Seasonal Variation in Nocturnal Roost Timing and Diurnal Movement in Endangered Crested Ibis (Nipponia nippon): An Adaptation Strategy to Environmental Changes
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
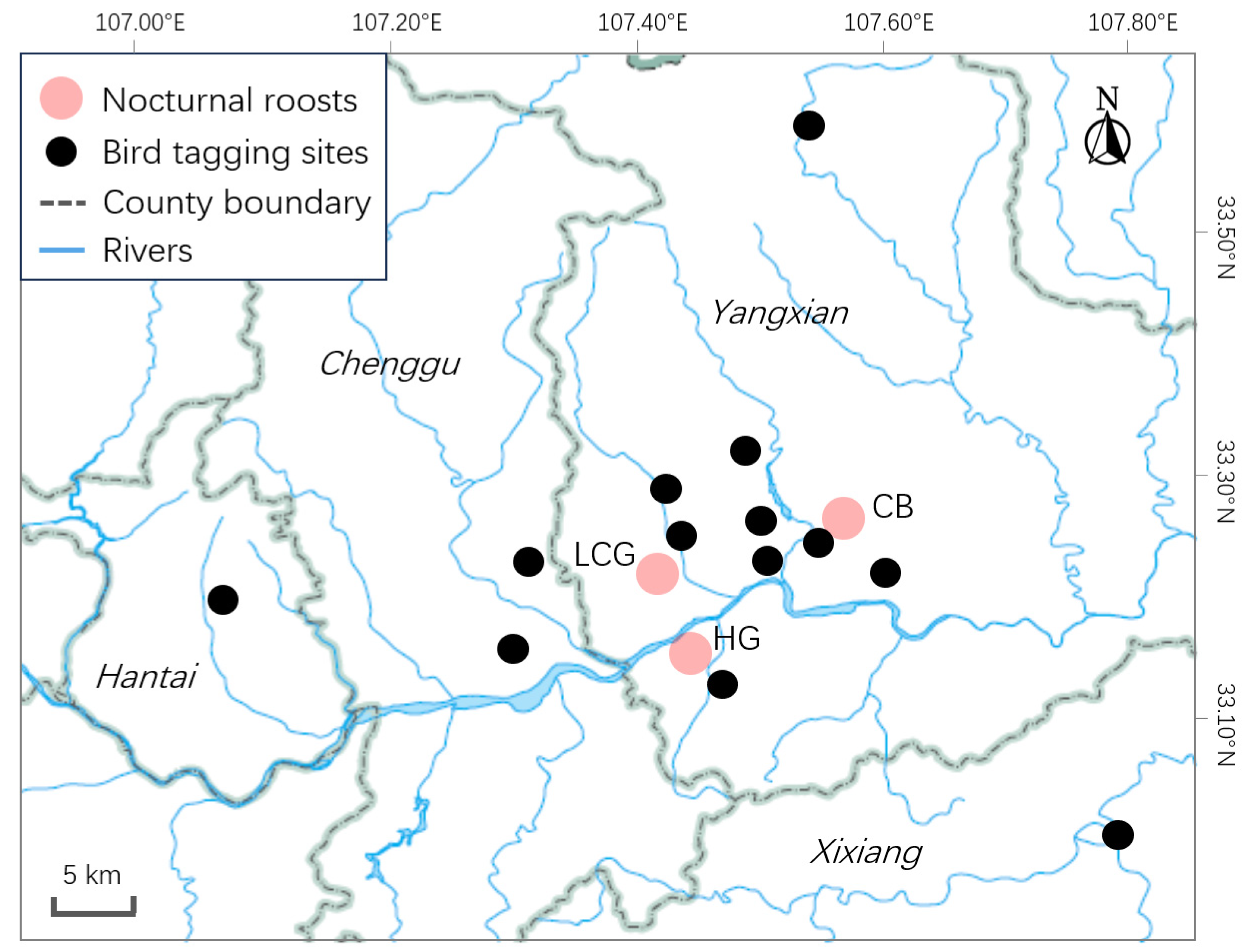
2.1. Roosting Counts
2.2. GPS-GSM Transmitter Attachment
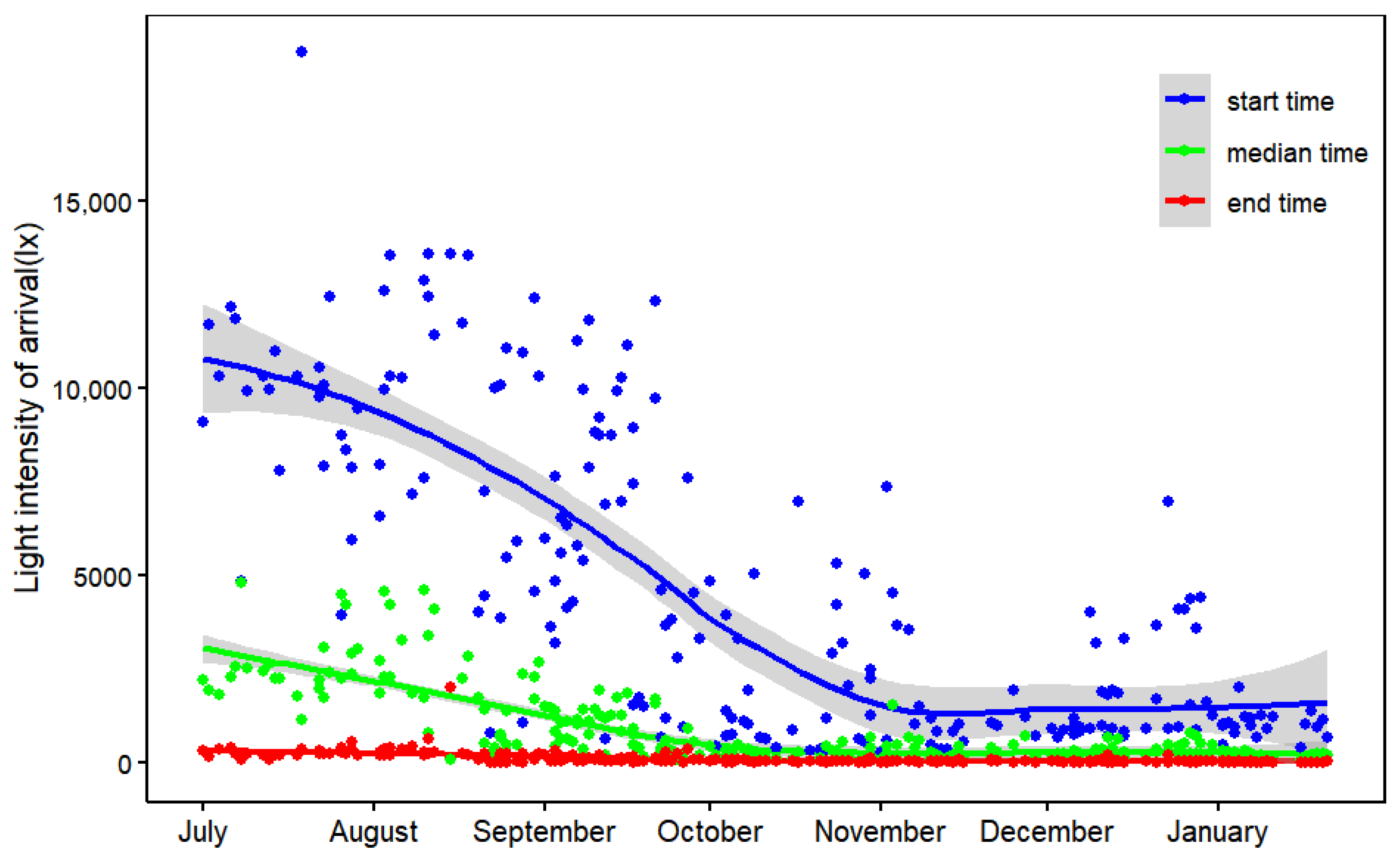
2.3. Roost Timing and Activity Time
2.4. Daily Movement Distance and Activity Level
3. Result
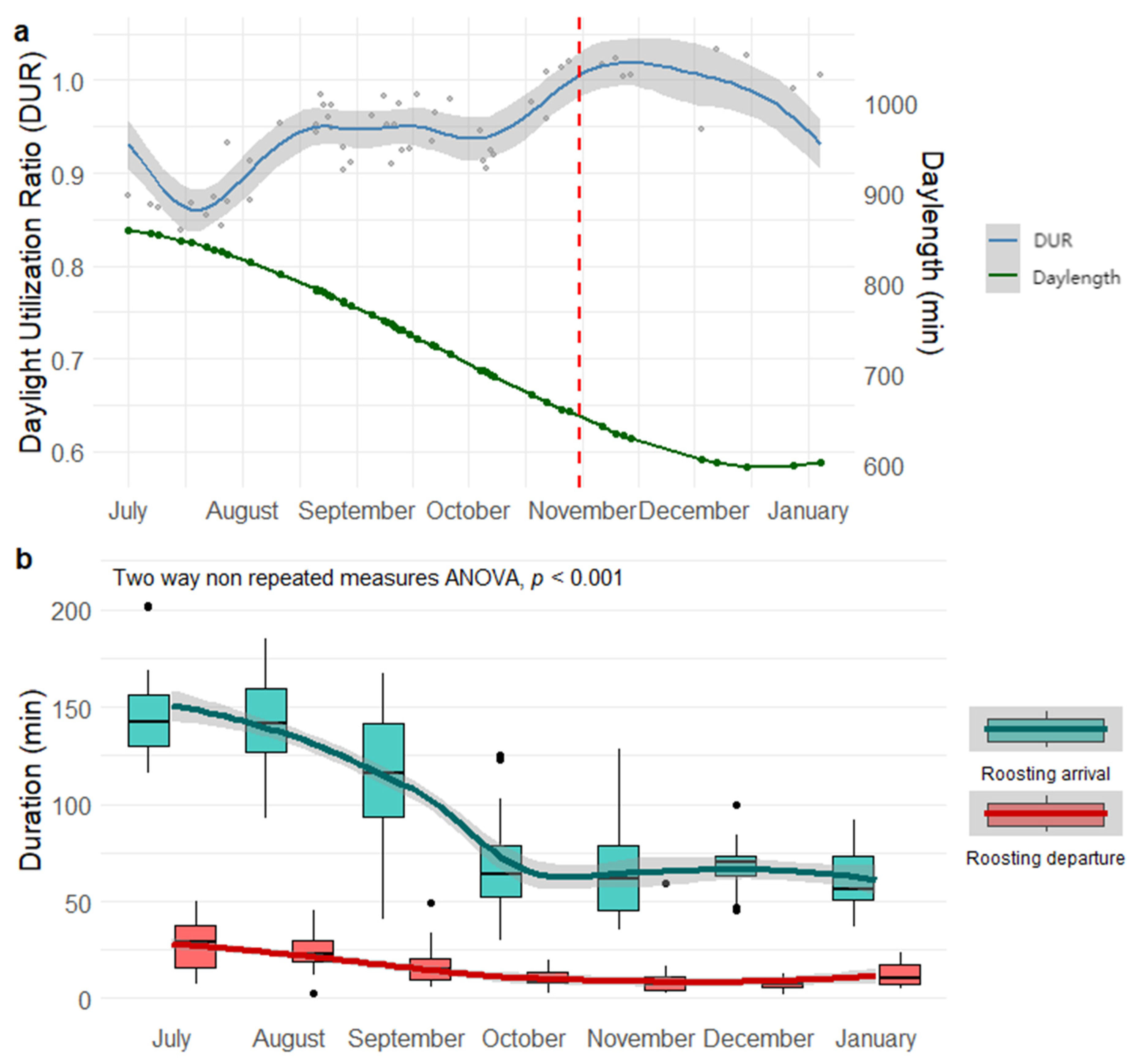
3.1. Seasonal Variation in Roost Timing
3.2. Allocation Between Roosting and Foraging
3.3. Seasonal Variation in Daily Movement Distance and Activity Level
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sutherland, W.J.; Newton, I.; Green, R.E. Bird Ecology and Conservation; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Both, C.; Visser, M.E. Adjustment to climate change is constrained by arrival date in a long-distance migrant bird. Nature 2001, 411, 296–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askren, R.J.; Massey, E.R.; James, J.D.; Osborne, D. Migration chronology and multi-scale habitat selection of wintering midcontinent greater white-fronted geese. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2022, 39, 2351–9894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubbe, N.; Czenze, Z.J.; Noakes, M.J.; McKechnie, A.E. The energetic significance of communal roosting and insulated roost nests in a small arid-zone passerine. Ostrich 2018, 89, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eerden, M.R.; Van Rijn, S. Social hierarchy within communal foraging flocks of Great Cormorants Phalacrocorax carbo as reflected by differences in prey composition and food intake at the roost. Ardea 2022, 109, 549–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, P.; Zahavi, A. The importance of certain assemblages of birds as “information centres” for food finding. IBIS 1973, 115, 517–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGowan, A.; Sharp, S.P.; Simeoni, M.; Hatchwell, B.J. Competing for position in the communal roosts of long-tailed tits. Anim. Behav. 2006, 72, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, M.A.; Buttemer, W.A.; Russell, A.F. Energetics of communal roosting in chestnut-crowned babblers: Implications for group dynamics and breeding phenology. J. Exp. Biol. 2016, 219, 3321–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.D.; Diez-Méndez, D.; Kempenaers, B. Effects of experimental night lighting on the daily timing of winter foraging in common European songbirds. J. Avian Biol. 2017, 48, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doucette, D.R.; Reebs, S.G. Influence of temperature and other factors on the daily roosting times of mourning doves in winter. Can. J. Zool. 1994, 72, 1287–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janicke, T.; Chakarov, N. Effect of weather conditions on the communal roosting behaviour of common ravens Corvus corax with unlimited food resources. J. Ethol. 2007, 25, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youcefi, A.; Baaloudj, A.; Zebsa, R.; Mahdjoub, H.; Bensakhri, Z.; Bensouilah, S.; Amari, H.; Bachir, A.S.; Khelifa, R. Weather conditions affect the collective roosting behaviour of the Cattle Egret Bubulcus ibis. Bird Study 2019, 66, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.J.; Gao, M.; Lv, H.W.; Zhou, L.; Yi, H.Q.; Liu, L.; Liu, D.P. Diurnal time budget and behavioral rhythm of an acclimatizing Crested Ibis Nipponia nippon population during non-breeding season in Beidaihe, Hebei Province, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 5487–5494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lázaro Romero, C.; Sanchez, C.; Casas, F.; Tizado, E. Avian responses to an extreme weather event: The case of the ‘Filomena’ snowstorm in Madrid (central Spain). Avian Res. 2024, 15, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BirdLife International. Nipponia nippon. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018, e.T22697548A132069229. Available online: https://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22697548A132069229.en (accessed on 16 May 2025).
- Shi, D.C.; Cao, Y.H. Chinese Crested Ibis; China Forestry Press: Beijing, China, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bowden, C.G.R.; Aghnaj, A.; Smith, K.W.; Ribi, M. The status and recent breeding performance of the critically endangered Northern Bald Ibis Geronticus eremita population on the Atlantic coast of Morocco. IBIS 2003, 145, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.Q. Research on the Crested Ibis; Shanghai Science and Technology Education Press: Shanghai, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.W.; Skidmore, A.K.; Wang, T.J.; van Gils, H.A.M.J.; Wang, Q.; Qing, B.P.; Ding, C.Q. Reduced Dependence of Crested Ibis on Winter-Flooded Rice Fields: Implications for Their Conservation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, B.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Quan, H.; Duan, Y.; Zhao, W.; Ding, C. Analysis on the Wild Population Rescue of Crested Ibis (Nipponia nippon) from 2016 to 2019. Chin. J. Zool. 2022, 57, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, D.; Li, W.; Duan, W.; Gao, J.; Wang, C. Moult-breeding trade-offs in the crested ibis (Nipponia nippon) could have management applications. Avian Res. 2025, 16, 100250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Z.P.; Guo, J.F.; Li, X.; Yu, X.P. Post-fledging dispersal and habitat use of a reintroduced population of the Crested Ibis (Nipponia nippon). Avian Res. 2014, 1, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.S.; Song, X.; Ding, C.Q.; Ye, Y.X.; Qing, B.P.; Wang, C. The Size of Winter-Flooded Paddy Fields No Longer Limits the Foraging Habitat Use of the Endangered Crested Ibis (Nipponia nippon) in Winter. Zool. Sci. 2016, 33, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Xu, X.; Ye, Y.; Wang, C.; Qing, B.; Duan, W.; Yan, J.; Huang, Y.; Ding, C. From fledging to independence: Post-fledging movements and space use of the Crested Ibis (Nipponia nippon). Avian Res. 2025, 16, 100266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; He, K.; Qin, S.; Li, W.; Wang, C.; Liu, D. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Crested Ibis (Nipponia nippon) Movement. Animals 2025, 15, 2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.Q.; He, X.L.; Han, J.L. PCR Method for Sex Identification of Crested Ibis (Nipponia nippon). Chinese Patent No. CN 1002134600 A, 27 July 2011. Available online: http://epub.cnki.net/kns/brief/result.aspx?dbPrefix=SCOD (accessed on 28 August 2025).
- Singhal, A.; Singhal, P. Roosting Behaviour and Population of Indian Mynas; & its Correlation with Sunset (light intensity) and the Time of Arrival. Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2023, 11, 2321–9653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, R.A.M.; Chen, Z.J. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis (2nd ed.). Meas. Interdiscip. Res. Perspect. 2019, 17, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, W.S. Robust Locally Weighted Regression and Smoothing Scatterplots. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1979, 74, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, A.Y. Generalized Additive Models: An Introduction with R. Technometrics 2007, 49, 360–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backman, J.; Andersson, A.; Pedersen, L.; Sjoberg, S.; Tøttrup, A.P.; Alerstam, T. Actogram analysis of free-flying migratory birds: New perspectives based on acceleration logging. J. Comp. Physiol. 2017, 203, 543–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Fox, J.; Weisberg, S. An R Companion to Applied Regression, 3rd ed.; Thousand Oaks: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kassambara, A. Pipe-Friendly Framework for Basic Statistical Tests, R package rstatix version 0.6.0; Free Software Foundation Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 2020.
- Kassambara, A. “ggplot2” Based Publication Ready Plots, R package ggpubr version 0.4.0; Free Software Foundation Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 2020.
- Ye, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, C.; Liu, Y.; Qing, B.; Wang, C.; Fernández-Juricic, E.; Ding, C. What makes a tactile forager join mixed-species flocks? A case study with the endangered Crested Ibis (Nipponia nippon). Auk 2017, 134, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caccamise, D.F.; Morrison, D.W. Avian Communal Roosting: Implications of Diurnal Activity Centers. Am. Nat. 1986, 128, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, A.; Naef-Daenzer, B.; Keil, H.; Korner-Nievergelt, F.; Perrig, M.; Grüebler, M. Roost site selection by Little Owls Athene noctua in relation to environmental conditions and life-history stages. Ibis 2013, 155, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, I. The Migration Ecology of Birds; Elsevier Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 837–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evens, R.; Beenaerts, N.; Witters, N.; Artois, T. Study on the foraging behaviour of the European nightjar Caprimulgus europaeus reveals the need for a change in conservation strategy in Belgium. J. Avian Biol. 2017, 48, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueffler, C.; Lehmann, L. Central place foragers, prey depletion halos, and how behavioral niche partitioning promotes consumer coexistence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyke, G.H. Animal Movements: An Optimal Foraging Theory Approach. In Encyclopedia of Animal Behavior, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1983; Volume 2, pp. 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahms, B.; Aikens, E.O.; Armstrong, J.B.; Deacy, W.W.; Kauffman, M.J.; Merkle, J.A. Emerging Perspectives on Resource Tracking and Animal Movement Ecology. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2020, 36, 308–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jirinec, V.; Burner, R.C.; Amaral, B.R.; Bierregaard, R.O.; Fernández-Arellano, G.; Hernández-Palma, A.; Johnson, E.I.; Lovejoy, T.E.; Powell, L.L.; Rutt, C.L. Morphological consequences of climate change for resident birds in intact amazonian rainforest. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabk1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X. Preliminary Study on the Roosting Behavior of the Reintroduced Population of Crested Ibis (Nipponia nippon); Shaanxi Normal University: Xi’an, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty, E.; Parzer, H.; Morton, E. Artificial light at night affects the timing of roosting by Chimney Swifts. IBIS 2024, 166, 732–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| No. | Age | Birth Year | Sex | Start Tracking Date | Tracking Days | Reason of Tracking Failure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Adult | 2012 | Female | 12 August 2014 | 1786 | Out of power |
| 2 | Adult | N/A | N/A | 10 April 2015 | 1915 | Tag malfunction |
| 3 | Juvenile | 2015 | N/A | 24 July 2015 | 2309 | Tag malfunction |
| 4 | Juvenile | 2016 | N/A | 9 July 2016 | 892 | Unknown |
| 5 | Juvenile | 2017 | Male | 8 June 2017 | 311 | Unknown |
| 6 | Juvenile | 2017 | Male | 8 June 2017 | 340 | Unknown |
| 7 | Juvenile | 2017 | Female | 8 June 2017 | 412 | Unknown |
| 8 | Juvenile | 2017 | Male | 8 June 2017 | 679 | Tag malfunction |
| 9 | Juvenile | 2017 | Female | 8 June 2017 | 796 | Unknown |
| 10 | Juvenile | 2017 | Female | 8 June 2017 | 1204 | Unknown |
| 11 | Juvenile | 2018 | N/A | 17 May 2018 | 1356 | Death |
| 12 | Juvenile | 2018 | N/A | 1 July 2018 | 1012 | Death |
| 13 | Adult | N/A | N/A | 6 April 2021 | 589 | Out of power |
| 14 | Adult | N/A | N/A | 19 April 2021 | 443 | Death |
| 15 | Sub-adult | 2020 | N/A | 30 April 2021 | 550 | Unknown |
| 16 | Adult | N/A | N/A | 21 July 2021 | 252 | Unknown |
| 17 | Juvenile | 2021 | N/A | 21 July 2021 | 406 | Out of power |
| 18 | Adult | N/A | N/A | 21 July 2021 | 1029 | Unknown |
| 19 | Adult | N/A | N/A | 16 September 2022 | 426 | Unknown |
| Seasons | Estimate | SE | df | t | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daily movement distance | Breeding vs. Wandering | 912.56 | 328.87 | 445.38 | 2.775 | 0.016 * |
| Breeding vs. Wintering | 1068.51 | 384.63 | 445.58 | 2.778 | 0.016 * | |
| Wandering vs. Wintering | 155.95 | 391.21 | 445.37 | 0.399 | 0.916 | |
| Daily activity level | Breeding vs. Wandering | −227.02 | 596.76 | 206.37 | −0.380 | 0.923 |
| Breeding vs. Wintering | 2635.85 | 687.01 | 207.42 | 3.837 | <0.001 *** | |
| Wandering vs. Wintering | 2862.86 | 683.11 | 206.97 | 4.191 | <0.001 *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Liu, D.; Liao, Y.; He, K.; Wang, C. Seasonal Variation in Nocturnal Roost Timing and Diurnal Movement in Endangered Crested Ibis (Nipponia nippon): An Adaptation Strategy to Environmental Changes. Biology 2025, 14, 1496. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111496
Li W, Liu D, Liao Y, He K, Wang C. Seasonal Variation in Nocturnal Roost Timing and Diurnal Movement in Endangered Crested Ibis (Nipponia nippon): An Adaptation Strategy to Environmental Changes. Biology. 2025; 14(11):1496. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111496
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Wei, Dongping Liu, Yuhe Liao, Ke He, and Chao Wang. 2025. "Seasonal Variation in Nocturnal Roost Timing and Diurnal Movement in Endangered Crested Ibis (Nipponia nippon): An Adaptation Strategy to Environmental Changes" Biology 14, no. 11: 1496. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111496
APA StyleLi, W., Liu, D., Liao, Y., He, K., & Wang, C. (2025). Seasonal Variation in Nocturnal Roost Timing and Diurnal Movement in Endangered Crested Ibis (Nipponia nippon): An Adaptation Strategy to Environmental Changes. Biology, 14(11), 1496. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14111496






