Exploring Brain Size Asymmetry and Its Relationship with Predation Risk Among Chinese Anurans
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Samples
2.2. Predation Risk
2.3. Brain Measurements
2.4. Phylogeny Reconstruction
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barneoud, P.; der Loos, H.V. Direction of handedness linked to hereditary asymmetry of a sensory system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 3246–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, L.J.; Vallortigara, G.; Andrew, R.J. Divided Brains: The Biology and Behaviour of Brain Asymmetry; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Duboc, V.; Dufourcq, P.; Blader, P.; Roussigné, M. Asymmetry of the brain: Development and implications. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2015, 49, 647–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, A.P.; Swaddle, J.P. Asymmetry, Developmental Stability and Evolution; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Polak, M.; Triners, R. The science of symmetry in biology. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1994, 9, 122–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waddington, C.H. Canalization of development and the inheritance of acquired characters. Nature 1942, 150, 563–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Valen, L. A study of fluctuating asymmetry. Evolution 1962, 16, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sion, G.; Tal, R.; Meiri, S. Asymmetric behavior in Ptyodactylus guttatus: Can a digit ratio reflect brain laterality? Symmetry 2020, 12, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, J.H.; Emlen, J.M.; Freeman, D.C.; Leamy, L.J.; Kieser, J.A. Directional asymmetry and the measurement of developmental instability. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 1998, 64, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, J.H.; Roe, K.E.; West, T.B. Effects of lead and benzene on the developmental stability of Drosophila melanogaster. Ecotoxicology 1993, 2, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, A.R. From symmetry to asymmetry: Phylogenetic patterns of asymmetry variation in animals and their evolutionary significance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 14279–14286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hettyey, A.; Laurila, A.; Herczeg, G.; Jonsson, K.I.; Kovacs, T.; Merilä, J. Does testis weight dechne towards the Subarctic? A case study on the common frog Rana temporaria. Naturwissenschaften 2005, 92, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotrschal, K.; Van Staaden, M.J.; Huber, R. Fish brains: Evolution and environmental relationships. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 1998, 8, 373–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, L. A comparison of encephalization between odontocete cetaceans and anthropoid primates. Brain Behav. Evol. 1998, 51, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, L.B.; Westcott, D.A.; Olster, D.H. Evolution of bower complexity and cerebellum size in bowerbirds. Brain Behav. Evol. 2005, 66, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aviles, J.M.; Garamszegi, L.Z. Egg rejection and brain size among potential hosts of the common cuckoo. Ethology 2007, 113, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonda, A.; Herczeg, G.; Merilä, J. Evolutionary ecology of intraspecific brain size variation: A review. Ecol. Evol. 2013, 3, 2751–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Woerden, J.T.; Willems, E.P.; van Schaik, C.P.; Isler, K. Large brains buffer energetic effects of seasonal habitats in catarrhine primates. Evolution 2011, 66, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Schotten, M.T.; Dell’Acqua, F.; Forkel, S.J.; Simmons, A.; Francesco, V. A lateralized brain network for visuospatial attention. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 1245–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.B.; Jiang, Y.; Jin, L.; Lüpold, S. How hibernation in frogs drives brain and reproductive evolution in opposing directions. eLife 2023, 12, RP88236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.B.; Jiang, Y.; Li, D.Y.; Jin, L.; Zhong, M.J.; Qi, Y.; Lüpold, S.; Kotrschal, A. Cognition contra camouflage: How the brain mediates predator-driven crypsis evolution. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabq1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Yuan, L.J.; Liao, W.B. Chemical defense mediates population-driven on anuran brain size evolution. Sci. China Life Sci. 2024, 67, 1076–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Luan, X.F.; Liao, W.B. Anuran brain size predicts food availability-driven population density. Sci. China Life Sci. 2023, 66, 415–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, C.; Liao, W.B. Anuran interorbital space variation: The role of ecological and behavioral factors. Integr. Zool. 2022, 17, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.T.; Wu, Z.J.; Liao, W.B. Large-brained birds display lower extra-pair paternity. Integr. Zool. 2023, 18, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Zhong, M.J.; Li, D.Y.; Jin, L.; Liao, W.B.; Kotrschal, A. Large-brained frogs mature later and live longer. Evolution 2018, 72, 1174–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Mai, C.L.; Liao, W.B.; Kotrschal, A. Body mass variation is negatively associated with brain size: Evidence for the fat-brain trade-off in anurans. Evolution 2020, 74, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai, C.L.; Liao, W.B.; Kotrschal, A.; Lüpold, S. Relative brain size is predicted by the intensity of intrasexual competition in frogs. Am. Nat. 2020, 196, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bialas, J.T.; Dylewski, L.; Tobolka, M. Brain size mediates the choice of breeding strategy in the red-backed shrike Lanius collurio. Integr. Zool. 2024, 19, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsuk, A.A.; Triseleva, T.A.; Narchuk, E.P.; Matyukhin, A.V.; Safonkin, A.F. Morphology of the wings and attachment apparatus in the evolution of the family Hippoboscidae (Diptera). Integr. Zool. 2023, 19, 941–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.J.; Nengovhela, A.; Denys, C.; Scott, G.R.; Ivy, C.M. Adaptation in brain structure and respiratory and olfactory structures across environmental gradients in African and North American muroid rodents. Integr. Zool. 2024, 19, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.C.; Cai, Y. The importance of brain size for the evolution of nest complexity in birds. Integr. Zool. 2023, 18, 1105–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Shao, W.J.; Zhu, X.; Yang, Y.J.; Jiang, Y.; Liao, W.B. Brain size predicts foraging and escaping abilities in the paddy frogs. Integr. Zool. 2023, 18, 958–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.B.; Liu, Y.X.; Du, X.L.; Li, G.P.; Liao, W.B. Nest complexity correlates with larger brain size but smaller body mass across bird species. Integr. Zool. 2024, 19, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Jiang, Y.; Han, L.X.; Luan, X.F.; Liu, X.; Liao, W.B. Big-brained alien birds tend to occur climatic niche shifts through enhanced behavioral innovation. Integr. Zool. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corballis, M.C. How many lateralities? Laterality 2021, 26, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocklenburg, S.; Güntürkün, O. The Lateralized Brain: The Neuroscience and Evolution of Hemispheric Asymmetries; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- McManus, C. Half a century of handedness research: Myths, truths; fictions, facts; backwards, but mostly forwards. Brain Neurosci. Adv. 2019, 3, 2398212818820513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knebel, D.; Rigosi, E. Temporal and structural neural asymmetries in insects. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2021, 48, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miletto-Petrazzini, M.E.; Sovrano, V.A.; Vallortigara, G.; Messina, A. Brain and behavioral asymmetry: A lesson from fish. Front. Neuroanat. 2020, 14, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, L.J.; Vallortigara, G. Brain and behavioural asymmetries in nonhuman species. Laterality 2021, 26, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güntürkün, O.; Ströckens, F.; Ocklenburg, S. Brain lateralization: A comparative perspective. Physiol. Rev. 2020, 100, 1019–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiebaut de Schotten, M.; Beckmann, C.F. Asymmetry of brain structure and function: 40 years after Sperry’s Nobel Prize. Brain Struct. Funct. 2022, 227, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhao, C.X.; Xiong, Y.R.; Zhong, S.Y.; Wu, D.; Peng, S.L.; Thiebaut de Schotten, M.; Gong, G.L. Callosal fiber length scales with brain size according to functional lateralization, evolution, and development. J. Neurosci. 2022, 42, 3599–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, D.V.M. What does lack of language lateralization signify? Evidence of fluctuating asymmetry rather than hemispheric equipoise on non-lateralized tasks. Roy. Soc. Open Sci. 2024, 11, 240495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Wang, F.; Wu, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; Shen, D.; Li, G. Mapping hemispheric asymmetries of the macaque cerebral cortex during early brain development. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2019, 41, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, Y.; Claidière, N.; Margiotoudi, K.; Marie, D.; Roth, M.; Nazarian, B.; Anton, J.L.; Coulon, O.; Meguerditchian, A. Broca’s cerebral asymmetry refects gestural communication’s lateralisation in monkeys (Papio anubis). eLife 2022, 11, e70521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marie, D.; Roth, M.; Lacoste, R.; Nazarian, B.; Bertello, A.; Anton, J.L.; Hopkins, W.D.; Margiotoudi, K.; Love, S.A.; Meguerditchian, A. Left brain asymmetry of the planum temporale in a nonhominid primate: Redefning the origin of brain specialization for language. Cereb. Cortex 2017, 28, 1808–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Robles, A.; Hopkins, W.D.; Schapiro, S.J.; Sherwood, C.C. The heritability of chimpanzee and human brain asymmetry. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 283, 20161319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, Y.; Meguerditchian, A. Structural brain asymmetries for language: A comparative approach across primates. Symmetry 2022, 14, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, L.J.; Sink, H.S. Transient asymmetry in the projections of the rostral thalamus to the visual hyperstriatum of the chicken, and reversal of its direction by light exposure. Exp. Brain Res. 1988, 70, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, L.J. Light experience and asymmetry of brain function in chickens. Nature 1982, 297, 223–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manns, M.; Gunturkun, O. Monocular deprivation alters the direction of functional and morphological asymmetries in the pigeon’s (Columba livia) visual system. Behav. Neurosci. 1999, 113, 1257–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisazza, A.; Facchin, L.; Pignatti, R.; Vallortigara, G. Lateralization of detour behaviour in poeciliid fish: The effect of species, gender and sexual motivation. Behav. Brain Res. 1998, 91, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budaev, S.; Andrew, R.J. Patterns of early embryonic light exposure determine behavioural asymmetries in zebrafish: A habenular hypothesis. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 200, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemali, M.; Guglielmotti, V.; Fiorino, L. The asymmetry of the habenular nuclei of female and male frogs in spring and in winter. Brain Res. 1990, 517, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamora-camacho, F.J. Sex and habitat differences in size and coloration of an amphibian’s poison glands match differential predator pressures. Integr. Zool. 2022, 17, 764–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.W.; Zhang, L.X.; Lu, X. Global gaps in age data based on skeletochronology for amphibians. Integr. Zool. 2022, 17, 752–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippolis, G.; Bisazza, A.; Rogers, L.J.; Vallortigara, G. Lateralisation of predator avoidance responses in three species of toads. Laterality 2002, 7, 163–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinmetz, H. Structure, functional and cerebral asymmetry: In vivo morphometry of the planum temporale. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1996, 20, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sion, G. Foot-preference underlies bite-scar asymmetry in the gecko Ptyodactylus guttatus. Laterality Asymmetries Body Brain Cogn. 2017, 23, 129–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennings, D.J.; Gammell, M.P. Fluctuating asymmetry of fallow deer antlers is associated with weapon damage but not tactical behaviour during fights. Symmetry 2023, 15, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versace, E.; Vallortigara, G. Forelimb preferences in human beings and other species: Multiple models for testing hypotheses on lateralization. Front. Psychol. 2015, 6, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, Y.L.; Rothenstein, D.; Sivan, N. Directional asymmetry in reptiles (Sauria: Gekkonidae: Ptyodactylus) and its possible role, with implications for biometrical methodology. J. Zool. 1991, 225, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, A.J.; Suchard, M.A.; Xie, D.; Rambaut, A. Bayesian phylogenetics with BEAUti and the BEAST 1.7. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 1969–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A. Tracer v1.6. 2014. Available online: http://beast.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/tracer/ (accessed on 28 June 2024).
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Development Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Freckleton, R.P.; Harvey, P.H.; Pagel, M. Phylogenetic analysis and comparative data: A test and review of evidence. Am. Nat. 2002, 160, 712–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagel, M. Inferring the historical patterns of biological evolution. Nature 1999, 401, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, E. Analysis of Phylogenetics and Evolution with R; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pagel, M. Detecting correlated evolution on phylogenies: A general method for the comparative analysis of discrete characters. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 1994, 255, 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Geschwind, N.; Galaburda, A.M. Cerebral lateralization. Biological mechanisms, associations, and pathology. Arch. Neurol. 1985, 42, 428–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calfayan, L.M.; Cavia, R.; Fraschina, J.; Guidobono, J.S.; Gorosito, I.L.; Busch, M. Environmental drivers of long-term variations in the abundance of the red hocicudo mouse (Oxymycterus rufus) in Pampas agroecosystems. Integr. Zool. 2024, 19, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massei, G.; Jacob, J.; Hinds, L.A. Developing fertility control for rodents: A framework for researchers and practitioners. Integr. Zool. 2024, 19, 87–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.X.; Song, C.; Wang, P.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhan, S. Generating dual active species by triple-atom-sites through peroxymonosulfate activation for treating micropollutants in complex water. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2300085120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.X.; Xue, W.; Cui, X.; Wang, P.; Zuo, S.; Mo, F.; Li, C.; Liu, G.; Ouyang, S.; Zhan, S.; et al. Oxygen bridging Fe, Co dual-metal dimers boost reversible oxygen electrocatalysis for rechargeable Zn-air batteries. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2404013121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.; Zhou, R.; Wang, P.; Zhou, Q.X. Selective hydroxyl generation for efficient pollutant degradation by electronic structure modulation at Fe sites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2305378120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringo, J.L.; Doty, R.W.; Demeter, S.; Simard, P.Y. Time is of the essence: A conjecture that hemispheric specialization arises from interhemispheric conduction delay. Cereb. Cortex 1994, 4, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cante-Bazán, E.; Luría-Manzano, R. Seasonal variation of the relationship between body condition and fluctuating asymmetry in two sympatric ranid frogs. Herpetol. J. 2024, 34, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasnelli, E.; Vallortigara, G.; Rogers, L.J. Left–right asymmetries of behaviour and nervous system in invertebrates. Neurosci. Bio-Behav. Rev. 2012, 36, 1273–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallortigara, G.; Rogers, L.J. Survival with an asymmetrical brain: Advantages and disadvantages of cerebral lateralization. Behav. Brain Sci. 2005, 28, 575–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, K.L.; Preuss, T.M. A comparative perspective on the human temporal lobe. In Digital Endocasts; Bruner, E., Ogihara, N., Tanabe, H., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2018; pp. 239–258. [Google Scholar]
- Vallortigara, G. Comparative neuropsychology of the dual brain: A stroll through animals’ left and right perceptual worlds. Brain Lang. 2000, 73, 189–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toga, A.W.; Thompson, P.M. Mapping brain asymmetry. Nat. Rev. 2003, 4, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roe, J.M.; Vidal-Pineiro, D.; Amlien, I.K.; Pan, M.Y.; Sneve, M.H.; de Schotten, M.T.; Friedrich, P.; Sha, Z.Q.; Francks, C.; Eilertsen, E.M.; et al. Tracing the development and lifespan change of population-level structural asymmetry in the cerebral cortex. eLife 2023, 12, e84685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Arnatkeviciute, A.; McTavish, E.; Pang, J.C.; Chopra, S.; Suo, C.; Fornito, A.; Aquino, K.M.; Initiative, A.D.N. The individuality of shape asymmetries of the human cerebral cortex. eLife 2022, 11, e75056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, B.; Bayrak, S.; Xu, T.; Schaare, H.L.; Bethlehem, R.A.I.; Bernhardt, B.C.; Valk, S.L. Heritability and cross-species comparisons of human cortical functional organization asymmetry. eLife 2022, 11, e77215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Persem, A.; Roumazeilles, L.; Folloni, D.; Marche, K.; Fouragnan, E.F.; Khalighinejad, N.; Rushworth, M.F.; Sallet, J. Diferential functional connectivity underlying asymmetric reward-related activity in human and nonhuman primates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 28452–28462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jepma, M.; Roy, M.; Ramlakhan, K.; van Velzen, M.; Dahan, A. Different brain systems support learning from received and avoided pain during human pain-avoidance learning. eLife 2022, 11, e74149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkes, L.; Kim, J.Z.; Stiso, J.; Calkins, M.E.; Cieslak, M.; Gur, R.E.; Gur, R.C.; Moore, T.M.; Ouellet, M.; Roalf, D.R.; et al. Asymmetric signaling across the hierarchy of cytoarchitecture within the human connectome. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eadd2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Hong, Y.Y.; Li, Y.B.; Qi, F.J.; Qing, H.T.; Su, H.; Yin, J. Physically intelligent autonomous soft robotic maze escaper. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadi3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merrick, C.M.; Dixon, T.C.; Breska, A.; Lin, J.; Chang, E.F.; King-Stephens, D.; Laxer, K.D.; Weber, P.B.; Carmena, J.; Knight, R.T.; et al. Left hemisphere dominance for bilateral kinematic encoding in the human brain. eLife 2022, 11, e69977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berretz, G.; Packheiser, J.; Wolf, O.T.; Ocklenburg, S. Acute stress increases left hemispheric activity measured via changes in frontal alpha asymmetries. iScience 2022, 25, 103841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costalunga, G.; Kobylkov, D.; Rosa-Salva, O.; Morandi-Raikova, A.; Vallortigara, G.; Mayer, U. Responses in the left and right entopallium are differently affected by light stimulation in embryo. iScience 2024, 27, 109268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedigo, B.D.; Powell, M.; Bridgeford, E.W.; Winding, M.; Priebe, C.E.; Vogelstein, J.T.; Ostojic, S. Generative network modeling reveals quantitative definitions of bilateral symmetry exhibited by a whole insect brain connectome. eLife 2023, 12, e83739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veréb, D.; Mijalkov, M.; Canal-Garcia, A.; Chang, Y.W.; Gomez-Ruiz, E.; Gerboles, B.Z.; Kivipelto, M.; Svenningsson, P.; Zetterberg, H.; Volpe, G.; et al. Age-related differences in the functional topography of the locus coeruleus and their implications for cognitive and affective functions. eLife 2023, 12, RP87188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringers, C.; Bialonski, S.; Ege, M.; Solovev, A.; Hansen, J.N.; Jeong, I.; Friedrich, B.M.; Jurisch-Yaksi, N.; Goldstein, R.E. Novel analytical tools reveal that local synchronization of cilia coincides with tissue-scale metachronal waves in zebrafish multiciliated epithelia. eLife 2023, 12, e77701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neubauer, S.; Gunz, P.; Scott, N.A.; Hublin, J.J.; Mitteroecker, P. Evolution of brain lateralization: A shared hominid pattern of endocranial asymmetry is much more variable in humans than in great apes. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaax9935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.L.; Liu, Q.; Hubbard, C.S.; Wang, D.H.; Zhu, W.Z.; Fox, M.D.; Liu, H.S. Robust dynamic brain coactivation states estimated in individuals. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eabq8566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocklenburg, S.; Strockens, F.; Gunturkun, O. Lateralisation of conspecifific vocalisation in non-human vertebrates. Laterality 2013, 18, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, K.; Kurashima, R.; Gokan, H.; Inoue, N.; Ito, I.; Watanabe, S. Left-right asymmetry defect in the hippocampal circuitry impairs spatial learning and working memory in IV mice. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual, A.; Huang, K.L.; Neveu, J.; Preat, T. Neuroanatomy: Brain asymmetry and long-term memory. Nature 2004, 427, 605–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, L.J.; Vallortigara, G. From antenna to antenna: Lateral shift of olfactory memory recall by honeybees. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, L.J. Hand and paw preferences in relation to the lateralized brain. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 943–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallortigara, G.; Rogers, L.J.; Bisazza, A.; Lippolis, G.; Robins, A. Complementary right and left hemififield use for predatory and agonistic behaviour in toads. Neuroreport 1998, 9, 3341–3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, L.J.; Zucca, P.; Vallortigara, G. Advantages of having a lateralized brain. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2004, 271, S420–S422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robins, A.; Rogers, L.J. Lateralized prey-catching responses in the cane toad, Bufo marinus: Analysis of complex visual stimuli. Anim. Behav. 2004, 68, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robins, A.; Rogers, L.J. Lateralized motor behaviour in the righting responses of the cane toad (Rhinella marina). Laterality 2022, 27, 129–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robins, A.; Lippolis, G.; Bisazza, A.; Vallortigara, G.; Rogers, L.J. Lateralized agonistic responses and hindlimb use in toads. Anim. Behav. 1998, 56, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, J.L.; Lewis, P.A.; Dunbar, R.I.M.; García-Fiñana, M.; Roberts, N. Orbital prefrontal cortex volume correlates with social cognitive competence. Neuropsychologia 2010, 48, 3554–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, L.J.; Rigosi, E.; Frasnelli, E.; Vallortigara, G. A right antenna for social behaviour in honeybees. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghirlanda, S.; Frasnelli, E.; Vallortigara, G. Intraspecific competition and coordination in the evolution of lateralization. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghirlanda, S.; Vallortigara, G. The evolution of brain lateralization: Game theoretical analysis of population structure. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2004, 271, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasnelli, E.; Vallortigara, G. Individual-level and population-level lateralization: Two sides of the same coin. Symmetry 2018, 10, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anfora, G.; Frasnelli, E.; Maccagnani, B.; Rogers, L.J.; Vallortigara, G. Behavioural and electrophysiological lateralization in a social (Apis mellifera) but not in a non-social (Osmia cornuta) species of bee. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 206, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisazza, A.; Cantalupo, C.; Capocchiano, M.; Vallortigara, G. Population lateralisation and social behaviour: A study with 16 species of fish. Laterality 2000, 5, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.F.; Qin, Y.Y.; Jin, Y.J.; Wang, J.C.; Liang, W. Snake-like bird hisses induce anti-predator responses in a frog. BMC Ecol. Evol. 2024, 24, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.B. Adaptation in Brain Size in Anurans; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]

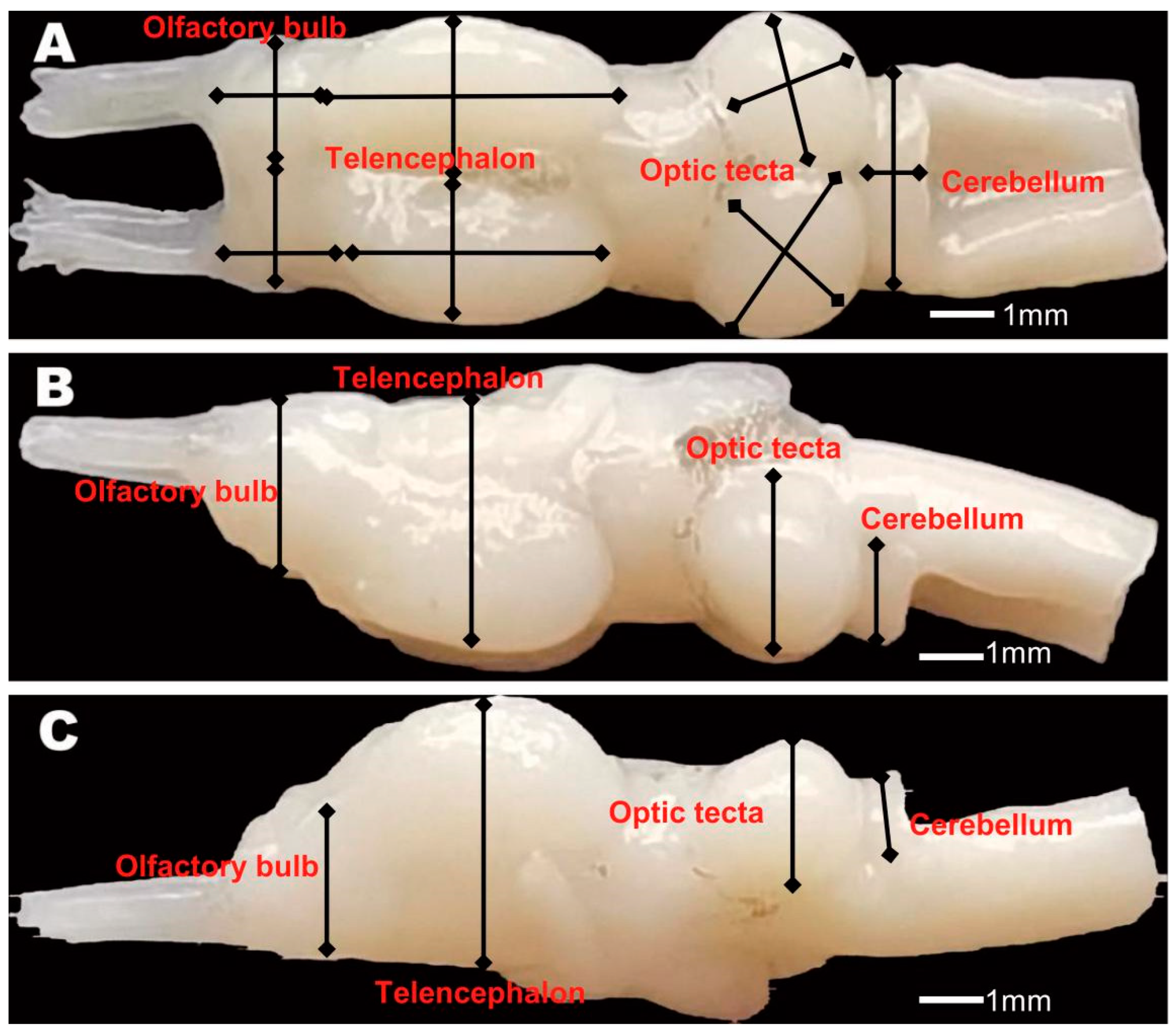
| Brain Regions | Left Hemisphere (mm3) | Right Hemisphere (mm3) | t | df | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Olfactory bulb | 2.745 ± 0.387 | 2.692 ± 0.393 | 10.636 | 54 | <0.001 |
| Telencephalon | 3.678 ± 0.338 | 3.641 ± 0.348 | 8.802 | 53 | <0.001 |
| Optic tecta | 3.500 ± 0.395 | 3.467 ± 0.405 | 2.202 | 22 | 0.038 |
| Total brain | 4.351 ± 0.362 | 4.315 ± 0.368 | 10.280 | 56 | <0.001 |
| Dependent Variable | Brain Regions | Independent Variable | λ | R2 | β | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
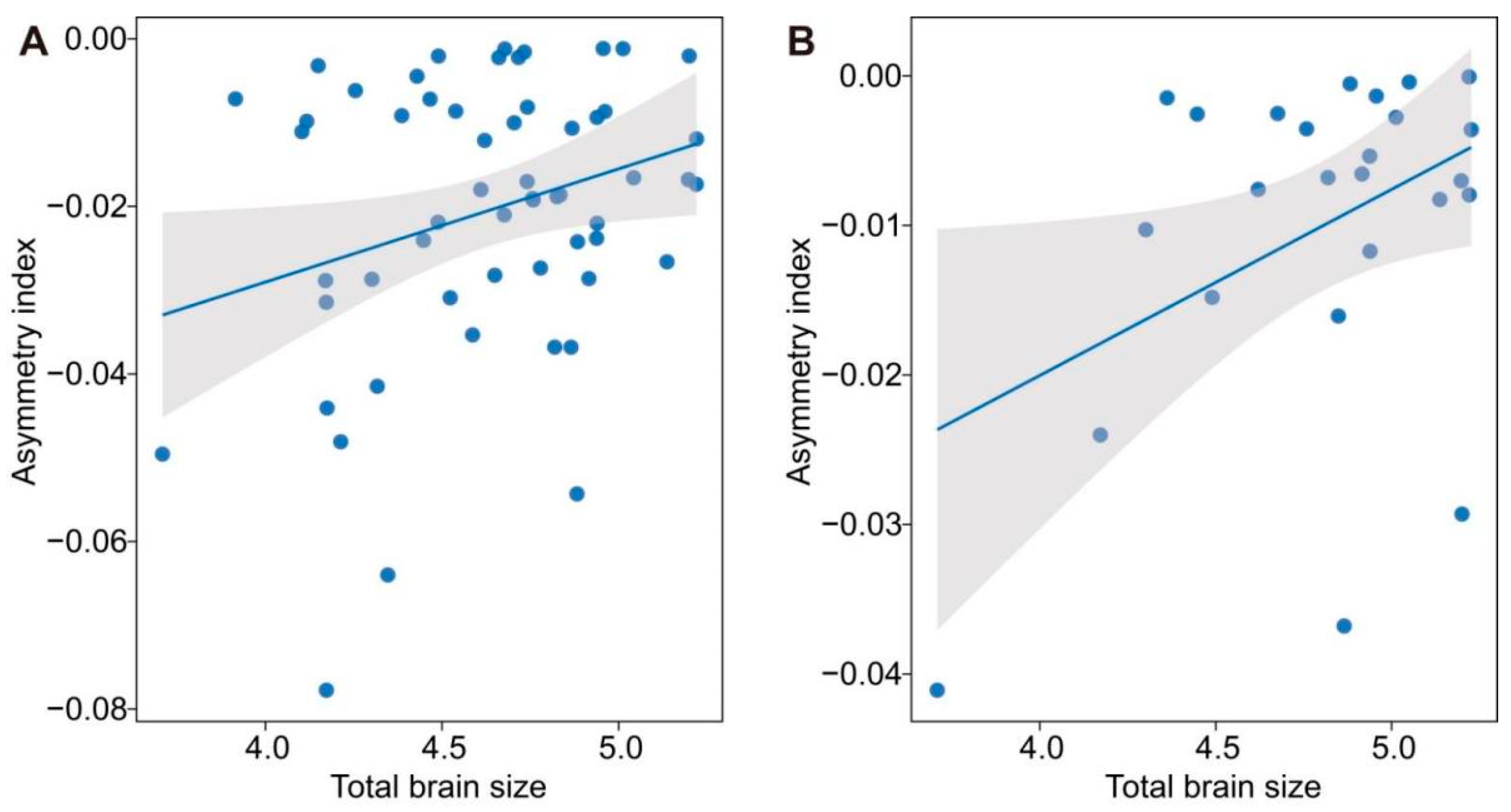
| Asymmetry index | Olfactory bulb | Total brain | <0.001(<0.001, 0.915) | 0.090 | 0.038 | 2.349 | 0.022 |
| SVL | −0.054 | −1.636 | 0.108 | ||||
| Telencephalon | Total size | <0.0001(<0.001, 0.348) | 0.128 | 0.019 | 1.801 | 0.077 | |
| SVL | −0.017 | −0.830 | 0.410 | ||||
| Optic tecta | Total brain | 0.460(<0.001, 0.952) | 0.140 | 0.035 | 2.378 | 0.027 | |
| SVL | −0.059 | −1.975 | 0.061 | ||||
| Total brain | Total size | 0.036(<0.001, 0.396) | 0.105 | 0.013 | 1.909 | 0.061 | |
| SVL | −0.013 | −0.944 | 0.349 |
| Brain Regions | Left Hemisphere (mm3) | Right Hemisphere (mm3) | t | df | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Olfactory bulb | 2.684 ± 0.416 | 2.739 ± 0.405 | −5.556 | 39 | <0.001 |
| Telencephalon | 3.759 ± 0.294 | 3.796 ± 0.292 | −2.517 | 40 | 0.016 |
| Optic tecta | 3.323 ± 0.343 | 3.373 ± 0.339 | −6.322 | 71 | <0.001 |
| Total brain | 4.365 ± 0.341 | 4.397 ± 0.341 | −4.077 | 37 | <0.001 |
| Dependent Variable | Brain Regions | Independent Variable | λ | R2 | β | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
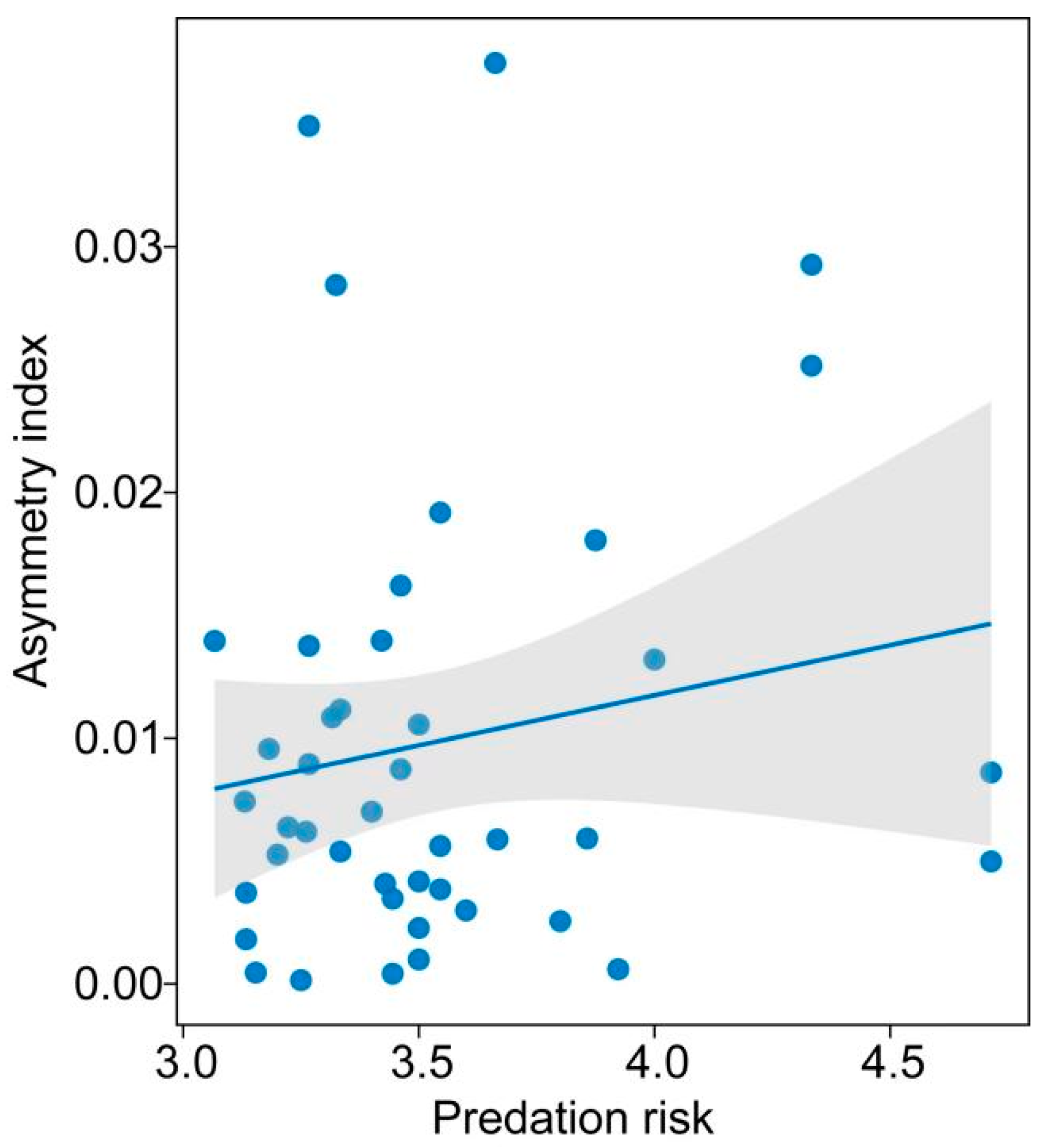
| Asymmetry index | Olfactory bulb | Predation risk | <0.001(<0.001, 0.332) | 0.070 | −0.022 | −1.785 | 0.082 |
| SVL | −0.049 | −2.171 | 0.036 | ||||
| Telencephalon | Predation risk | 1(0.032, <0.001) | 0.077 | 0.008 | 2.289 | 0.027 | |
| SVL | 0.016 | 1.600 | 0.118 | ||||
| Optic tecta | Predation risk | 0.060(<0.001, 0.434) | 0.017 | 0.002 | 0.335 | 0.739 | |
| SVL | −0.014 | −1.297 | 0.199 | ||||
| Total brain | Predation risk | 0.262(0.034, 0.676) | −0.015 | 0.003 | 1.080 | 0.287 | |
| SVL | 0.006 | 1.019 | 0.315 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, C.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Cao, L.; Liao, W. Exploring Brain Size Asymmetry and Its Relationship with Predation Risk Among Chinese Anurans. Biology 2025, 14, 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14010038
Chen C, Jiang Y, Wu Y, Cao L, Liao W. Exploring Brain Size Asymmetry and Its Relationship with Predation Risk Among Chinese Anurans. Biology. 2025; 14(1):38. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14010038
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Chuan, Ying Jiang, Yiming Wu, Lingsen Cao, and Wenbo Liao. 2025. "Exploring Brain Size Asymmetry and Its Relationship with Predation Risk Among Chinese Anurans" Biology 14, no. 1: 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14010038
APA StyleChen, C., Jiang, Y., Wu, Y., Cao, L., & Liao, W. (2025). Exploring Brain Size Asymmetry and Its Relationship with Predation Risk Among Chinese Anurans. Biology, 14(1), 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14010038





