The Association of the Levels of High-Density Lipoprotein and Apolipoprotein A1 with SARS-CoV-2 Infection and COVID-19 Severity: An Analysis of the N3C Database
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Data and Data Sources
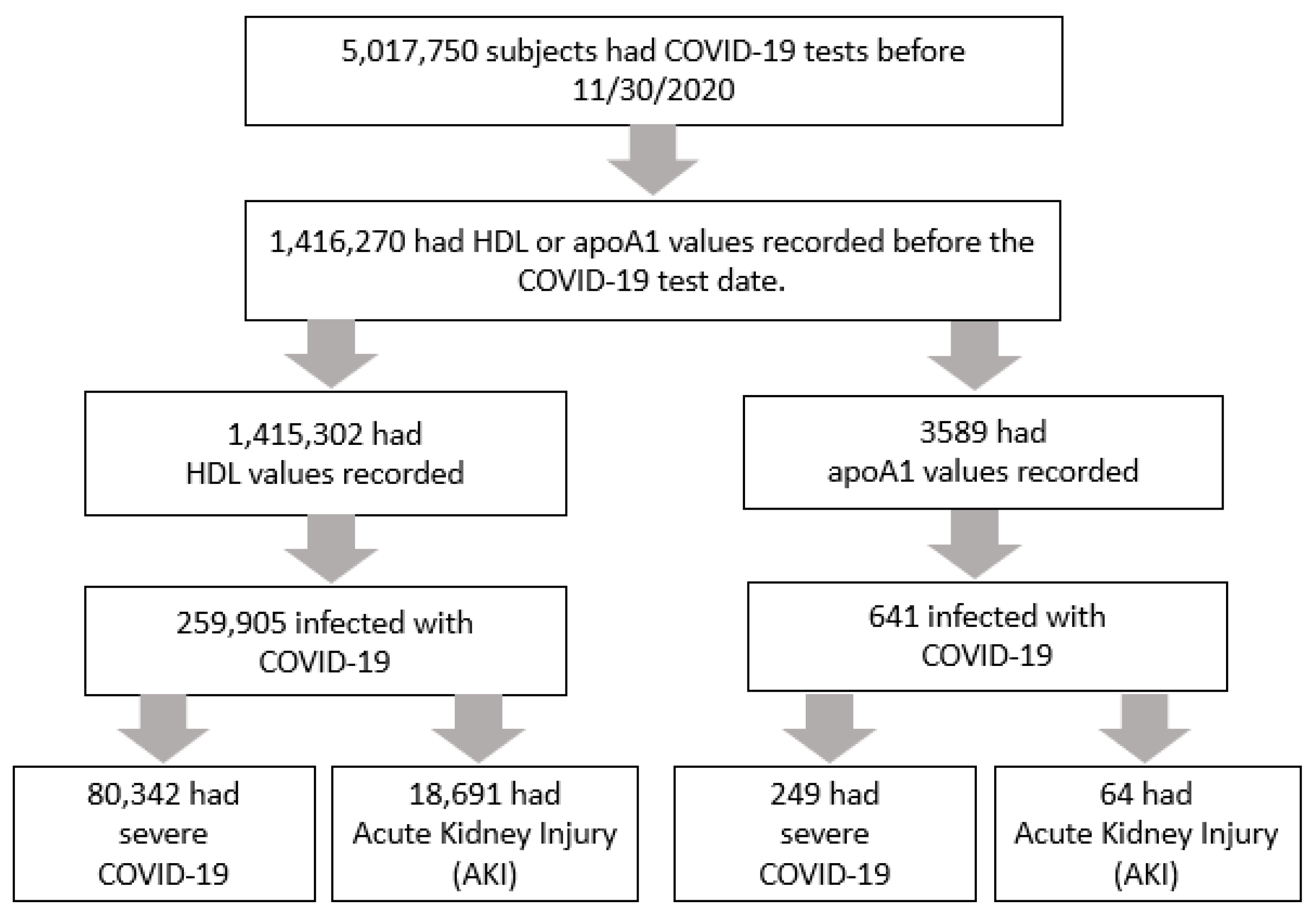
2.2. Population and Variables
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. SARS-CoV-2 Infection
3.2. SAR-CoV-2 Severity
3.3. Development of AKI
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Variable | Measure | Value |
|---|---|---|
| HDL | OMOP Concept ID | 3007070 |
| APOA1 | OMOP Concept ID | 37024265 |
| Acute Kidney Injury | ICD-10 | N17.0, N17.1, N17.2, N17.8, N17.9 |
| Pregnancy | OMOP Concept ID | 4218813, 4239938, 4244438 |
| Smoking | OMOP Concept ID | 4298794, 44789712, 4269997, 4190573, 4046886, 40486696, 4216174, 4052948, 40486518 |
| Obesity | OMOP Concept ID | 4215968, 438731, 4216214, 437525 |
| Hypertension | OMOP Concept ID | 316866, 4071202, 42709887 |
| Diabetes Complicated | OMOP Concept ID | Include: 442793, 44793113, 4096041, 45772060, 4321756, 36715417, 45769832, 43531616, 4096671, 4096670, 37204818, 40482883, 4265913 Exclude: 4034964, 42536605, 43531597, 37016350, 45769875, 42538715, 4082347, 37311673, 45757363, 4033942, 44789319 |
| Diabetes not Complicated | OMOP Concept ID | Include: 201820 Exclude: 192279, 43531616, 44793113, 442793, 44805490, 44812346, 36715417, 42535539, 4099651 |
| Cerebrovascular Disease | OMOP Concept ID | 381591, 434056 |
| Chronic Lung Disease | OMOP Concept ID | Include: 4027836, 4050877, 4121621, 4120270, 37116690, 37309675, 317009, 4283942, 42537657, 45763749, 257775, 4230358, 4148529, 45767051, 258780, 261889, 37311779, 255059, 4233477, 4052549, 42536541, 40482019, 437313, 4322024, 255841, 45768983, 40480461, 438791, 44782927, 4204998, 4232302, 45768892, 40483342, 37311903, 441267, 45769020, 4103099, 4105601, 256449, 762964, 4197819, 45769386, 45768915, 4341520, 3655634, 4052553, 4071743, 438782, 4138307, 4273378, 37116655, 4172303, 42537658, 4112813, 4306635, 4174275, 4084955, 4232485, 765431, 45769019, 36674196, 44810118, 45772934, 4141669, 4203619, 255573, 4137505, 4102140, 4144583, 45768987, 4500876, 3655347, 45771017, 4270139, 4078695, 4110637, 45771019, 44805713, 4028118, 42539687, 45769146, 44802278, 4119786, 4116317, 4052550, 36715501, 3655969, 4186898, 46272927, 4140605, 46273640, 45768996, 4052548, 4173466, 4173466, 4050874, 4309350, 46270493 Exclude: 4198434, 43020840, 44782989, 4337510 |
| Congestive Heart Failure | OMOP Concept ID | 319835 |
| Heart Failure | OMOP Concept ID | Include: 316139, 4236658, 321319 Exclude: 43020893 |
| Hemiplegia | OMOP Concept ID | 43531638, 43531639 |
| HIV | OMOP Concept ID | 439727 |
| Dementia | OMOP Concept ID | 4182210, 4236296, 4250118, 4233045, 4236297 |
| Depression | OMOP Concept ID | Include: 4327217, 440383, 4298317 Exclude: 4224940, 436665 |
| ESRD | OMOP Concept ID | 193782, 45769906, 4782717, 46273164, 4030520, 4128200, 37018886, 43020455, 43021864, 45769904, 762973 |
| Transplant | OMOP Concept ID | Include: 42538119, 42898004, 2741982, 42897987, 42897992, 2727298, 42898011, 42538117, 4287985, 42539502, 4121274, 2741697, 2741958, 42898007, 42537745, 2741961, 42897991, 42898012, 2741964, 2727190, 1524123, 2741979, 42897988, 42898008, 42898009, 4127554, 42898006, 2741970, 2750767, 1524124, 4341658, 42897993, 4208341, 42898003, 42538118, 2752914, 1524116, 44791468, 42898005, 1524118, 42897986, 2741973, 4121617, 1524122, 1524117, 2741976, 2774520, 42897990, 42539698, 42537742, 2774519, 42897989, 2774517, 2750764, 2774522 Exclude: 4265621, 44810212 |
| Cholesterol Drug | Drug Name | Niacin/nicotinic acid (Niacor, Nicobid, Nicolar, Niaspan), Gemfibrozil (Lopid), Fenofibrate (Tricor), Clofibrate (Atromid-S), Atorvastatin (Lipitor), Simvastatin (Zocor), Prevastatin (Pravachol), Lovastatin (Mevacor), Fluvastatin (Lescol), Rosuvastatin (Crestor), Pitavastatin (Livalo) |
| Diabetes Drug | Drug Name | Repaglinide (Prandin), Nateglinide (Starlix), Glipizide (Glucotrol XL), Glimepiride (Amaryl), Glyburide (DiaBeta, Glynase), Saxagliptin (Onglyza), Sitagliptin (Januvia), Linagliptin (Tradjenta), Alogliptin (Nesina), Metformin (Fortamet, Glumetza, others), Rosiglitazone (Avandia), Pioglitazone (Actos), Acarbose (Precose), Miglitol (Glyset), Canagliflozin (Invokana), Dapagliflozin (Farxiga), Empagliflozin (Jardiance), Ertugliflozin (Steglatro), Colesevelam (Welchol), Pramlintide (Symlin), Dulaglutide (Trulicity), Exenatide (Byetta, Bydureon Bcise), Liraglutide (Saxenda, Victoza), Lixisenatide (Adlyxin), Semaglutide (Ozempic, Rybelsus, Wegovy) |
Appendix B
- Disclaimer
- 2.
- IRB
- 3.
- Individual Acknowledgements for Core Contributors
- 4.
- Data Partners with Released Data
References
- Havel, R.J.; Eder, H.A.; Bragdon, J.H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J. Clin. Investig. 1955, 34, 1345–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, C.; Ramos, A. Lipids, lipoproteins, and apoproteins in serum during infection. Clin. Chem. 1986, 32, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontush, A.; Chapman, M.J. Functionally Defective High-Density Lipoprotein: A New Therapeutic Target at the Crossroads of Dyslipidemia, Inflammation, and Atherosclerosis. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 342–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, W.S.; Shah, A.S. High-Density Lipoprotein Subspecies in Health and Human Disease: Focus on Type 2 Diabetes. Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc. J. 2019, 15, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ference, B.A.; Ginsberg, H.N.; Graham, I.; Ray, K.K.; Packard, C.J.; Bruckert, E.; Hegele, R.A.; Krauss, R.M.; Raal, F.J.; Schunkert, H.; et al. Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. 1. Evidence from genetic, epidemiologic, and clinical studies. A consensus statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 2459–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Chen, D.; Wu, L.; He, G.; Ye, W. Declined serum high density lipoprotein cholesterol is associated with the severity of COVID-19 infection. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 510, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, S.; De Tymowski, C.; Assadi, M.; Zappella, N.; Jean-Baptiste, S.; Robert, T.; Peoc’h, K.; Lortat-Jacob, B.; Fontaine, L.; Bouzid, D.; et al. Lipoprotein concentrations over time in the intensive care unit COVID-19 patients: Results from the ApoCOVID study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239573. [Google Scholar]
- Scalsky, R.J.; Chen, Y.-J.; Desai, K.; O’Connell, J.R.; Perry, J.A.; Hong, C.C. Baseline cardiometabolic profiles and SARS-CoV-2 infection in the UK Biobank. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248602. [Google Scholar]
- Hilser, J.R.; Han, Y.; Biswas, S.; Gukasyan, J.; Cai, Z.; Zhu, R.; Tang, W.H.W.; Deb, A.; Lusis, A.J.; Hartiala, J.A.; et al. Association of serum HDL-cholesterol and apolipoprotein A1 levels with risk of severe SARS-CoV-2 infection. J. Lipid Res. 2021, 62, 100061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidambaram, V.; Kumar, A.; Majella, M.G.; Seth, B.; Sivakumar, R.K.; Voruganti, D.; Bavineni, M.; Baghal, A.; Gates, K.; Kumari, A.; et al. HDL cholesterol levels and susceptibility to COVID-19. EBioMedicine 2022, 82, 104166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masana, L.; Correig, E.; Ibarretxe, D.; Anoro, E.; Arroyo, J.A.; Jericó, C.; Guerrero, C.; Miret, M.; Näf, S.; Pardo, A.; et al. Low HDL and high triglycerides predict COVID-19 severity. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, X.; Dong, H.; Wu, C.; Wu, F.; Yu, B.; Lv, J.; Zhang, S.; Wu, G.; et al. Low high-density lipoprotein level is correlated with the severity of COVID-19 patients: An observational study. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afonso, C.B.; Spickett, C.M. Lipoproteins as targets and markers of lipoxidation. Redox Biol. 2019, 23, 101066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-W.; Huang, H.-C.; Chiang, H.-Y.; Chung, C.-W.; Chang, S.-N.; Chu, P.-L.; Kuo, C.-C. Longitudinal lipid trends and adverse outcomes in patients with CKD: A 13-year observational cohort study [S]. J. Lipid Res. 2019, 60, 648–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goek, O.-N.; Köttgen, A.; Hoogeveen, R.C.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Coresh, J.; Astor, B.C. Association of apolipoprotein A1 and B with kidney function and chronic kidney disease in two multiethnic population samples. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 2839–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Shi, S.; Zhao, X.-J.; Wang, J.-K.; Liu, Z.-W.; Liu, F.-Q.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, S.-M.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, S. Association Between the Lipid Profile and Renal Dysfunction in the Heart Failure Patients. KBR 2019, 44, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradi, H.; Pahl, M.V.; Elahimehr, R.; Vaziri, N.D. Impaired antioxidant activity of high-density lipoprotein in chronic kidney disease. Transl. Res. 2009, 153, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zewinger, S.; Speer, T.; Kleber, M.E.; Scharnagl, H.; Woitas, R.; Lepper, P.M.; Pfahler, K.; Seiler, S.; Heine, G.H.; März, W.; et al. HDL Cholesterol Is Not Associated with Lower Mortality in Patients with Kidney Dysfunction. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imam, Z.; Odish, F.; Gill, I.; O’Connor, D.; Armstrong, J.; Vanood, A.; Ibironke, O.; Hanna, A.; Ranski, A.; Halalau, A. Older age and comorbidity are independent mortality predictors in a large cohort of 1305 COVID-19 patients in Michigan, United States. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 288, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, L.E. High-Density Lipoproteins and Acute Kidney Injury. Semin. Nephrol. 2020, 40, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, M.C.; Dhadly, P.; Cockerill, G.W.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Mota-Filipe, H.; Hinds, C.J.; Miller, N.E.; Thiemermann, C. Reconstituted High-Density Lipoprotein Attenuates Organ Injury and Adhesion Molecule Expression in a Rodent Model of Endotoxic Shock. Shock 2003, 20, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Deng, J.; Li, J.; Wu, C.; Dong, H.; Wu, S.; Zhong, Y. The Role of High-Density Lipoprotein in COVID-19. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 720283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coutinho, A.E.; Chapman, K.E. The anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects of glucocorticoids, recent developments and mechanistic insights. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2011, 335, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alessi, J.; de Oliveira, G.B.; Schaan, B.D.; Telo, G.H. Dexamethasone in the era of COVID-19: Friend or foe? An essay on the effects of dexamethasone and the potential risks of its inadvertent use in patients with diabetes. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2020, 12, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, A.; Mañá, J.; Pintó, X.; Argimón, J.M.; Hurtado, I.; Pujol, R. Corticosteroid therapy increases HDL-cholesterol concentrations in patients with active sarcoidosis and hypoalphalipoproteinemia. Clin. Chim. Acta 2002, 320, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atik, N.; Hayati, R.U.; Hamijoyo, L. Correlation between Steroid Therapy and Lipid Profile in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients. Open Access Rheumatol. 2020, 12, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, F.M.; Jensen, M.K. From High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol to Measurements of Function: Prospects for the Development of Tests for High-Density Lipoprotein Functionality in Cardiovascular Disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Steeg, W.A.; Holme, I.; Boekholdt, S.M.; Larsen, M.L.; Lindahl, C.; Stroes, E.S.G.; Tikkanen, M.J.; Wareham, N.J.; Faergeman, O.; Olsson, A.G.; et al. High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol, High-Density Lipoprotein Particle Size, and Apolipoprotein A-I: Significance for Cardiovascular Risk. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 51, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackey, K.; Ayers, C.K.; Kondo, K.K.; Saha, S.; Advani, S.M.; Young, S.; Spencer, H.; Rusek, M.; Anderson, J.; Veazie, S.; et al. Racial and Ethnic Disparities in COVID-19–Related Infections, Hospitalizations, and Deaths: A Systematic Review. Ann. Intern. Med. 2021, 174, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinkuolie, A.O.; Paynter, N.P.; Padmanabhan, L.; Mora, S. High-Density Lipoprotein Particle Subclass Heterogeneity and Incident Coronary Heart Disease. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2014, 7, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohatgi, A.; Khera, A.; Berry, J.D.; Givens, E.G.; Ayers, C.R.; Wedin, K.E.; Neeland, I.J.; Yuhanna, I.S.; Rader, D.R.; De Lemos, J.A.; et al. HDL Cholesterol Efflux Capacity and Incident Cardiovascular Events. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2383–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xu, Y.; Gao, R.; Lu, R.; Han, K.; Wu, G.; Tan, W. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Different Types of Clinical Specimens. JAMA 2020, 323, 1843–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, B.E.; Ong, S.W.X.; Kalimuddin, S.; Low, J.G.; Tan, S.Y.; Loh, J.; Ng, O.-T.; Marimuthu, K.; Ang, L.W.; Mak, T.M.; et al. Epidemiologic Features and Clinical Course of Patients Infected With SARS-CoV-2 in Singapore. JAMA 2020, 323, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardu, C.; Gargiulo, G.; Esposito, G.; Paolisso, G.; Marfella, R. Impact of diabetes mellitus on clinical outcomes in patients affected by COVID-19. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2020, 19, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltramo, G.; Cottenet, J.; Mariet, A.-S.; Georges, M.; Piroth, L.; Tubert-Bitter, P.; Bonniaud, P.; Quantin, C. Chronic respiratory diseases are predictors of severe outcome in COVID-19 hospitalised patients: A nationwide study. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 58, 2004474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashim, M.J.; Alsuwaidi, A.R.; Khan, G. Population Risk Factors for COVID-19 Mortality in 93 Countries. JEGH 2020, 10, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aveyard, P.; Gao, M.; Lindson, N.; Hartmann-Boyce, J.; Watkinson, P.; Young, D.; Coupland, C.A.C.; Tan, P.S.; Clift, A.K.; Harrison, D.; et al. Association between pre-existing respiratory disease and its treatment, and severe COVID-19: A population cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 909–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer, D.; Pieters, T.T.; Verhaar, M.C.; Berger, S.P.; Bakker, S.J.L.; Van Zuilen, A.D.; Joles, J.A.; Vernooij, R.W.M.; Van Balkom, B.W.M. A systematic review and meta-analysis of COVID-19 in kidney transplant recipients: Lessons to be learned. Am. J. Transplant. 2021, 21, 3936–3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, E.; Dheir, H.; Safak, S.; Serra Artan, A.; Sipahi, S.; Turkmen, A. Differences in clinical outcomes of COVID-19 among vaccinated and unvaccinated kidney transplant recipients. Vaccine 2022, 40, 3313–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korth, J.; Jahn, M.; Dorsch, O.; Anastasiou, O.E.; Sorge-Hädicke, B.; Eisenberger, U.; Gäckler, A.; Dittmer, U.; Witzke, O.; Wilde, B.; et al. Impaired Humoral Response in Renal Transplant Recipients to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination with BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech). Viruses 2021, 13, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina-Pestana, J.; Covas, D.T.; Viana, L.A.; Dreige, Y.C.; Nakamura, M.R.; Lucena, E.F.; Requião-Moura, L.R.; Fortaleza, C.M.C.B.; Foresto, R.D.; Tedesco-Silva, H.; et al. Inactivated Whole-virus Vaccine Triggers Low Response Against SARS-CoV-2 Infection Among Renal Transplant Patients: Prospective Phase 4 Study Results. Transplantation 2022, 106, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Wu, G.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L. Risk Factors for Acute Kidney Injury in Adult Patients With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 719472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peckham, H.; De Gruijter, N.M.; Raine, C.; Radziszewska, A.; Ciurtin, C.; Wedderburn, L.R.; Rosser, E.C.; Webb, K.; Deakin, C.T. Male sex identified by global COVID-19 meta-analysis as a risk factor for death and ITU admission. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosino, I.; Barbagelata, E.; Ortona, E.; Ruggieri, A.; Massiah, G.; Giannico, O.V.; Politi, C.; Moretti, A.M. Gender differences in patients with COVID-19: A narrative review. Monaldi Arch. Chest Dis. 2020, 90, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, E.J.; Walker, A.J.; Bhaskaran, K.; Bacon, S.; Bates, C.; Morton, C.E.; Curtis, H.J.; Mehrkar, A.; Evans, D.; Inglesby, P.; et al. Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY. Nature 2020, 584, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Liu, X.; Hu, B.; Li, D.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Zhu, K.; Tu, Y.; Xiong, S.; Wang, G.; et al. Gender and Ethnic Disparities of Acute Kidney Injury in COVID-19 Infected Patients: A Literature Review. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 11, 778636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolhe, N.V.; Fluck, R.J.; Selby, N.M.; Taal, M.W. Acute kidney injury associated with COVID-19: A retrospective cohort study. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paleiron, N.; Mayet, A.; Marbac, V.; Perisse, A.; Barazzutti, H.; Brocq, F.-X.; Janvier, F.; Dautzenberg, B.; Bylicki, O. Impact of Tobacco Smoking on the Risk of COVID-19: A Large Scale Retrospective Cohort Study. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2021, 23, 1398–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoswa, W.N.; Khaliq, O.P. Is pregnancy a risk factor of COVID-19? Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2020, 252, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Yang, W.; Wu, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, W.; Xia, J. Clinical Manifestation and Laboratory Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Pregnant Women. Virol. Sin. 2020, 35, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, B. Organ and human trafficking in Nepal. Lancet 2016, 387, 1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price-Haywood, E.G.; Burton, J.; Fort, D.; Seoane, L. Hospitalization and Mortality among Black Patients and White Patients with Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2534–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geckin, B.; Zoodsma, M.; Kilic, G.; Debisarun, P.A.; Rakshit, S.; Adiga, V.; Ahmed, A.; Parthiban, C.; Kumar, N.C.; D’Souza, G.; et al. Differences in Immune Responses in Individuals of Indian and European Origin: Relevance for the COVID-19 Pandemic. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e00231-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, L.B.; Sitapati, A.M.; Zhang, J.; Zou, J.; Bui, Q.M.; Ren, J.; Longhurst, C.A.; Criqui, M.H.; Messer, K. Relation of Statin Use Prior to Admission to Severity and Recovery Among COVID-19 Inpatients. Am. J. Cardiol. 2020, 136, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.Y.T.; Young, B.E.; Lye, D.C.; Chew, D.E.K.; Dalan, R. Statin use is associated with lower disease severity in COVID-19 infection. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiglione, V.; Chiriacò, M.; Emdin, M.; Taddei, S.; Vergaro, G. Statin therapy in COVID-19 infection. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Pharm. 2020, 6, 258–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitacchione, G.; Schiavone, M.; Curnis, A.; Arca, M.; Antinori, S.; Gasperetti, A.; Mascioli, G.; Severino, P.; Sabato, F.; Caracciolo, M.M.; et al. Impact of prior statin use on clinical outcomes in COVID-19 patients: Data from tertiary referral hospitals during COVID-19 pandemic in Italy. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2021, 15, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, S.M.; Varghese, E.; Büsselberg, D. Therapeutic Potential of Metformin in COVID-19: Reasoning for Its Protective Role. Trends Microbiol. 2021, 29, 894–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zangiabadian, M.; Nejadghaderi, S.A.; Zahmatkesh, M.M.; Hajikhani, B.; Mirsaeidi, M.; Nasiri, M.J. The Efficacy and Potential Mechanisms of Metformin in the Treatment of COVID-19 in the Diabetics: A Systematic Review. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 645194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheen, A.J. Metformin and COVID-19: From cellular mechanisms to reduced mortality. Diabetes Metab. 2020, 46, 423–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukito, A.A.; Pranata, R.; Henrina, J.; Lim, M.A.; Lawrensia, S.; Suastika, K. The Effect of Metformin Consumption on Mortality in Hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2020, 14, 2177–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bramante, C.T.; Ingraham, N.E.; Murray, T.A.; Marmor, S.; Hovertsen, S.; Gronski, J.; McNeil, C.; Feng, R.; Guzman, G.; Abdelwahab, N.; et al. Metformin and risk of mortality in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: A retrospective cohort analysis. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2021, 2, e34–e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casqueiro, J.; Casqueiro, J.; Alves, C. Infections in patients with diabetes mellitus: A review of pathogenesis. Indian J. Endocr. Metab. 2012, 16, 27. [Google Scholar]
| Variable | Negative (n = 1,155,397) | Positive (n = 259,905) | p-Value 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| HDL value (mg/dL), Mean (SD) | 53.65 (16.90) | 50.71 (15.30) | <0.001 |
| Age, Mean (SD) | 56.11 (16.67) | 54.28 (16.82) | <0.001 |
| Female, n (%) | 656,556 (56.83) | 147,320 (56.68) | 0.184 |
| Race/Ethnicity, n (%) | <0.001 | ||
| White | 803,309 (69.53) | 184,587 (71.02) | |
| Asian | 34,990 (3.03) | 4608 (1.77) | |
| Black | 160,722 (13.91) | 34,266 (13.18) | |
| Hispanic | 55,755 (4.83) | 17,045 (6.56) | |
| Other | 100,621 (8.71) | 19,399 (7.46) | |
| Pregnancy (yes/no), n (%) | 48,425 (4.19) | 10,147 (3.90) | <0.001 |
| Smoking (yes/no), n (%) | 112,318 (9.72) | 9092 (3.50) | <0.001 |
| Comorbidity (yes/no), n (%) | |||
| Obesity | 616,601 (53.37) | 119,194 (45.86) | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 658,097 (56.96) | 129,675 (49.89) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes complicated | 190,240 (16.47) | 39,747 (15.29) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes not complicated | 301,278 (26.08) | 68,813 (26.48) | <0.001 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 133,195 (11.53) | 18,072 (6.95) | <0.001 |
| Chronic lung disease | 332,022 (28.74) | 52,513 (20.20) | <0.001 |
| Congestive heart failure | 135,533 (11.73) | 20,610 (7.93) | <0.001 |
| Heart Failure | 177,537 (15.37) | 28,613 (11.01) | <0.001 |
| Hemiplegia | 33,383 (2.89) | 4980 (1.92) | <0.001 |
| HIV | 14,306 (1.24) | 1899 (0.73) | <0.001 |
| Dementia | 46,146 (3.99) | 10,264 (3.95) | 0.291 |
| Depression | 336,067 (29.09) | 54,243 (20.87) | <0.001 |
| ESRD | 18,926 (1.64) | 3705 (1.43) | <0.001 |
| Transplant | 11,325 (0.98) | 1499 (0.58) | <0.001 |
| Cholesterol drug (yes/no), n (%) | 114,942 (9.95) | 12,953 (4.98) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes drug (yes/no), n (%) | 57,940 (5.01) | 14,678 (5.65) | <0.001 |
| Variable | Negative (n = 2948) | Positive (n = 641) | p-Value 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| apoA1 value (mg/dL), Mean (SD) | 144.11 (34.29) | 139.44 (31.02) | 0.002 |
| Age, Mean (SD) | 53.56 (14.12) | 53.00 (13.72) | 0.362 |
| Female, n (%) | 1350 (45.79) | 331 (51.64) | 0.007 |
| Race/Ethnicity, n (%) | 0.002 | ||
| White | 1937 (65.71) | 457 (71.29) | |
| Black | 446 (15.13) | 93 (14.51) | |
| Hispanic | 153 (5.19) | 35 (5.46) | |
| Asian/Other 2 | 412 (13.96) | 56 (8.74) | |
| Pregnancy (yes/no), n (%) | 100 (3.39) | 27 (4.21) | 0.308 |
| Smoking (yes/no), n (%) | 642 (21.78) | 51 (7.96) | <0.001 |
| Comorbidity (yes/no), n (%) | |||
| Obesity | 1553 (52.68) | 284 (44.31) | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 1693 (57.43) | 377 (58.81) | 0.520 |
| Diabetes complicated | 535 (18.15) | 134 (20.90) | 0.104 |
| Diabetes not complicated | 831 (28.19) | 228 (35.57) | <0.001 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 291 (9.87) | 51 (7.96) | 0.135 |
| Chronic lung disease | 1042 (35.35) | 172 (26.83) | <0.001 |
| Congestive heart failure | 336 (11.40) | 67 (10.45) | 0.492 |
| Heart Failure | 468 (15.88) | 96 (14.98) | 0.571 |
| Hemiplegia | 70 (2.37) | <20 (<3.12) | 0.440 |
| HIV | 172 (5.83) | <20 (<3.12) | <0.001 |
| Dementia | 79 (2.68) | <20 (<3.12) | 0.856 |
| Depression | 1175 (39.86) | 213 (33.23) | 0.002 |
| ESRD | 67 (2.27) | 22 (3.43) | 0.087 |
| Transplant | 40 (1.36) | <20 (<3.12) | 0.322 |
| Cholesterol drug (yes/no), n (%) | 323 (10.96) | 26 (4.06) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes drug (yes/no), n (%) | 149 (5.05) | 55 (8.58) | <0.001 |
| Variable | OR 1 | 95% CI 1 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| HDL value (mg/dL) | 0.98 | 0.98, 0.98 | <0.001 |
| ESRD | 1.20 | 1.15, 1.25 | <0.001 |
| Obesity | 0.68 | 0.67, 0.69 | <0.001 |
| Pregnancy | 0.82 | 0.80, 0.84 | <0.001 |
| Transplant | 0.63 | 0.60, 0.67 | <0.001 |
| Smoker | 0.39 | 0.38, 0.40 | <0.001 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 0.68 | 0.67, 0.70 | <0.001 |
| Chronic lung disease | 0.78 | 0.77, 0.79 | <0.001 |
| Congestive heart failure | 0.87 | 0.85, 0.90 | <0.001 |
| Dementia | 1.31 | 1.28, 1.34 | <0.001 |
| Depression | 0.72 | 0.71, 0.73 | <0.001 |
| Diabetes complicated | 0.97 | 0.95, 0.99 | <0.001 |
| Diabetes not complicated | 1.24 | 1.22, 1.26 | <0.001 |
| Heart Failure | 0.97 | 0.95, 1.0 | 0.018 |
| Hemiplegia | 1.01 | 0.98, 1.05 | 0.462 |
| HIV | 0.65 | 0.61, 0.68 | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 0.91 | 0.90, 0.92 | <0.001 |
| Cholesterol drug | 0.49 | 0.48, 0.50 | <0.001 |
| Diabetes drug | 1.35 | 1.33, 1.38 | <0.001 |
| Age | 0.997 | 1.00, 1.00 | <0.001 |
| Female | 1.21 | 1.20, 1.22 | <0.001 |
| Race 2 | |||
| Black | 1.03 | 1.01, 1.04 | <0.001 |
| Asian | 0.45 | 0.44, 0.46 | <0.001 |
| Hispanic | 1.19 | 1.17, 1.21 | <0.001 |
| Other | 0.73 | 0.71, 0.74 | <0.001 |
| Variable | OR 1 | 95% CI 1 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| ApoA1 value (mg/dL) | 0.99 | 0.99, 1.00 | <0.001 |
| ESRD | 1.74 | 0.94, 3.14 | 0.068 |
| Obesity | 0.58 | 0.48, 0.71 | <0.001 |
| Pregnancy | 1.00 | 0.61, 1.60 | 0.995 |
| Transplant | 1.10 | 0.49, 2.28 | 0.815 |
| Smoker | 0.32 | 0.23, 0.44 | <0.001 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 0.90 | 0.62, 1.27 | 0.550 |
| Chronic lung disease | 0.76 | 0.61, 0.94 | 0.011 |
| Congestive heart failure | 0.89 | 0.54, 1.50 | 0.664 |
| Dementia | 1.17 | 0.65, 2.00 | 0.578 |
| Depression | 0.84 | 0.69, 1.03 | 0.088 |
| Diabetes complicated | 0.90 | 0.65, 1.25 | 0.531 |
| Diabetes not complicated | 1.57 | 1.19, 2.06 | 0.001 |
| Heart Failure | 1.14 | 0.72, 1.75 | 0.567 |
| Hemiplegia | 1.15 | 0.56, 2.23 | 0.683 |
| HIV | 0.28 | 0.13, 0.51 | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 1.25 | 1.01, 1.56 | 0.042 |
| Cholesterol drug | 0.20 | 0.12, 0.32 | <0.001 |
| Diabetes drug | 2.55 | 1.70, 3.79 | <0.001 |
| Age | 0.99 | 0.98, 1.00 | 0.044 |
| Female | 1.39 | 1.15, 1.68 | <0.001 |
| Race 2 | |||
| Black | 0.95 | 0.72, 1.23 | 0.683 |
| Asian | 0.24 | 0.10, 0.46 | <0.001 |
| Hispanic | 0.92 | 0.61, 1.36 | 0.673 |
| Other | 0.59 | 0.42, 0.81 | 0.002 |
| Variable | Mild (n = 179,563) | Severe (n = 80,342) | p-Value 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| HDL value (mg/dL), Mean (SD) | 51.72 (15.32) | 48.46 (15.03) | <0.001 |
| Age, Mean (SD) | 51.27 (15.79) | 61.01 (17.12) | <0.001 |
| Female, n (%) | 104,656 (58.28) | 42,664 (53.10) | <0.001 |
| Race/Ethnicity, n (%) | <0.001 | ||
| White | 134,254 (74.77) | 50,333 (62.65) | |
| Asian | 3116 (1.74) | 1492 (1.86) | |
| Black | 18,944 (10.55) | 15,322 (19.07) | |
| Hispanic | 10,497 (5.85) | 6548 (8.15) | |
| Other | 12,752 (7.10) | 6647 (8.27) | |
| Pregnancy (yes/no), n (%) | 7442 (4.14) | 2705 (3.37) | <0.001 |
| Smoking (yes/no), n (%) | 4773 (2.66) | 4319 (5.38) | <0.001 |
| Comorbidity (yes/no), n (%) | |||
| Obesity | 76,600 (42.66) | 42,594 (53.02) | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 75,357 (41.97) | 54,318 (67.61) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes complicated | 17,831 (9.93) | 21,916 (27.28) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes not complicated | 36,325 (20.23) | 32,488 (40.44) | <0.001 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 7041 (3.92) | 11,031 (13.73) | <0.001 |
| Chronic lung disease | 25,909 (14.43) | 26,604 (33.11) | <0.001 |
| Congestive heart failure | 5823 (3.24) | 14,787 (18.41) | <0.001 |
| Heart Failure | 9377 (5.22) | 19,236 (23.94) | <0.001 |
| Hemiplegia | 1417 (0.79) | 3563 (4.43) | <0.001 |
| HIV | 1080 (0.60) | 819 (1.02) | <0.001 |
| Dementia | 3384 (1.88) | 6880 (8.56) | <0.001 |
| Depression | 32,663 (18.19) | 21,580 (26.86) | <0.001 |
| ESRD | 696 (0.39) | 3009 (3.75) | <0.001 |
| Transplant | 370 (0.21) | 1129 (1.41) | <0.001 |
| Cholesterol drug (yes/no), n (%) | 5869 (3.27) | 7084 (8.82) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes drug (yes/no), n (%) | 7588 (4.23) | 7090 (8.82) | <0.001 |
| Variable | Mild (n = 392) | Severe (n = 249) | p-Value 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ApoA1 value (mg/dL), Mean (SD) | 141.97 (29.24) | 135.45 (33.30) | 0.006 |
| Age, Mean (SD) | 51.45 (13.25) | 55.42 (14.10) | <0.001 |
| Female, n (%) | 214 (54.59) | 117 (46.99) | 0.060 |
| Race/Ethnicity, n (%) | 0.002 | ||
| White | 300 (76.53) | 157 (63.05) | |
| Asian | <20 (<5.10) | <20 (<8.03) | |
| Black | 43 (10.97) | 50 (20.08) | |
| Hispanic | <20 (<5.10) | <20 (<8.03) | |
| Other | 27 (6.89) | 21 (8.43) | |
| Pregnancy (yes/no), n (%) | 20 (5.10) | <20 (<8.03) | 0.159 |
| Smoking (yes/no), n (%) | 27 (6.89) | 24 (9.64) | 0.210 |
| Comorbidity (yes/no), n (%) | |||
| Obesity | 160 (40.82) | 124 (49.80) | 0.026 |
| Hypertension | 204 (52.04) | 173 (69.48) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes complicated | 42 (10.71) | 92 (36.95) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes not complicated | 104 (26.53) | 124 (49.80) | <0.001 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | <20 (<5.10) | 36 (14.46) | <0.001 |
| Chronic lung disease | 73 (18.62) | 99 (39.76) | <0.001 |
| Congestive heart failure | <20 (<5.10) | 48 (19.28) | <0.001 |
| Heart Failure | 33 (8.42) | 63 (25.30) | <0.001 |
| Hemiplegia | <20 (<5.10) | <20 (<8.03) | <0.001 |
| HIV | <20 (<5.10) | <20 (<8.03) | 0.522 |
| Dementia | <20 (<5.10) | <20 (<8.03) | 0.140 |
| Depression | 111 (28.32) | 102 (40.96) | <0.001 |
| ESRD | <20 (<5.10) | <20 (<8.03) | <0.001 |
| Transplant | 0 (0.00) | <20 (<8.03) | <0.001 |
| Cholesterol drug (yes/no), n (%) | <20 (<5.10) | <20 (<8.03) | 0.001 |
| Diabetes drug (yes/no), n (%) | 25 (6.38) | 30 (12.05) | 0.012 |
| Variable | OR 1 | 95% CI 1 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| HDL value (mg/dL) | 0.99 | 0.99, 0.99 | <0.001 |
| ESRD | 3.13 | 2.85, 3.45 | <0.001 |
| Obesity | 1.09 | 1.07, 1.12 | <0.001 |
| Pregnancy | 1.76 | 1.68, 1.85 | <0.001 |
| Transplant | 2.18 | 1.91, 2.51 | <0.001 |
| Smoker | 1.33 | 1.27, 1.40 | <0.001 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 1.36 | 1.31, 1.41 | <0.001 |
| Chronic lung disease | 1.70 | 1.67, 1.74 | <0.001 |
| Congestive heart failure | 1.38 | 1.30, 1.46 | <0.001 |
| Dementia | 1.79 | 1.70, 1.87 | <0.001 |
| Depression | 1.28 | 1.25, 1.31 | <0.001 |
| Diabetes complicated | 1.25 | 1.21, 1.29 | <0.001 |
| Diabetes not complicated | 1.19 | 1.15, 1.22 | <0.001 |
| Heart Failure | 1.66 | 1.58, 1.74 | <0.001 |
| Hemiplegia | 1.78 | 1.65, 1.91 | <0.001 |
| HIV | 1.32 | 1.20, 1.47 | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 1.15 | 1.13, 1.18 | <0.001 |
| Cholesterol drug | 1.31 | 1.25, 1.36 | <0.001 |
| Diabetes drug | 1.12 | 1.08, 1.17 | <0.001 |
| Age | 1.03 | 1.03, 1.03 | <0.001 |
| Female | 0.88 | 0.87, 0.90 | <0.001 |
| Race 2 | |||
| Black | 2.02 | 1.96, 2.07 | <0.001 |
| Asian | 1.52 | 1.42, 1.62 | <0.001 |
| Hispanic | 1.86 | 1.80, 1.93 | <0.001 |
| Other | 1.54 | 1.49, 1.59 | <0.001 |
| Variable | OR 1 | 95% CI 1 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| ApoA1 value (mg/dL) | 0.99 | 0.99, 1.00 | 0.075 |
| ESRD | 3.74 | 0.91, 20.2 | 0.087 |
| Obesity | 0.96 | 0.65, 1.42 | 0.841 |
| Pregnancy | 0.88 | 0.30, 2.33 | 0.798 |
| Transplant 2 | NA | NA, NA | NA |
| Smoker | 0.75 | 0.36, 1.52 | 0.429 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 2.12 | 1.03, 4.49 | 0.045 |
| Chronic lung disease | 2.08 | 1.33, 3.24 | 0.001 |
| Congestive heart failure | 2.41 | 0.83, 7.25 | 0.108 |
| Dementia | 0.79 | 0.25, 2.49 | 0.690 |
| Depression | 1.40 | 0.91, 2.13 | 0.122 |
| Diabetes complicated | 2.40 | 1.27, 4.56 | 0.007 |
| Diabetes not complicated | 1.06 | 0.62, 1.80 | 0.828 |
| Heart Failure | 0.73 | 0.27, 1.83 | 0.505 |
| Hemiplegia | 9.34 | 1.39, 190 | 0.051 |
| HIV | 0.77 | 0.16, 3.32 | 0.726 |
| Hypertension | 0.91 | 0.58, 1.40 | 0.660 |
| Cholesterol drug | 2.37 | 0.93, 6.44 | 0.076 |
| Diabetes drug | 0.85 | 0.41, 1.73 | 0.649 |
| Age | 1.00 | 0.9967, 0.9974 | 0.588 |
| Female | 0.81 | 0.54, 1.21 | 0.298 |
| Race 3 | |||
| Black | 1.74 | 1.02, 2.95 | 0.041 |
| Asian | 0.76 | 0.10, 3.62 | 0.746 |
| Hispanic | 1.98 | 0.91, 4.30 | 0.082 |
| Other | 1.38 | 0.68, 2.74 | 0.359 |
| Variable | No (n = 241,214) | Yes (n = 18,691) | p-Value 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| HDL value (mg/dL), Mean (SD) | 51.05 (15.29) | 46.30 (14.83) | <0.001 |
| Age, Mean (SD) | 53.34 (16.61) | 66.48 (14.61) | <0.001 |
| Female, n (%) | 138,933 (57.60) | 8387 (44.87) | <0.001 |
| Race/Ethnicity, n (%) | <0.001 | ||
| White | 173,427 (71.90) | 11,160 (59.71) | |
| Asian | 4287 (1.78) | 321 (1.72) | |
| Black | 29,461 (12.21) | 4805 (25.71) | |
| Hispanic | 15,734 (6.52) | 1311 (7.01) | |
| Other | 18,305 (7.59) | 1094 (5.85) | |
| Pregnancy (yes/no), n (%) | 9890 (4.10) | 257 (1.37) | <0.001 |
| Smoking (yes/no), n (%) | 7576 (3.14) | 1516 (8.11) | <0.001 |
| Comorbidity (yes/no), n (%) | |||
| Obesity | 107,184 (44.44) | 12,010 (64.26) | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 112,498 (46.64) | 17,177 (91.90) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes complicated | 30,180 (12.51) | 9567 (51.19) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes not complicated | 57,358 (23.78) | 11,455 (61.29) | <0.001 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 13,561 (5.62) | 4511 (24.13) | <0.001 |
| Chronic lung disease | 43,165 (17.89) | 9348 (50.01) | <0.001 |
| Congestive heart failure | 13,024 (5.40) | 7586 (40.59) | <0.001 |
| Heart Failure | 19,660 (8.15) | 8953 (47.90) | <0.001 |
| Hemiplegia | 3358 (1.39) | 1622 (8.68) | <0.001 |
| HIV | 1655 (0.69) | 244 (1.31) | <0.001 |
| Dementia | 7530 (3.12) | 2734 (14.63) | <0.001 |
| Depression | 47,607 (19.74) | 6636 (35.50) | <0.001 |
| Transplant | 741 (0.31) | 758 (4.06) | <0.001 |
| Cholesterol drug (yes/no), n (%) | 10,664 (4.42) | 2289 (12.25) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes drug (yes/no), n (%) | 12,419 (5.15) | 2259 (12.09) | <0.001 |
| Variable | No (n = 577) | Yes (n = 64) | p-Value 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| apoA1 value (mg/dL), Mean (SD) | 139.96 (30.67) | 134.72 (33.90) | 0.085 |
| Age, Mean (SD) | 52.46 (13.94) | 57.81 (10.41) | 0.005 |
| Female, n (%) | 305 (52.86) | 26 (40.62) | 0.063 |
| Race/Ethnicity, n (%) | 0.294 | ||
| White | 417 (72.27) | 40 (62.50) | |
| Black | 81 (14.04) | <20 (<31.25) | |
| Hispanic | 29 (5.03) | <20 (<31.25) | |
| Asian/Other 2 | 50 (8.67) | <20 (<31.25) | |
| Pregnancy (yes/no), n (%) | 27 (4.68) | 0 (0.00) | 0.098 |
| Smoking (yes/no), n (%) | 38 (6.59) | <20 (<31.25) | <0.001 |
| Comorbidity (yes/no), n (%) | |||
| Obesity | 244 (42.29) | 40 (62.50) | 0.002 |
| Hypertension | 319 (55.29) | 58 (90.62) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes complicated | 100 (17.33) | 34 (53.12) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes not complicated | 187 (32.41) | 41 (64.06) | <0.001 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 35 (6.07) | <20 (<31.25) | <0.001 |
| Chronic lung disease | 138 (23.92) | 34 (53.12) | <0.001 |
| Congestive heart failure | 48 (8.32) | <20 (<31.25) | <0.001 |
| Heart Failure | 70 (12.13) | 26 (40.62) | <0.001 |
| Hemiplegia | <20 (<3.47) | <20 (<31.25) | <0.001 |
| HIV | <20 (<3.47) | <20 (<31.25) | 0.263 |
| Dementia | <20 (<3.47) | <20 (<31.25) | 0.026 |
| Depression | 179 (31.02) | 34 (53.12) | <0.001 |
| Transplant | <20 (<3.47) | <20 (<31.25) | <0.001 |
| Cholesterol drug (yes/no), n (%) | 22 (3.81) | <20 (<31.25) | 0.317 |
| Diabetes drug (yes/no), n (%) | 47 (8.15) | <20 (<31.25) | 0.238 |
| Variable | OR 1 | 95% CI 1 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| HDL value (mg/dL) | 0.99 | 0.99, 1.0 | <0.001 |
| Obesity | 1.26 | 1.21, 1.31 | <0.001 |
| Pregnancy | 0.99 | 0.85, 1.14 | 0.859 |
| Transplant | 6.58 | 5.84, 7.43 | <0.001 |
| Smoker | 1.36 | 1.27, 1.46 | <0.001 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 1.33 | 1.27, 1.40 | <0.001 |
| Chronic lung disease | 1.73 | 1.66, 1.79 | <0.001 |
| Congestive heart failure | 1.83 | 1.70, 1.96 | <0.001 |
| Dementia | 1.54 | 1.45, 1.63 | <0.001 |
| Depression | 1.41 | 1.35, 1.46 | <0.001 |
| Diabetes complicated | 2.13 | 2.02, 2.24 | <0.001 |
| Diabetes not complicated | 1.14 | 1.08, 1.20 | <0.001 |
| Heart Failure | 1.68 | 1.57, 1.80 | <0.001 |
| Hemiplegia | 1.47 | 1.36, 1.59 | <0.001 |
| HIV | 1.36 | 1.15, 1.59 | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 3.35 | 3.16, 3.56 | <0.001 |
| Cholesterol drug | 1.02 | 0.96, 1.08 | 0.462 |
| Diabetes drug | 0.92 | 0.87, 0.98 | 0.005 |
| Age | 1.03 | 1.03, 1.03 | <0.001 |
| Female | 0.64 | 0.62, 0.66 | <0.001 |
| Race 2 | |||
| Black | 2.05 | 1.96, 2.14 | <0.001 |
| Asian | 1.43 | 1.25, 1.62 | <0.001 |
| Hispanic | 1.34 | 1.25, 1.44 | <0.001 |
| Other | 0.99 | 0.92, 1.06 | 0.812 |
| Variable | OR 1 | 95% CI 1 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| ApoA1 value (mg/dL) | 1.00 | 0.99, 1.01 | 0.872 |
| Obesity | 1.46 | 0.75, 2.87 | 0.271 |
| Pregnancy 2 | NA | NA, NA | NA |
| Transplant | 15.00 | 3.82, 70.1 | <0.001 |
| Smoker | 2.31 | 0.91, 5.60 | 0.068 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 2.35 | 0.98, 5.39 | 0.049 |
| Chronic lung disease | 1.75 | 0.89, 3.42 | 0.100 |
| Congestive heart failure | 0.75 | 0.23, 2.67 | 0.647 |
| Dementia | 1.38 | 0.30, 5.31 | 0.655 |
| Depression | 1.49 | 0.75, 2.93 | 0.250 |
| Diabetes complicated | 1.77 | 0.68, 4.84 | 0.250 |
| Diabetes not complicated | 0.82 | 0.30, 2.04 | 0.683 |
| Heart Failure | 2.30 | 0.71, 6.62 | 0.139 |
| Hemiplegia | 3.38 | 0.81, 14.3 | 0.091 |
| HIV | 0.64 | 0.07, 4.25 | 0.667 |
| Hypertension | 3.26 | 1.28, 9.54 | 0.019 |
| Cholesterol drug | 0.89 | 0.19, 3.20 | 0.874 |
| Diabetes drug | 0.60 | 0.21, 1.59 | 0.325 |
| Age | 1.00 | 0.97, 1.03 | 0.991 |
| Female | 0.70 | 0.36, 1.37 | 0.305 |
| Race 3 | |||
| Black | 0.96 | 0.40, 2.13 | 0.925 |
| Asian 2 | NA | NA, NA | NA |
| Hispanic | 3.13 | 0.94, 9.15 | 0.046 |
| Other | 1.26 | 0.40, 3.47 | 0.667 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.-H.; Kulkarni, R.; Koizumi, N.; Andalibi, A.; on behalf of the N3C Consortium. The Association of the Levels of High-Density Lipoprotein and Apolipoprotein A1 with SARS-CoV-2 Infection and COVID-19 Severity: An Analysis of the N3C Database. Biology 2023, 12, 852. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060852
Li M-H, Kulkarni R, Koizumi N, Andalibi A, on behalf of the N3C Consortium. The Association of the Levels of High-Density Lipoprotein and Apolipoprotein A1 with SARS-CoV-2 Infection and COVID-19 Severity: An Analysis of the N3C Database. Biology. 2023; 12(6):852. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060852
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Meng-Hao, Rajendra Kulkarni, Naoru Koizumi, Ali Andalibi, and on behalf of the N3C Consortium. 2023. "The Association of the Levels of High-Density Lipoprotein and Apolipoprotein A1 with SARS-CoV-2 Infection and COVID-19 Severity: An Analysis of the N3C Database" Biology 12, no. 6: 852. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060852
APA StyleLi, M.-H., Kulkarni, R., Koizumi, N., Andalibi, A., & on behalf of the N3C Consortium. (2023). The Association of the Levels of High-Density Lipoprotein and Apolipoprotein A1 with SARS-CoV-2 Infection and COVID-19 Severity: An Analysis of the N3C Database. Biology, 12(6), 852. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060852






