The Role of Aquaculture in Shaping the Morphology of Babylonia areolata: A Comparative Study of Cultured and Wild Populations
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sampling
2.2. Morphological Measurements
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Ethical Approval
3. Results
3.1. Morphological Parameter Comparison
3.2. Correlation Analysis
3.3. Standardized Data Descriptive Statistics
3.4. Significant Differences in Morphological Parameters
3.5. Results and Analysis of Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
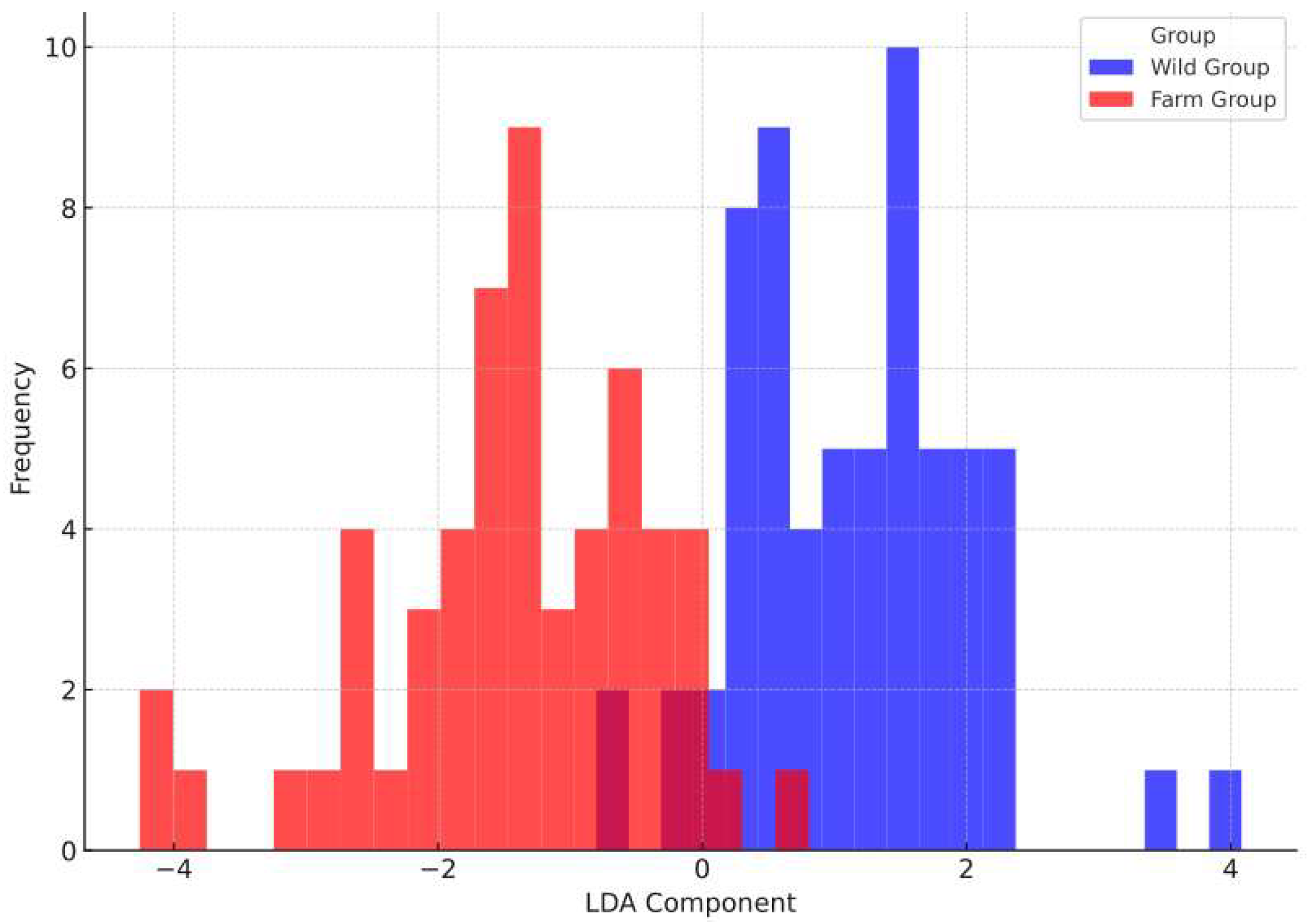
3.6. Discriminant Analysis Results
4. Discussion
4.1. The Influence of Environment on Morphological Development
4.2. The Role of Genetic and Environmental Interactions
4.3. Optimization of Aquaculture Management
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Padilla, D.K.; McCann, M.J.; Shumway, S.E. Marine invaders and bivalve aquaculture: Sources, impacts, and consequences. In Shellfish Aquaculture and the Environment; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 395–424. [Google Scholar]
- Allison, E.H.; Badjeck, M.C.; Meinhold, K. The implications of global climate change for molluscan aquaculture. In Shellfish Aquaculture and the Environment; Wiley-Blackwell: Singapore, 2011; pp. 461–490. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, H.; Zheng, J.; Long, K.; Shi, Y.; Gu, Z.; Wang, A. Eight polymorphic microsatellite markers for the spotted babylon, Babylonia areolata (Buccinidae). Genet. Mol. Res. 2011, 10, 3230–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaitanawisuti, N.; Kritsanapuntu, S.; Natsukari, Y. Economic analysis of a pilot commercial production for spotted babylon, Babylonia areolata (Link 1807), of marketable sizes using a flow-through culture system in Thailand. Aquac. Res. 2002, 33, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, W.; Zhong, M.; Fu, J.; Ke, S.; Gan, B.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, M.; Ke, C. Comparison and optimal prediction of growth of Babylonia areolata and B. lutosa. Aquac. Rep. 2020, 18, 100425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Liang, Y.; Shen, M.; Lü, W.; Luo, X.; You, W.; Ke, C. Survival and immune responses of two populations of Babylonia areolata and their hybrids under pathogenic Vibrio challenge. Aquaculture 2024, 584, 740646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.C.; Flemming, J.M.; Watson, R. Serial exploitation of global sea cucumber fisheries. Fish Fish. 2011, 12, 317–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, D.; Zeller, D. Catch reconstructions reveal that global marine fisheries catches are higher than reported and declining. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harasewych, M.G.; Kantor, Y.I. On the morphology and taxonomic position of Babylonia (Neogastropoda: Babyloniidae). Boll. Malacol. 2003, 38, 19–36. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Ke, C.H.; Zhang, S.Y. Feeding rate responses of Babylonia formosae habei (Prosobranchia: Buccinidae) larvae on cultured algae. Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 1538–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valladares, A.; Manríquez, G.; Suárez-Isla, B.A. Shell shape variation in populations of Mytilus chilensis (Hupe 1854) from southern Chile: A geometric morphometric approach. Mar. Biol. 2010, 157, 2731–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Ke, C.; Zhou, S.; Li, F. Effects of starvation on larval growth, survival and metamorphosis of Ivory shell Babylonia formosae habei Altena et al., 1981 (Neogastropoda: Buccinidae). Aquaculture 2005, 243, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, G.; Peletto, S.; Guo, X.; Pastorino, P.; Arillo, A.; Martini, I.; Acutis, P.L.; Mugetti, D.; Meloni, D.; Prearo, M. Genetic Variability in Mediterranean Coastal Ecosystems: Insights into Ostrea spp. (Bivalvia: Ostreidae). Biology 2024, 13, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callier, M.D.; Byron, C.J.; Bengtson, D.A.; Cranford, P.J.; Cross, S.F.; Focken, U.; Jansen, H.M.; Kamermans, P.; Kiessling, A.; Landry, T. Attraction and repulsion of mobile wild organisms to finfish and shellfish aquaculture: A review. Rev. Aquac. 2018, 10, 924–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulzar, I.; Kumar, S.; Shikari, A.B.; Tutlani, A. Exploring correlations, diversity and principal component analysis of agromorphological and seed quality traits in rajmash (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Plant Arch. 2024, 24, 1547–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-Q.; Guo, H.-Y.; Liu, B.-S.; Zhang, N.; Zhu, K.-C.; Zhang, D.-C. Analysis of morphological differences in five large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) populations. Isr. J. Aquac.-Bamidgeh 2024, 76, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.M.S.; Salem, M.M.I.; Ashour, A.F.; EL Nagar, A.G. Principal component analysis of phenotypic and breeding value data for semen traits in Egyptian buffalo bulls. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2024, 56, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Qayyum, A.; Sher, A.; Nadeem, F.; Fiaz, S.; Kumar, S.; Alharthi, B.; Ercisli, S. Analyzing phenotypic diversity in Brassica rapa genotypes based on morpho-physiological characteristics using multivariate analyses. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2024, 71, 2053–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Sturmer, L.N.; Baker, S. Molluscan shellfish aquaculture and production. EDIS 2014, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, M.; Esler, D.; Boyd, W.S. Morphology and density of mussels on natural and aquaculture structure habitats: Implications for sea duck predators. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 346, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, G.; Centoducati, G.; Gasco, L.; Gatta, P.P.; Moretti, V.M.; Piccolo, G.; Roncarati, A.; Terova, G.; Pais, A. Molluscs and echinoderms aquaculture: Biological aspects, current status, technical progress and future perspectives for the most promising species in Italy. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 11, e72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babushkin, E.; Dunaeva, D.; Murashko, Y.A. To the fauna end ecology of freshwater mollusks of the Konda River basin (Khanty-Mansi autonomous okrug–Yugra). In Proceedings of the 11th International Scientific and Practical Conference, Nizhnevartovsk, Russia, 9–10 November 2024; pp. 403–410. [Google Scholar]
- Jimi, N.; Britayev, T.A.; Sako, M.; Woo, S.P.; Martin, D. A new genus and species of nudibranch-mimicking Syllidae (Annelida, Polychaeta). Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 17123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroz-Barroso, S.A.; Guerrero-Arenas, R.; García-Barrera, P.; Sánchez-Beristain, F. Mollusca: Bivalvia and Gastropoda. In Past Environments of Mexico; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 63–97. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, K.; Wang, H.; Lu, K.; Zhu, W. Morphological variation and distinction in cultured and wild populations of Pseudosciaena crocea in the East China Sea. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2024, 22, 2065–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, N.J.; Aguilera, F. Spiralian genomics in a changing world. Front. Genet. 2024, 11, 1501345. [Google Scholar]
- Trussell, G.C. Phenotypic clines, plasticity, and morphological trade-offs in an intertidal snail. Evolution 2000, 54, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Trussell, G.C.; Etter, R.J. Integrating genetic and environmental forces that shape the evolution of geographic variation in a marine snail. Microevol. Rate Pattern Process 2001, 112, 321–337. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz, P.; Ramirez, J.L.; Garcia, G.A.; Ibarra, A.M. Genetic differences between two populations of catarina scallop (Argopecten ventricosus) for adaptations for growth and survival in a stressful environment. Aquaculture 1998, 166, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokrani, A.; Li, J.; Li, Q.; Liu, S. Toward understanding mechanistic regulation of body size and growth control in bivalve mollusks. Rev. Aquac. 2024, 17, e12962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, C.; Sato-Okoshi, W. Polydorid polychaetes on farmed molluscs: Distribution, spread and factors contributing to their success. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2015, 7, 147–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravalo, L.G. Native and Invasive Smooth Shelled Blue Mussels (Mytilus spp.) in New Zealand: Evolutionary, Biosecurity and Aquaculture Implications. Ph.D. Thesis, Te Herenga Waka—Victoria University of Wellington, Wellington, New Zealand, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X. Use and exchange of genetic resources in molluscan aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2009, 1, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollenbeck, C.M.; Johnston, I.A. Genomic tools and selective breeding in molluscs. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šegvić-Bubić, T.; Grubišić, L.; Trumbić, Ž.; Stanić, R.; Ljubković, J.; Maršić-Lučić, J.; Katavić, I. Genetic characterization of wild and farmed European seabass in the Adriatic sea: Assessment of farmed escapees using a Bayesian approach. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2017, 74, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šegvić-Bubić, T.; Žužul, I.; Talijančić, I.; Ugrin, N.; Lepen Pleić, I.; Žuvić, L.; Stagličić, N.; Grubišić, L. Translocation and aquaculture impact on genetic diversity and composition of wild self-sustainable Ostrea edulis populations in the Adriatic sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Thompson, S.; Glaser, M. Global aquaculture productivity, environmental sustainability, and climate change adaptability. Environ. Manag. 2019, 63, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
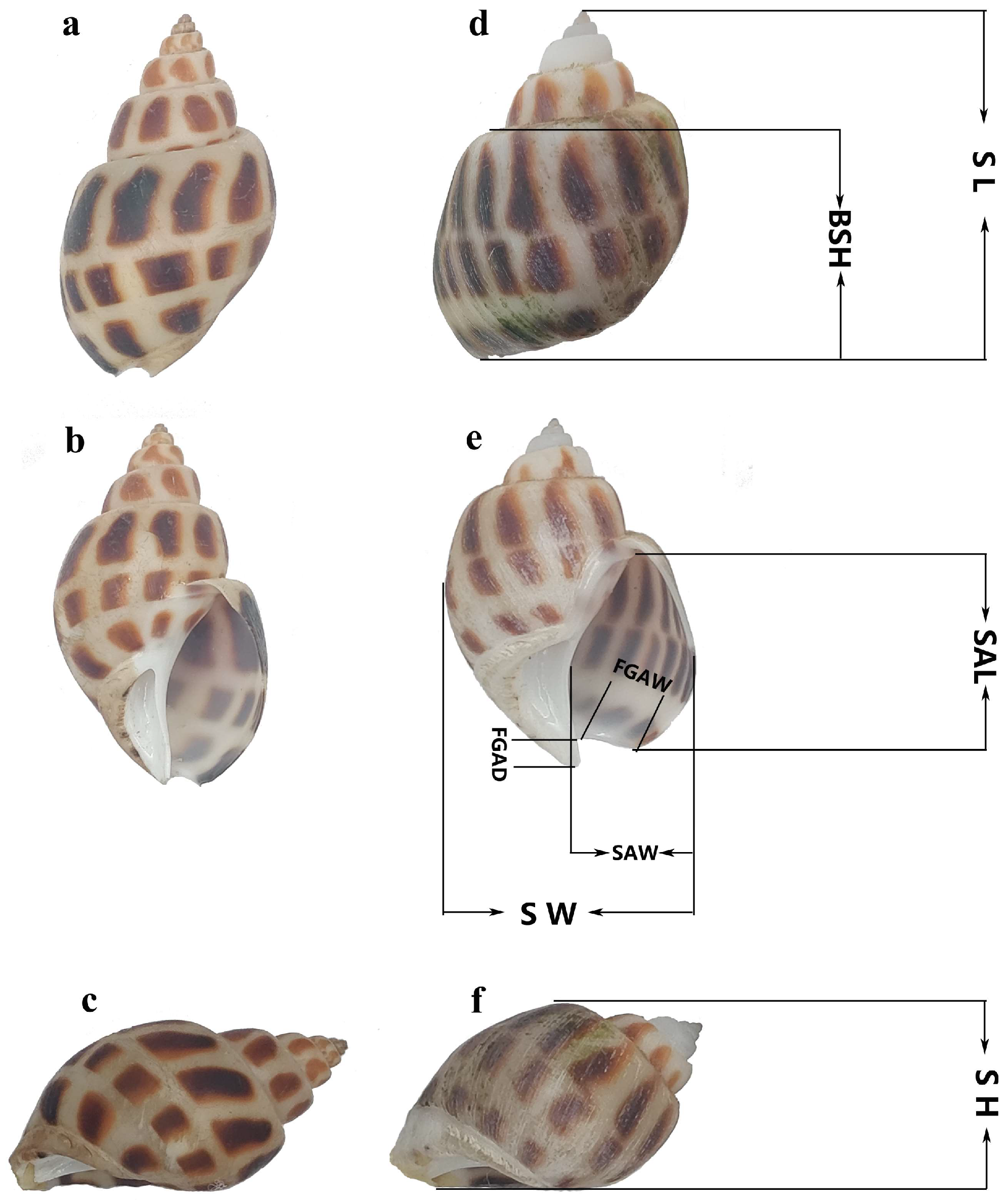
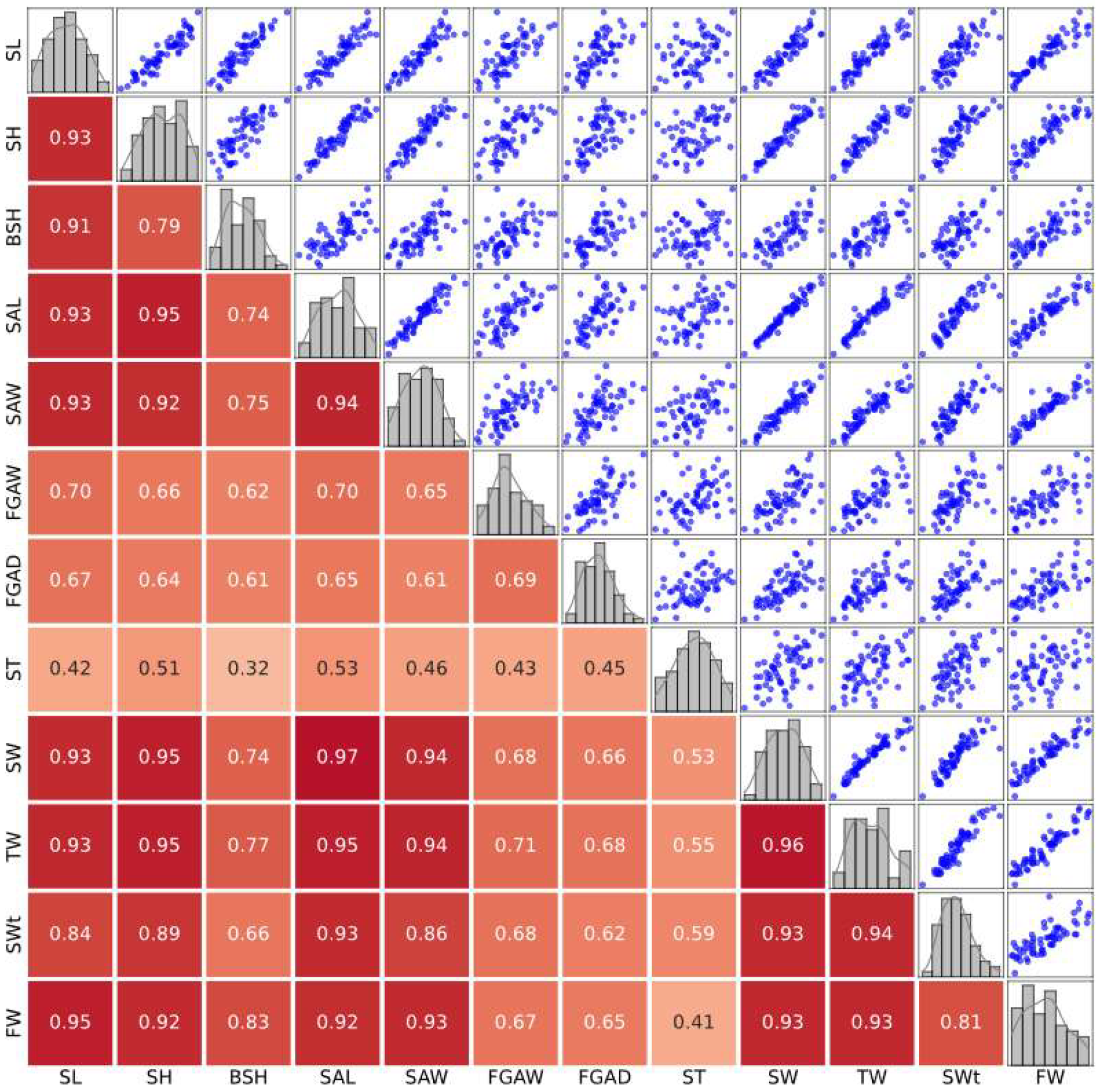
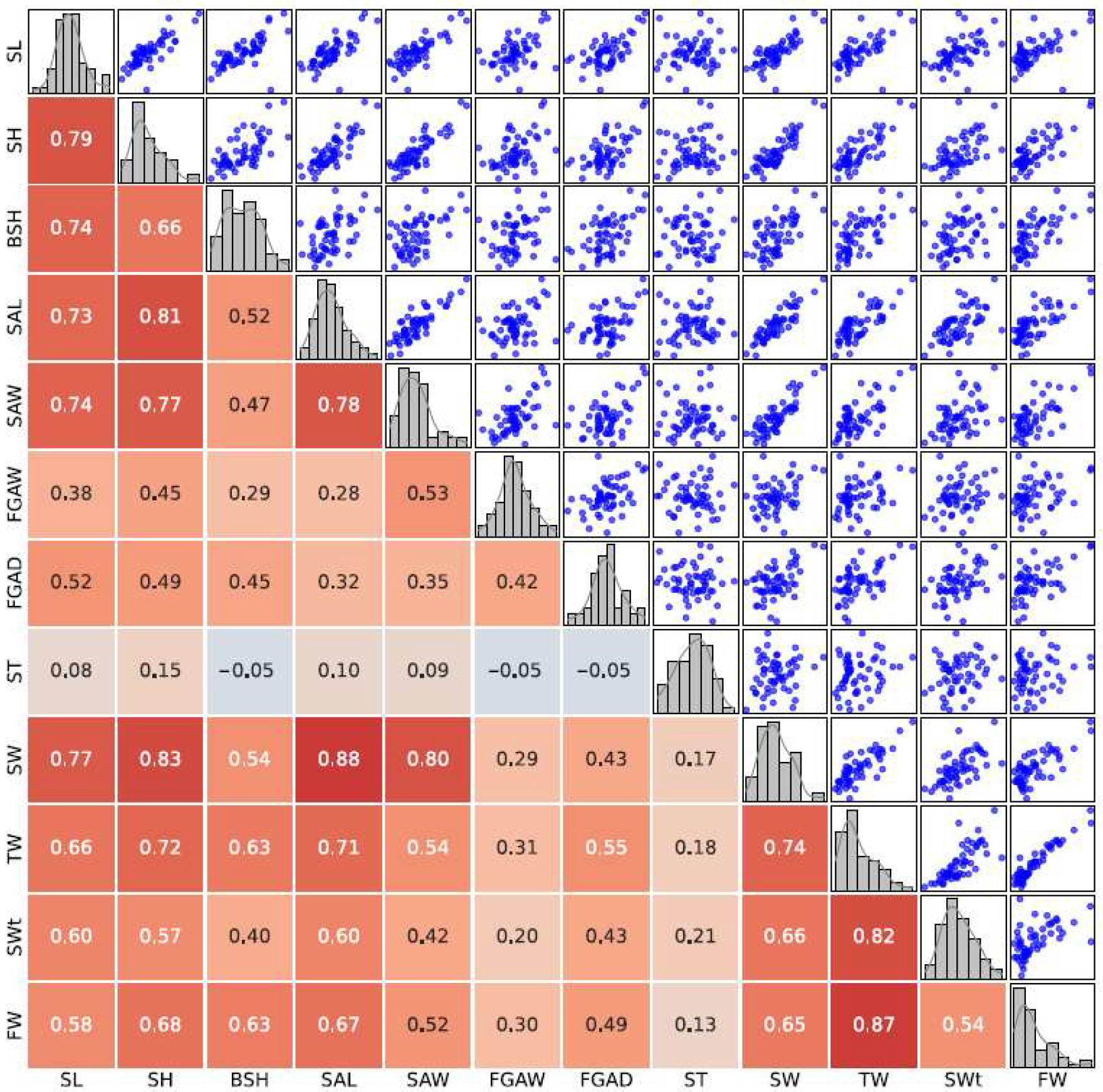


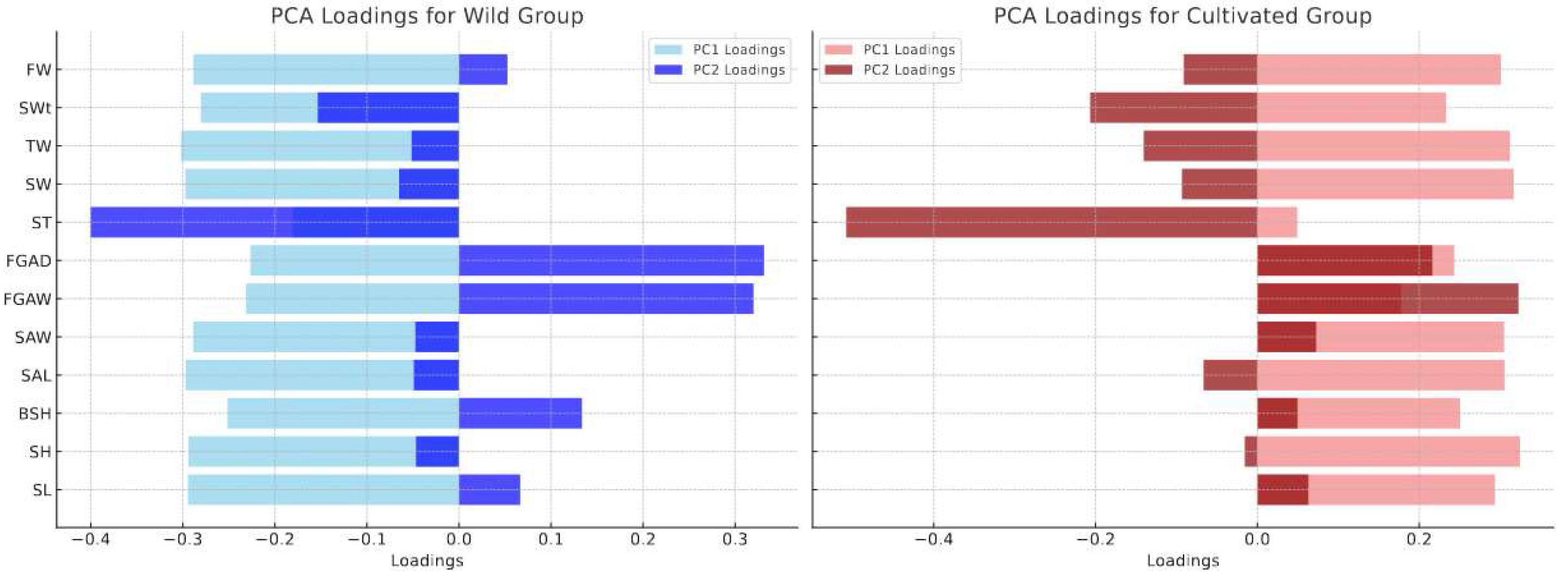
| Parameter | Wild Group | Cultivated Group | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | CV | Cultivated | CV | |
| SL | 36.48 ± 3.77 | 10.33% | 39.31 ± 2.41 | 6.14% |
| SH | 20.98 ± 2.25 | 10.73% | 23.27 ± 1.40 | 6.01% |
| BSH | 15.98 ± 2.21 | 13.85% | 17.32 ± 1.73 | 9.97% |
| SAL | 23.40 ± 2.46 | 10.52% | 25.69 ± 1.24 | 4.84% |
| SAW | 11.09 ± 1.30 | 11.75% | 12.49 ± 0.75 | 6.03% |
| FGAW | 4.58 ± 0.75 | 16.29% | 4.87 ± 0.67 | 13.86% |
| FGAD | 4.28 ± 0.61 | 14.24% | 4.57 ± 0.39 | 8.58% |
| ST | 0.51 ± 0.09 | 17.74% | 0.49 ± 0.07 | 14.41% |
| SW | 23.14 ± 2.40 | 10.39% | 26.10 ± 1.39 | 5.34% |
| TW | 9.43 ± 2.79 | 29.56% | 12.39 ± 2.31 | 18.66% |
| SWt | 5.30 ± 1.52 | 28.73% | 5.63 ± 0.84 | 14.93% |
| FW | 3.91 ± 1.30 | 33.19% | 6.39 ± 1.72 | 26.96% |
| Parameter | Wild Group | Cultivated Group | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | CV | Cultivated | CV | |
| R_BSH | 0.4371 ± 0.0261 | 5.98% | 0.4405 ± 0.0345 | 7.83% |
| R_FGAD | 0.1175 ± 0.0122 | 10.36% | 0.1164 ± 0.0080 | 6.91% |
| R_FGAW | 0.1256 ± 0.0145 | 11.51% | 0.1239 ± 0.0161 | 12.98% |
| R_FW | 0.1050 ± 0.0256 | 24.37% | 0.1616 ± 0.0377 | 23.32% |
| R_SAL | 0.6419 ± 0.0260 | 4.05% | 0.6545 ± 0.0297 | 4.53% |
| R_SAW | 0.3038 ± 0.0150 | 4.92% | 0.3180 ± 0.0130 | 4.09% |
| R_SH | 0.5753 ± 0.0233 | 4.04% | 0.5924 ± 0.0236 | 3.99% |
| R_ST | 0.0140 ± 0.0023 | 16.47% | 0.0125 ± 0.0019 | 15.14% |
| R_SW | 0.6349 ± 0.0268 | 4.23% | 0.6647 ± 0.0279 | 4.19% |
| R_SWt | 0.1434 ± 0.0302 | 21.06% | 0.1431 ± 0.0188 | 13.11% |
| R_TW | 0.2539 ± 0.0522 | 20.55% | 0.3142 ± 0.0488 | 15.53% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Chen, Z.; Tong, Y.; Ye, L.; Li, Y. The Role of Aquaculture in Shaping the Morphology of Babylonia areolata: A Comparative Study of Cultured and Wild Populations. Biology 2025, 14, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14010039
Wang H, Chen Z, Tong Y, Ye L, Li Y. The Role of Aquaculture in Shaping the Morphology of Babylonia areolata: A Comparative Study of Cultured and Wild Populations. Biology. 2025; 14(1):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14010039
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Haishan, Zhi Chen, Yuhe Tong, Le Ye, and Youming Li. 2025. "The Role of Aquaculture in Shaping the Morphology of Babylonia areolata: A Comparative Study of Cultured and Wild Populations" Biology 14, no. 1: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14010039
APA StyleWang, H., Chen, Z., Tong, Y., Ye, L., & Li, Y. (2025). The Role of Aquaculture in Shaping the Morphology of Babylonia areolata: A Comparative Study of Cultured and Wild Populations. Biology, 14(1), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14010039






