Silk Gland Factor 1 Plays a Pivotal Role in Larval Settlement of the Fouling Mussel Mytilopsis sallei
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
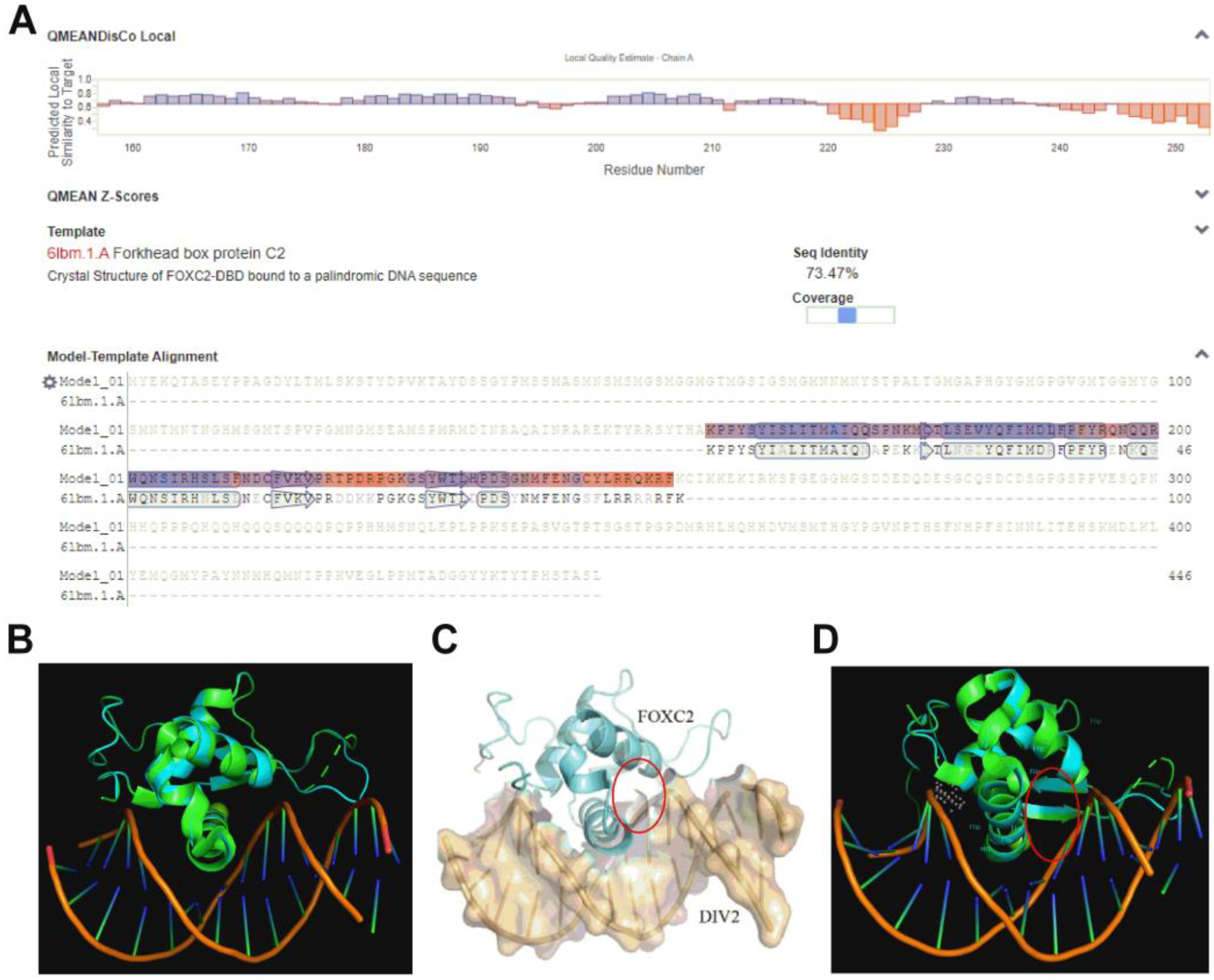
2.1. Homology Model
2.2. Virtual Screening
2.3. Spawning Induction and Larval Culture of M. sallei
2.4. Bioassays of Larval Settlement in Response to Compounds
2.5. Foot Proteins’ Gene Expression Analysis by qRT-PCR
2.6. Bioassays of Byssus Thread Secretion in Response to Compounds
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Homology Model and Virtual Screening
3.2. Larval Settlement in Response to the Targeted Binding Compounds of SGF1
3.3. Byssus Thread Secretion in Response to the Targeted Binding Compounds of SGF1
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maréchal, J.P.; Hellio, C. Challenges for the development of new non-toxic antifouling solutions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 4623–4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Wu, Q.; Yu, C.; Zhao, T.; Liu, M. Recent progress of biomimetic antifouling surfaces in marine. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 7, 2000966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusim, A.K.; Utama, I. An investigation into the drag increase on roughen surface due to marine fouling growth. IPTEK J. Technol. Sci. 2017, 28, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Hanh, B.M.; Chua, J.Q.I.; Daniel, D.; Ismail, M.H.; Marchioro, M.; Amini, S.; Rice, S.A.; Miserez, A. Green biolubricant infused slippery surfaces to combat marine biofouling. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 568, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Want, A.; Crawford, R.; Kakkonen, J.; Kiddie, G.; Miller, S.; Harris, R.E.; Porter, J.S. Biodiversity characterisation and hydrodynamic consequences of marine fouling communities on marine renewable energy infrastructure in the Orkney Islands Archipelago, Scotland, UK. Biofouling 2017, 33, 567–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ning, C. Latest research progress of marine microbiological corrosion and bio-fouling, and new approaches of marine anti-corrosion and anti-fouling. Bioact. Mater. 2019, 4, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permeh, S.; Lau, K.; Duncan, M. Degradation of coatings for steel in environments susceptible to corrosion associated with fouling. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2020, 16, 1186–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dafforn, K.A.; Lewis, J.A.; Johnston, E.L. Antifouling strategies: History and regulation, ecological impacts and mitigation. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gittens, J.E.; Smith, T.J.; Suleiman, R.; Akid, R. Current and emerging environmentally-friendly systems for fouling control in the marine environment. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 1738–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Tian, L.; Bing, W.; Zhao, J.; Ren, L. Bioinspired marine antifouling coatings: Status, prospects, and future. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2022, 124, 100889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, P.Y.; Xu, Y.; Fusetani, N. Natural products as antifouling compounds: Recent progress and future perspectives. Biofouling 2009, 26, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Yu, L.; Mou, J.; Wu, D.; Xu, M.; Zhou, P.; Ren, Y. Research strategies to develop environmentally friendly marine antifouling coatings. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Lee, S.; Ohkawa, K.; Hwang, D.S. Counterplotting the mechanosensing-based fouling mechanism of mussels against fouling. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 18566–18579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, P.Y.; Lau, S.C.; Dahms, H.U.; Dobretsov, S.; Harder, T. Marine biofilms as mediators of colonization by marine macroorganisms: Implications for antifouling and aquaculture. Mar. Biotechnol. 2007, 9, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prendergast, G.S. Settlement and behaviour of marine fouling organisms. In Biofouling; Dürr, S., Thomason, J.C., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2010; pp. 30–59. [Google Scholar]
- Garibay-Valdez, E.; Martínez-Córdova, L.R.; Vargas-Albores, F.; Emerenciano, M.G.C.; Miranda-Baeza, A.; Cortés-Jacinto, E.; Ortiz-Estrada, A.M.; Cicala, F.; Martínez-Porchas, M. The biofouling process: The science behind a valuable phenomenon for aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2023, 15, 976–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, A.; Vogeler, S. Molluscan bivalve settlement and metamorphosis: Neuroendocrine inducers and morphogenetic responses. Aquaculture 2018, 487, 64–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Deng, S.; Gavriouchkina, D.; Zhang, G. Transcriptional regulation analysis reveals the complexity of metamorphosis in the Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas). Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2023, 5, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nontunha, N.; Chaiyamoon, A.; Chaichotranunt, S.; Tinikul, R.; Poomtong, T.; Sobhon, P.; Tinikul, Y. Neurotransmitters induce larval settlement and juvenile growth of the sea cucumber, Holothuria scabra. Aquaculture 2021, 535, 736427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikuma, N.J.; Antoshechkin, I.; Medeiros, J.M.; Pilhofer, M.; Newman, D.K. Stepwise metamorphosis of the tubeworm Hydroides elegans is mediated by a bacterial inducer and MAPK signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 10097–10102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malter, K.E.; Esmerode, M.; Damba, M.; Alker, A.T.; Forsberg, E.M.; Shikuma, N.J. Diacylglycerol, PKC and MAPK signaling initiate tubeworm metamorphosis in response to bacteria. Dev. Biol. 2022, 487, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak, A.M. Environmental sciences: Troubled waters on the Great Lakes. Nature 2017, 543, 488–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wang, P.; Wang, Z.; Feng, D.; Zhang, D. TRPM7-mediated Ca2+ regulates mussel settlement through the CaMKKβ-AMPK-SGF1 pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, E.; Bordeaux, M.C.; Garel, A.; Couble, P. Fork head alternative binding drives stage-specific gene expression in the silk gland of Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 32, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Li, K.; Guo, Y.; Sun, X.; Deng, H.; Li, K.; Feng, Q.; Li, S. Ras-Raf-MAPK signaling promotes nuclear localization of FOXA transcription factor SGF1 via Ser91 phosphorylation. BBA-Mol. Cell Res. 2018, 1865, 560–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCartney, M.A. Structure, function and parallel evolution of the bivalve byssus, with insights from proteomes and the zebra mussel genome. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2021, 376, 20200155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, S.; Huang, X.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, J.; Zhan, A. Protein-mediated bioadhesion in marine organisms: A review. Mar. Environ. Res. 2021, 170, 105409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miserez, A.; Yu, J.; Mohammadi, P. Protein-based biological materials: Molecular design and artificial production. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 2049–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wu, Z.; Chen, L.; Dai, Q.; Hao, H.; Su, P.; Ke, C.; Feng, D. Adenosine triggers larval settlement and metamorphosis in the mussel Mytilopsis sallei through the ADK-AMPK-FoxO pathway. ACS Chem. Biol. 2021, 16, 1390–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Qi, J.F.; Feng, D.Q.; Ke, C.H. Embryonic and larval development of the invasive biofouler Mytilopsis sallei (Récluz, 1849)(Bivalvia: Dreissenidae). J. Molluscan Stud. 2016, 82, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Qi, J.F.; Huang, Y.Q.; Sheng, Y.Q.; Su, P.; Feng, D.Q.; Ke, C.H. Larval settlement and metamorphosis of the invasive biofouler, Mytilopsis sallei, in response to ions and neuroactive compounds. Mar. Biol. Res. 2017, 13, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, Y.; Sheng, Y.; Su, P.; Qiu, Y.; Ke, C.; Feng, D. Antifouling activity towards mussel by small-molecule compounds from a strain of Vibrio alginolyticus bacterium associated with sea anemone Haliplanella sp. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Dai, S.; Chen, X.; Liang, X.; Qu, L.; Jiang, L.; Guo, M.; Zhou, Z.; Wei, H.; Zhang, H.; et al. Mechanism of forkhead transcription factors binding to a novel palindromic DNA site. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 3573–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakhar, R.; Dangi, M.; Khichi, A.; Chhillar, A.K. Relevance of molecular docking studies in drug designing. Curr. Bioinform. 2020, 15, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrone, L.; Kumar, A.; Sutanto, C.N.; Patil, N.J.; Kannan, S.; Palaniappan, A.; Amini, S.; Zappone, B.; Verma, C.; Miserez, A. Mussel adhesion is dictated by time-regulated secretion and molecular conformation of mussel adhesive proteins. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, S.; Kolle, S.; Petrone, L.; Ahanotu, O.; Sunny, S.; Sutanto, C.N.; Hoon, S.; Cohen, L.; Weaver, J.C.; Aizenberg, J.; et al. Preventing mussel adhesion using lubricant-infused materials. Science 2017, 357, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramova, A.; Alm Rosenblad, M.; Blomberg, A.; Larsson, T.A. Sensory receptor repertoire in cyprid antennules of the barnacle Balanus improvisus. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, E.W.F.; Brosens, J.; Gomes, A.R.; Koo, C.Y. Forkhead box proteins: Tuning forks for transcriptional harmony. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 482–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, N.; Zeng, H.; Wu, J. Marine mussel adhesion: Biochemistry, mechanisms, and biomimetics. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2013, 27, 2139–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, N.; Zhang, L.; Gao, W.; Huang, C.; Huber, P.E.; Zhou, X.; Li, C.; Shen, G.; Zou, B. NAD+ metabolism: Pathophysiologic mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, R.T.; Pechenik, J.A.; Biggers, W.J.; Scavo, G.; Lehman, C. The B vitamins nicotinamide (B3) and riboflavin (B2) stimulate metamorphosis in larvae of the deposit-feeding polychaete Capitella teleta: Implications for a sensory ligand-gated ion channel. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Aidaroos, A.M.; Satheesh, S.; Devassy, R.P. Effects of pharmacological compounds on the barnacle larval development, metabolism and settlement. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 117, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraju, G.P.C. Is methyl farnesoate a crustacean hormone? Aquaculture 2007, 272, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBlanc, G.A. Crustacean endocrine toxicology: A review. Ecotoxicology 2007, 16, 61–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Qian, P.Y. Review on molecular mechanisms of antifouling compounds: An update since 2012. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Item | Catalog ID | Compound Name | Docking Score | Mw |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | HY-17383 | Levomefolate (calcium) | −11.232 | 457.44 |
| 2 | HY-B0080 | Folinic acid (calcium salt pentahydrate) | −10.728 | 471.42 |
| 3 | HY-B0445 | NAD+ | −10.011 | 663.43 |
| 4 | HY-13667 | Levoleucovorin (Calcium) | −9.938 | 471.42 |
| 5 | HY-107780B | Cyclic-di-GMP (diammonium) | −9.671 | 688.40 |
| 6 | HY-17379 | Atorvastatin (hemicalcium salt) | −9.629 | 557.63 |
| 7 | HY-125399 | PSMA-11 | −9.475 | 946.99 |
| 8 | HY-N6006 | 1,3,6-Tri-O-galloyl-beta-D-glucose | −9.304 | 636.47 |
| 9 | HY-111832 | 1,2,3,6-Tetragalloylglucose | −9.217 | 788.57 |
| 10 | HY-126126 | S-Adenosyl-DL-methionine | −9.110 | 398.44 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, J.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Chen, L.; Huang, J. Silk Gland Factor 1 Plays a Pivotal Role in Larval Settlement of the Fouling Mussel Mytilopsis sallei. Biology 2024, 13, 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13060417
He J, Wang Z, Wu Z, Chen L, Huang J. Silk Gland Factor 1 Plays a Pivotal Role in Larval Settlement of the Fouling Mussel Mytilopsis sallei. Biology. 2024; 13(6):417. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13060417
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Jian, Zhixuan Wang, Zhiwen Wu, Liying Chen, and Jianfang Huang. 2024. "Silk Gland Factor 1 Plays a Pivotal Role in Larval Settlement of the Fouling Mussel Mytilopsis sallei" Biology 13, no. 6: 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13060417
APA StyleHe, J., Wang, Z., Wu, Z., Chen, L., & Huang, J. (2024). Silk Gland Factor 1 Plays a Pivotal Role in Larval Settlement of the Fouling Mussel Mytilopsis sallei. Biology, 13(6), 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13060417






