues Organs 2013, 197, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontoura, J.C.; Viezzer, C.; Dos Santos, F.G.; Ligabue, R.A.; Weinlich, R.; Puga, R.D.; Antonow, D.; Severino, P.; Bonorino, C. Comparison of 2D and 3D cell culture models for cell growth, gene expression and drug resistance. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 107, 110264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thippabhotla, S.; Zhong, C.; He, M. 3D cell culture stimulates the secretion of in vivo like extracellular vesicles. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Ding, Y.; Sun, X.S.; Nguyen, T.A. Peptide hydrogelation and cell encapsulation for 3D culture of MCF-7 breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, S.; Carvalho, J.; Oliveira, P.; Voglstaetter, M.; Schvartz, D.; Thomsen, A.R.; Walter, N.; Khanduri, R.; Sanchez, J.C.; Keller, A.; et al. 3D Cellular Architecture Affects MicroRNA and Protein Cargo of Extracellular Vesicles. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1800948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraszti, R.A.; Miller, R.; Stoppato, M.; Sere, Y.Y.; Coles, A.; Didiot, M.C.; Wollacott, R.; Sapp, E.; Dubuke, M.L.; Li, X.; et al. Exosomes Produced from 3D Cultures of MSCs by Tangential Flow Filtration Show Higher Yield and Improved Activity. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 2838–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, A.L.; Lefavor, R.C.; Zubair, A.C. Characterization and cost-benefit analysis of automated bioreactor-expanded mesenchymal stem cells for clinical applications. Transfusion 2018, 58, 2374–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, P.J.; Mei, Z.; Durett, A.G.; Cabreira-Hansen Mda, G.; Klis, M.; Li, W.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, B.; Parsha, K.; Mir, O.; et al. Efficient manufacturing of therapeutic mesenchymal stromal cells with the use of the Quantum Cell Expansion System. Cytotherapy 2014, 16, 1048–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Wang, B.; Tang, T.; Lv, L.; Ding, Z.; Li, Z.; Hu, R.; Wei, Q.; Shen, A.; Fu, Y.; et al. Three-dimensional culture of MSCs produces exosomes with improved yield and enhanced therapeutic efficacy for cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Cerione, R.A.; Antonyak, M.A. Isolation and characterization of extracellular vesicles produced by cell lines. STAR Protoc. 2021, 2, 100295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, K.; Martin, K.; FitzGerald, S.P.; O’Sullivan, J.; Wu, Y.; Blanco, A.; Richardson, C.; McGee, M.M. A comparison of methods for the isolation and separation of extracellular vesicles from protein and lipid particles in human serum. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, S.C.; Horie, M.; Nagamori, E.; Kino-Oka, M. Size- and time-dependent growth properties of human induced pluripotent stem cells in the culture of single aggregate. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2017, 124, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nienow, A.W.; Rafiq, Q.A.; Coopman, K.; Hewitt, C.J. A potentially scalable method for the harvesting of hMSCs from microcarriers. Biochem. Eng. J. 2014, 85, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, R.M.S.; Rodrigues, S.C.; Gomes, C.F.; Duarte, F.V.; Romao, M.; Leal, E.C.; Freire, P.C.; Neves, R.; Simões-Correia, J. Development of an optimized and scalable method for isolation of umbilical cord blood-derived small extracellular vesicles for future clinical use. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2021, 10, 910–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witwer, K.W.; Van Balkom, B.W.M.; Bruno, S.; Choo, A.; Dominici, M.; Gimona, M.; Hill, A.F.; De Kleijn, D.; Koh, M.; Lai, R.C.; et al. Defining mesenchymal stromal cell (MSC)-derived small extracellular vesicles for therapeutic applications. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1609206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Lin, H.; Huang, K. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-derived Extracellular Vesicles Transmitting MicroRNA-34a-5p Suppress Tumorigenesis of Colorectal Cancer Through c-MYC/DNMT3a/PTEN Axis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Amigorena, S.; Raposo, G.; Clayton, A. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 2006, 30, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobin, J.; Muradia, G.; Mehic, J.; Westwood, C.; Couvrette, L.; Stalker, A.; Bigelow, S.; Luebbert, C.C.; Bissonnette, F.S.; Johnston, M.J.W.; et al. Hollow-fiber bioreactor production of extracellular vesicles from human bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells yields nanovesicles that mirrors the immuno-modulatory antigenic signature of the producer cell. Stem. Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida Fuzeta, M.; Bernardes, N.; Oliveira, F.D.; Costa, A.C.; Fernandes-Platzgummer, A.; Farinha, J.P.; Rodrigues, C.A.V.; Jung, S.; Tseng, R.J.; Milligan, W.; et al. Scalable Production of Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Under Serum-/Xeno-Free Conditions in a Microcarrier-Based Bioreactor Culture System. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 553444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simaria, A.S.; Hassan, S.; Varadaraju, H.; Rowley, J.; Warren, K.; Vanek, P.; Farid, S.S. Allogeneic cell therapy bioprocess economics and optimization: Single-use cell expansion technologies. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2014, 111, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, M.; Paramesh, V.; Kaviya, S.R.; Anuradha, E.; Solomon, F.D. 3D cell culture systems: Advantages and applications. J. Cell Physiol. 2015, 230, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, C.; Teng, Y. Is It Time to Start Transitioning From 2D to 3D Cell Culture? Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Liu, L.; Ma, F.; Wong, C.W.; Guo, X.E.; Chacko, J.V.; Farhoodi, H.P.; Zhang, S.X.; Zimak, J.; Ségaliny, A.; et al. Elucidation of Exosome Migration across the Blood-Brain Barrier Model In Vitro. Cell Mol. Bioeng. 2016, 9, 509–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachlos, E.; Auguste, D.T. Embryoid body morphology influences diffusive transport of inductive biochemicals: A strategy for stem cell differentiation. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 4471–4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Rhim, W.K.; Yoo, Y.I.; Kim, D.S.; Ko, K.W.; Heo, Y.; Park, C.G.; Han, D.K. Defined MSC exosome with high yield and purity to improve regenerative activity. J. Tissue Eng. 2021, 12, 20417314211008626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhoy, P.; Brown, C.W.; Amante, J.J.; Mercurio, A.M. Protocol for the separation of extracellular vesicles by ultracentrifugation from in vitro cell culture models. STAR Protoc. 2021, 2, 100303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Ha, D.H.; Go, H.K.; Youn, J.; Kim, H.K.; Jin, R.C.; Miller, R.B.; Kim, D.H.; Cho, B.S.; Yi, Y.W. Reproducible Large-Scale Isolation of Exosomes from Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells and Their Application in Acute Kidney Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busatto, S.; Vilanilam, G.; Ticer, T.; Lin, W.L.; Dickson, D.W.; Shapiro, S.; Bergese, P.; Wolfram, J. Tangential Flow Filtration for Highly Efficient Concentration of Extracellular Vesicles from Large Volumes of Fluid. Cells 2018, 7, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lyden, D. Asymmetric-flow field-flow fractionation technology for exomere and small extracellular vesicle separation and characterization. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 1027–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiest, E.F.; Zubair, A.C. Challenges of manufacturing mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles in regenerative medicine. Cytotherapy 2020, 22, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganini, C.; Capasso Palmiero, U.; Pocsfalvi, G.; Touzet, N.; Bongiovanni, A.; Arosio, P. Scalable Production and Isolation of Extracellular Vesicles: Available Sources and Lessons from Current Industrial Bioprocesses. Biotechnol. J. 2019, 14, e1800528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohde, E.; Pachler, K.; Gimona, M. Manufacturing and characterization of extracellular vesicles from umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stromal cells for clinical testing. Cytotherapy 2019, 21, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korchak, J.A.; Wiest, E.F.; Zubair, A.C. How do we assess batch-to-batch consistency between extracellular vesicle products? Transfusion 2023, 63, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsh, J.A.; Goberdhan, D.C.I.; O’Driscoll, L.; Buzas, E.I.; Blenkiron, C.; Bussolati, B.; Cai, H.; Di Vizio, D.; Driedonks, T.A.P.; Erdbrügger, U.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles (MISEV2023): From basic to advanced approaches. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimona, M.; Pachler, K.; Laner-Plamberger, S.; Schallmoser, K.; Rohde, E. Manufacturing of Human Extracellular Vesicle-Based Therapeutics for Clinical Use. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, H.H.; Nguyen, T.-H.; Hoang, D.H.; Vu, B.D.; Tran, M.-A.; Le, M.T.; Hoang, N.T.M.; Bui, A.V.; Than, U.T.T.; Nguyen, X.H. Manufacturing exosomes for wound healing: Comparative analysis of culture media. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0313697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, S.; Kang, M.H.; Jeyaraj, M.; Qasim, M.; Kim, J.H. Review of the Isolation, Characterization, Biological Function, and Multifarious Therapeutic Approaches of Exosomes. Cells 2019, 8, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Bioreactor Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Hollow Fiber Bioreactors |
|
|
| Stirred Tank Bioreactors |
|
|
| Microcarrier Bioreactors |
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wiest, E.F.; Zubair, A.C. Generation of Current Good Manufacturing Practices-Grade Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Using Automated Bioreactors. Biology 2025, 14, 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14030313
Wiest EF, Zubair AC. Generation of Current Good Manufacturing Practices-Grade Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Using Automated Bioreactors. Biology. 2025; 14(3):313. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14030313
Chicago/Turabian StyleWiest, Elani F., and Abba C. Zubair. 2025. "Generation of Current Good Manufacturing Practices-Grade Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Using Automated Bioreactors" Biology 14, no. 3: 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14030313
APA StyleWiest, E. F., & Zubair, A. C. (2025). Generation of Current Good Manufacturing Practices-Grade Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Using Automated Bioreactors. Biology, 14(3), 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14030313






