Simple Summary
Substances that are absent in the biosphere, but have been synthesized by humans in recent decades, are called xenobiotics. They are released into the environment in large volumes and can actively affect invertebrates and their intestinal parasites or commensals. Such an influence of xenobiotics on parasite–host relationships remained poorly studied until recently. In this article, the host–parasite system “larva of Tenebrio molitor—Gregarina polymorpha” under the influence of 24 organic compounds is investigated. We found that several substances increase the mortality of T. molitor larvae, and substances such as diphenyl ether, benzyl alcohol, catechol, and 3-aminobenzoic acid, on the contrary, reduce the number of parasites (G. polymorpha) without significantly affecting host insects (larva of T. molitor). Thus, various xenobiotics can destroy the parasite–host relationship, having a greater effect on the host in some cases and on the parasite in other cases.
Abstract
Environmental contamination with xenobiotics affects organisms and the symbiotic relations between them. A convenient object to study relationships between parasites and their hosts is the host–parasite system “Tenebrio molitor Linnaeus, 1758 (Coleoptera, Tenebrionidae)—Gregarina polymorpha (Hammerschmidt, 1838) Stein, 1848 (Eugregarinorida, Gregarinidae)”. For this experiment, we took 390 T. molitor larvae and 24 organic compounds. Groups of mealworms, 15 in each, were subjected to those compounds for 10 days. Then, we recorded the vitality of both the larvae of T. molitor and G. polymorpha. To assess how G. polymorpha had affected the hosts’ wellbeing, we looked for changes in the larvae’s body mass and compared them to the number of gregarines in their intestines. The vitality of the larvae was inhibited by cyclopentanol and 2-naphthol. The intensity of gregarine invasion was reduced by diphenyl ether, benzyl alcohol, catechol, and 3-aminobenzoic acid. No effect on the number of gregarines was produced by 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid, cyclohexanemethanol, phenol, benzalkonium chloride, maleic anhydride, cyclohexanol, resorcin, benzoic acid, 2-methylfuran, terpinen-4-ol, 1-phenylethylamine, dibutyl phthalate, 3-furancarboxylic acid, 5-methyl furfural, 6-aminohexanoic acid, succinic anhydride, o-xylene, and benzaldehyde. In the infected T. molitor individuals, the mean number of G. polymorpha equaled 45 specimens per host. The groups of smaller mealworms had fewer gregarines. Positive correlation was seen between growth rates of T. molitor larvae and the intensity of invasion by gregarines.
1. Introduction
Tenebrio molitor Linnaeus, 1758 (Coleoptera, Tenebrionidae) is now widespread all around the globe [1]. Imagoes and larvae of this beetle live under the bark of trees, in soil, under foliage, and in other humid, dark places [2]. The yellow mealworm beetle is mostly active at night, feeding on animal and plant products [3,4]. At the same time, it is a storage pest of grain and grain products [5]. In case of mass reproduction, it is able to destroy up to 15% of storage reserves [6]. Tenebrio molitor feeds on grain, and often lives in it as well, laying eggs and polluting the supplies with feces [7].
Similarly to other insects with complete metamorphosis, T. molitor undergoes four stages of ontogenesis: egg, larva, pupa, and imago. Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and access to food play crucial role in how long any T. molitor specimen may spend in each ontogenesis stage [8]. Tenebrio molitor is able to effectively adapt to unfavorable conditions and survive in them. It does not require a reliable source of water, since it is able to obtain moisture from food or the atmosphere [9]. Because of its low demand and easy maintenance, T. molitor is an insect that is cultivated at the industrial scale [10] and is used in many spheres. For example, mealworms are reared as food for pets: they are added to the diets of many fishes, birds, and arthropods, and are used as bait in fishing [1]. Dried T. molitor have a high content of protein (~50%) and many microelements, and therefore are notable edible insects [11,12]. Mass animal husbandry affects the environment by forming large volumes of greenhouse gasses and ammonia and also uses considerable amounts of water, energy, and areas of land. Therefore, insects are now being considered an alternative source of nutrients [13]. In 2021, the European Union certified the powder of mealworms as a food raw material [14].
Tenebrio molitor is also used in research in biology, biochemistry, evolution, etc. [15,16,17]. Researchers found that because of their gut microflora, mealworms are able to consume and degrade polystirol, polypropylene, and polyvinyl chloride [18]. At the same time, 35% to 50% of polymer is converted into carbon dioxide, while the rest does not remain in the organism for long [19]. Thanks to this ability, T. molitor can potentially improve the ecological condition of the planet. Tenebrio molitor is also used in the production of biodiesel [20], as a source of chitin and chitosan [21], and as bioactive extracts and compounds [22,23]. Thus, T. molitor is significant for mankind and has potential in various other spheres [24].
Gregarines belong to the Apicomplexa phylum and parasitize most groups of invertebrates. They have been studied only fragmentarily [25]. Mealworms harbor gregarines such as Gregarina cuneata Stein, 1848; G. polymorpha (Hammerschmidt, 1838) Stein, 1848; and G. steini Berndt, 1902, whereas the imago has not been found to be infected by any of those, only by G. niphandrodes, which, in turn, does not parasitize the larva stage [26,27,28].
The life cycle of gregarines comprises sporogony and gametogony [29]. Gregarine infection starts with the consumption of invasive oocysts that are released to the environment in the feces of already infested organisms [30]. In the host, oocysts release sporozoites, which attach to the cells through mucrons or epimerites [31]. Gregarines live in the digestive tract or internal cavity of their hosts.
Over 1600 gregarines have been discovered so far, but the number is suspected to be much higher—over a million—due to their high specificity (the species of gregarines that associate with a host can change over its life cycle) and wide distribution [32,33]. The effect gregarines have on their hosts has been the subject of numerous experimental studies. Gregarines are often considered commensals, i.e., such that they obtain benefits from another organism but provide no benefits in return, but at the same time cause no harm [34,35,36]. Despite this fact, from time to time they demonstrate a unique action towards their hosts, being both harmful and beneficial. Research has demonstrated the various effects gregarines have on their hosts: they can arrest development, cause greater mortality, and inhibit reproduction [36,37]. Excessive infestations of gregarines can occupy entire intestines, obstructing the entrance for food, ruining the intestinal wall of their host, and provoking other complications [38]. Growth rates of body mass in the host are related to the composition of its diet, whereas invertebrates that feed on dozens of types of feeds are not necessarily associated with the composition of diet [39,40]. Gregarines cause harm to some adaptive properties of dragonflies by reducing fat in their bodies, thus negatively impacting their reproduction [41]. Gregarines were observed to hinder the development of larvae and pupae in the Aedes triseriatus (Say, 1823) mosquito (Diptera, Culicidae) [42]. However, in other cases, gregarine infestation could give their host advantages. For example, in conditions of food scarcity or starvation, they had a positive effect on their hosts, including Enallagma boreale (Selys, 1875) (Odonata, Coenagrionidae) [43] and gregarine infection boosted the rates of development of their host Ctenocephalides felis (Bouché, 1835) (Pulicidae, Ctenocephalides) [44].
Issues of contamination of the environment have become especially acute in recent decades [45]. Xenobiotics are determined as alien compounds in the biosphere [46] and comprise the main group of pollutants. Xenobiotics include colorings, pharmaceutical drugs, means of personal hygiene, and pesticides [47]. They are resilient to degradation, and therefore are able to accumulate in large concentrations in the soil, damaging the chemical stability of the soil environment [48]. They enter surface and ground water in urban areas via industrial and municipal discharges of waste water, and also agricultural waste. Organisms living in water bodies are also among those harmed [49,50]. Xenobiotics and their metabolites can affect various physiological changes in organisms, causing immunological and reproductive malfunctions and altered cardiovascular parameters or systems of organs [51]. These pollutants can remain in the fatty tissues for many years and cause chronic problems such as growth arrest, relapse of diseases, long brain malfunctions, and cancer [52]. Substantial accumulation of xenobiotics in the environment threatens the existence of entire ecosystems. By affecting the populations of certain species, xenobiotics also cause the destruction of symbiotic relationships in ecosystems. In laboratory conditions, it is possible to accurately monitor the effects of xenobiotics on unicellular parasites in the host’s body and how this will affect the parasite system in general. The substances studied in this article are widely used in everyday life, construction, and the chemical industry, and, therefore, every year they enter the environment and accumulate near places of waste generation and storage. This causes the accumulation of xenobiotics in the bodies of organisms that live on the surface and in the upper horizons of the soil and feed on plant and animal remains, i.e., they are saprophages. Larvae of T. molitor are often found in places of accumulation in household and other types of organic waste, where the probability of the accumulation of many types of xenobiotics is highest. That is why they are a convenient object for evaluating the impact on the host–parasite system.
The objective of this study was to assess the effects of 24 organic compounds on the host–parasite system “Tenebrio molitor—Gregarina polymorpha”.
2. Materials and Methods
For this experiment, we chose 24 organic compounds (Table 1) and took 390 larvae of T. molitor from one laboratory population, where, prior to the experiment, they had been kept in the same conditions of temperature, humidity, and light for 3 months. All the larvae had the same access to food and fed on one medium, and had the same chance of becoming infected by gregarines. During the experiment, groups of 15 mealworms (5 in one of three cups) were exposed to each compound. The compounds affected the development of the larvae through their respiratory [53] and digestive systems. The control group comprised 30 larvae.

Table 1.
Effects of organic compounds on survivability of mealworms (n = 15, duration of the experiment—10 days).
Each larva was designated with a marker (one to five tergites were marked depending on assigned number) and transported in a 500 mL plastic cup with substrate of flaked oat groats. All the cups contained substrate from one lot of groats of the same density and water content. Inside the substrate (closer to the cup bottom), we dropped 0.05 mL of each studied compound using a pipette [54]. Onto the surface of the substrate, we put 5 g of inner leaf of cabbage to offer additional nutrients and provide optimal environmental humidity [55]. All the cups were on the surface of the table under direct sunlight in the conditions of the same humidity and temperature.
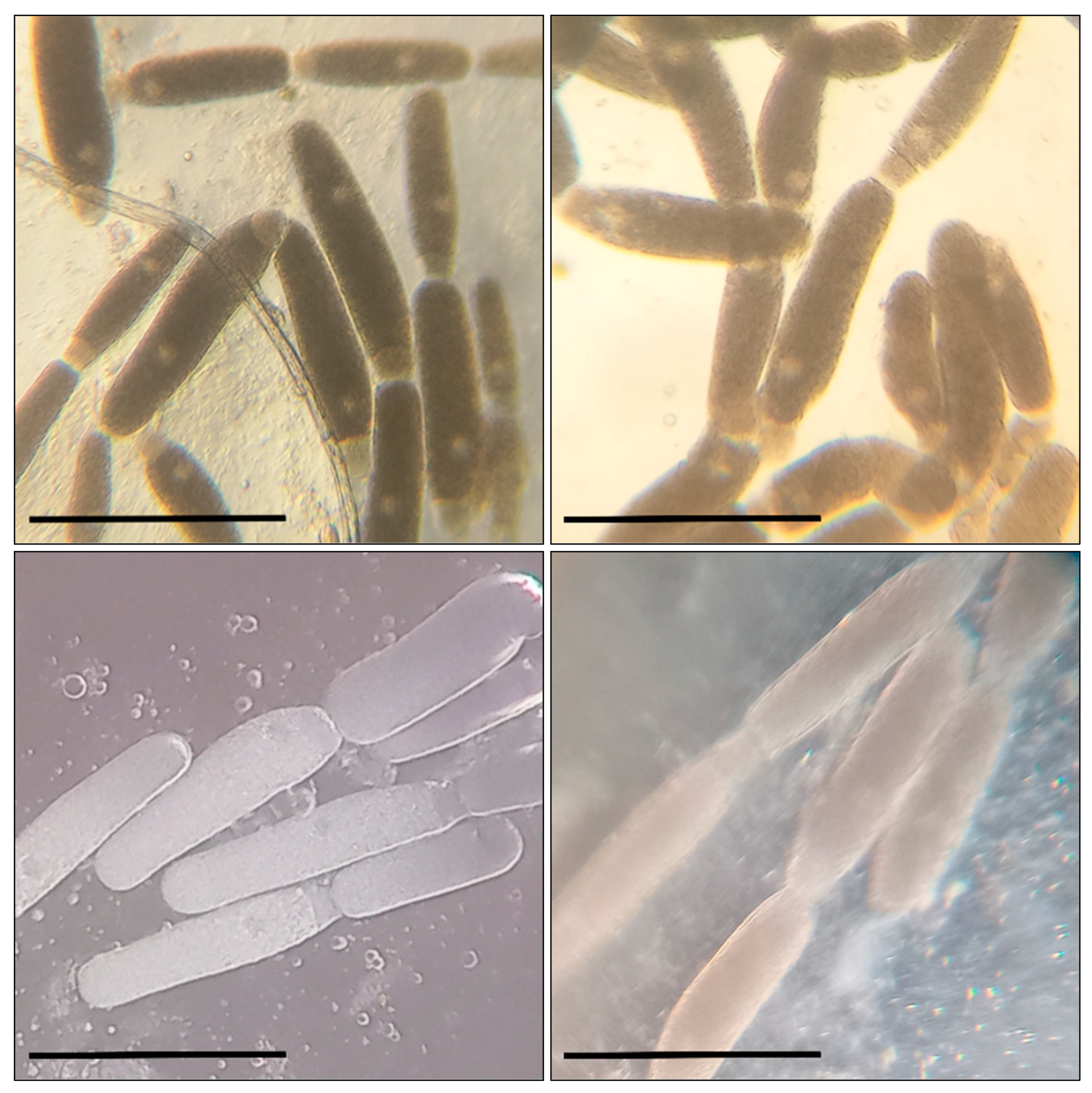
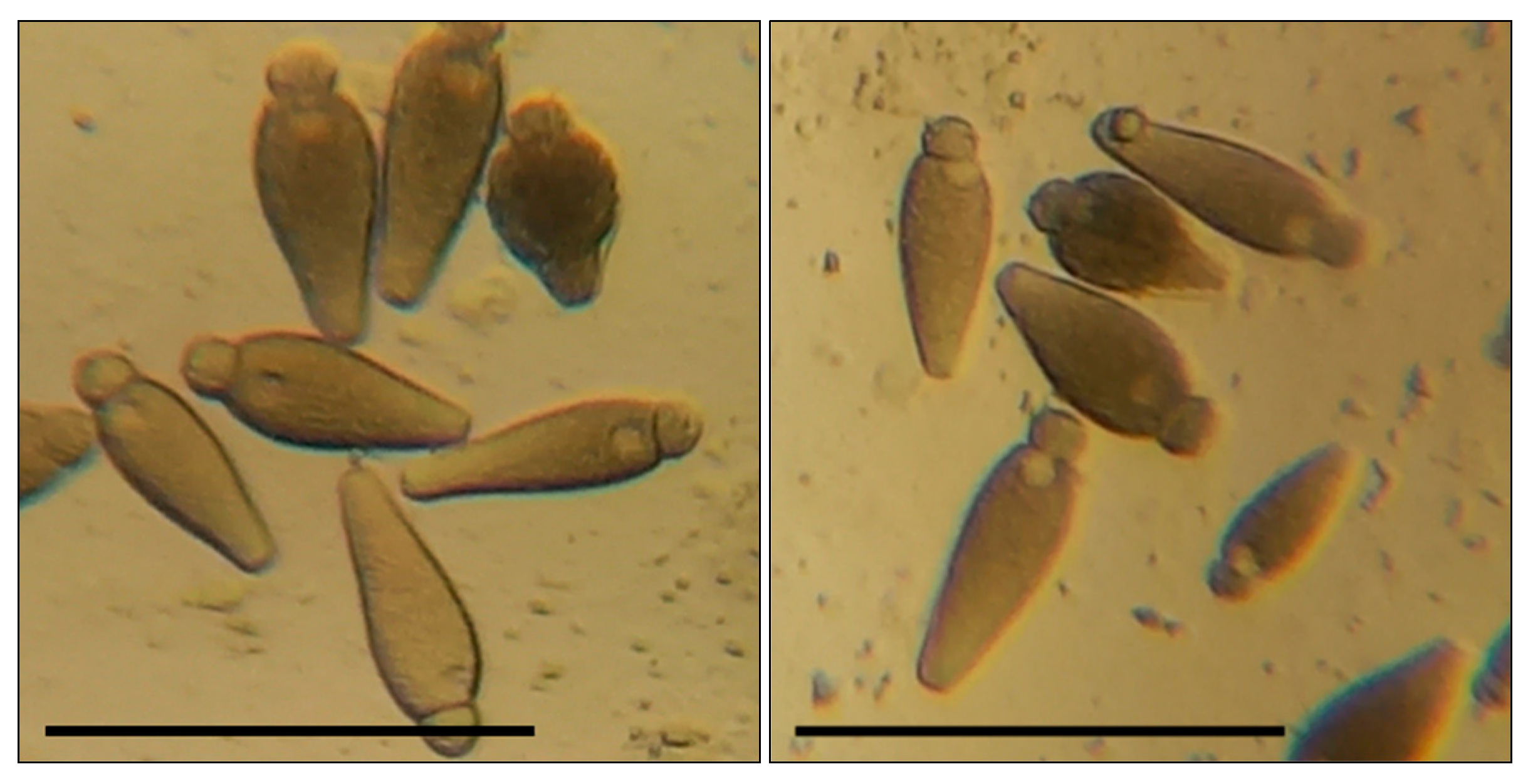
Before the larvae were transferred to a cup, each of them was weighed on scales with 1 mg accuracy. The mealworms were in the cups for 10 days, where their condition was checked regularly. On the fifth day of the experiment, we added 0.05 mL to support the effect of the tested compound on the insects’ development. After the experiment, the mealworms were weighed again to monitor changes in their body mass. Then, the intestines were removed from the larvae on a microscope slide; 12 transversal cuts were made on the intestines with a sharp blade at equal distance one from another. We carried out transverse sections of the middle intestine at an equal distance from each other in the segment between the stomach and the place of attachment of the Malpighian vessels to the intestine (the beginning of the hind intestine). Under a light microscope, we checked the temporary preparations of the intestines for gregarines, which, if found, were counted. In the mealworms used in the experiment, we found G. polymorpha (Figure 1) and G. steini (Figure 2), identified by microscopic measurements of their morphometric parameters and the guide by Geus [56]. The systematics were elucidated with regard to the new reports [25,26,32].
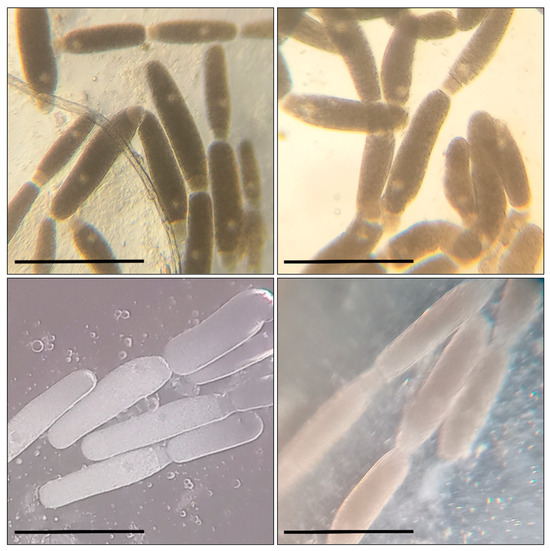
Figure 1.
Gregarina polymorpha in the intestines of T. molitor larvae: bar—200 µm; the sizes of the gamonts and syzygies of gregarines, as well as the ratio of morphometric indices for the primite and satellite (the length and width of the protomerite and deutomerite, the location and size of the nucleus, etc.) correspond to the data indicated in the taxonomic literature.
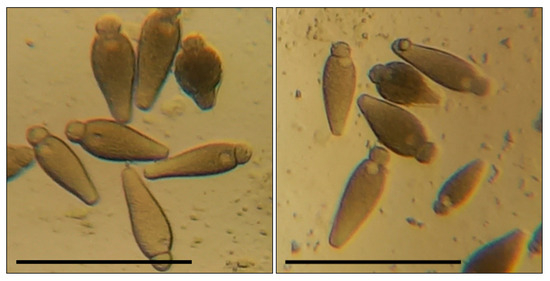
Figure 2.
Gregarina steini in the intestines of T. molitor larvae: bar—100 µm; the body sizes of greragins and their morphometric indices correspond to the characteristics indicated in the work of Geus [56].
During the statistical analysis of the results, we used the standard methods of variance statistics (we estimated mean value, median, the first and third quartiles, and maximum and minimum values); significance of differences was estimated using ANOVA (analysis of variance). Differences between the values of the experimental groups were determined using the Tukey test (with consideration of Boniferroni’s correction), where the differences were considered significant at p < 0.05. Estimations were carried out in the Statistica 12.0 software package (Statsoft Inc., Tulsa, OK, USA, 2018).
3. Results
Some organic compounds were lethal to some mealworms (Table 1). The greatest morbidity was seen after exposure to cyclopentanol (33.3%), 2-naphthol (33.3%), trihydroxybenzoic acid (26.6%), and 3-aminobenzoic acid (20.0%). In the control group, we saw no dead larvae, though some formed pupae.
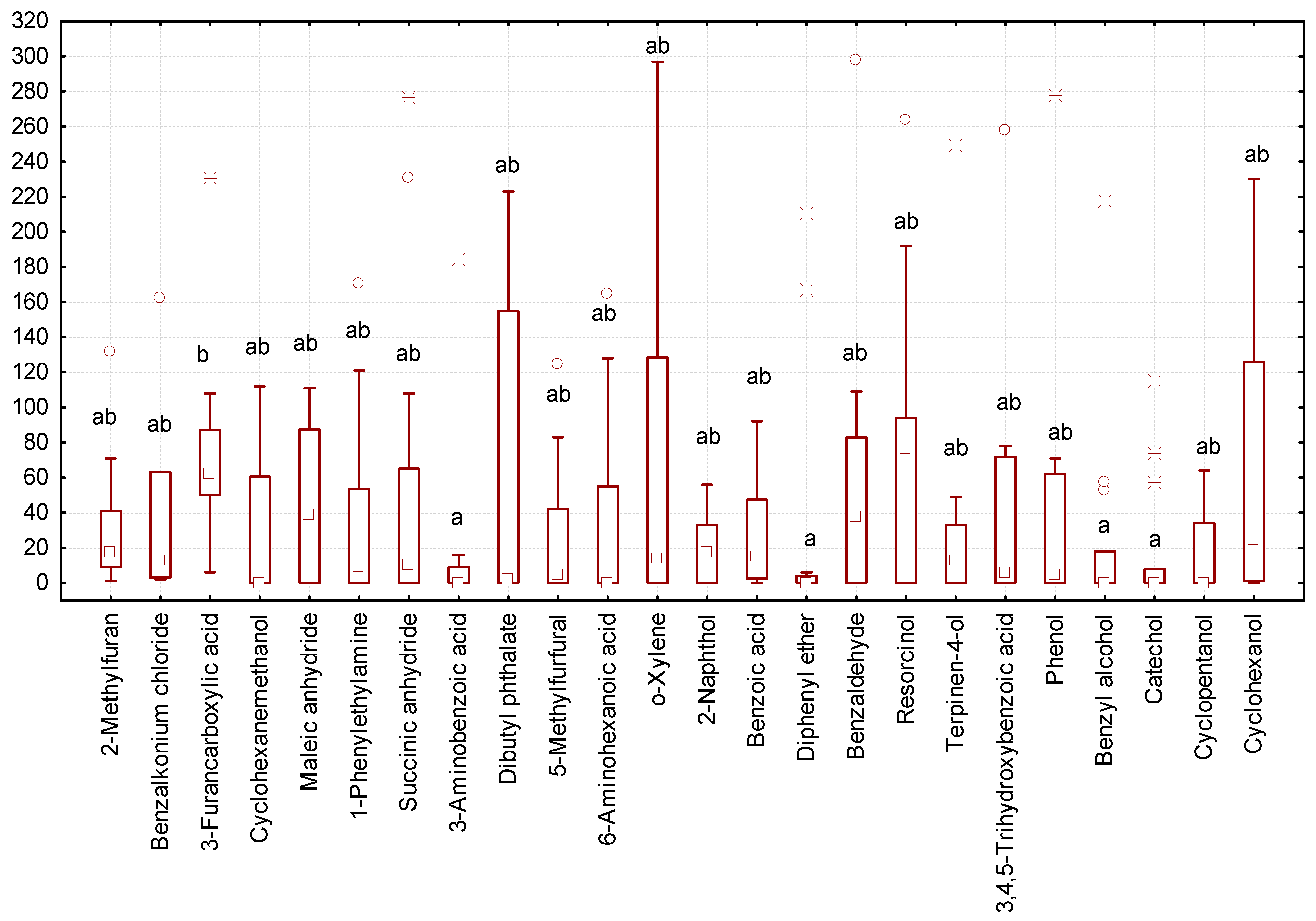
In some variants of the experiment, we recorded a minimal number of gregarines (zero to three individuals of gregarines per larva, Figure 3). The lowest number of gregarines in the intestines was observed after exposure to diphenyl ether, benzyl alcohol, catechol, and 3-aminobenzoic acid. The highest number of gregarines was observed after exposure to resorcin and 3-furancarboxylic acid.
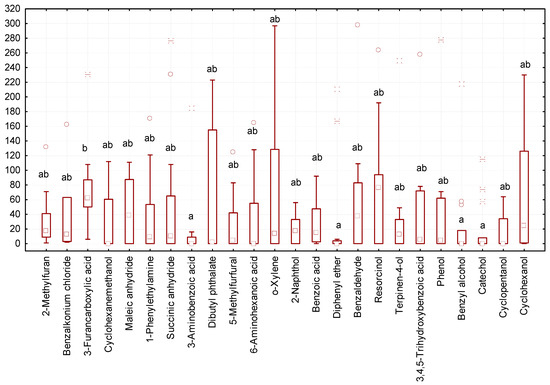
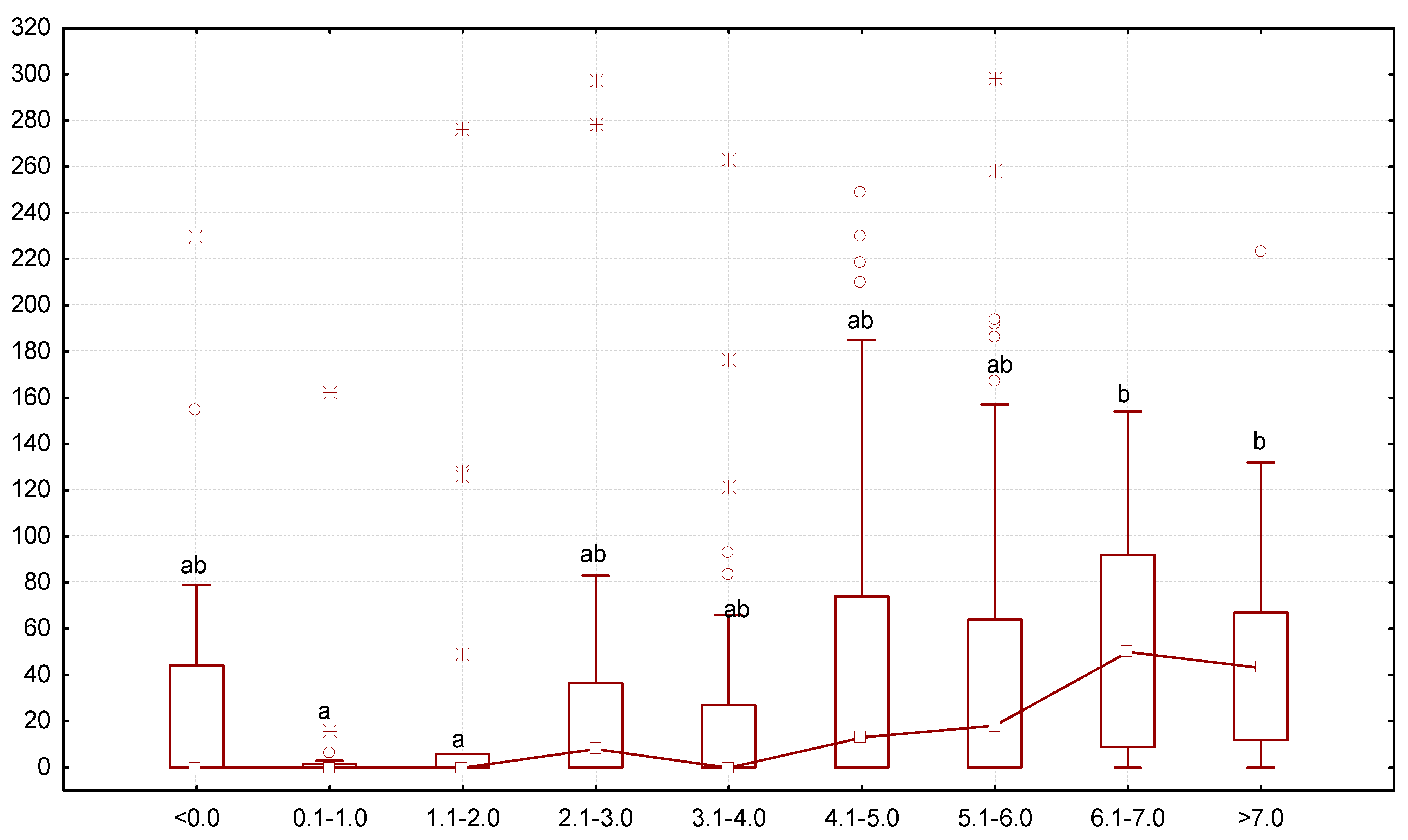
Figure 3.
Number of G. polymorpha in the intestines of T. molitor at the end of the 10-day experiment (ordinate axis, spec.) in different variants of the experiment (N = 323): small square—median; lower and upper thresholds of the rectangle—the first and third quartiles, respectively; the lower and upper parts of the vertical line correspond to the minimum and maximum values of samplings; circles and stars —releases; different letters indicate values which reliably differed one from another within one line of the table according to the results of comparison using the Tukey test with Bonferroni correction.
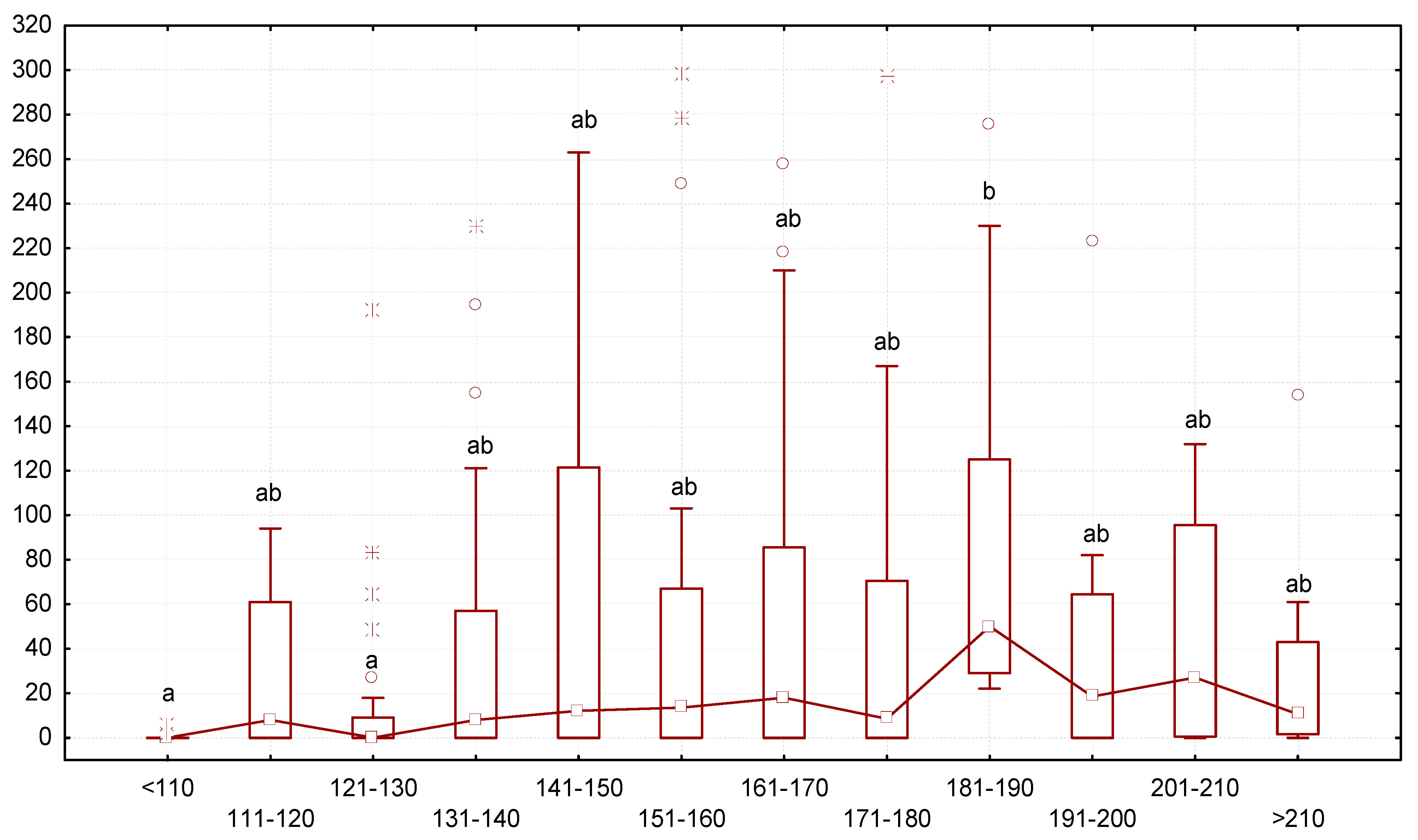
Analysis of the ratio of end mass and the number of gregarines in the larvae revealed that larvae with low body mass contained fewer gregarines, while larvae with greater body mass contained more gregarines. The intensity of gregarine infestation gradually increased starting from a body mass < 121–130 mg (Figure 4). The median number of gregarines reached the highest values in specimens with a body mass of 181–190 mg, measuring 52 gregarines per animal. If the body mass of the mealworms increased further, the number of gregarines had a downward tendency.
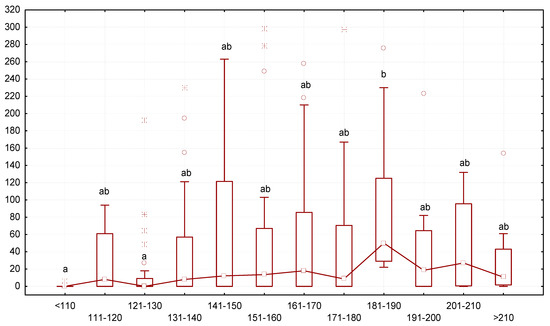
Figure 4.
Dependence between the number of G. polymorpha (ordinate axis, number of specimens of gregarines per one T. molitor) and body mass of the insects (axis abscissa, mg of body mass): N = 323; legend—see Figure 3.
The most active growth was noted for mealworms that contained greater numbers of G. polymorpha: the larvae that grew 0.1–1.0 or 1.1–2.0 mg/day or had been losing body mass (<0.0 mg/day) had the lowest number of gregarines, but as the body mass increased, so did the infection (Figure 5). The number of gregarines per mealworm was the highest in specimens growing at the rate of 6.1–7.0 mg/day (median was 50 gregarine specimens per one larva).
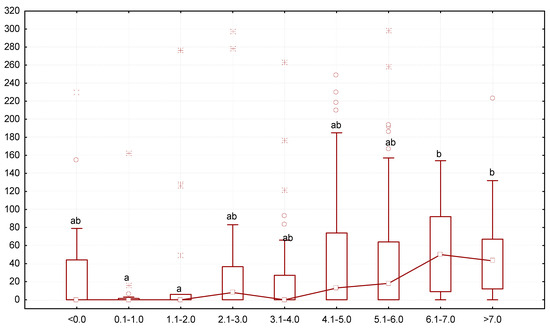
Figure 5.
Dependence between the number of G. polymorpha (ordinate axis, number of gregarine specimens in one host) and change in body mass of the T. molitor larvae (abscissa axis, mg/day): N = 323; legend—see Figure 3.
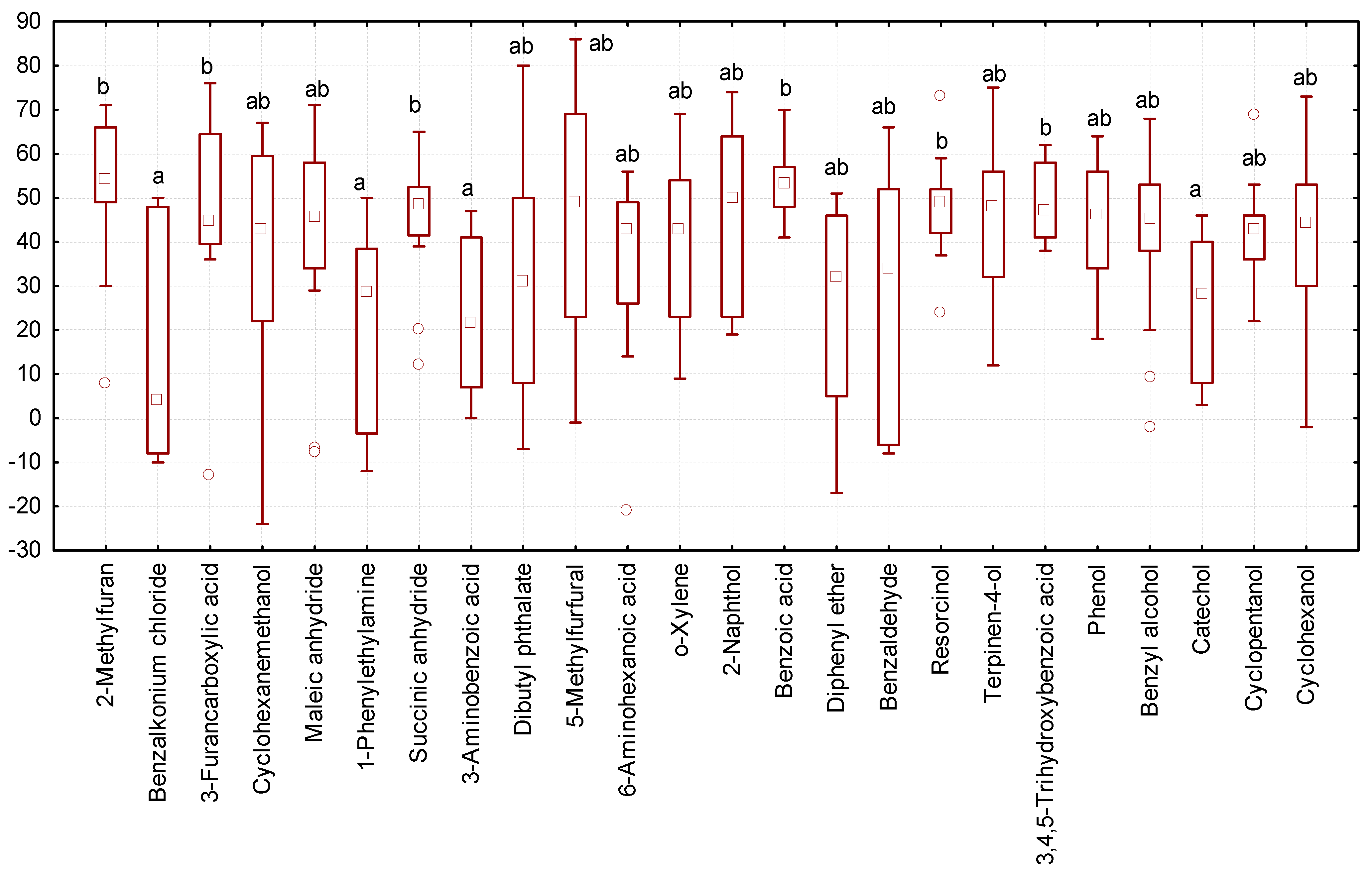
We observed the maximum increase in body weight of larvae (median equal to 45–55 mg of body weight gain over the course of a 10-day experiment) when exposed to 3-furancarboxylic acid, 2-methylfuran, succinic anhydride, benzoic acid, resorcinol, and 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid (Figure 6). Tenebrio molitor larvae had a significantly lower increase in body weight (median 4–29 mg) in the experimental variants where they were exposed to benzalkonium chloride, 1-phenylethylamine, 3-aminobenzoic acid, and catechol.
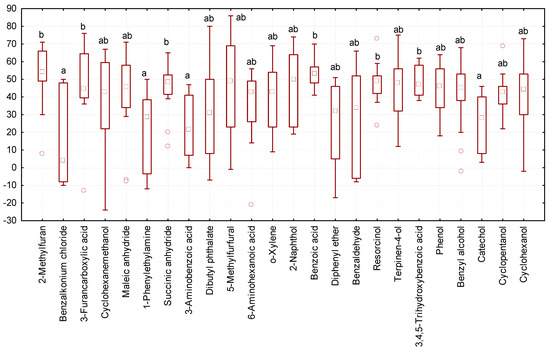
Figure 6.
Changes in the body weight of Tenebrio molitor larvae at the end of a 10-day experiment (ordinate axis, mg) under the influence of various organic substances: N = 323; legend—see Figure 3.
4. Discussion
Effects of the studied compounds on the mealworms. Subjecting the beetles’ larvae to close contact with the organic compounds caused some to die. Because the compounds were able to affect the insects through their respiratory ways, enter the organisms with the swallowed substrate, and exert toxic properties, high mortality and a decline in the number of gregarines were expected to be a consequence of exposure to those compounds [57]. No larvae died in the normal conditions of the control group, where they grew without exposure to the compounds, though some formed pupae. In some variants of the experiment, the number of pupa was higher, although high mortality was not observed. Such cases could be explained by the age of the larvae that were ready to continue metamorphosis.
The highest mortality was recorded in the groups that had contact with cyclopentanol and 2-naphthol (33.0% dead in each group). Cyclopentanol is the main compound extracted from Erica manipuliflora Salisb, exerting strong insecticide properties [58], and 2-naphthol is a natural nematocide, extracted from Actephila merrilliana Chun [59]. Cyclopentanol is used as an intermediate product for colorings, solvent in perfumery, and pharmaceutics, while 2-naphthol is used to prepare colorings, pigments, perfumes, and drugs. Those compounds can affect the vitality of T. molitor.
Effects of the studied compounds on gregarines. By affecting the physical state of T. molitor larvae, the compounds also altered the life conditions in their bodies. In the intestines of the mealworms that were used in the experiment, we found G. polymorpha and G. steini. Gregarina polymorpha accounted for around 96% of the general population of gregarines. Invasion intensity with G. polymorpha ranged from 0 to 298 specimens per one individual of T. molitor. The intensity of gregarine infection varied across the variants of the experiment. The median number of gregarines was the highest in study variants with resorcin and 3-aminobenzoic acid, equaling 75 and 65 specimens of gregarines per host, respectively. In the concentrations we used, those compounds were unable to inhibit the state of gregarine trophozoites and reduce their quantity. The larvae that were exposed to diphenyl ether, 3-aminobenzoic acid, catechol, and benzyl alcohol had the lowest intensity of gregarine invasion. Diphenyl ether is a compound widely used in industry; its residues have been found in water, soil, air, and animal and human tissues [60]. This organic compound displayed antibacterial properties [61]. Similar effects were produced by 3-aminobenzoic acid, which is usually used for the synthesis of other compounds [62]; catechol, which is used mainly in the synthesis of insecticides [63]; and benzyl alcohol, which exhibited toxicity and insecticidal properties towards species of the Tenebrionidae family [54]. Our study demonstrated that the effects those compounds had on the larvae created an unfavorable environment for gregarines, while at the same time not increasing the mortality of the T. molitor significantly.
Despite the insecticidal properties of some substances, in the concentrations we specified, they did not significantly increase the mortality of larvae. However, the changes they caused in the host’s body affected the number of gregarines. This has the practical potential to breed gregarine-free populations of T. molitor with organic matter, which will be useful in further research on parasite systems.
In total, 6 out of 24 organic substances selected by us in one way or another destroyed the parasitic system “Tenebrio molitor—Gregarina polymorpha”, causing the death of the host or reducing the number of Gregarina. Each of these substances is used in certain industries, as part of medicines, insecticides, dyes, etc. Human activity increases the concentration of these substances in the environment. Urbanization, the growth of the local population, and the increase in the volume of production of goods lead to significant contamination with xenobiotics. Studies report the presence of xenobiotic compounds in surface waters around the world, including in the Arctic and Antarctica [50]. Despite low concentrations, xenobiotics are able to accumulate in the tissues of living organisms over time. In addition to living organisms encountering xenobiotics in natural ecosystems, they may also be exposed to them in laboratory populations. Food consumed by animals contains natural and synthetic chemicals that can affect physiological processes; insufficiently purified water may contain various pollutants [64]. It is important to consider this factor when studying living organisms and their interactions in different environments.
Correlation between body mass and growth rates of the mealworms and gregarine-invasion intensity. Our study revealed that the larvae with greater body mass had a high intensity of gregarine invasion. It gradually increased with the body mass of the host and reached the maximum in specimens that had a mass of 181–190 mg, with, on average, 52 gregarines per larva. With further increases in mass, infestation intensity gradually decreased. This may indicate an “optimum” body mass of the host for gregarines in the interval of 181–190 mg. Rates of body-mass increment positively correlated with the intensity of gregarine infection. This can be explained by the life cycle of T. molitor. By consuming food, the larva increases the intensity of invasion by gregarines, since infection with gregarines occurs through the ingestion of infectious oocysts together with food. After spending some time in the host’s body, gregarine gametocysts are released into the environment with feces. It can be assumed that larvae with a higher body weight and fewer gregarines were preparing for pupation: a certain time before it, they reduce their activity and stop consuming as much food, which leads to the fact that new gregarines do not enter the body.
This tendency remained in each variant of the study. Infestation with gregarines increased with the swallowing of infectious oocysts, and therefore we observed larger numbers of gregarines in the larvae that had to consume a greater amount of food with gregarine oocysts. A positive correlation between body mass and the number of gregarines was observed by Sumner [64]: he stated that infection by gregarines is necessary for the normal growth and long life of T. molitor. Later, research on the symbiosis of gregarines with T. molitor demonstrated that gregarines either affected the development of the host negatively or had no effect at all. Harry [65] found no significant difference between the end mass of infected T. molitor larvae and the end mass of non-infected larvae on an optimal diet. However, Harry [65] saw a substantial negative impact of gregarines on the larvae grown on a non-optimal diet. At the same time, some infected larvae grown in non-optimal feeding conditions lived much longer. The gregarine-infested orthopterans Atractomorpha crenula Fabricius, 1793 (Orthoptera, Pyrgomorphidae) consumed less food and, therefore, lost body mass [66]. The study of Tribolium castaneum Herbst, 1797 (Coleoptera, Tenebrionidae) revealed that gregarines hindered the growth of those insects, arrested their development, and increased their mortality [67]. Gregarines were seen to decrease the mass and length of Tipula paludosa Meigen, 1830 (Diptera, Tipulidae) [68]. Wolz et al. [69] demonstrated that gregarines additionally inhibited the state of insects that had already been subject to stress from insecticides. We observed none of those effects in our experiment. Gregarines consume nutrients from the host organism and can obstruct the midgut, causing health issues, but nonetheless, in our study we recorded a much larger number of gregarines than indicated in other sources [70]. The results suggest that even a high-intensity invasion does not harm the vitality or growth rates of T. molitor larvae.
The increase in the intensity of invasion by gregarines with an increase in the weight of the larva (and, accordingly, the amount of food it consumes) is natural, but a high load of gregarines must have consequences for the host, since gregarines tend to clog the midgut in case of a high-intensity invasion. But despite the fact that the intensity of G. polymorpha infection was much higher than indicated in other sources [70], we did not observe these complications. Gregarines are supposed to absorb nutrients from the host’s body, weakening it, but in our study it was shown that they do not interfere with the increase in the body weight of the larva. Although gregarines are considered parasites, in the case of T. molitor symbiosis with G. polymorpha, they do not cause visible damage to the host, even with high numbers.
5. Conclusions
In the concentrations we used, cyclopentanol and 2-naphthol inhibited the vitality of the mealworms, and 3-aminobenzoic acid, diphenyl ether, benzyl alcohol, and catechol decreased the invasion intensity by G. polymorpha. In the beetle larvae with lower body mass, the intensity of infestation with gregarines was lower, and the rates of the host’s body-mass increment correlated positively with a larger number of gregarines in their intestines. High-intensity loading with gregarines had no negative impact on the larvae.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.L. and V.B.; Methodology, V.L. and V.B.; Validation, V.L. and V.B.; Formal Analysis, V.B.; Investigation, V.L. and V.B.; Resources, V.L.; Data Curation, V.L. and V.B.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, V.L. and V.B.; Writing—Review and Editing, V.L. and V.B.; Visualization, V.L. and V.B.; Supervision, V.L. and V.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Experiments were conducted on invertebrate species not protected in the European Union and although ethical approval was not required the highest possible standards of animal welfare were applied.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data are either published with the manuscript or are available on request from the lead author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ramos-Elorduy, J.; González, E.A.; Hernández, A.R.; Pino, J.M. Use of Tenebrio molitor (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) to recycle organic wastes and as feed for broiler chickens. J. Econ. Entomol. 2002, 95, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosentrater, K.A. Chapter 21—Insects in grains: Identification, damage, and detection. In Storage of Cereal Grains and Their Products, 5th ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2022; pp. 607–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.B.; Choi, W.H.; Kim, S.; Jin, H.; Han, Y.S.; Lee, Y.; Kim, N.J. Developmental characteristics of Tenebrio molitor larvae (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) in different instars. Int. J. Ind. Entomol. 2014, 28, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martynov, V.O.; Brygadyrenko, V.V. The impact of some inorganic substances on change in body mass of Tenebrio molitor (Coleoptera, Tenebrionidae) larvae in a laboratory experiment. Folia Oecol. 2018, 45, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martynov, V.O.; Brygadyrenko, V.V. The influence of synthetic food additives and surfactants on the body weight of larvae of Tenebrio molitor (Coleoptera, Tenebrionidae). Biosyst. Divers. 2017, 25, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neethirajan, S.; Karunakaran, C.; Jayas, D.S.; White, N.D.G. Detection techniques for stored-product insects in grain. Food Control 2007, 18, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemianowska, E.; Kosewska, A.; Aljewicz, M.; Skibniewska, K.; Polak-Juszczak, L.; Jarocki, A.; Jędras, M. Larvae of mealworm (Tenebrio molitor L.) as European novel food. Agric. Sci. 2013, 4, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørge, J.D.; Overgaard, J.; Malte, H.; Gianotten, N.; Heckmann, L.H. Role of temperature on growth and metabolic rate in the tenebrionid beetles Alphitobius diaperinus and Tenebrio molitor. J. Insect Physiol. 2018, 107, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, N.; Abelho, M.; Costa, R. A review of the scientific literature for optimal conditions for mass rearing Tenebrio molitor (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). J. Entomol. Sci. 2018, 53, 434–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, J.A.C.; Ruiz, A.T.; Morales-Ramos, J.A.; Thomas, M.; Rojas, M.G.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Yi, L.; Han, R.; Giroud, L.; Jullien, R.L. Chapter 6—Insect mass production technologies. In Insects as Sustainable Food Ingredients; Dossey, T., Morales-Ramos, J.A., Rojas, M.G., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 153–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makkar, H.P.S.; Tran, G.; Heuzé, V.; Ankers, P. State-of-the-art on use of insects as animal feed. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2014, 197, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.P.; Williams, J.R.; Kirabo, A.; Chester, D.; Peterson, M. Chapter 3—Nutrient content and health benefits of insect. In Insects as Sustainable Food Ingredients; Dossey, T., Morales-Ramos, J.A., Rojas, M.G., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 61–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grau, T.; Vilcinskas, A.; Joop, G. Sustainable farming of the mealworm Tenebrio molitor for the production of food and feed. Z. Naturforschung C J. Biosci. 2017, 72, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Nutrition, Novel Foods and Food Allergens (NDA); Turck, D.; Castenmiller, J.; De Henauw, S.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Kearney, J.; Maciuk, A.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H.J.; Naska, A.; et al. Safety of dried yellow mealworm (Tenebrio molitor larva) as a novel food pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283. EFSA J. 2021, 19, e06343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martynov, V.O.; Brygadyrenko, V.V. The influence of the synthetic food colourings tartrazine, allura red and indigo carmine on the body weight of Tenebrio molitor (Coleoptera, Tenebrionidae) larvae. Regul. Mech. Biosyst. 2018, 9, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martynov, V.O.; Hladkyi, O.Y.; Kolombar, T.M.; Brygadyrenko, V.V. Impact of essential oil from plants on migratory activity of Sitophilus granarius and Tenebrio molitor. Regul. Mech. Biosyst. 2019, 10, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brai, A.; Poggialini, F.; Vagaggini, C.; Pasqualini, C.; Simoni, S.; Francardi, V.; Dreassi, E. Tenebrio molitor as a simple and cheap preclinical pharmacokinetic and toxicity model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.M.; Criddle, C.S. Characterization of biodegradation of plastics in insect larvae. Method. Enzymol. 2021, 648, 95–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tang, T. Effects of polystyrene diet on the growth and development of Tenebrio molitor. Toxics 2022, 10, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Hou, Y.; Li, W.; Yang, S.; Li, Q.; Yu, Z. Exploring the potential of grease from yellow mealworm beetle (Tenebrio molitor) as a novel biodiesel feedstock. Appl. Energy 2013, 101, 618–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.J.; Hwang, I.K.; Nho, C.W.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, S.H. Determination of carbohydrate composition in mealworm (Tenebrio molitor L.) larvae and characterization of mealworm chitin and chitosan. Foods 2021, 10, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.; Kim, M.A.; Park, I.; Hwang, J.S.; Na, M.; Bae, J.S. Novel direct factor Xa inhibitory compounds from Tenebrio molitor with anti-platelet aggregation activity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 109, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.R.; Lee, S.O. Novel hepatoprotective peptides derived from protein hydrolysates of mealworm (Tenebrio molitor). Food Res. Int. 2020, 133, 109194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moruzzo, R.; Riccioli, F.; Espinosa Diaz, S.; Secci, C.; Poli, G.; Mancini, S. Mealworm (Tenebrio molitor): Potential and challenges to promote circular economy. Animals 2021, 11, 2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desportes, I.; Schrével, J. Treatise on zoology—Anatomy, taxonomy, biology. The gregarines. In The Early Branching Apicomplexa; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Clopton, R.E.; Janovy, J., Jr.; Percival, T.J. Host stadium specificity in the gregarine assemblage parasitizing Tenebrio molitor. J. Parasitol. 1992, 78, 334–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clopton, R.E.; Janovy, J. Developmental niche structure in the gregarine assemblage parasitizing Tenebrio molitor. J. Parasitol. 1993, 79, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slowik, A.R.; Herren, P.; Bessette, E.; Lim, F.S.; Hernández-Pelegrín, L.; Savio, C. Harmful and beneficial symbionts of Tenebrio molitor and their implications for disease management. J. Insect. Food Feed 2023, 9, 1381–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoonvaere, K.; Brunain, M.; Baeke, F.; De Bruyne, M.; De Rycke, R.; de Graaf, D.C. Comparison between Apicystis cryptica sp. n. and Apicystis bombi (Arthrogregarida, Apicomplexa): Gregarine parasites that cause fat body hypertrophism in bees. Eur. J. Protistol. 2020, 73, 125688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schawang, J.E.; Janovy, J., Jr. The response of Gregarina niphandrodes (Apicomplexa: Eugregarinida: Septatina) to host starvation in Tenebrio molitor (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) adults. J. Parasitol. 2001, 87, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessette, E.; Williams, B. Protists in the insect rearing industry: Benign passengers or potential risk? Insects 2022, 13, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clopton, R.E. Phylum Apicomplexa Levine, 1970: Order Eugregarinorida Leger, 1900. In Illustrated Guide to the Protozoa, 2nd ed.; Lee, J.J., Leedale, G., Patterson, D., Bradbury, P.C., Eds.; Society of Protozoologists: Lawrence, KS, USA, 2002; pp. 205–288. [Google Scholar]
- Rueckert, S.; Betts, E.L.; Tsaousis, A.D. The symbiotic spectrum: Where do the gregarines fit? Trends Parasitol. 2019, 35, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parhomenko, O.V.; Brygadyrenko, V.V. Effects of biphenyl on Blaberus craniifer (Blattodea, Blaberidae) cockroaches and their parasites—Gregarines and nematodes. Biosyst. Divers. 2023, 31, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhomenko, O.V.; Lagutenko, O.T.; Lebedynets, N.V.; Brygadyrenko, V.V. Body-weight gains in Blaberus craniifer cockroaches and the intensity of their infection with gregarines and nematodes. Biosyst. Divers. 2023, 31, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuk, M. The effects of gregarine parasites, body size, and time of day on spermatophore production and sexual selection in field crickets. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 1987, 21, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, Y.; Omoto, C.K.; Gomulkiewicz, R. Individual and population effects of eugregarine, Gregarina niphandrodes (Eugregarinida: Gregarinidae), on Tenebrio molitor (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). Environ. Entomol. 2007, 36, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mita, K.; Kawai, N.; Rueckert, S.; Sasakura, Y. Large-scale infection of the ascidian Ciona intestinalis by the gregarine Lankesteria ascidiae in an inland culture system. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2012, 101, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brygadyrenko, V.V.; Svyrydchenko, A.O. Influence of the gregarine Stenophora julipusilli (Eugregarinorida, Stenophoridae) on the trophic activity of Rossiulus kessleri (Diplopoda, Julidae). Folia Oecol. 2015, 42, 10–20. [Google Scholar]
- Brygadyrenko, V.V.; Reshetniak, D.Y. Morphometric variability of Clitellocephalus ophoni (Eugregarinida, Gregarinidae) in the intestines of Harpalus rufipes (Coleoptera, Carabidae). Arch. Biol. Sci. 2016, 68, 587–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siva-Jothy, M.T.; Plaistow, S.J. A fitness cost of eugregarine parasitism in a damselfly. Ecol. Entomol. 2001, 24, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, J.C. Effects of gregarine parasites on the development of Dirofilaria immitis in Aedes triseriatus (Diptera: Culicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 1983, 20, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecker, K.R.; Forbes, M.R.; Léonard, N.J. Parasitism of damselflies (Enallagma boreale) by gregarines: Sex biases and relations to adult survivorship. Can. J. Zool. 2002, 80, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcón, M.E.; Jara, F.A.; Briones, R.C.; Dubey, A.K.; Slamovits, C.H. Gregarine infection accelerates larval development of the cat flea Ctenocephalides felis (Bouché). Parasitology 2017, 144, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štefanac, T.; Grgas, D.; Landeka Dragičević, T. Xenobiotics-division and methods of detection: A review. J. Xenobiot. 2021, 11, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croom, E. Metabolism of xenobiotics of human environments. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2012, 112, 31–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miglani, R.; Parveen, N.; Kumar, A.; Ansari, M.A.; Khanna, S.; Rawat, G.; Panda, A.K.; Bisht, S.S.; Upadhyay, J.; Ansari, M.N. Degradation of xenobiotic pollutants: An environmentally sustainable approach. Metabolites 2022, 12, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, A.; Rastogi, A.; Pandey, S.; Gupta, S. Assessment of the consequences of xenobiotics in soil ecosystem. In Xenobiotics in Urban Ecosystems; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonelli, F.C.P.; Tonelli, F.M.P. Concerns and threats of xenobiotics on aquatic ecosystems. Bioremediat. Biotechnol. 2020, 3, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piwowarska, D.; Kiedrzyńska, E. Xenobiotics as a contemporary threat to surface waters. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2022, 22, 337–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, S.E.; Hankenson, F.C. Nonexperimental xenobiotics: Unintended consequences of intentionally administered substances in terrestrial animal models. ILAR J. 2022, 60, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, A.; Ghosh, B.; Sarmah, D.; Chaudhary, A.; Borah, A.; Bhattacharya, P. Aspects of xenobiotics and their receptors in stroke. Neuroprotection 2023, 1, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raś, M.; Iwan, D.; Kamiński, M.J. The tracheal system in post-embryonic development of holometabolous insects: A case study using the mealworm beetle. J. Anat. 2018, 232, 997–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboelhadid, S.M.; Ibrahium, S.M.; Abdel-Tawab, H.; Hassan, A.O.; Al-Quraishy, S.; Saleh, F.E.R.; Abdel-Baki, A.S. Toxicity and repellency efficacy of benzyl alcohol and benzyl benzoate as eco-friendly choices to control the red flour beetle Tribolium castaneum (Herbst, 1797). Molecules 2023, 28, 7731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Masri, J.; Perez, V.; Maya, C.; Zhao, J. Growth performance and nutrient composition of mealworms (Tenebrio molitor) fed on fresh plant materials-supplemented diets. Foods 2020, 9, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geus, A. Sporentierchen, Sporozoa: Die Gregarinida der land- und su¨ßwasserbewohnenden Arthropoden Mitteleuropas. In Die Tierwelt Deutschlands und der Angrenzenden Meeresteile nach Ihren Merkmalen und Nach Ihrer Lebensweise; Dahl, F., Ed.; VEB Gustav Fischer: Jena, Germany, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Castilla, A.M.; Dauwe, T.; Mora, I.; Palmer, M.; Guitart, R. Mortality of the yellow mealworm Tenebrio molitor exposed to fertilizers and herbicides commonly used in agriculture. Vie Milieu 2008, 58, 263–275. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, B.; Gurdal, B.; Estep, A.S.; Tabanca, N.; Kurkcuoglu, M.; Goger, F.; Gul, Z.; Bardakci, H.; Becnel, J.; Mat, A.; et al. The insecticidal activities of Erica manipuliflora Salisb. extracts in the flowering and fruiting periods and their evaluation in term of chemical profiles of active extracts. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2022, 187, 115380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, Z.; Wang, S.; Yin, F.; Wei, Y.; Xie, J.; Sun, R. Discovery of 2-naphthol from the leaves of Actephila merrilliana as a natural nematicide candidate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 13209–13219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poston, R.G.; Saha, R.N. Epigenetic effects of polybrominated diphenyl ethers on human health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.B.; Chen, W.J.; Shan, T.Z.; Sun, B.Y.; Yan, P.C.; Jiang, W. Antibacterial diphenyl ether, benzophenone and xanthone derivatives from Aspergillus flavipes. Chem. Biodivers. 2020, 17, e1900640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jose, A.; Bansal, M.; Svirskis, D.; Swift, S.; Gizdavic-Nikolaidis, M.R. Synthesis and characterization of antimicrobial colloidal polyanilines. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2024, 238, 113912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morash, M.G.; Soanes, K.H.; Achenbach, J.C.; Ellis, L.D. Assessing the morphological and behavioral toxicity of catechol using larval zebrafish. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumner, R. Relation of gregarines to growth and longevity in the mealworm Tenebrio molitor L. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1936, 29, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harry, O.G. The effect of a eugregarine Gregarina polymorpha (Hammerschmidt) on the mealworm larva of Tenebrio molitor (L.). J. Protozool. 1967, 14, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johny, S.; Muralirangan, M.; Sanjayan, P. Parasitization potential of two cephaline gregarines, Leidyana subramanii Pushkala and Muralirangan and Retractocephalus dhawanii sp. n. on the tobacco grasshopper, Atractomorpha crenulata (Fab.). J. Orthoptera Res. 2000, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigliolli, A.A.; Julio, A.H.; Conte, H. The life cycle of Gregarina cuneata in the midgut of Tribolium castaneum and the effects of parasitism on the development of insects. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2016, 106, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Er, M.K.; Gökçe, A. Effect of Diplocystis tipulae Sherlock (Eugregarinida: Apicomplexa), a coelomic gregarine pathogen of tipulids, on the larval size of Tipula paludosa Meigen (Tipulidae: Diptera). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2005, 89, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolz, M.; Schrader, A.; Whitelaw, E.; Müller, C. Gregarines modulate insect responses to sublethal insecticide residues. Oecologia 2022, 198, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koura, E.A.; Kamel, E.G. A survey of gregarines associated with Tenebrio molitor and Opatriodes vicinus in the central region of Saudi Arabia. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 1993, 23, 213–220. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).