The Evolution of Nutrient and Microbial Composition and Maturity During the Composting of Different Plant-Derived Wastes
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
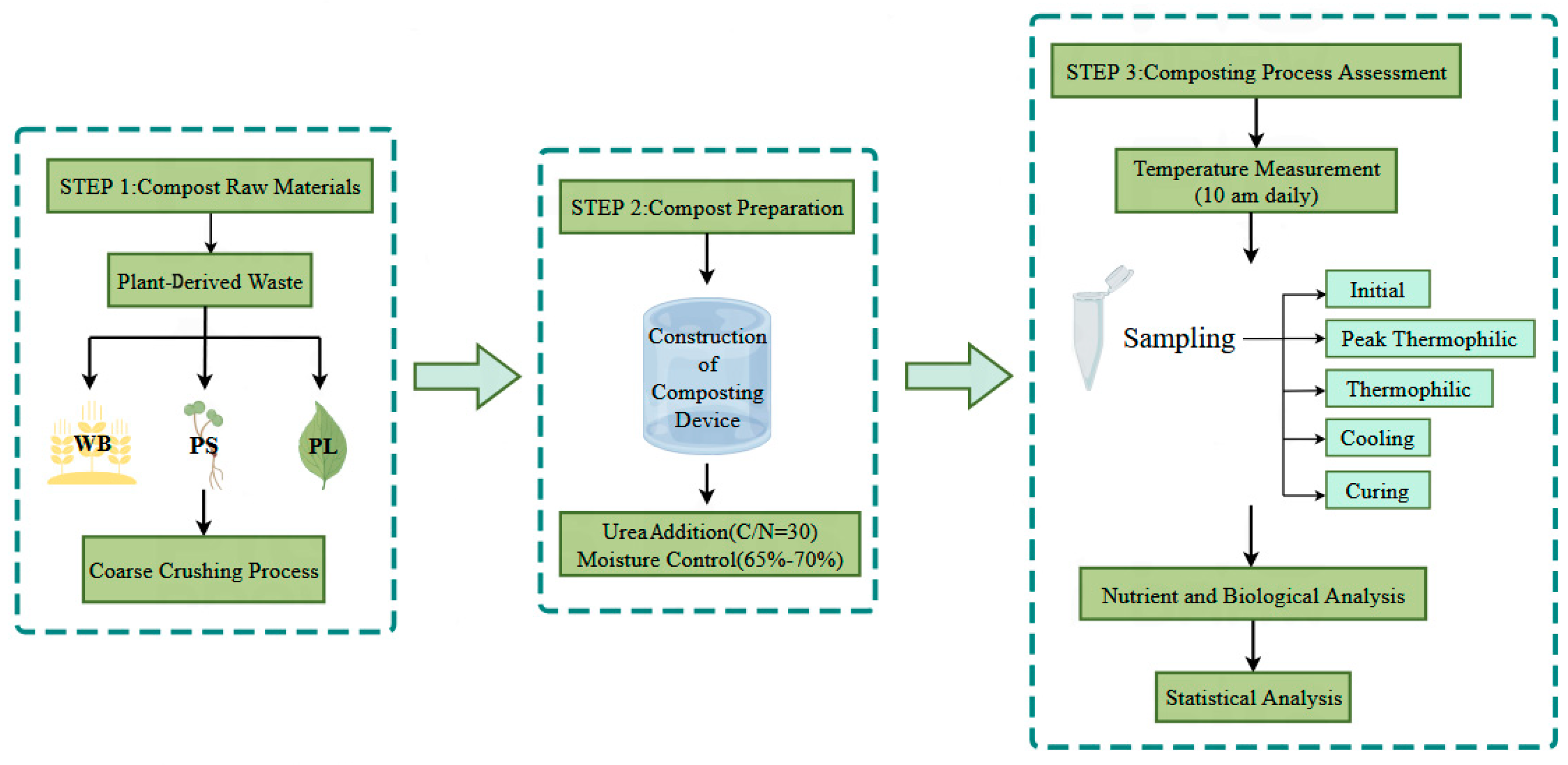
2.1. Composting Materials and Trials
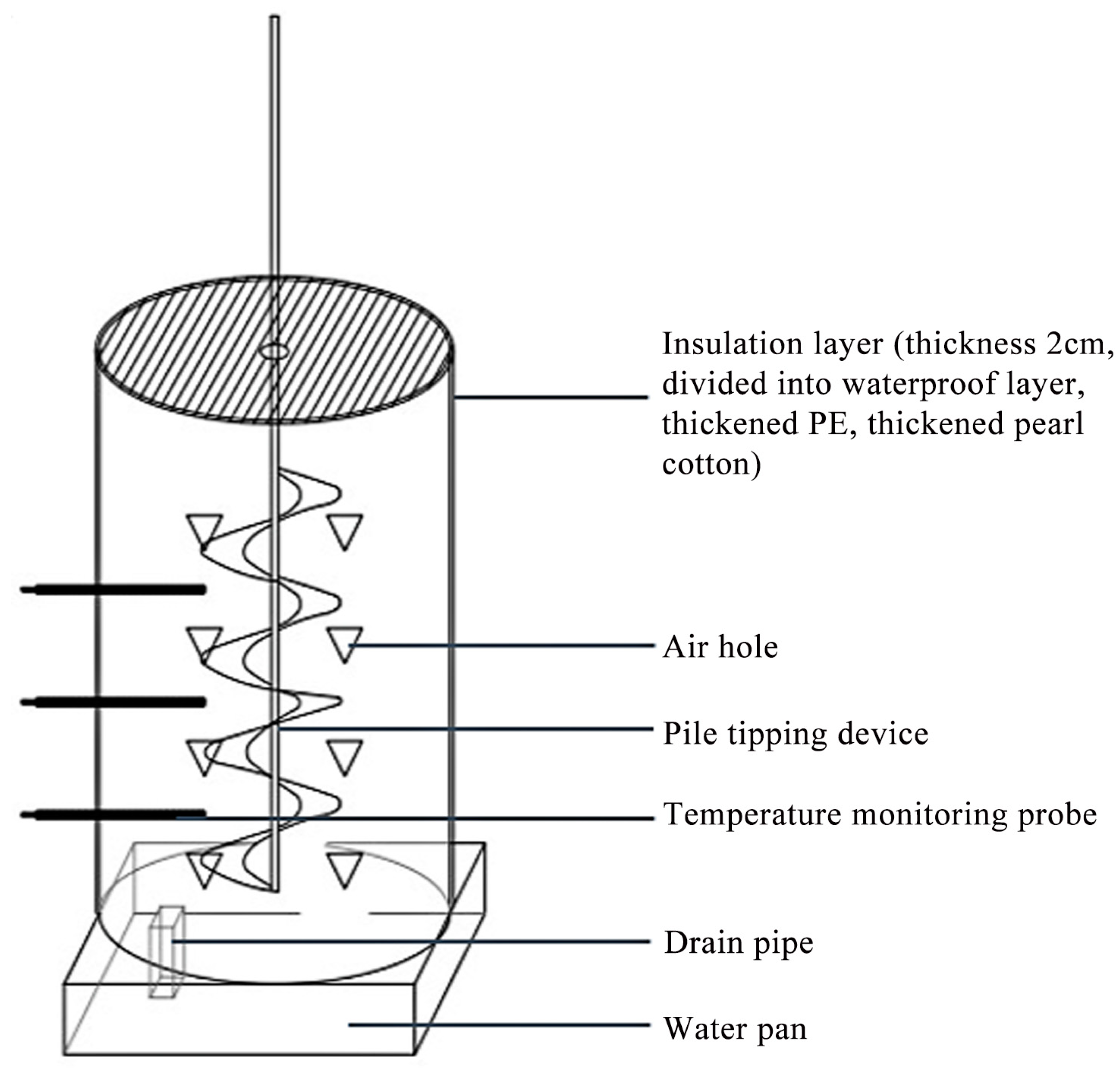
2.1.1. Composting Materials and Experimental Design
2.1.2. Sampling Protocol
2.1.3. Sample Processing Methodology
2.1.4. Microbiological Preservation Strategy
2.2. Analytical Methods
2.2.1. Bioassay and Analytical Procedures
2.2.2. Nutrient Element Analysis
2.2.3. Humic Substance Characterization
2.2.4. Microbial Community Profiling
2.3. Data Processing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Basic Physical and Chemical Indices in Composting Process
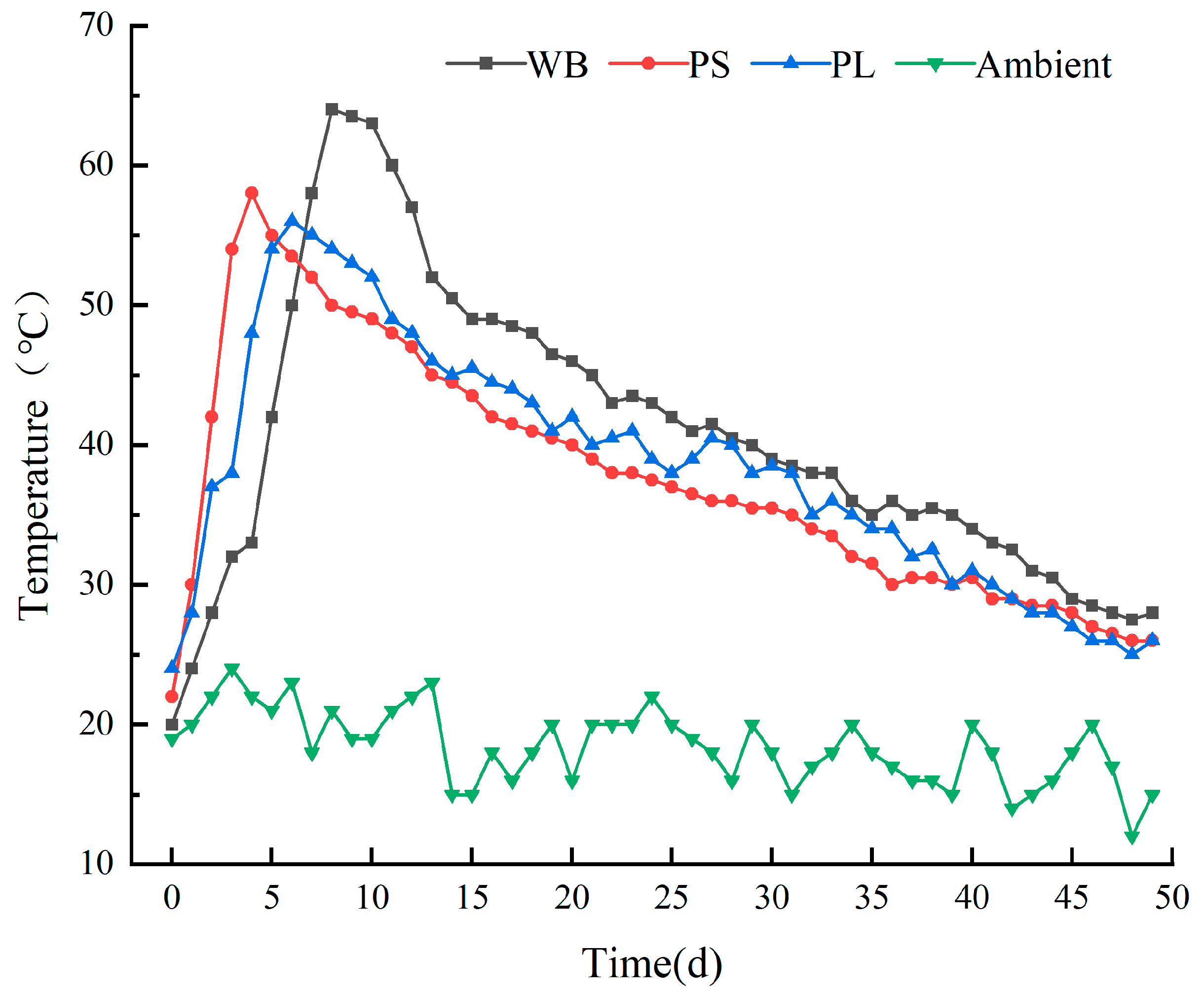
3.1.1. Temperature
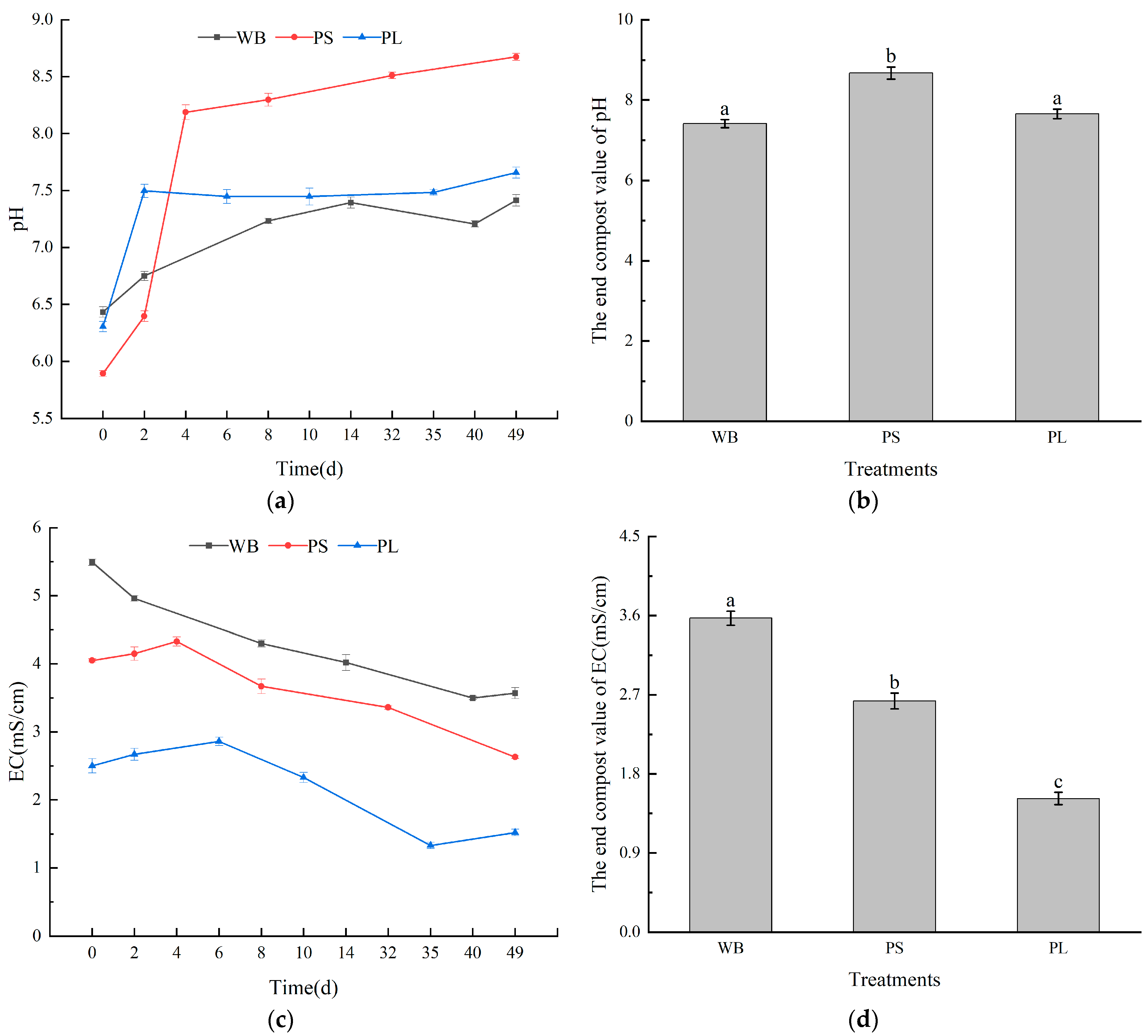
3.1.2. pH and EC Values
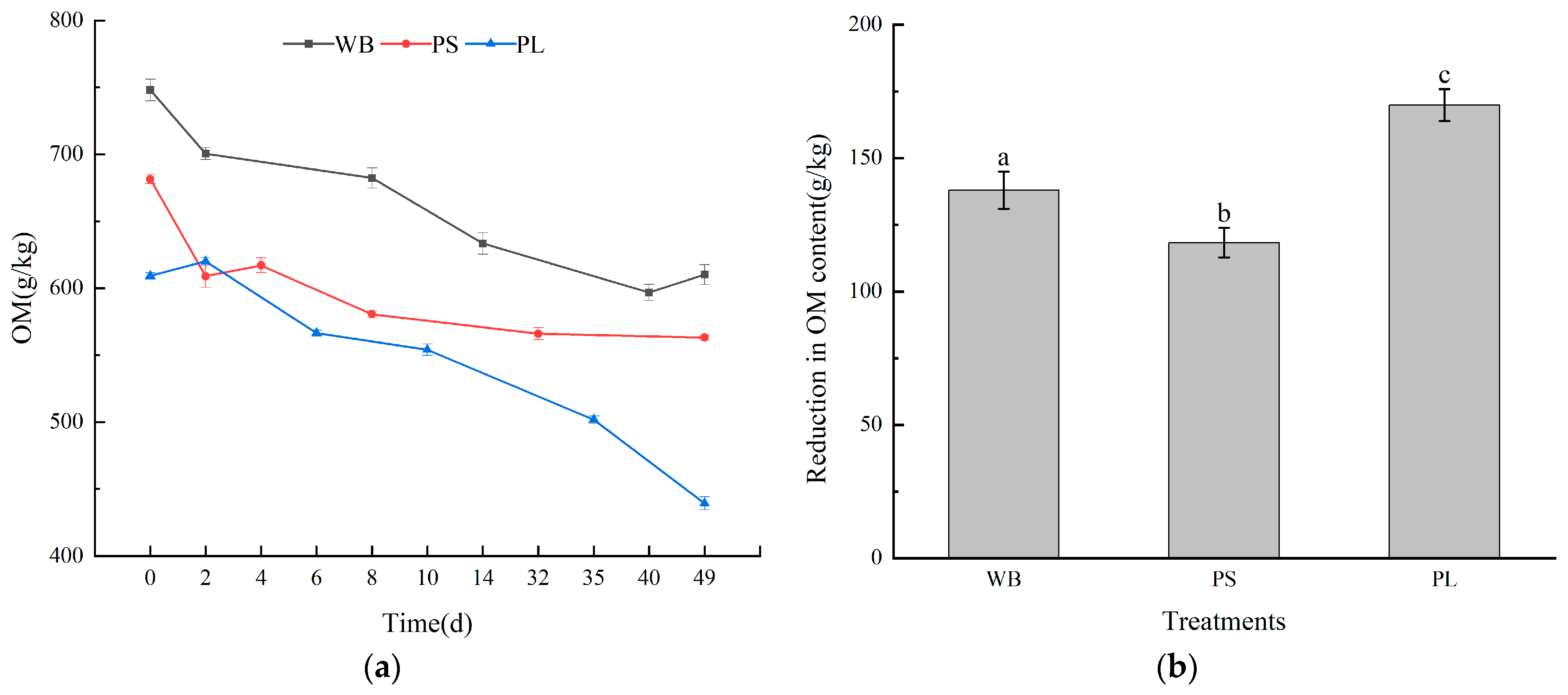
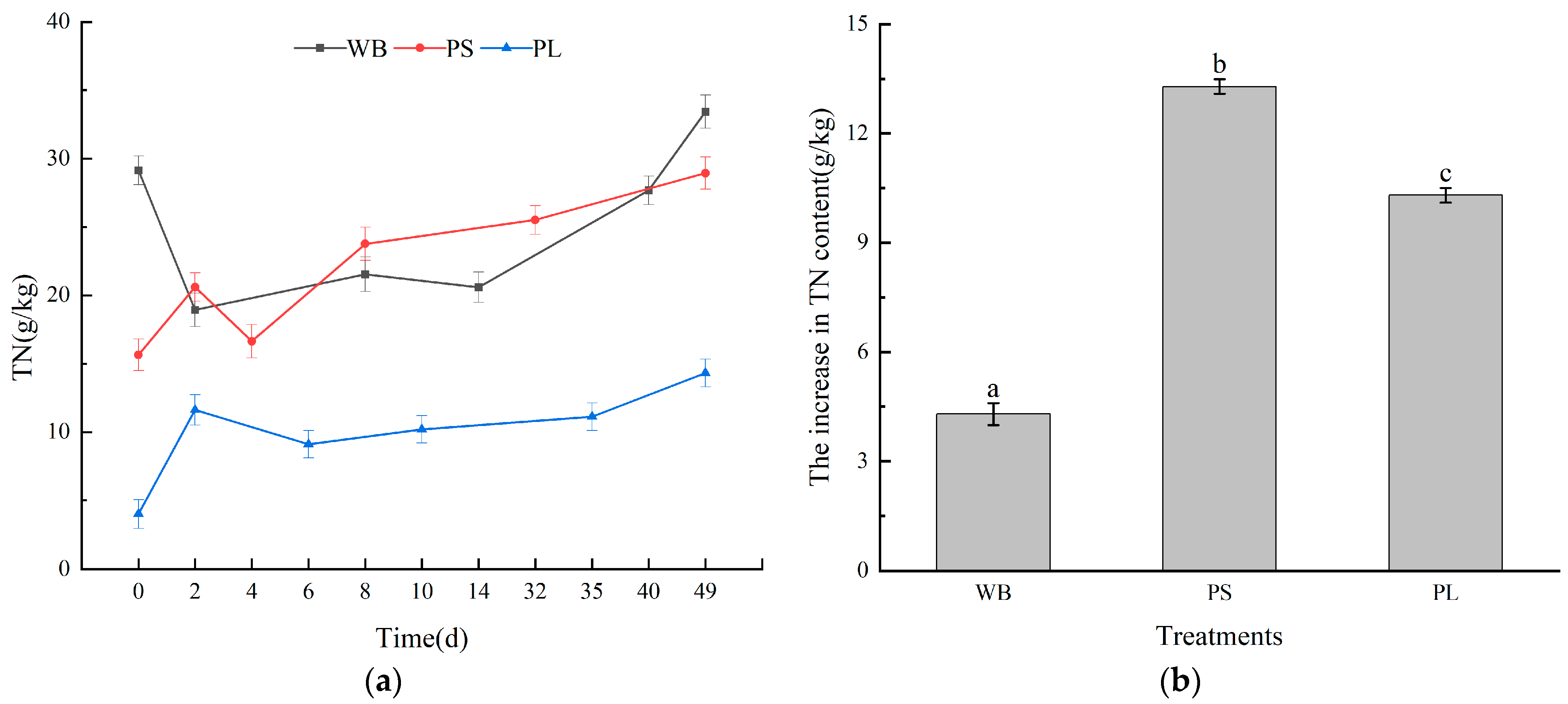
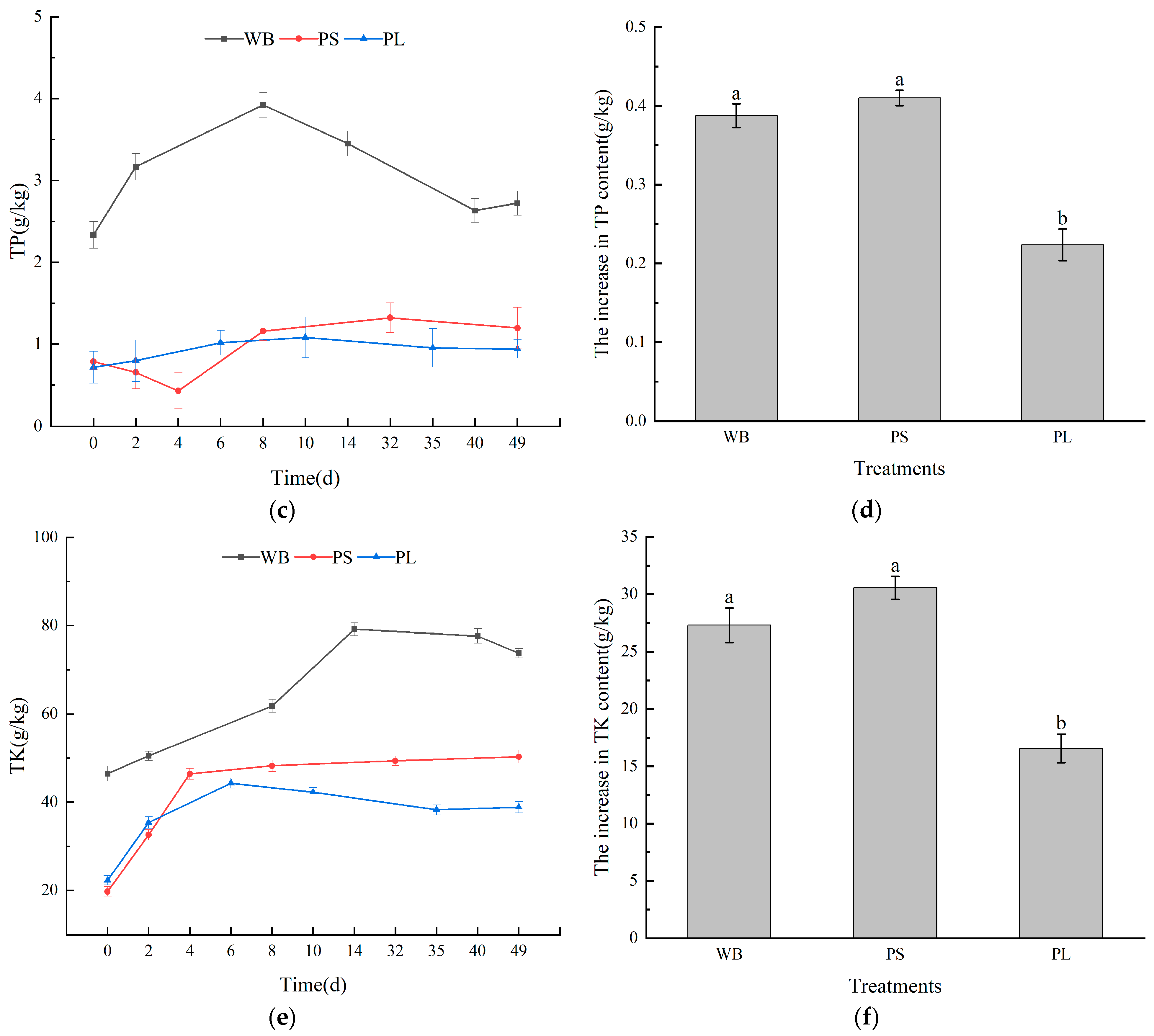
3.2. Nutrient Content in the Composting Process
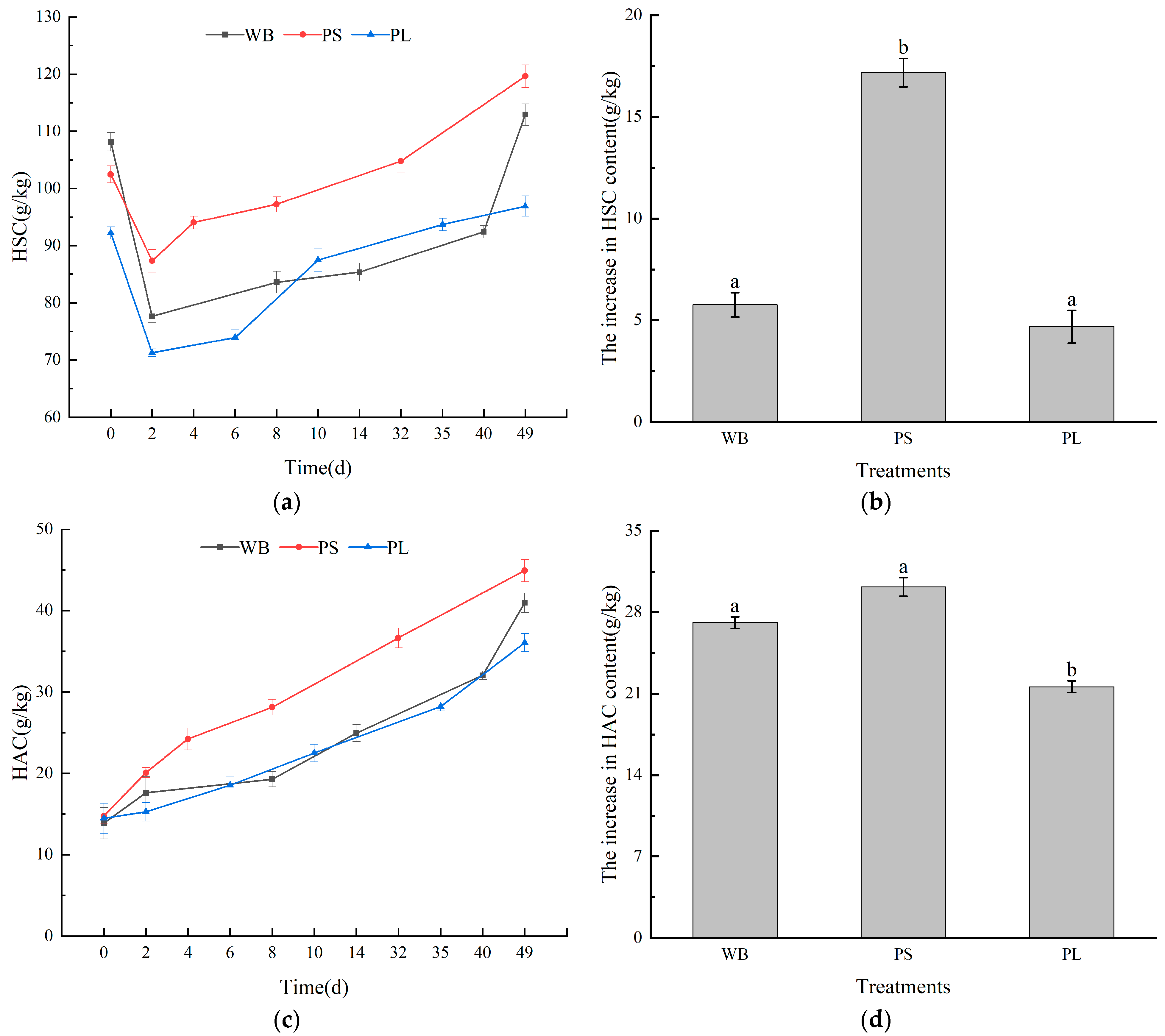
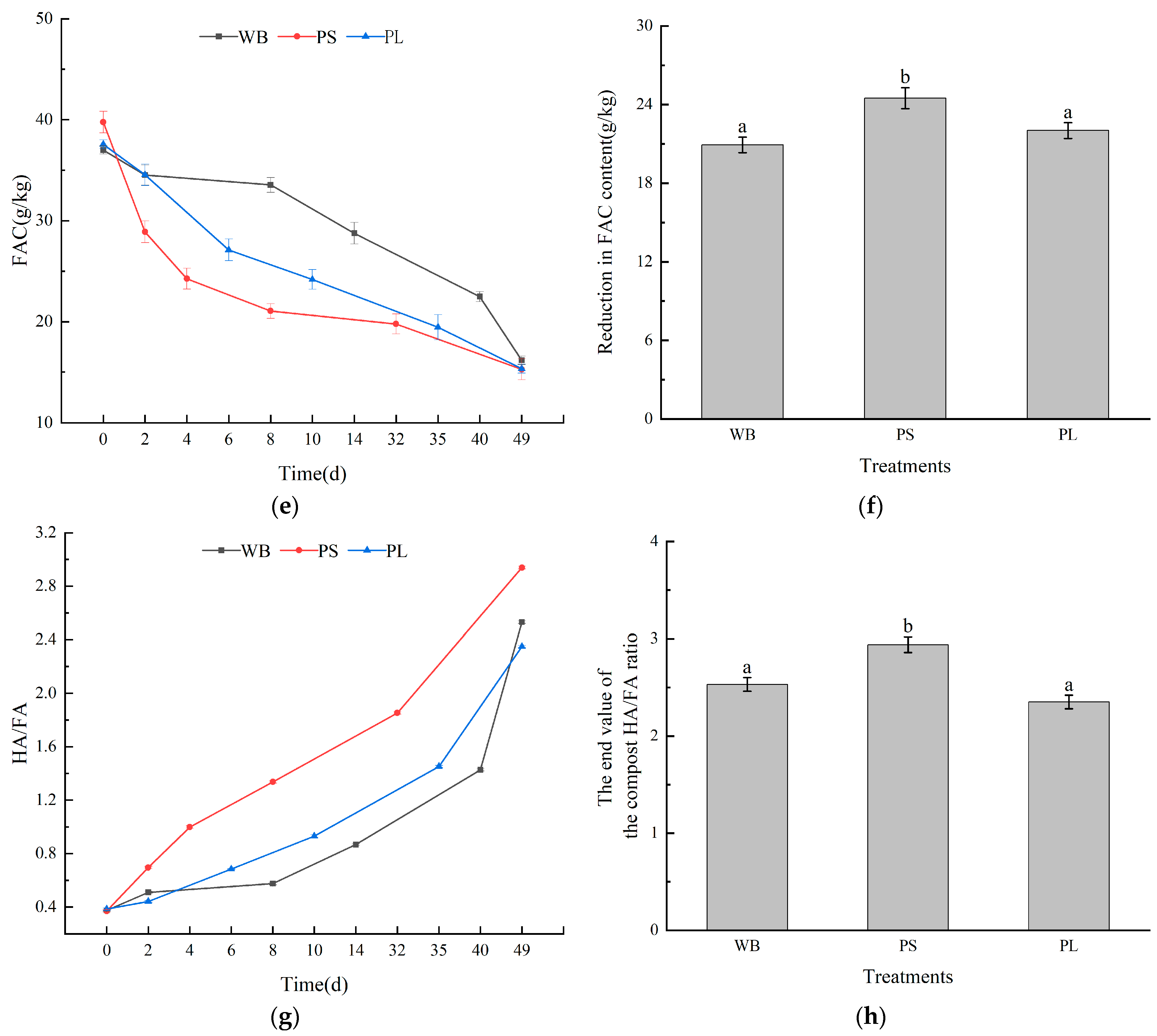
3.3. Humus Carbon in the Composting Process
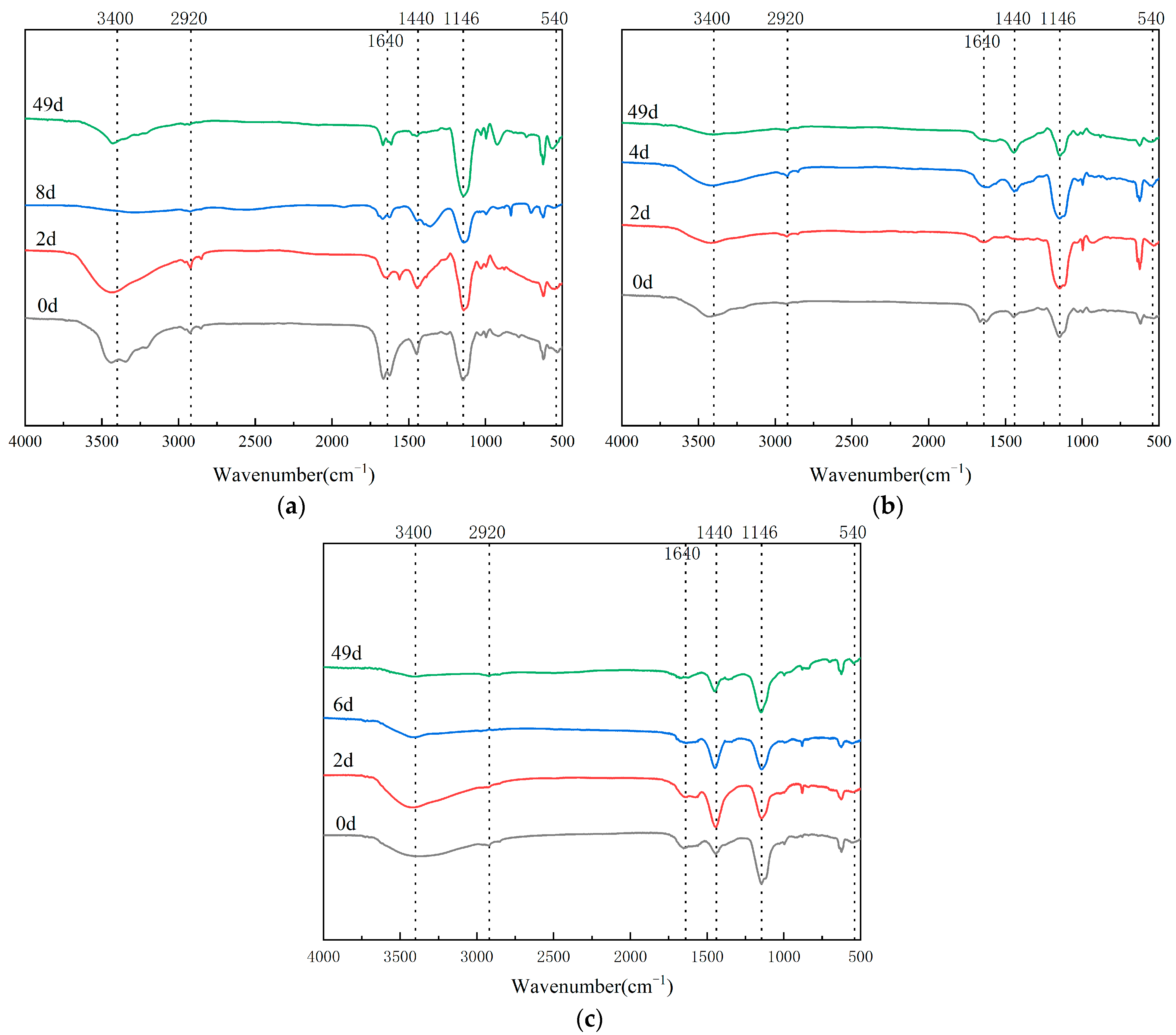
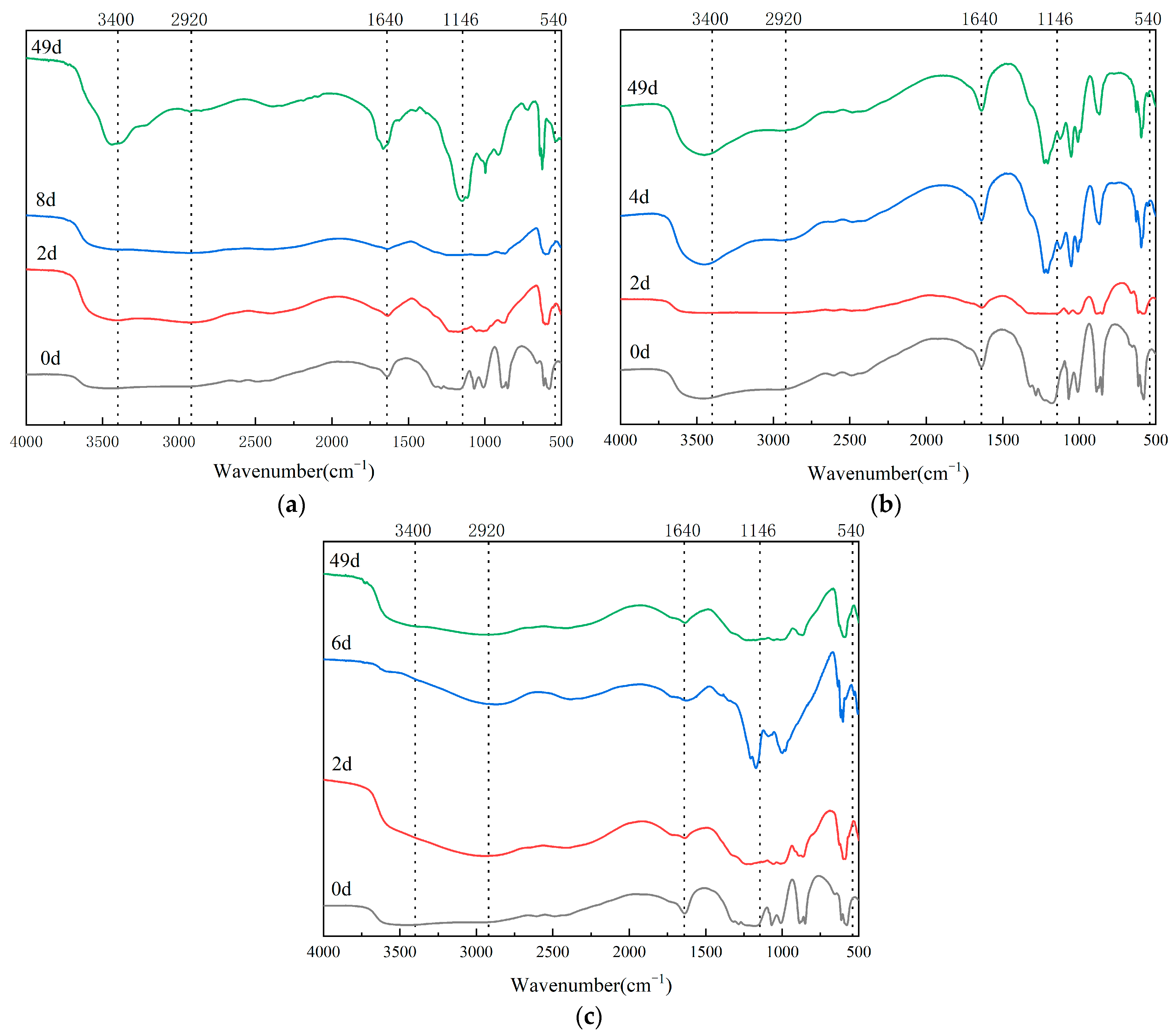
3.4. Infrared Spectrum Analysis in Composting Process
3.5. Compost Safety Index
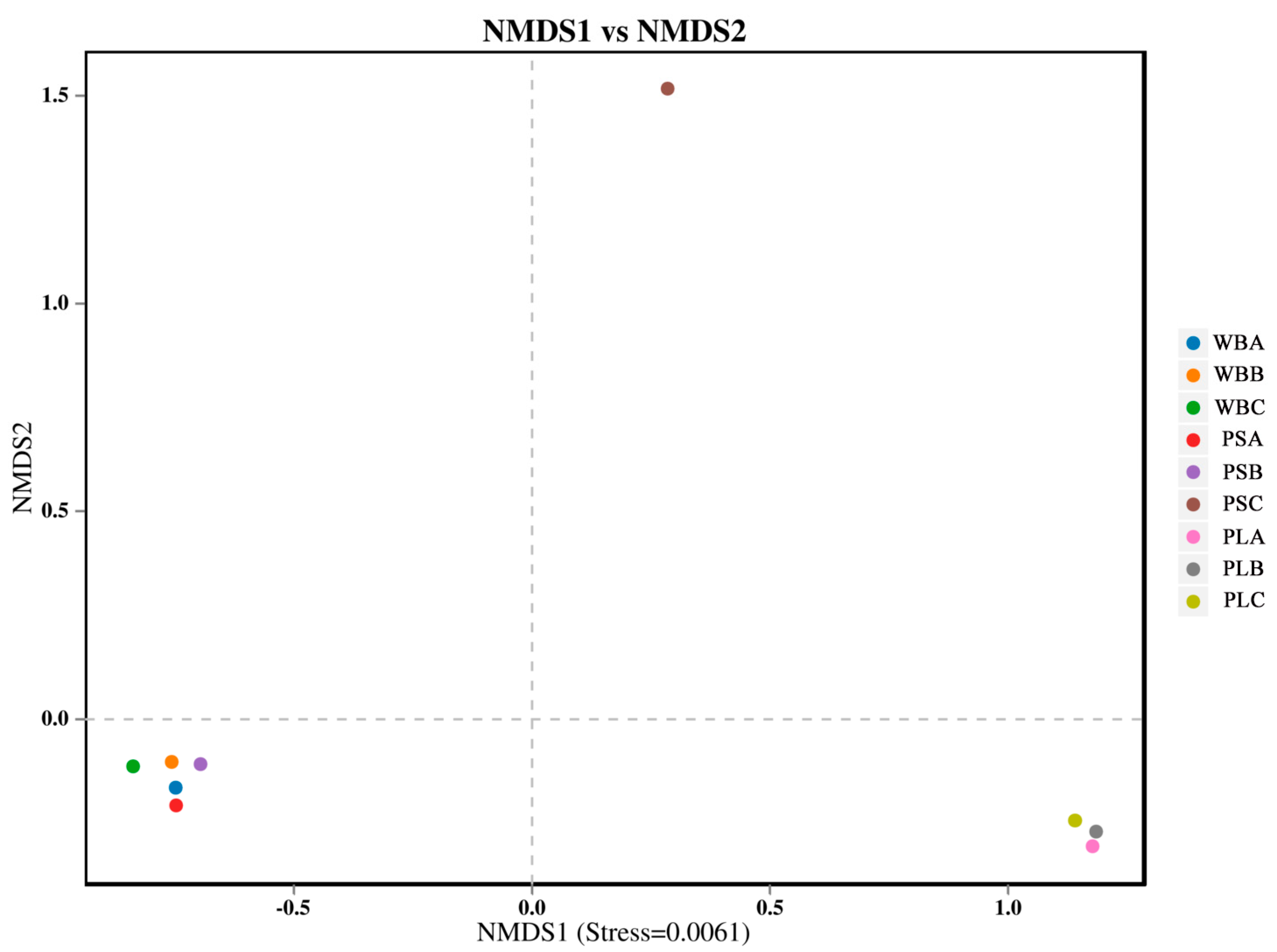
3.6. Bacterial Community Structure and Diversity During Composting
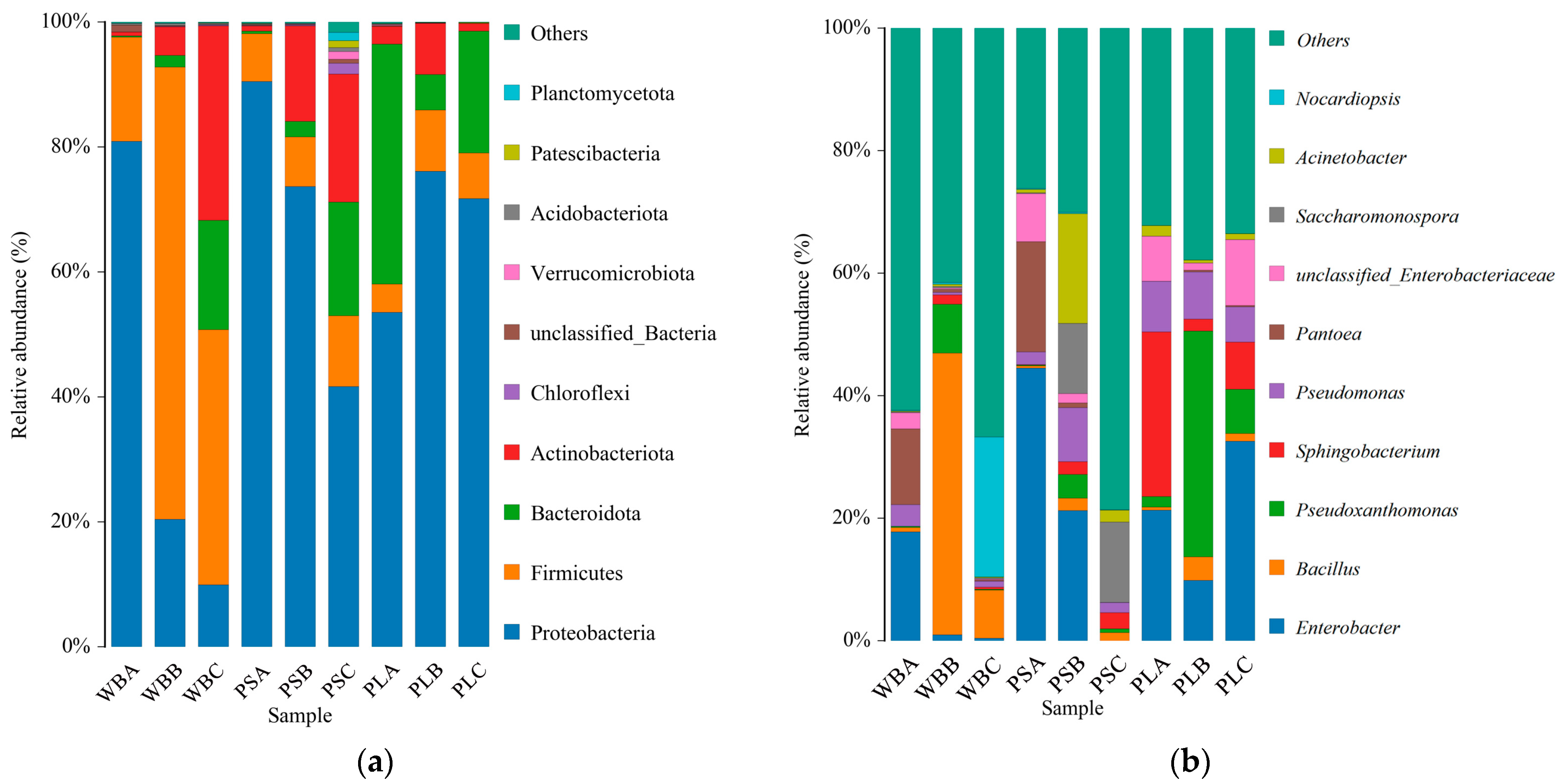
3.6.1. Bacterial Community Structure
3.6.2. Bacterial Community Diversity
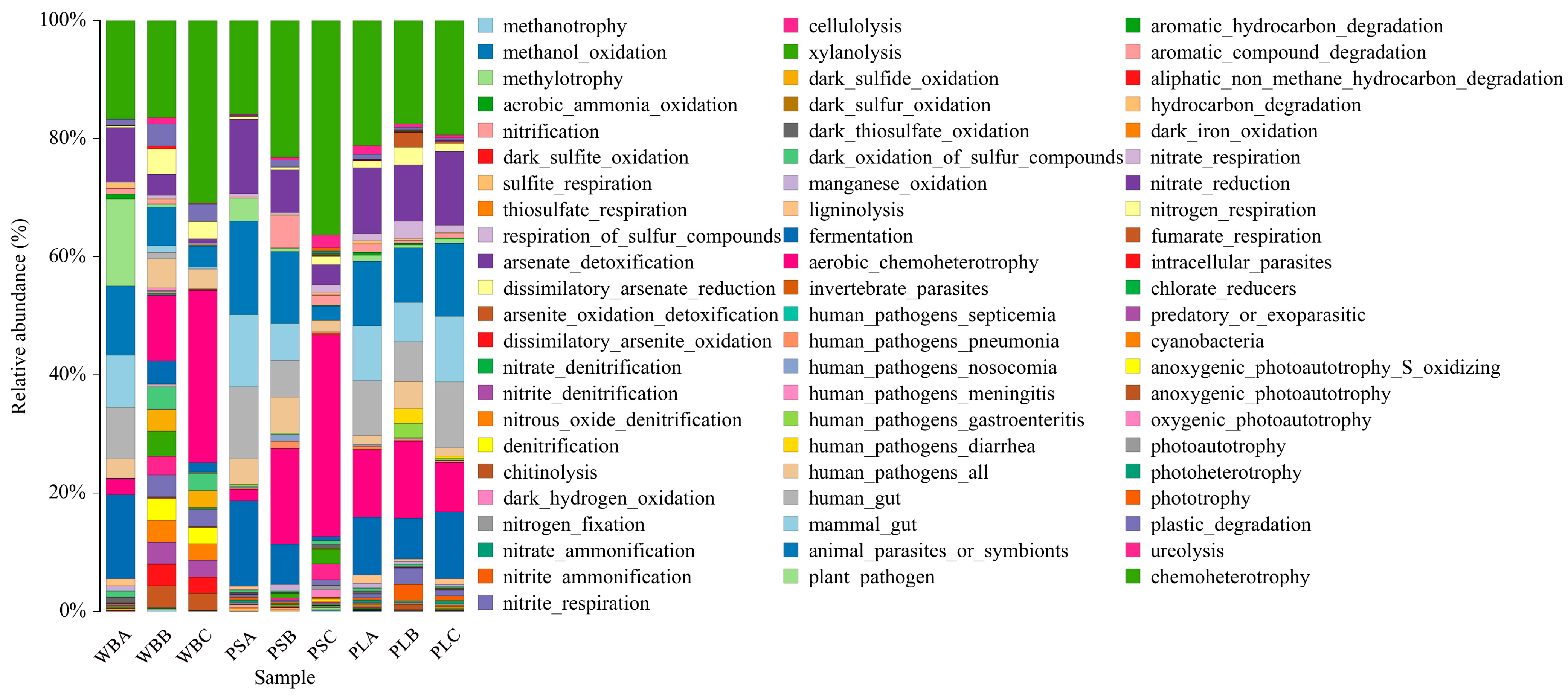
3.6.3. Functional Analysis of Bacterial Communities
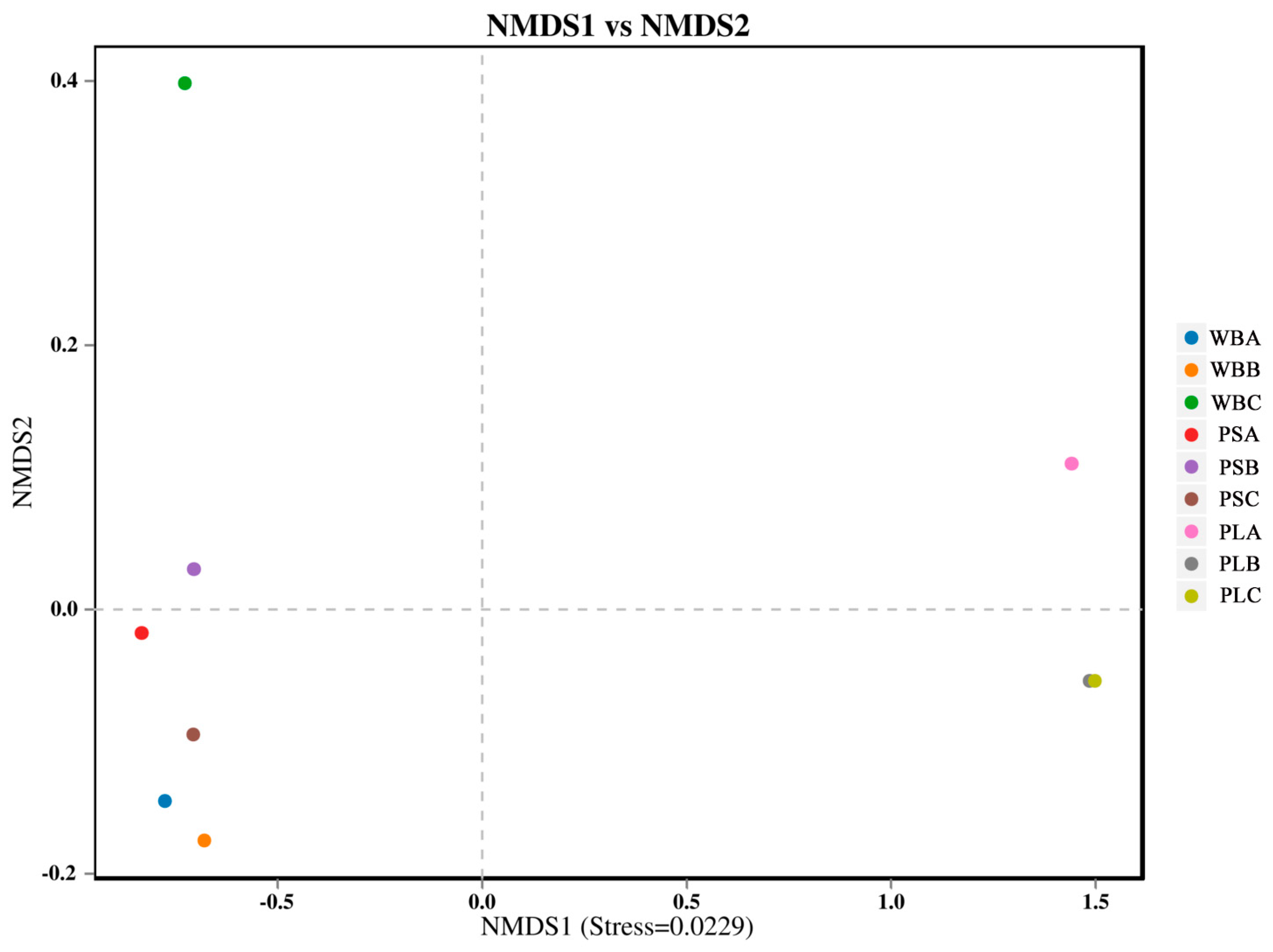
3.7. Fungal Community Structure and Diversity During Composting
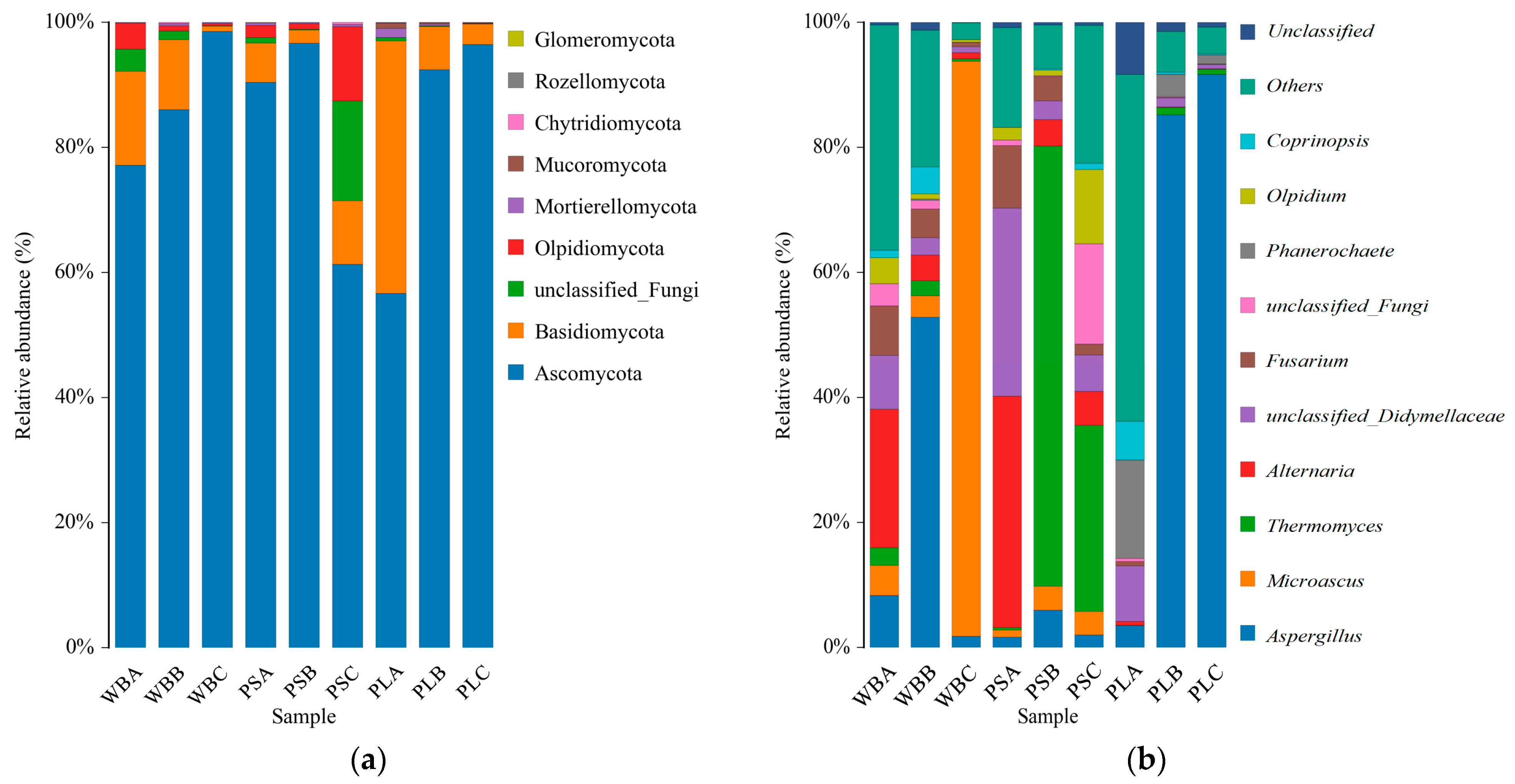
3.7.1. Fungal Community Structure
3.7.2. Fungal Community Diversity
3.7.3. Functional Analysis of Fungal Communities
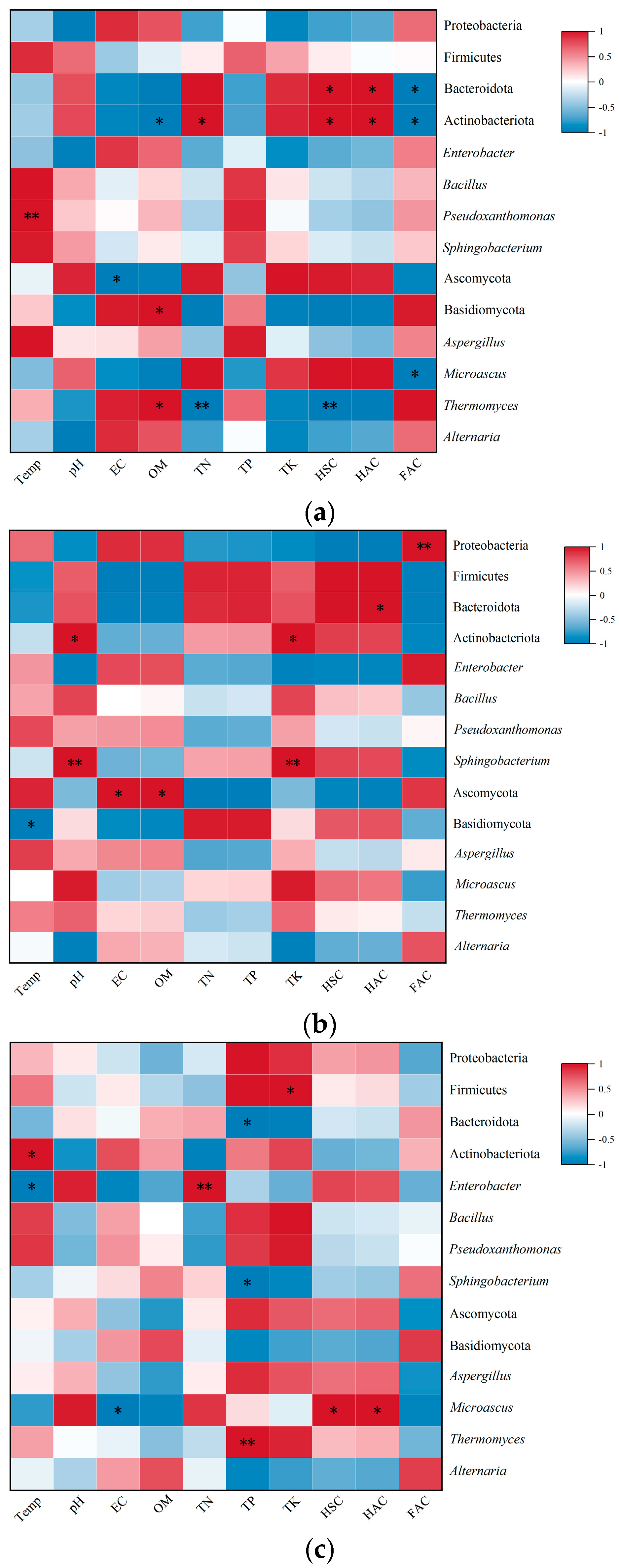
3.8. Correlation Between Microbial Community Structure and Nutrient Indicators in Compost
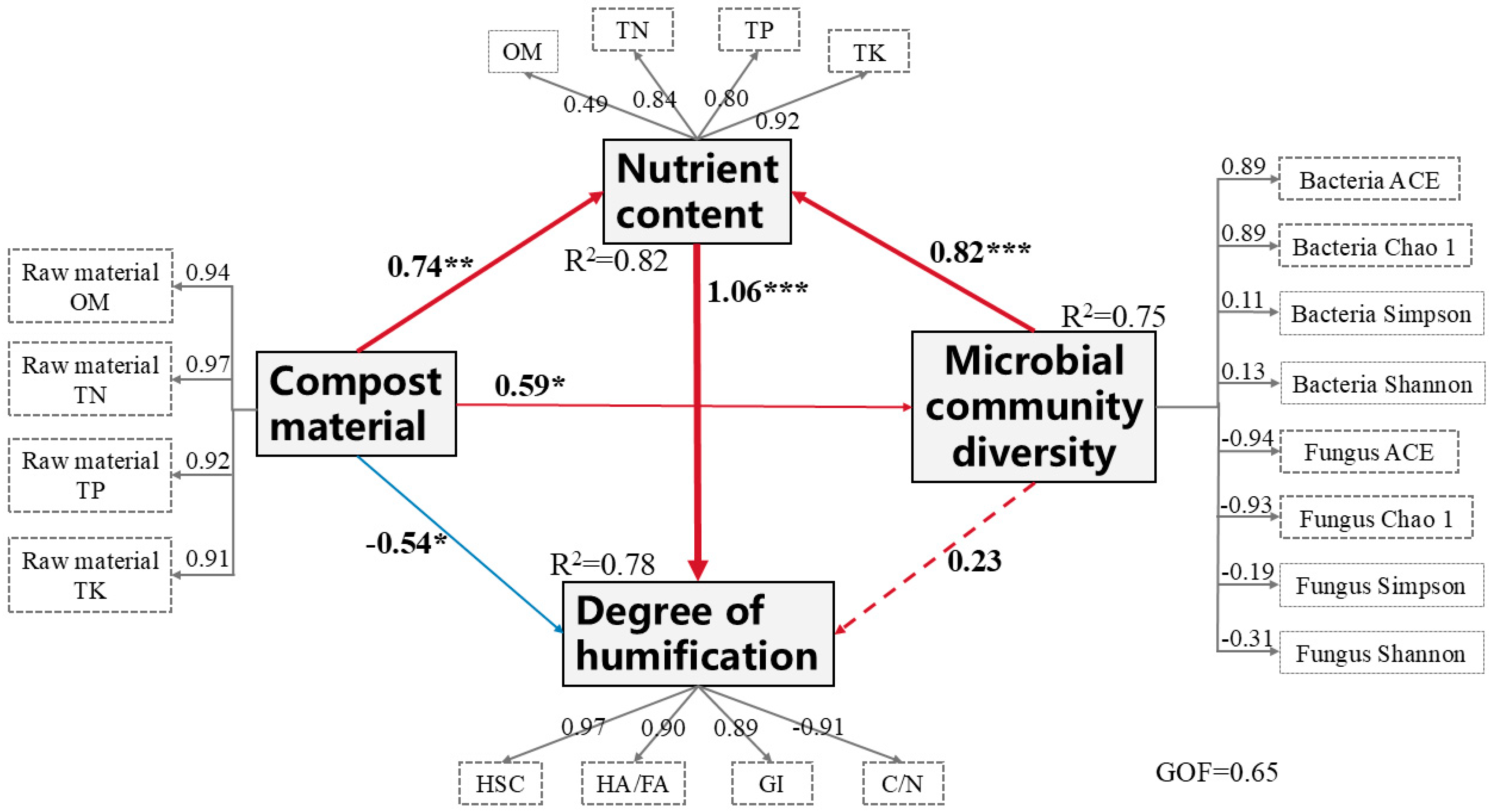
3.9. Structural Equation Model of Humification Degree of Compost
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.C.; Cui, W.Z.; Qi, Z.Y.; Wu, L.Y.; Zhou, W.L. Plant-Derived Waste as a Component of Growing Media: Manifestations, Assessments, and Sources of Their Phytotoxicity. J. Plants 2024, 13, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imanni, M.; Seecharran, D.; Sirpaul, J. Comparative review of aerobic and anaerobic composting for the reduction of organic waste. J. Agric. Rev. 2022, 43, 234–238. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.; Wang, Y.Y.; Sun, H.R.; Xu, Z. Analysis of humus formation and factors for driving the humification process during composting of different agricultural wastes. J. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 954158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.Z. Resource Utilization of Agricultural Waste: From Biomass Energy to Organic Fertilizer. J. Energy Biosci. 2024, 15, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.R.; Shang Guan, P.K.; Li, S.H.; Zhang, C.H.; Lou, J.M.; Guo, L.; Liu, L.; Lu, Y. The influence of carbon dioxide on fermentation products, microbial community, and functional gene in food waste fermentation with uncontrol pH. J. Environ. Res. 2025, 267, 120645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.B.; Zheng, J.M.; Gong, Y.T.; Zhao, Y.C.; Zhang, J.Q. Effects of garden waste reuse treatments on soil nutrients and microbial carbon source utilization in plantation soil. J. Zhejiang AF Univ. 2023, 40, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.M.; Yao, H.Y. Effects of Composting Different Types of Organic Fertilizer on the Microbial Community Structure and Antibiotic Resistance Genes. J. Microorg. 2020, 8, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pot, S.; Tender, C.D.; Ommeslag, S.; Delcour, I.; Ceusters, J.; Vandecasteele, B.; Debode, J.; Vancampenhout, K. Elucidating the microbiome of the sustainable peat replacers composts and nature management residues. J. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 983855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zhang, Y.M.; Yang, Z.J.; Zhang, Q.R.; He, X.; Song, Y.; Tian, L.L.; Wu, H. Improving Aerobic Digestion of Food Waste by Adding a Personalized Microbial Inoculum. J. Curr. Microbiol. 2024, 81, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.Y.; Zhang, X.M.; Wan, Y.; Deng, R.L.; Zhu, H.H.; Wang, X.H.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.M. Effect of Different Livestock Manure Ratios on the Decomposition Process of Aerobic Composting of Wheat Straw. J. Agron. 2023, 13, 2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Chen, Q.H.; Quan, H.Y.; Zhao, C.Y.; Wang, Y.Z.; Zhu, T. Combined Treatment for Chicken Manure and Kitchen Waste Enhances Composting Effect by Improving pH and C/N. J. Waste Biomass Valorization 2024, 13, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.Q.; Li, D.; Wang, J.W.; Huang, Y.; Mo, J.C. Research Progress on the Resource Utilization of Agricultural and Forestry Waste. J. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2023, 39, 77–81. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, S.; Jiang, L.; Hu, J.; Huang, W.; Lou, L. Microbiome data analysis via machine learning models: Exploring vital players to optimize kitchen waste composting system. J. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 388, 129731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, J.; Li, B.; Su, L.H.; Zhou, X.J.; Duan, E.S. Effects of potassium persulfate on nitrogen loss and microbial community during cow manure and corn straw composting. J. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 363, 127919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos Cordeiro, A.A.; Sousa Antunes, L.F.; Costa Rodrigues dos Santos, G.; Guerra, J.G.M.; Berbara, R.L.L.; Silva Araújo, E.; Espindola, J.A.A. Agronomic potential of different fermented organic composts based on agro-industrial plant waste. J. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahongnao, S.; Sharma, P.; Singh, D.; Ahamad, A.; Kumar, P.V.; Kumar, P.; Nanda, S. Formation and characterization of leaf waste into organic compost. J. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 75823–75837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.N.; Liu, H.T.; Wu, S. Immobilization pathways of heavy metals in composting: Interactions of microbial community and functional gene under varying C/N ratios and bulking agents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 426, 128103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.H.; Lu, T.J.; Feng, W.; Jin, Q.C.; Wu, Z.G.; Yang, Y. Development of the degradation bacteria in household food waste and analysis of the microbial community in aerobic composting. J. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2023, 70, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.L.; Cao, J.; Wang, P.J.; Li, R.R.; Qi, Z.C.; Fu, J.J.; Chen, Y.S.; Chen, M.J. Volatile organic compounds and dominant bacterial community during aerobic composting of vegetable waste and cow manure co-complexing. J. BioResources 2022, 17, 1338–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oueld Lhaj, M.; Moussadek, R.; Mouhir, L.; Mdarhri Alaoui, M.; Sanad, H.; Iben Halima, O.; Zouahri, A. Assessing the Evolution of Stability and Maturity in Co-Composting Sheep Manure with Green Waste Using Physico-Chemical and Biological Properties and Statistical Analyses: A Case Study of Botanique Garden in Rabat, Morocco. J. Agron. 2024, 14, 1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, N.; Toma, Y.; Ueno, H. Microbial diversity and community structure in co-composted bamboo powder and tea leaves based on carbon substrate utilization patterns of the BIOLOG EcoPlate method. J. Adv. Bamboo Sci. 2024, 8, 100101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.Y.; Liang, X.N.; Wang, P.; Ren, L.H. Effect of thermophilic bacterial complex agents on synergistic humification of carbon and nitrogen during lignocellulose-rich kitchen waste composting. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Chen, J.; Qi, C.R.; Li, G.X.; Luo, W.H.; Xu, Z.C. Impact of Agricultural and Forestry Waste on Humification and Microbial Driving Mechanisms in Kitchen Waste Com-posting. J. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2023, 39, 191–201. [Google Scholar]
- Cattle, S.R.; Robinson, C.; Whatmuff, M. The character and distribution of physical contaminants found in soil previously treated with mixed waste organic outputs and garden waste compost. J. Waste Manag. 2020, 101, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.; Liang, L.R.; Shi, Y.; Yin, H.; Li, L.; Xiao, J.M.; Huang, N.N.; Zhao, A.G.; Xia, Y.R.C.; Hou, J.W. Biofilms in plastisphere from freshwater wetlands: Biofilm formation, bacterial community assembly, and biogeochemical cycles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 476, 134930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Li, Z.J.; Liu, C.F.; Yan, T.Z.; Shi, H.D.; Yang, R.J. Effects of the Ingredients on Maturity and Humification during Kitchen Waste Composting as Illustrated by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. J. Sustain. 2023, 15, 13436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, B.D.; Zhao, X.Y.; He, X.S.; Huang, C.H.; Tan, W.B.; Gao, R.T.; Zhang, H.; Li, D. Successions and diversity of humic-reducing microorganisms and their association with physical-chemical parameters during composting. J. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 219, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.Y.; Ji, M.H.; Chen, A.; Zhang, B.G.; Shi, J.P.; Liu, L.; Li, X.; Sun, J.S. Evaluating the impact of rice husk on successions of bacterial and fungal communities during cow manure composting. J. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 102084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xiao, G.Z.; Li, L.B.; Su, F.K.; Yang, J. Optimal Color Development Conditions and Spectrophotometric Wavelength for Determination of Total Phosphorus in Soil by Mo-Sb Anti Colorimetric Method. J. Soil Fertil. Sci. China 1992, 2, 46–48. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, S.H.; Gong, H.R.; Chen, Z.W.; Chen, Y.Z.; Miao, X.X.; Wang, J.M. Determination of Total Potassium in Plants by Microwave Digestion-Flame Photometry. J. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2019, 58, 142–145. [Google Scholar]
- Kuwatsuka, S.; Watanabe, A.; Itoh, K.; Arai, S. Comparision of Two Methods of Preparation of Humic and Fulvic Acids, IHSS Method and NAGOYA Method. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1992, 38, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Y.; Kong, Y.L.; Yang, Y.; Ma, R.N.; Shen, Y.J.; Li, G.X.; Yuan, J. Superphosphate, Biochar, and a Microbial Inoculum Regulate Phytotoxicity and Humification During Chicken Manure Composting. J. Soc. Sci. Electron. Publ. 2022, 824, 153958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalremruati, M.; Devi, A.S. Changes in physico-chemical properties during composting of three common household organic solid wastes amended with garden soil. J. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2021, 15, 100727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayed, F.; Boussadia, O.; Grissa, H.; Aydi Ben Abdallah, R.; Jabnoun-Khiareddine, H.; Daami-Remadi, M. Assessment of Physico-chemical, Microbial and Phytotoxic Changes of Various Organic Wastes During their Composting Process. J. Environ. Agric. Stud. 2021, 2, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.Y.; Wang, J.S.; Amanze, C.; Yu, R.L.; Li, J.K.; Wu, X.L.; Shen, L.; Liu, Y.D.; Yu, Z.J.; Zeng, W.M. Exploring the dynamic of microbial community and metabolic function in food waste composting amended with traditional Chinese medicine residues. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 319, 115765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-mrini, S.; Aboutayeb, R.; Zouhri, A. Effect of initial C/N ratio and turning frequency on quality of final compost of turkey manure and olive pomace. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2022, 69, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sülük, K.; Tosun, İ.; Ekinci, K. Co-composting of two-phase olive-mill pomace and poultry manure with tomato harvest stalks. J. Environ. Technol. 2017, 38, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; He, X.L.; Liang, J. Succession of Microbial Community during the Co-Composting of Food Waste Digestate and Garden Waste. J. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šubová, E.; Sasáková, N.; Zigo, F.; Mindžáková, I.; Vargová, M.; Kachnič, J.; Laktičová, K.V. Amendment of Livestock Manure with Natural Zeolite-Clinoptilolite and Its Effect on Decomposition Processes during Composting. J. Agric. 2021, 11, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.H.; Yang, X.P.; Mao, J.; Wang, Z.F.; Xie, Y.Q.; Zhou, L.Y. Effects of Exogenous Microbial Agents on Microbial Community and Maturation Effect During Cotton Straw Composting. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2024, 40, 1376–1384. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Y.M.; Awasthi, M.K.; Wu, H.H.; Yang, J.F.; Li, Z.L.; Ni, X.H.; Zhang, J.T.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Li, H.K. Biochar regulates bacterial-fungal diversity and associated enzymatic activity during sheep manure composting. J. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 346, 126647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.N.; Zhang, H.Y.; Zheng, L. Influence of Organic Amendments Based on Garden Waste for Microbial Community Growth in Coastal Saline Soil. J. Sustain. 2023, 15, 5038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.J.; Wang, B.; Jiang, X.Y.; Zeng, W.M.; Yu, R.L.; Wu, X.Y.; Shen, L.; Wu, X.L.; Li, J.K.; Liu, Y.K. Behavior and Biochemical Mechanism of High Iron Attapulgite Dosages Affecting Sewage Sludge Composting. J. Sustain. 2023, 15, 12527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargougui, L.; Guergueb, Z.; Chaieb, M.; Mekki, A. Co-composting of Olive Industry Wastes with Poultry Manure and Evaluation of the Obtained Compost Maturity. J. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 6235–6247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.Q.; Jiang, Z.W.; Li, M.Q.; Li, Q.L. A compost-derived thermophilic microbial consortium enhances the humification process and alters the microbial diversity during composting. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 243, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.L.; Geng, G.; Wu, X.M.; Ye, M.F.; Lin, D.Y. Effects of Different Carbon-to-Nitrogen Ratios on the Composting of Spirulina Algal Sludge and Pig Manure Residue. J. Fujian Agric. Sci. Technol. 2022, 53, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, J.J.; Li, Y.M.; Chang, R.X.; Wang, J.; Peng, L.H. Nitrogen Transformation and Loss During Co-composting of Kitchen and Garden Wastes. J. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 37, 192–197. [Google Scholar]
- Soudejani, H.T.; Kazemian, H.; Inglezakis, V.J.; Zorpas, A.A. Application of zeolites in organic waste composting: A review. J. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 22, 101396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, K.; Gang, S.; Xu, W.; Wei, Q.; Fangyi, P.; Hongzhi, L.; Wenxiang, P.; Jingping, G. Aerobic composting with sauerkraut fermentation waste water: Increasing the stability and complexity of bacterial community and changing bacterial community assembly processes. J. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 376, 128883. [Google Scholar]
- Hemati, A.; Aliasgharzad, N.; Khakvar, R.; Khoshmanzar, E.; Asgari Lajayer, B.; van Hullebusch, E.D. Role of lignin and thermophilic lignocellulolytic bacteria in the evolution of humification indices and enzymatic activities during compost production. J. Waste Manag. 2021, 119, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Fan, B.W.; Zhao, L.Q.; Zhao, C.J.; Yang, F.J. Biochar promotes compost humification by regulating bacterial and fungal communities. J. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1470930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, J.; Zhao, Z.H.; Zhou, K.Y.; Zhan, X.M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, N.; Han, X.R.; Li, X. Soil Organic Carbon and Humus Characteristics: Response and Evolution to Long-Term Direct/Carbonized Straw Return to Field. J. Agron. 2024, 14, 2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.Q.; Zou, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, J.X. Biochar improves compost humification, maturity and mitigates nitrogen loss during the vermicomposting of cattle manure-maize straw. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maffia, A.; Marra, F.; Canino, F.; Battaglia, S.; Mallamaci, C.; Oliva, M.; Muscolo, A. Humic Substances from Waste-Based Fertilizers for Improved Soil Fertility. J. Agron. 2024, 14, 2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.T.; Lee, C.H.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Chen, T.C.; Jien, S.H. Using Fluorescence Spectroscopy to Assess Compost Maturity Degree During Composting. J. Agron. 2023, 13, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jiao, M.N.; Zhan, X.Y.; Hu, C.H.; Zhang, Z.Q. Humification and fungal community succession during pig manure composting: Membrane covering and mature compost addition. J. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 393, 130030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Wang, Y.Y.; Li, L.; Ma, L.T.; Deng, Y.Q.; Xu, Z. Adjusting pH of the Secondary Composting Materials to Further Enhance the Lignocellulose Degradation and Promote the Humification Process. J. Sustain. 2023, 15, 9032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Bi, Z.T.; Zhang, Y.C.; Wu, H.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, H.Q. Impact of wine grape pomace on humification performance and microbial dynamics during pig manure composting. J. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 358, 127380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.C.; Yang, H.K.; Wang, B.; Chen, C.; Zou, X.S.; Cheng, T.; Li, J. Aerobic co-composting of mature compost with cattle manure: Organic matter conversion and microbial community characterization. J. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 382, 129187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biyada, S.; Merzouki, M.; Dėmčėnko, T.; Vasiliauskienė, D.; Urbonavičius, J.; Marčiulaitienė, E.; Vasarevičius, S.; Benlemlih, M. Evolution of Microbial Composition and Enzymatic Activities during the Composting of Textile Waste. J. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, D.Z.; Yu, J.X.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, H.H.; Sun, X.J.; Lu, Z. Spectroscopic Analysis of Fulvic Acid in Composting of Biological Leaching Sludge with Different Amendments. J. Environ. Eng. World 2023, 41, 119–128. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Z.B.; Xie, Y.P.; Cao, C.C.; Xu, J.T. Spectroscopic Characterization of Humic Substances in Composting with Different Ratios of Corn Biochar. J. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2023, 23, 11459–11475. [Google Scholar]
- Nevase, D.; Rathod, J.; Phatake, Y. Waste to Compost: Application of Indigenous Microbes for Conversion of Vegetable Waste into Compost. J. Biol. Bull. 2024, 51, S66–S74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa-Bustos, A.; Berti, F.; Salas-Sanjuán, M.d.C.; Segura-Pérez, M.L. Characterization of Mixtures of Rugulopteryx okamurae Compost and Plant Residues to Determine the Most Effective Composition as a Substrate and Source of Nutrients. J. Hortic. 2024, 10, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parzych, A.E. Urban Leaf Litters as a Potential Compost Component. J. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 23, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.H.; Huang, Y.M.; Chen, M.L.; Qi, X.P.; Hou, H.Y. Comprehensive evaluation of spent mushroom substrate-chicken manure co-composting by garden waste improvement: Physicochemical properties, humification process, and the spectral characteristics of dissolved organic matter. J. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 8987–8997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.F.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.Z.; Yang, R.; Zhang, D.D.; Zhou, W.L.; Qi, Z.Y.; Lin, W. Nitrogen transformation and its microbial mechanism under co-composting of biogas slurry with garden waste. J. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao = J. Appl. Ecol. 2023, 34, 1745–1753. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Z.P.; Li, M.X.; Song, L.Y.; Wang, C.; Yang, S.; Yan, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.Q. Study on nitrogen-retaining microbial agent to reduce nitrogen loss during chicken manure composting and nitrogen transformation mechanism. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 285, 124813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.Z.; Li, X.X.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, S.P.; Sun, Z.Y.; Tang, Y.Q. Dynamic change of bacterial community during dairy manure composting process revealed by high-throughput sequencing and advanced bioinformatics tools. J. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 306, 123091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.Y.; Yang, X.P.; Wang, X.W.; Feng, L.; Wang, Z.F.; Dai, J.P.; Zhang, H.T.; Xie, Y.Q. Effects of bacterial inoculation on lignocellulose degradation and microbial properties during cow dung composting. J. Bioeng. 2023, 14, 2185945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loakasikarn, T.; Kubota, Y.; Koyama, M.; Nakasaki, K. Effect of seeding materials on organic matter degradation and microbial community succession during model organic waste composting. J. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 37, 102182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.R.; Zhang, Y.L.; Cui, R.Q.; Ren, L.H.; Zhang, M.L.; Wang, Y.J. Effects of Two Different Proportions of Microbial Formulations on Microbial Communities in Kitchen Waste Composting. J. Microorg. 2023, 11, 2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langille, M.G.I.; Zaneveld, J.; Caporaso, J.G.; McDonald, D.; Knights, D.; Reyes, J.A.; Clemente, J.C.; Burkepile, D.E.; Vega Thurber, R.L.; Knight, R.; et al. Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. J. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Lara, A.; Ros, M.; Cuartero, J.; Bustamante, M.Á.; Moral, R.; Andreu-Rodríguez, F.J.; Fernández, J.A.; Egea-Gilabert, C.; Pascual, J.A. Bacterial and fungal community dynamics during different stages of agro-industrial waste composting and its relationship with compost suppressiveness. J. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.H.; Zhao, X.; Dong, X.Y.; Zheng, J.M.; Jiang, L.W. Effect of sludge and garden waste composting rates on heavy metal content and microbial activity in plantation soil. J. Zhejiang AF Univ. 2021, 38, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Ozer, H.; Ozdemir, N.; Ates, A.; Koklu, R.; Ozturk Erdem, S.; Ozdemir, S. Circular Utilization of Coffee Grounds as a Bio-Nutrient through Microbial Transformation for Leafy Vegetables. J. Life 2024, 14, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.Y.; Liu, Z.Z.; Wang, K.Y.; Zhao, J.F.; Fang, J.; Liu, G.; Yao, H.; Pan, J.T. Comparison analysis of microbial agent and different compost material on microbial community and nitrogen transformation genes dynamic changes during pig manure compost. J. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 395, 130359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.Y.; Liu, S.Y.; Kang, Z.Y.; Zhu, Y.W.; Zhang, C.B.; Xiang, E.; Lin, Z.; Liu, W.Z. Effects of atmosphere and stepwise pyrolysis on the pyrolysis behavior, product characteristics, and N/S migration mechanism of vancomycin fermentation residue. J. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 498, 155012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, B.; Xue, Y.; Xiao, K.K.; Yang, J.K.; Chen, H.B.; Guan, W.Y.; Cheg, Q.X. Study on proteinaceous components conversion and microbial community during composting of food waste added by straw bulking agents. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2022, 50, 83–96. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuo, T.Y.; He, L.X.; Chai, B.B.; Zhou, S.L.; Wan, Q.; Lei, X.H.; Zhou, Z.M.; Chen, B. Micro-pressure promotes endogenous phosphorus release in a deep reservoir by favouring microbial phosphate mineralisation and solubilisation coupled with sulphate reduction. J. Water Res. 2023, 245, 120647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.H.; Chai, B.B.; Zhuo, T.Y.; Tang, Q.F.; Gao, X.; Wang, J.M.; He, L.X.; Lei, X.H.; Chen, B. Hydrostatic pressure drives microbe-mediated biodegradation of microplastics in surface sediments of deep reservoirs: Novel findings from hydrostatic pressure simulation experiments. J. Water Res. 2023, 242, 120185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.W.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, C.J.; Jim, C.Y.; Johnson, V.C.; Tan, M.L. Determining the main contributing factors to nutrient concentration in rivers in arid northwest China using partial least squares structural equation modeling. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 343, 118249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M.; Smith, D.; Reams, R.; Hair, J.F. Partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM): A useful tool for family business researchers. J. Fam. Bus. Strategy 2014, 5, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X.J.; Yao, Q.; Zhu, H.H. Both Soil Bacteria and Soil Chemical Property Affected the Micropredator Myxobacterial Community: Evidence from Natural Forest Soil and Greenhouse Rhizosphere Soil. J. Microorg. 2020, 8, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Test Treatment | Organic Matter (g/kg) | Total Nitrogen (g/kg) | Compost C/N | Moisture Content (%) | Raw Material (kg) | Urea (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WB | 748.06 | 29.12 | 30/1 | 65–70% | 10 | 140 |
| PS | 681.38 | 15.64 | 30/1 | 65–70% | 10 | 130 |
| PL | 609.17 | 4.01 | 30/1 | 65–70% | 10 | 110 |
| Sample Collection | WB | PS | PL |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Stage | 2d (9.26) | 2d (9.26) | 2d (9.26) |
| Peak Thermophilic Stage | 8d (10.2) | 4d (9.28) | 6d (9.30) |
| Thermophilic Stage | 14d (10.10) | 8d (10.2) | 10d (10.4) |
| Cooling Stage | 40d (11.3) | 32d (10.26) | 35d (10.29) |
| Curing Stage | 49d (11.12) | 49d (11.12) | 49d (11.12) |
| Test Grouping | Sampling Time | Sampling Day | Number of Samples |
|---|---|---|---|
| WB | Initial period | 26 September 2023 | WBA |
| Thermophilic period | 2 October 2023 | WBB | |
| Curing period | 12 November 2023 | WBC | |
| PS | Initial period | 26 September 2023 | PSA |
| Thermophilic period | 28 September 2023 | PSB | |
| Curing period | 12 November 2023 | PSC | |
| PL | Initial period | 26 September 2023 | PLA |
| Thermophilic period | 30 September 2023 | PLB | |
| Curing period | 12 November 2023 | PLC |
| Samples | Germination Index (%) | Pb (mg/kg) | Cd (mg/kg) | Cr (mg/kg) | As (mg/kg) | Hg (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WB | 87.56 a | 18.2 ± 2.3 a | 1.8 ± 0.3 a | 45.7 ± 5.2 a | 4.2 ± 0.6 a | 0.7 ± 0.1 ab |
| PS | 94.79 b | 9.5 ± 1.1 b | 0.6 ± 0.1 b | 28.3 ± 3.8 b | 1.9 ± 0.2 b | 0.2 ± 0.05 b |
| PL | 80.32 c | 24.6 ± 3.0 c | 2.5 ± 0.4 c | 62.4 ± 6.5 c | 6.8 ± 0.9 c | 1.1 ± 0.2 a |
| Samples | ACE Index | Chao1 Index | Simpson Index | Shannon Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WBA | 636.65 ± 9.38 Aa | 636.50 ± 7.23 Aa | 0.94 ± 0.05 Aa | 5.36 ± 0.12 Aa |
| WBB | 808.35 ± 13.75 Ba | 810.00 ± 10.04 Ba | 0.95 ± 0.07 Aa | 6.15 ± 0.13 Ba |
| WBC | 773.51 ± 15.99 Ca | 774.33 ± 6.33 Ca | 0.93 ± 0.09 Aa | 5.47 ± 0.23 Aa |
| PSA | 925.34 ± 10.88 Ab | 925.66 ± 5.67 Ab | 0.95 ± 0.07 Aa | 5.63 ± 0.03 Aa |
| PSB | 825.15 ± 6.42 Ba | 825.00 ± 8.82 Ba | 0.94 ± 0.06 Aa | 5.83 ± 0.03 Aa |
| PSC | 1273.84 ± 11.65 Cb | 1274.20 ± 9.57 Cb | 0.97 ± 0.07 Ba | 7.95 ± 0.33 Bb |
| PLA | 300.19 ± 15.13 Ac | 300.00 ± 15.07 Aa | 0.97 ± 0.03 Aa | 6.55 ± 0.18 Ab |
| PLB | 299.60 ± 15.58 Ab | 300.50 ± 9.27 Ab | 0.87 ± 0.05 Bb | 5.18 ± 0.35 Ba |
| PLC | 562.00 ± 12.82 Bc | 562.00 ± 7.06 Bc | 0.97 ± 0.07 Aa | 6.61 ± 0.43 Ac |
| Samples | ACE Index | Chao1 Index | Simpson Index | Shannon Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WBA | 62.55 ± 6.38 Aa | 62.66 ± 13.67 Aa | 0.92 ± 0.04 Aa | 4.74 ± 0.27 Aa |
| WBB | 69.06 ± 10.67 Aa | 70.75 ± 15.77 Aa | 0.82 ± 0.04 Aa | 3.93 ± 0.31 Aa |
| WBC | 63.93 ± 10.44 Aa | 66.25 ± 10.82 Aa | 0.22 ± 0.04 Ba | 1.04 ± 0.35 Ba |
| PSA | 117.62 ± 8.74 Ab | 118.14 ± 17.29 Ab | 0.76 ± 0.06 Ab | 3.26 ± 0.84 Ab |
| PSB | 67.28 ± 7.28 Ba | 69.20 ± 11.35 Ba | 0.50 ± 0.04 Bb | 2.19 ± 0.65 Bb |
| PSC | 63.40 ± 12.28 Ba | 73.00 ± 9.15 Ba | 0.86 ± 0.08 Ab | 3.94 ± 0.26 Ab |
| PLA | 309.56 ± 13.16 Ac | 309.50 ± 16.22 Ac | 0.95 ± 0.05 Aa | 5.81 ± 0.51 Ac |
| PLB | 198.16 ± 9.88 Bb | 203.11 ± 9.11 Bb | 0.54 ± 0.02 Bb | 2.24 ± 0.19 Bb |
| PLC | 225.10 ± 11.13 Bb | 225.27 ± 14.27 Bb | 0.50 ± 0.07 Bc | 1.88 ± 0.47 Ba |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, Y.; Wu, P.; Qu, Y.; Guo, X.; Zheng, J.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Q. The Evolution of Nutrient and Microbial Composition and Maturity During the Composting of Different Plant-Derived Wastes. Biology 2025, 14, 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14030268
Xie Y, Wu P, Qu Y, Guo X, Zheng J, Xing Y, Zhang X, Liu Q. The Evolution of Nutrient and Microbial Composition and Maturity During the Composting of Different Plant-Derived Wastes. Biology. 2025; 14(3):268. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14030268
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Yuxin, Pengbing Wu, Ying Qu, Xingchi Guo, Junyan Zheng, Yuhe Xing, Xu Zhang, and Qian Liu. 2025. "The Evolution of Nutrient and Microbial Composition and Maturity During the Composting of Different Plant-Derived Wastes" Biology 14, no. 3: 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14030268
APA StyleXie, Y., Wu, P., Qu, Y., Guo, X., Zheng, J., Xing, Y., Zhang, X., & Liu, Q. (2025). The Evolution of Nutrient and Microbial Composition and Maturity During the Composting of Different Plant-Derived Wastes. Biology, 14(3), 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14030268





