NF-κB-Inducing Kinase Is Essential for Effective c-Rel Transactivation and Binding to the Il12b Promoter in Macrophages
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mice
2.2. Cells
2.3. Reagents
2.4. Cytokine Determination
2.5. Flow Cytometry
2.6. Real-Time PCR
2.7. Transient Transfection and Luciferase Assays
2.8. Western Blot and Immunoprecipitation
2.9. Confocal Imaging
2.10. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Assay
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
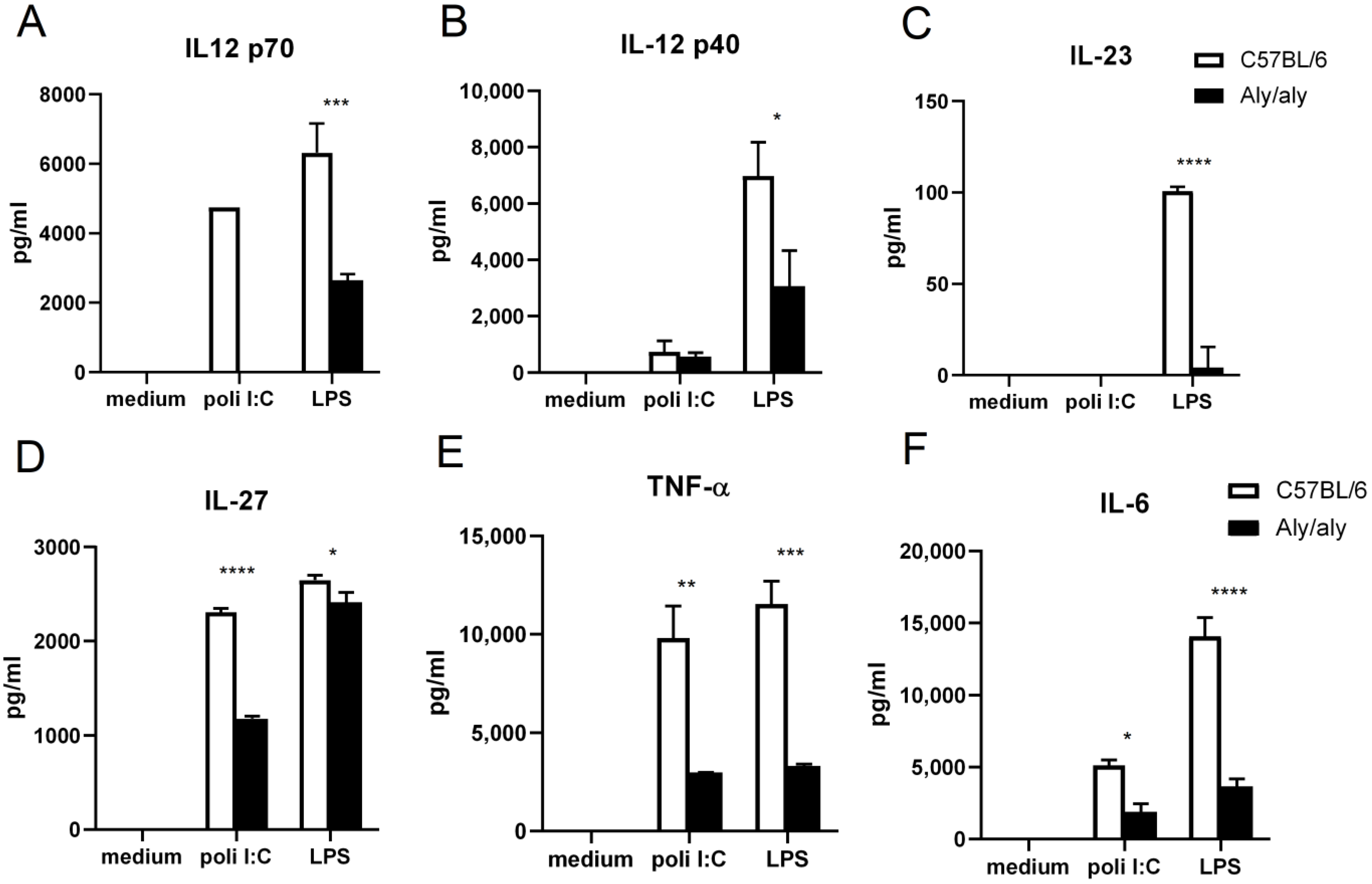
3.1. Defective Activation of aly/aly Macrophages in Response to TLR Agonists
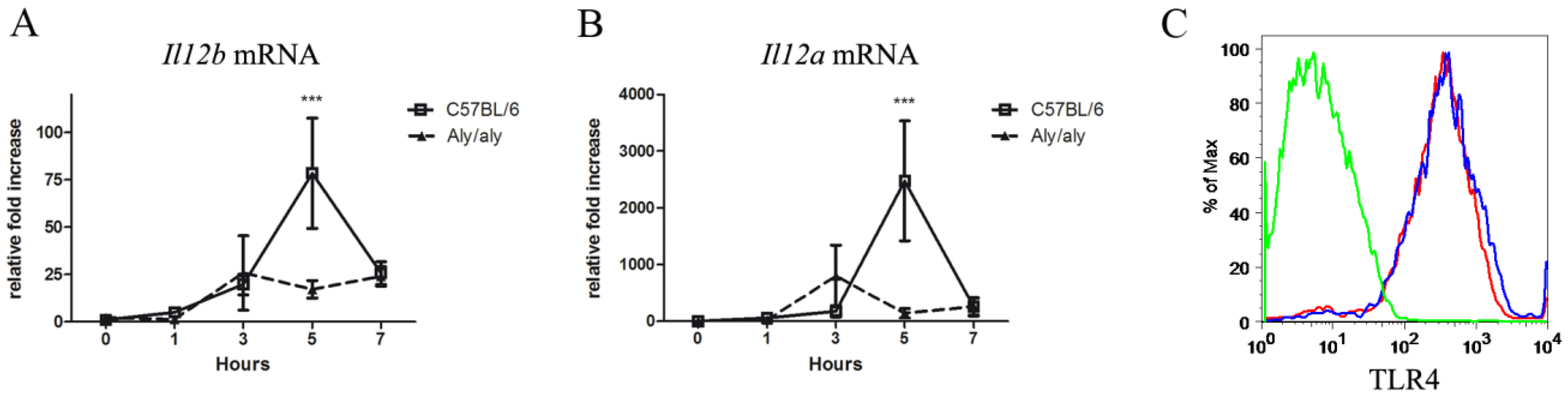
3.2. The aly/aly Mutation Affects the Transcription of the Il12b and Il12a Genes
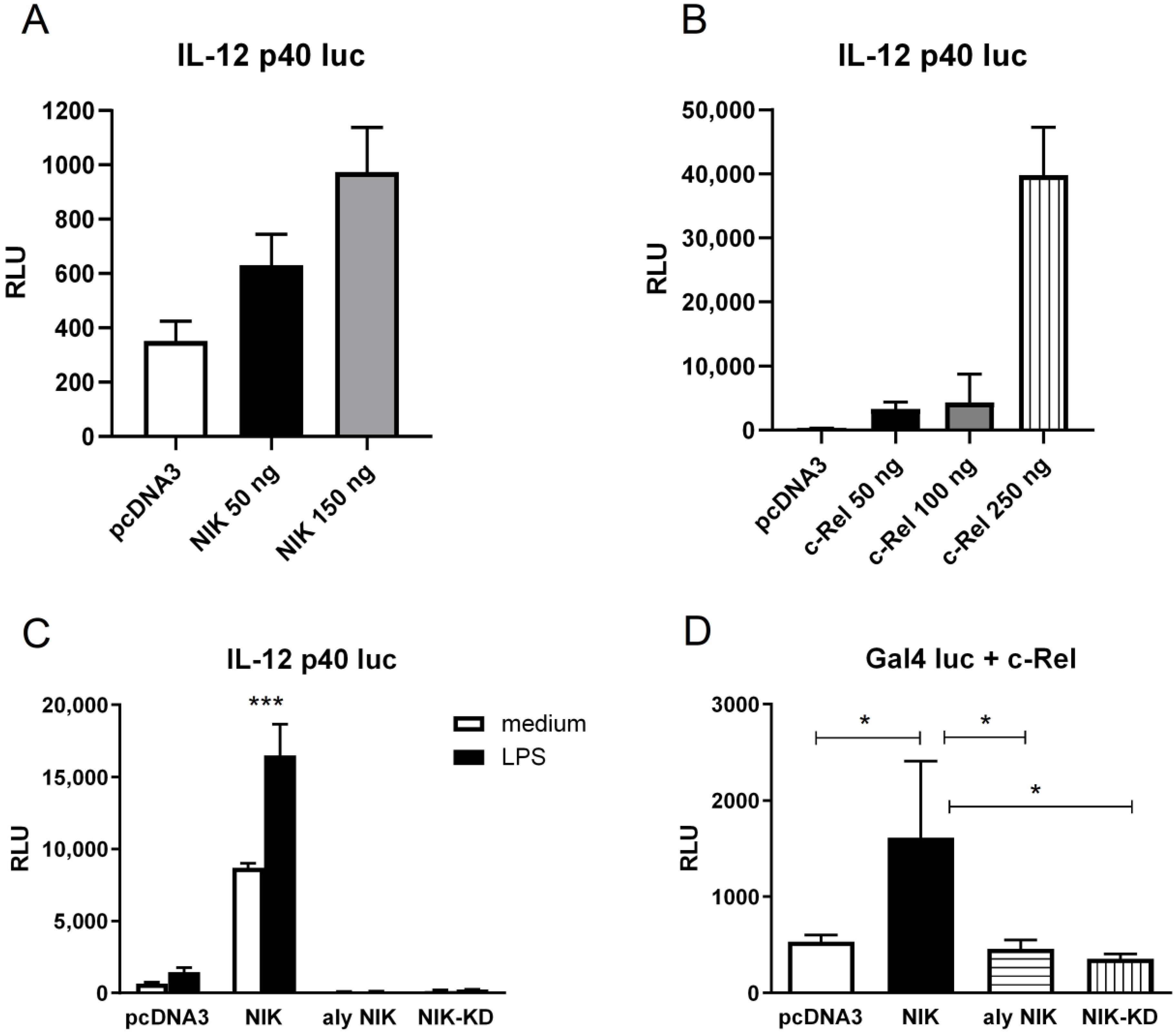
3.3. NIK Regulates Il12b Gene Transcription in Macrophages Through the Stimulation of c-Rel Transactivating Activity
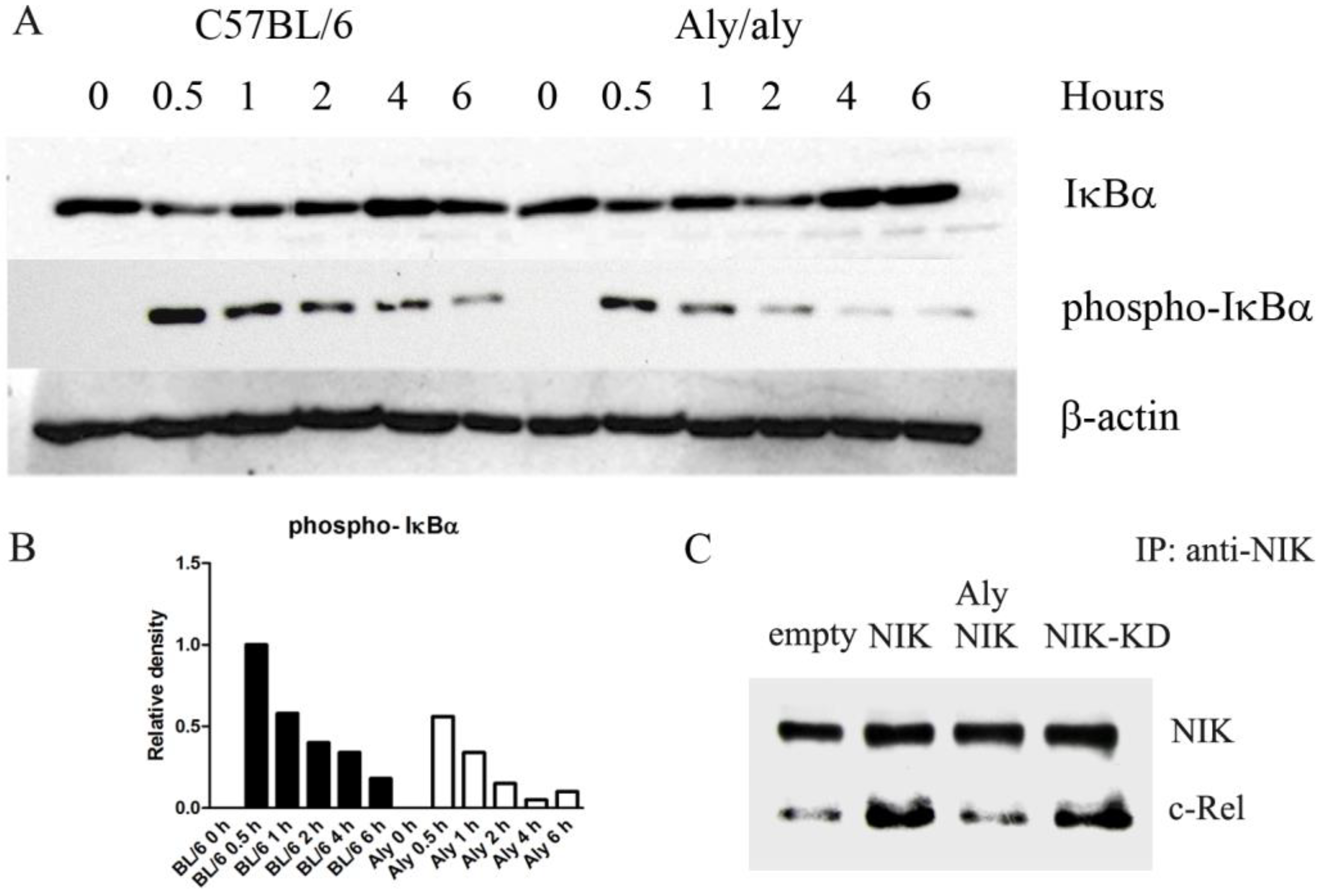
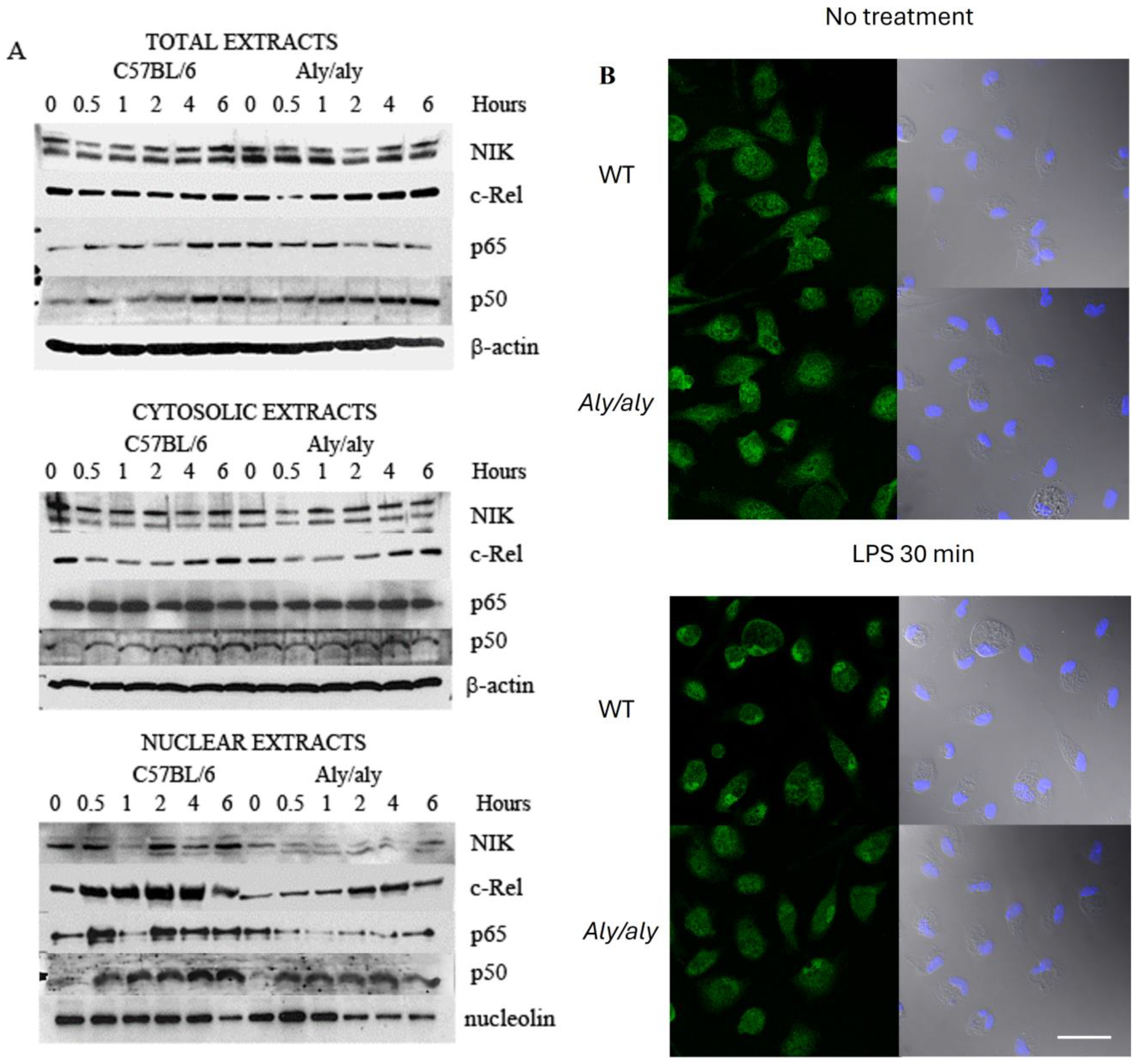
3.4. Aly/aly NIK Impedes Complete NF-κB Activation and Prevents Binding of NIK to c-Rel After LPS Challenge
3.5. Accumulation of c-Rel in the Nucleus upon LPS Challenge Is Inhibited in aly/aly Macrophages
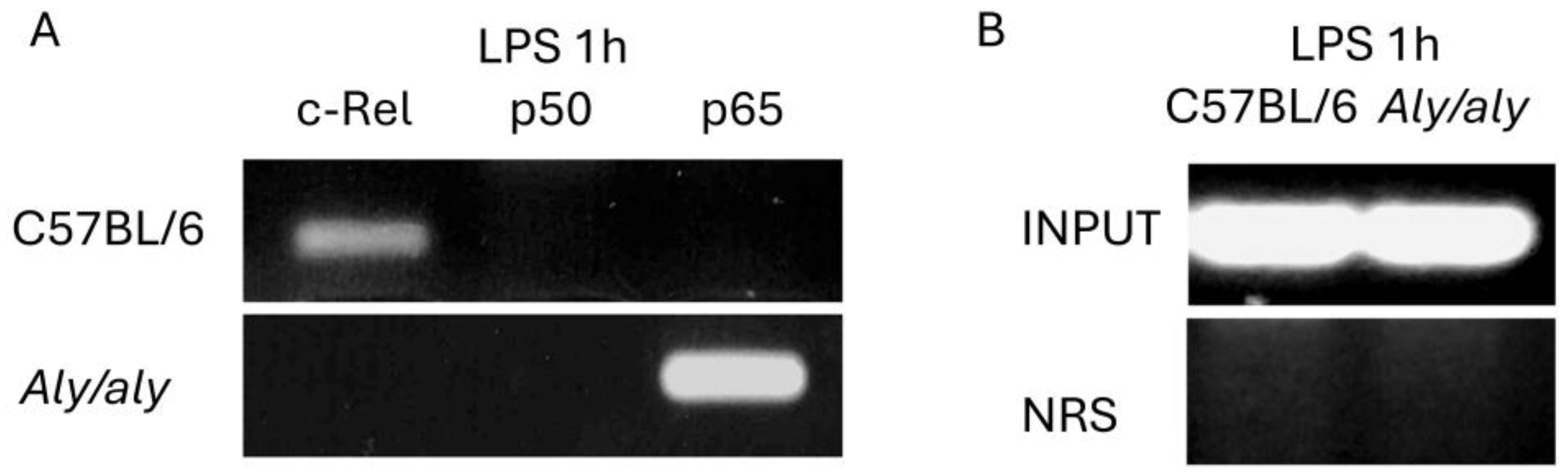
3.6. c-Rel Is Bound to the NF-κB Consensus Sequence in the Il12b Promoter After LPS Challenge in Mouse Peritoneal Macrophages and the aly/aly Mutation Results in p65 Being Recruited Instead
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tait Wojno, E.D.; Hunter, C.A.; Stumhofer, J.S. The Immunobiology of the Interleukin-12 Family: Room for Discovery. Immunity 2019, 50, 851–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Zhao, J.; Perlman, S. Differential effects of IL-12 on Tregs and non-Treg T cells: Roles of IFN-γ, IL-2 and IL-2R. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geils, C.; Kathrein, K.L. Augmentation of Solid Tumor Immunotherapy With IL-12. J. Gene Med. 2024, 26, e70000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, E.; Carson, W.E., 3rd. Analysis of potential biomarkers of response to IL-12 therapy. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2022, 112, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullrich, K.A.; Schulze, L.L.; Paap, E.M.; Müller, T.M.; Neurath, M.F.; Zundler, S. Immunology of IL-12: An update on functional activities and implications for disease. EXCLI J. 2020, 19, 1563–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinchieri, G. Interleukin-12: A cytokine at the interface of inflammation and immunity. Adv. Immunol. 1998, 70, 83–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, J.G.; Eyerich, K.; Kuchroo, V.K.; Ritchlin, C.T.; Abreu, M.T.; Elloso, M.M.; Fourie, A.; Fakharzadeh, S.; Sherlock, J.P.; Yang, Y.W.; et al. IL-23 past, present, and future: A roadmap to advancing IL-23 science and therapy. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1331217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floss, D.M.; Moll, J.M.; Scheller, J. IL-12 and IL-23-Close Relatives with Structural Homologies but Distinct Immunological Functions. Cells 2020, 9, 2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, T.L.; Cleveland, M.G.; Kulesza, P.; Magram, J.; Murphy, K.M. Regulation of interleukin 12 p40 expression through an NF-kappa B half-site. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1995, 15, 5258–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, M.N.; Zhou, L.; Smale, S.T. C/EBPbeta regulation in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 4841–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plevy, S.E.; Gemberling, J.H.; Hsu, S.; Dorner, A.J.; Smale, S.T. Multiple control elements mediate activation of the murine and human interleukin 12 p40 promoters: Evidence of functional synergy between C/EBP and Rel proteins. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1997, 17, 4572–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Gagnidze, K.; Gemberling, J.H.M.; Plevy, S.E. Characterization of an activation protein-1-binding site in the murine interleukin-12 p40 promoter: Demonstration of novel functional elements by a reductionist approach. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 18519–18528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Rao, K.; Xiong, H.; Gagnidze, K.; Li, F.; Horvath, C.; Plevy, S. Activation of the murine interleukin-12 p40 promoter by functional interactions between NFAT and ICSBP. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 39372–39382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama, S.; Sumita, K.; Shen, H.; Kanoh, M.; Xu, X.; Sato, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Shinomiya, H.; Asano, Y. Identification of IFN regulatory factor-1 binding site in IL-12 p40 gene promoter. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 997–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulero, M.C.; Huxford, T.; Ghosh, G. NF-κB, IκB, and IKK: Integral Components of Immune System Signaling. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1172, 207–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Beller, D. Aberrant production of IL-12 by macrophages from several autoimmune-prone mouse strains is characterized by intrinsic and unique patterns of NF-kappa B expression and binding to the IL-12 p40 promoter. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjabi, S.; Hoffmann, A.; Liou, H.C.; Baltimore, D.; Smale, S.T. Selective requirement for c-Rel during IL-12 P40 gene induction in macrophages. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 12705–12710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnabei, L.; Laplantine, E.; Mbongo, W.; Rieux-Laucat, F.; Weil, R. NF-κB: At the Borders of Autoimmunity and Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 716469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pflug, K.M.; Sitcheran, R. Targeting NF-κB-Inducing Kinase (NIK) in Immunity, Inflammation, and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, P.D.; Pittet, M.J.; Weissleder, R. The chemical biology of IL-12 production via the non-canonical NF-kB pathway. RSC Chem. Biol. 2020, 1, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Sekine, T.; Okamoto, T. Identification of a new serine kinase that activates NF kappa B by direct phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 26790–26795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasuhara, Y.; Adcock, I.M.; Catley, M.; Barnes, P.J.; Newton, R. Differential IkappaB kinase activation and IkappaBalpha degradation by interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in human U937 monocytic cells. Evidence for additional regulatory steps in kappaB-dependent transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 19965–19972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garceau, N.; Kosaka, Y.; Masters, S.; Hambor, J.; Shinkura, R.; Honjo, T.; Noelle, R.J. Lineage-restricted function of nuclear factor kappaB-inducing kinase (NIK) in transducing signals via CD40. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.P.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Diao, F.C.; Chen, D.; Zhai, Z.; Shu, H.B. Differential regulation of IKK alpha-mediated activation of IRF3/7 by NIK. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 1926–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Hayden, M.S. New regulators of NF-kappaB in inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreakos, E.; Williams, R.O.; Wales, J.; Foxwell, B.M.; Feldmann, M. Activation of NF-kappaB by the intracellular expression of NF-kappaB-inducing kinase acts as a powerful vaccine adjuvant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 14459–14464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solan, N.J.; Miyoshi, H.; Carmona, E.M.; Bren, G.D.; Paya, C.V. RelB cellular regulation and transcriptional activity are regulated by p100. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 1405–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiño-Rivas, L.; Vaquero, J.J.; Sucunza, D.; Gutierrez, S.; Sanz, A.B.; Fresno, M.; Ortiz, A.; Sanchez-Niño, M.D. NIK as a Druggable Mediator of Tissue Injury. Trends Mol. Med. 2019, 25, 341–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opitz, B.; Schröder, N.W.; Spreitzer, I.; Michelsen, K.S.; Kirschning, C.J.; Hallatschek, W.; Zähringer, U.; Hartung, T.; Göbel, U.B.; Schumann, R.R. Toll-like receptor-2 mediates Treponema glycolipid and lipoteichoic acid-induced NF-kappaB translocation. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 22041–22047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, N.D. Post-translational modifications regulating the activity and function of the nuclear factor kappa B pathway. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6717–6730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Valdepeñas, C.; Martín, A.G.; Ramakrishnan, P.; Wallach, D.; Fresno, M. NF-kappaB-inducing kinase is involved in the activation of the CD28 responsive element through phosphorylation of c-Rel and regulation of its transactivating activity. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 4666–4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinkura, R.; Kitada, K.; Matsuda, F.; Tashiro, K.; Ikuta, K.; Suzuki, M.; Kogishi, K.; Serikawa, T.; Honjo, T. Alymphoplasia is caused by a point mutation in the mouse gene encoding Nf-kappa b-inducing kinase. Nat. Genet. 1999, 22, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Mu, Y.; Cunningham, E.T., Jr.; Marcu, K.B.; Geleziunas, R.; Greene, W.C. Molecular determinants of NF-kappaB-inducing kinase action. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 5899–5907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, G.; Harhaj, E.W.; Sun, S.C. NF-kappaB-inducing kinase regulates the processing of NF-kappaB2 p100. Mol. Cell 2001, 7, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagarasan, S.; Shinkura, R.; Kamata, T.; Nogaki, F.; Ikuta, K.; Tashiro, K.; Honjo, T. Alymphoplasia (aly)-type nuclear factor kappaB-inducing kinase (NIK) causes defects in secondary lymphoid tissue chemokine receptor signaling and homing of peritoneal cells to the gut-associated lymphatic tissue system. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 1477–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinin, N.L.; Boldin, M.P.; Kovalenko, A.V.; Wallach, D. MAP3K-related kinase involved in NF-kappaB induction by TNF, CD95 and IL-1. Nature 1997, 385, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.G.; Fresno, M. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha activation of NF-kappa B requires the phosphorylation of Ser-471 in the transactivation domain of c-Rel. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 24383–24391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.G.; San-Antonio, B.; Fresno, M. Regulation of nuclear factor kappa B transactivation. Implication of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and protein kinase C zeta in c-Rel activation by tumor necrosis factor alpha. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 15840–15849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel-Muiños, F.X.; Muñoz-Fernández, M.A.; Fresno, M. Control of T lymphocyte activation and IL-2 receptor expression by endogenously secreted lymphokines. J. Immunol. 1994, 152, 5714–5722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Guan, X.; Ma, X. Regulation of IL-27 p28 gene expression in macrophages through MyD88- and interferon-gamma-mediated pathways. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falvo, J.V.; Tsytsykova, A.V.; Goldfeld, A.E. Transcriptional control of the TNF gene. Curr. Dir. Autoimmun. 2010, 11, 27–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlo, S.; Haegeman, G.; Vanden Berghe, W. Transcriptional regulation of autocrine IL-6 expression in multiple myeloma cells. Cell Signal. 2008, 20, 1489–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birbach, A.; Gold, P.; Binder, B.R.; Hofer, E.; de Martin, R.; Schmid, J.A. Signaling molecules of the NF-kappa B pathway shuttle constitutively between cytoplasm and nucleus. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 10842–10851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birbach, A.; Bailey, S.T.; Ghosh, S.; Schmid, J.A. Cytosolic, nuclear and nucleolar localization signals determine subcellular distribution and activity of the NF-kappaB inducing kinase NIK. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117 Pt 16, 3615–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, J.R.; Siebenlist, U. Lymphotoxin beta receptor induces sequential activation of distinct NF-kappa B factors via separate signaling pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 12006–12012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.; Andreakos, E.; Crawley, J.B.; Brennan, F.M.; Feldmann, M.; Foxwell, B.M. NF-kappaB-inducing kinase is dispensable for activation of NF-kappaB in inflammatory settings but essential for lymphotoxin beta receptor activation of NF-kappaB in primary human fibroblasts. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 5895–5903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boddupalli, C.S.; Ghosh, S.; Rahim, S.S.; Nair, S.; Ehtesham, N.Z.; Hasnain, S.E.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Nitric oxide inhibits interleukin-12 p40 through p38 MAPK-mediated regulation of calmodulin and c-rel. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 42, 686–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushima, A.; Kaisho, T.; Rennert, P.D.; Nakano, H.; Kurosawa, K.; Uchida, D.; Takeda, K.; Akira, S.; Matsumoto, M. Essential role of nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB-inducing kinase and inhibitor of kappaB (IkappaB) kinase alpha in NF-kappaB activation through lymphotoxin beta receptor, but not through tumor necrosis factor receptor I. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 193, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luftig, M.A.; Cahir-McFarland, E.; Mosialos, G.; Kieff, E. Effects of the NIK aly mutation on NF-kappaB activation by the Epstein-Barr virus latent infection membrane protein, lymphotoxin beta receptor, and CD40. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 14602–14606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Kravchenko, V.; Katz, A.; Huang, S.; Ii, M.; Mathison, J.C.; Kobayashi, K.; Flavell, R.A.; Schreiber, R.D.; Goeddel, D.; et al. NF-kappa B-inducing kinase regulates selected gene expression in the Nod2 signaling pathway. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 2121–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, G.; Fong, A.; Sun, S.C. Induction of p100 processing by NF-kappaB-inducing kinase involves docking IkappaB kinase alpha (IKKalpha) to p100 and IKKalpha-mediated phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 30099–30105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, N.; Li, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Stechschulte, D.J.; Dileepan, K.N. Transient degradation of NF-kappaB proteins in macrophages after interaction with mast cell granules. Mediat. Inflamm. 1998, 7, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grumont, R.; Hochrein, H.; O’Keeffe, M.; Gugasyan, R.; White, C.; Caminschi, I.; Cook, W.; Gerondakis, S. c-Rel regulates interleukin 12 p70 expression in CD8+ dendritic cells by specifically inducing p35 gene transcription. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 194, 1021–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The NF-κB family is a critical Ma, X.; Neurath, M.; Gri, G.; Trinchieri, G. Identification and characterization of a novel Ets-2-related nuclear complex implicated in the activation of the human interleukin-12 p40 gene promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 10389–10395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cuesta, N.; Staniszewska, A.D.; Moreno, C.; Punzón, C.; Fresno, M. NF-κB-Inducing Kinase Is Essential for Effective c-Rel Transactivation and Binding to the Il12b Promoter in Macrophages. Biology 2025, 14, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14010033
Cuesta N, Staniszewska AD, Moreno C, Punzón C, Fresno M. NF-κB-Inducing Kinase Is Essential for Effective c-Rel Transactivation and Binding to the Il12b Promoter in Macrophages. Biology. 2025; 14(1):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14010033
Chicago/Turabian StyleCuesta, Natalia, Anna D. Staniszewska, Cristóbal Moreno, Carmen Punzón, and Manuel Fresno. 2025. "NF-κB-Inducing Kinase Is Essential for Effective c-Rel Transactivation and Binding to the Il12b Promoter in Macrophages" Biology 14, no. 1: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14010033
APA StyleCuesta, N., Staniszewska, A. D., Moreno, C., Punzón, C., & Fresno, M. (2025). NF-κB-Inducing Kinase Is Essential for Effective c-Rel Transactivation and Binding to the Il12b Promoter in Macrophages. Biology, 14(1), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14010033





