Simple Summary
The Bighead carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis) is an economically important freshwater species in China. To promote scientific management strategies and guide the future monitoring of H. nobilis genetic resources in the Yangtze River, we genotyped multiple bighead carp populations sampled alongside the Yangtze River in China using RAD sequencing, explored their genetic diversity and population structure, and investigated their population demographic history. The findings in the study will make a meaningful contribution to the conservation and utilization of bighead carp germplasm resources in China.
Abstract
The Bighead carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis), a primary freshwater aquaculture species in China, faces challenges due to over-exploitation and environmental changes. We leveraged RAD-seq to perform a comprehensive population genetic analysis on 14 H. nobilis populations sampled from the Yangtze River (13 populations) and the Marseilles Reach of the Illinois River (one population). Analysis of genetic diversity showed that different parameters demonstrated varied inferences, and notably, Zhongxian (ZX2), Wanhzou (WZ2), Yangzhou hatchery (YZYZ), Yangzhou (YZ), and Taihu (TH) populations showed apparent heterozygote deficiency. Linkage disequilibrium (LD) analysis exhibited a trend of higher linkage disequilibrium in populations from the upper reaches of the Yangtze River, followed by those from the middle reaches and then those from the lower reaches. Additionally, the reconstructed polygenetic tree and PCA plot clustered all populations into 2 major subgroups, while the results of structure analysis indicated 4 ancestors. The pairwise FST values ranged from 0 to 0.5530. Among these, high FST values (0.1931–0.5530) were only observed between populations WZ2, YZ, YZYZ, and the remaining 11 populations. Furthermore, genetic bottlenecks were observed in all populations 20–30 thousand years ago. Overall, the research offers insights essential for genetic management practices for sustainable aquaculture and biodiversity conservation of bighead carp.
1. Introduction
Bighead carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis), taxonomically classified in Cypriniformes, Cyprinidae, and Aristichthys, is a highly valued freshwater aquaculture species in China, ranking third in fish production with an annual yield of 3.27 million tons in 2022 [1]. As a semi-migratory species, growing in floodplain lakes and spawning in large rivers, H. nobilis is natively distributed in the Yangtze River, Qiantang River, Pearl River, Yellow River, and Haihe basin in China and has been introduced to over 70 countries since the 1970s due to its economic and ecological significance [2,3]. Among them, the Yangtze River, being the largest and longest river in China, has historically been the primary habitat for H. nobilis. Prior to the advent of artificial propagation in 1958, juvenile fish used for aquaculture were predominantly sourced from the Yangtze River. Presently serving as a vital germplasm resource bank of H. nobilis, the Yangtze River supplies high-quality broodstock to those national hatcheries located near the middle and lower reaches [4]. Unfortunately, over-exploitation and water pollution have precipitated a significant aquatic biodiversity crisis in the Yangtze River. Additionally, hydrological changes induced by hydraulic projects, such as alterations in temperature, water chemistry, and water levels, have adversely affected the migration and reproduction of H. nobilis and hindered its genetic exchange across different watersheds [5,6].
Continuous efforts have been made in recent years to conserve water bio-resources and recover biodiversity. Among those initiatives, restocking and stock enhancement through releasing hatchery-reared juveniles into the wild has been considered a tantalizing tactic in response to the depletion of germplasm resources, which has been applied to species such as Nibea japonica [7], Penaeus penicillatus [8] in China, Garra cambodgiensis [9] in Thailand, Paracentrotus lividus [10] in Italy. To restore the declining resources of H. nobilis and strike a balance between its conservation and exploitation, restocking and stock enhancement projects alongside the Yangtze River have been ongoing since the 1950s [11]. However, the absence of scientific management results in the release of fingerlings from unidentified sources during the stocking process, inevitably affecting the genetic structure of wild populations. Moreover, some hatcheries encounter issues, including small breeding populations and significant inbreeding during artificial reproduction, which adversely affect the quality of fingerlings and degrade the economic traits of H. nobilis [12].
To design effective breeding programs and provide scientific guidance for restocking and stock enhancement, a thorough investigation into the genetic background of H. nobilis populations is critical. The limited studies carried out thus far usually focused on genetic evaluation using morphological characteristics [3], isoenzymes [13], mitochondrial DNA [14], RELP [15], or microsatellites [12,16,17]. Nonetheless, a comprehensive understanding of the genetic structure of H. nobilis populations along the Yangtze River remains elusive due in part to limited molecular markers and small sample sizes in the previous literature. Notably, the advent of high-throughput sequencing technologies is revolutionizing the field of genetics by providing organism’s detailed genotyping data. Among them, the RAD-seq (Restriction-site associated DNA-sequencing) technique, involving digesting genomic DNA with restriction enzymes followed by sequencing the digested fragments, is characterized by its simple workflow, low cost, and independence from the reference genome and has been widely applied to the genetic map construction [18,19], genetic dissection of economic traits [20,21] and population genetic studies [22,23,24].
In this study, we utilized RAD-seq to perform the population genetic analysis of H. nobilis in the Yangtze River. Using genome-wide DNA markers, we investigated their genetic diversity, evaluated the population differentiation, and provided genomic evidence on the historical population dynamics, which are vital for formulating scientific management strategies and guiding the future monitoring of H. nobilis genetic resources in the Yangtze River.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
The Yangtze River Basin, spanning a total length of 6300 km, is divided into three reaches—upper, middle, and lower—based on geographical environment and hydrological characteristics. From upper to lower reaches, the current slows to a gentle flow while human activity steadily picks up. Considering the ecological characteristics of the Yangtze River basin and the distribution patterns of bighead carp, 13 geographic populations along the Yangtze River and one population in the Marseilles Reach of the Illinois River were sampled in 2017. At each sampling site, H. nobilis individuals weighing 1 to 2 kg were sampled using fishing nets. The individuals were identified by their typical and unambiguous morphological characteristics, including the big head with a length exceeding 30% of the total length and the abdominal keel extending from the base of the ventral fin to the anus. Following the collection of tail fin clips from each individual, preserved in 95% ethanol and stored at −20 °C, the individuals were subsequently released back into their environment. Collectively, a total of 157 individuals were sampled. Detailed sampling information is presented in Table 1 and Figure 1.

Table 1.
Detailed information of the 14 sampled H. nobilis populations.
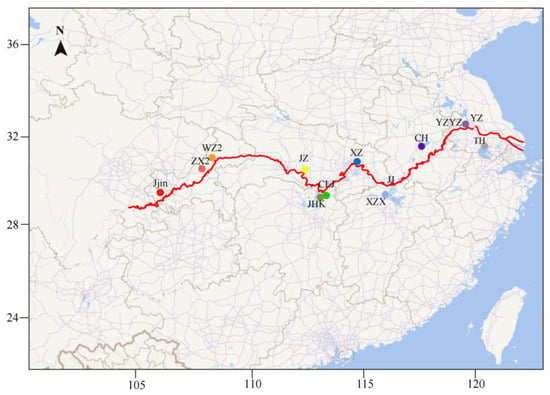
Figure 1.
Geographic map showing the sample sites (solid circles) along the Yangtze River. YZYZ was sampled from the broodstock of a national hatchery, and the remaining populations were sampled from the wild.
2.2. RAD-Seq Library Preparation and Sequencing
The genomic DNA of each specimen was extracted using a DNA extraction kit (Tiangen, Beijing, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The integrity and purity of DNA were assessed using 0.8% agarose electrophoresis and NanoDrop 2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), respectively, and the DNA concentration was determined using a Qubit 2.0 fluorometer (Life Technologies, Gaithersburg, MD, USA). High-quality DNA was used to construct the RAD-seq library at Wuhan Frasergen Bioinformatics Co., Ltd. (Wuhan, China). Briefly, 100 to 1000 ng of genomic DNA from each specimen was digested with the EcoRI restriction enzyme, and the digested fragments were ligated to the Solexa P1 adapter. The samples were then pooled together and randomly sheared ultrasonically, and fragments ranging from 300 bp to 700 bp were selected using agarose gel electrophoresis. Following the ligation to the Solexa P2 adapter, additional PCR amplification was performed to enrich fragments containing adapters at both ends. After pooling according to the effective concentration and target data volume, the qualified libraries were sequenced on an Illumina HiSeq2000 system (Illumina Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) with 150 bp paired-end reads.
2.3. Genotyping
To ensure high-quality data for subsequent analysis, the obtained raw data were filtered using the fastp program [25]: trimming bases with a Phred quality score of less than 20 and removing reads with adapters or with lengths less than 50 bases. Then, the obtained clean data were aligned to the reference genome of H. nobilis (HypMol1.0 with a Genebank number of GCA_004193235.1) using BWM-MEM (v 0.7.17) with default parameters [26]. The alignment results were sorted using Samtools (v1.9), and PCR duplicates were removed using MarkDuplicates in Picard Tools (v2.13.2) (http://broadinstitute.github.io/picard/) (accessed on 17 September 2024). SNP calling for each individual was then carried out using GATK HaplotypeCaller (v4.1.4.1) [27] with default settings. To ensure the reliability of the subsequent analysis, we filtered the calls using GATK VariantFiltration with the following parameters: QD < 2.0, FS > 60.0, MQ < 40.0, MQRankSum < −12.5, ReadPosRankSum < −8.0. The SNP calls for each sample were then combined using GATK CombineGVCFs under default settings. Each SNP was further assessed and filtered at the population level if (1) minor allele frequency < 0.01, (2) samples with missing genotypes > 0.2, and (3) sequencing depth < 4. The remaining SNPs were used to perform the population genetic analyses.
2.4. Genetic Diversity and Linkage Disequilibrium Analysis
Genetic parameters were analyzed using VCFtools (v0.1.13) [28], including nucleotide diversity (Pi), observed heterozygosity (HO), expected heterozygosity (HE), and the inbreeding coefficient (FIS). Pi was analyzed using a sliding-window approach with a window size of 5 kb. The Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium (HWE) test for each population was also performed using VCFtools. Additionally, PopLDdecay (v3.40) was used to perform linkage disequilibrium (LD) analysis based on the filtered SNP data [29].
2.5. Population Differentiation and Structure Analyses
To determine genetic differentiation among all sampled populations, the pairwise F-statistics (FST) among populations were calculated, and nonparametric multivariate analysis of variance (non-parametric MANOVA) was performed using the function adonis in the package Vegan [30]. To further enhance comprehension of the sampled H. nobilis population, we utilized Admixture v1.3.0 software [31] to analyze the population structure, in which the putative number of genetic groups (K-value) was assumed to be 1–8 and ten independent runs for each K-value were conducted. The K-value with the minimum cross-validation error (CV error) was chosen as the best population structure. A phylogenetic tree was constructed using the neighbor-joining (NJ) method with Treebest software 1.9.2 [32]. Bootstrap analysis, repeated 1000 times, was employed to assess the reliability of the NJ tree, and the phylogenetic tree was plotted using iTOL (https://itol.embl.de) (accessed on 17 September 2024). Principal components analysis (PCA) was then performed using GCTA (1.91.4) [33], and the results were plotted with the first and second eigenvalues using the “ggplot2” package in R [34]. The Markovian Coalescent (MSMC) model [35] was used to estimate effective population size using heterozygous sites across the genome.
3. Results
3.1. Sequencing and SNP Calling
A total of 221 Gb clean bases with an average Q20 of 97.0% and an average Q30 of 91.7% were obtained (Table S1). Alignment to the reference genome depicted an average sequencing depth of 14.6× and an average sequencing coverage of 15.8%. Following SNP detection and high-quality filtering, a total of 1,405,783 SNP loci were retained for further analysis. All SNPs were categorized as either transitions (Ti) or transversions (Tv), with transversions accounting for 54.7% of the SNP sites and an observed Ti: Tv ratio of 1.235.
3.2. Results of Genetic Diversity and LD Analysis
Important genetic parameters were calculated to assess the genetic diversity using the high-quality SNPs (Table 2). The results revealed that Pi ranged from 0.0002 (BH, CLJ, JJ, Jjin) to 0.0013 (YZ and YZYZ), which demonstrated relatively low genetic variation at the nucleotide level across all populations. The expected heterozygosity (HE) varied from 0.2116 to 0.3997, with the highest value in XZX and the lowest value in ZX2. The observed heterozygosity (HO) was lowest in CH (0.0656) and highest in YZ (0.4248). The expected heterozygosity of loci was greatly reduced relative to the observed heterozygosity in populations ZX2, WZ2, YZ, YZYZ, and TH. Additionally, the number of loci showing significant deviations from the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium among the 14 populations ranged from 4663 (JZ) to 919,153 (YZ). The inbreeding coefficient (FIS), occupied in determining the extent of inbreeding within a population, depicts the lowest value in JJ (−0.2905) and the highest value in YZ (0.8131).

Table 2.
Genetic diversity measurement of the 14 sampled H. nobilis populations.
Analysis of LD decay revealed that all populations generally exhibited three levels of LD decay rate. Among them, the American population (BH) and six populations of the Yangtze River (Jjin, WZ2, JZ, CLJ, JHK, CH) displayed the fastest LD decay, with r2 = 0.5 at distances less than 10 kb. XZ and XZX exhibited moderate decay rates, also reaching r2 = 0.5 at distances less than 10 kb. While populations ZX2, JJ, YZ, TH, and YZYZ displayed the slowest decay rate, and the r2 value gradually stabilized around 0.6 as the physical distance between markers increased. The LD decay rate generally exhibited a trend of being higher in populations from the upper reaches of the Yangtze River, followed by those from the middle reaches and then those from the lower reaches (Figure 2).
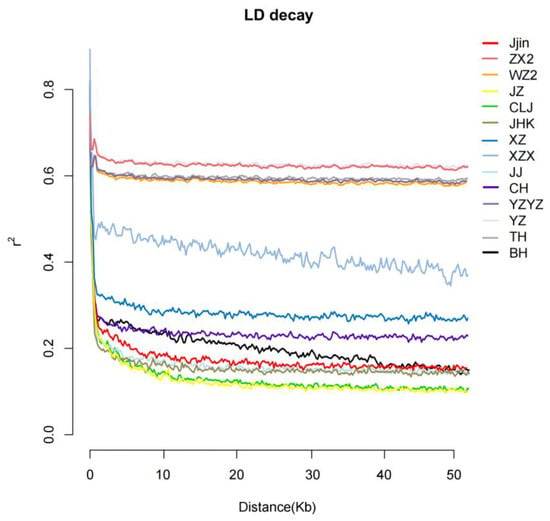
Figure 2.
Patterns of linkage disequilibrium (LD) decay.
3.3. Results of Genetic Differentiation and Population Structure
The pairwise F-statistics (FST) were calculated to investigate genetic differentiation. The pairwise FST values among all populations ranged from 0 to 0.5530. High FST values (0.1931–0.5530) were observed only between populations WZ2, YZ, YZYZ, and the remaining 11 populations. Low to moderate FST values (0–0.1538) were observed within the three aforementioned populations and the remaining 11 populations (Figure 3). Additionally, results of nonparametric MANOVA showed 40.22% variation within individuals and 59.78% among populations (Table 3).
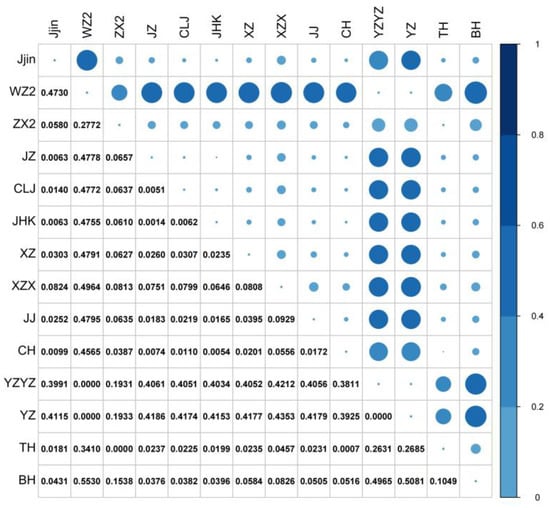
Figure 3.
Pairwise Fst among the 14 sampled H. nobilis populations. The size of the dots is proportional to the represented Fst values.

Table 3.
Results of the nonparametric MANOVA of the 14 sampled H. nobilis populations.
To further explore the genetic relationship among the investigated populations, population structure was analyzed. First, the reconstructed phylogenetic tree clustered the 157 H. nobilis specimens into two main clades. Clade 1 featured 25 individuals, of which 22 belonged to populations YZ, YZYZ and WZ2. Clade 2 featured 131 individuals, with individuals from the same geographical populations distributed across different branches (Figure 4A). Subsequently, the PCA plot, based on the first and second principal components explaining 82.87% and 1.11% of the total variance, respectively, revealed similar patterns of clustering (Figure 4B). Additionally, Admixture analysis indicated that the inferred genetic clusters of 2–4 were all presented with high probabilities. Nevertheless, all sampled populations were speculated to be oriented from four ancestral populations, which was supported by the cross-validation (when k = 4, the cross-validation was minimum). Specifically, populations YZ, YZYZ and WZ2 were dominated by the sample ancestor; population BH was dominated by an ancestor alone; partial specimens of populations YZYZ and ZX2 were dominated by the same ancestor; the remaining specimens were dominated by another common ancestor (Figure 4C,D).
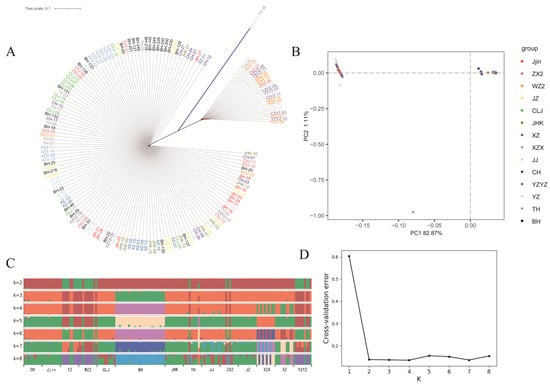
Figure 4.
Results of population structure analyses. (A) phylogenetic tree for the 157 H. nobilis individuals. (B) PCA plot with the first and second eigenvector. (C) Result of the admixture analysis. The length of each colored segment represents the proportion of the individual genome inferred from ancestral populations (K = 2~8). (D) Cross-validation (CV) error for different K values in admixture analysis.
3.4. Population Demographic History
The MSMC model, with a generation time (g) of five years and a mutation rate per generation (μ) of 2 × 10−9, was used to estimate the historical effective population sizes (Ne). The reconstructed demographic history showed evidence that all populations experienced their lowest Ne between 20–30 thousand years ago, followed by a recovery to effective population sizes ranging from 6000 to 20,000 individuals. Subsequently, a remarkable stability in Ne was observed in all populations until a slight change occurred in the last 10 years (Figure 5).
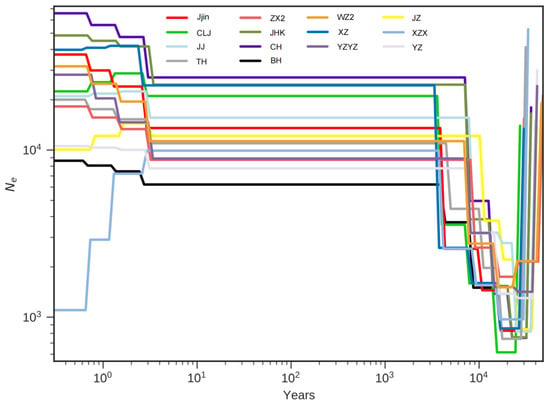
Figure 5.
The estimated effective population size over time of the 14 H. nobilis populations using the MSMC model with a generation time of five years and a mutation rate of 2 × 10−9.
4. Discussion
With the advancement of high-throughput sequencing techniques, research in fish population genetics has been increasingly important and popular in ecological, evolutionary, and conservation fields [24,36]. In the present study, we sampled 13 H. nobilis geographical populations from the Yangtze River basin and one American population, totaling 157 individuals, and performed population genetic analyses based on the 909,301 high-quality SNP loci obtained through the RAD-seq technique, dissecting the genetic background of H. nobilis in the Yangtze River at the genome-wide level.
Genetic diversity, reflecting the extent of genetic variation within a population and influenced by mutation, gene flow, genetic drift, or selection [37], has been considered essential for ensuring the evolutionary potential and environmental adaptability of a species [38,39]. Thus, genetic parameters, including nucleotide diversity, heterozygosity, and inbreeding coefficient, were initially calculated to determine the genetic diversity of the sampled populations. Expected and observed heterozygosity ranging from 0.2116 to 0.3997 and from 0.0656 to 0.4248, respectively, were observed in the 14 investigated populations, which were substantially lower than those reported in the previous literature using microsatellites [12,16,17,40]. A similar phenomenon was also observed in other fish species in the Yangtze River, such as Mylopharyngodon piceus [41], Ctenopharyngodon idella [42], Misgurnus anguillicaudatus [43], likely due to the use of different DNA markers. Furthermore, the nucleotide diversity analyzed in our study ranged from 0.2 × 10−3 to 1.3 × 10−3, falling into a similar range to that observed in Megalobrama (based on genome-wide SNP) [44] and grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon Idella) (based on mitochondrial DNA) [45], appearing to be very low overall, which might be due to the low mutation rate and long generation time (4–5 years in the wild) [46]. Nevertheless, the comparable expected heterozygosity to other Cyprinidae species that still maintain high genetic diversity, such as Mylopharyngodon piceus (HE = 0.273–0.292) [41], Ctenopharyngodon Idella (HE = 0.2523–0.2418) [42] and Gymnocypris przewalskii (HE = 0.3367–0.3444) [47], suggested that the H. nobilis populations investigated in our study still had high genetic diversity.
Among the 14 populations, populations ZX2, WZ2, YZ, YZYZ, and TH showed apparent heterozygote deficiency, with HE ranging from 0.2439 to 0.3997 and HO ranging from 0.0656 to 0.0897. such a large discrepancy was also observed in a mito-gynogenetic population of olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) that was theoretically homozygous at all loci [48], indicating that these five populations might suffer strong inbreeding or the Wahlund effect [49,50,51], which was further confirmed by the high FIS value. This was the first time that such a high level of inbreeding coefficients has been documented in wild or farmed H. nobilis populations, which might be attributed to the high resolution provided by the genome-wide SNP markers. Usually, different from the heterozygote deficiency caused by null allele, the Wahlund effect or inbreeding should theoretically affect all loci equally, which was indeed observed in the five populations, wherein over 16% of loci in TH and over 50% of loci in YZ, YZYZ, WZ2, and ZX2 deviated from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. It was noteworthy that the aforementioned five populations exhibited higher expected heterozygosity and nucleotide diversity than the remaining populations despite showing higher inbreeding coefficients. Bjornerfeldt et al. [52] also reported such a rare phenomenon in a population of poodles and attributed the reason to the inclusion of multiple genetically distinct subgroups in the experimental population.
Linkage disequilibrium (LD) describes the non-random association of alleles at different SNPs within a given population and is extensively used to investigate the evolution and demographic process [53]. Typically, the rate of LD decay in a population is positively correlated with its genetic diversity, as observed in studies of Megalobrama [44], Litopenaeus vannamei [54], Hyriopsis cumingii [55] and Pinctada fucata [56]. However, the opposite was observed in the present study, wherein populations ZX2, WZ2, YZ, YZYZ, and TH, with higher nucleotide diversity and expected heterozygosity, exhibited the slowest LD decay rate, and the remaining populations also exhibited some degree of long-range LD. Similar phenomena were also reported in Salmo salar [57] and Litopenaeus vannamei [58], where admixture was suggested to be the major factor. The commonly recognized factors such as founder effect, inbreeding, selection, admixture, genetic drift, recombination as well as mutation are all key elements determining LD, thus the use of LD analysis alone to infer the genetic background of populations may generate spurious results. Preliminarily, based on the results of genetic diversity and LD Analysis, we observed a decline in genetic variation in ZX2, WZ2, YZ, YZYZ, and TH and speculated that YZYZ, sampled from the broodstocks in a national hatchery might have possessed admixed origin and suffered strong inbreeding, and ZX2, WZ2, YZ, TH were highly likely to have been undergoing events of admixture caused by large-scale restocking and stock enhancement activities.
To better understand the genetic structure of H. nobilis, pairwise Fst values were calculated, and analysis of the phylogenetic tree, STRUCTURE, and PCA were performed. Significant genetic differentiation, with high FST values ranging from 0.1931 to 0.5530, was detected between populations YZYZ, YZ, WZ2 (assigned as group A) and the remaining 11 populations (assigned as group B), while low genetic differentiation was detected within the two groups, respectively. The reconstructed phylogenetic tree and PCA plot also demonstrated similar results, with YZYZ, YZ, and WZ2 clustering into a single subgroup and the remaining populations clustering into another subgroup. Additionally, the result of structure analysis further divided the 14 population into four ancestral sources, wherein the BH population was dominated by an ancestor alone, in agreement with the previous report [59], suggesting that prolonged geographical isolation had led to a certain degree of genetic differentiation. Notably, in the PCA plot and phylogenetics tree, the BH population does not segregate into a discrete cluster from other populations. While the variation in algorithms contributes to this pattern, we posited that the underlying cause was the short introduction history from China (around 50 years), the extended generational interval with 4–5 years in natural environments, and the absence of intense anthropogenic or natural selective pressures in the BH population, which lead to the low genetic differentiation between the BH population and most domestic counterparts.
Generally, the clustering pattern observed here did not correspond to geographical distribution, as observed in silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) [60] and grenadier anchovy (Coilia nasus) [61]. Typically, frequent genetic exchange reduces the level of genetic differentiation, whereas geographic isolation, mutation, genetic drift, or artificial selection accelerate the genetic differentiation process among populations [62]. The widespread genetic similarity observed among most populations in our study was similar to findings by Zhu et al. [12] and Fu et al. [59], who noted a similar situation among H. nobilis populations in the middle and upper reaches of the Yangtze River using microsatellite markers and mitochondrial DNA, respectively. They attributed the similarity to similar ecological environments and anthropogenic factors. Considering the influence of anthropogenic activities and the possibility of gene flow among the sampling sites, we speculated that the intensive restocking and stock enhancement activities using mixed germplasm along the Yangtze River, followed by subsequent random mating in the natural spawning grounds, might explain the high genetic similarity observed. However, an unexpected result was that the WZ2 exhibited high genetic similarity to the YZ and YZYZ despite being over 1000 km apart, while these three populations exhibited high genetic differentiation from other populations. Previous literature showed that the natural spawning grounds of the four major Chinese carps were mainly distributed in the upper and middle reaches of the Yangtze River, whereas WZ2 was in the inundated area of the Gerges Reservoir, where changes in hydrological conditions have led to the disappearance of the original spawning grounds [63]. Thus, we tentatively speculated that the fingerlings released in WZ2 and YZ might come from the Yangzhou hatchery (YZYZ), and the absence of the spawning ground impeded the gene flow with the neighboring population, which requires further investigation. Finally, a general decline in effective population size was observed 20–30 thousand years ago in all populations during the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), consistent with observations in a considerable number of other species, such as Megalobrama [44], Mysticeti [64], Ectopistes migratorius [65] and Ailuropoda melanoleuca [66]. The cold climate conditions and the shortage of food supplies during the LGM were likely causes of the population bottleneck. Additionally, a mild population expansion has been noticed in recent years, which might be attributed to conservation efforts.
5. Conclusions
In summary, we identified 1,405,783 high-quality SNPs in 157 H. nobilis from 14 populations using RAD sequencing. Population genetic analysis indicated that most populations, including the American population BH, showed low genetic differentiation. Additionally, the genetic diversity of populations generally tends to decline from upstream to downstream, with the exception of populations WZ2, YZ, and YZYZ, which were suffering heterozygote deficiency and inbreeding degradation. Overall, these findings will be instrumental in devising effective conservation and management strategies for H. nobilis populations in the Yangtze River basin.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/biology13100837/s1, Table S1: Statistics of sequncing data.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.L.; Visualization, W.L and E.W.; Investigation, J.Y. and X.H.; Writing—original draft preparation, W.L. and X.L.; Writing-review and editing, W.L., X.L. and J.Y.; Formal analysis, Y.Q.; Funding acquisition, B.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31572593; 51579160), the Department of Three Gorges Project Management, the Ministry of Water Resources of China (grant number: 12620200600020J005) and the Department of Science and Technology of Wuhan City (2023020201020298).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of the Institue of Hydroecology (IHE), Ministry of Water Resources and Chinese Academic of Science (protocol code IHE_IACUC_20170428_01).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The sequence data involved in this study have been deposited in NCBI with the BioProject accession number PRJNA1117638.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Fishery Statistical Yearbook; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, G.W.; Zhao, J.; Liao, X.; Wang, J.; Luo, M.; Zhu, L.; Bernatzhez, L.; Li, S. Evolution and genetics of bighead and silver carps: Native population conservation versus invasive species control. Evol. Appl. 2020, 13, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhou, B.; Ni, C.; Chen, Z. Morphological variations of silver carp, bighead and grass carp from Changjiang, Zhujiang and Heilongjiang river. Acta Zool. Sin. 1989, 35, 390. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Li, S.; Wang, K. Enhancement and conservation of inland fisheries resources in China. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2011, 93, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Hua, Q.; Zhou, H.; Wu, Z.; Wu, X. The effect of dams on the larval abundance and composition of four carp species in key river systems in China. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2014, 98, 1201–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Qu, X.; Xiong, F.; Lu, Y.; Wang, L.; Hughes, R.M. Challenges to saving China’s freshwater biodiversity: Fishery exploitation and landscape pressures. Ambio 2019, 49, 926–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Wang, W.; Lin, G.; Xu, K.; Guo, A. Effect and assessment of enhancement release of Nibea japonica and Sparus macrocephalus in artificial reef habitat waters of Zhoushan, Zhejiang. J. Fish. Sci. China 2010, 17, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.Q.; Shih, Y.J.; Huang, L.M.; Li, J.; Li, W.W.; Shih, C.H.; Chu, T.J. Evaluating the effects related to restocking and stock replenishment of Penaeus penicillatus in the Xiamen Bay, China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osathanunkul, M.; Suwannapoom, C. Sustainable fisheries management through reliable restocking and stock enhancement evaluation with environmental DNA. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglioli, A.A.; Addis, P.; Pasquini, V.; Secci, M.; Hannon, C. First assessment of restocking efficacy of the depleted sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus populations in two contrasted sites. Aquacult. Res. 2021, 52, 2896–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zeng, Y.; Ren, T. Study on the problems and countermeasures of fishery stock enhancement in China. China Fish. 2021, 9, 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Fu, J.; Luo, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, P.; Liu, Q.; Dong, Z. Genetic diversity and population structure of bighead carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis) from the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River revealed using microsatellite markers. Aquacult. Rep. 2022, 27, 101377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, S. Isoenzyme analysis of population diversity of silver carp, bighead carp, grass carp and black carp in the middle and lower stream of Changjiang River. J. Fish. China 1996, 20, 104–110. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Huang, J.; Chen, Q.; Chen, F.; Ma, X.; Zhu, G.; Song, D.; Nie, G.; Li, X. Analysis on genetic diversity and selective pressure in farmed bighead carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis) from Henan province. Freshw. Fish. 2018, 48, 22–29. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Zhao, J.; Li, S.; Zheng, D.; Cao, Y. Genetic variation of bighead carp Aristichthys nobilis from Chinese native populations and introduced populations by AFLP. J. Fish. Sci. China 2011, 18, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Zhang, G.; Xue, X.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Fang, D.a.; Xu, D. Current germplasm situation of bighead carp (Aristichthys nobilis) candidate parent and parent from hatchery in the lower reaches of Changjiang River based on SSR markers. J. Fish. Sci. China 2020, 27, 589–597. [Google Scholar]
- Sha, H.; Luo, X.; Zou, G.; Liang, H. Genetic diversity analysis of Aristichthys nobilis in middle reaches of Yangtze River based on the microsatellite makers. Freshw. Fish. 2020, 50, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Gonen, S.; Lowe, N.R.; Cezard, T.; Gharbi, K.; Bishop, S.C.; Houston, R.D. Linkage maps of the Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) genome derived from RAD sequencing. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Luo, Q.; Ou, M.; Zhu, X.P.; Zhao, J.; Chen, K.C. High-density genetic linkage map and QTL fine mapping of growth and sex in snakehead (Channa argus). Aquaculture 2020, 519, 734760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; You, X.X.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.H.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, S.J.; Lin, X.Q.; Lin, H.R.; Meng, Z.N.; Shi, Q. A genome-wide association study on growth traits in orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) with RAD-seq genotyping. Sci. China-Life Sci. 2018, 61, 934–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejo, R.L.; Liu, S.X.; Gao, G.T.; Fragomeni, B.O.; Hernandez, A.G.; Leeds, T.D.; Parsons, J.E.; Martin, K.E.; Evenhuis, J.P.; Welch, T.J.; et al. Similar genetic architecture with shared and unique quantitative trait loci for bacterial cold water disease resistance in two rainbow trout breeding populations. Front. Genet. 2017, 8, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yu, S.; Ren, H.; Tang, J.; Gao, J.; Li, X.; Fu, Z.; He, Z. Genetic diversity and population structure of the endangered Japanese sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus) in natural seas of northern China. Aquacult. Rep. 2023, 30, 101595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufresnes, C.; Dutoit, L.; Brelsford, A.; Goldstein-Witsenburg, F.; Clement, L.; Lopez-Baucells, A.; Palmeirim, J.; Pavlinic, I.; Scaravelli, D.; Sevcik, M.; et al. Inferring genetic structure when there is little: Population genetics versus genomics of the threatened bat Miniopterus schreibersii across Europe. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowell, N.; Suhrbier, A.; Tarpey, C.; May, S.; Carson, H.; Hauser, L. Population structure and adaptive differentiation in the sea cucumber Apostichopus californicus and implications for spatial resource management. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0280500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The genome analysis toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danecek, P.; Auton, A.; Abecasis, G.; Albers, C.A.; Banks, E.; DePristo, M.A.; Handsaker, R.E.; Lunter, G.; Marth, G.T.; Sherry, S.T.; et al. The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2156–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Dong, S.S.; Xu, J.Y.; He, W.M.; Yang, T.L. PopLDdecay: A fast and effective tool for linkage disequilibrium decay analysis based on variant call format files. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 1786–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J. A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral Ecol. 2001, 26, 32–46. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, D.H.; Novembre, J.; Lange, K. Fast model-based estimation of ancestry in unrelated individuals. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1655–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilella, A.J.; Severin, J.; Ureta-Vidal, A.; Heng, L.; Durbin, R.; Birney, E. EnsemblCompara GeneTrees: Complete, duplication-aware phylogenetic trees in vertebrates. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.A.; Lee, S.H.; Goddard, M.E.; Visscher, P.M. GCTA: A tool for genome-wide complex trait analysis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 88, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginestet, C. ggplot2: Elegant graphics for data analysis. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A Stat. Soc. 2011, 174, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffels, S.; Wang, K. MSMC and MSMC2: The multiple sequentially markovian coalescent. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2090, 147–166. [Google Scholar]
- Urvois, T.; Perrier, C.; Roques, A.; Saune, L.; Courtin, C.; Kajimura, H.; Hulcr, J.; Cognato, A.I.; Auger-Rozenberg, M.A.; Kerdelhue, C. The worldwide invasion history of a pest ambrosia beetle inferred using population genomics. Mol. Ecol. 2023, 32, 4381–4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellegren, H.; Galtier, N. Determinants of genetic diversity. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eizaguirre, C.; Baltazar-Soares, M. Evolutionary conservation-evaluating the adaptive potential of species. Evol. Appl. 2014, 7, 963–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booy, G.; Hendriks, R.J.J.; Smulders, M.J.M.; Van Groenendael, J.M.; Vosman, B. Genetic diversity and the survival of populations. Plant Biol. 2000, 2, 379–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, K.; Xu, D.; Duan, J.; Zhou, Y.; Fang, D.; Shi, W. Analysis of genetic diversity in populations released for stock enhancement and population caught in natural water of bighead carp in the lower reaches of the Yangtze River using microsatellite markers. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis 2013, 35, 579–586. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H.P.; Mao, S.Q.; Xu, X.Y.; Li, J.L.; Shen, Y.B. Genetic diversity analysis of different geographic populations of black carp (Mylopharyngodon piceus) based on whole genome SNP markers. Aquaculture 2024, 582, 740542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Liu, X.M.; Huang, W.J.; Wang, Y.; Anwarullah, K.; Luo, L.F.; Gao, Z.X. Whole-genome resequencing reveals genetic diversity and signatures of selection in mono-female grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Aquaculture 2023, 575, 739816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.K.; Wang, W.M.; Zhou, X.Y. Genomic evidence for the population genetic differentiation of Misgurnus anguillicaudatus in the Yangtze River basin of China. Genomics 2019, 111, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Liu, H.; Gooneratne, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.M. Population Genomics of Megalobrama Provides Insights into Evolutionary History and Dietary Adaptation. Biology 2022, 11, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Dang, Y.; Li, L.; Huang, W.; Fang, Y.; Wang, F.; Shen, Y.; Li, J. genetic variation of mitochondrial DNA d-loop region in wild and breeding populations of grass carp. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2017, 41, 947–955. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, A.R.; Harpending, H. Population-growth makes waves in the distribution of pairwise genetic-differences. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1992, 9, 552–569. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.; Fang, D.a.; He, M.; Mao, C.; Kuang, Z.; Qi, H.; Xu, D. Genetic diversity and population structure of Gymnocypris przewalskii based on SNP markers. South China Fish. Sci. 2023, 19, 86–96. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wu, Z.; Zou, C.; Lu, Y.; Yue, X.; Song, Z.; Yang, R.; You, F. Genetic diversity and signatures of selection in the mito-gynogenetic olive flounder Paralichthys olivaceus revealed by genome-wide SNP markers. Aquaculture 2022, 553, 738062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castric, V.; Bernatchez, L.; Belkhir, K.; Bonhomme, F. Heterozygote deficiencies in small lacustrine populations of brook charr Salvelinus Fontinalis Mitchill (Pisces, Salmonidae): A test of alternative hypotheses. Heredity 2002, 89, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selkoe, K.A.; Toonen, R.J. Microsatellites for ecologists: A practical guide to using and evaluating microsatellite markers. Ecol. Lett. 2006, 9, 615–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.S.; Black, R. The wahlund effect and the geographical scale of variation in the intertidal limpet siphonaria sp. Mar. Biol. 1984, 79, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjornerfeldt, S.; Hailer, F.; Nord, M.; Vila, C. Assortative mating and fragmentation within dog breeds. BMC Evol. Biol. 2008, 8, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slatkin, M. Linkage disequilibrium-understanding the evolutionary past and mapping the medical future. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, B.F.; Bonaguro, A.; Araya, C.; Carvalheiro, R.; Yanez, J.M. Application of a novel 50K SNP genotyping array to assess the genetic diversity and linkage disequilibrium in a farmed Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) population. Aquacult. Rep. 2021, 20, 100691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Wang, Z.; Jia, L.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Lv, G.; Bai, Z.; Li, J. Genetic differentiation and identification of key genes related to biomineralization and coloration in three Hyriopsis cumingii strains exhibiting different inner shell colors. Aquacult. Rep. 2024, 35, 101939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Peng, H.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, S. Genetic Relationship among Three populations of pearl oyster Pinctada fucata ssp. martensii in Guangxi, China. Fish. Sci. 2023, 42, 466–473. [Google Scholar]
- Barria, A.; López, M.E.; Yoshida, G.; Carvalheiro, R.; Lhorente, J.P.; Yáñez, J.M. Population genomic structure and genome-wide linkage disequilibrium in farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) using dense SNP genotypes. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Teng, M.X.; Liu, P.P.; Zhao, M.Y.; Wang, S.; Hu, J.J.; Bao, Z.M.; Zeng, Q.F. Selection signatures of Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei revealed by whole-genome resequencing analysis. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 844597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Zhu, W.; Luo, M.; Wang, L.; Dong, Z. Population genetic analyses in bighead carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis) from the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River based on D-loop sequences. J. Shanghai Ocean. Univ. 2024, 33, 521–532. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, D.; Luo, Y.; Xu, D.; Yang, X.; Wang, X. Relationship between genetic risk and stock enhancement of the silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) in the Yangtze River. Fish. Res. 2021, 235, 105829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.; Yang, Q.; Li, Y.; Zong, S.; Gao, T.; Liu, J. Comprehensive assessment of population genetic structure of the overexploited Japanese grenadier anchovy (Coilia nasus): Implications for fisheries management and conservation. Fish. Res. 2019, 213, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balloux, F.; Lugon-Moulin, N. The estimation of population differentiation with microsatellite markers. Mol. Ecol. 2002, 11, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xinqiang, N.; Peilun, T.J.C.W.R. Studies on biological regulation of Three Gorges Project. China Water Resour. 2006, 14, 8–24. [Google Scholar]
- Arnason, U.; Lammers, F.; Kumar, V.; Nilsson, M.A.; Janke, A. Whole-genome sequencing of the blue whale and other rorquals finds signatures for introgressive gene flow. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaap9873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, C.M.; Shaner, P.J.L.; Zink, R.M.; Liu, W.C.; Chu, T.C.; Huang, W.S.; Li, S.H. Drastic population fluctuations explain the rapid extinction of the passenger pigeon. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 10636–10641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.C.; Zheng, P.P.; Dong, S.S.; Zhan, X.J.; Wu, Q.; Guo, X.S.; Hu, Y.B.; He, W.M.; Zhang, S.N.; Fan, W.; et al. Whole-genome sequencing of giant pandas provides insights into demographic history and local adaptation. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).