Maternal Low-Protein Diet During Nursing Leads to Glucose–Insulin Dyshomeostasis and Pancreatic-Islet Dysfunction by Disrupting Glucocorticoid Responsiveness in Male Rats
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Animal Groups and Dietary Manipulation
2.3. Effects of Starvation Challenge on Hormone Parameters and Intravenous Glucose Tolerance Test (ivGTT) Results
2.4. Intracerebroventricular (icv) Cannula Implantation Surgery and Assessment of the Central Effect of Dexamethasone
2.5. Measurement of the Fat Pad Stores
2.6. Effects of Chronic Dexamethasone Challenge on Biochemical and Metabolic Parameters
2.7. Intravenous Glucose Tolerance Test (ivGTT)
2.8. Insulin Sensitivity Index
2.9. Pancreatic Islet Isolation
2.10. Stimulation of Insulin Secretion
2.11. Hormone Plasma Levels
2.12. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Biometric Profile of Offspring from Maternal Rats Fed a Low-Protein Diet
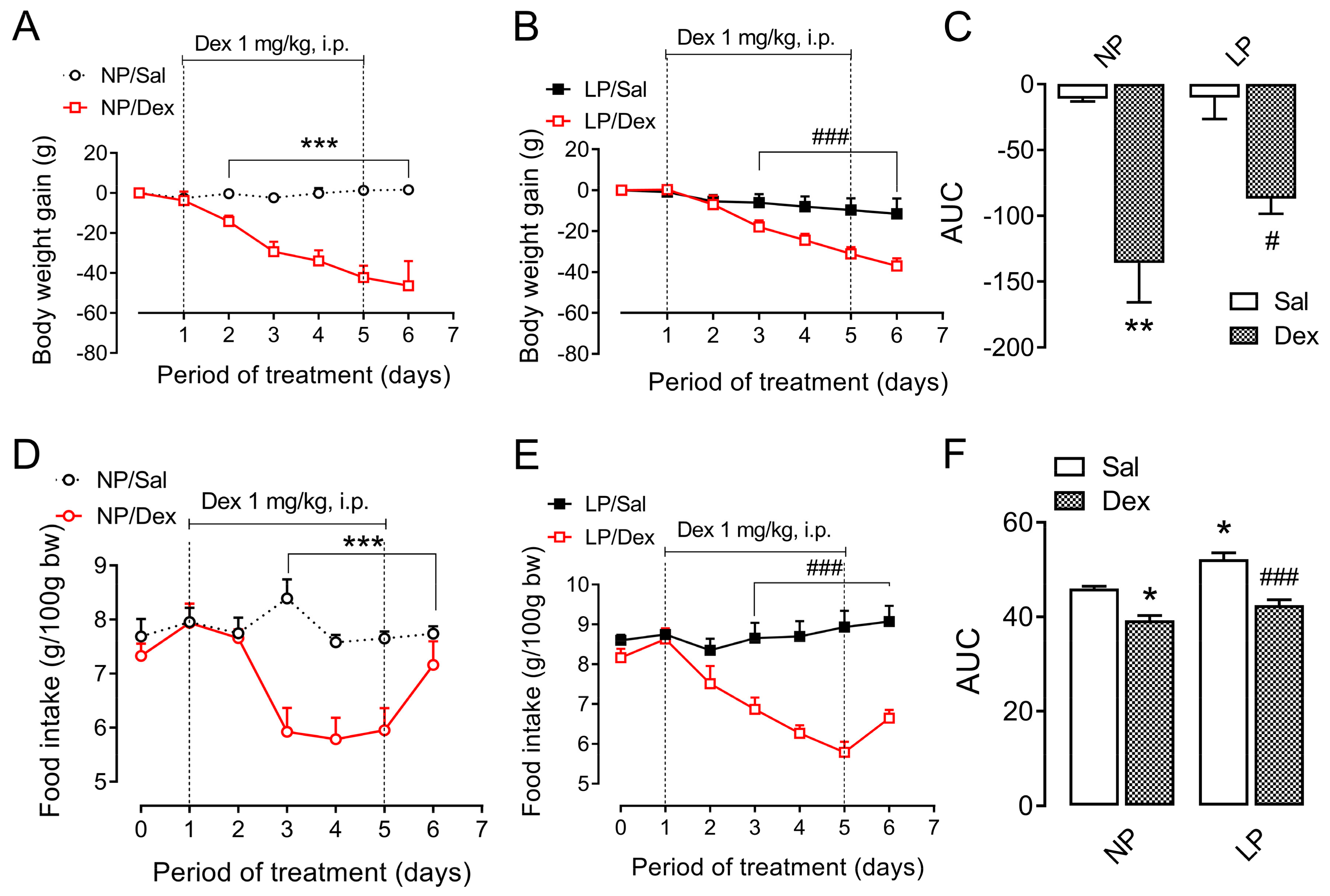
3.2. Body Weight and Food Intake During Dexamethasone Treatment
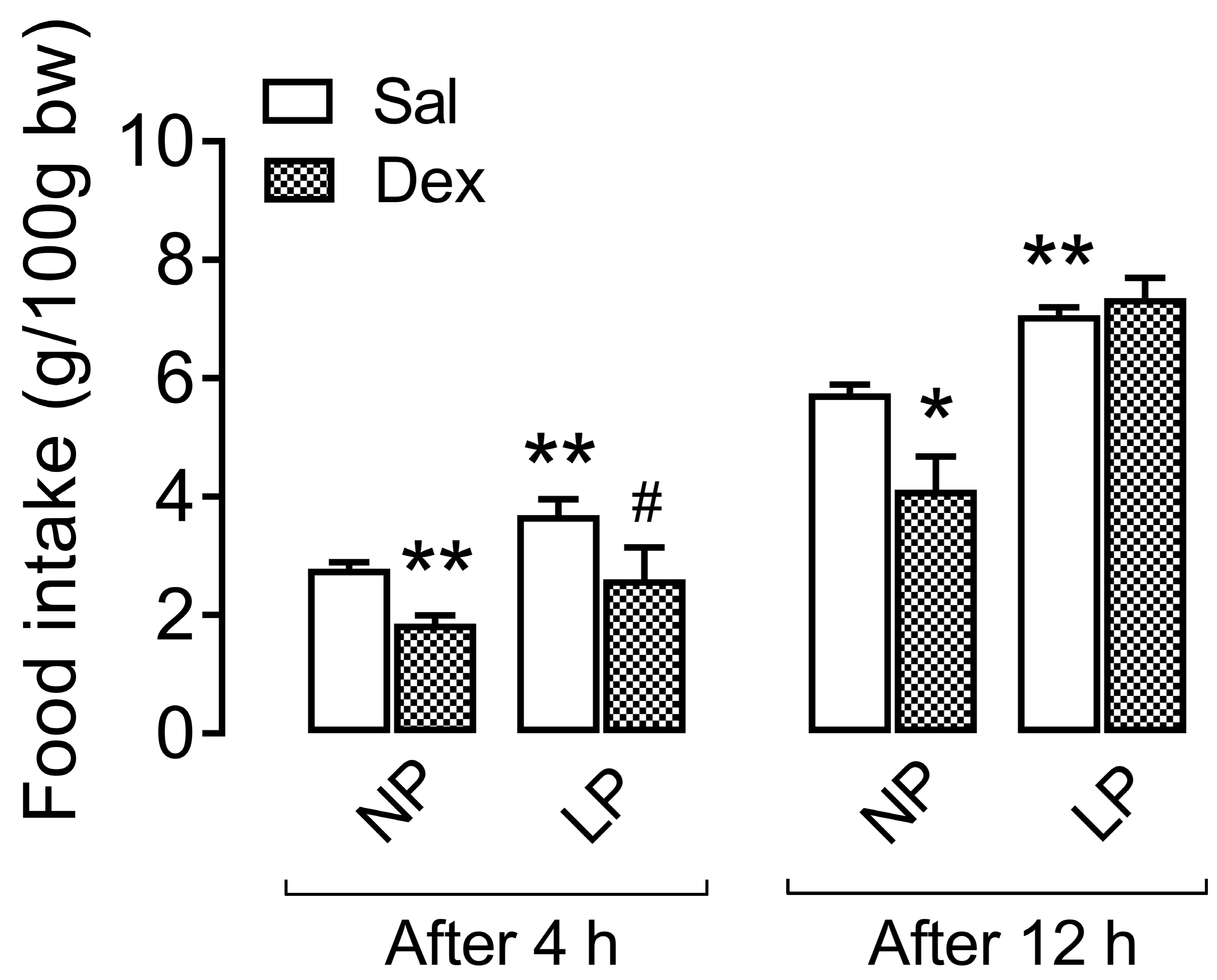
3.3. Central Effect of Dexamethasone on Food Intake During the Dark Cycle
3.4. Biochemical Profile After Starvation Challenge
3.5. Biochemical Profile After Chronic Dexamethasone Challenge
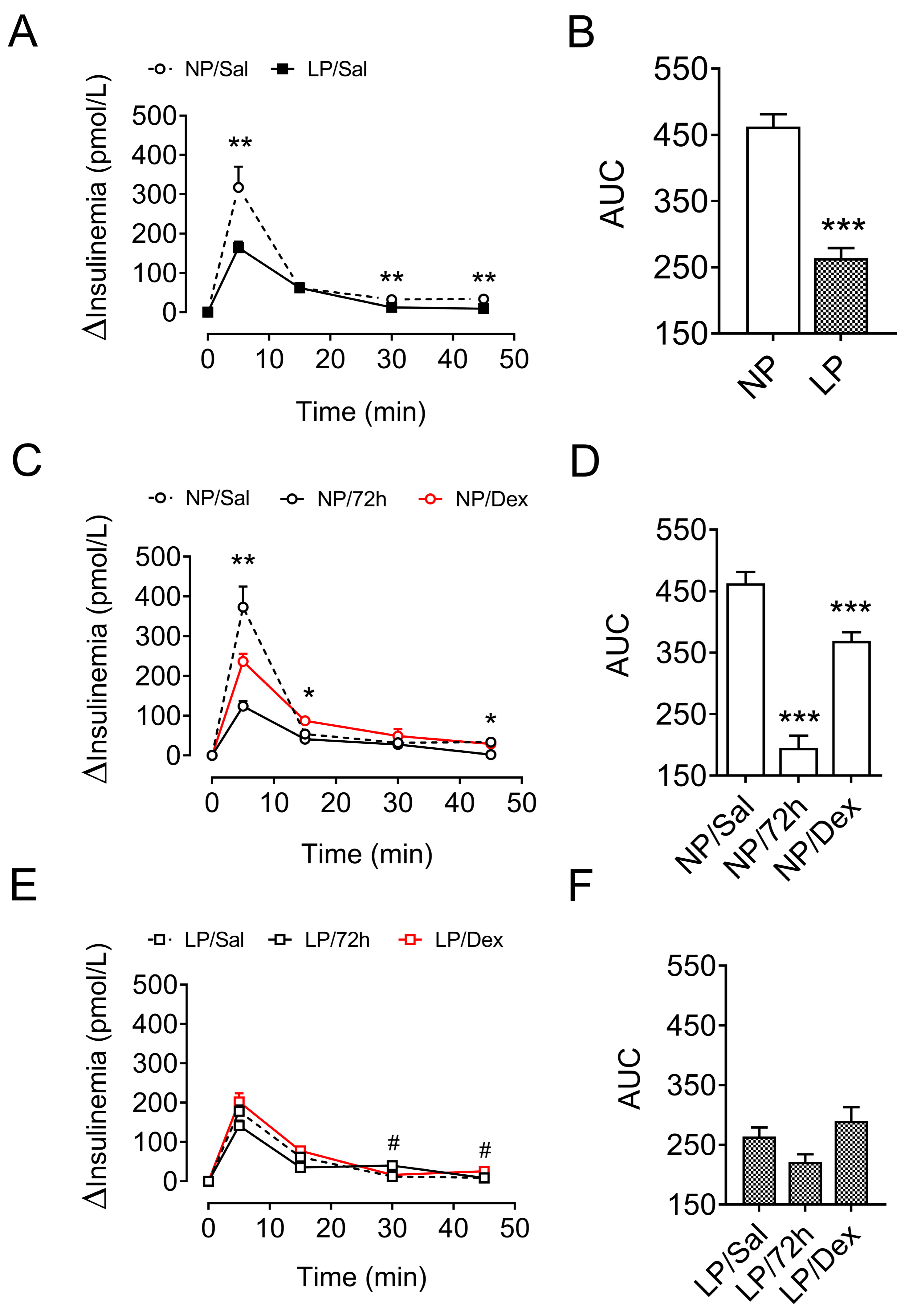
3.6. Insulin Homeostasis After Metabolic-Stress Challenge
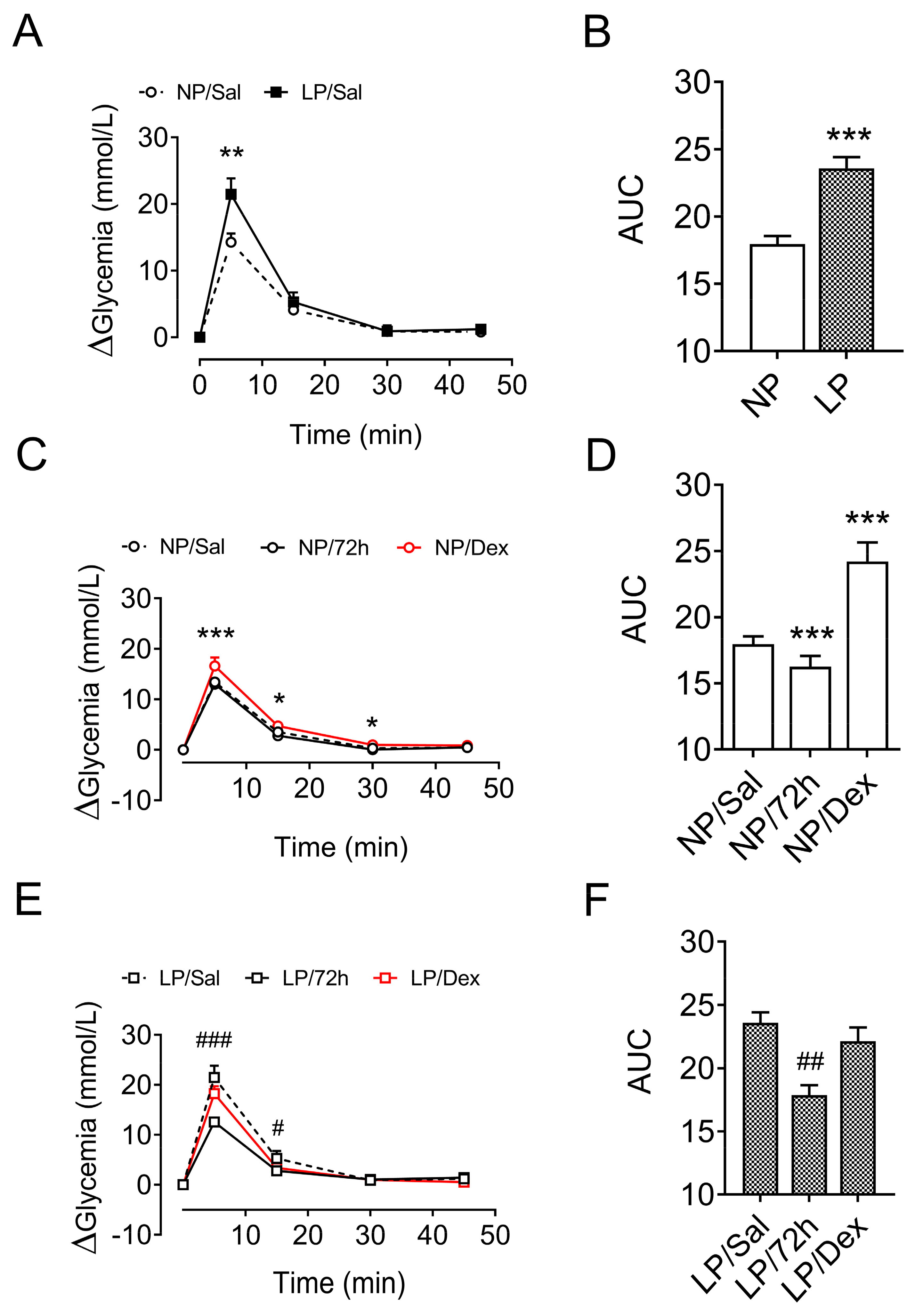
3.7. Glucose Homeostasis After Metabolic-Stress Challenge
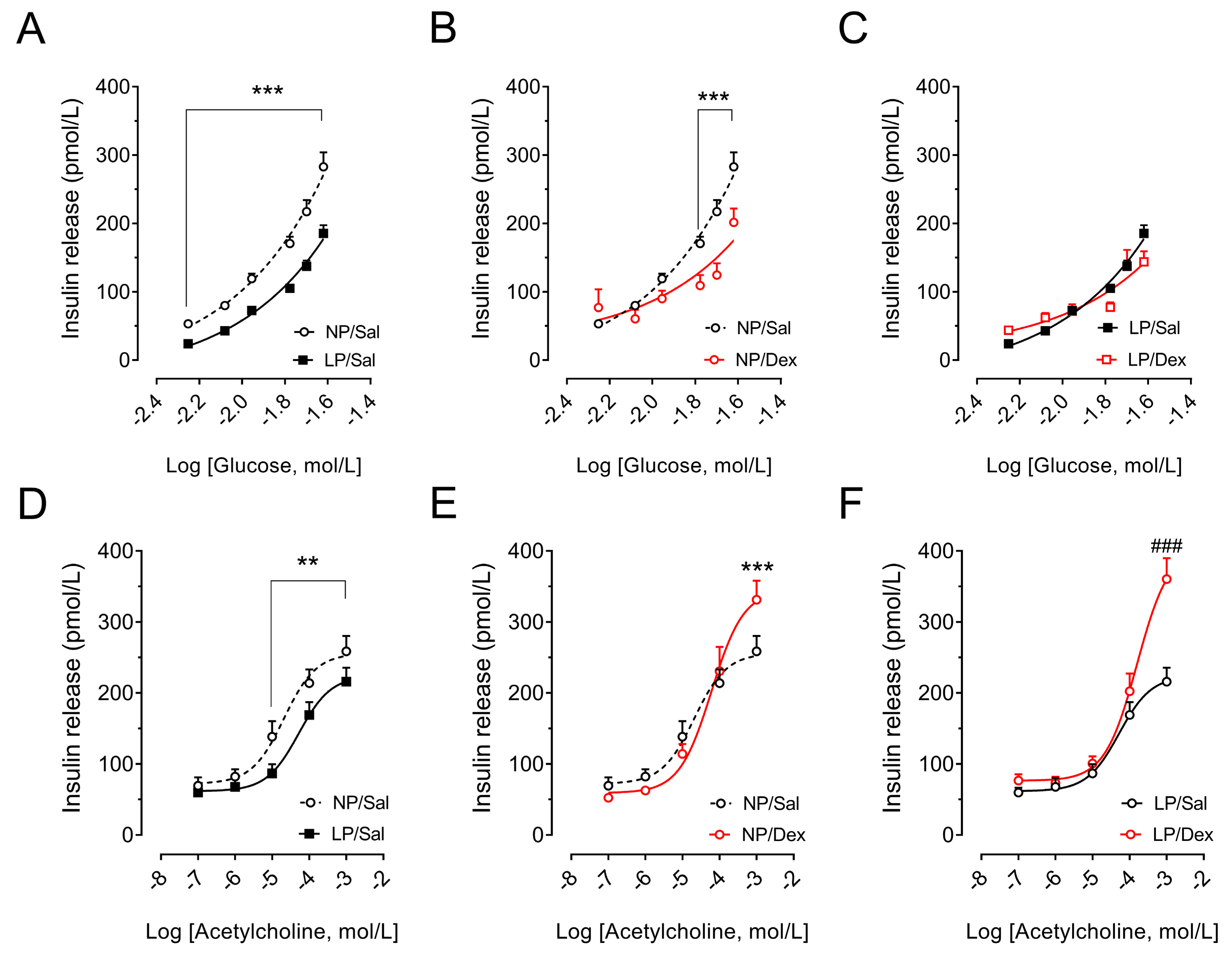
3.8. Effect of Chronic Dexamethasone Treatment on the Insulin Secretion of Pancreatic Islets
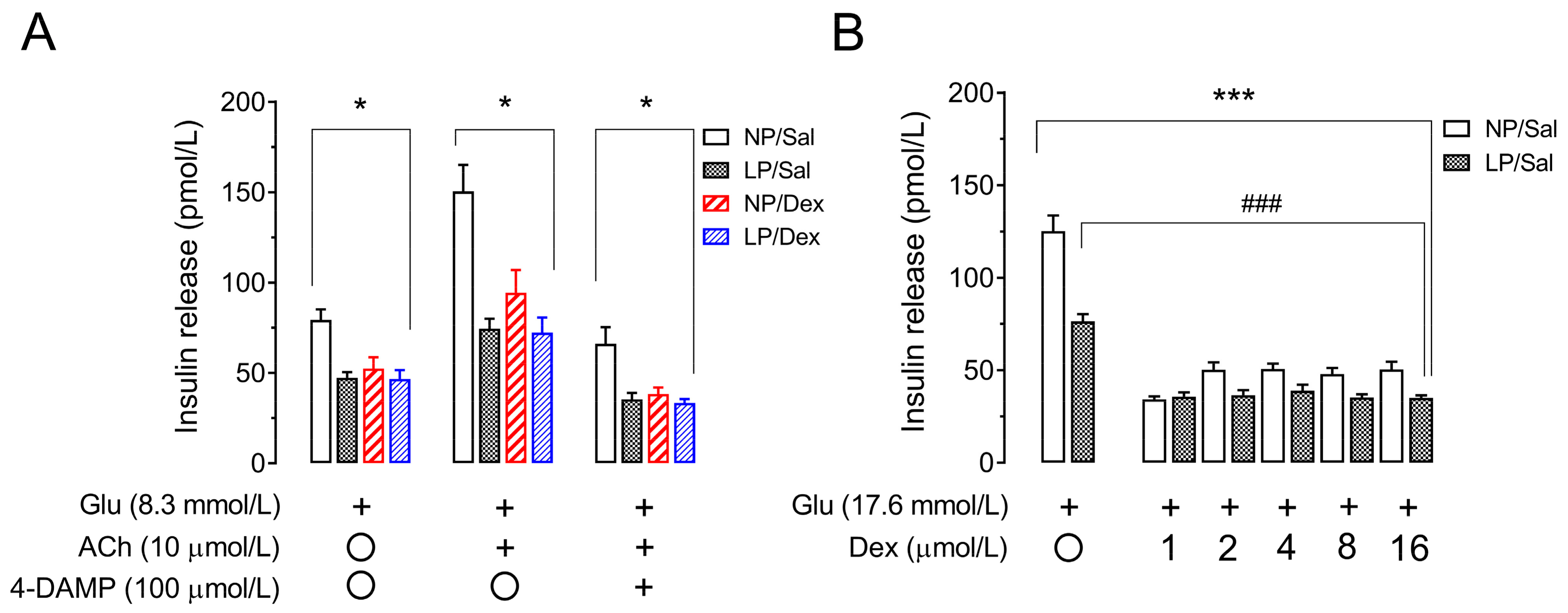
3.9. Assessment of Muscarinic Receptor Action and Direct Effects of Dexamethasone on Insulin Secretion in Pancreatic Islets from Rats That Were Not Chronically Treated with Dexamethasone
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACh | acetylcholine |
| ACTH | adrenocorticotrophic hormone |
| AUC | area under the curve |
| BSA | bovine serum albumin |
| 4-DAMP | 4-diphenylacetoxy-N-methylpiperidine methiodide |
| HBSS | Hanks’ buffered saline solution |
| HEPES | N-(2-hydroxyethyl-piperazine)-N’-(2-ethanesulfonic acid) |
| HOMA-IR | homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance |
| HPA | hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal |
| ICV | intracerebroventricular |
| ISI | insulin sensitivity index |
| ivGTT | intravenous glucose tolerance test |
| LP | low-protein |
| M3mAChR | subtype M3 muscarinic ACh receptor |
| NP | normal-protein |
| PGC-1α | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator-1α |
References
- Facchi, J.C.; Lima, T.A.L.; Oliveira, L.R.; Costermani, H.O.; Miranda, G.D.S.; de Oliveira, J.C. Perinatal programming of metabolic diseases: The role of glucocorticoids. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2020, 104, 154047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, D.J.; Osmond, C. Diet and coronary heart disease in England and Wales during and after the second world war. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 1986, 40, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alejandro, E.U.; Gregg, B.; Wallen, T.; Kumusoglu, D.; Meister, D.; Chen, A.; Merrins, M.J.; Satin, L.S.; Liu, M.; Arvan, P.; et al. Maternal diet-induced microRNAs and mTOR underlie beta cell dysfunction in offspring. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 4395–4410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holness, M.J.; Langdown, M.L.; Sugden, M.C. Early-life programming of susceptibility to dysregulation of glucose metabolism and the development of Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Biochem. J. 2000, 349, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berends, L.M.; Dearden, L.; Tung, Y.C.L.; Voshol, P.; Fernandez-Twinn, D.S.; Ozanne, S.E. Programming of central and peripheral insulin resistance by low birthweight and postnatal catch-up growth in male mice. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 2225–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, D.J.; Hales, C.N.; Fall, C.H.; Osmond, C.; Phipps, K.; Clark, P.M. Type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus, hypertension and hyperlipidaemia (syndrome X): Relation to reduced fetal growth. Diabetologia 1993, 36, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamson-Reig, A.; Thyssen, S.M.; Hill, D.J.; Arany, E. Exposure of the pregnant rat to low protein diet causes impaired glucose homeostasis in the young adult offspring by different mechanisms in males and females. Exp. Biol. Med. 2009, 234, 1425–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, A.E.; Janson, J.; Soeller, W.C.; Butler, P.C. Increased beta-cell apoptosis prevents adaptive increase in beta-cell mass in mouse model of type 2 diabetes: Evidence for role of islet amyloid formation rather than direct action of amyloid. Diabetes 2003, 52, 2304–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, A.E.; Janson, J.; Bonner-Weir, S.; Ritzel, R.; Rizza, R.A.; Butler, P.C. Beta-cell deficit and increased beta-cell apoptosis in humans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2003, 52, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, A.S.; Carpinelli, A.R.; Barbosa, F.B.; Gravena, C.; Mathias, P.C. Undernutrition during early lactation as an alternative model to study the onset of diabetes mellitus type II. Res. Commun. Mol. Pathol. Pharmacol. 1996, 92, 73–84. [Google Scholar]
- Ozanne, S.E.; Dorling, M.W.; Wang, C.L.; Nave, B.T. Impaired PI 3-kinase activation in adipocytes from early growth-restricted male rats. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 280, E534–E539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petry, C.J.; Ozanne, S.E.; Wang, C.L.; Hales, C.N. Effects of early protein restriction and adult obesity on rat pancreatic hormone content and glucose tolerance. Horm. Metab. Res. 2000, 32, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura, A.S.; Caldeira Filho, J.S.; de Freitas Mathias, P.C.; de Sa, C.C. Insulin secretion impairment and insulin sensitivity improvement in adult rats undernourished during early lactation. Res. Commun. Mol. Pathol. Pharmacol. 1997, 96, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, J.C.; Scomparin, D.X.; Andreazzi, A.E.; Branco, R.C.; Martins, A.G.; Gravena, C.; Grassiolli, S.; Rinaldi, W.; Barbosa, F.B.; Mathias, P.C. Metabolic imprinting by maternal protein malnourishment impairs vagal activity in adult rats. J. Neuroendocr. 2011, 23, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, F.; Kawai, M.; Kanazawa, H.; Okanoya, K.; Myowa-Yamakoshi, M. The development of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis during infancy may be affected by antenatal glucocorticoid therapy. J. Neonatal-Perinat. Med. 2019, 13, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafacho, A.; Ortsater, H.; Nadal, A.; Quesada, I. Glucocorticoid treatment and endocrine pancreas function: Implications for glucose homeostasis, insulin resistance and diabetes. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 223, R49–R62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarrete, M.; Nunez, H.; Ruiz, S.; Soto-Moyano, R.; Valladares, L.; White, A.; Perez, H. Prenatal undernutrition decreases the sensitivity of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis in rat, as revealed by subcutaneous and intra-paraventricular dexamethasone challenges. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 419, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somm, E.; Vauthay, D.M.; Guerardel, A.; Toulotte, A.; Cettour-Rose, P.; Klee, P.; Meda, P.; Aubert, M.L.; Huppi, P.S.; Schwitzgebel, V.M. Early metabolic defects in dexamethasone-exposed and undernourished intrauterine growth restricted rats. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riveline, J.P.; Baz, B.; Nguewa, J.L.; Vidal-Trecan, T.; Ibrahim, F.; Boudou, P.; Vicaut, E.; Brac de la Perriere, A.; Fetita, S.; Breant, B.; et al. Exposure to glucocorticoids in the first part of fetal life is associated with insulin secretory defect in adult human. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 105, e191–e199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entringer, S.; Buss, C.; Rasmussen, J.M.; Lindsay, K.; Gillen, D.L.; Cooper, D.M.; Wadhwa, P.D. Maternal Cortisol During Pregnancy and Infant Adiposity: A Prospective Investigation. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 1366–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafacho, A.; Roma, L.P.; Taboga, S.R.; Boschero, A.C.; Bosqueiro, J.R. Dexamethasone-induced insulin resistance is associated with increased connexin 36 mRNA and protein expression in pancreatic rat islets. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2007, 85, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, H.; Ahren, B. Insulin resistant subjects lack islet adaptation to short-term dexamethasone-induced reduction in insulin sensitivity. Diabetologia 1999, 42, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabregat, M.E.; Fernandez-Alvarez, J.; Franco, C.; Malaisse, W.J.; Gomis, R. Dexamethasone-induced changes in FAD-glycerophosphate dehydrogenase mRNA, content and activity, and insulin release in human pancreatic islets. Diabetes Nutr. Metab. 1999, 12, 388–393. [Google Scholar]
- Gravena, C.; Andreazzi, A.E.; Mecabo, F.T.; Grassiolli, S.; Scantamburlo, V.M.; Mathias, P.C. Protein restriction during lactation alters the autonomic nervous system control on glucose-induced insulin secretion in adult rats. Nutr. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, J.C.; Miranda, R.A.; Barella, L.F.; Torrezan, R.; Agostinho, A.R.; Ribeiro, T.A.; Franco, C.C.; Malta, A.; Tofolo, L.P.; Gravena, C.; et al. Impaired beta-cell function in the adult offspring of rats fed a protein-restricted diet during lactation is associated with changes in muscarinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 111, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundy, D. Principles and standards for reporting animal experiments in The Journal of Physiology and Experimental Physiology. J. Physiol. 2015, 593, 2547–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes Da Costa, C.; Sampaio De Freitas, M.; Sanchez Moura, A. Insulin secretion and GLUT-2 expression in undernourished neonate rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2004, 15, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C.; Pennisi, M.; Topple, A. Bregma, lambda and the interaural midpoint in stereotaxic surgery with rats of different sex, strain and weight. J. Neurosci. Methods 1985, 13, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoppa, G.R.; Cesquini, M.; Roman, E.A.; Prada, P.O.; Torsoni, A.S.; Romanatto, T.; Saad, M.J.; Velloso, L.A.; Torsoni, M.A. Intracerebroventricular injection of citrate inhibits hypothalamic AMPK and modulates feeding behavior and peripheral insulin signaling. J. Endocrinol. 2008, 198, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinley, M.J.; Allen, A.M.; May, C.N.; McAllen, R.M.; Oldfield, B.J.; Sly, D.; Mendelsohn, F.A. Neural pathways from the lamina terminalis influencing cardiovascular and body fluid homeostasis. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2001, 28, 990–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida-Takahashi, R.; Uotani, S.; Abe, T.; Degawa-Yamauchi, M.; Fukushima, T.; Fujita, N.; Sakamaki, H.; Yamasaki, H.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Eguchi, K. Rapid inhibition of leptin signaling by glucocorticoids in vitro and in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 19658–19664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, J.C.; Gomes, R.M.; Miranda, R.A.; Barella, L.F.; Malta, A.; Martins, I.P.; Franco, C.C.; Pavanello, A.; Torrezan, R.; Natali, M.R.; et al. Protein Restriction During the Last Third of Pregnancy Malprograms the Neuroendocrine Axes to Induce Metabolic Syndrome in Adult Male Rat Offspring. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 1799–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafacho, A.; Marroqui, L.; Taboga, S.R.; Abrantes, J.L.; Silveira, L.R.; Boschero, A.C.; Carneiro, E.M.; Bosqueiro, J.R.; Nadal, A.; Quesada, I. Glucocorticoids in vivo induce both insulin hypersecretion and enhanced glucose sensitivity of stimulus-secretion coupling in isolated rat islets. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinder, P. Determination of blood glucose using an oxidase-peroxidase system with a non-carcinogenic chromogen. J. Clin. Pathol. 1969, 22, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.M.; Atwater, I.; Rojas, E. A method for the simultaneous measurement of insulin release and B cell membrane potential in single mouse islets of Langerhans. Diabetologia 1981, 21, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, M.; DeFronzo, R.A. Insulin sensitivity indices obtained from oral glucose tolerance testing: Comparison with the euglycemic insulin clamp. Diabetes Care 1999, 22, 1462–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, T.M.; Levy, J.C.; Matthews, D.R. Use and abuse of HOMA modeling. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, J.C.; Lisboa, P.C.; de Moura, E.G.; Barella, L.F.; Miranda, R.A.; Malta, A.; Franco, C.C.; Ribeiro, T.A.; Torrezan, R.; Gravena, C.; et al. Poor pubertal protein nutrition disturbs glucose-induced insulin secretion process in pancreatic islets and programs rats in adulthood to increase fat accumulation. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 216, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, F.B.; Gravena, C.; Mathias, P.; Moura, A.S. Blockade of the 32P phosphate flush of pancreatic beta cells from adult rats who received a low-protein diet during early lactation. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 1993, 26, 1355–1358. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa, F.B.; Capito, K.; Kofod, H.; Thams, P. Pancreatic islet insulin secretion and metabolism in adult rats malnourished during neonatal life. Br. J. Nutr. 2002, 87, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packard, A.E.; Egan, A.E.; Ulrich-Lai, Y.M. HPA Axis Interactions with Behavioral Systems. Compr. Physiol. 2016, 6, 1897–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathias, P.C.F.; Miranda, G.D.S.; Barella, L.F.; Miranda, R.A.; Pavanello, A.; Martins, I.P.; Facchi, J.C.; Costermani, H.O.; Lima, T.A.L.; de Oliveira, J.C. Cholinergic-pathway-weakness-associated pancreatic islet dysfunction: A low-protein-diet imprint effect on weaned rat offspring. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2020, 11, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valtat, B.; Riveline, J.P.; Zhang, P.; Singh-Estivalet, A.; Armanet, M.; Venteclef, N.; Besseiche, A.; Kelly, D.P.; Tronche, F.; Ferre, P.; et al. Fetal PGC-1alpha overexpression programs adult pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1206–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumortier, O.; Blondeau, B.; Duvillie, B.; Reusens, B.; Breant, B.; Remacle, C. Different mechanisms operating during different critical time-windows reduce rat fetal beta cell mass due to a maternal low-protein or low-energy diet. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 2495–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumortier, O.; Theys, N.; Ahn, M.T.; Remacle, C.; Reusens, B. Impairment of rat fetal beta-cell development by maternal exposure to dexamethasone during different time-windows. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davani, B.; Portwood, N.; Bryzgalova, G.; Reimer, M.K.; Heiden, T.; Ostenson, C.G.; Okret, S.; Ahren, B.; Efendic, S.; Khan, A. Aged transgenic mice with increased glucocorticoid sensitivity in pancreatic beta-cells develop diabetes. Diabetes 2004, 53 (Suppl. 1), S51–S59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davani, B.; Khan, A.; Hult, M.; Martensson, E.; Okret, S.; Efendic, S.; Jornvall, H.; Oppermann, U.C. Type 1 11beta -hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase mediates glucocorticoid activation and insulin release in pancreatic islets. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 34841–34844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swali, A.; Walker, E.A.; Lavery, G.G.; Tomlinson, J.W.; Stewart, P.M. 11beta-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 regulates insulin and glucagon secretion in pancreatic islets. Diabetologia 2008, 51, 2003–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fine, N.H.F.; Doig, C.L.; Elhassan, Y.S.; Vierra, N.C.; Marchetti, P.; Bugliani, M.; Nano, R.; Piemonti, L.; Rutter, G.A.; Jacobson, D.A.; et al. Glucocorticoids Reprogram beta-Cell Signaling to Preserve Insulin Secretion. Diabetes 2018, 67, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizumi, M.; Yada, T. Sub-chronic stimulation of glucocorticoid receptor impairs and mineralocorticoid receptor protects cytosolic Ca2+ responses to glucose in pancreatic beta-cells. J. Endocrinol. 2008, 197, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Biochemical Parameters | NP | LP | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 h | 72 h | 12 h | 72 h | |
| Glycemia (mmol/L) | 5.20 ± 0.14 | 5.17 ± 0.26 | 5.08 ± 0.11 | 4.62 ± 0.39 |
| Insulinemia (pmol/L) | 29.31 ± 2.63 | 8.06 ± 1.78 *** | 17.58 ± 2.50 ** | 7.58 ± 1.62 |
| HOMA-IR | 0.71 ± 0.07 | 0.19 ± 0.05 *** | 0.43 ± 0.07 * | 0.16 ± 0.03 # |
| ISI | 9.55 ± 0.52 | 16.27 ± 1.47 *** | 17.30 ± 1.91 *** | 27.91 ± 2.72 ## |
| Corticosteronemia (nmol/L) | 1364.01 ± 67.27 | 1810.22 ± 80.31 * | 1892.02 ± 123.10 ** | 1878.70 ± 118.50 |
| Biochemical Parameters | NP | LP | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sal | Dex | Sal | Dex | |
| Glycemia (mmol/L) | 5.14 ± 0.11 | 6.20 ± 0.11 *** | 5.28 ± 0.16 | 6.46 ± 0.10 ### |
| Insulinemia (pmol/L) | 29.31 ± 2.63 | 48.42 ± 3.025 *** | 14.52 ± 1.62 *** | 45.83 ± 5.72 ### |
| HOMA-IR | 0.71 ± 0.07 | 1.38 ± 0.12 *** | 0.35 ± 0.04 *** | 1.36 ± 0.08 ### |
| ISI | 9.55 ± 0.52 | 5.70 ± 0.22 *** | 17.30 ± 1.91 *** | 9.89 ± 0.38 ### |
| ACTH (pmol/L) | 57.83 ± 5.86 | 26.50 ± 6.75 ** | 21.17 ± 2.26 ** | 22.97 ± 2.94 |
| Corticosteronemia (nmol/L) | 1364.01 ± 67.27 | 870.5 ± 45.69 * | 1892.02 ± 123.1 ** | 1027.82 ± 23.23 ### |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Freitas Mathias, P.C.; Dantas Rodrigues, A.M.; Lisboa, P.C.; Miranda, R.A.; Malta, A.; Ribeiro, T.A.; Barella, L.F.; Dias, G.; Lima, T.A.L.; Gomes, R.M.; et al. Maternal Low-Protein Diet During Nursing Leads to Glucose–Insulin Dyshomeostasis and Pancreatic-Islet Dysfunction by Disrupting Glucocorticoid Responsiveness in Male Rats. Biology 2024, 13, 1036. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13121036
de Freitas Mathias PC, Dantas Rodrigues AM, Lisboa PC, Miranda RA, Malta A, Ribeiro TA, Barella LF, Dias G, Lima TAL, Gomes RM, et al. Maternal Low-Protein Diet During Nursing Leads to Glucose–Insulin Dyshomeostasis and Pancreatic-Islet Dysfunction by Disrupting Glucocorticoid Responsiveness in Male Rats. Biology. 2024; 13(12):1036. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13121036
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Freitas Mathias, Paulo Cezar, Aline Milena Dantas Rodrigues, Patrícia Cristina Lisboa, Rosiane Aparecida Miranda, Ananda Malta, Tatiane Aparecida Ribeiro, Luiz Felipe Barella, Ginislene Dias, Thalyne Aparecida Leite Lima, Rodrigo Mello Gomes, and et al. 2024. "Maternal Low-Protein Diet During Nursing Leads to Glucose–Insulin Dyshomeostasis and Pancreatic-Islet Dysfunction by Disrupting Glucocorticoid Responsiveness in Male Rats" Biology 13, no. 12: 1036. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13121036
APA Stylede Freitas Mathias, P. C., Dantas Rodrigues, A. M., Lisboa, P. C., Miranda, R. A., Malta, A., Ribeiro, T. A., Barella, L. F., Dias, G., Lima, T. A. L., Gomes, R. M., de Moura, E. G., & de Oliveira, J. C. (2024). Maternal Low-Protein Diet During Nursing Leads to Glucose–Insulin Dyshomeostasis and Pancreatic-Islet Dysfunction by Disrupting Glucocorticoid Responsiveness in Male Rats. Biology, 13(12), 1036. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13121036










