Synergistic Effects of Earthworms and Plants on Chromium Removal from Acidic and Alkaline Soils: Biological Responses and Implications
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil, Earthworms, and Other Materials
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Cr in Soil
2.4. Biological Responses of Earthworms to Cr Exposure
2.5. Biological Responses of Plants to Cr Exposure
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
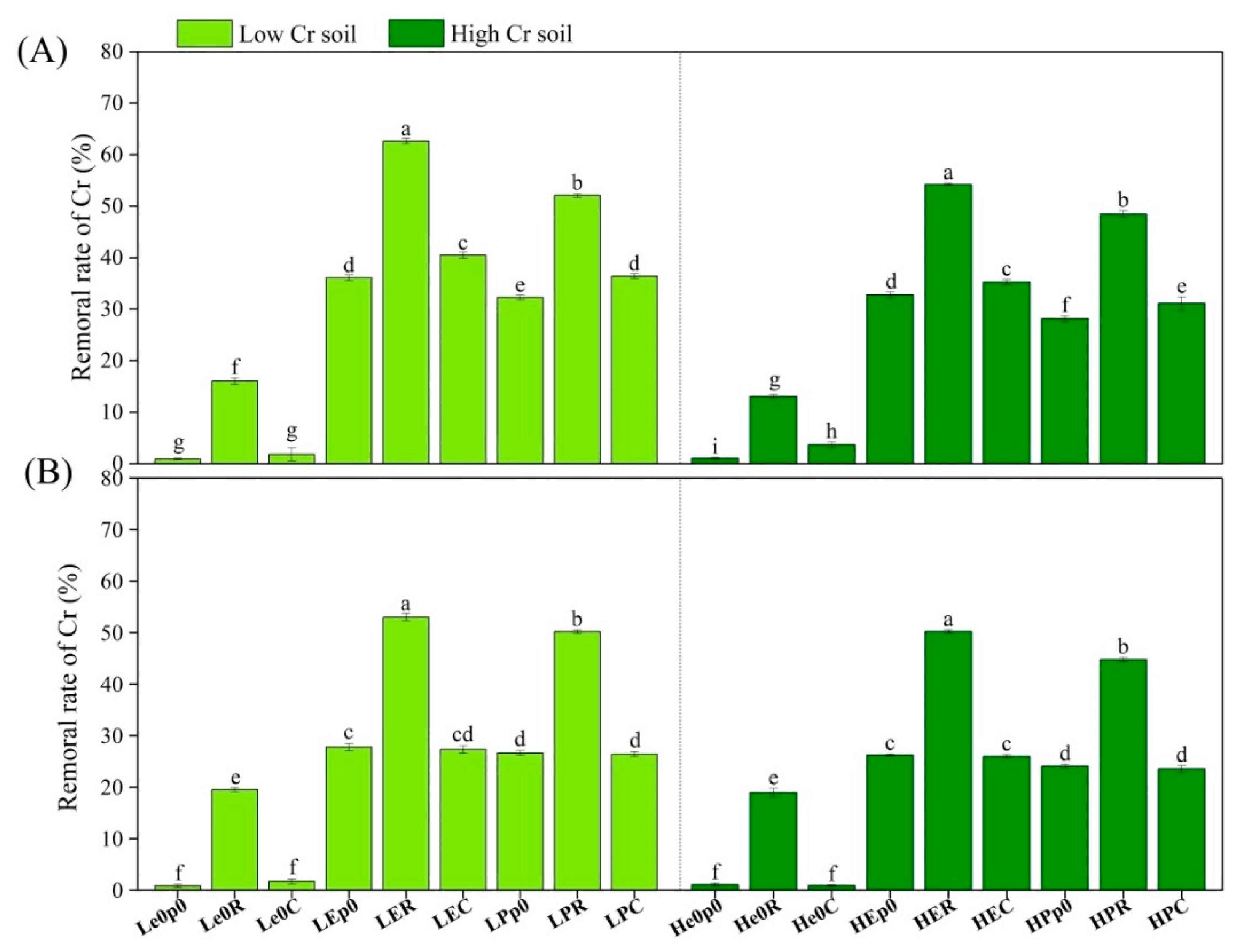
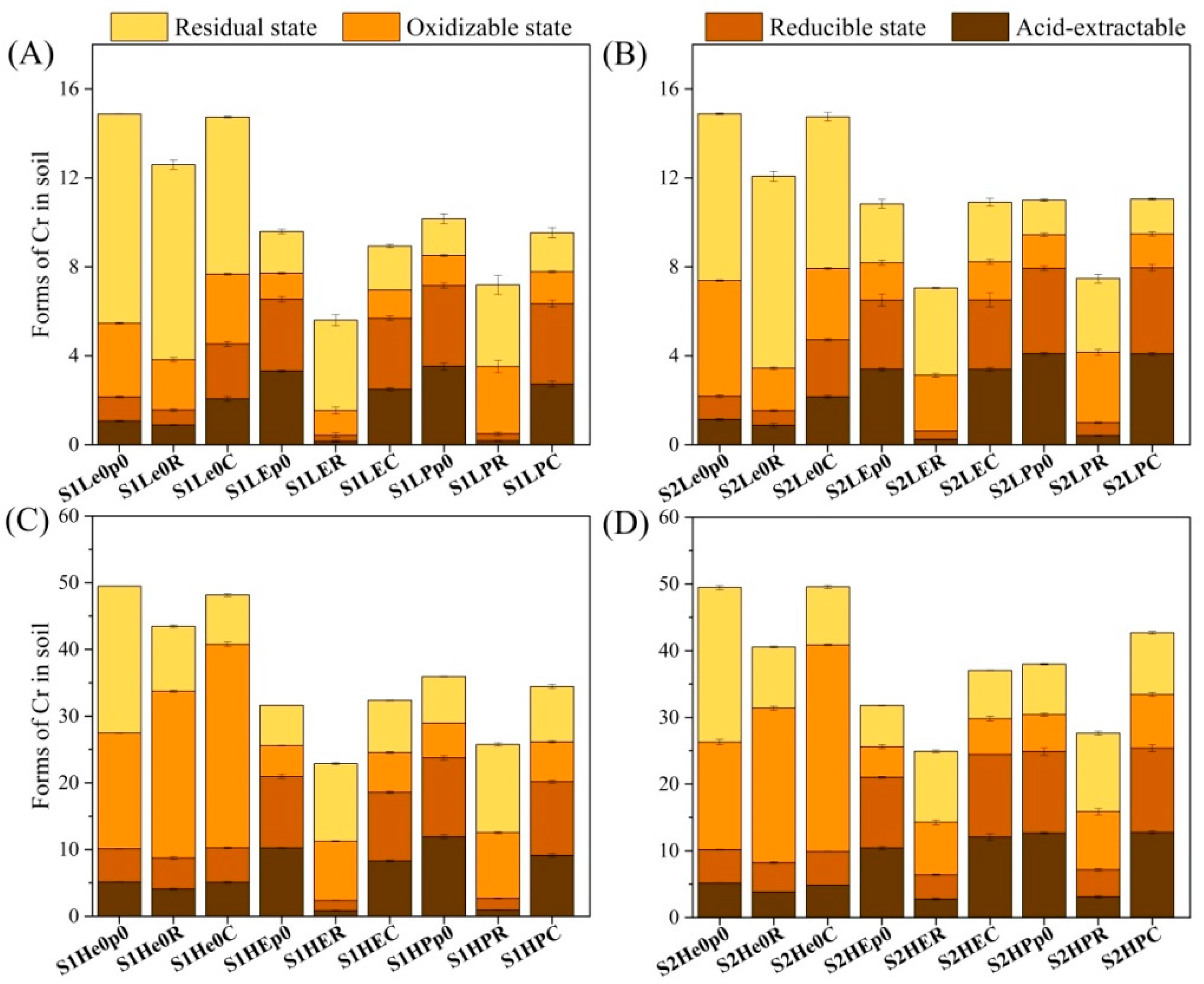
3.1. Removal and Speciation Characteristics of Chromium in Soil
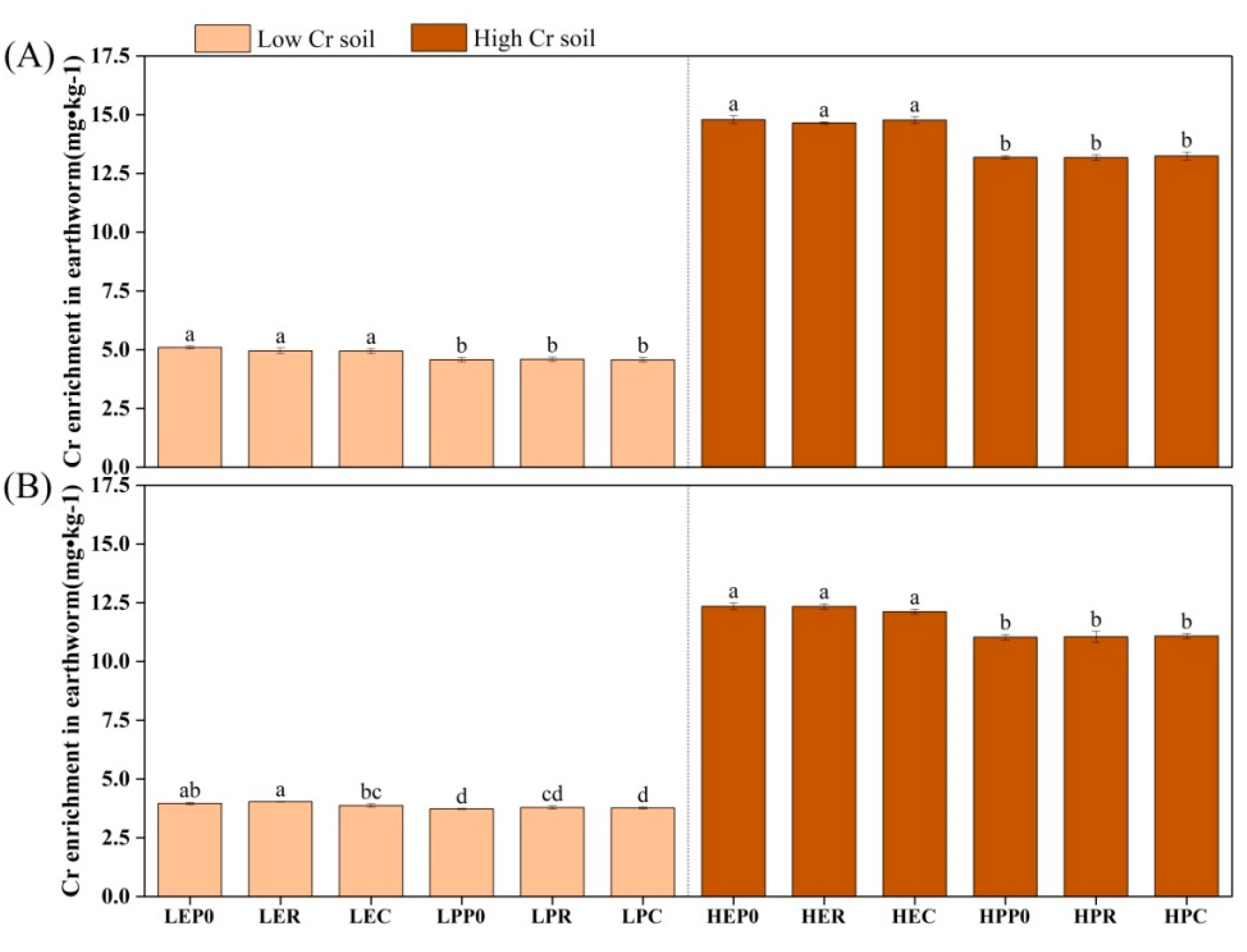
3.2. Accumulation of Chromium in Organisms
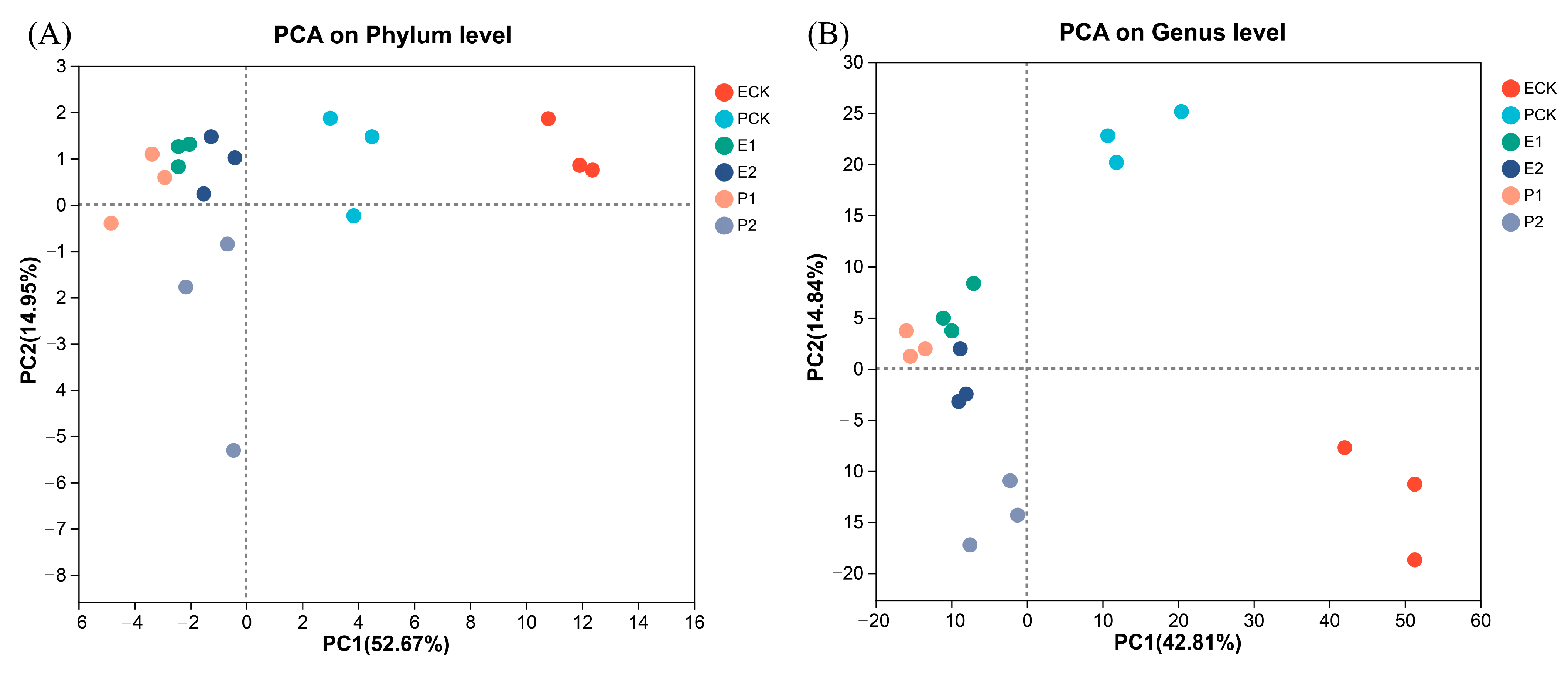
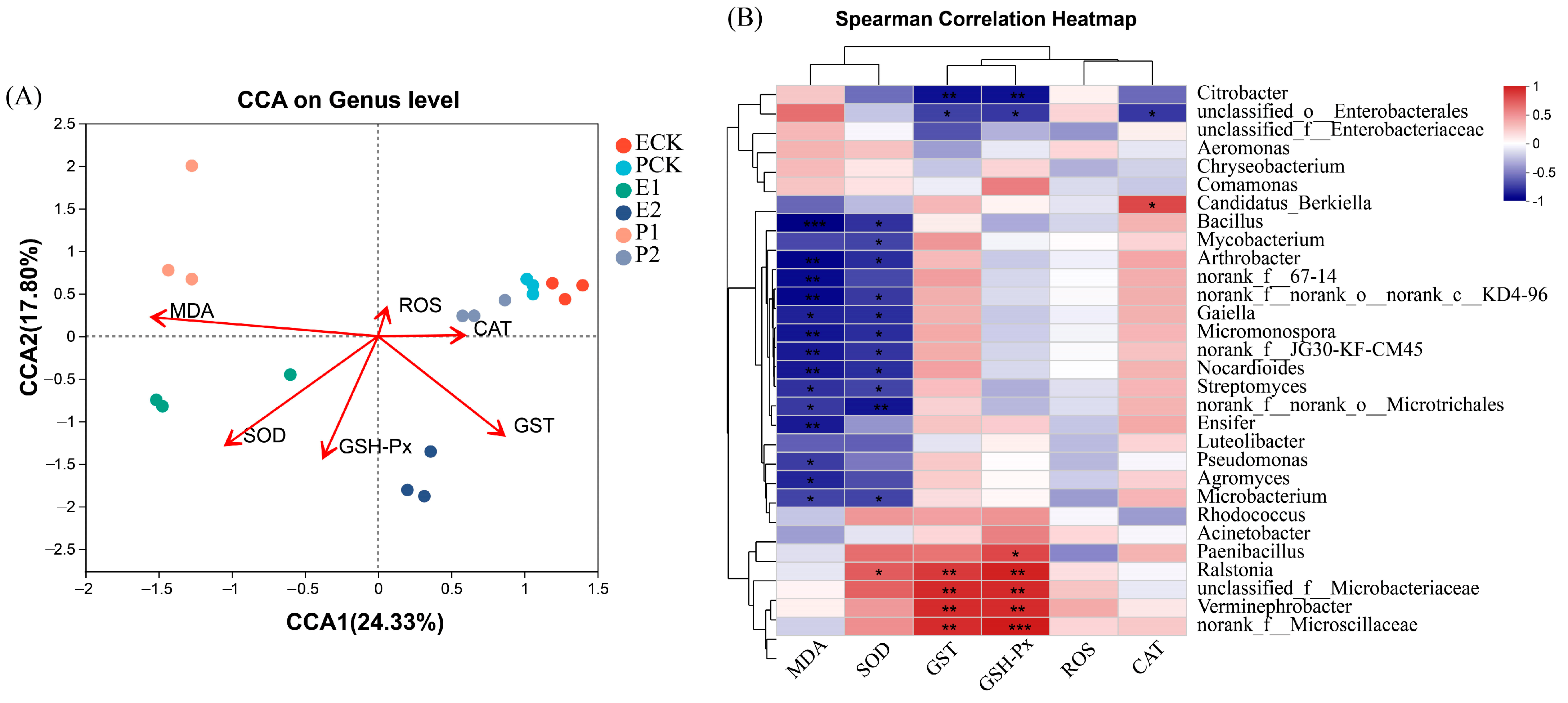
3.3. Gut Microbiota of Earthworms
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Earthworms and Plants on Chromium Removal
4.2. Scavenging of Chromium by Earthworms and Plants
4.3. Responses of Earthworm Gut Microbial Communities
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sugden, K.D.; Campo, C.K.; Martin, B.D. Direct oxidation of guanine and 7,8-dihydro-8-oxoguanine in DNA by a high-valent chromium complex: A possible mechanism for chromate genotoxicity. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2001, 14, 1315–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Cai, L.M.; Wen, H.H.; Luo, J.; Wang, Q.S.; Liu, X. Spatial distribution and source apportionment of heavy metals in soil from a typical county-level city of Guangdong Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farid, M.; Ali, S.; Rizwan, M.; Ali, Q.; Abbas, F.; Bukhari, S.A.H.; Saeed, R.; Wu, L.H. Citric acid assisted phytoextraction of chromium by sunflower; morpho-physiological and biochemical alterations in plants. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2017, 145, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Yan, S.S.; Liu, M.; Wang, B.; Hu, D.; Guo, D.B.; Wang, J.; Xu, W.T.; Fan, C. Seafood consumption among Chinese coastal residents and health risk assessment of heavy metals in seafood. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2016, 23, 16834–16844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andleeb, S.; Mahmood, T.; Khalid, A.; Akrim, F.; Fatima, H. Hexavalent chromium induces testicular dysfunction in small Indian mongoose (Herpestes javanicus) inhabiting tanneries area of Kasur District, Pakistan. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2018, 148, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumpiene, J.; Nordmark, D.; Carabante, I.; Suziedelyte-Visockiene, J.; Aksamitauskas, V.C. Remediation of soil contaminated with organic and inorganic wood impregnation chemicals by soil washing. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.J.; Ma, Y.B.; Zhu, Y.G.; Tang, Z.; McGrath, S.P. Soil Contamination in China: Current Status and Mitigation Strategies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojuederie, O.B.; Babalola, O.O. Microbial and Plant-Assisted Bioremediation of Heavy Metal Polluted Environments: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, L.; Ma, F.; You, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.J.; Yang, D.G. Integration of earthworms and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi into phytoremediation of cadmium-contaminated soil by Solanum nigrum L. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Miao, C.Y.; Mao, L.A.; Zhou, P.; Jin, Z.G.; Shi, W.J. Improvement of phytoextraction and antioxidative defense in Solanum nigrum L. under cadmium stress by application of cadmium-resistant strain and citric acid. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Wu, W.Y.; Liu, F.; Liao, R.K.; Hu, Y.Q. Accumulation of heavy metals in soil-crop systems: A review for wheat and corn. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 15209–15225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, X.L. Phytoextraction of Heavy Metals from Contaminated Soil by Co-Cropping Solanum nigrum L. with Ryegrass Associated with Endophytic Bacterium. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 1806–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.Y.; Lee, J.K.; Ro, H.M.; Kim, Y.H. Short-Term Effects of Low-Level Heavy Metal Contamination on Soil Health Analyzed by Nematode Community Structure. Plant Pathol. J. 2016, 32, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhao, C.H.; Xing, M.Y.; Lin, Y.A. Enhancement stabilization of heavy metals (Zn, Pb, Cr and Cu) during vermifiltration of liquid-state sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 146, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blouin, M.; Hodson, M.E.; Delgado, E.A.; Baker, G.; Brussaard, L.; Butt, K.R.; Dai, J.; Dendooven, L.; Peres, G.; Tondoh, J.E.; et al. A review of earthworm impact on soil function and ecosystem services. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2013, 64, 161–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Azcarate, J.; Ruiz, E.; Rodriguez, L. Changes in heavy metal speciation induced by earthworm feeding activity. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2011, 20, 26–35. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.D.; Li, H.X.; Wei, Z.G.; Wang, X.; Hu, F. Effect of earthworms on the phytoremediation of zinc-polluted soil by ryegrass and Indian mustard. Biol. Fertil. Soils. 2006, 43, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Mora, P.; Dai, J.; Chen, X.F.; Giusti-Miller, S.; Ruiz-Camacho, N.; Velasquez, E.; Lavelle, P. Earthworm and organic amendment effects on microbial activities and metal availability in a contaminated soil from China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 104, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Ji, H.Y.; Lyu, H.H.; Liu, Y.X.; He, L.L.; You, L.C.; Zhou, C.H.; Yang, S.M. Simultaneous alleviation of Sb and Cd availability in contaminated soil and accumulation in Lolium multiflorum Lam. After amendment with Fe-Mn-Modified biochar. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 231, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.R.; Ali, S.; Zhang, H.T.; Ouyang, Y.B.; Qiu, B.Y.; Wu, F.B.; Zhang, G.P. The influence of pH and organic matter content in paddy soil on heavy metal availability and their uptake by rice plants. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hook, R.I. Cadmium, lead, and zinc distributions between earthworms and soils: Potentials for biological accumulation. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1974, 12, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Qiao, Y.H.; Zhang, H.Q.; Yue, S.Z.; Li, H.F.; Ji, X.H.; Liu, L.S. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in earthworms from field contaminated soil in a subtropical area of China. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2018, 148, 876–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breton, J.; Massart, S.; Vandamme, P.; De Brandt, E.; Pot, B.; Foligne, B. Ecotoxicology inside the gut: Impact of heavy metals on the mouse microbiome. BMC. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 14, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemtiri, A.; Lienard, A.; Alabi, T.; Brostaux, Y.; Cluzeau, D.; Francis, F.; Colinet, G. Earthworms Eisenia fetida affect the uptake of heavy metals by plants Vicia faba and Zea mays in metal-contaminated soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 104, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymann, K.; Shaffer, Z.; Moran, N.A. Antibiotic exposure perturbs the gut microbiota and elevates mortality in honeybees. PLoS Biol. 2017, 15, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Brule, S.; Ambroise, J.; Lecloux, H.; Levard, C.; Soulas, R.; De Temmerman, P.J.; Palmai-Pallag, M.; Marbaix, E.; Lison, D. Dietary silver nanoparticles can disturb the gut microbiota in mice. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2016, 13, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Chen, Q.L.; An, X.L.; Yang, X.R.; Christie, P.; Ke, X.; Wu, L.H.; Zhu, Y.G. Exposure of soil collembolans to microplastics perturbs their gut microbiota and alters their isotopic composition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 124, 277–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Luo, J.W.; Yu, J.D.; Xia, L.D.; Zhou, C.F.; Cai, L.P.; Ma, X.Q. Improvement of the phytoremediation efficiency of Neyraudia reynaudiana for lead-zinc mine-contaminated soil under the interactive effect of earthworms and EDTA. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noronha, F.R.; Manikandan, S.K.; Nair, V. Role of coconut shell biochar and earthworm (Eudrilus euginea) in bioremediation and palak spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) growth in cadmium-contaminated soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 302, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.N.; ZHU, L.; Liu, H.Y.; Wu, L.H. Effect of Eisenia foetida on the metal uptake by Sedum plumbizincicola in different types of contaminated soils. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2020, 36, 549–559. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.Z.; Cheng, J.; Wong, M.H. Earthworm-mycorrhiza interaction on Cd uptake and growth of ryegrass. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conyers, M.K.; Davey, B.G. Observations on some routine methods for soil pH determination. Soil Sci. 1988, 145, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettler, T.A.; Doran, J.W.; Gilbert, T.L. Simplified Method for Soil Particle-Size Determination to Accompany Soil-Quality Analyses. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2001, 65, 849–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Xue, N.D.; Liu, L.; Li, F.S. Distribution of Cd, Pb, Zn and Cu and their chemical speciations in soils from a peri-smelter area in northeast China. Environ Geol. 2008, 55, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuana, R.A.; Okieimen, F.E.; Imborvungu, J.A. Removal of heavy metals from a contaminated soil using organic chelating acids. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 7, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leleyter, L.; Probst, J.L. A new sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace elements in river sediments. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 1999, 73, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavehei, A.; Hose, G.C.; Gore, D.B. Effects of red earthworms (Eisenia fetida) on leachability of lead minerals in soil. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.Z.; Zhou, D.M.; Wang, P.; Allen, H.E.; Sauve, S. Predicting Cd partitioning in spiked soils and bioaccumulation in the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2009, 42, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutorabi, L.; Rajabi, M.; Bazregar, M.; Asghari, A. Selective determination of chromium (VI) ions using in-tube electro-membrane extraction followed by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2017, 132, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabpai, S.; Charerntanyarak, L.; Siri, B.; Moore, M.R.; Noller, B.N. Effects of residues from municipal solid waste landfill on corn yield and heavy metal content. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 2316–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortimer, R.J.G.; Rae, J.E. Metal speciation (Cu, Zn, Pb, Cd) and organic matter in oxic to suboxic salt marsh sediments, Severn Estuary, southwest Britain. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2000, 40, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaggiotti, S.; Ruperti, B.; Pizzeghello, D.; Francioso, O.; Tugnoli, V.; Nardi, S. Effect of low molecular size humic substances on nitrate uptake and expression of genes involved in nitrate transport in maize (Zea mays L.). J. Exp. Bot. 2004, 55, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Liu, Y.; Hu, X.; Shan, X. Effect of earthworms (Eisenia fetida) on the fractionation and bioavailability of rare earth elements in nine Chinese soils. Chemosphere 2006, 63, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakuria, D.; Schmidt, O.; Finan, D.; Egan, D.; Doohan, F.M. Gut wall bacteria of earthworms: A natural selection process. ISME J. 2010, 4, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jisu, B.; Dean, H. Dissolution of Trace Element Contaminants from Two Coastal Plain Soils as Affected by pH. J. Environ. Qual. 2004, 33, 891–901. [Google Scholar]
- Sukreeyapongse, O.; Holm, P.E.; Strobel, B.W.; Panichsakpatana, S.; Magid, J.; Hansen, H. pH-Dependent Release of Cadmium, Copper, and Lead from Natural and Sludge-Amended Soils. J. Environ. Qual. 2002, 31, 1901–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, J.; Kleber, M. The contentious nature of soil organic matter. Nature 2015, 528, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, M.; Dumat, C.; Khalid, S.; Niazi, N.K.; Antunes, P.M.C. Cadmium Bioavailability, Uptake, Toxicity and Detoxification in Soil-Plant System. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; DeVoogt, P., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 241, pp. 73–137. [Google Scholar]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Lauber, C.L.; Weintraub, M.N.; Ahmed, B.; Zeglin, L.H. Stoichiometry of soil enzyme activity at global scale. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauret, G.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.F.; Sahuquillo, A.; Rubio, R.; Davidson, C.; Ure, A.; Quevauviller, P. Improvement of the BCR three step sequential extraction procedure prior to the certification of new sediment and soil reference materials. J. Environ. Monit. 1999, 1, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sizmur, T.; Hodson, M.E. Do earthworms impact metal mobility and availability in soil?—A review. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1981–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sizmur, T.; Tilston, E.L.; Charnock, J.; Palumbo-Roe, B.; Watts, M.J.; Hodson, M.E. Impacts of epigeic, anecic and endogeic earthworms on metal and metalloid mobility and availability. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernando, V.K.; Perera, I.C.; Dangalle, C.D.; Premawansa, S.; Wijesinghe, M.R. Histological Alterations in the Body Wall of the Tropical Earthworm Eudrilus eugeniae Exposed to Hexavalent Chromium. B. Environ. Contam. Tox. 2015, 94, 744–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.K.; Srivastava, R.; Mathur, N.; Saxena, P.N. The comparative effects of metals on the hatching of earthworm cocoons. ATLA-Altern. Lab. Anim. 2006, 34, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arancon, N.Q.; Edwards, C.A.; Bierman, P. Influences of vermicomposts on field strawberries: Part 2. Effects on soil microbiological and chemical properties. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hu, C.; Zhang, S. Effects of earthworm activity on fertility and heavy metal bioavailability in sewage sludge. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 874–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Tang, C.; Li, H.; Wei, Z.; Hu, F. Earthworm Mucus Enhanced Cadmium Accumulation of Tomato Seedlings. Int. J. Phytorem. 2009, 12, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Yang, Y.; Li, M. Responses of soil and earthworm gut bacterial communities to heavy metal contamination. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quirantes, M.; Vivas, A.; Fernandez-Gomez, M.J.; Nogales, R. Vermicomposts and/or Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungal Inoculation in Relation to Metal Availability and Biochemical Quality of a Soil Contaminated with Heavy Metals. Wat. Air. Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 2707–2718. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; He, M.; Ying, W. Influence of combined pollution of antimony and arsenic on culturable soil microbial populations and enzyme activities. Ecotoxicology 2011, 20, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boughattas, I.; Hattab, S.; Boussetta, H.; Banni, M.; Navarro, E. Impact of heavy metal contamination on oxidative stress of Eisenia andrei and bacterial community structure in Tunisian mine soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 18083–18095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srut, M.; Menke, S.; Hockner, M.; Sommer, S. Earthworms and cadmium—Heavy metal resistant gut bacteria as indicators for heavy metal pollution in soils? Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2019, 171, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.D.; Xin, L.; Rong, W.T.; Liu, X.Y.; Deng, W.A.; Qin, Y.C.; Li, X.L. Effect of heavy metals pollution on the composition and diversity of the intestinal microbial community of a pygmy grasshopper (Eucriotettix oculatus). Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2021, 223, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafaii, G.R.; Aseman, E.; Asgharnia, H.; Akbari, H.; Iranshahi, L.; Sayyaf, H. Efficiency of the earthworm Eisenia fetida under the effect of organic matter for bioremediation of soils contaminated with cadmium and chromium. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 33, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hait, S.; Tare, V. Transformation and availability of nutrients and heavy metals during integrated composting-vermicomposting of sewage sludges. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2012, 79, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.; Moon, H.S.; Nam, K.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, T.S. Application of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria for enhancing bioavailability and phytoextraction of cadmium (Cd) from polluted soil. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Tong, Z.H.; Li, L.L.; Yu, H.Q. Toxic effects of imidazolium-based ionic liquids on Caenorhabditis elegans: The role of reactive oxygen species. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 2399–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Song, W.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhu, L. Ecotoxicological effects of different size ranges of industrial-grade polyethylene and polypropylene microplastics on earthworms Eisenia fetida. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 783, 147007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zheng, H.; Zhao, J.; Luo, X.X.; Zhenyu, W.; Xing, B.S. Photodegradation Elevated the Toxicity of Polystyrene Microplastics to Grouper (Epinephelus moara) through Disrupting Hepatic Lipid Homeostasis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6202–6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhu, L.; Wang, J.; Hui, X.; Wang, J.; Han, Y.; Yang, J. Oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation in the earthworm Eisenia fetida induced by low doses of fomesafen. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demars, M.; Samora, N.L.; Yang, S.; Garcia-Borràs, M.; Sanders, J.N.; Houk, K.N.; Podust, L.M.; Sherman, D.H. Exploring the molecular basis for substrate specificity in homologous macrolide biosynthetic cytochromes P450. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 15947–15961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryal, M.; Liakopoulou-Kyriakides, M. Bioremoval of heavy metals by bacterial biomass. Environ. Monit. Assess 2015, 187, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trujillo, M.E.; Raúl, R.; Patricia, B.; Lorena, C. Endophytic Actinobacteria and the Interaction of Micromonospora and Nitrogen Fixing Plants. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fosso-Kankeu, E.; Mulaba-Bafubiandi, A.F.; Mamba, B.B.; Barnard, T.G. Prediction of metal-adsorption behaviour in the remediation of water contamination using indigenous microorganisms. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 2786–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neilands, J.B.; Leong, S.A. Siderophores in Relation to Plant Growth and Disease. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 1986, 37, 187–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, M.B.; Schatzle, S.; Schramm, A.; Kjeldsen, K.U. Verminephrobacter aporrectodeae sp. nov. subsp. tuberculatae and subsp. caliginosae, the specific nephridial symbionts of the earthworms Aporrectodea tuberculata and A. caliginosa. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2012, 101, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.Q.; Zhao, H.T.; Wu, Y.F.; Han, S.W.; Mi, W.H.; Kang, Y.J.; Hu, J.; Feng, K. Effect of feeding conditions on the degradation of tetracycline in sewage sludge by earthworm. Biochem. Eng. J. 2020, 160, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilias, M.; Rafiqullah, I.M.; Debnath, B.C.; Mannan, K.; Hoq, M.M. Isolation and Characterization of Chromium (VI)-Reducing Bacteria from Tannery Effluents. Indian J. Microbiol. 2011, 51, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Soil Properties | Acidic Soil | Alkaline Soil |
|---|---|---|
| pH value | 5.88 ± 0.06 | 8.97 ± 0.12 |
| Organic matter Cr (mg kg−1) | 32.25 ± 0.36 | 14.38 ± 0.14 |
| Acid-extractable Cr (mg kg−1) | 1.13 ± 0.08 | 1.16 ± 0.10 |
| Reducible Cr (mg kg−1) | 1.12 ± 0.03 | 1.07 ± 0.04 |
| Oxidizable Cr (mg kg−1) | 3.37 ± 0.10 | 5.24 ± 0.13 |
| Residual Cr (mg kg−1) | 9.55 ± 0.08 | 7.49 ± 0.09 |
| Total Cr content (mg kg−1) | 15.17 ± 0.33 | 14.96 ± 0.14 |
| (a) Factors | Treatments | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Soils | Acidic soil (S1) | ||
| Alkaline soil (S2) | |||
| Concentration | 15 mg/kg (L), 50 mg/kg (H) | ||
| Earthworms | No earthworms (e0) | ||
| E. fetida (E) | |||
| P. guillelmi (P) | |||
| Plants | No plants (p0) | ||
| Ryegrass (R) | |||
| Maize (C) | |||
| (b) Treatment | Description | Treatment | Description |
| 1 | S1Le0p0 | 19 | S2Le0p0 |
| 2 | S1Le0R | 20 | S2Le0R |
| 3 | S1Le0C | 21 | S2Le0C |
| 4 | S1LEp0 | 22 | S2LEp0 |
| 5 | S1LER | 23 | S2LER |
| 6 | S1LEC | 24 | S2LEC |
| 7 | S1LPp0 | 25 | S2LPp0 |
| 8 | S1LPR | 26 | S2LPR |
| 9 | S1LPC | 27 | S2LPC |
| 10 | S1He0p0 | 28 | S2He0p0 |
| 11 | S1He0R | 29 | S2He0R |
| 12 | S1He0C | 30 | S2He0C |
| 13 | S1HEp0 | 31 | S2HEp0 |
| 14 | S1HER | 32 | S2HER |
| 15 | S1HEC | 33 | S2HEC |
| 16 | S1HPp0 | 34 | S2HPp0 |
| 17 | S1HPR | 35 | S2HPR |
| 18 | S1HPC | 36 | S2HPC |
| Soil Index | S1-L | S1-H | S2-L | S2-H |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 0.856 ** | 0.868 ** | −0.892 ** | −0.720 ** |
| OM | −0.949 ** | −0.869 ** | 0.929 ** | 0.763 ** |
| Taxonomy | Characteristics | Sums of Sqs | Mean Sqs | F_Model | R2 | P_Adjust |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phylum | E-P | 0.100 | 0.100 | 0.542 | 0.083 | 0.740 |
| Genus | E-P | 0.589 | 0.589 | 1.992 | 0.249 | 0.060 |
| Phylum | S1-S2 | 0.353 | 0.354 | 2.472 | 0.293 | 0.070 |
| Genus | S1-S2 | 0.681 | 0.681 | 2.433 | 0.289 | 0.031 |
| Phylum | H-L | 0.228 | 0.228 | 1.396 | 0.189 | 0.261 |
| Genus | H-L | 0.253 | 0.253 | 0.721 | 0.107 | 0.730 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, P.; Song, Y.; Wei, J.; Mao, W.; Ju, J.; Zheng, S.; Zhao, H. Synergistic Effects of Earthworms and Plants on Chromium Removal from Acidic and Alkaline Soils: Biological Responses and Implications. Biology 2023, 12, 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060831
Liu P, Song Y, Wei J, Mao W, Ju J, Zheng S, Zhao H. Synergistic Effects of Earthworms and Plants on Chromium Removal from Acidic and Alkaline Soils: Biological Responses and Implications. Biology. 2023; 12(6):831. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060831
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ping, Yan Song, Jie Wei, Wei Mao, Jing Ju, Shengyang Zheng, and Haitao Zhao. 2023. "Synergistic Effects of Earthworms and Plants on Chromium Removal from Acidic and Alkaline Soils: Biological Responses and Implications" Biology 12, no. 6: 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060831
APA StyleLiu, P., Song, Y., Wei, J., Mao, W., Ju, J., Zheng, S., & Zhao, H. (2023). Synergistic Effects of Earthworms and Plants on Chromium Removal from Acidic and Alkaline Soils: Biological Responses and Implications. Biology, 12(6), 831. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060831






