Effect of Acute Thermal Stress Exposure on Ecophysiological Traits of the Mediterranean Sponge Chondrilla nucula: Implications for Climate Change
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sponge Collection and Preparation
2.2. Respiration Rates
2.3. Clearance Rates
2.4. Statistics and Modelling
2.4.1. Statistical Analysis
2.4.2. Thermal Risk Map
3. Results
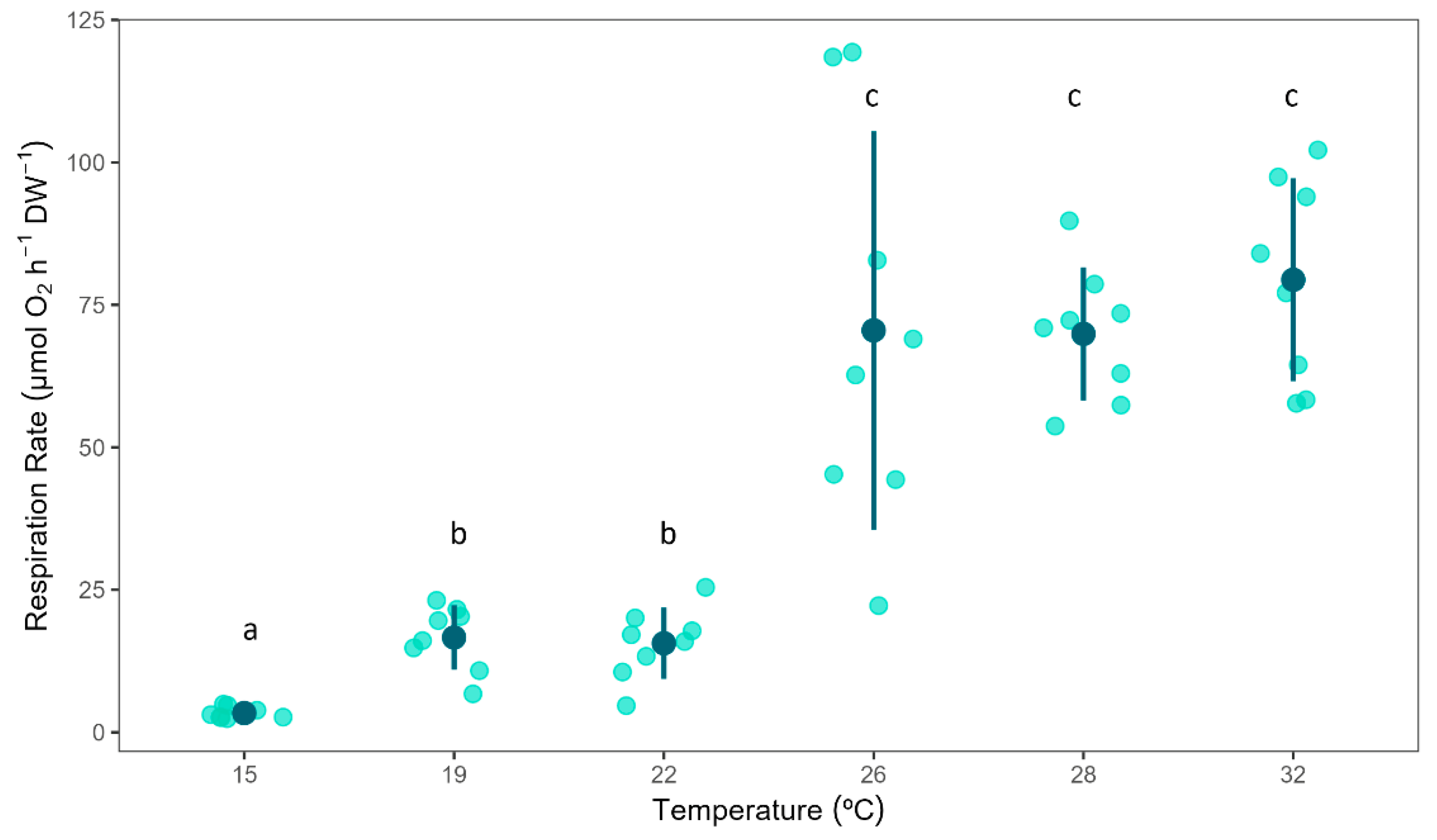
3.1. Respiration Rates
3.2. Clearance Rates
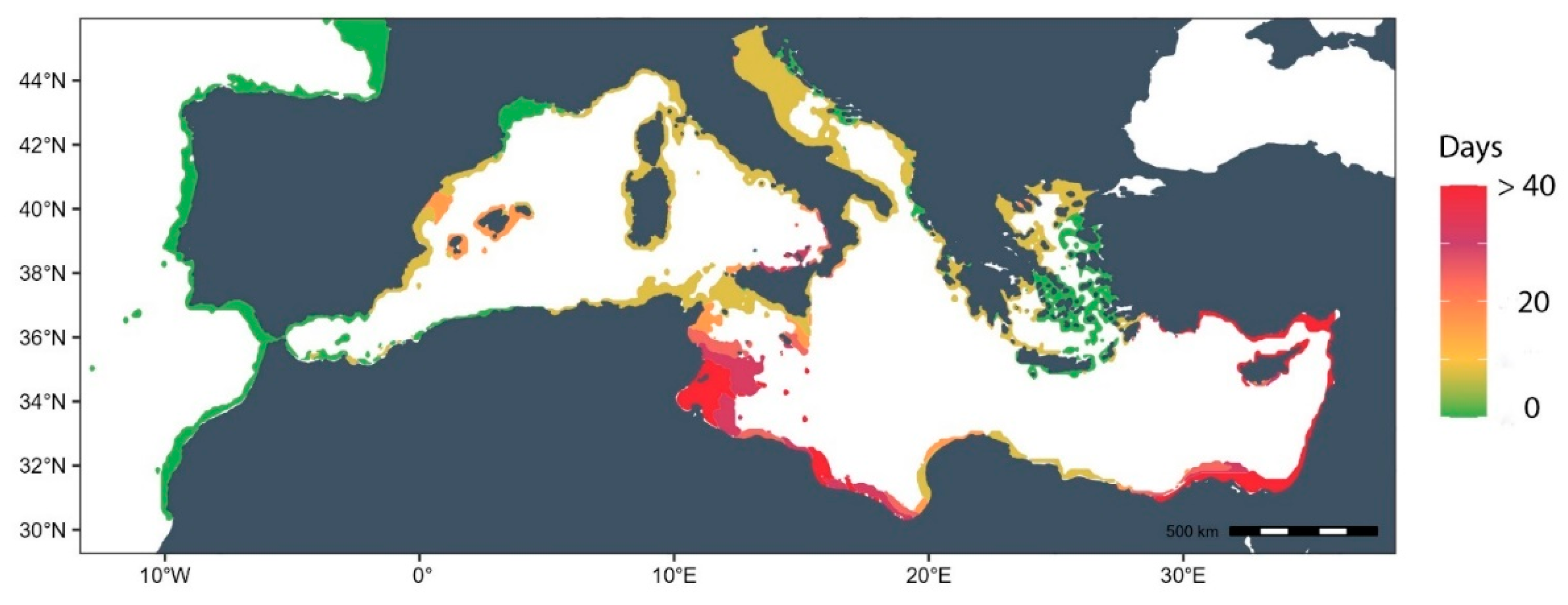
3.3. Thermal Risk Map
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coll, M.; Piroddi, C.; Albouy, C.; Ben Rais Lasram, F.; Cheung, W.W.L.; Christensen, V.; Karpouzi, V.S.; Guilhaumon, F.; Mouillot, D.; Paleczny, M.; et al. The Mediterranean Sea under Siege: Spatial Overlap between Marine Biodiversity, Cumulative Threats and Marine Reserves. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2012, 21, 465–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, C.N.; Morri, C.; Chiantore, M.; Montefalcone, M.; Parravicini, V.; Rovere, A. Mediterranean Sea Biodiversity between the Legacy from the Past and a Future of Change. In Life in the Mediterranean Sea: A Look at Habitat Changes; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 1–55. [Google Scholar]
- Coll, M.; Piroddi, C.; Steenbeek, J.; Kaschner, K.; Lasram, F.B.R.; Aguzzi, J.; Ballesteros, E.; Bianchi, C.N.; Corbera, J.; Dailianis, T.; et al. The Biodiversity of the Mediterranean Sea: Estimates, Patterns, and Threats. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchi, C.N.; Morri, C. Southern Species in the Ligurian Sea (Northern Mediterranean): New Records and a Review. Boll. Mus. Ist. Biol. Univ. Genova 1994, 58–59, 181–197. [Google Scholar]
- Cramer, W.; Guiot, J.; Fader, M.; Garrabou, J.; Gattuso, J.-P.; Iglesias, A.; Lange, M.A.; Lionello, P.; Llasat, M.C.; Paz, S.; et al. Climate Change and Interconnected Risks to Sustainable Development in the Mediterranean. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 8, 972–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, M.; Dalu, G.A.; Maracchi, G.; Pasqui, M.; Cesarone, F. Heat Waves in the Mediterranean: A Local Feature or a Larger-scale Effect? Int. J. Climatol. 2006, 26, 1477–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson-Delmotte, V.; Zhai, P.; Pirani, A.; Connors, S.L.; Péan, C.; Berger, S.; Caud, N.; Chen, Y.; Goldfarb, L.; Gomis, M.I.; et al. (Eds.) IPCC Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Garrabou, J.; Coma, R.; Bensoussan, N.; Bally, M.; Chevaldonné, P.; Cigliano, M.; Diaz, D.; Harmelin, J.G.; Gambi, M.C.; Kersting, D.K.; et al. Mass Mortality in Northwestern Mediterranean Rocky Benthic Communities: Effects of the 2003 Heat Wave. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 15, 1090–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrabou, J.; Gómez-Gras, D.; Medrano, A.; Cerrano, C.; Ponti, M.; Schlegel, R.; Bensoussan, N.; Turicchia, E.; Sini, M.; Gerovasileiou, V.; et al. Marine Heatwaves Drive Recurrent Mass Mortalities in the Mediterranean Sea. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2022, 28, 5708–5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Gras, D.; Linares, C.; López-Sanz, A.; Amate, R.; Ledoux, J.B.; Bensoussan, N.; Drap, P.; Bianchimani, O.; Marschal, C.; Torrents, O.; et al. Population Collapse of Habitat-Forming Species in the Mediterranean: A Long-Term Study of Gorgonian Populations Affected by Recurrent Marine Heatwaves. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2021, 288, 20212384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarà, G.; Giommi, C.; Giacoletti, A.; Conti, E.; Mulder, C.; Mangano, M.C. Multiple Climate-Driven Cascading Ecosystem Effects after the Loss of a Foundation Species. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 770, 144749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrano, C.; Bavestrello, G.; Bianchi, C.N.; Cattaneo-Vietti, R.; Bava, S.; Morganti, C.; Morri, C.; Picco, P.; Sara, G.; Schiaparelli, S.; et al. A Catastrophic Mass-Mortality Episode of Gorgonians and Other Organisms in the Ligurian Sea (North-Western Mediterranean), Summer 1999. Ecol. Lett. 2000, 3, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, T.; Garrabou, J.; Sartoretto, S.; Harmelin, J.G.; Francour, P.; Vacelet, J. Massive mortality of marine invertebrates: An unprecedented event in northwestern Mediterranean. Comptes Rendus De L’academie Des Sci. Ser. III Sci. De La Vie 2000, 323, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klautau, M.; Russo, C.A.M.; Lazoski, C.; Boury-Esnault, N.; Thorpe, J.P.; Solé-Cava, A.M. Does Cosmopolitanism Result from Overconservative Systematics? A Case Study Using the Marine Sponge Chondrilla nucula. Evolution 1999, 53, 1414–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cebrian, E.; Uriz, M.J.; Garrabou, J.; Ballesteros, E. Sponge Mass Mortalities in a Warming Mediterranean Sea: Are Cyanobacteria-Harboring Species Worse Off? PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ereskovsky, A.; Ozerov, D.A.; Pantyulin, A.N.; Tzetlin, A.B. Mass Mortality Event of White Sea Sponges as the Result of High Temperature in Summer 2018. Polar Biol. 2019, 42, 2313–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.J. The Functional Roles of Marine Sponges. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2008, 79, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiswig, H.M. In Situ Pumping Activities of Tropical Demospongiae. Mar. Biol. 1971, 9, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiswig, H.M. Water Transport, Respiration and Energetics of Three Tropical Marine Sponges. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1974, 14, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, S.M.; Omena, E.P.; Muricy, G. Macrofauna Associated to Mycale Microsigmatosa (Porifera, Demospongiae) in Rio de Janeiro State, SE Brazil. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2003, 57, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pile, A.J.; Young, C.M. The Natural Diet of a Hexactinellid Sponge: Benthic–Pelagic Coupling in a Deep-Sea Microbial Food Web. Deep. Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2006, 53, 1148–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, C.R.; Evans, E. Sponge Distribution across Davies Reef, Great Barrier Reef, Relative to Location, Depth, and Water Movement. Coral Reefs 1989, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo, F.J.; Muñoz, P.D.; Cristobo, J.; Ríos, P.; González, C.; Kenchington, E.; Serrano, A. Deep-Sea Sponge Grounds of the Flemish Cap, Flemish Pass and the Grand Banks of Newfoundland (Northwest Atlantic Ocean): Distribution and Species Composition. Mar. Biol. Res. 2012, 8, 842–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, M.; Aguilar, R.; Bannister, R.J.; Bell, J.J.; Conway, K.W.; Dayton, P.K.; Díaz, C.; Gutt, J.; Kelly, M.; Kenchington, E.L.R.; et al. Sponge Grounds as Key Marine Habitats: A Synthetic Review of Types, Structure, Functional Roles, and Conservation Concerns BT—Marine Animal Forests: The Ecology of Benthic Biodiversity Hotspots; Rossi, S., Bramanti, L., Gori, A., Orejas Saco del Valle, C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 1–39. ISBN 978-3-319-17001-5. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, J.J.; Barnes, D.K.A. The Importance of Competitor Identity, Morphology and Ranking Methodology to Outcomes in Interference Competition between Sponges. Mar. Biol. 2003, 143, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, B.; Chester, C.; Jochem, F.; Fourqurean, J. Potential Role of Sponge Communities in Controlling Phytoplankton Blooms in Florida Bay. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 328, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, O.; Buckley, L.B.; Keitt, T.H.; Angilletta, M.J. Ontogeny Constrains Phenology: Opportunities for Activity and Reproduction Interact to Dictate Potential Phenologies in a Changing Climate. Ecol. Lett. 2016, 19, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.H.; Gillooly, J.F.; Allen, A.P.; Savage, V.M.; West, G.B. Toward a Metabolic Theory of Ecology. Ecology 2004, 85, 1771–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooijman, B. Dynamic Energy Budget Theory for Metabolic Organisation, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, J.J.; Bennett, H.M.; Rovellini, A.; Webster, N.S. Sponges to Be Winners under Near-Future Climate Scenarios. Bioscience 2018, 68, 955–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.N.; Strychar, K.B.; Shirley, T.C.; Rützler, K. Effects of Heat and Salinity Stress on the Sponge Cliona celata. Int. J. Biol. 2010, 2, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Duckworth, A.R.; West, L.; Vansach, T.; Stubler, A.; Hardt, M. Effects of Water Temperature and PH on Growth and Metabolite Biosynthesis of Coral Reef Sponges. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 462, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.J.; Smith, D. Ecology of Sponge Assemblages (Porifera) in the Wakatobi Region, South-East Sulawesi, Indonesia: Richness and Abundance. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2004, 84, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelmo, F.; Bell, J.J.; Attrill, M.J. Tolerance of Sponge Assemblages to Temperature Anomalies: Resilience and Proliferation of Sponges Following the 1997-8 El-Niño Southern Oscillation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronson, R.; Precht, W.; Toscano, M.; Koltes, K. The 1998 Bleaching Event and Its Aftermath on a Coral Reef in Belize. Mar. Biol. 2002, 141, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Gras, D.; Linares, C.; de Caralt, S.; Cebrian, E.; Frleta-Valić, M.; Montero-Serra, I.; Pagès-Escolà, M.; López-Sendino, P.; Garrabou, J. Response Diversity in Mediterranean Coralligenous Assemblages Facing Climate Change: Insights from a Multispecific Thermotolerance Experiment. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 4168–4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.J.; Davy, S.K.; Jones, T.; Taylor, M.W.; Webster, N.S. Could Some Coral Reefs Become Sponge Reefs as Our Climate Changes? Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 2613–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massaro, A.J.; Weisz, J.B.; Hill, M.S.; Webster, N.S. Behavioral and Morphological Changes Caused by Thermal Stress in the Great Barrier Reef Sponge Rhopaloeides Odorabile. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2012, 416–417, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beepat, S.S.; Davy, S.K.; Woods, L.; Bell, J.J. Short-Term Responses of Tropical Lagoon Sponges to Elevated Temperature and Nitrate. Mar. Environ. Res. 2020, 157, 104922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, H.M.; Altenrath, C.; Woods, L.; Davy, S.K.; Webster, N.S.; Bell, J.J. Interactive Effects of Temperature and PCO(2) on Sponges: From the Cradle to the Grave. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 2031–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, N.S. Sponge Disease: A Global Threat? Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 1363–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achlatis, M.; Van Der Zande, R.M.; Schönberg, C.H.L.; Fang, J.K.H.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Dove, S. Sponge Bioerosion on Changing Reefs: Ocean Warming Poses Physiological Constraints to the Success of a Photosymbiotic Excavating Sponge. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strano, F.; Micaroni, V.; Costa, G.; Bertocci, I.; Bertolino, M. Shallow-Water Sponge Grounds along the Apulian Coast (Central Mediterranean Sea). Mar. Biodivers. 2020, 50, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, O. Die Spongien des adriatischen Meeres; Wilhelm Engelmann: Leipzig, Germany, 1862; i–viii, 1–88, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Chelossi, E.; Pantile, R.; Pronzato, R.; Milanese, M.; Hentschel, U. Bacteria with Antimicrobial Properties Isolated from the Mediterranean Sponges Chondrilla nucula and Petrosia ficiformis. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2007, 49, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Prusina, I.; Sarà, G.; De Pirro, M.; Dong, Y.W.; Han, G.D.; Glamuzina, B.; Williams, G.A. Variations in Physiological Responses to Thermal Stress in Congeneric Limpets in the Mediterranean Sea. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2014, 456, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalto, V.; Bagarella, R.; Rinaldi, A.; Sarà, G.; Mirto, S. Thermal Adaptation and Physiological Responses to Environmental Stress in Tunicates. Aquat. Biol. 2017, 26, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsuwaiyan, N.; Vranken, S.; Filbee-Dexter, K.; Cambridge, M.; Coleman, M.; Wernberg, T. Genotypic Variation in Response to Extreme Events May Facilitate Kelp Adaptation under Future Climates. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2021, 672, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch-Belmar, M.; Giacoletti, A.; Giommi, C.; Girons, A.; Milisenda, G.; Sarà, G. Short-Term Exposure to Concurrent Biotic and Abiotic Stressors May Impair Farmed Molluscs Performance. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 179, 113724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobday, A.J.; Alexander, L.V.; Perkins, S.E.; Smale, D.A.; Straub, S.C.; Oliver, E.C.J.; Benthuysen, J.A.; Burrows, M.T.; Donat, M.G.; Feng, M.; et al. A Hierarchical Approach to Defining Marine Heatwaves. Prog. Ocean. 2016, 141, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juza, M.; Fernández-Mora, À.; Tintoré, J. Sub-Regional Marine Heat Waves in the Mediterranean Sea from Observations: Long-Term Surface Changes, Sub-Surface and Coastal Responses. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 785771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarà, G.; Palmeri, V.; Montalto, V.; Rinaldi, A.; Widdows, J. Parameterisation of Bivalve Functional Traits for Mechanistic Eco-Physiological Dynamic Energy Budget (DEB) Models. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2013, 480, 99–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.C.F.; Sarà, G.; Williams, G.A. Combined Effects of Thermal Conditions and Food Availability on Thermal Tolerance of the Marine Bivalve, Perna Viridis. J. Therm. Biol. 2018, 78, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch-Belmar, M.; Giommi, C.; Milisenda, G.; Abbruzzo, A.; Sarà, G. Integrating Functional Traits into Correlative Species Distribution Models to Investigate the Vulnerability of Marine Human Activities to Climate Change. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 799, 149351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarà, G.; Milisenda, G.; Mangano, M.C.; Bosch-belmar, M. The Buffer Effect of Canopy-Forming Algae on Vermetid Reefs’ Functioning: A Multiple Stressor Case Study. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 171, 112713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlan, J. The estimation of filtering rate from the clearance of suspensions. Mar. Biol. 1969, 2, 356–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, B. On the Comparison of Several Mean Values: An Alternative Approach. Biometrika 1951, 38, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Games, P.A.; Howell, J.F. Pairwise Multiple Comparison Procedures with Unequal N’s and/or Variances: A Monte Carlo Study. J. Educ. Behav. Stat. 1976, 1, 113–125. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, S.S.; Wilk, M.B. An Analysis of Variance Test for Normality (Complete Samples). Biometrika 1965, 52, 591–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levene, H. Robust Tests for Equality of Variances. In Contributions to Probability and Statistics; Olkin, I., Ed.; Stanford University Press: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1960; pp. 278–292. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cheshire, A.C.; Butler, A.; Westphalen, G.; Rowland, B.C.; Stevenson, J.; Wilkinson, C.R. Preliminary Study of the Distribution and Photophysiology of the Temperate Phototrophic Sponge Cymbastela sp. from South Australia. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1995, 46, 1211–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coma, R.; Ribes, M.; Gili, J.M.; Zabala, M. Seasonality of In Situ Respiration Rate in Three Temperate Benthic Suspension Feeders. Limnol. Ocean. 2002, 47, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beepat, S.S.; Davy, S.K.; Oakley, C.A.; Mashini, A.; Peng, L.; Bell, J.J. Increased cellular detoxification, cytoskeletal activities and protein transport explain physiological stress in a lagoon sponge. J. Exp. Biol. 2021, 224, jeb242820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riisgard, H.U.; Thomassen, S.; Jakobsen, H.; Weeks, J.M.; Larsen, P.S. Suspension Feeding in Marine Sponges Halichondria panicea and Haliclona urceolus: Effects of Temperature on Filtration Rate and Energy Cost of Pumping. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1993, 96, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribes, M.; Coma, R.; Gili, J.M. Natural Diet and Grazing Rate of the Temperate Sponge Dysidea Avara (Demospongiae, Dendroceratida) throughout an Annual Cycle. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 176, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerrodette, T.; Flechsig, A.O. Sediment-Induced Reduction in the Pumping Rate of the Tropical Sponge Verongia lacunosa. Mar. Biol. 1979, 55, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalan, S.; Ettinger-Epstein, P.; Battershill, C.; de Nys, R. Larval Vertical Migration and Hierarchical Selectivity of Settlement in a Brooding Marine Sponge. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 368, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Legentil, S.; Song, B.; McMurray, S.E.; Pawlik, J.R. Bleaching and Stress in Coral Reef Ecosystems: Hsp70 Expression by the Giant Barrel Sponge Xestospongia muta. Mol. Ecol. 2008, 17, 1840–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantile, R.; Webster, N. Strict Thermal Threshold Identified by Quantitative PCR in the Sponge Rhopaloeides Odorabile. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 431, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Camacho, J.M.; McCormack, G. Molecular Responses of Sponges to Climate Change. In Climate Change, Ocean Acidification and Sponges: Impacts Across Multiple Levels of Organization; Carballo, J.L., Bell, J.J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–452. ISBN 9783319590080. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, T.P.; Kerry, J.T.; Álvarez-Noriega, M.; Álvarez-Romero, J.G.; Anderson, K.D.; Baird, A.H.; Babcock, R.C.; Beger, M.; Bellwood, D.R.; Berkelmans, R.; et al. Global Warming and Recurrent Mass Bleaching of Corals. Nature 2017, 543, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, C.; Hadjioannou, L.; Petrou, A.; Nikolaidis, A.; Evriviadou, M.; Lange, M.A. Mortality of the Scleractinian Coral Cladocora Caespitosa during a Warming Event in the Levantine Sea (Cyprus). Reg. Environ. Chang. 2016, 16, 1963–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Aravena, M.; Kenny, N.J.; Osorio, M.; Font, A.; Riesgo, A.; Cárdenas, C.A. Warm Temperatures, Cool Sponges: The Effect of Increased Temperatures on the Antarctic Sponge Isodictya sp. PeerJ 2019, 7, e8088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, N.R.; Monk, J.; Soler, G.; Gallagher, P.; Barrett, N.S. Bleaching in Sponges on Temperate Mesophotic Reefs Observed Following Marine Heatwave Events. Clim. Chang. Ecol. 2022, 3, 100046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bosch-Belmar, M.; Milanese, M.; Sarà, A.; Mobilia, V.; Sarà, G. Effect of Acute Thermal Stress Exposure on Ecophysiological Traits of the Mediterranean Sponge Chondrilla nucula: Implications for Climate Change. Biology 2024, 13, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13010009
Bosch-Belmar M, Milanese M, Sarà A, Mobilia V, Sarà G. Effect of Acute Thermal Stress Exposure on Ecophysiological Traits of the Mediterranean Sponge Chondrilla nucula: Implications for Climate Change. Biology. 2024; 13(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleBosch-Belmar, Mar, Martina Milanese, Antonio Sarà, Valeria Mobilia, and Gianluca Sarà. 2024. "Effect of Acute Thermal Stress Exposure on Ecophysiological Traits of the Mediterranean Sponge Chondrilla nucula: Implications for Climate Change" Biology 13, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13010009
APA StyleBosch-Belmar, M., Milanese, M., Sarà, A., Mobilia, V., & Sarà, G. (2024). Effect of Acute Thermal Stress Exposure on Ecophysiological Traits of the Mediterranean Sponge Chondrilla nucula: Implications for Climate Change. Biology, 13(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13010009






