Metabolite Diversity and Carbohydrate Distribution in Brassica campestris ssp. chinensis L. Cultivars: A UPLC-MS/MS Approach
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Plants and Chemical Agents
2.2. Standardization for Mass Spectrometry Analysis
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. Factors of UPLC and Tandem Mass Spectrometry (MS/MS)
2.5. ESI-Q TRAP-MS/MS
2.6. Analysis of Metabolites
2.7. Analytical Stability of Data
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Morphological and Phenotypic Variations in Pak Choi Cultivars
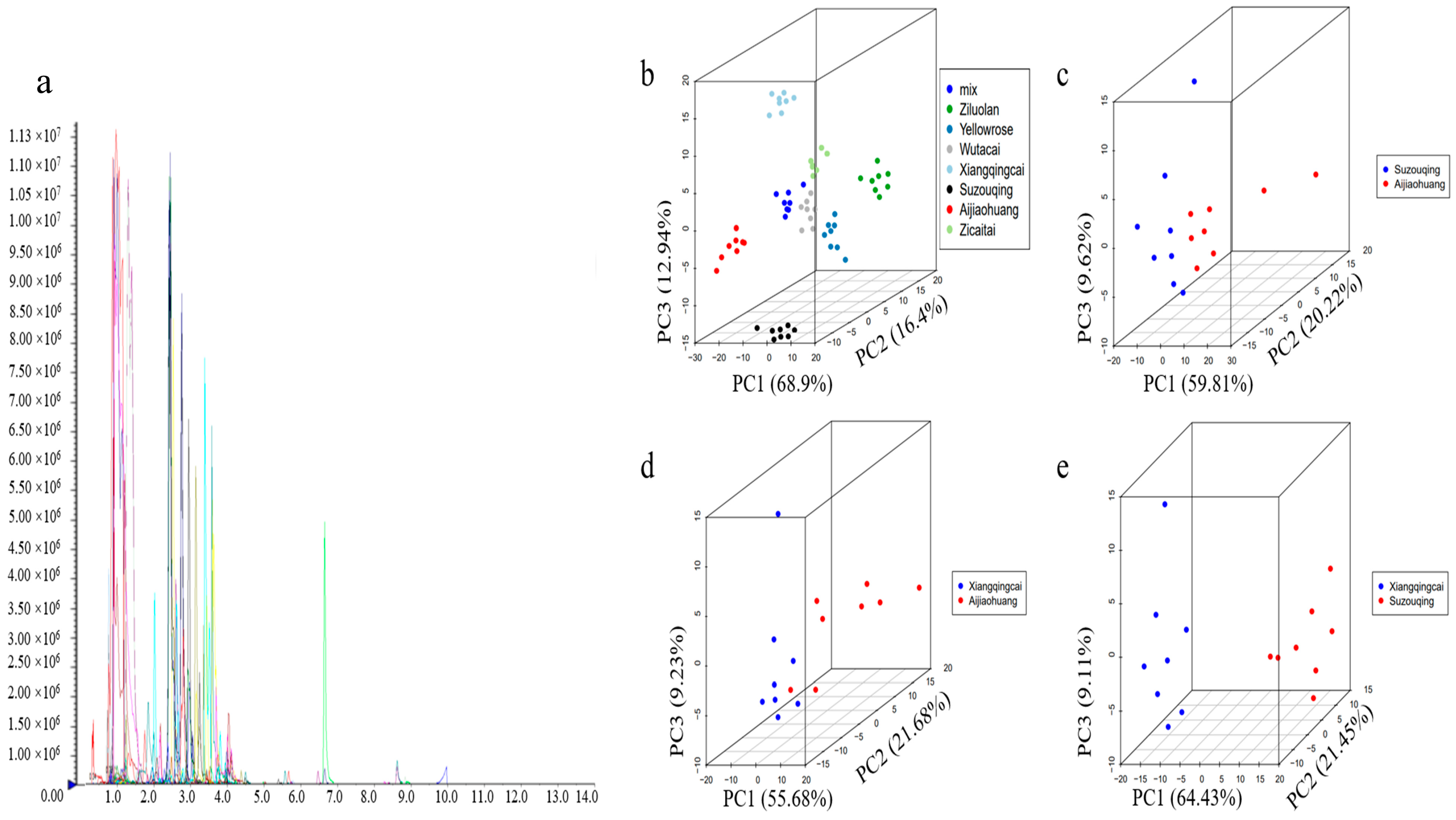
3.2. Metabolic Profiling and Principal Component Analysis of Metabolites (PCA)
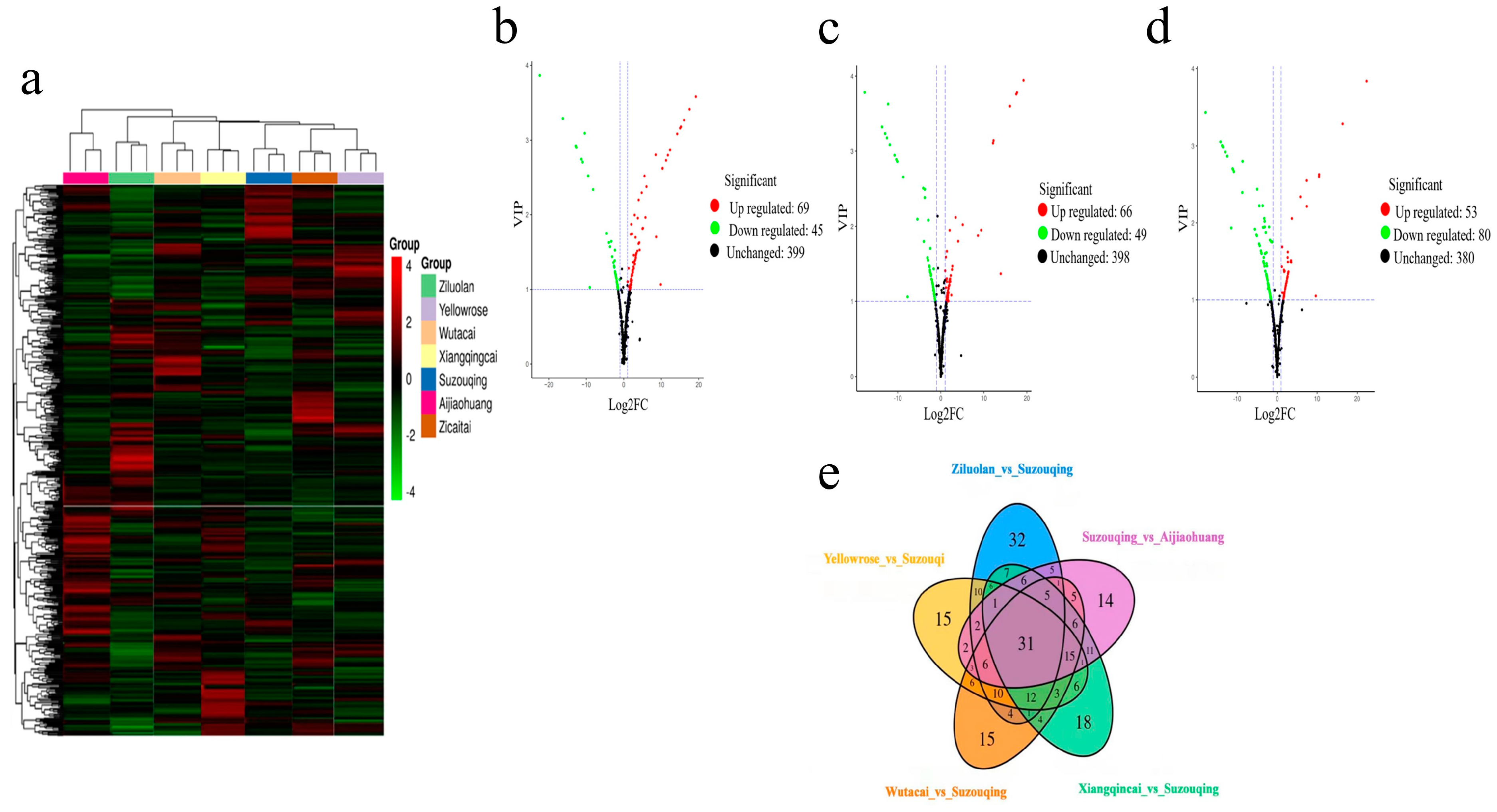
3.3. Identification of Differentially Accumulated Metabolites
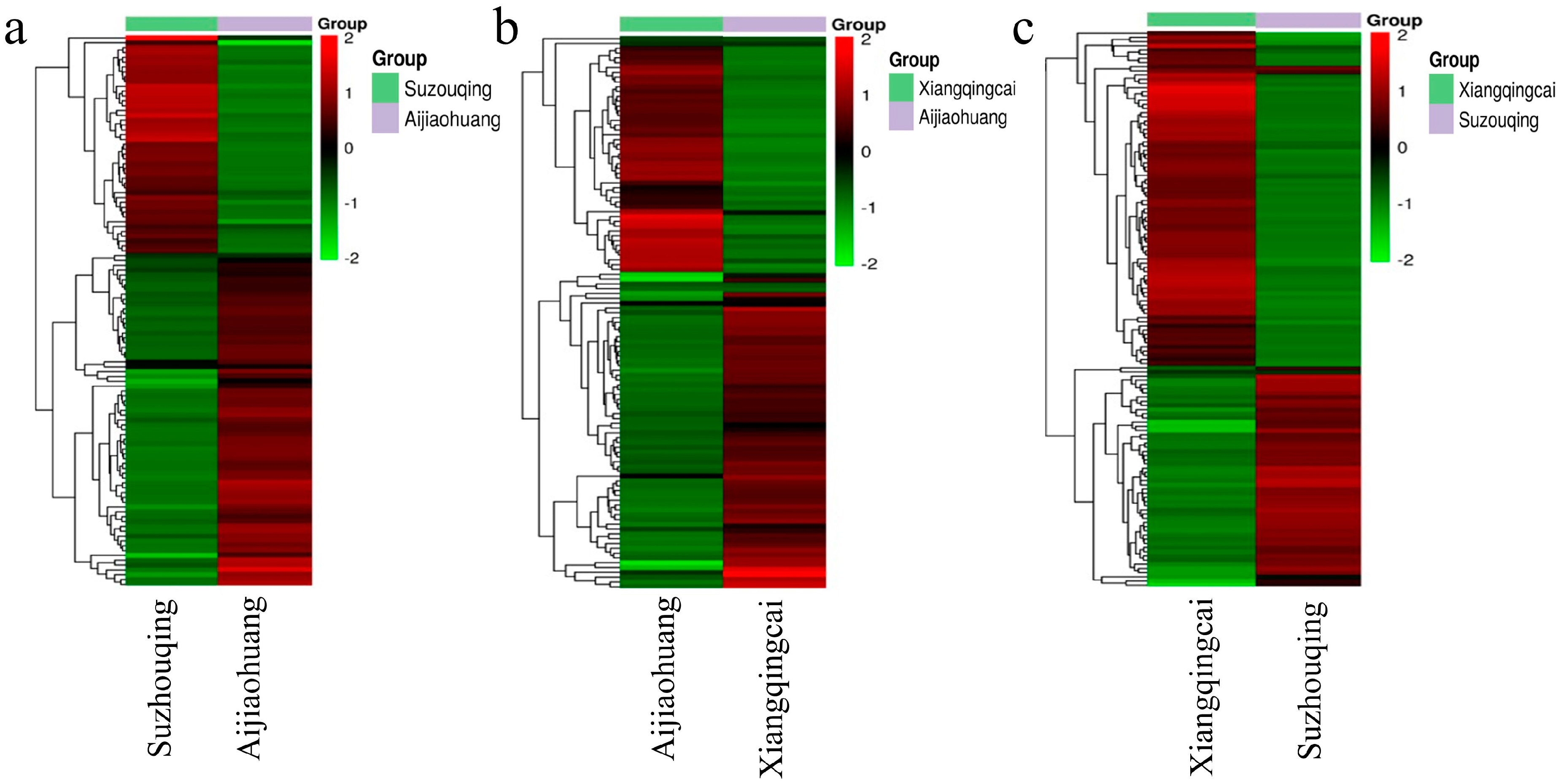
3.4. Clustering of Differentially Expressed Metabolites
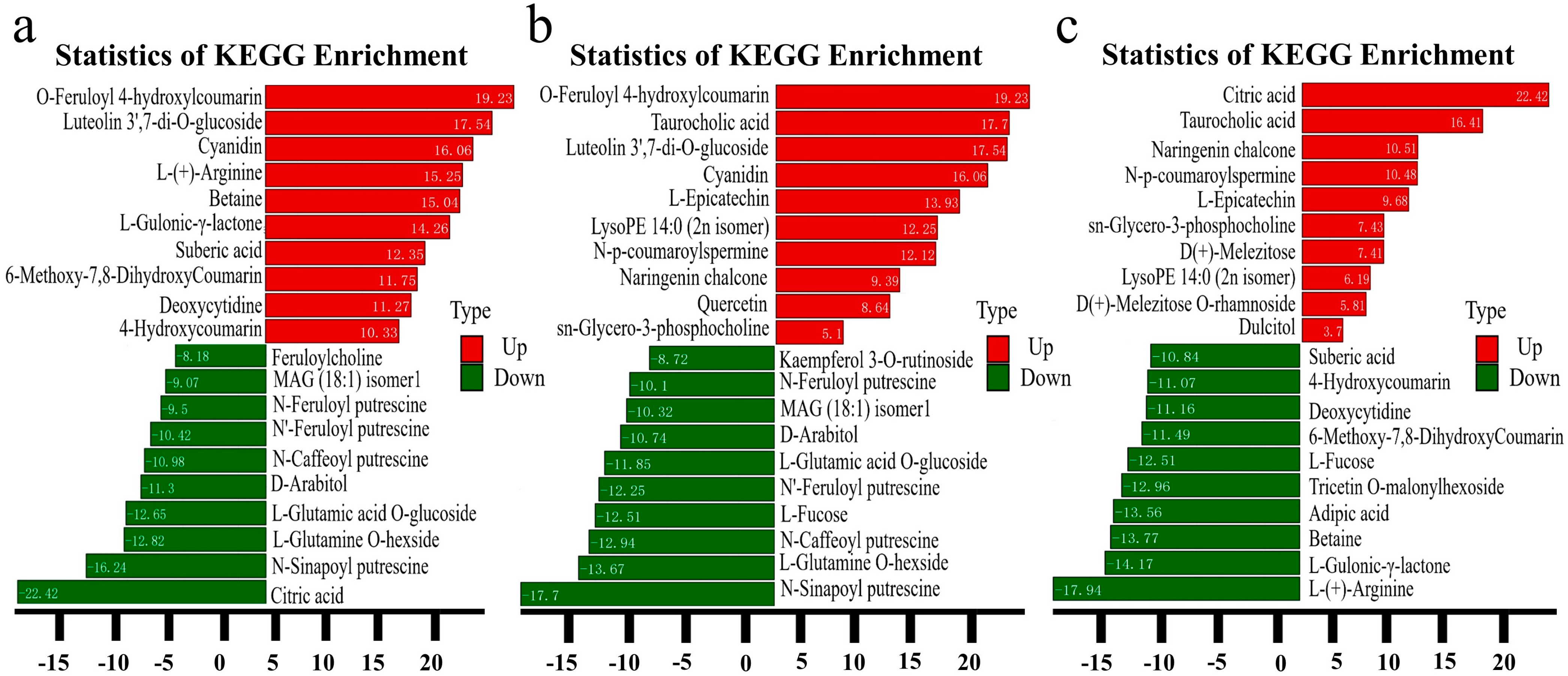
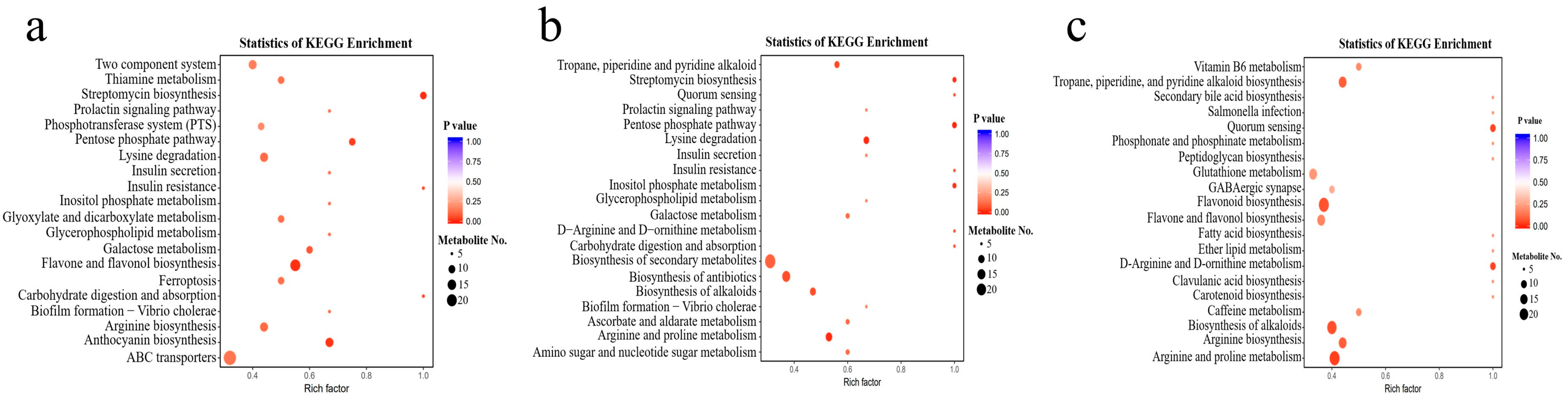
3.5. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) Enrichment and Functional Annotation of Differential Metabolites
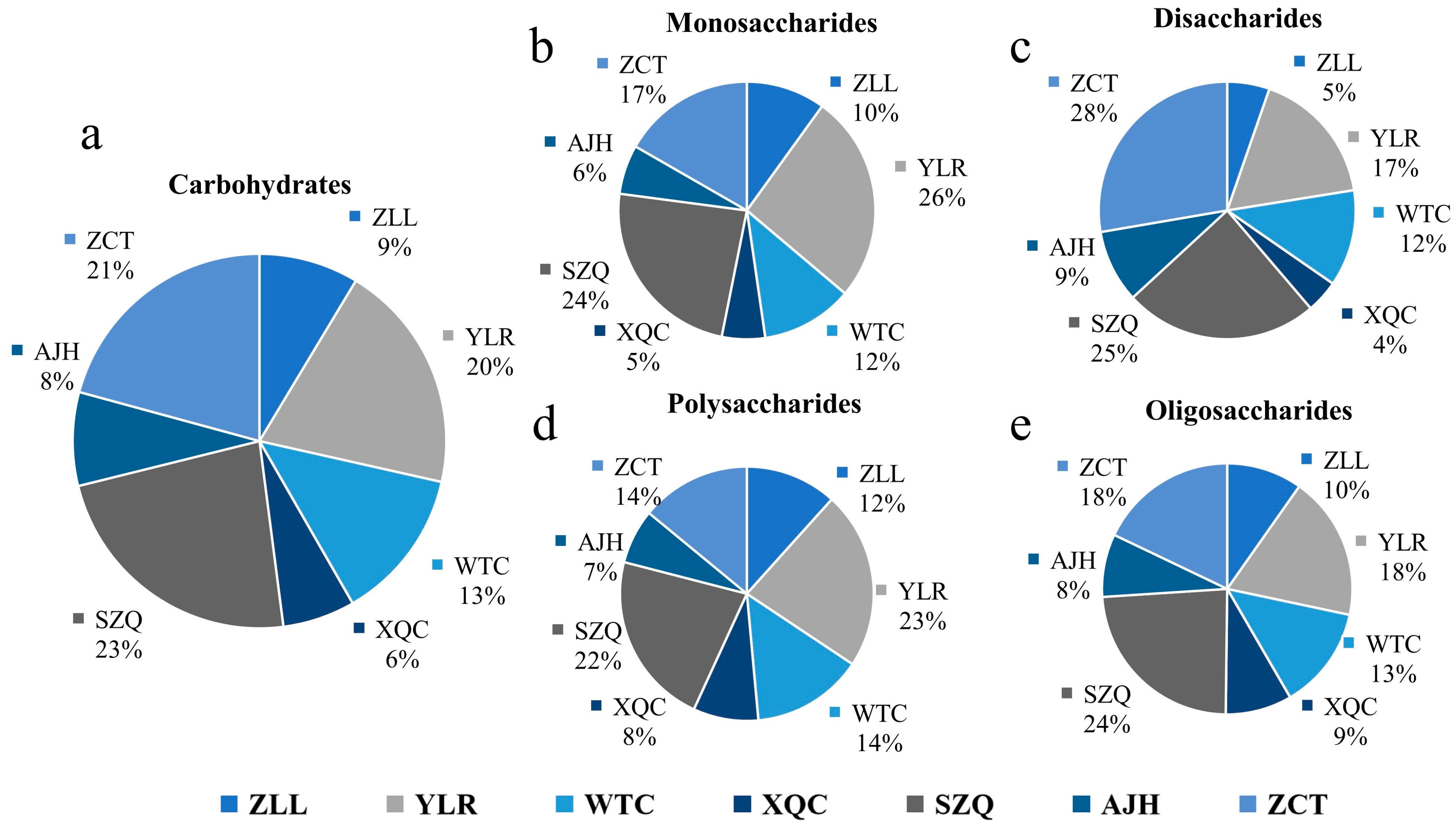
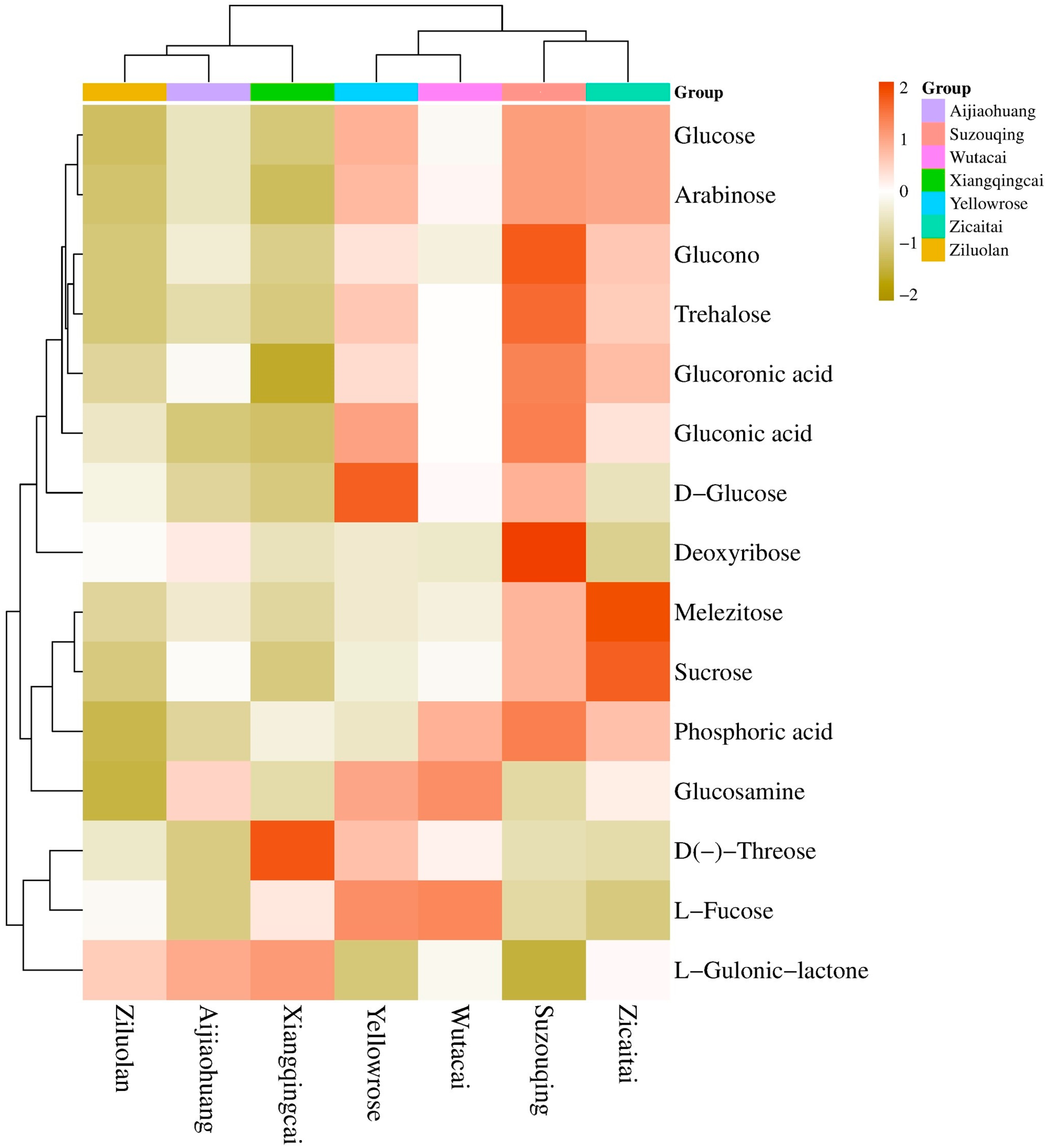
3.6. Descriptive Analysis of Carbohydrates
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, W.A.; Hu, H.; Ann Cuin, T.; Hao, Y.; Ji, X.; Wang, J.; Hu, C. Untargeted metabolomics and comparative flavonoid analysis reveal the nutritional aspects of Pak choi. Food Chem. 2021, 383, 132375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naseri, E.; Xiangyu, K.; Hu, C.; Ayaz, A.; Rahmani, M.M.; Nasim, M.; Hamdard, E.; Zahir, A.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, J.; et al. Bok-choy promotes growth performance, lipid metabolism and related gene expression in Syrian golden hamsters fed with a high-fat diet. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 2693–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, H.J.; Baek, S.A.; Sathasivam, R.; Kim, J.K.; Park, S.U. Metabolomic analysis reveals the interaction of primary and secondary metabolism in white, pale green, and green Pak choi (Brassica rapa subsp. chinensis). Appl. Biol. Chem. 2021, 64, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaźmierczak-Barańska, J.; Boguszewska, K.; Adamus-Grabicka, A.; Karwowski, B.T. Two faces of vitamin c-antioxidative and pro-oxidative agent. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, A.E.; Dulnoan, D.; Voong, K.; Ayis, S.; Mangelis, A.; Gorska, R.; Harrington, D.J.; Tang, J.C.Y.; Fraser, W.D.; Hampson, G. The additive effect of vitamin K supplementation and bisphosphonate on fracture risk in post-menopausal osteoporosis: A randomised placebo-controlled trial. Arch. Osteoporos. 2023, 18, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Peng, Y.Q.; Xiang, G.S.; Song, W.L.; Feng, L.; Jiang, X.-Y.; Li, X.-J.; He, S.-M.; Yang, S.-C.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Functional characterization of genes related to triterpene and flavonoid biosynthesis in Cyclocarya Paliurus. Planta 2024, 259, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palermo, A. Metabolomics-and systems-biology-guided discovery of metabolite lead compounds and druggable targets. Drug Discov. Today 2023, 28, 103460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bellis, P.; Sisto, A.; Lavermicocca, P. Probiotic bacteria and plant-based matrices: An association with improved health-promoting features. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 87, 104821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojwach, J.; Adetunji, A.I.; Mutanda, T.; Mukaratirwa, S. Oligosaccharides production from coprophilous fungi: An emerging functional food with potential health-promoting properties. Biotechnol. Rep. 2022, 33, e00702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Muzafar, H.M.; Alshehri, F.S.; Amin, K.A. The role of pioglitazone in antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and insulin sensitivity in a high fat-carbohydrate diet-induced rat model of insulin resistance. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2021, 54, e10782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.Y.; Ali, B.; Zhang, S.; Stoffella, P.J.; Yuan, S.; Xia, Q.; Qu, H.; Shi, Y.; Cui, X.; Guo, Y. Effects of antibiotics stress on growth variables, ultrastructure, and metabolite pattern of Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chlumská, Z.; Janeček, Š.; Doležal, J. How to Preserve Plant Samples for Carbohydrate Analysis? Test of Suitable Methods Applicable in Remote Areas. Folia Geobot. 2014, 49, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Gong, L.; Guo, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Yu, S.; Xiong, L.; Luo, J. A novel integrated method for large-scale detection, identification, and quantification of widely targeted metabolites: Application in the study of rice metabolomics. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 1769–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begou, O.; Gika, H.G.; Theodoridis, G.; Wilson, I.D. Quality control and validation issues in LC-MS metabolomics. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1738, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, W.B.; Wilson, I.D.; Nicholls, A.W.; Broadhurst, D. The importance of experimental design and QC samples in large-scale and MS-driven untargeted metabolomic studies of humans. Bioanalysis 2022, 4, 2249–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; Version 4.3.3; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2009; Available online: http://www.R-Project.Org (accessed on 22 June 2024).
- Thévenot, E.A.; Roux, A.; Xu, Y.; Ezan, E.; Junot, C. Analysis of the Human Adult Urinary Metabolome Variations with Age, Body Mass Index, and Gender by Implementing a Comprehensive Workflow for Univariate and OPLS Statistical Analyses. J. Proteome. Res. 2015, 14, 3322–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Xu, Y.L.; Duan, F.M.; Du, X.; Yang, Q.C.; Zheng, Y.-J. Improvement of the growth and nutritional quality of two-leaf-color Pak choi by supplemental alternating red and blue light. J. Hortic Sci. 2021, 56, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veazie, P.; Cockson, P.; Henry, J.; Perkins-Veazie, P.; Whipker, B. Characterization of nutrient disorders and impacts on chlorophyll and anthocyanin concentration of Brassica rapa var. chinensis. Agriculture 2020, 10, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, J.H.; Stephen, A.M. Carbohydrate terminology and classification. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 61, S5–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, J.K.; Lynch, J.H.; Matos, J.O.; Dudareva, N. Adaptive mechanisms of plant specialized metabolism connecting chemistry to function. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2021, 17, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajas, F.; Gautier-Stein, A.; Mithieux, G. Glucose-6 phosphate, A central hub for liver carbohydrate metabolism. Metabolites 2019, 9, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasmans, K.; Meex, R.C.R.; van Loon, L.J.C.; Blaak, E.E. Nutritional strategies to attenuate postprandial glycemic response. Obes. Rev. 2022, 23, e13486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinders, A.; Ward, J. SUC1’s mode of low-affinity transport. Nat. Plants 2023, 9, 856–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, S.; Gunn, P.; Wittekind, A.; Cottrell, R. The Effects of Sucrose on Metabolic Health: A Systematic Review of Human Intervention Studies in Healthy Adults. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 53, 591–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, M.J.; Primavesi, L.F.; Jhurreea, D.; Zhang, Y. Trehalose metabolism and signaling. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 417–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponnu, J.; Wahl, V.; Schmid, M. Trehalose-6-phosphate: Connecting plant metabolism and development. Front Plant Sci. 2011, 2, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, A.S.A.; Naveed, M.; Jost, N. Polysaccharides; Classification, Chemical Properties, and Future Perspective Applications in Fields of Pharmacology and Biological Medicine (A Review of Current Applications and Upcoming Potentialities). J. Environ. Polym. Degrad. 2021, 29, 2359–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Shen, M.; Song, Q.; Xie, J. Biological activities and pharmaceutical applications of polysaccharide from natural resources: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 183, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Li, R.; Ren, L.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Ma, D.; Luo, Y. A comparative metabolomics study of flavonoids in sweet potato with different flesh colors (Ipomoea batatas L. Lam). Food Chem. 2018, 260, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Su, Y.; Dong, G.; Qian, G.; Shi, Y.; Mi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, J.; Du, W.; Shi, T.; et al. Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry-based metabolomics analysis of flavonoids and anthraquinones in Fagopyrum tataricum L. Gaertn. (tartary buckwheat) seeds to trace morphological variations. Food Chem. 2020, 331, 127354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchak, N.; El Bacha, E.; Bou Khouzam, R.; Rizk, T.; Akoka, S.; Bejjani, J. Geoclimatic, morphological, and temporal effects on Lebanese olive oils composition and classification: A 1H NMR metabolomic study. Food Chem. 2017, 217, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Xu, J.; Fan, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, L.; Yuan, J.; Yu, Y. Effect of disaccharides of different composition and linkage on corn and waxy corn starch retrogradation. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Tester, R.F. Lactose, Maltose, and Sucrose in Health and Disease. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2020, 64, 1901082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, J.; Gao, H.; Li, G.L.; Sun, J.; Ma, H. Comparison of effects of oligosaccharides on physicochemical properties of corn starch. Trop. J. Pharma. Res. 2014, 13, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delzenne, N.M. Oligosaccharides: State of the art. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2003, 62, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinsorn, P.; Oikawa, A.; Watanabe, M.; Sasaki, R.; Ngamchuachit, P.; Hoefgen, R.; Saito, K.; Sirikantaramas, S. Metabolic variation in the pulps of two durian cultivars: Unraveling the metabolites that contribute to the flavor. Food Chem. 2018, 268, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J.; Shi, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Ye, Y. Metabolite Profiling of Wheat Response to Cultivar Improvement and Nitrogen Fertilizer. Metabolites 2023, 13, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Lim, S.H.; Ha, S.H.; Yeo, Y.; Park, W.T.; Kwon, D.Y.; Park, S.U.; Kim, J.K. Metabolite profiling approach reveals the interface of primary and secondary metabolism in colored cauliflowers (Brassica oleracea L. ssp. botrytis). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 6999–7007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
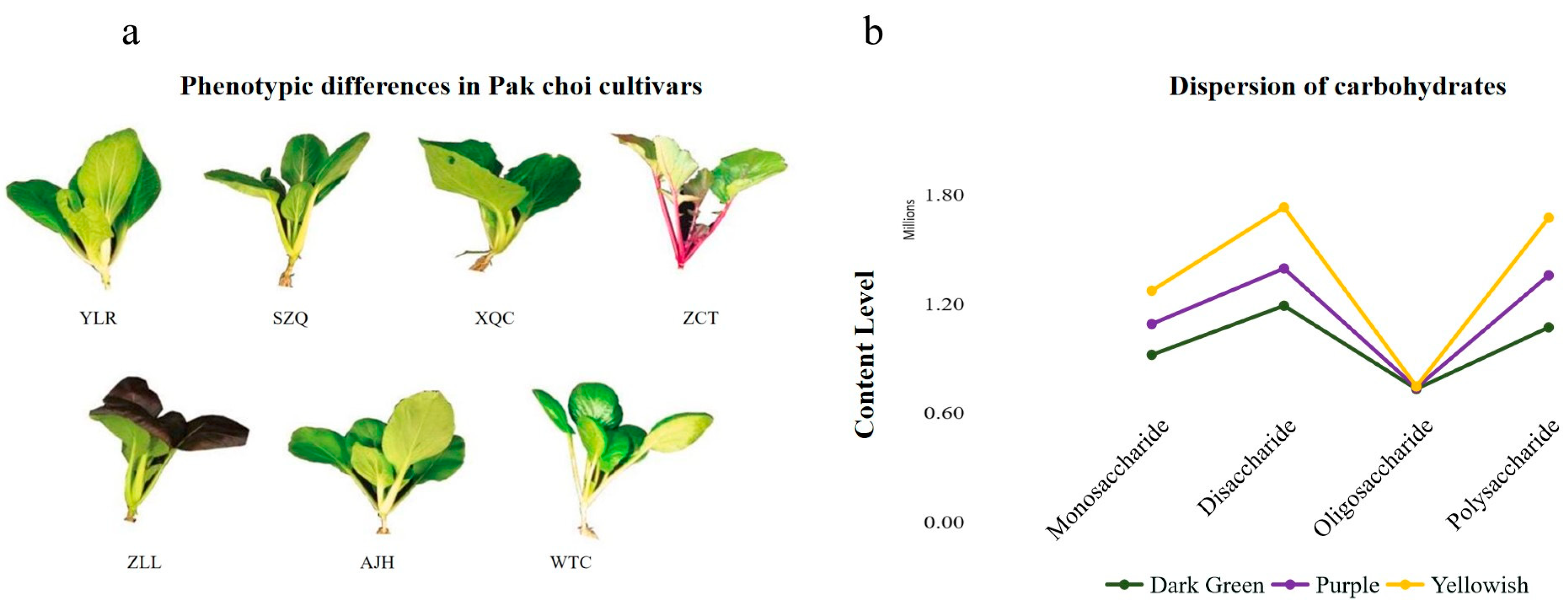
| Phenotypic Characters | Pak Choi Cultivars | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Suzhouqing | Yellowrose | Wutacai | Aijiaohuang | Xiangqingcai | Zicaitai | Ziluolan | |
| Leaf | |||||||
| color | Yellow | Yellow | Dark green | Yellow | Dark green | Yellow | purple |
| size (cm) | 21 × 18 | 16 × 19 | 4 × 10 | 23 × 19 | 14 × 18 | 21 × 15 | 6 × 8 |
| shape | oval | oval | obovate | oval | oval | oval | oval |
| apex | obtuse | obtuse | obtuse | obtuse | obtuse | obtuse | obtuse |
| margins | entire | acute | entire | acute | entire | undulate | entire |
| surface | smooth | entire | smooth | entire | smooth | smooth | smooth |
| arrangement | alternate | smooth | alternate | smooth | alternate | alternate | alternate |
| stem | |||||||
| color | light green | light green | light green | light green | light green | pink | light green |
| surface | smooth | smooth | smooth | smooth | smooth | smooth | smooth |
| plant height (cm) | 29 | 32–39 | 27–38 | 31 | 23–37 | 34–70 | 20 |
| Category | Monosaccharide | Disaccharide | Oligosaccharide | Polysaccharide |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dark Green | 5.91 × 105 | 1.40 × 106 | 2.68 × 104 | 1.05 × 106 |
| Purple | 5.10 × 105 | 6.17 × 105 | 1.97 × 104 | 8.59 × 105 |
| Yellowish | 5.51 × 105 | 1.01 × 106 | 2.33 × 104 | 9.53 × 105 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mubeen, H.M.; Li, Y.; Hu, C. Metabolite Diversity and Carbohydrate Distribution in Brassica campestris ssp. chinensis L. Cultivars: A UPLC-MS/MS Approach. Biology 2024, 13, 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13080568
Mubeen HM, Li Y, Hu C. Metabolite Diversity and Carbohydrate Distribution in Brassica campestris ssp. chinensis L. Cultivars: A UPLC-MS/MS Approach. Biology. 2024; 13(8):568. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13080568
Chicago/Turabian StyleMubeen, Hafiz Muhammad, Ying Li, and Chunmei Hu. 2024. "Metabolite Diversity and Carbohydrate Distribution in Brassica campestris ssp. chinensis L. Cultivars: A UPLC-MS/MS Approach" Biology 13, no. 8: 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13080568
APA StyleMubeen, H. M., Li, Y., & Hu, C. (2024). Metabolite Diversity and Carbohydrate Distribution in Brassica campestris ssp. chinensis L. Cultivars: A UPLC-MS/MS Approach. Biology, 13(8), 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13080568






