Sequence-Only Prediction of Super-Enhancers in Human Cell Lines Using Transformer Models
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Software Implementation
2.2. Datasets
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. The Model Used for SE Prediction
2.3.2. Evaluation Metrics
2.3.3. Interpretation of the Results
3. Results and Discussion
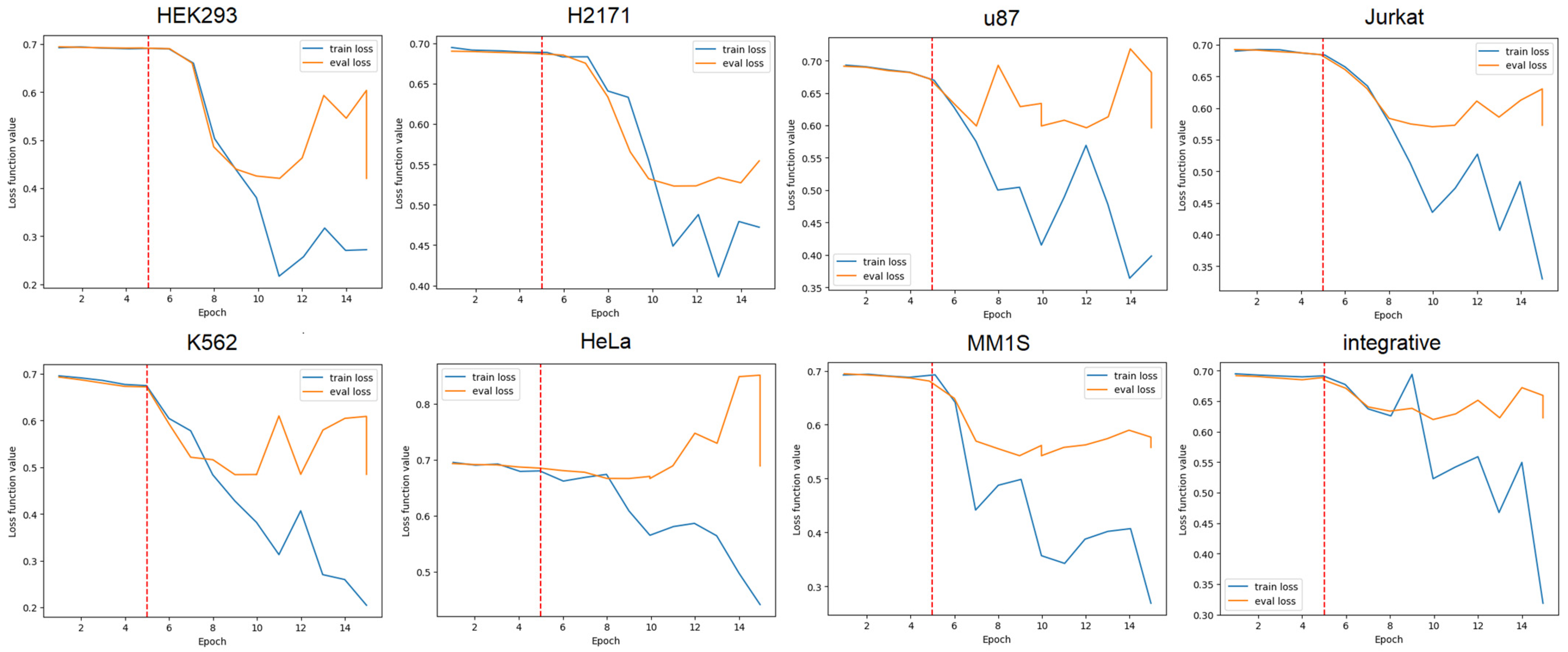
3.1. GENA-LM Fine-Tuning for Solving the Problem of Predicting Super Enhancers
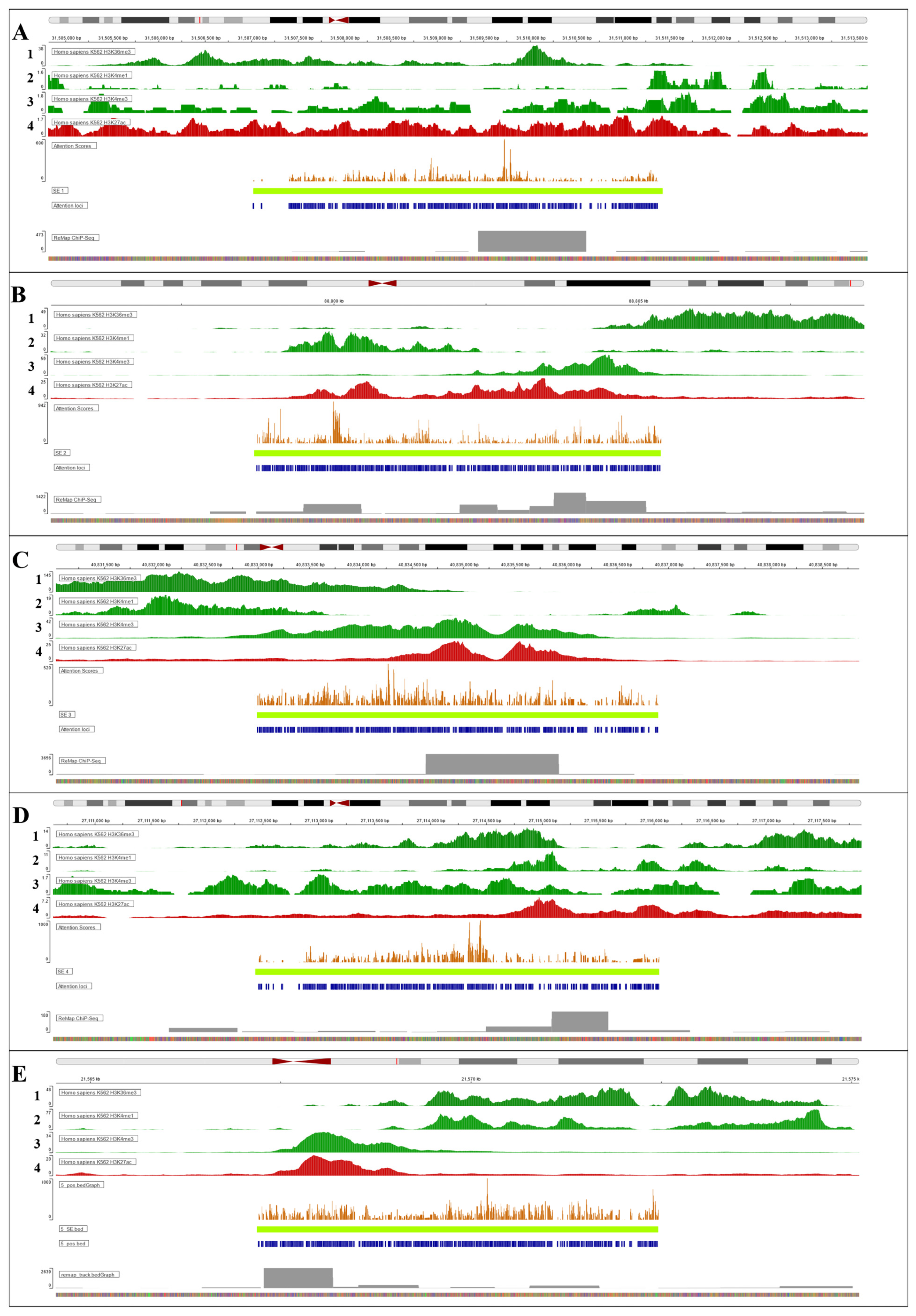
3.2. Interpretation of Fine-Tuned Model
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Whyte, W.A.; Orlando, D.A.; Hnisz, D.; Abraham, B.J.; Lin, C.Y.; Kagey, M.H.; Rahl, P.B.; Lee, T.I.; Young, R.A. Master Transcription Factors and Mediator Establish Super-Enhancers at Key Cell Identity Genes. Cell 2013, 153, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, S.C.J.; Stitzel, M.L.; Taylor, D.L.; Orozco, J.M.; Erdos, M.R.; Akiyama, J.A.; Van Bueren, K.L.; Chines, P.S.; Narisu, N.; NISC Comparative Sequencing Program; et al. Chromatin Stretch Enhancer States Drive Cell-Specific Gene Regulation and Harbor Human Disease Risk Variants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17921–17926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hnisz, D.; Abraham, B.J.; Lee, T.I.; Lau, A.; Saint-André, V.; Sigova, A.A.; Hoke, H.A.; Young, R.A. Super-Enhancers in the Control of Cell Identity and Disease. Cell 2013, 155, 934–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovén, J.; Hoke, H.A.; Lin, C.Y.; Lau, A.; Orlando, D.A.; Vakoc, C.R.; Bradner, J.E.; Lee, T.I.; Young, R.A. Selective Inhibition of Tumor Oncogenes by Disruption of Super-Enhancers. Cell 2013, 153, 320–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Zhang, X. Integrative Modeling Reveals Key Chromatin and Sequence Signatures Predicting Super-Enhancers. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekaran, H.; Ramalakshmi, K.; Rex Macedo Arokiaraj, A.; Deepa Kanmani, S.; Venkatesan, C.; Suresh Gnana Dhas, C. Analysis of DNA Sequence Classification Using CNN and Hybrid Models. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2021, 2021, 1835056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Liu, F.; Ren, C.; Ouyang, Z.; Xie, Z.; Bo, X.; Shu, W. BiRen: Predicting Enhancers with a Deep-Learning-Based Model Using the DNA Sequence Alone. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 1930–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, H.; Davuluri, R.V. DNABERT: Pre-Trained Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers Model for DNA-Language in Genome. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 2112–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, V.; Kuratov, Y.; Petrov, M.; Shmelev, A.; Shepelin, D.; Chekanov, N.; Kardymon, O.; Burtsev, M. GENA-LM: A Family of Open-Source Foundational DNA Language Models for Long Sequences (version 1). bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, A.; Lim, S.; Kim, S. Enhancer Prediction with Histone Modification Marks Using a Hybrid Neural Network Model. Methods 2019, 166, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Ding, P.; Yu, Y.; Luo, L. SENet: A Deep Learning Framework for Discriminating Super- and Typical Enhancers by Sequence Information. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2023, 105, 107905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaheer, M.; Guruganesh, G.; Dubey, A.; Ainslie, J.; Alberti, C.; Ontanon, S.; Pham, P.; Ravula, A.; Wang, Q.; Yang, L.; et al. Big Bird: Transformers for Longer Sequences. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 17283–17297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Zhang, X. dbSUPER: A Database of Super-Enhancers in Mouse and Human Genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D164–D171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Song, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Feng, C.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, J.; Wang, F.; Qian, F.; et al. SEdb 2.0: A Comprehensive Super-Enhancer Database of Human and Mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D280–D290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Qian, J. EnhancerAtlas 2.0: An Updated Resource with Enhancer Annotation in 586 Tissue/Cell Types across Nine Species. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D58–D64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Johnson, J.; Grant, C.E.; Noble, W.S. The MEME Suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W39–W49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gage, P. A New Algorithm for Data Compression. C Users J. 1994, 12, 23–38. [Google Scholar]
- Sennrich, R.; Haddow, B.; Birch, A. Neural Machine Translation of Rare Words with Subword Units. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1508.07909. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.; Donegan, S.; Shah, M.; Chi, Y. A Lightweight Transformer for Faster and Robust EBSD Data Collection. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 21253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, G.; Roweis, S. Stochastic Neighbor Embedding. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2002; pp. 857–864. [Google Scholar]
- Sidak, D.; Schwarzerová, J.; Weckwerth, W.; Waldherr, S. Interpretable machine learning methods for predictions in systems biology from omics data. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 926623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwegler, M.; Müller, C.; Reiterer, A. Integrated Gradients for Feature Assessment in Point Cloud-Based Data Sets. Algorithms 2023, 16, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundararajan, M.; Taly, A.; Yan, Q. Axiomatic Attribution for Deep Networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.01365. [Google Scholar]
- Kent, W.J.; Sugnet, C.W.; Furey, T.S.; Roskin, K.M.; Pringle, T.H.; Zahler, A.M.; Haussler, A.D. The Human Genome Browser at UCSC. Genome Res. 2002, 12, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammal, F.; de Langen, P.; Bergon, A.; Lopez, F.; Ballester, B. ReMap 2022: A Database of Human, Mouse, Drosophila and Arabidopsis Regulatory Regions from an Integrative Analysis of DNA-Binding Sequencing Experiments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D316–D325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Ohta, T.; Oki, S. ChIP-Atlas 3.0: A Data-Mining Suite to Explore Chromosome Architecture Together with Large-Scale Regulome Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, W45–W53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.-Y.; Gong, X.-J.; Li, H.-M.; Du, P.-F. DeepSE: Detecting Super-Enhancers among Typical Enhancers Using Only Sequence Feature Embeddings. Genomics 2021, 113, 4052–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benayoun, B.A.; Pollina, E.A.; Ucar, D.; Mahmoudi, S.; Karra, K.; Wong, E.D.; Devarajan, K.; Daugherty, A.C.; Kundaje, A.B.; Mancini, E.; et al. H3K4me3 Breadth Is Linked to Cell Identity and Transcriptional Consistency. Cell 2014, 158, 673–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Fan, Z.; Shliaha, P.V.; Miele, M.; Hendrickson, R.C.; Jiang, X.; Helin, K. H3K4me3 Regulates RNA Polymerase II Promoter-Proximal Pause-Release. Nature 2023, 615, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, N.; Chen, P.B.; Hu, R.; Ye, Z.; Sasaki, H.; Ren, B. H3K4me1 Facilitates Promoter-Enhancer Interactions and Gene Activation during Embryonic Stem Cell Differentiation. Mol. Cell 2024, 84, 1742–1752.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Kim, Y.W.; Kang, J.; Kim, A. Histone H3K4me1 and H3K27ac Play Roles in Nucleosome Eviction and eRNA Transcription, Respectively, at Enhancers. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beacon, T.H.; Delcuve, G.P.; López, C.; Nardocci, G.; Kovalchuk, I.; van Wijnen, A.J.; Davie, J.R. The Dynamic Broad Epigenetic (H3K4me3, H3K27ac) Domain as a Mark of Essential Genes. Clin. Epigenet. 2021, 13, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Postnikov, Y.; Lobanov, A.; Furusawa, T.; Deng, T.; Bustin, M. H3K27ac Nucleosomes Facilitate HMGN Localization at Regulatory Sites to Modulate Chromatin Binding of Transcription Factors. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, U.T.F.; Tan, B.K.Y.; Poh, J.J.X.; Chen, E.S. Structural and Functional Specificity of H3K36 Methylation. Epigenetics Chromatin 2022, 15, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terashima, M.; Tange, S.; Ishimura, A.; Suzuki, T. MEG3 Long Noncoding RNA Contributes to the Epigenetic Regulation of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Lung Cancer Cell Lines. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 82–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cawley, N.X.; Huang, J.; Peng Loh, Y.; Dhanvantari, S. Prohormone Convertases. In Reference Module in Biomedical Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; ISBN 978-0-12-801238-3. [Google Scholar]
- Cirillo, E.; Giardino, G.; Gallo, V.; Galasso, G.; Romano, R.; D’Assante, R.; Scalia, G.; Del Vecchio, L.; Nitsch, L.; Genesio, R.; et al. DiGeorge-like Syndrome in a Child with a 3p12.3 Deletion Involving MIR4273 Gene Born to a Mother with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2017, 173, 1913–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheu, J.J.-C.; Lee, C.-H.; Ko, J.-Y.; Tsao, G.S.W.; Wu, C.-C.; Fang, C.-Y.; Tsai, F.-J.; Hua, C.-H.; Chen, C.-L.; Chen, J.-Y. Chromosome 3p12.3-P14.2 and 3q26.2-Q26.32 Are Genomic Markers for Prognosis of Advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2009, 18, 2709–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, W.; Geng, S.; Fang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Hu, H.; Liang, Z.; Yan, Z. Slit2 and Robo1 Expression as Biomarkers for Assessing Prognosis in Brain Glioma Patients. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 25, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasperoni, J.G.; Fuller, J.N.; Darido, C.; Wilanowski, T.; Dworkin, S. Grainyhead-like (Grhl) Target Genes in Development and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayama, K.; Mitsuhashi, S.; Shin, J.-Y.; Tanaka, R.; Fujii, T.; Tsuburaya, R.; Mukaida, S.; Noguchi, S.; Nonaka, I.; Nishino, I. Japanese Multiple Epidermal Growth Factor 10 (MEGF10) Myopathy with Novel Mutations: A Phenotype–Genotype Correlation. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2016, 26, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlet, J.; Tomari, A.; Dallosso, A.R.; Szemes, M.; Kaselova, M.; Curry, T.J.; Almutairi, B.; Etchevers, H.C.; McConville, C.; Malik, K.T.A.; et al. Genome-wide DNA Methylation Analysis Identifies MEGF10 as a Novel Epigenetically Repressed Candidate Tumor Suppressor Gene in Neuroblastoma. Mol. Carcinog. 2017, 56, 1290–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanović, O.; Fernandez-Miñán, A.; Tena, J.J.; De La Calle-Mustienes, E.; Hidalgo, C.; Van Kruysbergen, I.; Van Heeringen, S.J.; Veenstra, G.J.C.; Gómez-Skarmeta, J.L. Dynamics of Enhancer Chromatin Signatures Mark the Transition from Pluripotency to Cell Specification during Embryogenesis. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 2043–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; He, C.; Guo, X.; Fang, Y.; Lai, Q.; Wang, X.; Pan, X.; Li, H.; Qin, K.; Li, A.; et al. DDX39B Contributes to the Proliferation of Colorectal Cancer through Direct Binding to CDK6/CCND1. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schott, G.; Garcia-Blanco, M.A. MHC Class III RNA Binding Proteins and Immunity. RNA Biol. 2021, 18, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagriantsev, S.N.; Gracheva, E.O.; Gallagher, P.G. Piezo Proteins: Regulators of Mechanosensation and Other Cellular Processes. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 31673–31681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swiatlowska, P.; Tipping, W.; Marhuenda, E.; Severi, P.; Fomin, V.; Yang, Z.; Xiao, Q.; Graham, D.; Shanahan, C.; Iskratsch, T. Hypertensive Pressure Mechanosensing Alone Triggers Lipid Droplet Accumulation and Transdifferentiation of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells to Foam Cells. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2308686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lv, Y.; Hao, J.; Sun, H.; Gao, N.; Zhang, C.; Lu, R.; Wang, S.; Yin, L.; Pu, Y.; et al. Role of microRNA-4516 Involved Autophagy Associated with Exposure to Fine Particulate Matter. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 45385–45397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Xing, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Li, M.; Li, X.; Wang, D.; Dong, Z. The Value of H2BC12 for Predicting Poor Survival Outcomes in Patients with WHO Grade II and III Gliomas. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 816939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Sun, Z.; Ji, F. Comprehensive Analysis Identifies Histone 2A Ubiquitination as a Marker for Aging and Pan-Cancer Prognosis. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar]
- West, M.B.; Wickham, S.; Parks, E.E.; Sherry, D.M.; Hanigan, M.H. Human GGT2 Does Not Autocleave into a Functional Enzyme: A Cautionary Tale for Interpretation of Microarray Data on Redox Signaling. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 1877–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravchuk, E.V.; Ashniev, G.A.; Gladkova, M.G.; Orlov, A.V.; Vasileva, A.V.; Boldyreva, A.V.; Burenin, A.G.; Skirda, A.M.; Nikitin, P.I.; Orlova, N.N. Experimental Validation and Prediction of Super-Enhancers: Advances and Challenges. Cells 2023, 12, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamamoto, R.; Takasawa, K.; Shinkai, N.; Machino, H.; Kouno, N.; Asada, K.; Komatsu, M.; Kaneko, S. Analysis of Super-Enhancer Using Machine Learning and Its Application to Medical Biology. Brief. Bioinform. 2023, 24, bbad107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasileva, A.V.; Gladkova, M.G.; Ashniev, G.A.; Osintseva, E.D.; Orlov, A.V.; Kravchuk, E.V.; Boldyreva, A.V.; Burenin, A.G.; Nikitin, P.I.; Orlova, N.N. Super-Enhancers and Their Parts: From Prediction Efforts to Pathognomonic Status. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushkarev, A.V.; Orlov, A.V.; Znoyko, S.L.; Bragina, V.A.; Nikitin, P.I. Rapid and Easy-to-Use Method for Accurate Characterization of Target Binding and Kinetics of Magnetic Particle Bioconjugates for Biosensing. Sensors 2021, 21, 2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, A.E.; Pushkarev, A.V.; Orlov, A.V.; Nikitin, M.P.; Nikitin, P.I. Interferometric Detection of Chloramphenicol via Its Immunochemical Recognition at Polymer-Coated Nano-Corrugated Surfaces. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 282, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlov, A.V.; Malkerov, J.A.; Novichikhin, D.O.; Znoyko, S.L.; Nikitin, P.I. Multiplex Label-Free Kinetic Characterization of Antibodies for Rapid Sensitive Cardiac Troponin I Detection Based on Functionalized Magnetic Nanotags. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nekrasov, N.; Yakunina, N.; Pushkarev, A.V.; Orlov, A.V.; Gadjanski, I.; Pesquera, A.; Centeno, A.; Zurutuza, A.; Nikitin, P.I.; Bobrinetskiy, I. Spectral-Phase Interferometry Detection of Ochratoxin a via Aptamer-Functionalized Graphene Coated Glass. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlova, N.N.; Bogatova, O.V.; Orlov, A.V. High-Performance Method for Identification of Super Enhancers from ChIP-Seq Data with Configurable Cloud Virtual Machines. MethodsX 2020, 7, 101165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Cell Line | Number of Sequences | Resources |
|---|---|---|
| HeLa | 3150 | dbSuper, SEdb, Encode |
| HEK293 | 1260 | SEdb, EnhancerAtlas 2.0 |
| H2171 | 872 | dbSuper, SEdb, EnhancerAtlas 2.0 |
| Jurkat | 2374 | dbSuper, SEdb, EnhancerAtlas 2.0 |
| K562 | 4016 | dbSuper, SEdb, EnhancerAtlas 2.0 |
| MM1S | 1729 | dbSuper, SEdb, Encode |
| U87 | 2626 | dbSuper, SEdb, EnhancerAtlas 2.0 |
| Cell Line | Accuracy | F1 | Precision | Recall | ROC AUC | MCC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HeLa | 0.5978 | 0.5973 | 0.5988 | 0.5984 | 0.5978 | 0.1966 |
| HEK293 | 0.8093 | 0.8096 | 0.8098 | 0.8095 | 0.8093 | 0.6180 |
| H2171 | 0.7461 | 0.7478 | 0.7489 | 0.7487 | 0.7461 | 0.4952 |
| Jurkat | 0.7008 | 0.6842 | 0.7352 | 0.6947 | 0.70008 | 0.4317 |
| K562 | 0.7519 | 0.7491 | 0.7569 | 0.7500 | 0.7519 | 0.5075 |
| MM1S | 0.7557 | 0.7575 | 0.7658 | 0.7601 | 0.7557 | 0.5230 |
| U87 | 0.6521 | 0.6522 | 0.6523 | 0.6521 | 0.6514 | 0.3026 |
| Integrative | 0.6944 | 0.6963 | 0.6986 | 0.6980 | 0.6944 | 0.3933 |
| Cell Line | Accuracy | F1 | Precision | Recall | ROC AUC | MCC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HeLa | 0.5698 | 0.5555 | 0.5802 | 0.5698 | 0.5698 | 0.1496 |
| HEK293 | 0.6696 | 0.6800 | 0.6853 | 0.6865 | 0.6696 | 0.3538 |
| H2171 | 0.5752 | 0.5541 | 0.5904 | 0.5721 | 0.5752 | 0.1642 |
| Jurkat | 0.6610 | 0.6612 | 0.6616 | 0.6611 | 0.6610 | 0.3218 |
| K562 | 0.4684 | 0.4559 | 0.4642 | 0.4768 | 0.4684 | −0.0687 |
| MM1S | 0.6062 | 0.5981 | 0.6231 | 0.6127 | 0.6062 | 0.2297 |
| U87 | 0.5698 | 0.5555 | 0.5802 | 0.5698 | 0.5698 | 0.1496 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kravchuk, E.V.; Ashniev, G.A.; Gladkova, M.G.; Orlov, A.V.; Zaitseva, Z.G.; Malkerov, J.A.; Orlova, N.N. Sequence-Only Prediction of Super-Enhancers in Human Cell Lines Using Transformer Models. Biology 2025, 14, 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14020172
Kravchuk EV, Ashniev GA, Gladkova MG, Orlov AV, Zaitseva ZG, Malkerov JA, Orlova NN. Sequence-Only Prediction of Super-Enhancers in Human Cell Lines Using Transformer Models. Biology. 2025; 14(2):172. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14020172
Chicago/Turabian StyleKravchuk, Ekaterina V., German A. Ashniev, Marina G. Gladkova, Alexey V. Orlov, Zoia G. Zaitseva, Juri A. Malkerov, and Natalia N. Orlova. 2025. "Sequence-Only Prediction of Super-Enhancers in Human Cell Lines Using Transformer Models" Biology 14, no. 2: 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14020172
APA StyleKravchuk, E. V., Ashniev, G. A., Gladkova, M. G., Orlov, A. V., Zaitseva, Z. G., Malkerov, J. A., & Orlova, N. N. (2025). Sequence-Only Prediction of Super-Enhancers in Human Cell Lines Using Transformer Models. Biology, 14(2), 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14020172







