Promoter Hypomethylation Unleashes HMGA1 to Orchestrate Immune Evasion and Therapy Resistance Across Cancers
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
2.2. Protein Expression, Cellular Localization and Prognostic Analysis
2.3. Correlation Between HMGA1 Expression and DNA Methylation
2.4. Analysis of Stemness, Tumor Microenvironment, and Immune Infiltration
2.5. Gene Set Enrichment and Drug Sensitivity Analysis
2.6. Evaluation of HMGA1 Expression and Functional Validation in Breast Cancer Cell Lines
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
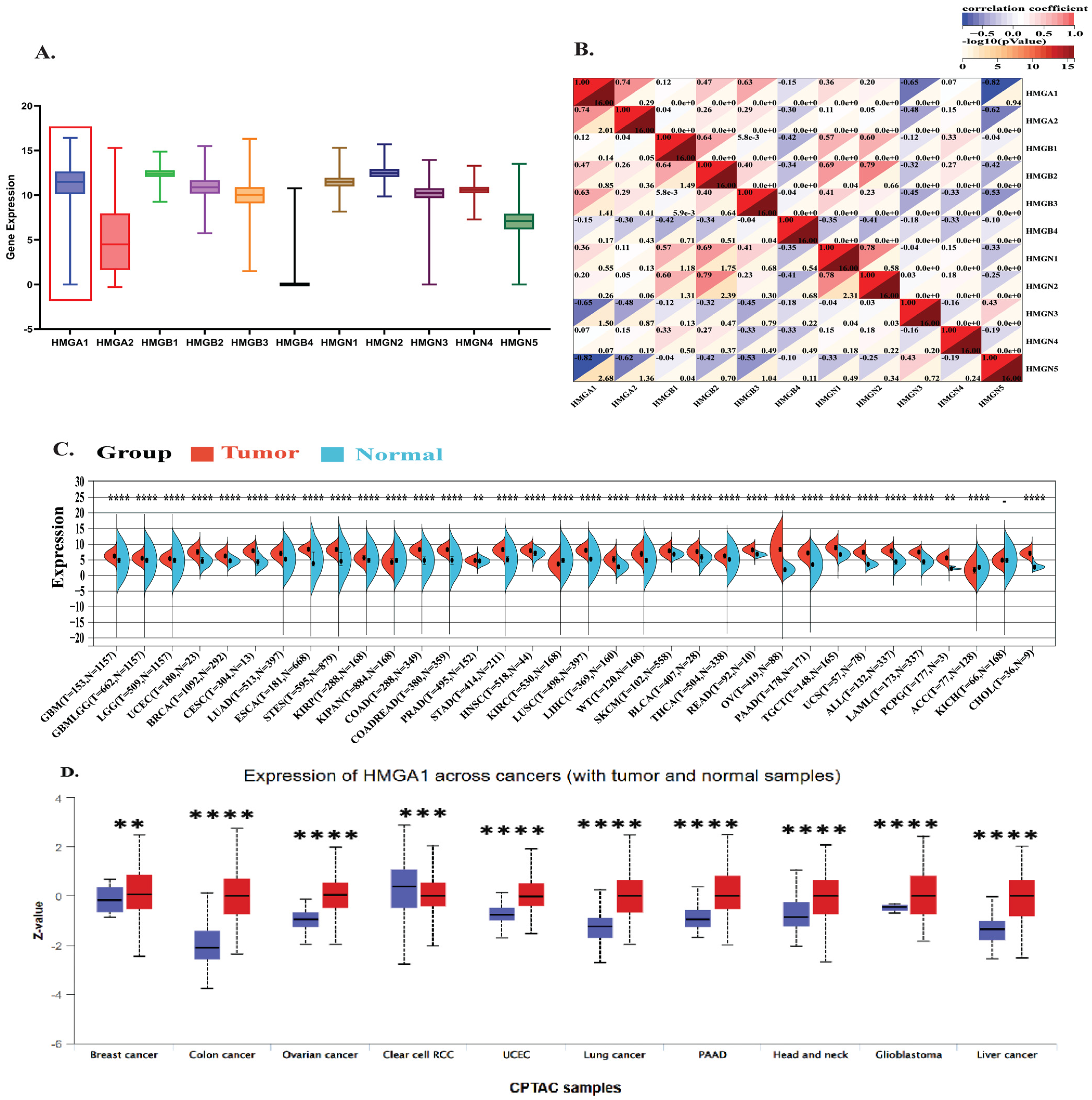
3.1. HMGA1 Exhibits Pan-Cancer Overexpression and Nuclear Localization
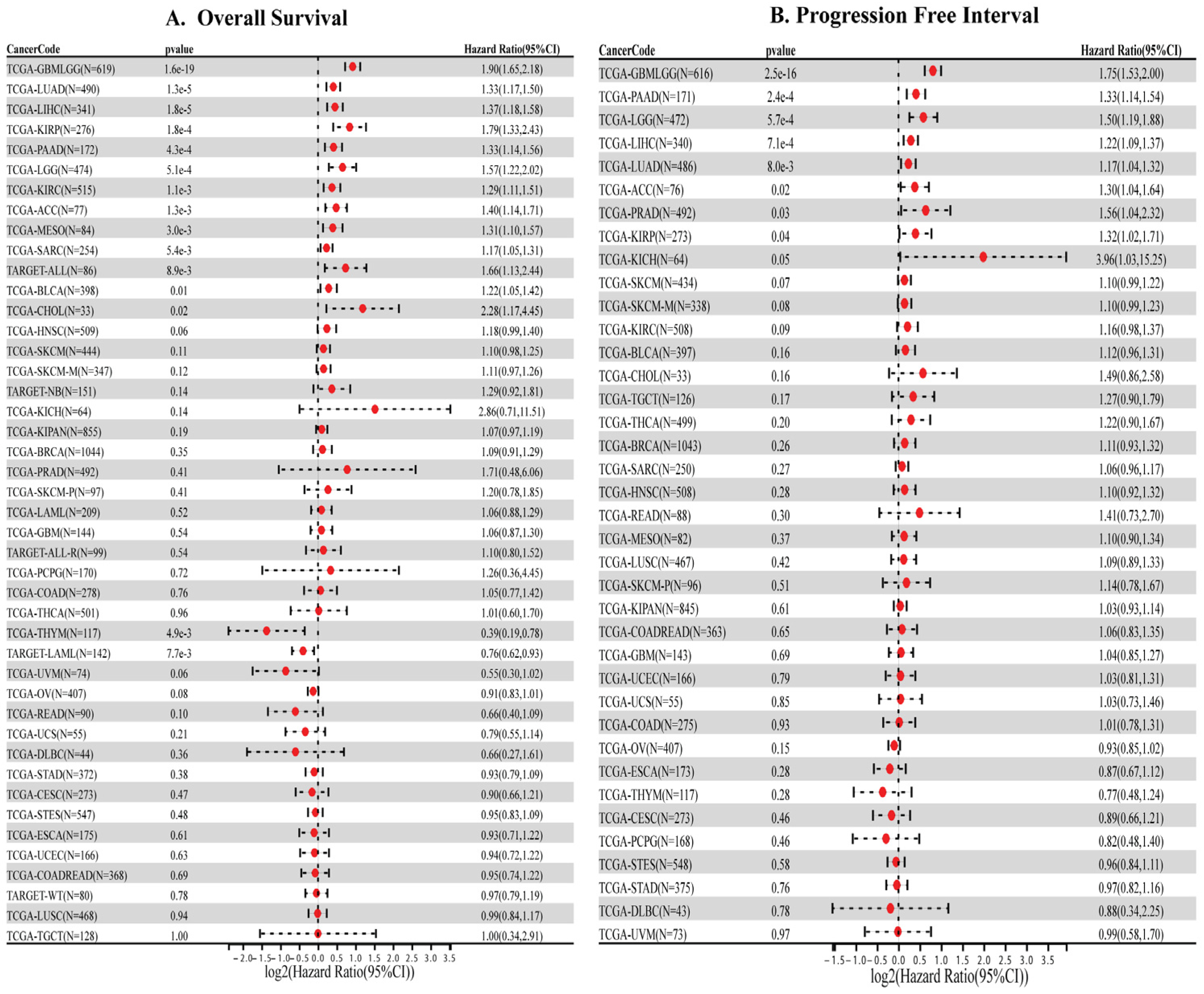
3.2. High HMGA1 Expression Predicts Poor Prognosis
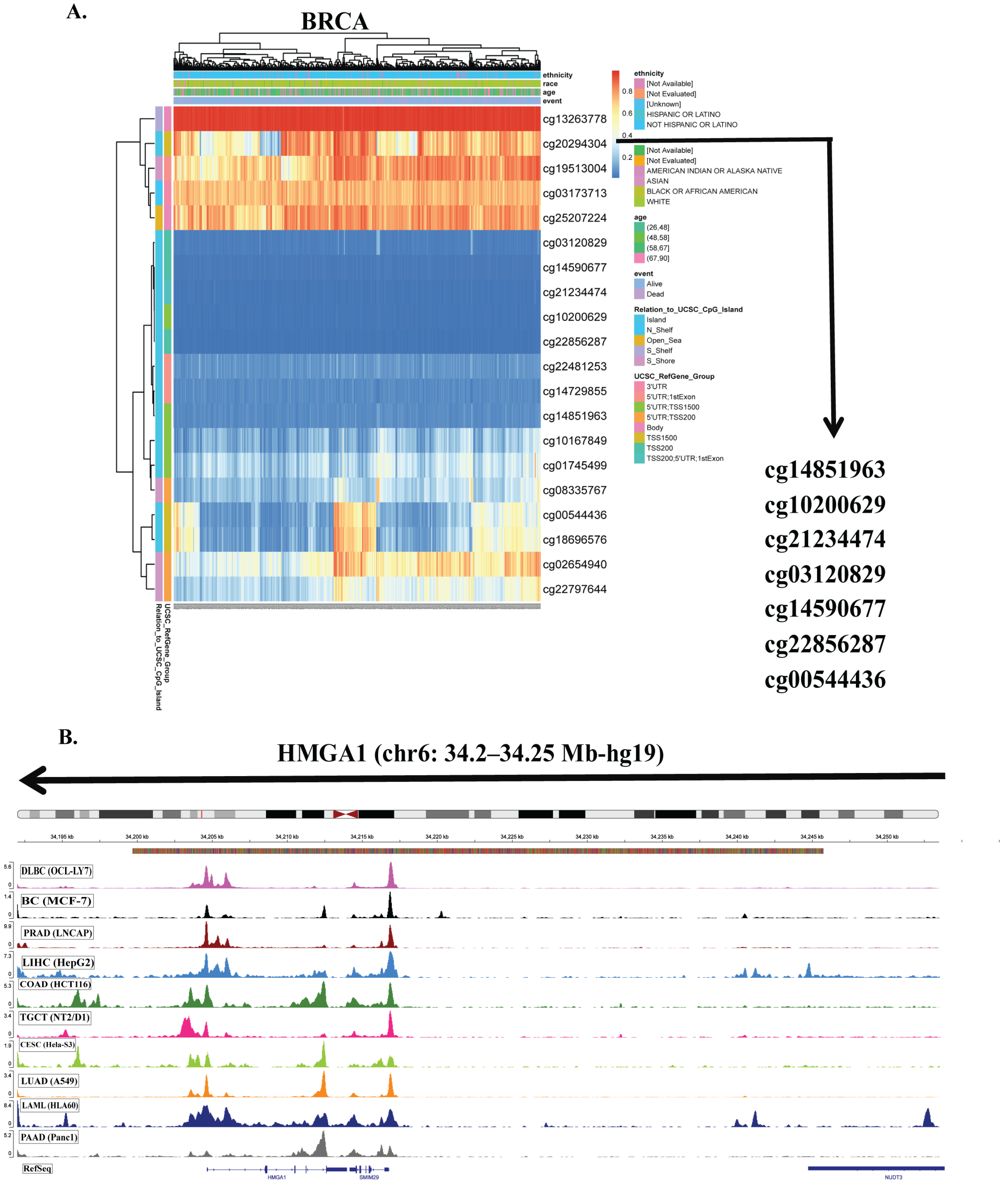
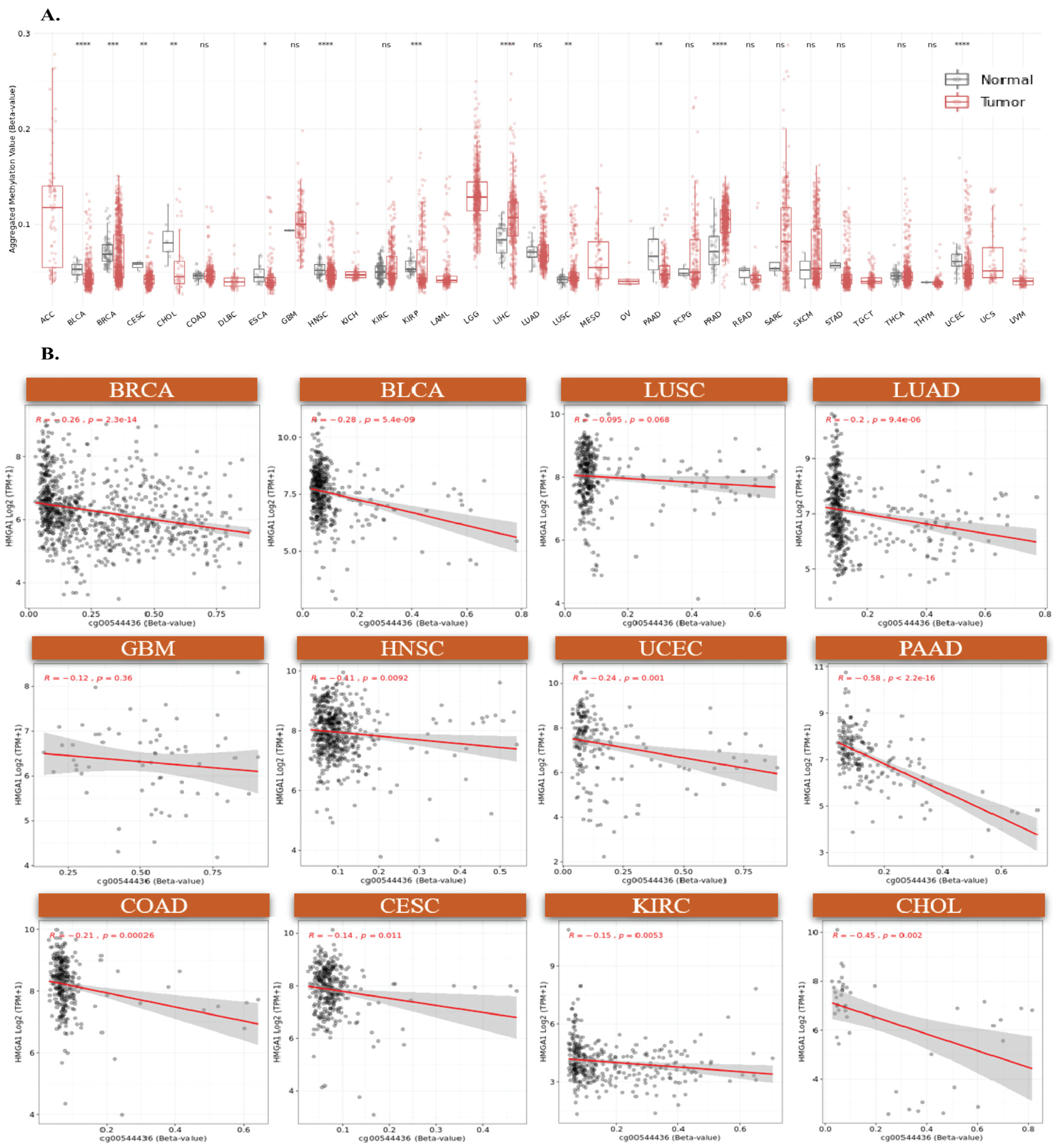
3.3. HMGA1 Overexpression Is Driven by Promoter Hypomethylation and Genetic Alterations
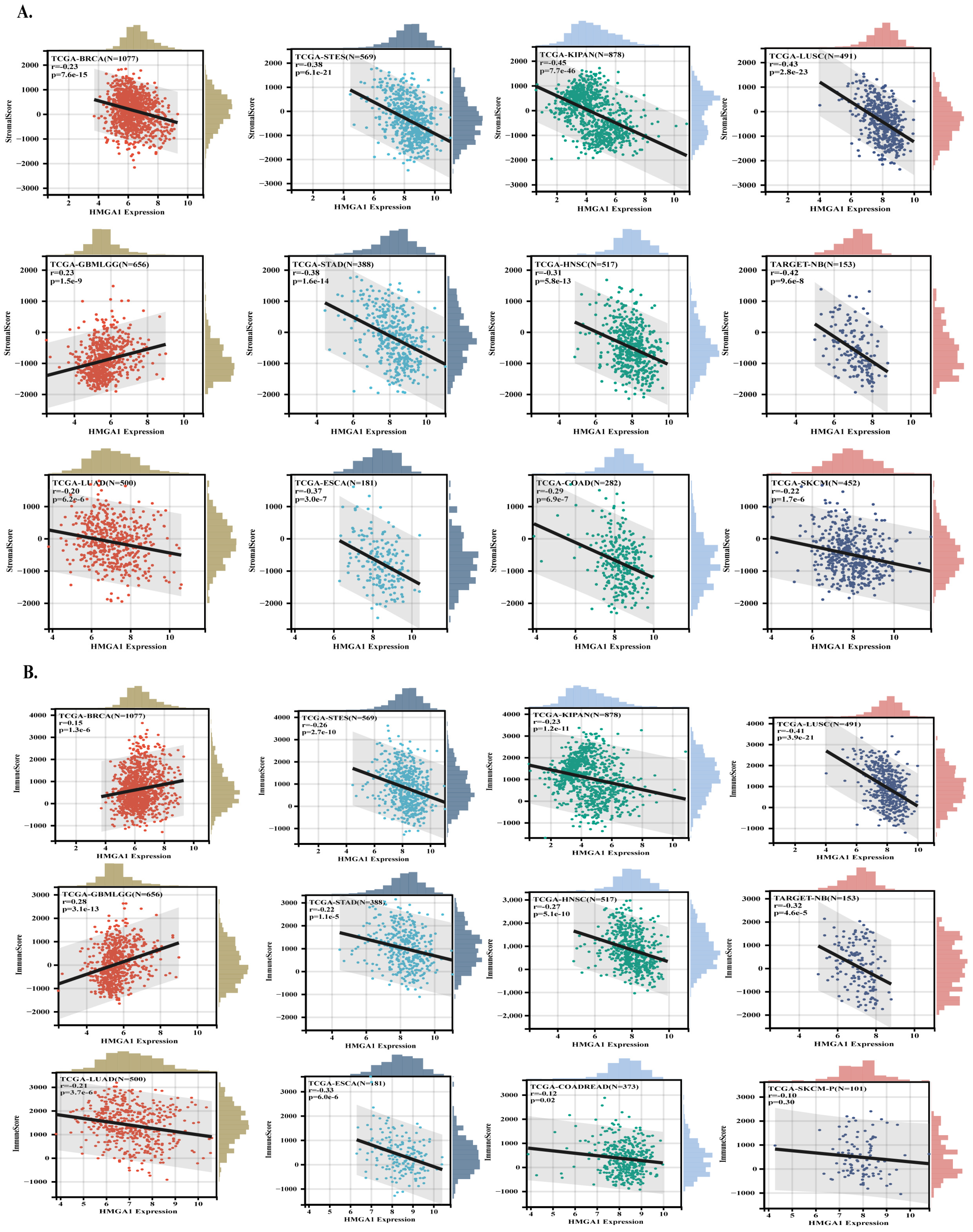
3.4. HMGA1 Expression Correlates with Tumor Stemness and Immune Exclusion
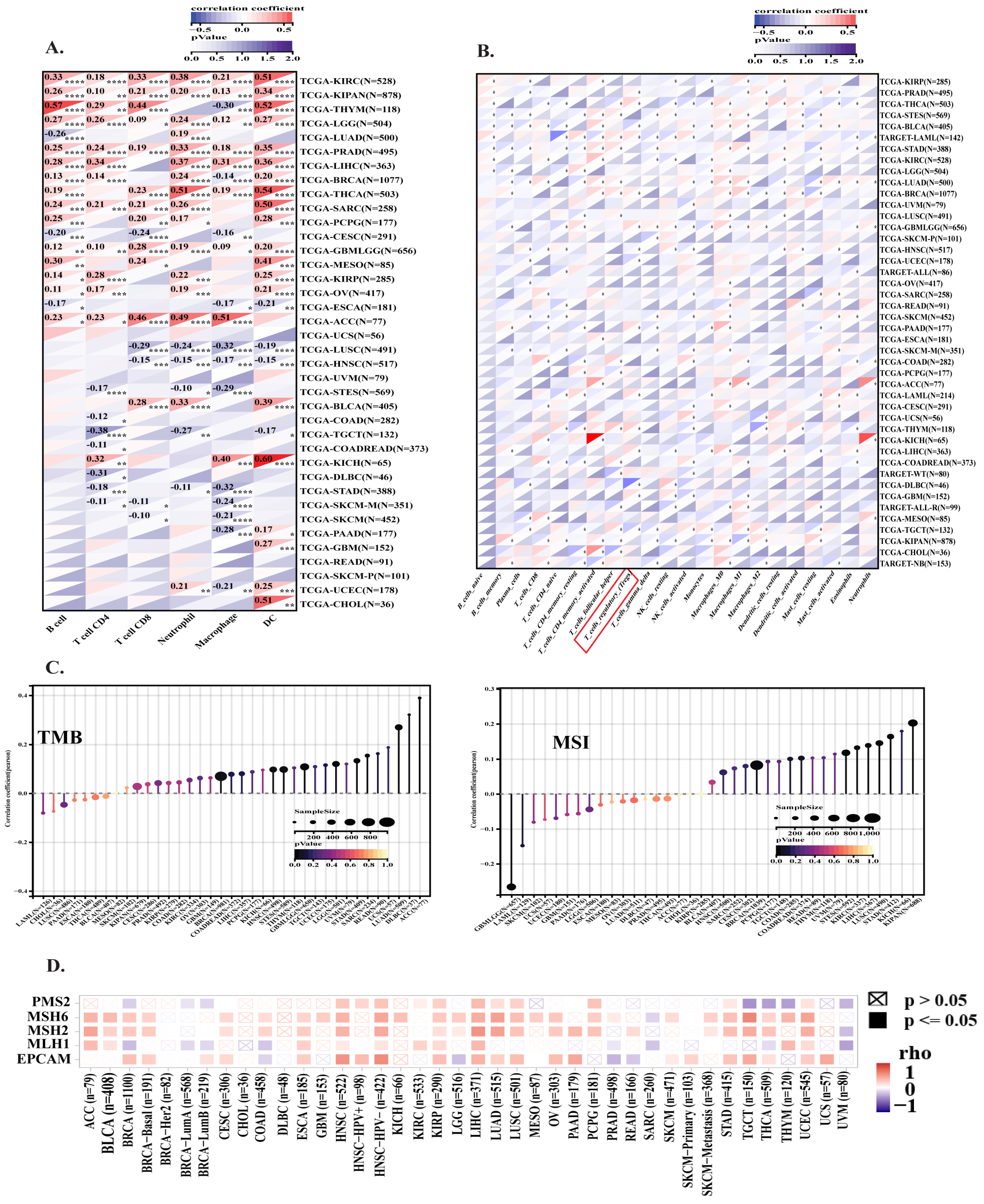
3.5. HMGA1 Expression Fosters an Immunosuppressive Tumor Microenvironment Across Multiple Cancers
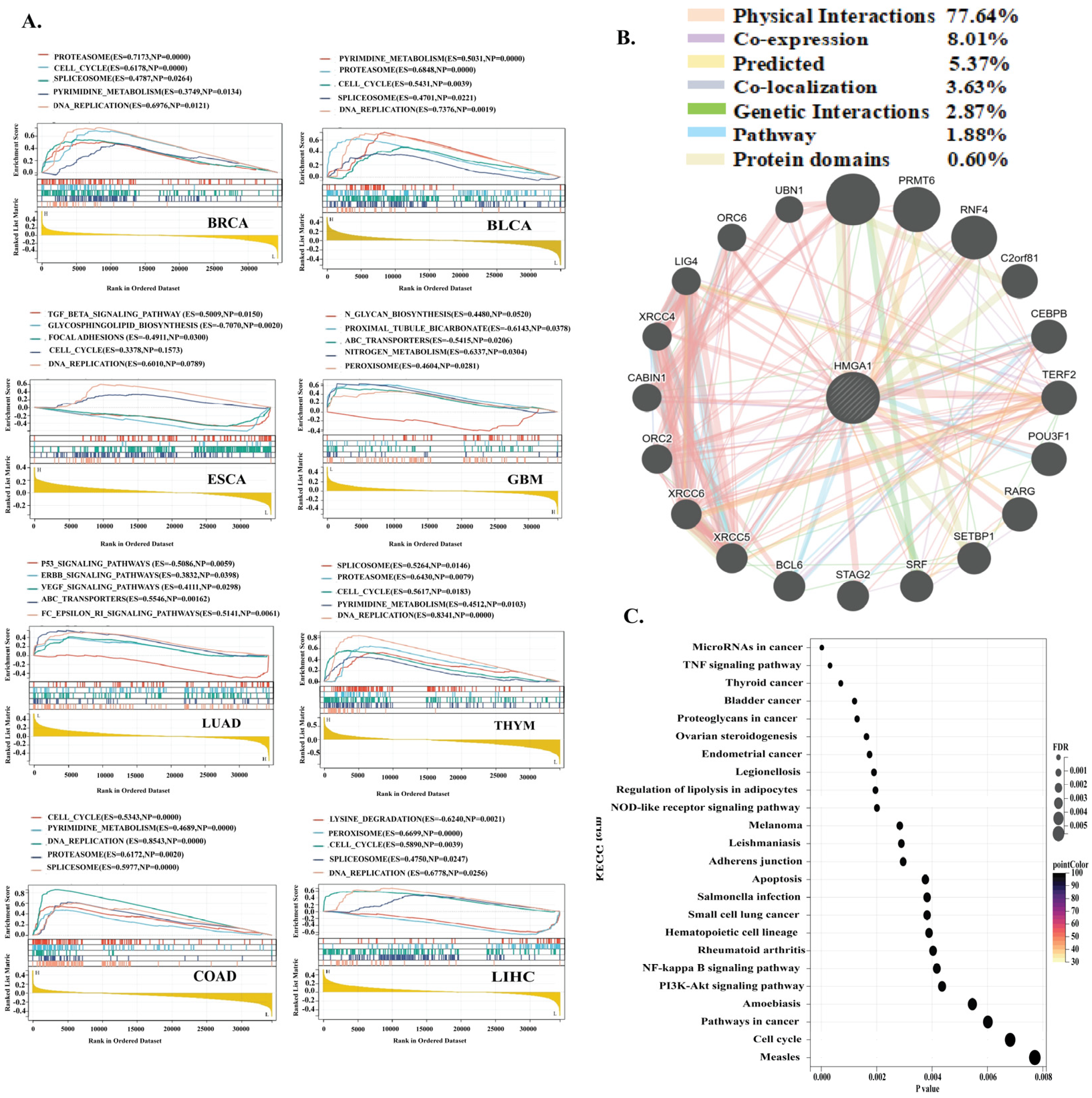
3.6. Gene Set Enrichment and Interaction Analysis of HMGA1 Across Cancers
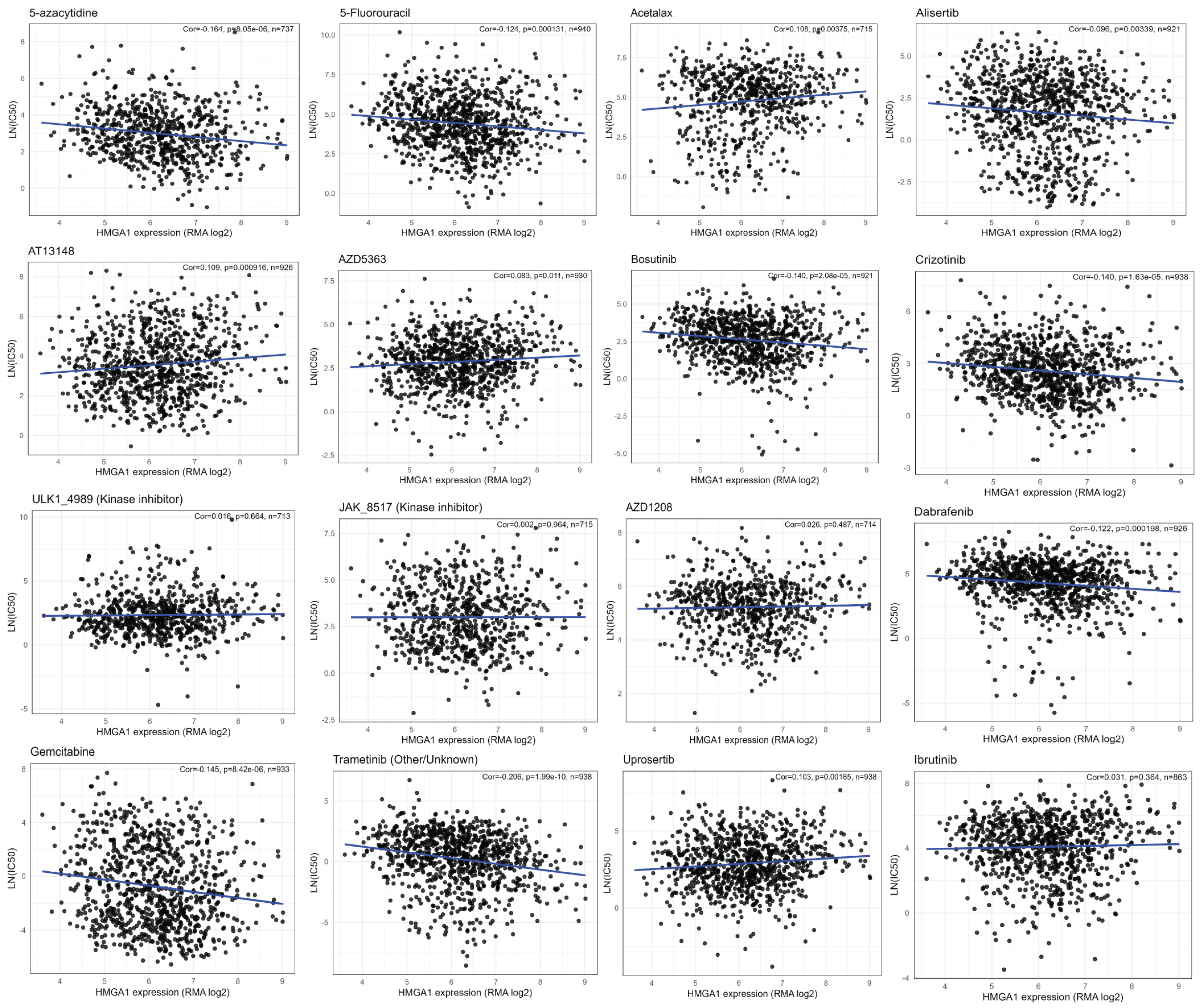
3.7. HMGA1 Associates with Drug-Specific Sensitivity Patterns
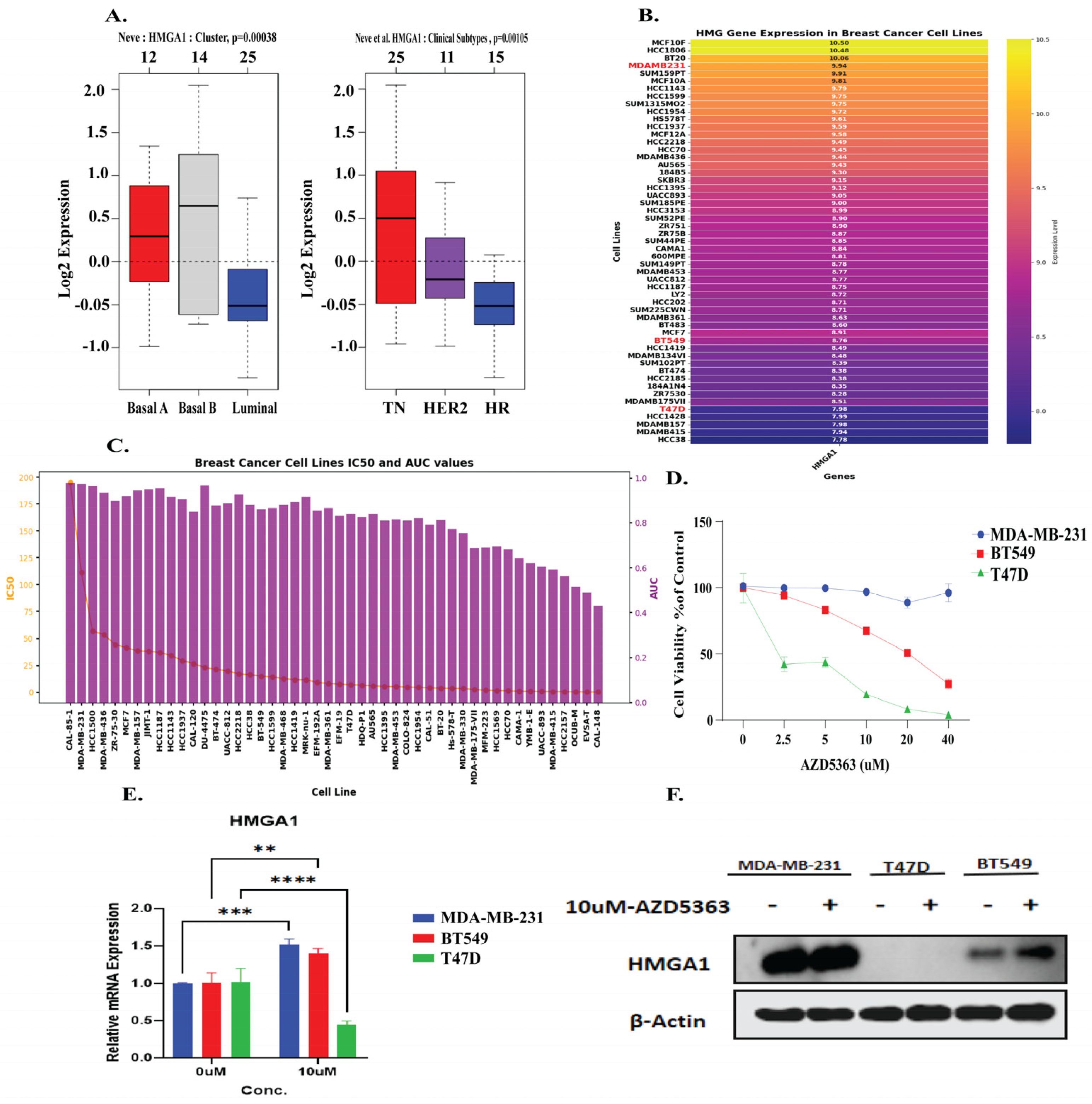
3.8. HMGA1 Expression Patterns and Differential Response to AZD5363 in Breast Cancer
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, K.-X.; Liang, X.; Zhu, Q.; Wu, H.-L.; Zhang, G.-Y.; Yao, Y.; Li, X.; Zheng, R.S.; Zuo, J.; Wei, W.-Q. Global patterns and trends in cancer-related premature death and their impact on life expectancy across 185 countries: A population-based analysis. Mil. Med. Res. 2025, 12, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soerjomataram, I.; Bray, F. Planning for tomorrow: Global cancer incidence and the role of prevention 2020–2070. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 18, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montégut, L.; López-Otín, C.; Kroemer, G. Aging and cancer. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-Y.; Park, J.Y. Epidemiology of cancer. In Anesthesia for Oncological Surgery; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, W.; Chen, H.-D.; Yu, Y.-W.; Li, N.; Chen, W.-Q. Changing profiles of cancer burden worldwide and in China: A secondary analysis of the global cancer statistics 2020. Chin. Med. J. 2021, 134, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufail, M.; Jiang, C.-H.; Li, N. Immune evasion in cancer: Mechanisms and cutting-edge therapeutic approaches. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2025, 10, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Shao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Wang, F.X.; Mu, J.; Li, J.; Yao, H.; Chen, K. Role of tumor microenvironment in cancer progression and therapeutic strategy. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 11149–11165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Dou, Y.; Leprevost, F.D.V.; Geffen, Y.; Calinawan, A.P.; Aguet, F.; Akiyama, Y.; Anand, S.; Birger, C.; Cao, S. Proteogenomic data and resources for pan-cancer analysis. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 1397–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanharo, C.V.; dos Santos Silveira, L.V.; Meira, D.D.; Casotti, M.C.; Altoé, L.S.C.; Louro, I.D.; Gonçalves, A.F.M.; Machado, A.M.; Paiva, B.S.; de Souza Inocencio, E. Pan-cancer and multiomics: Advanced strategies for diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy in the complex genetic and molecular universe of cancer. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2024, 27, 2936–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Miao, Y.; Xi, F.; Jiang, P.; Xiao, L.; Jin, X.; Fang, M. Identification of potential biomarkers for pan-cancer diagnosis and prognosis through the integration of large-scale transcriptomic data. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 870660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, H.; Huang, Y.; Tang, Q. The role of high mobility group proteins in cellular senescence mechanisms. Front. Aging 2024, 5, 1486281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papantonis, A. HMGs as rheostats of chromosomal structure and cell proliferation. Trends Genet. 2021, 37, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; He, Z. High mobility group proteins in sepsis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 911152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battista, S.; Fedele, M.; Secco, L.; Ingo, A.M.D.; Sgarra, R.; Manfioletti, G. Binding to the other side: The AT-Hook DNA-binding domain allows nuclear factors to exploit the DNA minor groove. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8863. [Google Scholar]
- Noreen, S.; Simonelli, N.; Benedetti, R.; Carafa, V.; Grieco, M.; Ambrosino, C.; Dell’Aversana, C.; Nebbioso, A.; Conte, M.; Del Gaudio, N. Unravelling the impact of the chromobox proteins in human cancers. Cell Death Dis. 2025, 16, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veglia Tranchese, R.; Battista, S.; Cerchia, L.; Fedele, M. Ferroptosis in cancer: Epigenetic control and therapeutic opportunities. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Xia, M.; Liu, C.; Zu, X.; Zhong, J. High mobility group A1 (HMGA1): Structure, biological function, and therapeutic potential. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Din, S.U.; Sufiyan, S.; Shah, A.A.; Fatima, H.; Salam, H.; Naeem, S.; Laghari, A.A.; Kayani, H.A.; Enam, S.A.; Mughal, N. HMGA1 as a prognostic biomarker for gliomas: Expression patterns, survival correlations, and clinical insights from a Pakistani cohort. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2025, 173, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumter, T.F.; Xian, L.; Huso, T.; Koo, M.; Chang, Y.T.; Almasri, T.N.; Chia, L.; Inglis, C.; Reid, D.; Resar, L.M. The High Mobility Group A1 (HMGA1) Transcriptome in Cancer and Development. Curr. Mol. Med. 2016, 16, 353–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, N.; Singh, I.; Mehta, A.; Braun, T.; Barreto, G. HMGA proteins as modulators of chromatin structure during transcriptional activation. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saed, L.; Balcerczak, E.; Łochowski, M.; Olechnowicz, E.; Sałagacka-Kubiak, A. HMGA1 gene expression level in cancer tissue and blood samples of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients: Preliminary report. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2022, 297, 1505–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Chen, T.; Sun, R.; Liu, Z.; Qiu, B.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z. HMGA1-TRIP13 axis promotes stemness and epithelial mesenchymal transition of perihilar cholangiocarcinoma in a positive feedback loop dependent on c-Myc. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez, O.; Peg, V.; Salvans, C.; Pujals, M.; Fernández, Y.; Abasolo, I.; Pérez, J.; Matres, A.; Valeri, M.; Gregori, J. Extracellular HMGA1 promotes tumor invasion and metastasis in triple-negative breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 6367–6382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreozzi, M.; Quintavalle, C.; Benz, D.; Quagliata, L.; Matter, M.; Calabrese, D.; Tosti, N.; Ruiz, C.; Trapani, F.; Tornillo, L. HMGA1 expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma correlates with poor prognosis and promotes tumor growth and migration in in vitro models. Neoplasia 2016, 18, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Cheng, T.; Zhao, Y.; Qu, Y. HMGA1 exacerbates tumor progression by activating miR-222 through PI3K/Akt/MMP-9 signaling pathway in uveal melanoma. Cell. Signal. 2019, 63, 109386. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Minervini, A.; Coccaro, N.; Anelli, L.; Zagaria, A.; Specchia, G.; Albano, F. HMGA proteins in hematological malignancies. Cancers 2020, 12, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Li, X.; Zhou, F.; Xi, Y.; Xu, G. HMGA2 promotes resistance against paclitaxel by targeting the p53 signaling pathway in colorectal cancer cells. Heliyon 2024, 10, e31431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luboff, A.J.; DeRemer, D.L. Capivasertib: A Novel AKT Inhibitor Approved for Hormone-Receptor-Positive, HER-2-Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer. Ann. Pharmacother. 2024, 58, 1229–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas, R.; Pancholi, S.; Guest, S.K.; Marangoni, E.; Gao, Q.; Thuleau, A.; Simigdala, N.; Polanska, U.M.; Campbell, H.; Rani, A.; et al. AKT Antagonist AZD5363 Influences Estrogen Receptor Function in Endocrine-Resistant Breast Cancer and Synergizes with Fulvestrant (ICI182780) In Vivo. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 2035–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, E.M.; Dry, H.; Cross, D.; Guichard, S.; Davies, B.R.; Alessi, D.R. Elevated SGK1 predicts resistance of breast cancer cells to Akt inhibitors. Biochem. J. 2013, 452, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Noord, V.E.; McLaughlin, R.P.; Smid, M.; Foekens, J.A.; Martens, J.W.M.; Zhang, Y.; van de Water, B. An increased cell cycle gene network determines MEK and Akt inhibitor double resistance in triple-negative breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanin, R.; Pegoraro, S.; Ros, G.; Ciani, Y.; Piazza, S.; Bossi, F.; Bulla, R.; Zennaro, C.; Tonon, F.; Lazarevic, D.; et al. HMGA1 promotes breast cancer angiogenesis supporting the stability, nuclear localization and transcriptional activity of FOXM1. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, M.J.; Craft, B.; Hastie, M.; Repečka, K.; McDade, F.; Kamath, A.; Banerjee, A.; Luo, Y.; Rogers, D.; Brooks, A.N.; et al. Visualizing and interpreting cancer genomics data via the Xena platform. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carithers, L.J.; Moore, H.M. The Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) Project. Biopreserv. Biobank. 2015, 13, 307–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Fu, J.; Zeng, Z.; Cohen, D.; Li, J.; Chen, Q.; Li, B.; Liu, X.S. TIMER2.0 for analysis of tumor-infiltrating immune cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W509–W514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrashekar, D.S.; Bashel, B.; Balasubramanya, S.A.H.; Creighton, C.J.; Ponce-Rodriguez, I.; Chakravarthi, B.; Varambally, S. UALCAN: A Portal for Facilitating Tumor Subgroup Gene Expression and Survival Analyses. Neoplasia 2017, 19, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontén, F.; Jirström, K.; Uhlen, M. The Human Protein Atlas—A tool for pathology. J. Pathol. J. Pathol. Soc. Great Br. Irel. 2008, 216, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lichtenberg, T.; Hoadley, K.A.; Poisson, L.M.; Lazar, A.J.; Cherniack, A.D.; Kovatich, A.J.; Benz, C.C.; Levine, D.A.; Lee, A.V. An integrated TCGA pan-cancer clinical data resource to drive high-quality survival outcome analytics. Cell 2018, 173, 400–416.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modhukur, V.; Iljasenko, T.; Metsalu, T.; Lokk, K.; Laisk-Podar, T.; Vilo, J. MethSurv: A web tool to perform multivariable survival analysis using DNA methylation data. Epigenomics 2018, 10, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ge, D.; Lu, C. The SMART App: An interactive web application for comprehensive DNA methylation analysis and visualization. Epigenet. Chromatin 2019, 12, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sloan, C.A.; Chan, E.T.; Davidson, J.M.; Malladi, V.S.; Strattan, J.S.; Hitz, B.C.; Gabdank, I.; Narayanan, A.K.; Ho, M.; Lee, B.T. ENCODE data at the ENCODE portal. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D726–D732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Robinson, J.T.; Mesirov, J.P. Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV): High-performance genomics data visualization and exploration. Brief. Bioinform. 2013, 14, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mermel, C.H.; Schumacher, S.E.; Hill, B.; Meyerson, M.L.; Beroukhim, R.; Getz, G. GISTIC2. 0 facilitates sensitive and confident localization of the targets of focal somatic copy-number alteration in human cancers. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malta, T.M.; Sokolov, A.; Gentles, A.J.; Burzykowski, T.; Poisson, L.; Weinstein, J.N.; Kamińska, B.; Huelsken, J.; Omberg, L.; Gevaert, O.; et al. Machine Learning Identifies Stemness Features Associated with Oncogenic Dedifferentiation. Cell 2018, 173, 338–354.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, I.; López-Reig, R.; Giner, E.; Fernández-Serra, A.; Requena, C.; Llombart, B.; Giner, F.; Cruz, J.; Traves, V.; Lavernia, J.; et al. Integration of an OS-Based Machine Learning Score (AS Score) and Immunoscore as Ancillary Tools for Predicting Immunotherapy Response in Sarcomas. Cancers 2025, 17, 2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, A.M.; Liu, C.L.; Green, M.R.; Gentles, A.J.; Feng, W.; Xu, Y.; Hoang, C.D.; Diehn, M.; Alizadeh, A.A. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beroukhim, R.; Mermel, C.H.; Porter, D.; Wei, G.; Raychaudhuri, S.; Donovan, J.; Barretina, J.; Boehm, J.S.; Dobson, J.; Urashima, M. The landscape of somatic copy-number alteration across human cancers. Nature 2010, 463, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonneville, R.; Krook, M.A.; Kautto, E.A.; Miya, J.; Wing, M.R.; Chen, H.-Z.; Reeser, J.W.; Yu, L.; Roychowdhury, S. Landscape of microsatellite instability across 39 cancer types. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2017, 2017, PO.17.00073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Wang, Y.; Dong, X.; Sun, D.; Liu, Z.; Yue, J.; Wang, H.; Li, T.; Wang, C. TISCH2: Expanded datasets and new tools for single-cell transcriptome analyses of the tumor microenvironment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D1425–D1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Walker, M.G. Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) for interpreting gene expression profiles. Curr. Bioinform. 2007, 2, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberzon, A.; Birger, C.; Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Ghandi, M.; Mesirov, J.P.; Tamayo, P. The Molecular Signatures Database (MSigDB) hallmark gene set collection. Cell Syst. 2015, 1, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warde-Farley, D.; Donaldson, S.L.; Comes, O.; Zuberi, K.; Badrawi, R.; Chao, P.; Franz, M.; Grouios, C.; Kazi, F.; Lopes, C.T.; et al. The GeneMANIA prediction server: Biological network integration for gene prioritization and predicting gene function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, W214–W220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringnér, M.; Fredlund, E.; Häkkinen, J.; Borg, Å.; Staaf, J. GOBO: Gene expression-based outcome for breast cancer online. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnenblick, A.; Venet, D.; Brohée, S.; Pondé, N.; Sotiriou, C. pAKT pathway activation is associated with PIK3CA mutations and good prognosis in luminal breast cancer in contrast to p-mTOR pathway activation. npj Breast Cancer 2019, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignatiadis, M.; Sotiriou, C. Luminal breast cancer: From biology to treatment. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 10, 494–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichhorn, S.W.; Guo, H.; McGeary, S.E.; Rodriguez-Mias, R.A.; Shin, C.; Baek, D.; Hsu, S.-h.; Ghoshal, K.; Villén, J.; Bartel, D.P. mRNA destabilization is the dominant effect of mammalian microRNAs by the time substantial repression ensues. Mol. Cell 2014, 56, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.T.; Westerling, T.; Brown, M. Loss of estrogen-regulated microRNA expression increases HER2 signaling and is prognostic of poor outcome in luminal breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.L.; Jeong, K.W. Histone modifications in drug-resistant cancers: From a cancer stem cell and immune evasion perspective. Exp. Mol. Med. 2023, 55, 1333–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrier, A.; Didelot, A.; Laurent-Puig, P.; Blons, H.; Garinet, S. Epigenetic Mechanisms of Resistance to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallik, R.; Kundu, A.; Chaudhuri, S. High mobility group proteins: The multifaceted regulators of chromatin dynamics. Nucleus 2018, 61, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Ye, S.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, W. HMGA2 promotes cancer metastasis by regulating epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1320887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegoraro, S.; Ros, G.; Piazza, S.; Sommaggio, R.; Ciani, Y.; Rosato, A.; Sgarra, R.; Del Sal, G.; Manfioletti, G. HMGA1 promotes metastatic processes in basal-like breast cancer regulating EMT and stemness. Oncotarget 2013, 4, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saed, L.; Jeleń, A.; Mirowski, M.; Sałagacka-Kubiak, A. Prognostic significance of HMGA1 expression in lung cancer based on bioinformatics analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colamaio, M.; Tosti, N.; Puca, F.; Mari, A.; Gattordo, R.; Kuzay, Y.; Federico, A.; Pepe, A.; Sarnataro, D.; Ragozzino, E. HMGA1 silencing reduces stemness and temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma stem cells. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2016, 20, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, G.B.; Wang, R.T.; Wang, S.N.; Tao, S.L.; Tan, Q.Y.; Jin, H. GRP75-mediated upregulation of HMGA1 stimulates stage I lung adenocarcinoma progression by activating JNK/c-JUN signaling. Thorac. Cancer 2021, 12, 1558–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Q.; Zhao, B.; She, X.; Liu, X. HMGA2 as a prognostic and immune biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma: Comprehensive analysis of the HMG family and experiments validation. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0311204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betancor, Y.Z.; Ferreiro-Pantín, M.; Anido-Herranz, U.; Fuentes-Losada, M.; León-Mateos, L.; García-Acuña, S.M.; Vaamonde-Rodríguez, V.; García-Pinel, B.; Cebey-López, V.; Villaverde-Viaño, R. A three-gene expression score for predicting clinical benefit to anti-PD-1 blockade in advanced renal cell carcinoma. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1374728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olan, I.; Ando-Kuri, M.; Parry, A.J.; Handa, T.; Schoenfelder, S.; Fraser, P.; Ohkawa, Y.; Kimura, H.; Narita, M.; Narita, M. HMGA1 orchestrates chromatin compartmentalization and sequesters genes into 3D networks coordinating senescence heterogeneity. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Mohapatra, T. Deciphering epitranscriptome: Modification of mRNA bases provides a new perspective for post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 628415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Lei, Y.; Li, J.-K.; Du, W.-X.; Li, R.-G.; Yang, J.; Li, J.; Li, F.; Tan, H.-B. Immune cells within the tumor microenvironment: Biological functions and roles in cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Lett. 2020, 470, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgarra, R.; Zammitti, S.; Sardo, A.L.; Maurizio, E.; Arnoldo, L.; Pegoraro, S.; Giancotti, V.; Manfioletti, G. HMGA molecular network: From transcriptional regulation to chromatin remodeling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gene Regul. Mech. 2010, 1799, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.-H.; Zhang, J.-X.; Jin, H.-S.; Huang, J. Crosstalk Between Metabolic Reprogramming and Epigenetic Modifications in Colorectal Cancer: Mechanisms and Clinical Applications. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozga, A.J.; Chow, M.T.; Luster, A.D. Chemokines and the immune response to cancer. Immunity 2021, 54, 859–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, K.; Yoshie, O.; Nakayama, T. Multifaceted roles of chemokines and chemokine receptors in tumor immunity. Cancers 2021, 13, 6132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasidharan Nair, V.; Toor, S.M.; Taha, R.Z.; Shaath, H.; Elkord, E. DNA methylation and repressive histones in the promoters of PD-1, CTLA-4, TIM-3, LAG-3, TIGIT, PD-L1, and galectin-9 genes in human colorectal cancer. Clin. Epigenet. 2018, 10, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karin, N. Chemokines in the landscape of cancer immunotherapy: How they and their receptors can be used to turn cold tumors into hot ones? Cancers 2021, 13, 6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.-C.; Chang, J.; Sie, Z.-L.; Ho, A.-S.; Peng, C.-L.; Chang, C.-C. CXCL9/10 is critical for immunotherapeutic efficacy by recruiting and activating T lymphocytes in tumor microenvironment. Cancer Res. 2024, 84 (Suppl. S6), 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Liu, J.; Yang, Q.; Gao, Y.; Ding, X.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Wu, Y. Targeting HMGA1 contributes to immunotherapy in aggressive breast cancer while suppressing EMT. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2023, 212, 115582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Liu, C.; Li, H.; Wen, N.; Jiao, W.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, H.; Lv, Y. Reversal of HMGA1-mediated immunosuppression synergizes with immunogenic magnetothermodynamic for improved hepatocellular carcinoma therapy. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 9209–9223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhter, M.Z.; Luthra, K.; Rajeswari, M.R. Molecular aspects on adriamycin interaction with hmga1 regulatory region and its inhibitory effect on HMGA1 expression in human cervical cancer. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2016, 34, 877–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Li, Y.; Chen, K.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Qin, W.; Zeng, Y.; Fu, J.; Ma, X.; Zheng, W. Targeting HMGA1-driven leukemic transformation in myeloproliferative neoplasms with pacritinib. bioRxiv 2025, bioRxiv:2025.2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Liu, B.; Feng, Y. CCL17, CCL22 and their receptor CCR4 in hematologic malignancies. Discov. Oncol. 2024, 15, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, M.J.; Crown, J. Biomarkers for predicting response to immunotherapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer patients. Clin. Chem. 2019, 65, 1228–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Que, T.; Zheng, H.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, X.; Qi, G.; La, Q.; Liang, T.; Li, Z.; Yi, G.; Zhang, S. HMGA1 stimulates MYH9-dependent ubiquitination of GSK-3β via PI3K/Akt/c-Jun signaling to promote malignant progression and chemoresistance in gliomas. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Cui, D.; Wang, J.; Qin, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhai, X.; Ma, H.; Ma, D.; Liu, Y.; et al. Overexpression of HMGA1 confers radioresistance by transactivating RAD51 in cholangiocarcinoma. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shahzadi, I.; Ahsan, T.; Anwaar, S.; Zaman, W.; Xia, H. Promoter Hypomethylation Unleashes HMGA1 to Orchestrate Immune Evasion and Therapy Resistance Across Cancers. Biology 2025, 14, 1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121758
Shahzadi I, Ahsan T, Anwaar S, Zaman W, Xia H. Promoter Hypomethylation Unleashes HMGA1 to Orchestrate Immune Evasion and Therapy Resistance Across Cancers. Biology. 2025; 14(12):1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121758
Chicago/Turabian StyleShahzadi, Iram, Taswar Ahsan, Shoaib Anwaar, Wajid Zaman, and Houjun Xia. 2025. "Promoter Hypomethylation Unleashes HMGA1 to Orchestrate Immune Evasion and Therapy Resistance Across Cancers" Biology 14, no. 12: 1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121758
APA StyleShahzadi, I., Ahsan, T., Anwaar, S., Zaman, W., & Xia, H. (2025). Promoter Hypomethylation Unleashes HMGA1 to Orchestrate Immune Evasion and Therapy Resistance Across Cancers. Biology, 14(12), 1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14121758






