Habitat Enrichment Causes Changes in Fish Behavioural Characteristics: A Case Study of Sparus latus
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals and Fish Maintenance
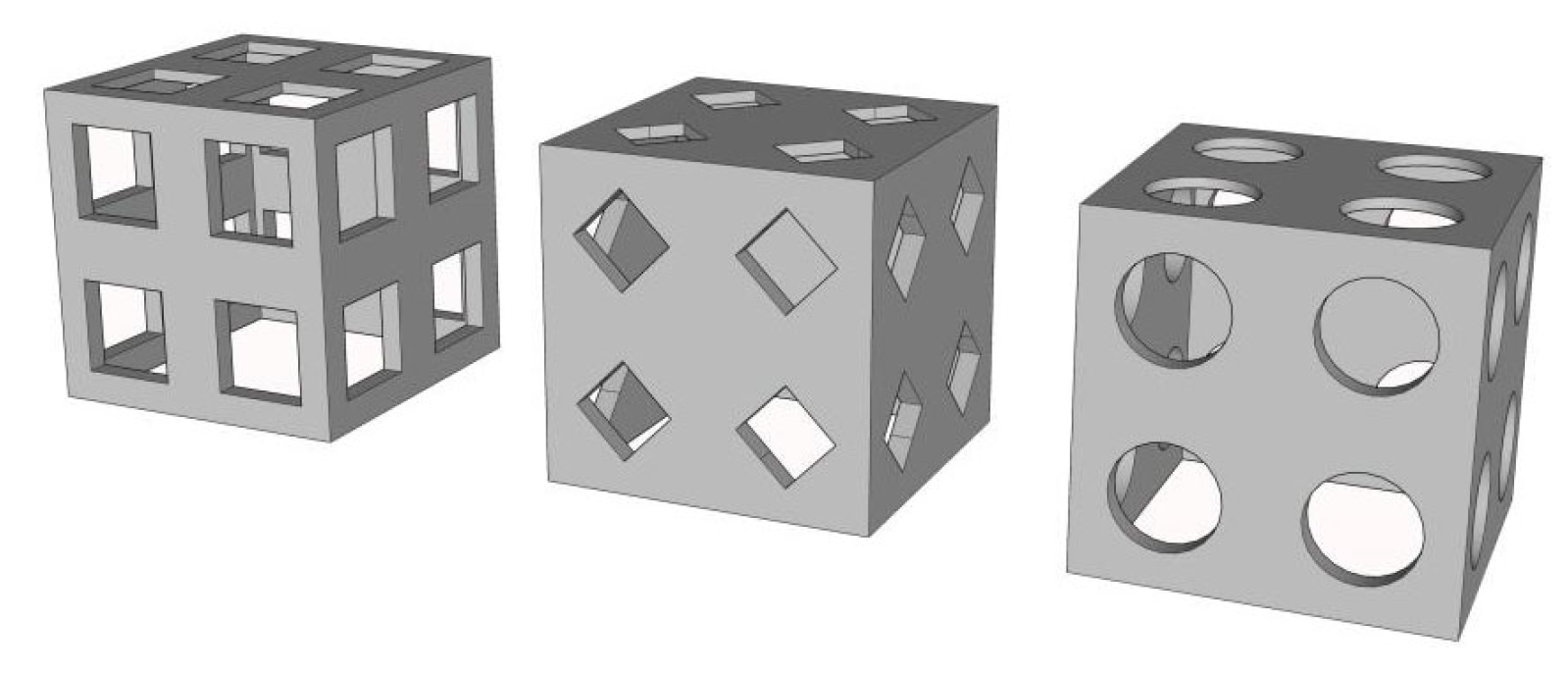
2.2. Experimental Reef Types
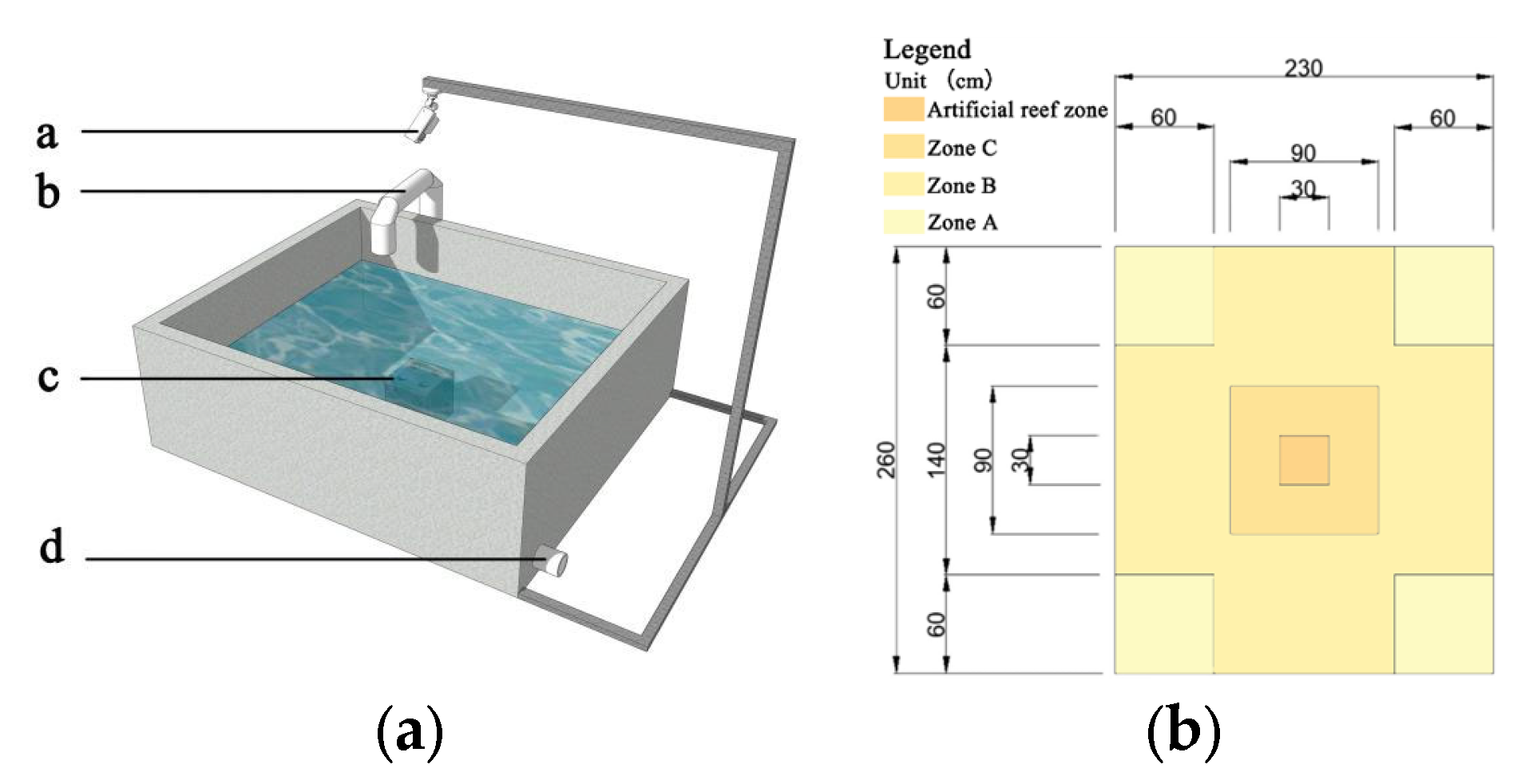
2.3. Experimental Environment and Equipment
2.4. Daytime Experiment
2.5. Nighttime Experiment
2.6. Evaluated Parameters and Statistical Analysis
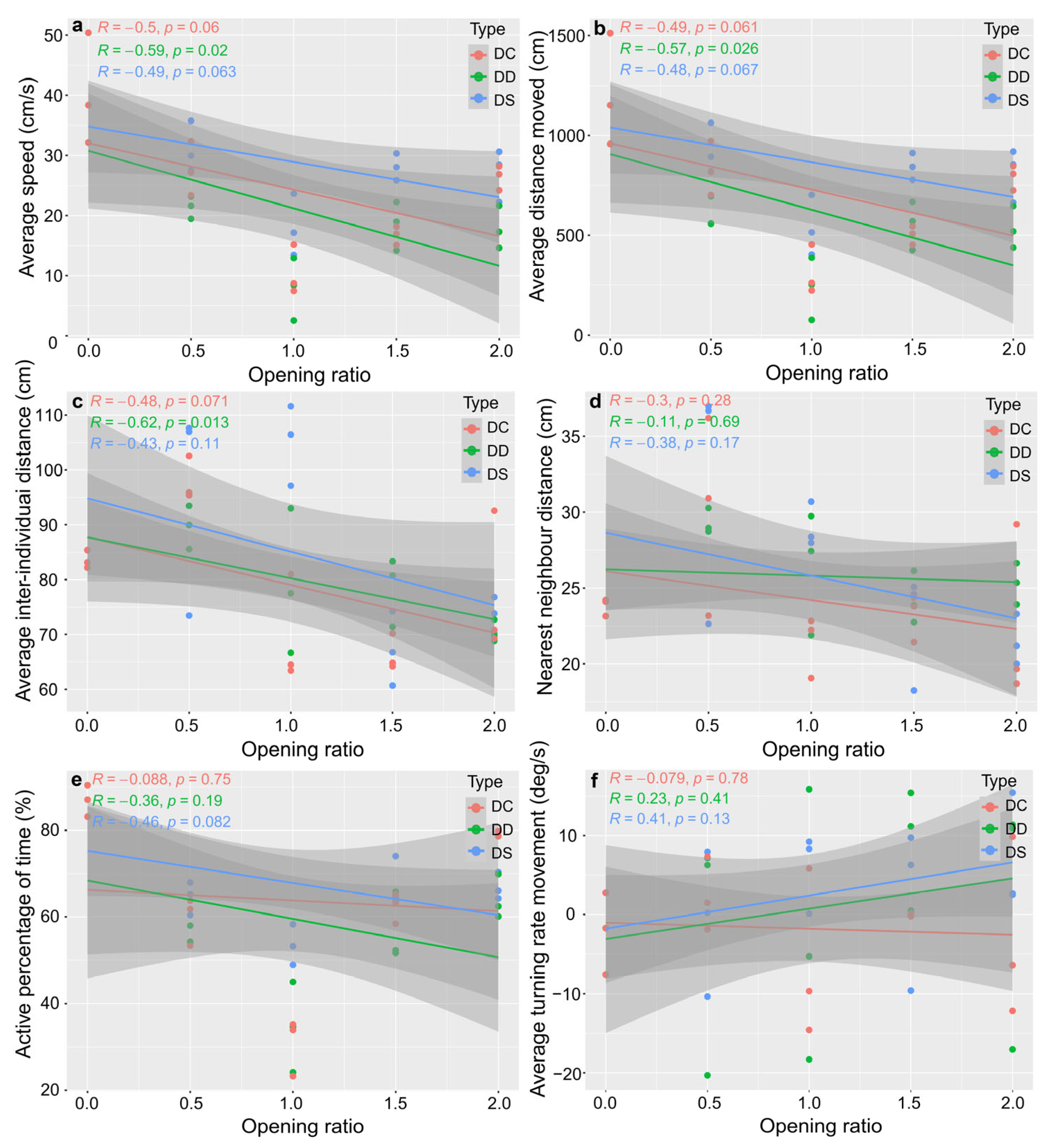
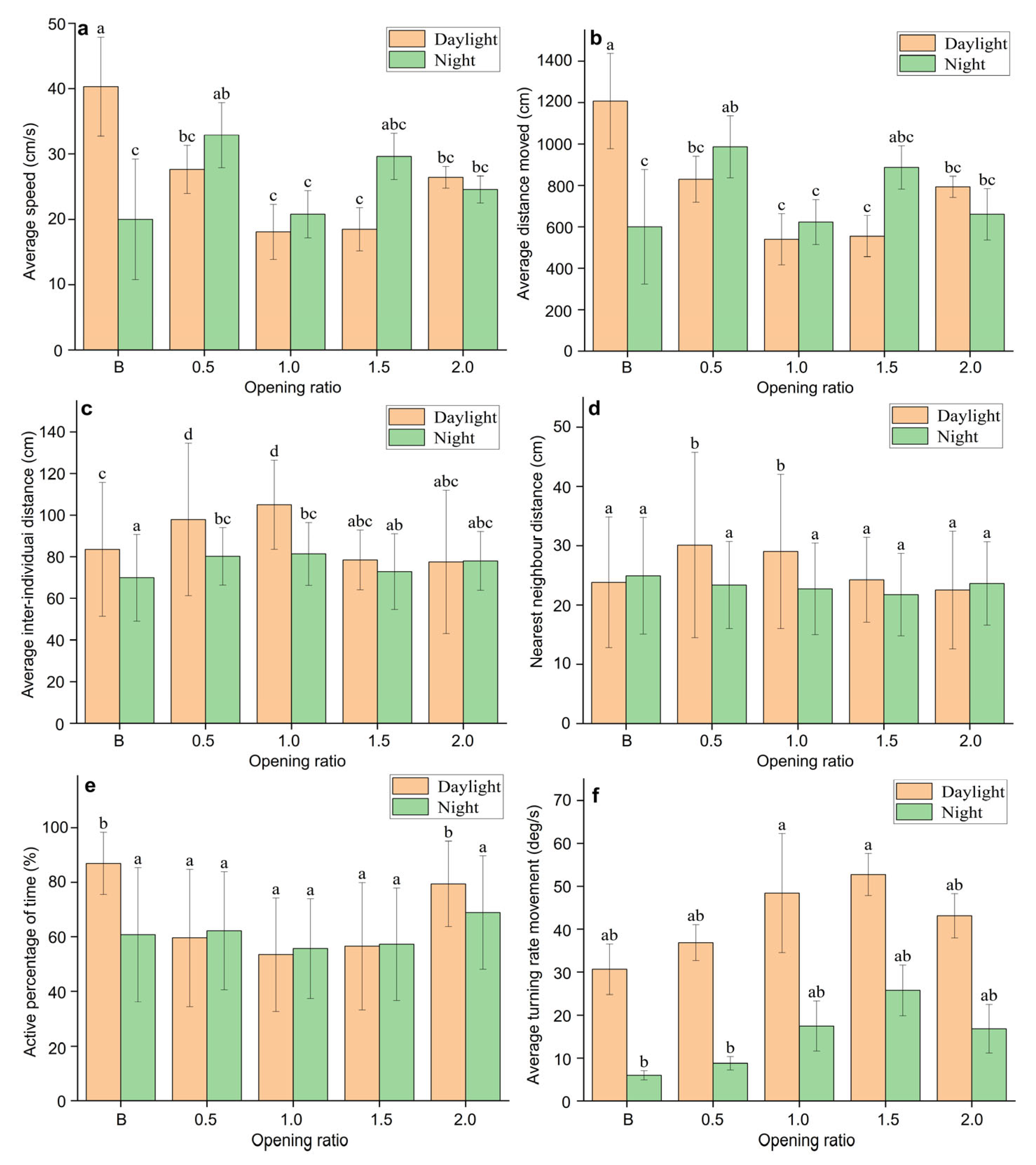
3. Results
3.1. First Contact Time
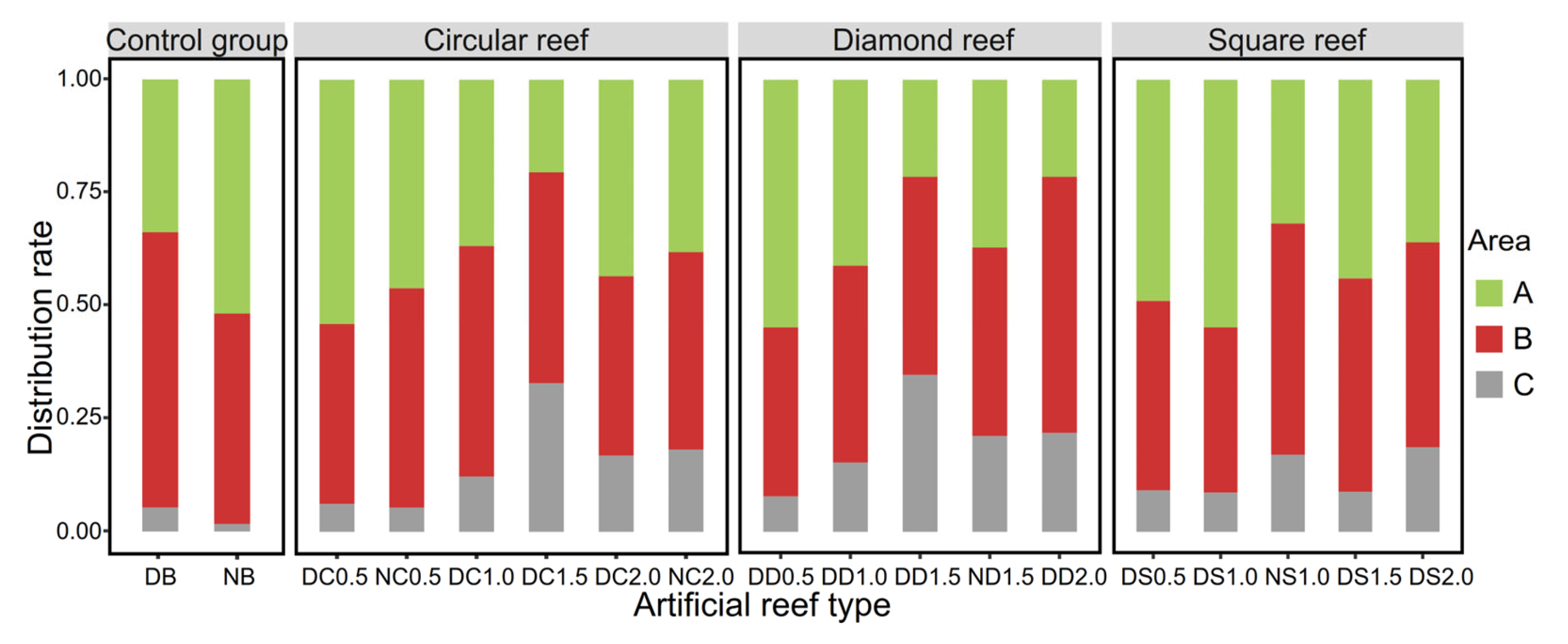
3.2. Habitat Preferences
3.3. Swimming Behaviour
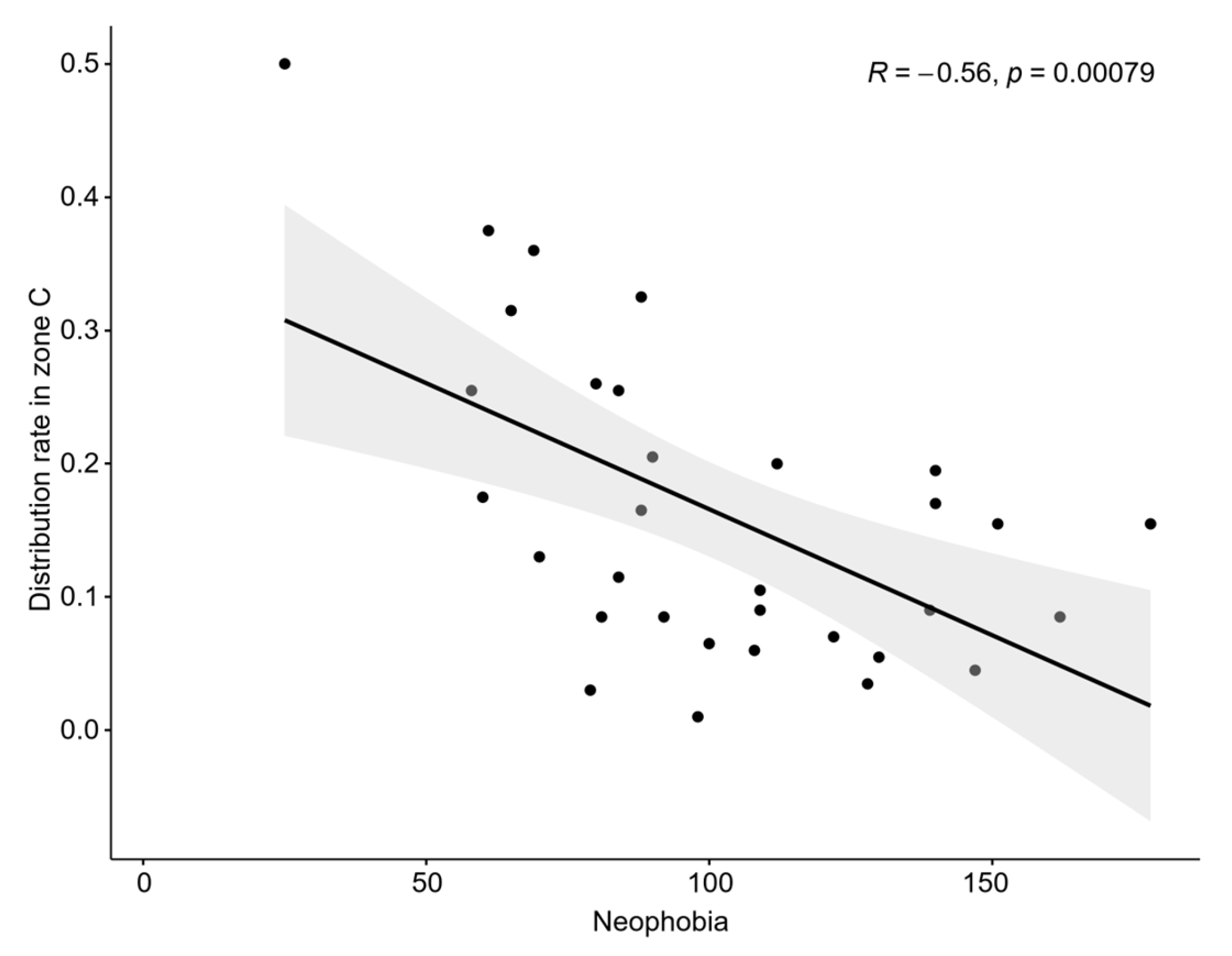
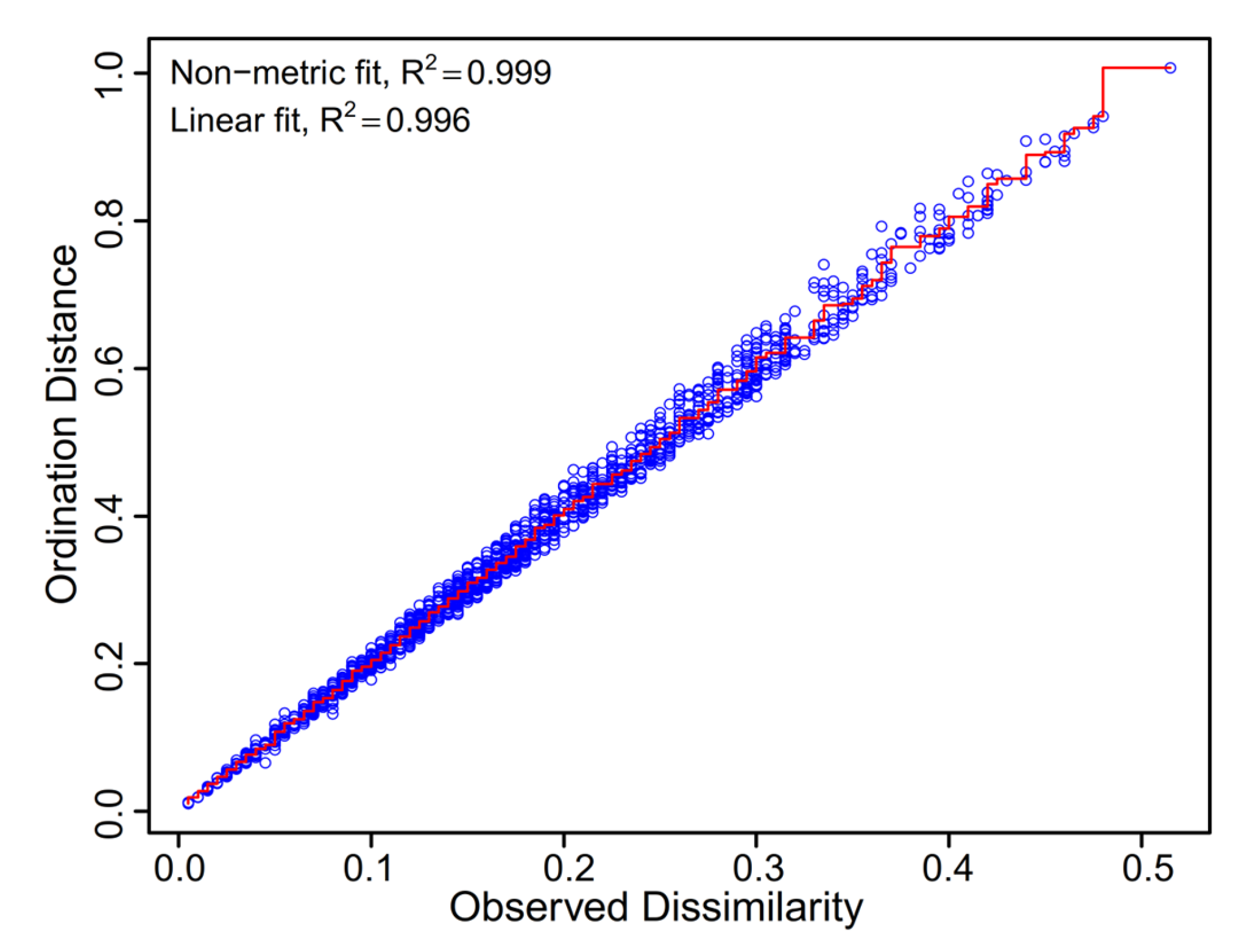
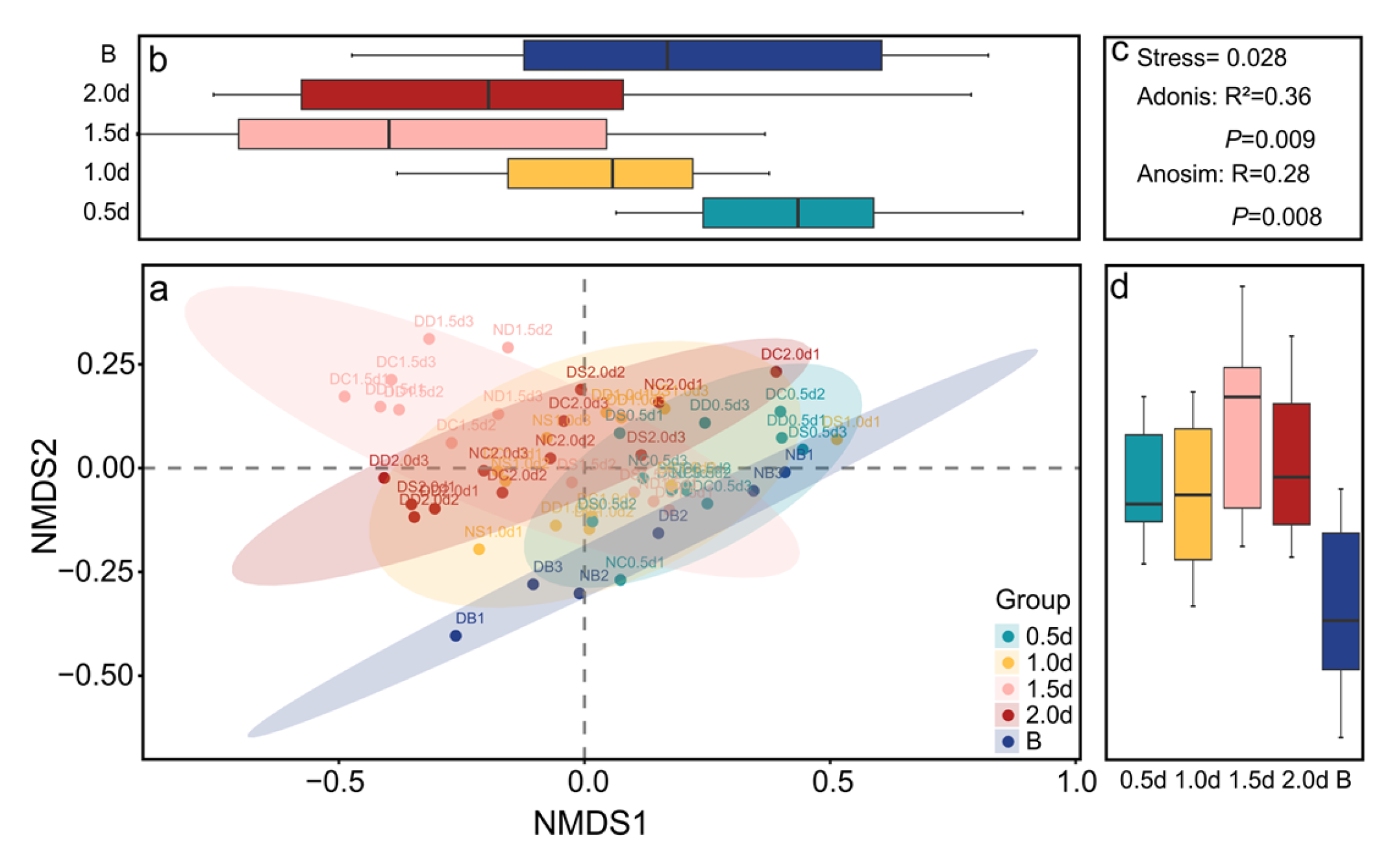
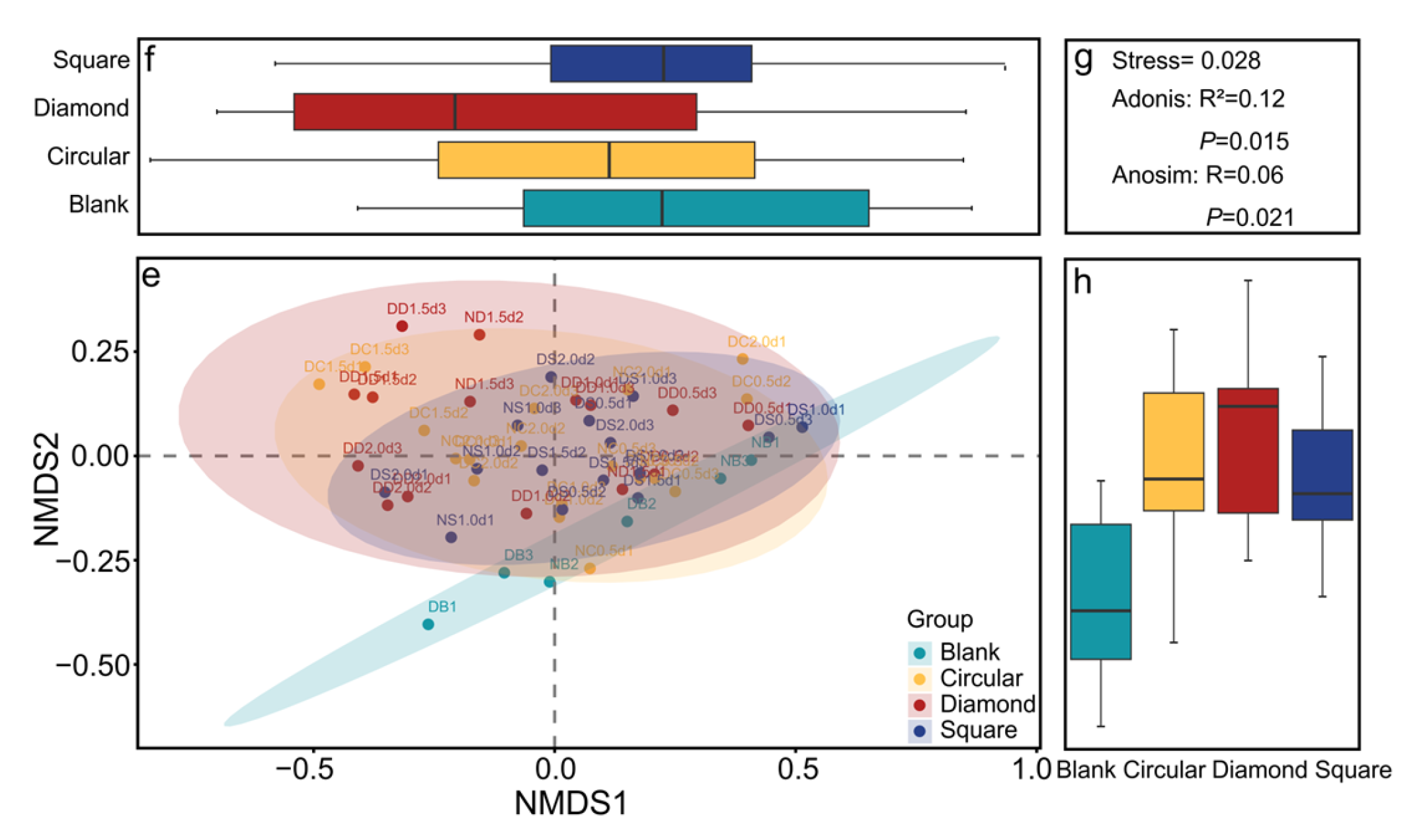
3.4. Driving Factors of Behaviour
4. Discussion
4.1. Importance of Artificial Reef Habitats in the Natural Environment
4.2. Role of Shoaling Behaviour in Habitat Enrichment
4.3. Impact of Habitat Enrichment on First Contact Time
4.4. Driving Factors of Habitat Enrichment for Sparus latus Behaviour
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Knoester, E.G.; Rienstra, J.J.; Schürmann, Q.J.F.; Wolma, A.E.; Murk, A.J.; Osinga, R. Community-managed coral reef restoration in southern Kenya initiates reef recovery using various artificial reef designs. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1152106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraufvelin, P.; Bergström, L.; Sundqvist, F.; Ulmestrand, M.; Wennhage, H.; Wikström, A.; Bergström, U. Rapid re-establishment of top-down control at a no-take artificial reef. Ambio 2022, 52, 556–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swift, R.J.; Anteau, M.J.; Ellis, K.S.; Ring, M.M.; Sherfy, M.H.; Toy, D.L. Conspecific density and habitat quality affect breeding habitat selection: Support for the social attraction hypothesis. Ecosphere 2023, 14, e4524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, D.H. Scale-dependence of fish habitat associations in a North American river system. Freshw. Biol. 2022, 68, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.L.; Dong, Y.M.; Cao, L.; Verreth, J.; Olsen, Y.; Liu, W.J.; Fang, Q.Z.; Zhou, Y.G.; Li, L.; Li, J. Optimization of aquaculture sustainability through ecological intensification in China. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 14, 1249–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauvaud, P.; Day, R.; Roussel, S. No evident effect of domestication on the anti-predator behaviour of European abalone (Haliotis tuberculata): Implications for stock enhancement programs. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2021, 244, 105470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvaa, A.d.; Limab, M.R.; Melettic, P.C.; Jerep, F.C. Impact of environmental enrichment and social group size in the aggressiveness and foraging activity of Serrapinnus notomelas. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2020, 224, 104943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.H.; Choi, S.H.; Lee, Y.D.; Lee, C.H. Annual changes in ovarian development stages of farmed female red-spotted grouper, Epinephelus akaara, and inducing sexual maturity using photoperiod manipulation. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2022, 54, 1040–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bal, A.; Paital, B. Anthropization, Salinity and Oxidative Stress in Animals in the Coastal Zone. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2023, 25, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.B.; Pinheiro, H.T.; Francini-Filho, R.B.; Ferreira, C.E.L.; Joyeux, J.C. Habitat use of five sympatric predatory reef fishes at a remote island in the south-western Atlantic. J. Fish Biol. 2023, 103, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, O.; Inostroza, K.; Hyndes, G.A.; Friedlander, A.M.; Serrano, E.; Rae, C.; Ballesteros, E. Seagrass Posidonia escarpments support high diversity and biomass of rocky reef fishes. Ecosphere 2023, 14, e4599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, A.; Viard, F.; Lizé, A.; Corre, E.; Valentini, A.; Thiriet, P. Coastal rocky reef fish monitoring in the context of the Marine Strategy Framework Directive: Environmental DNA metabarcoding complements underwater visual census. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2023, 241, 106625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, F.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, Y.; Ma, H.; Sun, Y. Preference of juvenile tiger puffer for light spectrum and tank colours based on different body size and breeding background. Animal 2023, 17, 101021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Näslund, J. Reared to become wild-like: Addressing behavioral and cognitive deficits in cultured aquatic animals destined for stocking into natural environments—A critical review. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2021, 97, 489–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetzlaff, S.J.; Sperry, J.H.; DeGregorio, B.A. Effects of antipredator training, environmental enrichment, and soft release on wildlife translocations: A review and meta-analysis. Biol. Conserv. 2019, 236, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, Q.; Guan, X.; Gong, M.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, F.; Zhang, X. Physical and social enrichment influences the adaptability-related behaviors of black rockfish Sebastes schlegelii: An effect mediated by social behaviors, HPI axis and neurogenesis. Aquaculture 2023, 564, 739056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, L. Evolution of marine ranching policies in China: Review, performance and prospects. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongsheng, Y.; Dewen, D. Marine Ranching Version 3.0: History Status and Prospects. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2022, 6, 832–839. [Google Scholar]
- Higgs, D.M.; Fakan, E.P.; Allan, B.J.M.; Illing, B.; Hoey, A.S.; McCormick, M.I. Habitat complexity and predator odours impact on the stress response and antipredation behaviour in coral reef fish. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0286570. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, T.; Ding, G.; Yu, D.; Yang, W.; Sun, Q.; Wang, X.; Lin, H. Moderate relative size of covered and non-covered structures of artificial reef enhances the sheltering effect on reef fish. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1130626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyten, L.E.A.; Ramnarine, I.W.; Brown, G.E. Microhabitat conditions drive uncertainty of risk and shape neophobic responses in Trinidadian guppies, Poecilia reticulata. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 13, e10554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lin, W.; He, D.; Wu, Q.; Cai, C.; Chen, H.; Shang, Y.; Zhang, X. Aquaculture environment changes fish behavioral adaptability directly or indirectly through personality traits: A case study. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2023, 33, 1423–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Bai, Q.; Xu, X.; Guo, H.; Zhang, X. Effects of environmental enrichment on the welfare of juvenile black rockfish Sebastes schlegelii: Growth, behavior and physiology. Aquaculture 2020, 518, 734782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozanzadeh, M.T.; Bahabadi, M.N.; Morshedi, V.; Azodi, M.; Agh, N.; Gisbert, E. Weaning strategies affect larval performance in yellowfin seabream (Acanthopagrus latus). Aquaculture 2021, 539, 736673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Qin, C.; Zuo, T.; Yu, G.; Zhu, W.; Ma, H.; Xi, S. Is Metagenomic Analysis an Effective Way to Analyze Fish Feeding Habits? A Case of the Yellowfin Sea Bream Acanthopagrus latus (Houttuyn) in Daya Bay. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 634651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Zheng, M.; Li, S.; Xie, J.; Fang, W.; Gao, D.; Huang, J.; Lu, J. Response of gut microbiota and immune function to hypoosmotic stress in the yellowfin seabream (Acanthopagrus latus). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 745, 140976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brydges, N.M.; Braithwaite, V.A. Does environmental enrichment affect the behaviour of fish commonly used in laboratory work? Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2009, 118, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brydges, N.M.; Colegrave, N.; Heathcote, R.J.P.; Braithwaite, V.A. Habitat stability and predation pressure affect temperament behaviours in populations of three-spined sticklebacks. J. Anim. Ecol. 2008, 77, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 2.3-5; R Foundation: Vienna, Austria, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, J. Trophic interactions of reef-associated predatory fishes (Hexagrammos otakii and Sebastes schlegelii) in natural and artificial reefs along the coast of North Yellow Sea, China. Sci Total Env. 2021, 791, 148250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arechavala, L.P.; Diaz, G.C.; Saraiva, J.L.; Moranta, D.; Castanheira, M.F.; Nuñez-Velázquez, S.; Ledesma-Corvi, S.; Mora-Ruiz, M.R.; Grau, A. Effects of structural environmental enrichment on welfare of juvenile seabream (Sparus aurata). Aquac. Rep. 2019, 15, 100224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arechavala-Lopez, P.; Toledo-Guedes, K.; Izquierdo-Gomez, D.; Šegvić-Bubić, T.; Sanchez-Jerez, P. Implications of Sea Bream and Sea Bass Escapes for Sustainable Aquaculture Management: A Review of Interactions, Risks and Consequences. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2017, 26, 214–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moberg, O.; Braithwaite, V.; Jensen, K.; Salvanes, A. Effects of habitat enrichment and food availability on the foraging behaviour of juvenile Atlantic Cod (Gadus morhua L). Environ. Biol. Fishes 2011, 91, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-Y.; Lan, K.-W.; Chang, H.-H.; Naimullah, M. Residency and swimming behavior of Acanthopagrus schlegelii, Trachinotus blochii, and Acanthopagrus latus in relation to artificial reef models in a captivity experiment. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2022, 257, 105778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Cai, W.; Chen, H.; Chen, P.; Lv, G.; Jia, X. Attraction effect of various artificial reef models on Sparus macrocephalus. J. Fish. China 2011, 35, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, H.; Ji, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, T.; Xian, W.; Zhang, H. Application of environmental DNA technology in marine ranching-case study of Bailong Pearl Bay Demonstration area in Beibu Gulf. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xie, X.; Chen, P.; Yuan, H.; Feng, X.; Tong, F.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zou, J.; Chen, Z. Study on attraction effect of artificial reefs vertical plate with different square apertures on Sparus macrocephalus. South China Fish. Sci. 2022, 18, 52–58. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, P.; Tan, J.; Gao, Z.; Dai, H.; Shi, X.; Huang, T. The analysis of fish movement behavior in vertical slot fishway based on video tracking. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2018, 42, 250–254. [Google Scholar]
- Watz, J. Structural complexity in the hatchery rearing environment affects activity, resting metabolic rate and post-release behaviour in brown trout Salmo trutta. J. Fish Biol. 2019, 95, 638–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, L.; Alanärä, A. The effect of shelter on welfare of juvenile Atlantic salmon Salmo salar reared under a feed restriction regimen. J. Fish Biol. 2014, 85, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Han, J.; Jin, Y.; Chen, Y. Effects of Population Size on the Collective Behavior of Juvenile Bighead Carp. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2022, 38, 134–149. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Tang, Z.; Huang, Q.; Kuang, L.; Fu, S. Effect of body size variation of group members on shoal behavior of two cyprinids preferring different habitats. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2017, 43, 552–559. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Li, J.; Gong, P.; Guan, C. Effects of the artificial reef and flow field environment on the habitat selection behavior of Sebastes schlegelii juveniles. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2021, 245, 105492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatiana, C.; Fabrice, T.; Pascal, F.; Alain, P. Temperature modifies activity, inter-individual relationships and group structure in fish. Curr. Zool. 2017, 63, 175–183. [Google Scholar]
- Hurst, T.P. Thermal effects on behavior of juvenile walleye pollock (Theragra chalcogramma): Implications for energetics and food web models. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2007, 64, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ma, H.; Yu, C.; Liu, S.; Lei, J.; Zeng, L. Effects of water temperature rising and ecological context on collective behaviour of gibel carp. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Orpwood, J.E.; Magurran, A.E.; Armstrong, J.D.; Griffiths, S.W. Minnows and the selfish herd: Effects of predation risk on shoaling behaviour are dependent on habitat complexity. Anim. Behav. 2008, 76, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, M.; Winder, L.; Watt, P. Enrichment Increases Aggression in Zebrafish. Fishes 2019, 4, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanheira, M.F.; Conceição, L.E.C.; Millot, S.; Rey, S.; Bégout, M.L.; Damsgård, B.; Kristiansen, T.; Höglund, E.; Øverli, Ø.; Martins, C.I.M. Coping styles in farmed fish: Consequences for aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2015, 9, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, A.; Stauffacher, M.; Langhans, W.; Würbel, H. Enrichment-dependent differences in novelty exploration in rats can be explained by habituation. Behav. Brain Res. 2001, 121, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, C.; Merali, Z.; Harrison, C. Therapeutic and protective effect of environmental enrichment against psychogenic and neurogenic stress. Behav. Brain Res. 2006, 175, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pounder, K.C.; Mitchell, J.L.; Thomson, J.S.; Pottinger, T.G.; Buckley, J.; Sneddon, L.U. Does environmental enrichment promote recovery from stress in rainbow trout? Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2016, 176, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelleyy, J.L.; Magurran, A.E.M. Learned predator recognition and antipredator responses in fishes. Fish Fish. 2003, 4, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, T.M.; Kumar, R.S.; Nair, M.; Hauber, M.E.; Dor, R. Innovation and decreased neophobia drive invasion success in a widespread avian invader. Anim. Behav. 2020, 163, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.E.; Demers, E.E.M.; Goldman, J.A.; Singh, A.; Chivers, D.P.; Ferrari, M.C.O. Unpredictable risk enhances induced neophobia in northern redbellied dace. Anim. Behav. 2020, 168, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiser, S.; Pohlmann, D.M.; Koops, U.; Gröger, J.P.; Focken, U. Using gravel for environmental enrichment in salmonid hatcheries: The effect of gravel size during egg incubation, endogenous and first feeding in rainbow trout. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2019, 35, 456–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batzina, A.; Karakatsouli, N. The presence of substrate as a means of environmental enrichment in intensively reared gilthead seabream Sparus aurata: Growth and behavioral effects. Aquaculture 2012, 370–371, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drangsholt, T.M.K.; Damsgård, B.; Olesen, I. Quantitative genetics of behavioral responsiveness in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.). Aquaculture 2014, 420–421, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, B.J.; Demers, E.E.M.; Chivers, D.P.; Ferrari, M.C.O.; Brown, G.E. Risk-induced neophobia is constrained by ontogeny in juvenile convict cichlids. Anim. Behav. 2016, 114, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlinghieri, L.B.; Panizzon, P.; Penry-Williams, I.L.; Brown, C. Laterality and fish welfare—A review. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2021, 236, 105239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Näslund, J.; Johnsson, J.I. Environmental enrichment for fish in captive environments: Effects of physical structures and substrates. Fish Fish. 2016, 17, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, L.; Berg, S.; Jepsen, N.; Skov, C. Does roach behaviour differ between shallow lakes of different environmental state? J. Fish Biol. 2010, 65, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxton, C. Shoaling and activity levels in Corydoras. J. Fish Biol. 2010, 51, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.; Fang, C.; Hong, F.; Kuang, W.; Lin, C.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Bo, J. Developing and applying a classification system for ranking the biological effects of endocrine disrupting chemicals on male rockfish Sebastiscus marmoratus in the Maowei Sea, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 163, 111931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, N.A.R.; Spence, R.; Jones, F.A.M.; Spence-Jones, H.C. Shade as enrichment: Testing preferences for shelter in two model fish species. J. Fish Biol. 2019, 95, 1161–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Y.; Chen, Z.; Qin, C.; Yu, G.; Zhang, J. Habitat Enrichment Causes Changes in Fish Behavioural Characteristics: A Case Study of Sparus latus. Biology 2024, 13, 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13060364
Guo Y, Chen Z, Qin C, Yu G, Zhang J. Habitat Enrichment Causes Changes in Fish Behavioural Characteristics: A Case Study of Sparus latus. Biology. 2024; 13(6):364. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13060364
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Yu, Zhanlong Chen, Chuanxin Qin, Gang Yu, and Jia Zhang. 2024. "Habitat Enrichment Causes Changes in Fish Behavioural Characteristics: A Case Study of Sparus latus" Biology 13, no. 6: 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13060364
APA StyleGuo, Y., Chen, Z., Qin, C., Yu, G., & Zhang, J. (2024). Habitat Enrichment Causes Changes in Fish Behavioural Characteristics: A Case Study of Sparus latus. Biology, 13(6), 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13060364






