Dominance of Sulfur-Oxidizing Bacteria, Thiomicrorhabdus, in the Waters Affected by a Shallow-Sea Hydrothermal Plume
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
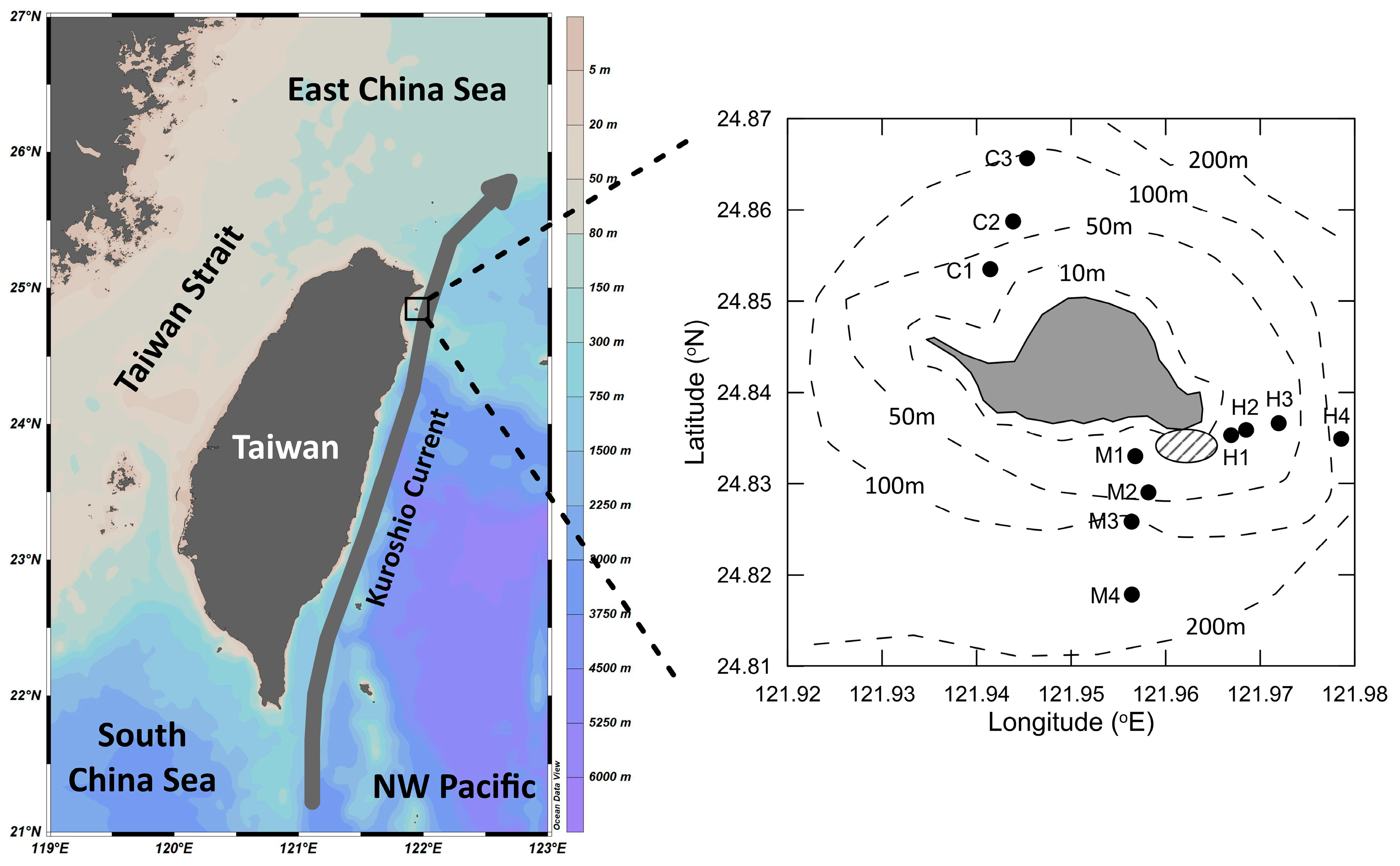
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Determination of Hydrographic Features
2.3. Determination of Dissolved Inorganic Carbon (DIC) Fixation Efficiency
2.4. Enumeration of Picoplankton
2.5. Environment DNA Isolation
2.6. Environment Total RNA Isolation
2.7. The Diversity of Microbial Population Composition
2.8. Analysis of RNA Expression Profiles
2.9. Sequence Deposition
3. Results
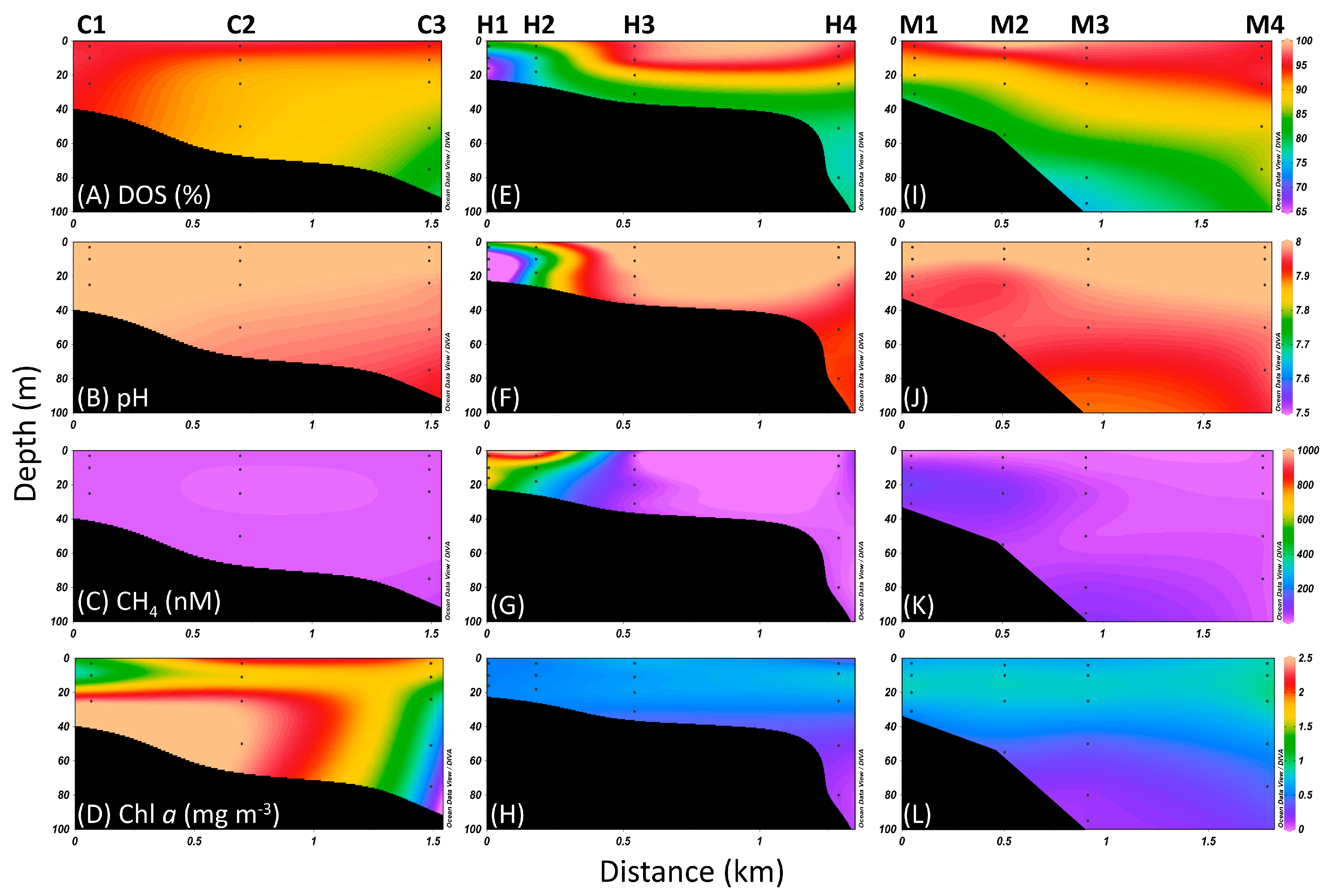
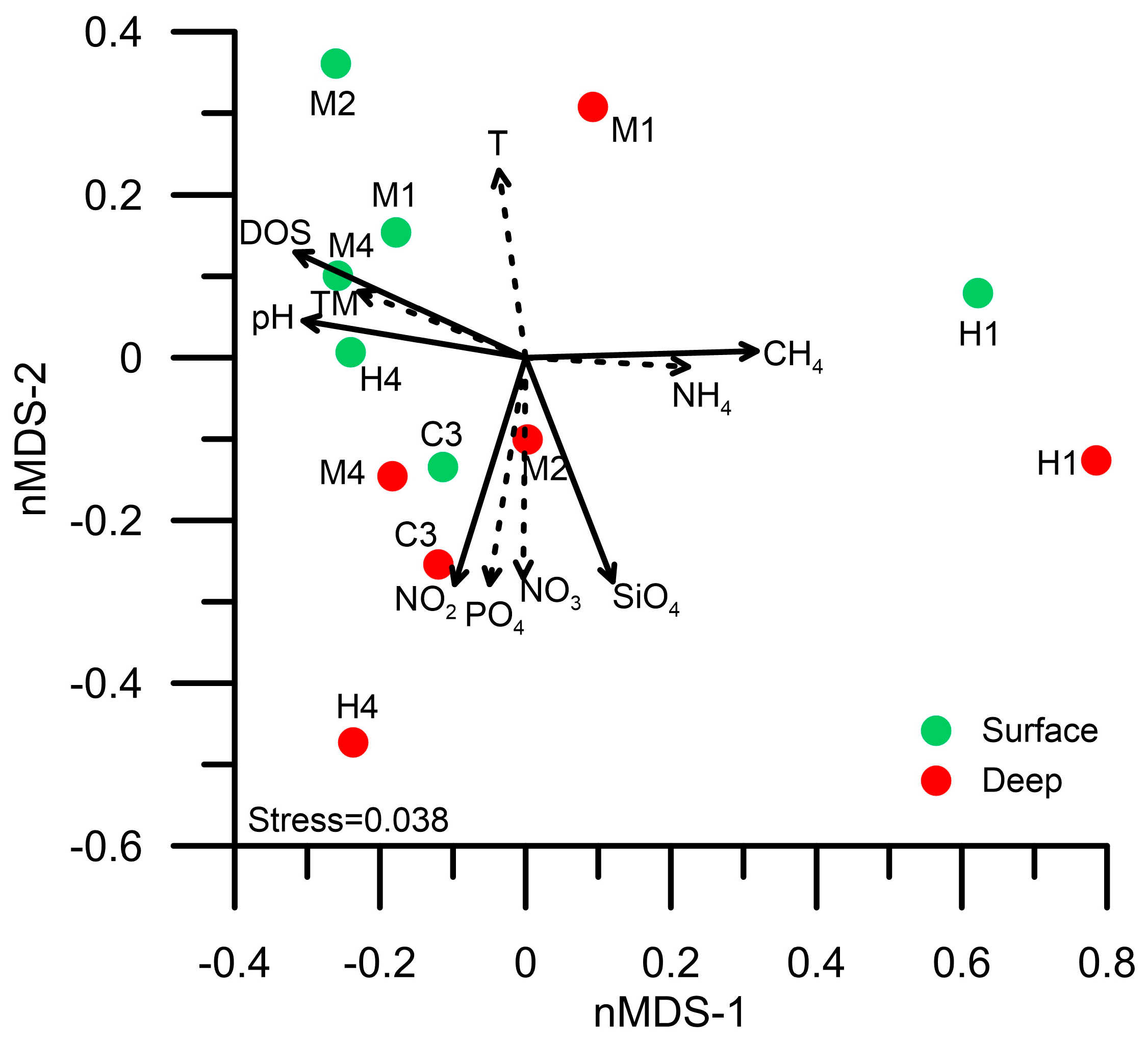
3.1. Hydrographic Features
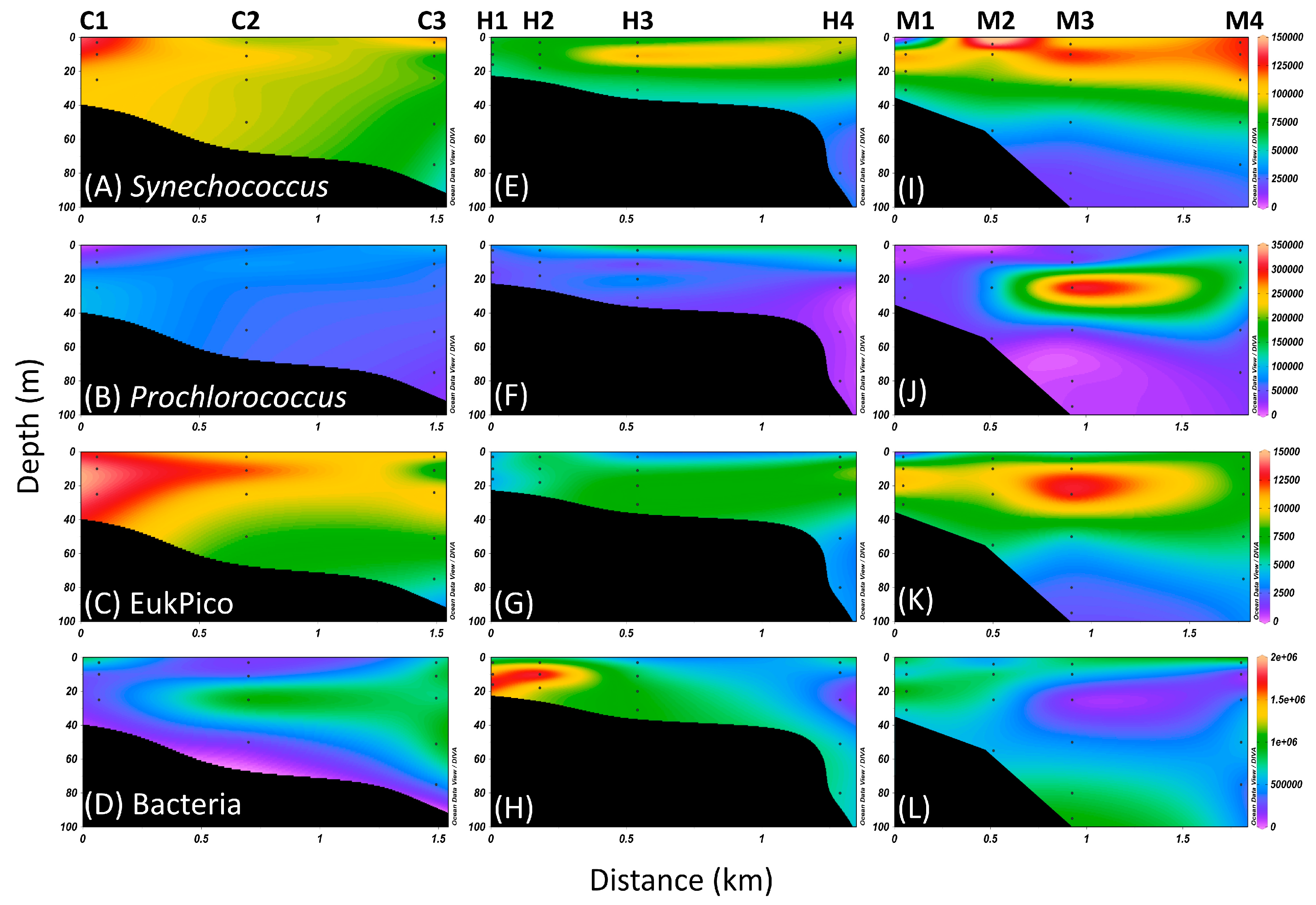
3.2. Distribution of Picoplankton
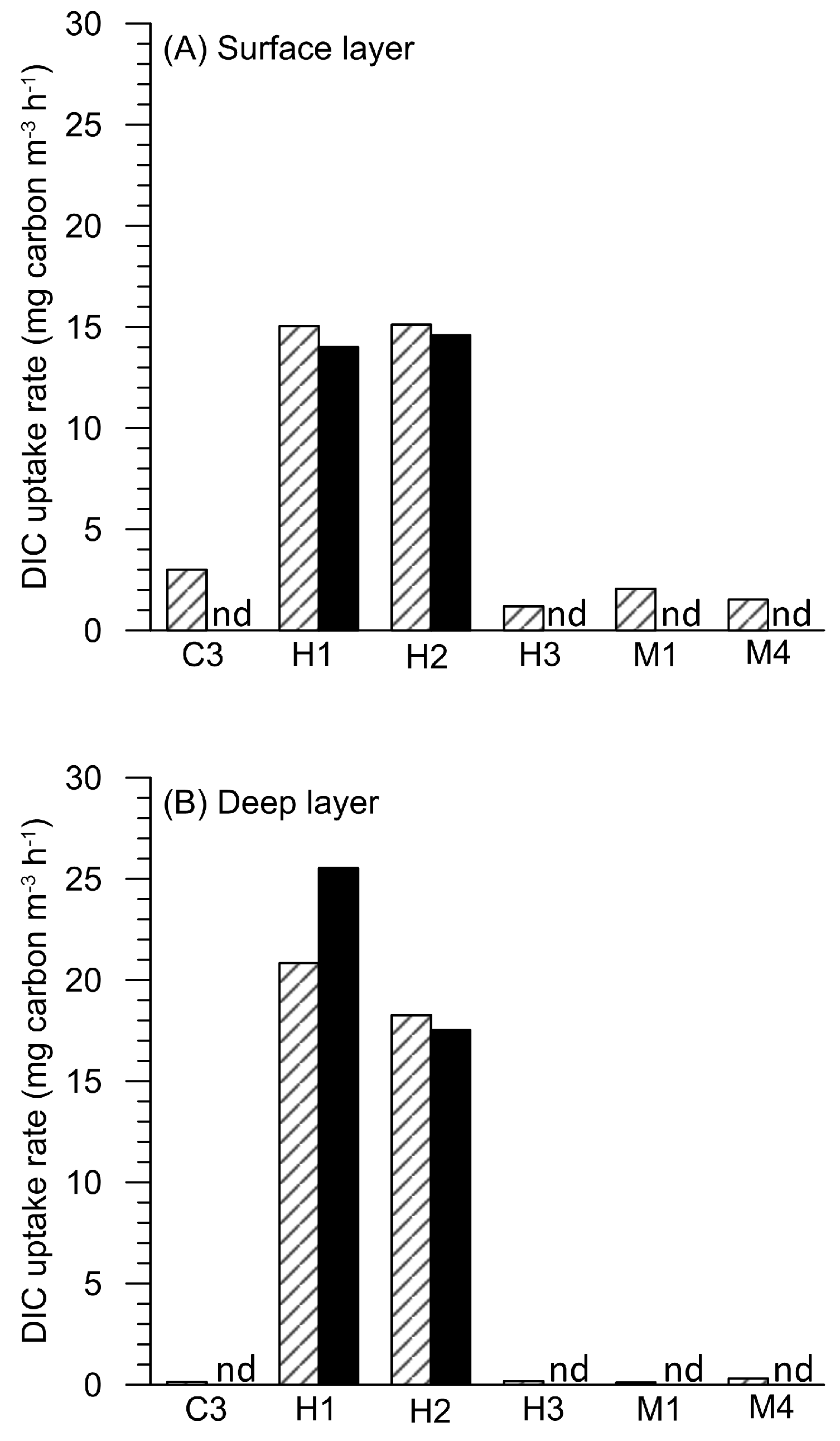
3.3. Dissolved Inorganic Carbon (DIC) Fixation Efficiency
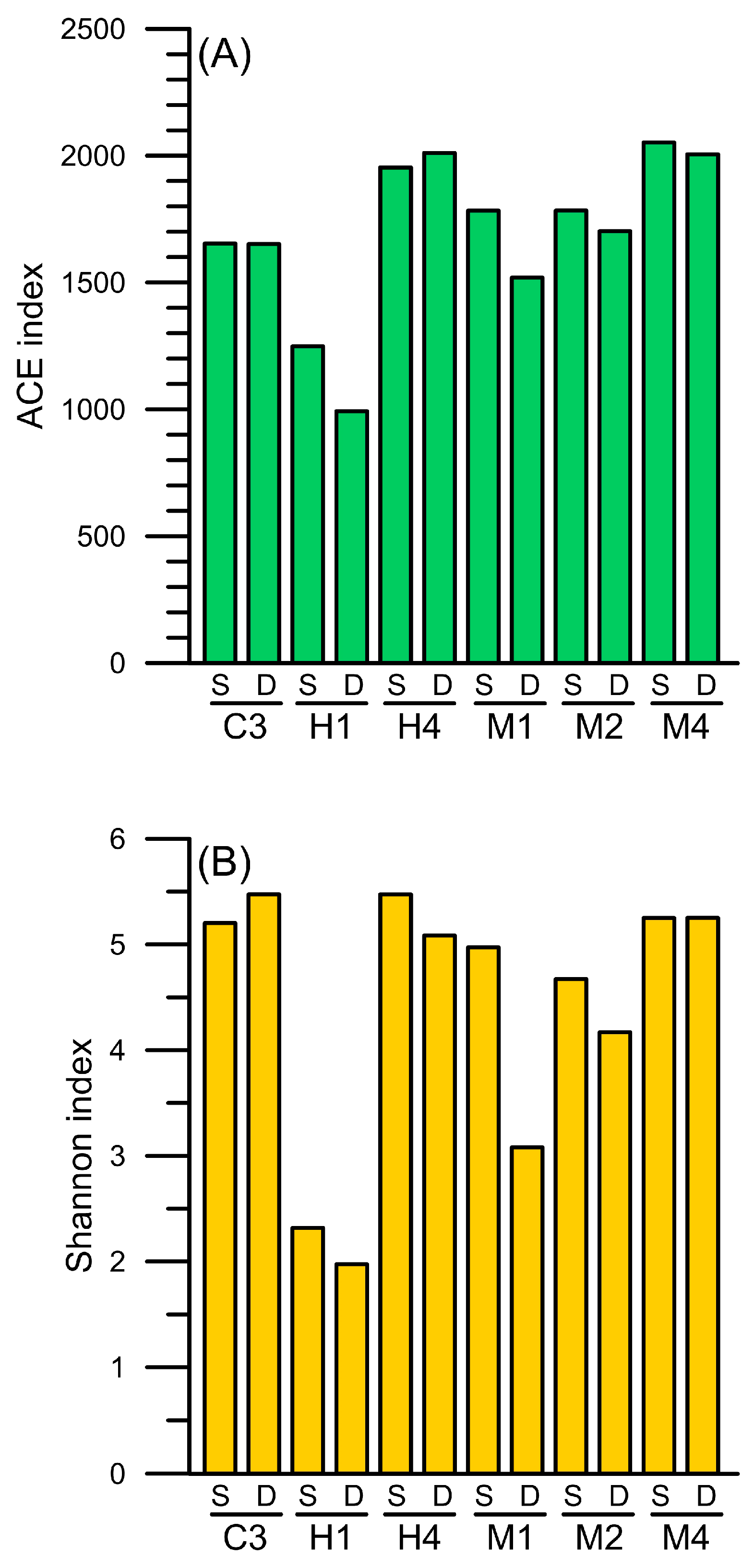
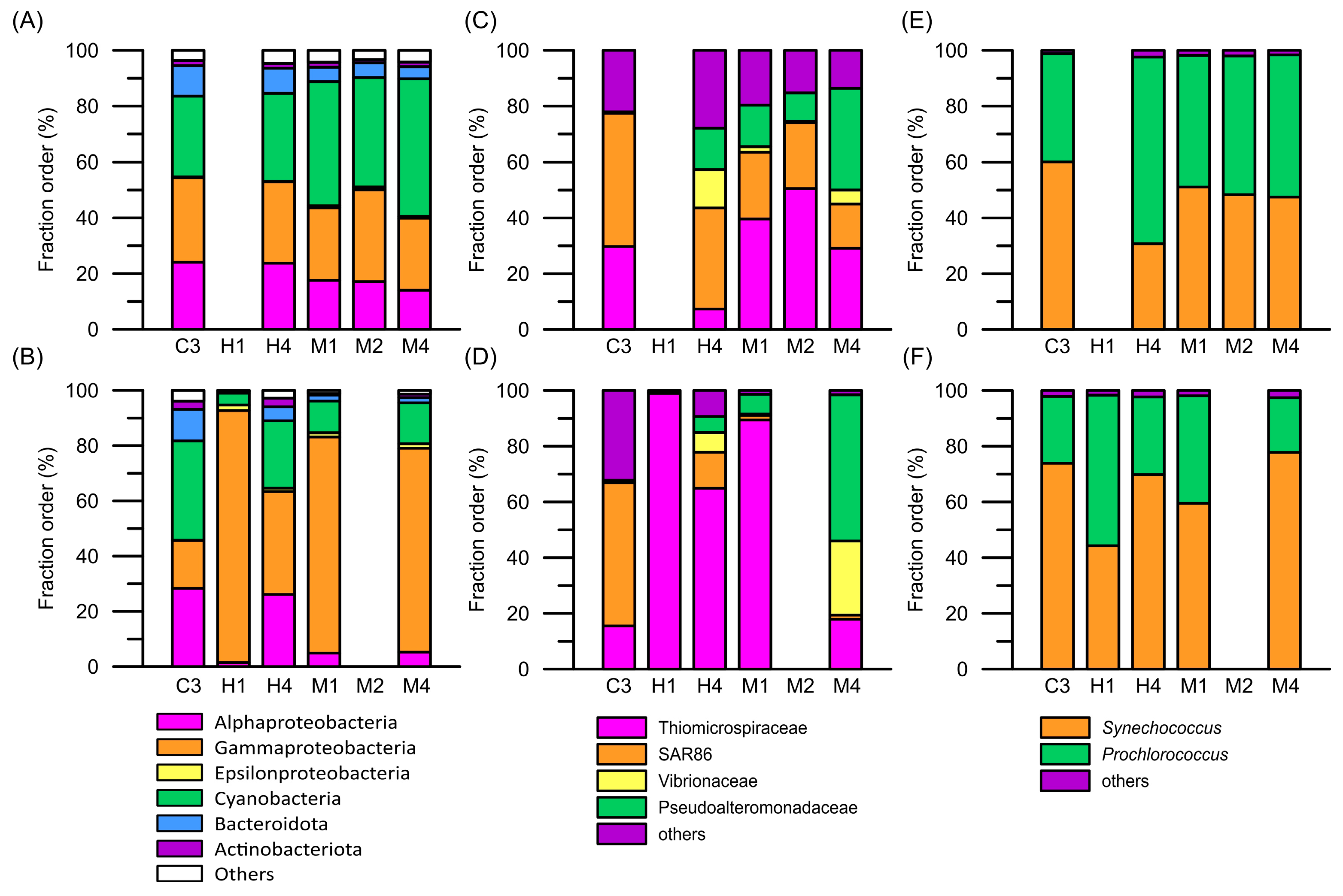
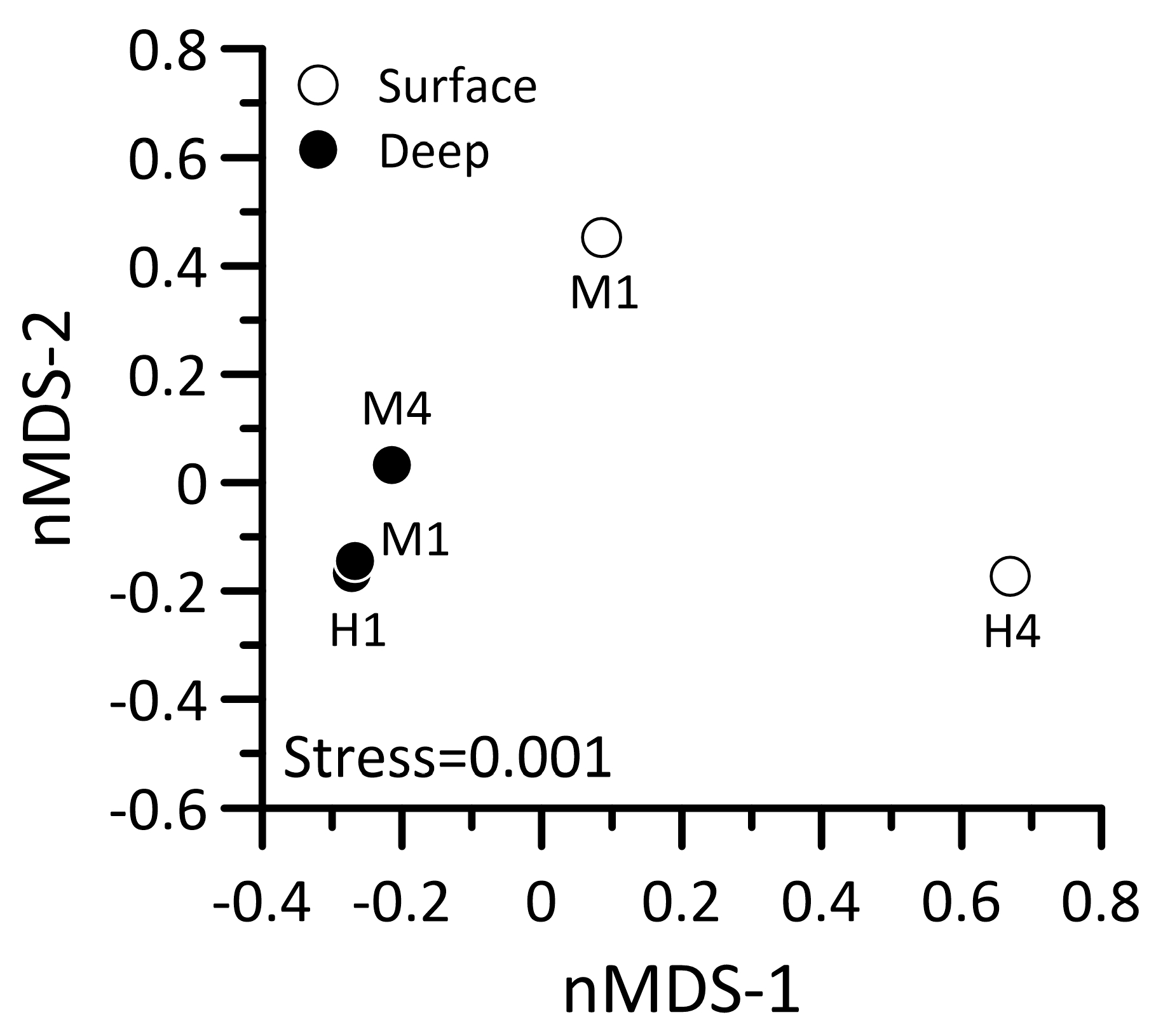
3.4. Diversity of Prokaryotic Picoplankton Community Composition
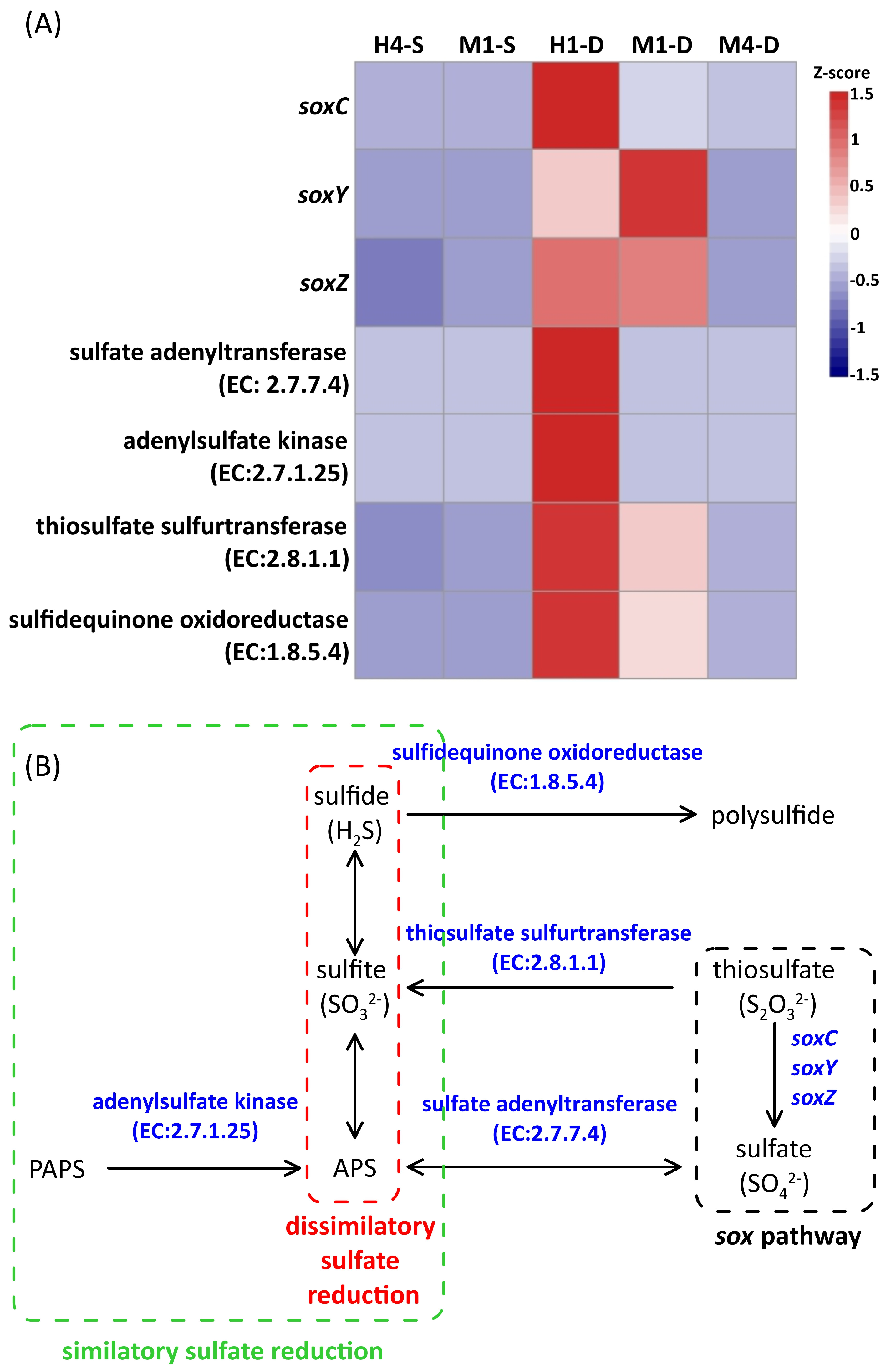
3.5. Gene Expression Profiles of Prokaryotic Picoplankton
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dick, G.; Anantharaman, K.; Baker, B.; Li, M.; Reed, D.; Sheik, C. The microbiology of deep-sea hydrothermal vent plumes: Ecological and biogeographic linkages to seafloor and water column habitats. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baross, J.A.; Hoffman, S.E. Submarine hydrothermal vents and associated gradient environments as sites for the origin and evolution of life. Orig. Life Evol. Biosph. 1985, 15, 327–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tang, K.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Xie, X.; Chen, C.-T.A.; Wang, D.; Jiao, N.; Zhang, Y. Coupled carbon, sulfur, and nitrogen cycles mediated by microorganisms in the water column of a shallow-water hydrothermal ecosystem. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-S.; Lin, H.-T.; Wang, B.-S.; Huang, W.-J.; Lin, L.-H.; Tsai, A.-Y. Intense but variable autotrophic activity in a rapidly flushed shallow-water hydrothermal plume (Kueishantao Islet, Taiwan). Geobiology 2021, 19, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorokin, Y.I.; Sorokin, P.Y.; Zakouskina, O.Y. Microplankton and its function in a zone of shallow hydrothermal activity:the Craternaya Bay, Kurile Islands. J. Plankton Res. 2003, 25, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sorokin, Y.I.; Sorokin, P.Y.; Zakuskina, O.Y. Microplankton and its functional activity in zones of shallow hydrotherms in the Western Pacific. J. Plankton Res. 1998, 20, 1015–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, D.; Han, Y.; Chen, C.-T.A.; Wang, D.; Lin, Y.-S.; Sun, J.; Zheng, Q.; Jiao, N. Cultivation-independent and cultivation-dependent analysis of microbes in the shallow-sea hydrothermal system off Kueishantao Island, Taiwan: Unmasking heterotrophic bacterial diversity and functional capacity. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarasov, V.G.; Gebruk, A.V.; Mironov, A.N.; Moskalev, L.I. Deep-sea and shallow-water hydrothermal vent communities: Two different phenomena? Chem. Geol. 2005, 224, 5–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, H.; Sunamura, M.; Takai, K.; Nunoura, T.; Noguchi, T.; Oida, H.; Furushima, Y.; Yamamoto, H.; Oomori, T.; Horikoshi, K. Culture-dependent and -independent characterization of microbial communities associated with a shallow submarine hydrothermal system occurring within a coral reef off Taketomi Island, Japan. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 7642–7656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentini, V.; Gugliandolo, C.; Bunk, B.; Overmann, J.; Maugeri, T.L. Diversity of prokaryotic community at a shallow marine hydrothermal site elucidated by Illumina sequencing technology. Curr. Microbiol. 2014, 69, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, C.-T.A.; Tang, K.; Su, J.; Jiao, N. Sulfur metabolizing microbes dominate microbial communities in andesite-hosted shallow-sea hydrothermal systems. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-T.A.; Zeng, Z.; Kuo, F.-W.; Yang, T.F.; Wang, B.-J.; Tu, Y.-Y. Tide-influenced acidic hydrothermal system offshore NE Taiwan. Chem. Geol. 2005, 224, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-G.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Li, X.; Chen, C.-T.A.; Yang, T.F.; Ye, Y. The chemical and isotopic compositions of gas discharge from shallow-water hydrothermal vents at Kueishantao, offshore northeast Taiwan. Geochem. J. 2016, 50, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, S.-C.; Tsau, Y.-J.; Yang, T.-I. pH and buffering capacity problems involved in the determination of ammonia in saline water using the indophenol blue spectrophotometric method. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 434, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, G.-C.; Chen, Y.-L.L.; Liu, K.-K. Chemical hydrography and chlorophyll a distribution in the East China Sea in summer: Implications in nutrient dynamics. Cont. Shelf Res. 1996, 16, 1561–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, J.D.H.; Parsons, T.R. A Practical Handbook of Seawater Analysis; Fisheries Research Board of Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Pai, S.-C.; Yang, C.-C.; Riley, J.P. Effects of acidity and molybdate concentration on the kinetics of the formation of the phosphoantimonylmolybdenum blue complex. Anal. Chim. Acta 1990, 229, 115–120. [Google Scholar]
- Lui, H.-K.; Liu, M.-Y.; Lin, H.-C.; Tseng, H.-C.; Liu, L.-L.; Wang, F.-Y.; Hou, W.-P.; Chang, R.; Chen, C.-T.A. Hydrogeochemistry and acidic property of submarine groundwater discharge around two coral islands in the Northern South China Sea. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 697388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, R.F. Determinations of carbon dioxide and methane by dual catalyst flame ionization chromatography and nitrous oxide by electron capture chromatography. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 1981, 19, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, W.-C.; Gong, G.-C.; Yang, C.-Y.; Chuang, K.-Y. A comparison between field and laboratory pH measurements for seawater on the East China Sea shelf. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2016, 14, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.-F.; Qiu, S.-Q.; Chou, W.-C. Carbonate chemistry of the Dongsha Atoll Lagoon in the northern South China Sea. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2021, 32, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, T.R.; Maita, Y.; Lalli, C.M. A Manual of Chemical and Biological Methods for Seawater Analysis; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1984; p. 173. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, G.-C.; Shiah, F.-K.; Liu, K.-K.; Wen, Y.-H.; Liang, M.-H. Spatial and temporal variation of chlorophyll a, primary productivity and chemical hydrography in the southern East China Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2000, 20, 411–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, G.-C.; Wen, Y.-H.; Wang, B.-W.; Liu, G.-J. Seasonal variation of chlorophyll a concentration, primary production and environmental conditions in the subtropical East China Sea. Deep Sea Res. II 2003, 50, 1219–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.-C.; Gong, G.-C.; Huang, C.-Y.; Lin, J.-Y.; Lin, Y.-C. Changes in the Synechococcus assemblage composition at the surface of the East China Sea due to flooding of the Changjiang River. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 70, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Nolla, H.A.; Campell, L. Prochlorococcus growth rate and contribution to primary production in the equatorial and subtropical North Pacific Ocean. Aqua. Microb. Ecol. 1997, 12, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.; et al. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; Oshlack, A. A scaling normalization method for differential expression analysis of RNA-seq data. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, B.; Lai, Q.; Shao, Z.; Jiang, L. Thiomicrorhabdus sediminis sp. nov. and Thiomicrorhabdus xiamenensis sp. nov., novel sulfur-oxidizing bacteria isolated from coastal sediments and an emended description of the genus Thiomicrorhabdus. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2021, 71, 004660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.-Y.; Liu, X.-J.; Li, Z.; Yu, F.; Yang, H.; Du, Z.-J.; Ye, M.-Q. Thiomicrorhabdus marina sp.nov., an obligate chemolithoautotroph isolated from tidal zone sediment, and genome insight into the genus Thiomicrorhabdus. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1144912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götz, S.; García-Gómez, J.M.; Terol, J.; Williams, T.D.; Nagaraj, S.H.; Nueda, M.J.; Robles, M.; Talón, M.; Dopazo, J.; Conesa, A. High-throughput functional annotation and data mining with the Blast2GO suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 3420–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.-C.; Gong, G.-C. Attribution of the growth of a distinct population of Synechococcus to the coverage of lateral water on an upwelling. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2019, 30, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.-F.; Chung, C.-C.; Gong, G.-C.; Hsu, C.-W. Spatial variation of abundant picoeukaryotes in the subtropical Kuroshio Current in winter. Mar. Ecol. 2020, 41, e12579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeng, M.-S.; Ng, N.K.; Ng, P.K.L. Hydrothermal vent crabs feast on sea ‘snow’. Nature 2004, 432, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, G.-C.; Chang, J.; Wen, Y.-H. Estimation of annual primary production in the Kuroshio waters northeast of Taiwan using a photosynthesis-irradiance model. Deep Sea Res. I Oceanogra. Res. 1999, 46, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-C.; Lu, C.-Y.; Jan, S.; Hsieh, C.-h.; Chung, C.-C. Effects of the coastal uplift on the Kuroshio ecosystem, Eastern Taiwan, the western boundary current of the North Pacific Ocean. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 796187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-S.; Lee, J.; Lin, L.-H.; Fu, K.-H.; Chen, C.-T.A.; Wang, Y.-H.; Lee, I.H. Biogeochemistry and dynamics of particulate organic matter in a shallow-water hydrothermal field (Kueishantao Islet, NE Taiwan). Mar. Geol. 2020, 422, 106121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.-N. Advances in the bacterial organelles for CO2 fixation. Trends Microbiol. 2022, 30, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, M.; Beardall, J.; Raven, J.A. CO2 Concentrating mechanisms in algae: Mechanisms, environmental modulation, and evolution. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2005, 56, 99–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffine, C.A.; Zhao, R.; Tang, Y.J.; Cameron, J.C. Role of carboxysomes in cyanobacterial CO2 assimilation: CO2 concentrating mechanisms and metabolon implications. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 25, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badger, M.R.; Price, G.D. CO2 concentrating mechanisms in cyanobacteria: Molecular components, their diversity and evolution. J. Exp. Bot. 2003, 54, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, K.M.; Leonard, J.M.; Boden, R.; Chaput, D.; Dennison, C.; Haller, E.; Harmer, T.L.; Anderson, A.; Arnold, T.; Budenstein, S.; et al. Diversity in CO2-concentrating mechanisms among chemolithoautotrophs from the genera Hydrogenovibrio, Thiomicrorhabdus, and Thiomicrospira, ubiquitous in sulfidic habitats worldwide. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e02096-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, W.; Dam, B. Biochemistry and molecular biology of lithotrophic sulfur oxidation by taxonomically and ecologically diverse bacteria and archaea. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 33, 999–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boden, R.; Scott, K.M.; Williams, J.; Russel, S.; Antonen, K.; Rae, A.W.; Hutt, L.P. An evaluation of Thiomicrospira, Hydrogenovibrio and Thioalkalimicrobium: Reclassification of four species of Thiomicrospira to each Thiomicrorhabdus gen. nov. and Hydrogenovibrio, and reclassification of all four species of Thioalkalimicrobium to Thiomicrospira. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 1140–1151. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vetriani, C.; Voordeckers, J.; Crespo-Medina, M.; O’Brien, C.E.; Giovannelli, D.; Lutz, R.A. Deep-sea hydrothermal vent Epsilonproteobacteria encode a conserved and widespread nitrate reduction pathway (Nap). ISME J. 2014, 8, 1510–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chung, C.-C.; Gong, G.-C.; Tseng, H.-C.; Chou, W.-C.; Ho, C.-H. Dominance of Sulfur-Oxidizing Bacteria, Thiomicrorhabdus, in the Waters Affected by a Shallow-Sea Hydrothermal Plume. Biology 2025, 14, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14010028
Chung C-C, Gong G-C, Tseng H-C, Chou W-C, Ho C-H. Dominance of Sulfur-Oxidizing Bacteria, Thiomicrorhabdus, in the Waters Affected by a Shallow-Sea Hydrothermal Plume. Biology. 2025; 14(1):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14010028
Chicago/Turabian StyleChung, Chih-Ching, Gwo-Ching Gong, Hsiao-Chun Tseng, Wen-Chen Chou, and Chuan-Hsin Ho. 2025. "Dominance of Sulfur-Oxidizing Bacteria, Thiomicrorhabdus, in the Waters Affected by a Shallow-Sea Hydrothermal Plume" Biology 14, no. 1: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14010028
APA StyleChung, C.-C., Gong, G.-C., Tseng, H.-C., Chou, W.-C., & Ho, C.-H. (2025). Dominance of Sulfur-Oxidizing Bacteria, Thiomicrorhabdus, in the Waters Affected by a Shallow-Sea Hydrothermal Plume. Biology, 14(1), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14010028






