Bull Shark (Carcharhinus leucas) Occurrence along Beaches of South-Eastern Australia: Understanding Where, When and Why
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Shark Tagging and Acoustic Telemetry Data
2.2. Environmental Data
2.3. Statistical Analyses
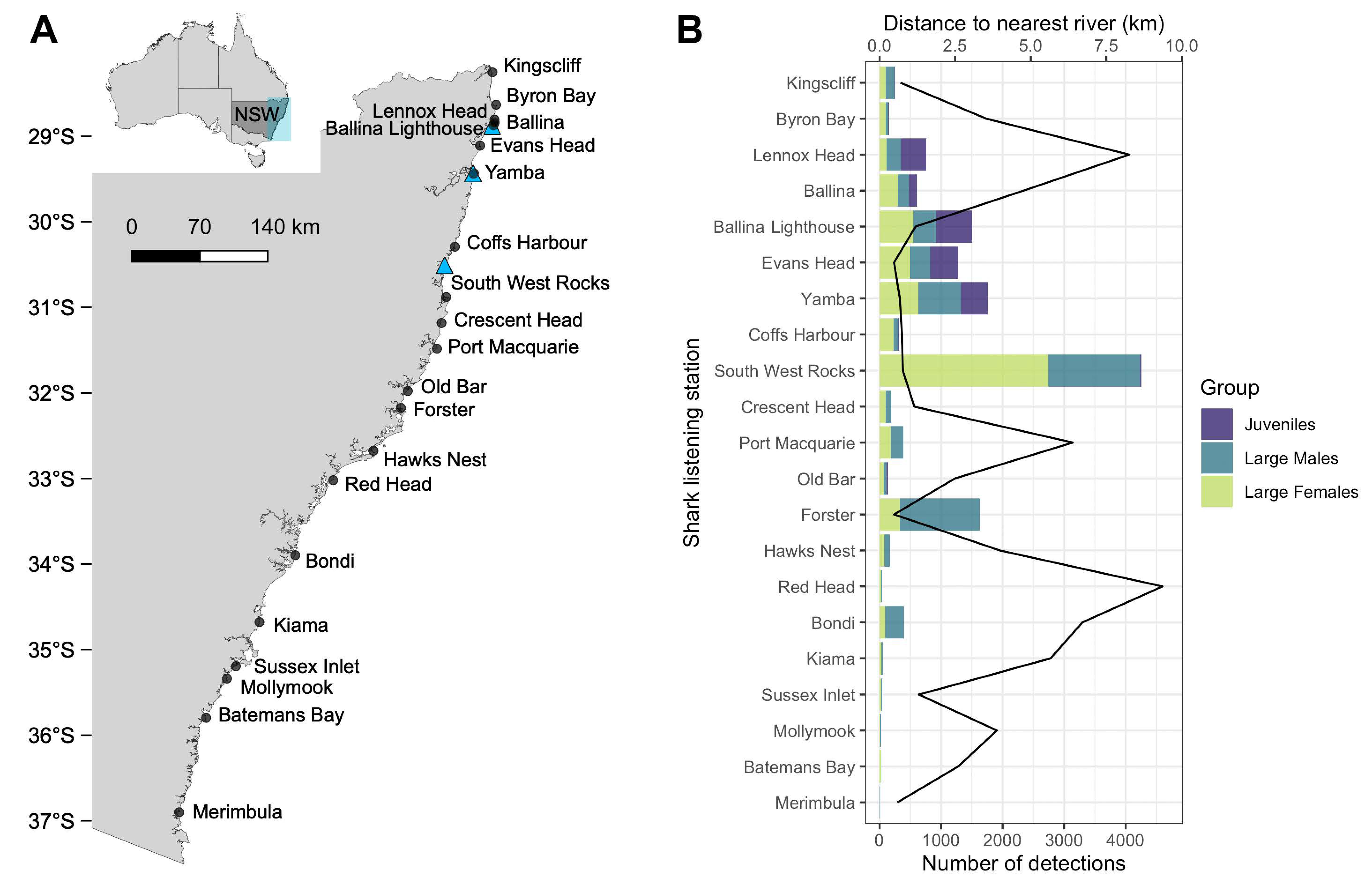
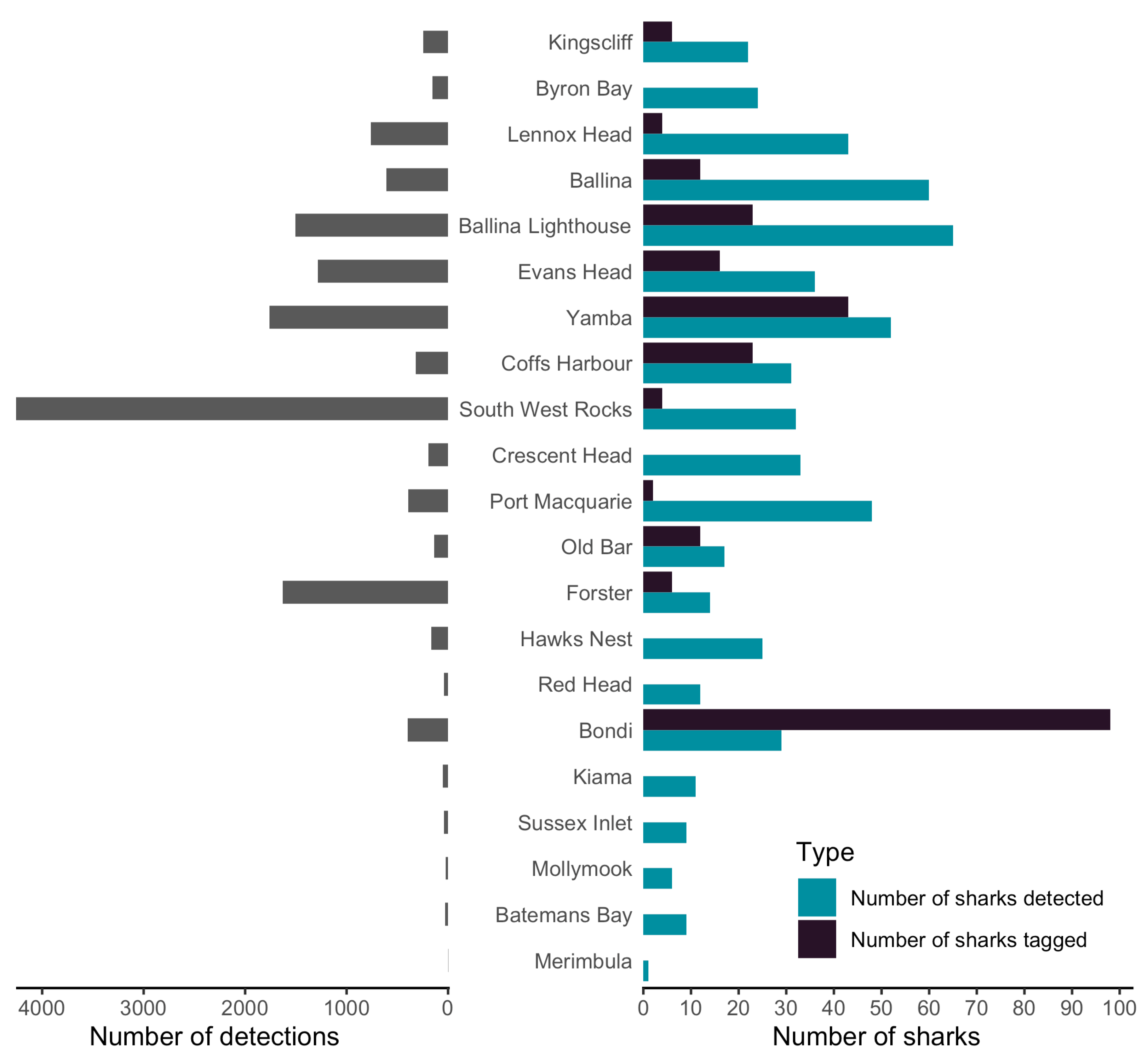
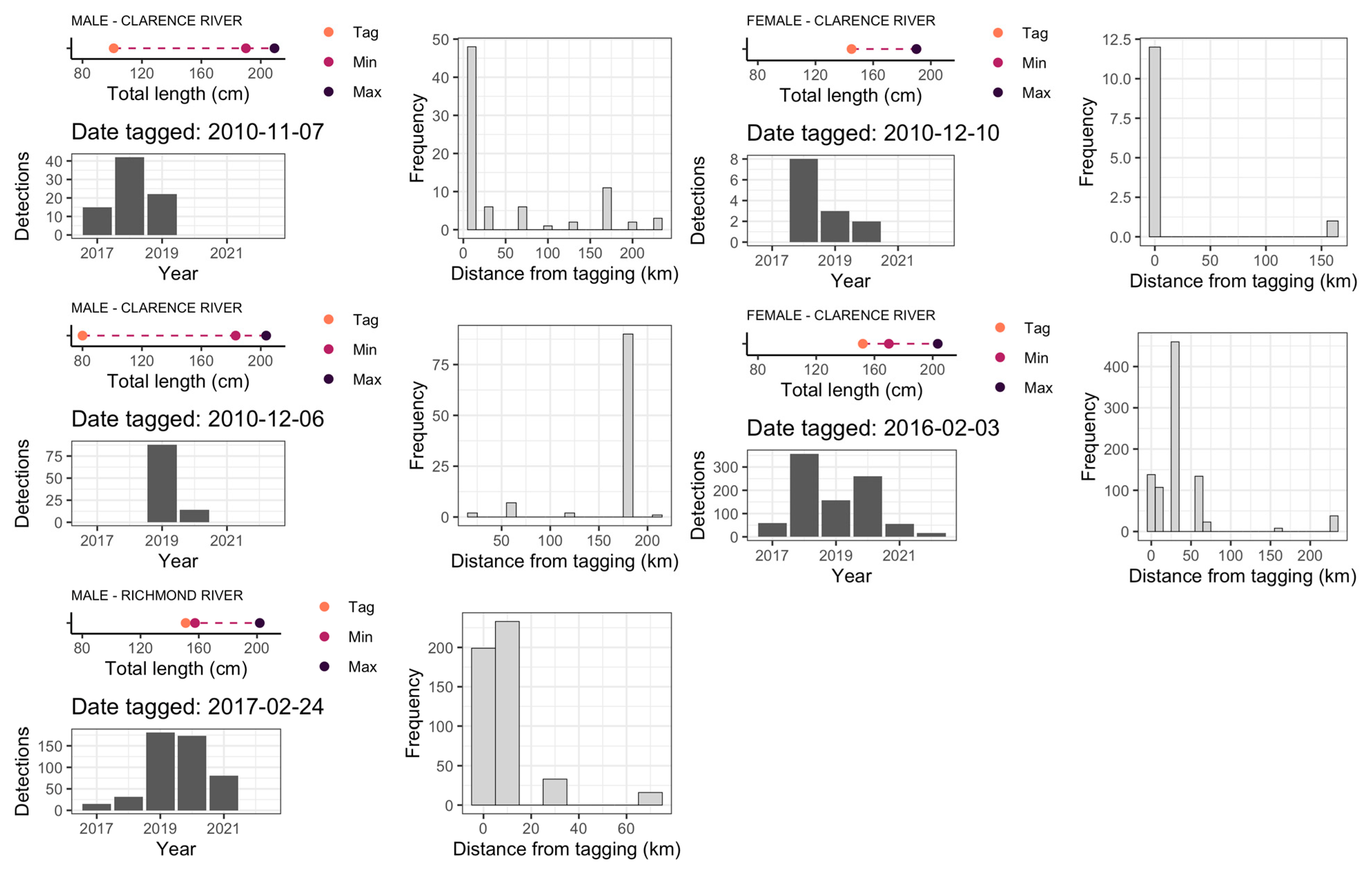
3. Results
3.1. Patterns of Bull Shark Occurrence
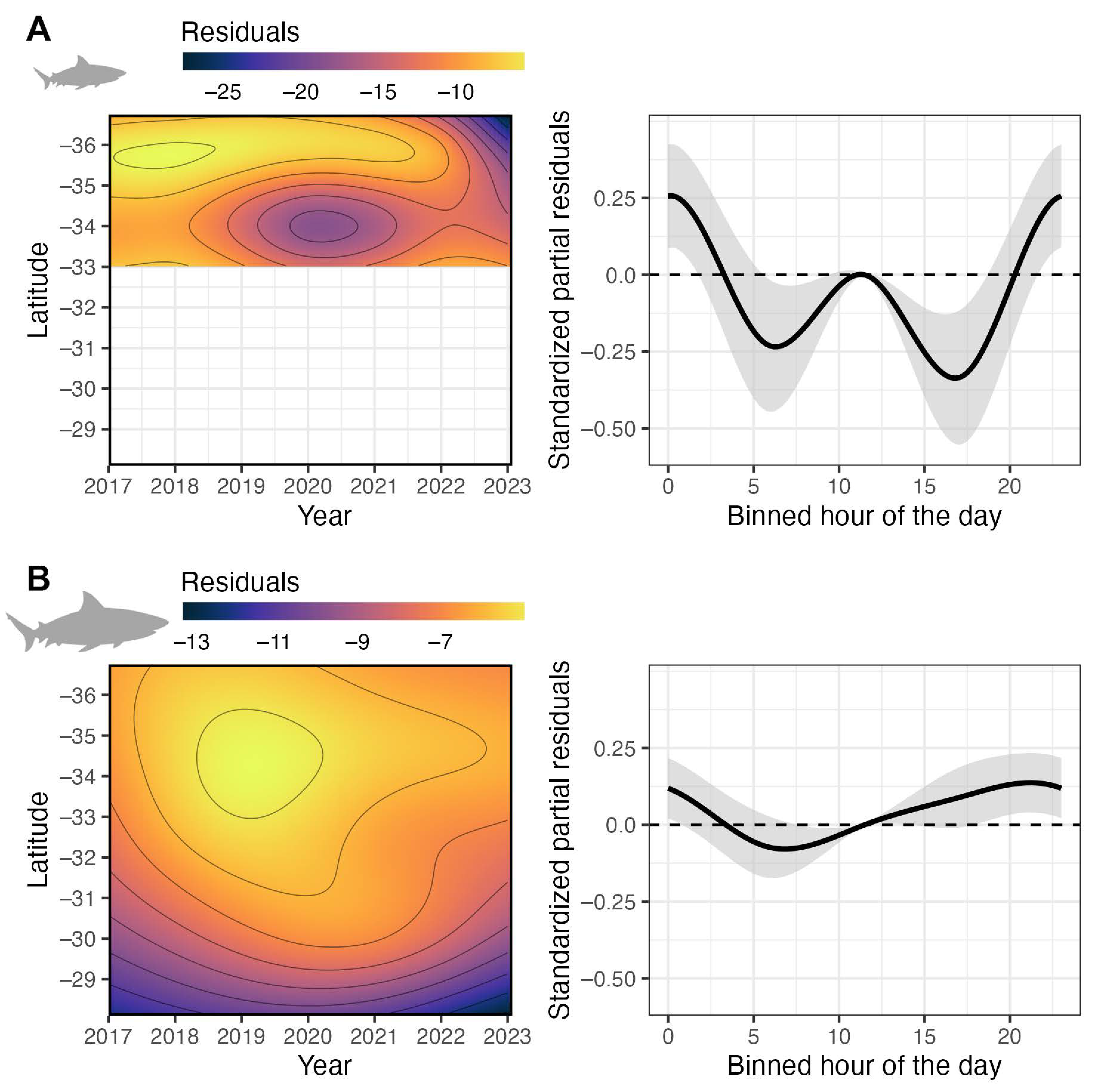
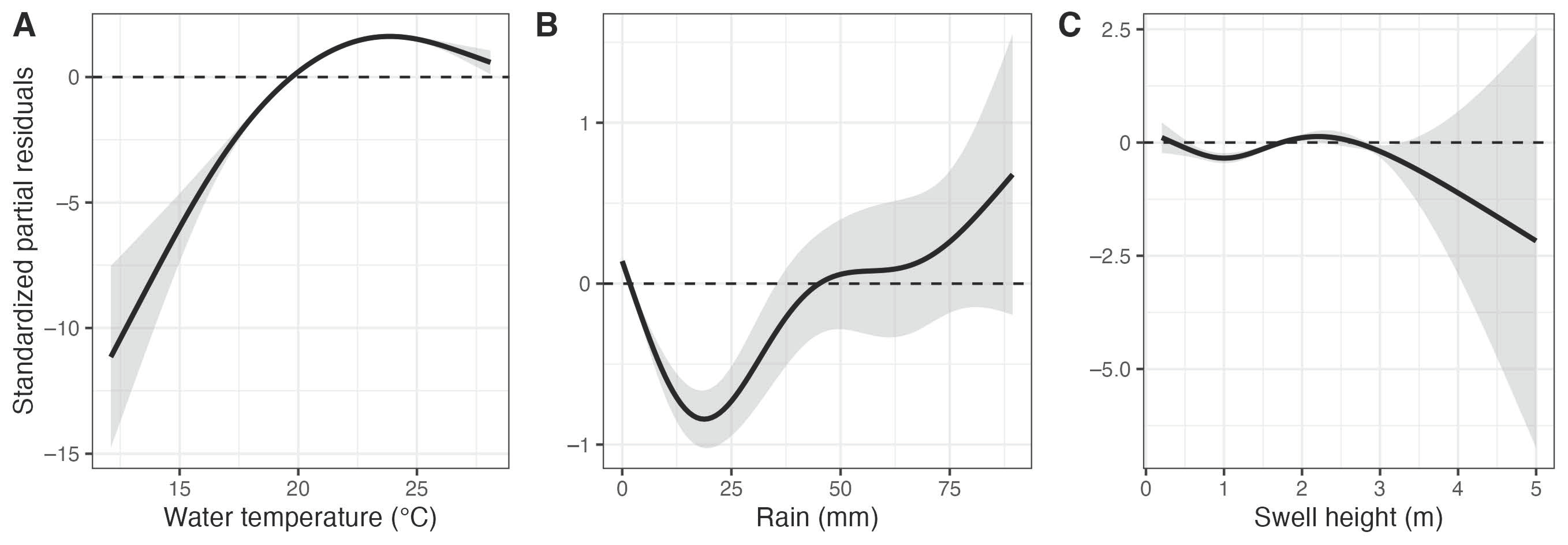
3.2. Drivers of Bull Shark Occurrence
4. Discussion
Implications for Management of Shark–Human Interactions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chapman, B.K.; McPhee, D. Global Shark Attack Hotspots: Identifying Underlying Factors behind Increased Unprovoked Shark Bite Incidence. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2016, 133, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPhee, D. Unprovoked Shark Bites: Are They Becoming More Prevalent? Coast. Manag. 2014, 42, 478–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, J.G. Changing Patterns of Shark Attacks in Australian Waters. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2011, 62, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagabrielle, E.; Allibert, A.; Kiszka, J.J.; Loiseau, N.; Kilfoil, J.P.; Lemahieu, A. Environmental and Anthropogenic Factors Affecting the Increasing Occurrence of Shark-Human Interactions around a Fast-Developing Indian Ocean Island. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, L.A.; Lynch, S.K.; Harcourt, R.; Slip, D.J.; Peddemors, V.; Everett, J.D.; Harrison, L.M.; Hart, N.S. Environmental Predictive Models for Shark Attacks in Australian Waters. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2019, 631, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midway, S.R.; Wagner, T.; Burgess, G.H. Trends in Global Shark Attacks. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardiman, N.; Burgin, S.; Shao, J. How Sharks and Shark-Human Interactions Are Reported in Major Australian Newspapers. Sustainblity 2020, 12, 2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.; Sumpton, W.; Ham, T. Fine-Scale Spatial and Seasonal Partitioning among Large Sharks and Other Elasmobranchs in South-Eastern Queensland, Australia. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2011, 62, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Reid, D.D.; Robbins, W.D.; Peddemors, V.M. Decadal Trends in Shark Catches and Effort from the New South Wales, Australia, Shark Meshing Program 1950–2010. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2011, 62, 676–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cliff, G.; Dudley, S.F.J. Reducing the Environmental Impact of Shark-Control Programs: A Case Study from KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2011, 62, 700–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colefax, A.P.; Butcher, P.A.; Kelaher, B.P. The Potential for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) to Conduct Marine Fauna Surveys in Place of Manned Aircraft. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2018, 75, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butcher, P.A.; Colefax, A.P.; Gorkin, R.A.; Kajiura, S.M.; López, N.A.; Mourier, J.; Purcell, C.R.; Skomal, G.B.; Tucker, J.P.; Walsh, A.J.; et al. The Drone Revolution of Shark Science: A Review. Drones 2021, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, R.D.; Kelaher, B.P.; Brand, C.P.; Cullis, B.R.; Gallen, C.R.; Smith, S.D.A.; Butcher, P.A. The Effectiveness of Shark-Management-Alert-in-Real-Time (SMART) Drumlines as a Tool for Catching White Sharks, Carcharodon Carcharias, off Coastal New South Wales, Australia. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2021, 28, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipscombe, R.S.; Scott, A.; Morris, S.; Peddemors, V.M.; Smoothey, A.F.; Butcher, P.A. The Influence of Bait Position on the Catch of Target and Non-Target Sharks in a SMART Drumline Bather Protection Program. Fish. Res. 2023, 257, 106501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huveneers, C.; Whitmarsh, S.; Thiele, M.; Meyer, L.; Fox, A.; Bradshaw, C.J.A. Effectiveness of Five Personal Shark-Bite Deterrents for Surfers. PeerJ 2018, 2018, e5554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, N.S.; Collin, S.P. Sharks Senses and Shark Repellents. Integr. Zool. 2015, 10, 38–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blount, C.; Pygas, D.; Lincoln Smith, M.P.; McPhee, D.P.; Bignell, C.; Ramsey, O. Effectiveness against White Sharks of the Rpela Personal Shark Deterrent Device Designed for Surfers. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2021, 29, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoothey, A.F.; Lee, K.A.; Peddemors, V.M. Long-Term Patterns of Abundance, Residency and Movements of Bull Sharks (Carcharhinus leucas) in Sydney Harbour, Australia. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niella, Y.; Smoothey, A.F.; Peddemors, V.; Harcourt, R. Predicting Changes in Distribution of a Large Coastal Shark in the Face of the Strengthening East Australian Current. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2020, 642, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.A.; Smoothey, A.F.; Harcourt, R.G.; Roughan, M.; Butcher, P.A.; Peddemors, V.M. Environmental Drivers of Abundance and Residency of a Large Migratory Shark, Carcharhinus leucas, Inshore of a Dynamic Western Boundary Current. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2019, 622, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, C.G.; Anderson, J.M.; Coffey, D.M.; Hutchinson, M.R.; Royer, M.A.; Holland, K.N. Habitat Geography around Hawaii’s Oceanic Islands Influences Tiger Shark (Galeocerdo cuvier) Spatial Behaviour and Shark Bite Risk at Ocean Recreation Sites. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipscombe, R.S.; Spaet, J.L.Y.; Scott, A.; Lam, C.H.; Brand, C.P.; Butcher, P.A. Habitat Use and Movement Patterns of Tiger Sharks (Galeocerdo cuvier) in Eastern Australian Waters. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2020, 77, 3127–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niella, Y.; Butcher, P.; Holmes, B.; Barnett, A.; Harcourt, R. Forecasting Intraspecific Changes in Distribution of a Wide-Ranging Marine Predator under Climate Change. Oecologia 2022, 198, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce, B.D.; Harasti, D.; Lee, K.; Gallen, C.; Bradford, R. Broad-Scale Movements of Juvenile White Sharks Carcharodon Carcharias in Eastern Australia from Acoustic and Satellite Telemetry. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2019, 619, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaet, J.L.Y.; Patterson, T.A.; Bradford, R.W.; Butcher, P.A. Spatiotemporal Distribution Patterns of Immature Australasian White Sharks (Carcharodon carcharias). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaet, J.L.Y.; Manica, A.; Brand, C.P.; Gallen, C.; Butcher, P.A. Environmental Conditions Are Poor Predictors of Immature White Shark Carcharodon Carcharias Occurrences on Coastal Beaches of Eastern Australia. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2020, 653, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.A.; Butcher, P.A.; Harcourt, R.G.; Patterson, T.A.; Peddemors, V.M.; Roughan, M.; Harasti, D.; Smoothey, A.F.; Bradford, R.W. Oceanographic Conditions Associated with White Shark (Carcharodon carcharias) Habitat Use along Eastern Australia. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2021, 659, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, A.; Fitzpatrick, R.; Bradley, M.; Miller, I.; Sheaves, M.; Chin, A.; Smith, B.; Diedrich, A.; Yick, J.L.; Lubitz, N.; et al. Scientific Response to a Cluster of Shark Bites. People Nat. 2022, 4, 963–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.L.; Curley, B.; Wolfenden, K.; Green, M.; Moltschaniwskyj, N.A. The Social Dimension to the New South Wales Shark Management Strategy, 2015–2020, Australia: Lessons Learned. Mar. Policy 2022, 141, 105079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, R.W.; Bruce, B.D.; Mcauley, R.B.; Robinson, G. An Evaluation of Passive Acoustic Monitoring Using Satellite Communication Technology for Near Real-Time Detection of Tagged Animals in a Marine Setting. Open Fish Sci. J. 2011, 4, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigby, C.L.; Espinoza, M.; Derrick, D.; Pacoureau, N.; Dicken, M. Carcharhinus leucas, The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2021: E.T39372A2910670. 2021. Available online: https://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2021-2.RLTS.T39372A2910670.en (accessed on 4 February 2022).
- Pirog, A.; Ravigné, V.; Fontaine, M.C.; Rieux, A.; Gilabert, A.; Cliff, G.; Clua, E.; Daly, R.; Heithaus, M.R.; Kiszka, J.J.; et al. Population Structure, Connectivity, and Demographic History of an Apex Marine Predator, the Bull Shark Carcharhinus leucas. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 12980–13000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Last, P.R.; Stevens, J.D. Sharks and Rays of Australia, 2nd ed.; CSIRO Publishing: Collingwood, VIC, Australia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Devloo-Delva, F.; Burridge, C.P.; Kyne, P.M.; Brunnschweiler, J.M.; Chapman, D.D.; Charvet, P.; Chen, X.; Cliff, G.; Daly, R.; Drymon, J.M.; et al. From Rivers to Ocean Basins: The Role of Ocean Barriers and Philopatry in the Genetic Structuring of a Cosmopolitan Coastal Predator. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 13, e9837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werry, J.M.; Lee, S.Y.; Lemckert, C.J.; Otway, N.M. Natural or Artificial? Habitat-Use by the Bull Shark, Carcharhinus leucas. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werry, J.M.; Lee, S.Y.; Otway, N.M.; Hu, Y.; Sumpton, W. A Multi-Faceted Approach for Quantifying the Estuarine nearshore Transition in the Life Cycle of the Bull Shark, Carcharhinus leucas. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2011, 62, 1421–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, M.; Heupel, M.R.; Tobin, A.J.; Simpfendorfer, C.A. Evidence of Partial Migration in a Large Coastal Predator: Opportunistic Foraging and Reproduction as Key Drivers? PLoS ONE 2016, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niella, Y.; Smoothey, A.F.; Taylor, M.D.; Peddemors, V.M.; Harcourt, R. Environmental Drivers of Fine-Scale Predator and Prey Spatial Dynamics in Sydney Harbour, Australia, and Adjacent Coastal Waters. Estuaries Coasts 2022, 45, 1465–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werry, J.M.; Sumpton, W.; Otway, N.M.; Lee, S.Y.; Haig, J.A.; Mayer, D.G. Rainfall and Sea Surface Temperature: Key Drivers for Occurrence of Bull Shark, Carcharhinus leucas, in Beach Areas. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2018, 15, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heupel, M.; Simpfendorfer, C.; Espinoza, M.; Smoothey, A.; Tobin, A.; Peddemors, V. Conservation Challenges of Sharks with Continental Scale Migrations. Front. Mar. Sci. 2015, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, M.; Lédée, E.J.I.; Smoothey, A.F.; Heupel, M.R.; Peddemors, V.M.; Tobin, A.J.; Simpfendorfer, C.A. Intra-Specific Variation in Movement and Habitat Connectivity of a Mobile Predator Revealed by Acoustic Telemetry and Network Analyses. Mar. Biol. 2021, 168, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haig, J.A.; Lambert, G.I.; Sumpton, W.D.; Mayer, D.G.; Werry, J.M. Habitat Features Influence Catch Rates of Near-Shore Bull Shark (Carcharhinus leucas) in the Queensland Shark Control Program, Australia 1996–2012. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 200, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoothey, A.F.; Gray, C.A.; Kennelly, S.J.; Masens, O.J.; Peddemors, V.M.; Robinson, W.A. Patterns of Occurrence of Sharks in Sydney Harbour, a Large Urbanised Estuary. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyomard, D.; Perry, C.; Tournoux, P.U.; Cliff, G.; Peddemors, V.; Jaquemet, S. An Innovative Fishing Gear to Enhance the Release of Non-Target Species in Coastal Shark-Control Programs: The SMART (Shark Management Alert in Real-Time) Drumline. Fish. Res. 2019, 216, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijmans, R.J. Geosphere: Spherical Trigonometry. 2021. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=geosphere (accessed on 16 November 2022).
- Lazaridis, E. Lunar: Lunar Phase & Distance, Seasons and Other Environmental Factors. Available online: http://statistics.lazaridis.eu (accessed on 1 February 2019).
- Hoenner, X.; Huveneers, C.; Steckenreuter, A.; Simpfendorfer, C.; Tattersall, K.; Jaine, F.; Atkins, N.; Babcock, R.; Brodie, S.; Burgess, J.; et al. Australia’s Continental-Scale Acoustic Tracking Database and Its Automated Quality Control Process. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niella, Y.; Raoult, V.; Gaston, T.; Goodman, K.; Harcourt, R.; Peddemors, V.; Smoothey, A.F. Reliance of Young Sharks on Threatened Estuarine Habitats for Nutrition Implies Susceptibility to Climate Change. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2022, 268, 107790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Martínez, A.; Chiappa-Carrara, X.; Arenas-Fuentes, V. Age and Growth of the Bull Shark, Carcharhinus leucas, from Southern Gulf of Mexico. J. North. Atl. Fish. Sci. 2005, 35, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.N. Generalized Additive Models: An Introduction with R, 2nd ed.; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Heupel, M.R.; Simpfendorfer, C.A. Movement and Distribution of Young Bull Sharks Carcharhinus leucas in a Variable Estuarine Environment. Aquat. Biol. 2008, 1, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heupel, M.R.; Yeiser, B.G.; Collins, A.B.; Ortega, L.; Simpfendorfer, C.A. Long-Term Presence and Movement Patterns of Juvenile Bull Sharks, Carcharhinus leucas, in an Estuarine River System. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2010, 61, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matich, P.; Heithaus, M.R. Individual Variation in Ontogenetic Niche Shifts in Habitat Use and Movement Patterns of a Large Estuarine Predator (Carcharhinus leucas). Oecologia 2015, 178, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardeñosa, D.; Glaus, K.B.J.; Brunnschweiler, J.M. Occurrence of Juvenile Bull Sharks (Carcharhinus leucas) in the Navua River in Fiji. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2017, 68, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, R.G.; Campbell, H.A.; Cramp, R.L.; Burke, C.L.; Micheli-Campbell, M.A.; Pillans, R.D.; Lyon, B.J.; Franklin, C.E. Niche Partitioning between River Shark Species Is Driven by Seasonal Fluctuations in Environmental Salinity. Funct. Ecol. 2020, 34, 2170–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillans, R.D.; Fry, G.C.; Steven, A.D.L.; Patterson, T. Environmental Influences on Long-Term Movement Patterns of a Euryhaline Elasmobranch (Carcharhinus leucas) within a Subtropical Estuary. Estuaries Coasts 2020, 43, 2152–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, M.L.; McCallister, M.; Brewster, L.R.; Bangley, C.W.; Curtis, T.H.; Ogburn, M.B.; Ajemian, M.J. Multi-Year Assessment of Immature Bull Shark Carcharhinus leucas Residency and Activity Spaces in an Expansive Estuarine Nursery. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2022, 695, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, T.H.; Adams, D.H.; Burgess, G.H. Seasonal Distribution and Habitat Associations of Bull Sharks in the Indian River Lagoon, Florida: A 30-Year Synthesis. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2011, 140, 1213–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heithaus, M.R.; Delius, B.K.; Wirsing, A.J.; Dunphy-Daly, M.M. Physical Factors Influencing the Distribution of a Top Predator in a Subtropical Oligotrophic Estuary. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heupel, M.R.; Simpfendorfer, C.A. Estuarine Nursery Areas Provide a Low-Mortality Environment for Young Bull Sharks Carcharhinus leucas. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 433, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heupel, M.R.; Carlson, J.K.; Simpfendorfer, C.A. Shark Nursery Areas: Concepts, Definition, Characterization and Assumptions. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 337, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, K.; Niella, Y.; Bliss-Henaghan, T.; Harcourt, R.; Smoothey, A.F.; Peddemors, V.M. Ontogenetic Changes in the Tooth Morphology of Bull Sharks (Carcharhinus leucas). J. Fish. Biol. 2022, 101, 1033–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudley, S.F.J. Shark Nets in KwaZulu-Natal—An Evaluation of Catches and Alternatives. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Tillett, J.; Meekan, M.G.; Field, I.C.; Thorburn, D.C.; Ovenden, J.R. Evidence for Reproductive Philopatry in the Bull Shark Carcharhinus leucas. J. Fish. Biol. 2012, 80, 2140–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangley, C.W.; Paramore, L.; Shiffman, D.S.; Rulifson, R.A. Increased Abundance and Nursery Habitat Use of the Bull Shark (Carcharhinus leucas) in Response to a Changing Environment in a Warm-Temperate Estuary. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Cai, W.; Zhang, L.; Nakamura, H.; Timmermann, A.; Joyce, T.; McPhaden, M.J.; Alexander, M.; Qiu, B.; Visbeck, M.; et al. Enhanced Warming over the Global Subtropical Western Boundary Currents. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetina-Heredia, P.; Roughan, M.; Van Sebille, E.; Coleman, M.A. Long-Term Trends in the East Australian Current Separation Latitude and Eddy Driven Transport. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2014, 119, 4351–4366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, D.D.; Feldheim, K.A.; Papastamatiou, Y.P.; Hueter, R.E. There and Back Again: A Review of Residency and Return Migrations in Sharks, with Implications for Population Structure and Management. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2015, 7, 547–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, J.D.; Bester-van der Merwe, A.E.; Dicken, M.L.; Mmonwa, K.L.; Teske, P.R. Reproductive Philopatry in a Coastal Shark Drives Age-Related Population Structure. Mar. Biol. 2019, 166, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, H.L., Jr.; Pratt, T.C.; Knotek, R.J.; Carrier, J.C.; Whitney, N.M. Long-Term Use of a Shark Breeding Ground: Three Decades of Mating Site in the Nurse Shark, Ginglymostoma Cirratum. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0275323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, A.; Abrantes, K.G.; Stevens, J.D.; Semmens, J.M. Site Fidelity and Sex-Specific Migration in a Mobile Apex Predator: Implications for Conservation and Ecosystem Dynamics. Anim. Behav. 2011, 81, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lea, J.S.E.; Humphries, N.E.; Clarke, C.R.; Sims, D.W. To Madagascar and Back: Long-Distance, Return Migration across Open Ocean by a Pregnant Female Bull Shark Carcharhinus leucas. J. Fish. Biol. 2015, 87, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubitz, N.; Daly, R.; Filmalter, J.D.; Sheaves, M.; Cowley, P.D.; Naesje, T.F.; Barnett, A. Context Drives Movement Patterns in a Mobile Marine Predator. Mov. Ecol. 2023, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papastamatiou, Y.P.; Meyer, C.G.; Carvalho, F.; Dale, J.J.; Hutchinson, M.R.; Holland, K.N. Telemetry and Random-Walk Models Reveal Complex Patterns of Partial Migration in a Large Marine Predator. Ecology 2013, 94, 2595–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, R.; Smale, M.J.; Cowley, P.D.; Froneman, P.W. Residency Patterns and Migration Dynamics of Adult Bull Sharks (Carcharhinus leucas) on the East Coast of Southern Africa. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e0109357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, N.L.; Meyer, C.G.; Smith, J.A.; Houghton, J.D.R.; Barnett, A.; Holmes, B.J.; Nakamura, I.; Papastamatiou, Y.P.; Royer, M.A.; Coffey, D.M.; et al. Combining Abundance and Performance Data Reveals How Temperature Regulates Coastal Occurrences and Activity of a Roaming Apex Predator. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 1884–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammerschlag, N.; McDonnell, L.H.; Rider, M.J.; Street, G.M.; Hazen, E.L.; Natanson, L.J.; McCandless, C.T.; Boudreau, M.R.; Gallagher, A.J.; Pinsky, M.L.; et al. Ocean Warming Alters the Distributional Range, Migratory Timing, and Spatial Protections of an Apex Predator, the Tiger Shark (Galeocerdo cuvier). Glob. Chang. Biol. 2022, 28, 1990–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteforte, K.I.P.; Butcher, P.A.; Morris, S.G.; Kelaher, B.P. The Relative Abundance and Occurrence of Sharks off Ocean Beaches of New South Wales, Australia. Biology 2022, 11, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cliff, G. Shark Attacks on the South African Coast between 1960 and 1990. S. Afr. J. Sci. 1991, 87, 513–518. [Google Scholar]
- Kock, A.A.; Photopoulou, T.; Durbach, I.; Mauff, K.; Meÿer, M.; Kotze, D.; Griffiths, C.L.; O’Riain, M.J. Summer at the Beach: Spatio-Temporal Patterns of White Shark Occurrence along the Inshore Areas of False Bay, South Africa. Mov. Ecol. 2018, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunnschweiler, J.M.; Queiroz, N.; Sims, D.W. Oceans Apart? Short-term Movements and Behaviour of Adult Bull Sharks Carcharhinus leucas in Atlantic and Pacific Oceans Determined from Pop-off Satellite Archival Tagging. J. Fish. Biol. 2010, 77, 1343–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, J.K.; Ribera, M.M.; Conrath, C.L.; Heupel, M.R.; Burgess, G.H. Habitat Use and Movement Patterns of Bull Sharks Carcharhinus leucas Determined Using Pop-up Satellite Archival Tags. J. Fish. Biol. 2010, 77, 661–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dicken, M.L.; Booth, A.J.; Smale, M.J. Preliminary Observations of Tag Shedding, Tag Reporting, Tag Wounds, and Tag Biofouling for Raggedtooth Sharks (Carcharias taurus) Tagged off the East Coast of South Africa. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2006, 63, 1640–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
| Group | Variable | Source | Spline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spatio-temporal | Latitude (°) | Global Positioning System | Cubic-regression |
| Binned hour of the day—Hour (h) | AEST/AEDT | Cyclic-cubic-regression | |
| Month | Calendar | Cyclic-cubic-regression | |
| Environmental | Daily rainfall—Rain (mm) | Australian Bureau of Meteorology | Cubic-regression |
| Lunar phase—Moon | R package ‘lunar’ | Cyclic-cubic-regression | |
| Swell height—Height (m) | Manly Hydraulics Laboratory, NSW, Australia | Cubic-regression | |
| Tidal height—Tide (m) | Manly Hydraulics Laboratory, NSW, Australia | Cubic-regression | |
| Water temperature—Temperature (°C) | Sentinel tags | Cubic-regression |
| Group | Variable | Edf. | Ref.df. | χ2 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Juvenile | Latitude × Year | 13.76 | 13.98 | 1096.77 | <0.001 |
| Hour | 2.82 | 3.00 | 28.76 | <0.001 | |
| Adult | Latitude × Year | 13.35 | 13.90 | 1295.95 | <0.001 |
| Hour | 2.29 | 3.00 | 17.57 | <0.001 |
| Variable | Type | Edf. | Ref.df. | χ2 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temp | Fixed | 3.71 | 3.92 | 1804.69 | <0.001 |
| Rain | Fixed | 3.69 | 3.94 | 94.47 | <0.001 |
| Height | Fixed | 3.16 | 3.45 | 38.96 | <0.001 |
| Year | Random | <0.01 | 1.00 | <0.01 | 0.406 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smoothey, A.F.; Niella, Y.; Brand, C.; Peddemors, V.M.; Butcher, P.A. Bull Shark (Carcharhinus leucas) Occurrence along Beaches of South-Eastern Australia: Understanding Where, When and Why. Biology 2023, 12, 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091189
Smoothey AF, Niella Y, Brand C, Peddemors VM, Butcher PA. Bull Shark (Carcharhinus leucas) Occurrence along Beaches of South-Eastern Australia: Understanding Where, When and Why. Biology. 2023; 12(9):1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091189
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmoothey, Amy F., Yuri Niella, Craig Brand, Victor M. Peddemors, and Paul A. Butcher. 2023. "Bull Shark (Carcharhinus leucas) Occurrence along Beaches of South-Eastern Australia: Understanding Where, When and Why" Biology 12, no. 9: 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091189
APA StyleSmoothey, A. F., Niella, Y., Brand, C., Peddemors, V. M., & Butcher, P. A. (2023). Bull Shark (Carcharhinus leucas) Occurrence along Beaches of South-Eastern Australia: Understanding Where, When and Why. Biology, 12(9), 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12091189






