Simple Summary
Models to study the effects of exercise-induced benefits on bone-forming osteoblasts are limited and expensive. Although an orbital shaker model is simple and inexpensive, the impact of the flow produced by an orbital shaker on osteoblasts is not well defined, and this was evaluated in this study using an in vitro model. The findings of this study show that the flow produced by orbital shaking at physiological levels stimulates anabolic effects on osteoblasts, as evident from an increase in cell number and expression levels of osteoblast differentiation markers and mechanosensitive genes. Therefore, an orbital shaker at lower frequency provides an inexpensive and appropriate model to study mechanical strain effects on osteoblasts in vitro.
Abstract
Flow induced by an orbital shaker is known to produce shear stress and oscillatory flow, but the utility of this model for studying mechanical loading effects in osteoblasts is not well defined. To test this, osteoblasts derived from the long bones of adult male C57BL/6J mice were plated on 6-well plates and subjected to orbital shaking at various frequencies (0.7, 1.4, and 3.3 Hz) for 30 and 60 min in serum-free differentiation media. The shear stress on cells produced by 0.7, 1.4, and 3.3 Hz shaking frequencies were 1.6, 4.5, and 11.8 dynes/cm2, respectively. ALP activity measured 72 h after shaking (orbital flow) showed a significant increase at 0.7 and 1.4 Hz, but not at 3.3 Hz, compared to static controls. Orbital flow-induced mechanical stress also significantly increased (25%) osteoblast proliferation at a 0.7 Hz flow compared to static controls. Additionally, expression levels of bone formation markers Osf2, Hif1a, Vegf, and Cox2 were significantly increased (1.5- to 3-fold, p < 0.05) in cells subjected to a 0.7 Hz flow compared to non-loaded control cells. We also evaluated the effect of orbital flow on key signaling pathways (mTOR, JNK, and WNT) known to mediate mechanical strain effects on osteoblasts. We found that blocking mTOR and WNT signaling with inhibitors significantly reduced (20–30%) orbital flow-induced ALP activity compared to cells treated using a vehicle. In contrast, inhibition of JNK signaling did not affect flow-induced osteoblast differentiation. In conclusion, our findings show that the flow produced by an orbital shaker at a lower frequency is an appropriate inexpensive model for studying the molecular pathways mediating mechanical strain effects on primary cultures of osteoblasts in vitro.
1. Introduction
Mechanical loading is an important regulator of skeletal growth and maintenance [1,2,3,4]. Previous studies have shown that loading stimulates new bone formation [2,5,6,7], while non-loading results in bone loss leading to pathological conditions like osteopenia and osteoporosis [8,9,10]. Thus, exercise has been used as a strategy to reduce or prevent bone loss [2,11,12]. However, in conditions where patients are bedridden [13] (spinal cord injury and aging), exercise is not feasible. Therefore, our studies have focused on understanding the mechanisms by which exercise regulates bone-forming osteoblast function in an effort to identify novel therapeutic targets whose regulation might stimulate new bone formation when exercise is not possible.
It is known from studies that bones are not loaded in a sinusoidal manner, but are loaded repetitively, inducing fluid flow through the lacunar/canalicular network, which is reversed, causing oscillatory flow [14]. To mimic this loading effect in vitro on bone cells, several loading models have been developed that include a fluid flow chamber and an oscillatory flow apparatus [5,14,15]. These models involve complex equipment setups and are relatively expensive. As the flow induced by an orbital shaker is also known to produce shear stress and oscillatory flow, this study evaluated the utility of this model for mechanical loading effects on osteoblasts.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Osteoblasts Cultures
Cells were isolated from marrow flushed long bones of adult C57BL/6J mice using collagenase digestion. These cells were cultured in alpha minimal essential medium (αMEM) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and antibiotics (penicillin, 100 units/mL, and streptomycin, 100 µg/mL).
2.2. Orbital Shaker and Rocker Flow Models
First-passage cells (approximately 10,000/well) in a 300 µL volume of medium were plated on the peripheral region of 6-well plates. The plates were incubated for 20 min in a 5% CO2 incubator so the cells could attach. Subsequently, 2 mL of media containing serum and antibiotics were added to each plate, and incubation at 5% CO2 continued for 24 h. Media was replaced with serum-free media containing 0.1% bovine serum albumin (BSA), and twenty-four hours later cells were subjected to orbital shaking in serum-free media at speeds of 3, 4, and 5, which corresponded to 0.7, 1.4, and 3.3 frequencies (Hz), respectively, for 30 and 60 min. For the rocker model, cells were subjected to rocking using a see-saw rocker for 30 min, at speeds of 6 and 8, which corresponded to 0.2 and 0.28 Hz, respectively. For both models, no-flow plates (static controls) were kept inside the 5% CO2 incubator for the same time. Videos depicting the orbital shaker and see-saw rocker models used in this study are shown in the Supplementary Materials.
2.3. Osteoblast Proliferation Assay
First-passage cells were plated in 6-well plates and cultured in αMEM containing 10% CS and antibiotics for 24 h, followed by another 24 h in αMEM containing 0.1% BSA and antibiotics. Cells were subjected to mechanical stress produced by an orbital shaker or a see-saw rocker. The experiment was terminated 48 h after the flow cycle, and proliferation was assessed using a Cy-Quant Dye Kit (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
2.4. Differentiation Assay
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity was used as a measure of osteoblast differentiation. For the ALP assay, prior to in vitro mechanical loading, osteoblasts were cultured in serum containing media for 24 h, followed by 24 h in serum-free media. Next, the differentiation medium containing 0.1% BSA, ascorbic acid (100 µg/mL), and β-glycerophosphate (10 mM) was added to the plates, and then subjected to orbital flow. Seventy hours post flow, the experiment was terminated. Briefly, cells were washed with 1× PBS, and 100 µL of ALP lysis buffer was added. Cell lysates were stored at −80 °C. Twenty-four hours later, the ALP substrate was added to the lysate, and plates were read at 410–490 nm. The total protein was also measured from cell lysates using a bicinchoninic acid (BCA) assay, and ALP activity was quantitated as described [16].
Subsequently, orbital flow-induced ALP activity was assessed in the presence or absence of inhibitors of signaling pathways that are known to mediate mechanical loading effects. Prior to in vitro mechanical loading, the differentiation medium containing 0.1% BSA, ascorbic acid (100 µg/mL), and β-glycerophosphate (10 mM) was added to the plates. Inhibitors of either WNT (50 µM, JW74, Tocris, MN, USA), mTOR (200 mM, Rapamycin, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), or JNK (1 µM, Inhibitor II, Millipore Sigma, Burlington, MA, USA) signaling were added, and plates were incubated for 1 h and then subjected to orbital shaking (orbital flow) for 60 min. After the flow treatment, plates were incubated at 5% CO2 for 72 h and then terminated to quantitate ALP activity by measuring para-nitrophenol (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) using a plate reader [16].
2.5. Gene Expression
We isolated total ribonucleic acid (RNA) from cells subjected to flow and no-flow using a Qiagen isolation kit protocol as per the manufacturer’s instructions (Qiagen, Germantown, MD, USA). Two hundred nanograms of purified total RNA was used to synthesize the first strand complementary deoxyribose nuclei acid (cDNA) by reverse transcription as per the manufacturer’s instructions (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). The first strand DNA was subjected to real-time PCR amplification using a SYBR green master mix and gene-specific primers (IDT DNA technology, San Diego, CA, USA) on a ViiA7 real-time PCR system (Applied Biosystems, Waltham, MA, USA). The endogenous control (β-actin) was used to normalize data, and normalized values were subjected to the 2∆∆Ct formula (where C+ is the contraction threshold) to calculate the fold change between the vehicle and experimental groups [17].
2.6. Immunofluorescence Labeling of Cells
Cells on 6-well plates were subjected to orbital flow for 60 min and terminated 30 min after the flow experiment. The static control was kept inside the incubator without orbital flow. Cells were rinsed with 1× PBS and fixed with 2 mL of 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 min. Cells were rinsed three times with 1× PBS for 5 min, with gentle shaking, and then treated with 2 mL of 1% SDS to increase cellular permeability. Cells were washed with 1× PBS once and then blocked with 0.4% goat serum with the blocking buffer for 1 h. Cells were incubated with mTOR rabbit primary antibody (Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA, USA) or mouse β-catenin monoclonal antibody (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA), diluted 1:500 and 1:1000, respectively, in the antibody dilution buffer for 48 h at 4 °C, with gentle shaking. Forty-eight hours later, cells were washed with 1× PBS containing 0.01% Tween-20 three times for 5 min and incubated with Alexa 555 fluorochrome-conjugated secondary antibody and Alexa 488 fluorochrome-conjugated secondary antibody (mouse anti-goat, Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR, USA) diluted in antibody dilution buffer for 2 h while being protected from light, with gentle shaking. After 2 h, cells were rinsed with 1× PBS once, incubated with DAPI (Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA, USA) for nuclear staining, and rinsed three times for 5 min with 1× PBS. Cells were protected from light, and the fluorescent signal for key signaling proteins was visualized under 50× magnification using a Lecia fluorescence microscope.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. The Student t-test was used to evaluate differences between flow-induced effects on cells compared to static controls. A p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results and Discussion
Multiple mechanical loading devices have been developed and tested to study the effects of mechanical strain on bone-forming osteoblast cell function. Among these models, rocker and orbital flow models are known to produce shear stress and oscillatory flow, respectively. As these two models are easy to set up and relatively inexpensive, we evaluated the mechanical strain effects produced using orbital flow and rocker models on osteoblast proliferation and ALP activity, which are well-established measures of osteoblast differentiation. Prior to subjecting osteoblasts to in vitro flow stress, we first assessed the flow output produced at different speeds by orbital and see-saw rocker models by adding 2 mL of medium into 6-well plates. We found that the flow induced by the orbital shaker at speeds 1 and 2 and by the see-saw rocker at speed 5 produced only 10–13 and 9 revolutions per minute (rpm), respectively. Because of the relatively slow oscillation speed, it was unlikely that there would be effects on cells in the short duration of loading using these speeds. Therefore, other rotational speeds in both models were assessed. In the orbital shaker model, at speed 3 the flow around cells was visible and 42 rpm was produced in the 6-well plate. In the see-saw model, the flow produced was 16–20 rpm (see-saw rocking) at speed settings 6 and 8 in the 6-well plate. The amount of mechanical strain (dyne/cm2) applied to cells in 6-well plates at speed 3 in the orbital shaker and at speeds 6 and 8 in the see-saw rocker model were determined using the formulas τmax = a√ηp(2πf)3 and τ = πµθmax/2δ2T, respectively, as described [18]. In the formula τmax = a√ηp(2πf)3, τmax corresponds to shear stress expressed as dynes/cm2. The “a” is the orbital radius of the rotation of the orbital shaker, η is the viscosity of the culture medium, p is the density of the culture medium, and f is the frequency of the rotation (rotation/second). In the formula τ = πµθmax/2δ2T, τ represents shear stress at the bottom of the plate, µ is the fluid viscosity, θmax corresponds to the maximum flip angle, δ2 is the fluid depth to well length, and T is the time required for one cycle per second [19]. Using the above formula, in the orbital shaker we found that 42 rpm represented approximately 0.7 Hz, which corresponded to 1.61 dyne/cm2/min of shear stress applied to the cells. In the rocker model, we found that 12 and 17 rpm corresponded to 0.2 and 0.28 Hz, respectively, which corresponded to 0.03 and 0.043 dyne/cm2/min of shear stress applied to the cells, respectively. Based on these data, we subjected osteoblasts to orbital shaking at 0.7 Hz and to see-saw rocking at 0.2 and 0.28 Hz.
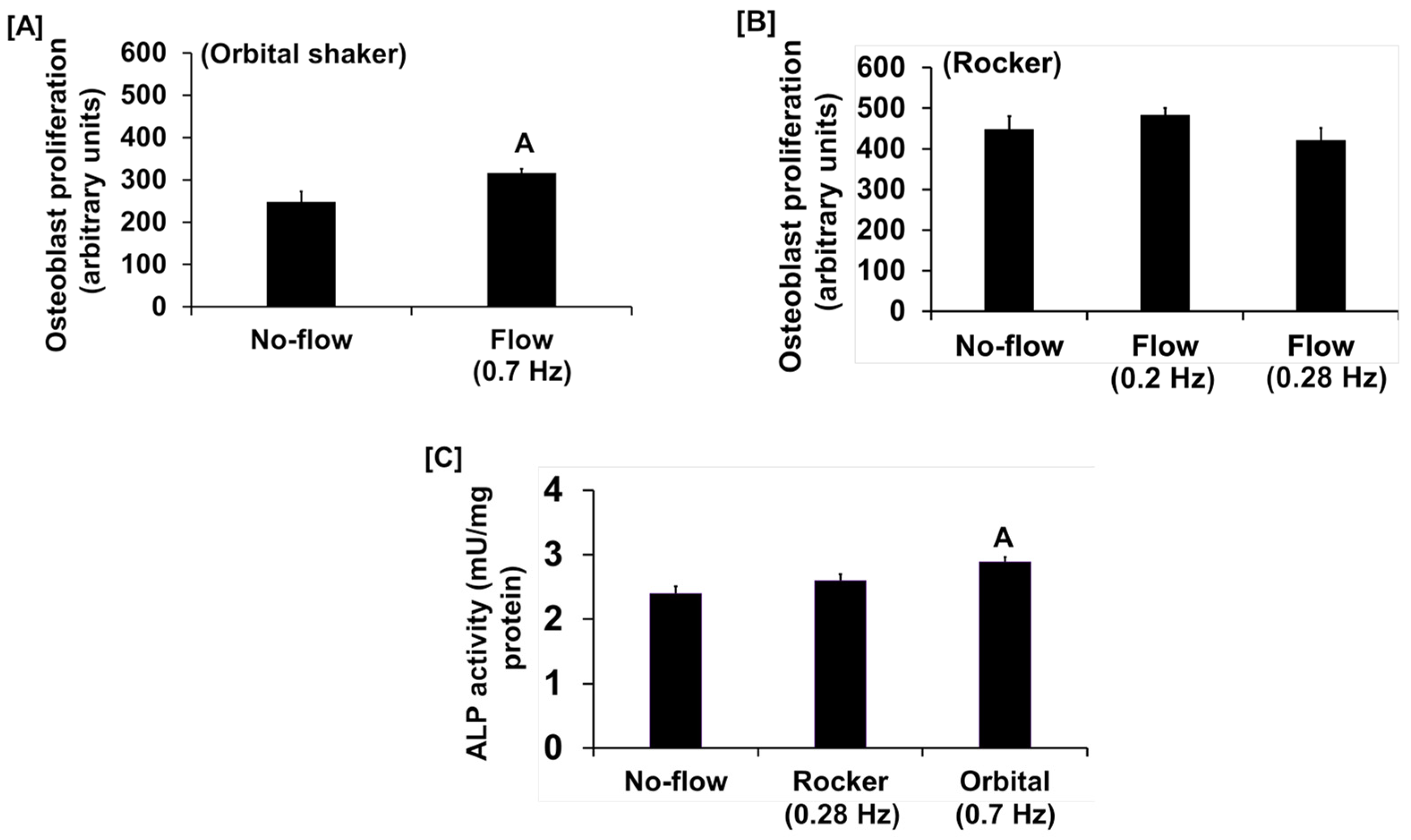
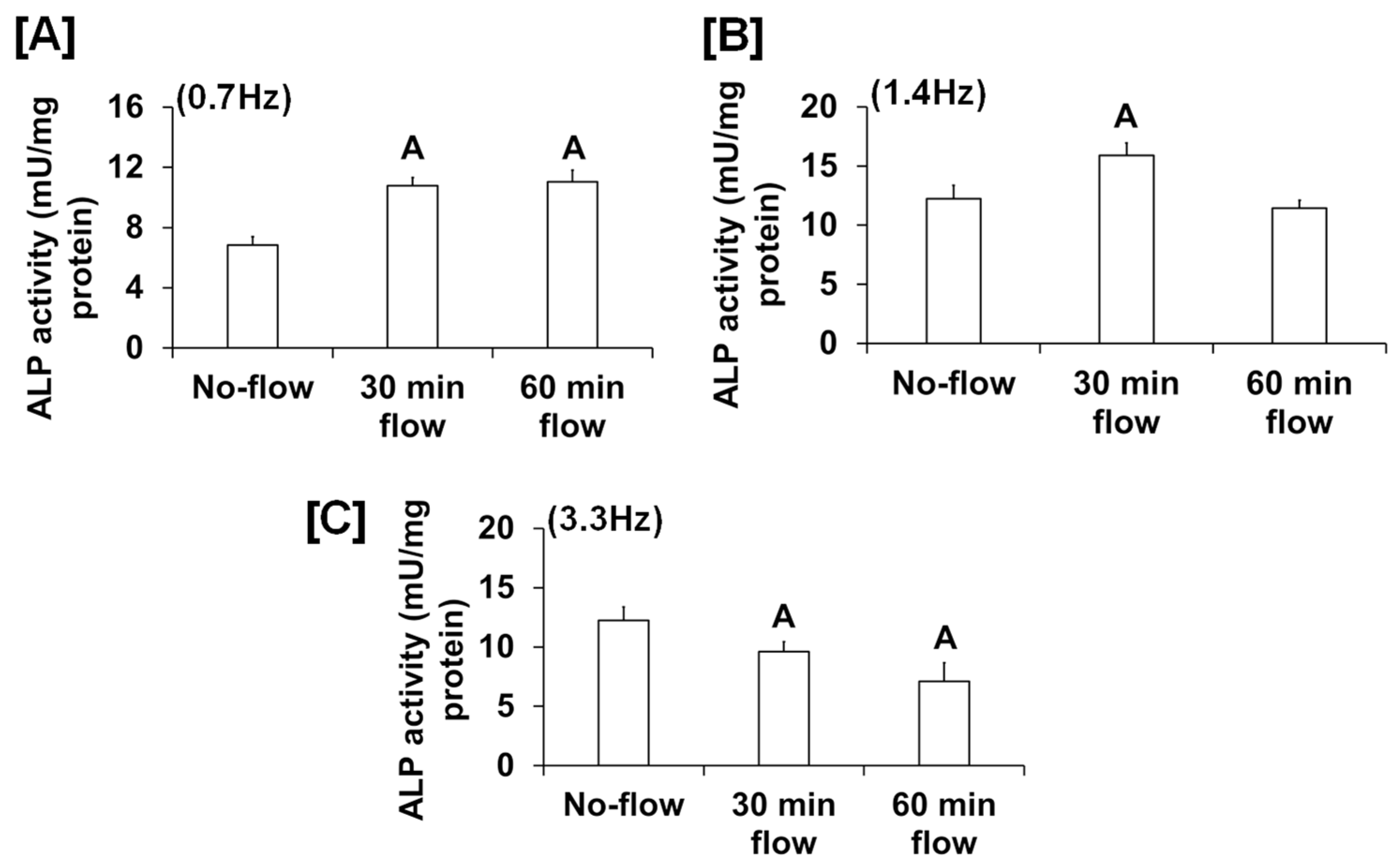
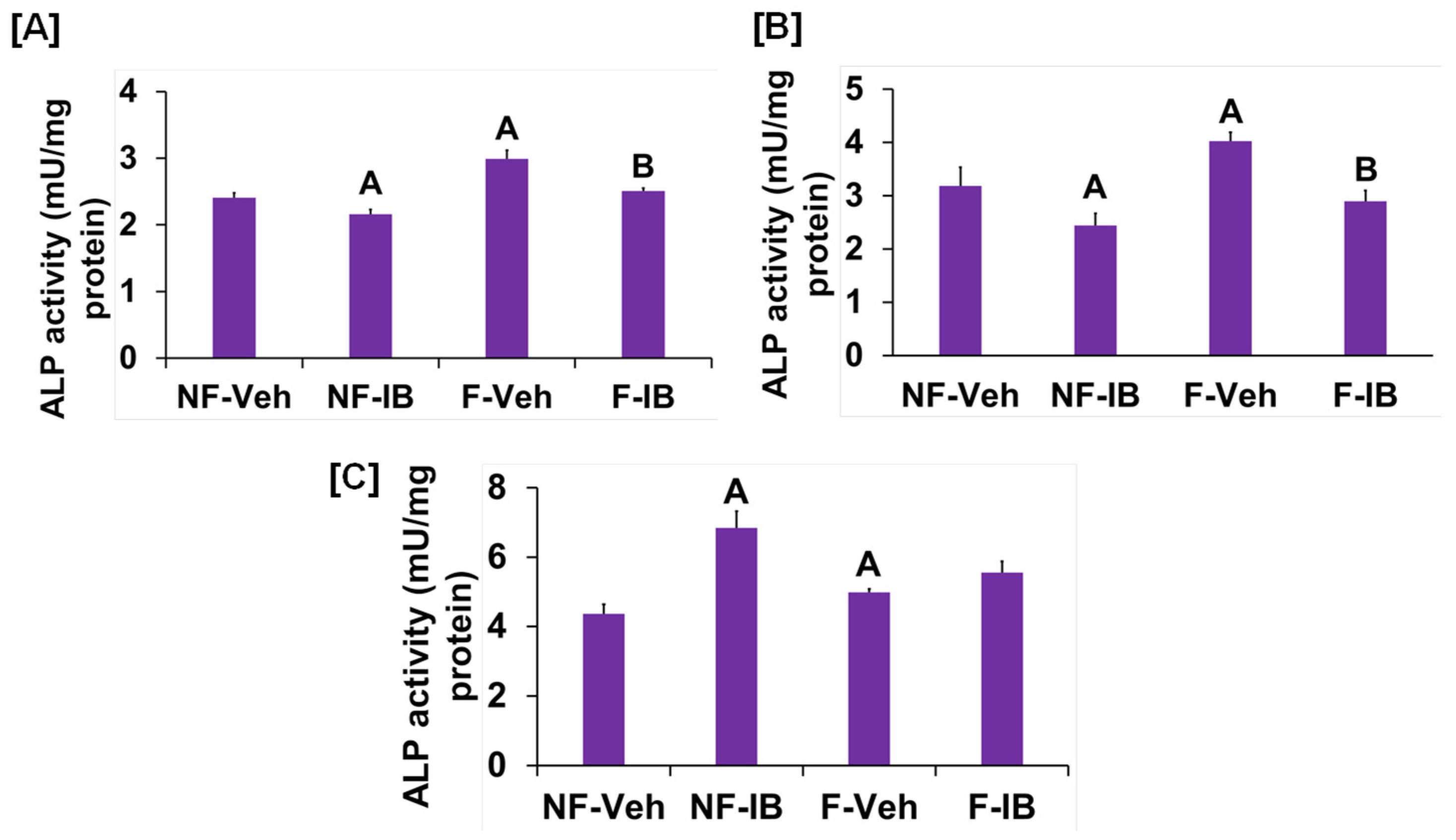
We found that the fluid flow generated by an orbital shaker moving at 0.7 Hz significantly increased osteoblast proliferation (Figure 1A), while this effect was not significant for the flow applied to cells at 0.2 Hz by the see-saw rocker model (Figure 1B). In addition to proliferation, we found that the orbital shaker model produced a significant increase in osteoblast differentiation, as measured by ALP activity compared to stationary osteoblasts (static control) (Figure 1C). However, there was no increase in osteoblast differentiation using the rocker model in response to an applied flow of 0.28 Hz. The most likely explanation for the lack of an ALP response in the rocker model could be that the amount of shear stress applied to the cells was too low, and a higher frequency of flow may be required to stimulate an anabolic effect on the cells. We next evaluated whether increasing the frequency and duration of orbital shaking maximized flow-induced anabolic effects on the cells. To test this, osteoblasts were subjected to the established speeds 3, 4, and 5, which produced 42, 84, and 198 rpm, respectively, in the 6-well plates, which corresponded to 0.7, 1.4, and 3.3 Hz and 1.6, 4.5, and 11.8 dyne/cm2/min shear stresses, respectively, on the cells. We found that the flow at 0.7 Hz for 30 and 60 min was anabolic, as represented by increased ALP activity (Figure 2A). However, for the flow applied at 1.4 Hz, this effect was observed only at 30 min, and not at 60 min (Figure 2B). Furthermore, in cells subjected to a flow of 3.3 Hz, the ALP activity was significantly decreased (Figure 2C). These data suggest that increasing the frequency of loading beyond 0.7 Hz in the orbital shaker did not increase osteoblast function.
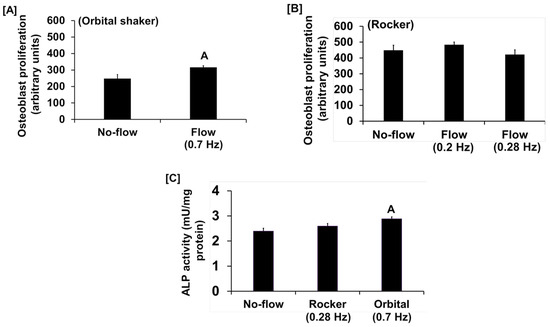
Figure 1.
Proliferation response of cultured osteoblasts to (A) orbital shaking and (B) rocker shaking, and (C) ALP activity response to orbital and rocker shaking. Values are mean ± SEM, n = 8, and A p < 0.05 vs. no-flow.
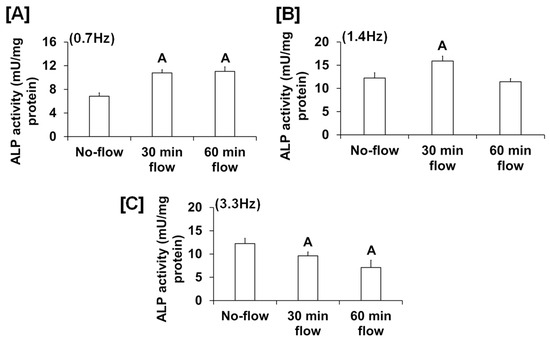
Figure 2.
ALP activity in osteoblasts subjected to orbital flow stress at different frequencies: (A) 0.7 Hz, (B) 1.4 Hz, and (C) 3.3 Hz for 30 and 60 min durations. Values are mean ± SEM, n = 5, and A p < 0.05 vs. no-flow.
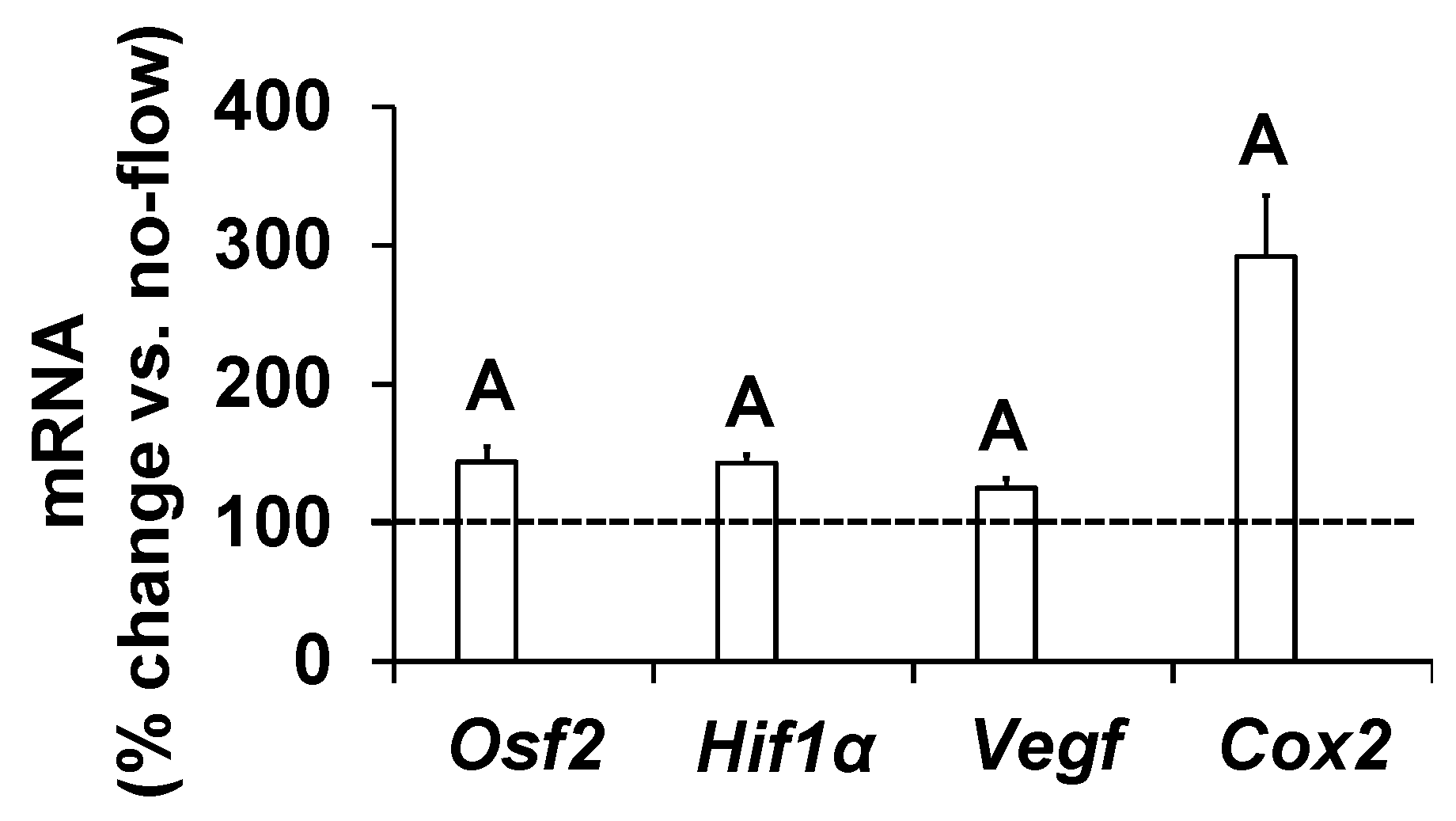
To further determine if increased osteoblast activity in response to orbital shaking was the consequence of increased gene expression, we measured expression levels of genes that have been implicated as mediators of mechanical strain in osteoblasts [17,20,21,22]. Cells were exposed to an orbital flow of 0.7 Hz for 60 min, and the study was terminated after four hours. Total RNA was isolated, and cDNA was synthesized. Real-time PCR was used to quantitate the expression of genes in cells subjected to flow and no-flow. We found that the expression levels of Osf2, Cox2, Vegf, and Hif1α significantly increased in response to this orbital flow, demonstrating that the orbital shaker was effective at increasing the expression of genes involved in promoting bone formation (Figure 3).
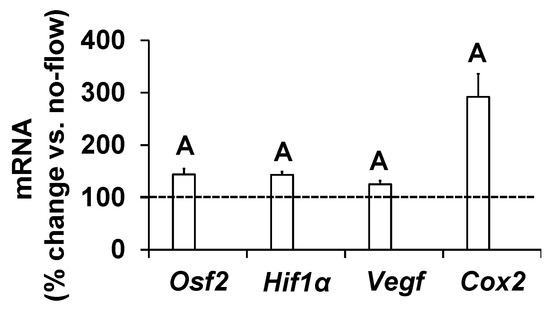
Figure 3.
Expression levels of mechanosensitive genes in response to orbital flow in osteoblasts. Values are mean ± SEM, n = 5, and A p < 0.05 vs. no-flow.
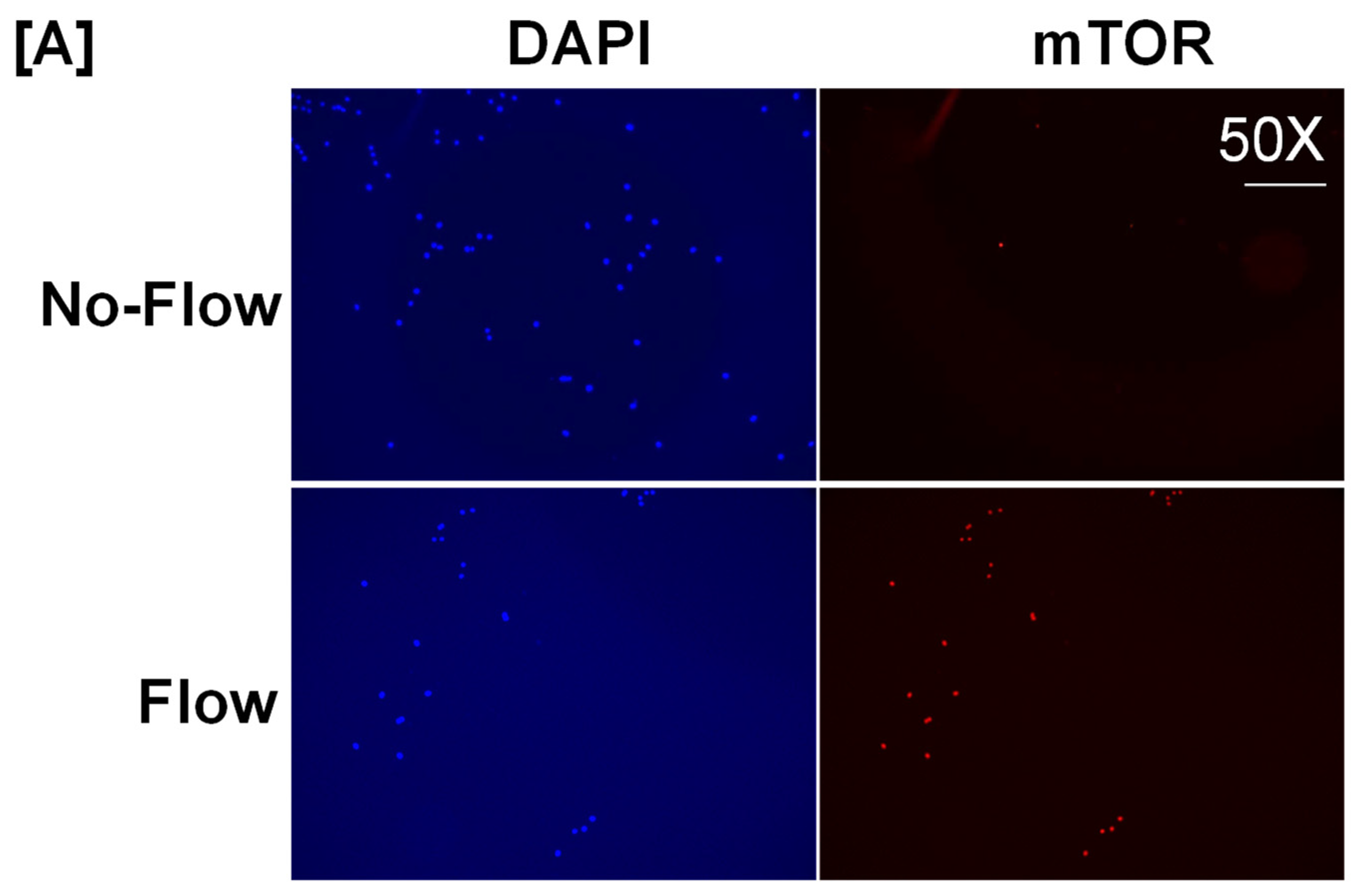
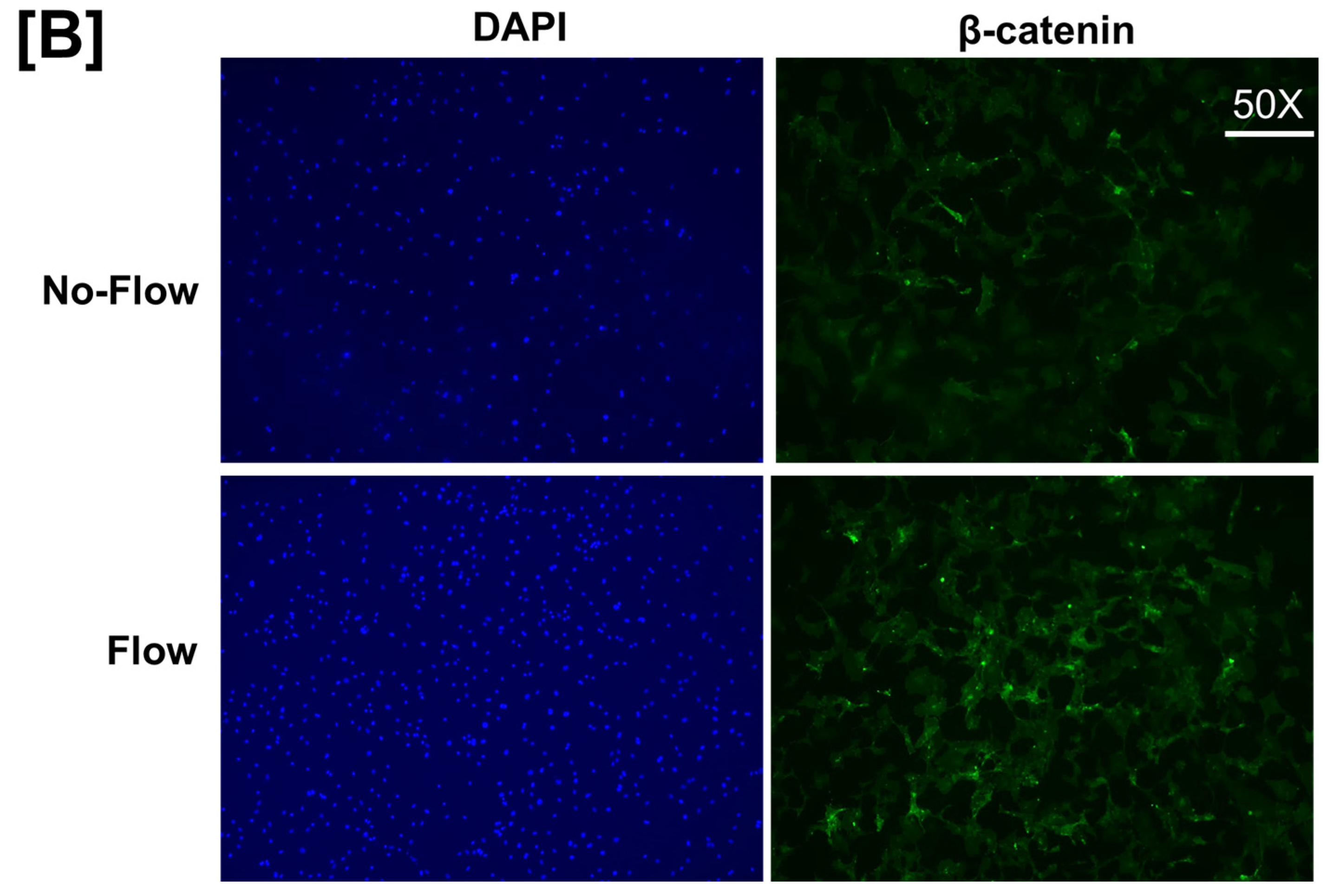
It is well known from previous studies that integrins and receptors on the surface of bone cells convert mechanical signals into biochemical signals, which stimulates different cellular processes that contribute to bone formation [23,24]. In this regard, studies using in vitro and in vivo models reported that some of the key signaling pathways (WNT, BMP, mTOR, and JNK) respond to mechanical strain [25,26,27,28]. Therefore, we assessed if these signaling pathways were activated in response to orbital flow. mTOR protein expression was evaluated using immunofluorescent antibodies 30 min after orbital shaking. Figure 4A shows mTOR positive cells, represented by a red dot, in the flow and no-flow groups. We found that there were three times more mTOR positive osteoblasts (16.3 ± 4.4 vs. 5 ± 1.73, p = 0.07, n = 3) in the flow group compared to the no-flow group. In addition to mTOR, we also tested if β-catenin expression was stimulated in response to orbital flow, and found that a higher number (15.66 ± 2.6 vs. 6.33 ± 0.33, p = 0.02, n = 3) of osteoblasts expressed detectable levels of β-catenin, as represented by the green signal, 30 min post flow compared to no-flow (Figure 4B). The consequences of blocking specific pathways using specific inhibitors on osteoblast differentiation were evaluated, and it was found that blocking mTOR signaling with inhibitors significantly reduced orbital flow-induced ALP activity compared to vehicle-treated controls (Figure 5A). A similar finding was also observed after blocking the WNT signaling pathway (Figure 5B). In contrast, JNK signaling inhibitors did not significantly affect flow-induced osteoblast differentiation (Figure 5C). These data demonstrate that the orbital shaker, like other established in vitro mechanical loading models, stimulated intra-cellular anabolic signaling pathways in response to flow.
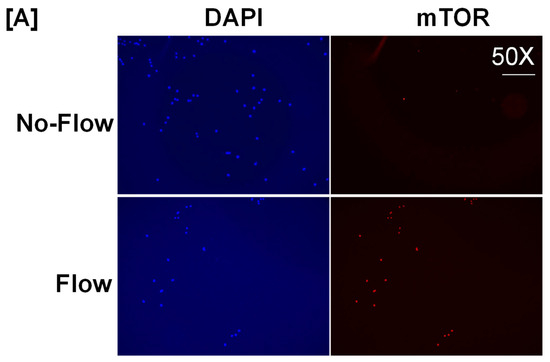
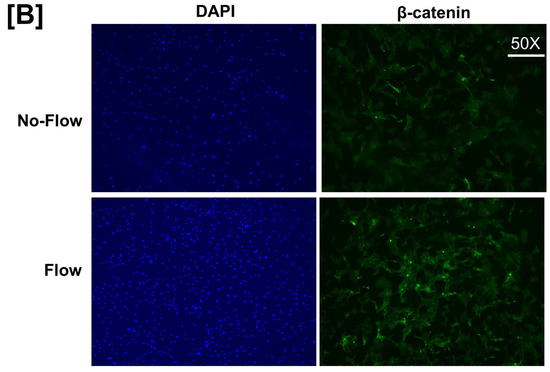
Figure 4.
Higher numbers of osteoblasts expressed detectable levels of (A) mTOR and (B) β-catenin after 30 min of orbital flow compared to No-flow. Red color represents mTOR expression, green represents β-catenin, and blue corresponds to nuclei stained with DAPI. n = 3.
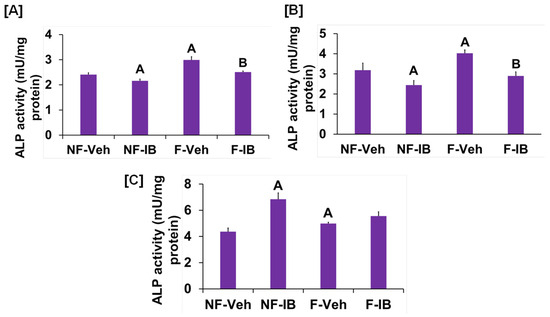
Figure 5.
Effects of (A) WNT, (B) mTOR, and (C) JNK signaling inhibitors on orbital flow-induced osteoblast differentiation. NF, No-flow; F, Flow; Veh, vehicle; IB, inhibitor. A p < 0.05 vs. NF-Veh, B p < 0.05 vs. F-Veh. Values are mean ± SEM, n = 5.
4. Conclusions
Our findings demonstrate that the flow produced by orbital shaking at a lower frequency is a useful inexpensive model for studying the molecular pathways mediating mechanical strain effects in primary cultures of osteoblasts in vitro.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/biology13090646/s1, Supplemental File S1. Video showing orbital shaker used in this study. Supplemental File S2. Video showing see-saw shaker used in this study.
Author Contributions
Study design, writing, editing, and interpretation, S.M. and C.K.; cell culture experiments, data collection, and analysis, S.M., R.S. and C.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by funding from the NIAMS (R01-048139), the NIH, and the Veterans Administration (BX005263 and BX005381) awarded to Dr. Subburaman Mohan.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted according to the guidelines of the National Institute of Health (USA) and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Jerry L. Pettis Memorial Veterans Affairs Medical Center.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Raw data are available up on request.
Acknowledgments
We thank Donna Strong for proofreading this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Bergmann, P.; Body, J.J.; Boonen, S.; Boutsen, Y.; Devogelaer, J.P.; Goemaere, S.; Kaufman, J.; Reginster, J.Y.; Rozenberg, S. Loading and skeletal development and maintenance. J. Osteoporos. 2010, 2011, 786752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Xu, S.; Zhang, H. Regulation of bone health through physical exercise: Mechanisms and types. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1029475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, T.E.; Shea, B.; Dawson, L.J.; Downie, F.; Murray, A.; Ross, C.; Harbour, R.T.; Caldwell, L.M.; Creed, G. Exercise for preventing and treating osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011, 7, CD000333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, C.T.; Lanyon, L.E. Regulation of bone mass by mechanical strain magnitude. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1985, 37, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesavan, C.; Wergedal, J.E.; Lau, K.H.; Mohan, S. Conditional disruption of IGF-I gene in type 1alpha collagen-expressing cells shows an essential role of IGF-I in skeletal anabolic response to loading. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 301, E1191–E1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.M.; Guerriere, K.I.; Popp, K.L.; Castellani, C.M.; Pasiakos, S.M. Exercise for optimizing bone health after hormone-induced increases in bone stiffness. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1219454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L. Effects of Exercise or Mechanical Stimulation on Bone Development and Bone Repair. Stem Cells Int. 2022, 2022, 5372229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eimori, K.; Endo, N.; Uchiyama, S.; Takahashi, Y.; Kawashima, H.; Watanabe, K. Disrupted Bone Metabolism in Long-Term Bedridden Patients. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaul, E.; Malcov, T.; Menczel, J. Osteoporosis in tube-fed bed-ridden elderly female patients. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2009, 57, 1318–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafaro, L.; Napoli, N. Current and Emerging Treatment of Osteoporosis. In Orthogeriatrics: The Management of Older Patients with Fragility Fractures, 2nd ed.; Falaschi, P., Marsh, D., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 257–272. [Google Scholar]
- Benedetti, M.G.; Furlini, G.; Zati, A.; Letizia Mauro, G. The Effectiveness of Physical Exercise on Bone Density in Osteoporotic Patients. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 4840531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, A.R.; Kim, S.W. Effects of Resistance Exercise on Bone Health. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 33, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglino, R.A.; Lazzari, A.A.; Garshick, E.; Morse, L.R. Spinal cord injury-induced osteoporosis: Pathogenesis and emerging therapies. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2012, 10, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael Delaine-Smith, R.; Javaheri, B.; Helen Edwards, J.; Vazquez, M.; Rumney, R.M. Preclinical models for in vitro mechanical loading of bone-derived cells. Bonekey Rep. 2015, 4, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzaka, T.; Matsugaki, A.; Nakano, T. Control of osteoblast arrangement by osteocyte mechanoresponse through prostaglandin E2 signaling under oscillatory fluid flow stimuli. Biomaterials 2021, 279, 121203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farley, J.R.; Hall, S.L.; Tanner, M.A.; Wergedal, J.E. Specific activity of skeletal alkaline phosphatase in human osteoblast-line cells regulated by phosphate, phosphate esters, and phosphate analogs and release of alkaline phosphatase activity inversely regulated by calcium. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1994, 9, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.; Kesavan, C. T-cell factor 7L2 is a novel regulator of osteoblast functions that acts in part by modulation of hypoxia signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 322, E528–E539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardik, A.; Chen, L.; Frattini, J.; Asada, H.; Aziz, F.; Kudo, F.A.; Sumpio, B.E. Differential effects of orbital and laminar shear stress on endothelial cells. J. Vasc. Surg. 2005, 41, 869–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittkowske, C.; Reilly, G.C.; Lacroix, D.; Perrault, C.M. In Vitro Bone Cell Models: Impact of Fluid Shear Stress on Bone Formation. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2016, 4, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.J.; Brodt, M.D.; Lynch, M.A.; Stephens, A.L.; Wood, D.J.; Civitelli, R. Tibial loading increases osteogenic gene expression and cortical bone volume in mature and middle-aged mice. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, J.A.; Bixby, E.C.; Silva, M.J. Differential gene expression from microarray analysis distinguishes woven and lamellar bone formation in the rat ulna following mechanical loading. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e29328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Yu, W.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, X.; Yuan, R.; Guo, Q. Expression of HIF-1alpha in cycling stretch-induced osteogenic differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 4489–4498. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lau, K.H.; Kapur, S.; Kesavan, C.; Baylink, D.J. Up-regulation of the Wnt, estrogen receptor, insulin-like growth factor-I, and bone morphogenetic protein pathways in C57BL/6J osteoblasts as opposed to C3H/HeJ osteoblasts in part contributes to the differential anabolic response to fluid shear. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 9576–9588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, K.; Ito, M.; Naoe, Y.; Lacy-Hulbert, A.; Ikeda, K. Integrin alphav in the mechanical response of osteoblast lineage cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 447, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakker, A.D.; Gakes, T.; Hogervorst, J.M.; de Wit, G.M.; Klein-Nulend, J.; Jaspers, R.T. Mechanical Stimulation and IGF-1 Enhance mRNA Translation Rate in Osteoblasts via Activation of the AKT-mTOR Pathway. J. Cell. Physiol. 2016, 231, 1283–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, D.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, H.; Kang, Y. Cyclic Compressive Stress Regulates Apoptosis in Rat Osteoblasts: Involvement of PI3K/Akt and JNK MAPK Signaling Pathways. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.A.; Chatterjee-Kishore, M.; Yaworsky, P.J.; Cullen, D.M.; Zhao, W.; Li, C.; Kharode, Y.; Sauter, L.; Babij, P.; Brown, E.L.; et al. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling is a normal physiological response to mechanical loading in bone. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 31720–31728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopf, J.; Petersen, A.; Duda, G.N.; Knaus, P. BMP2 and mechanical loading cooperatively regulate immediate early signalling events in the BMP pathway. BMC Biol. 2012, 10, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).