Intrinsic Immunogenic Tumor Cell Death Subtypes Delineate Prognosis and Responsiveness to Immunotherapy in Lung Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Datasets and Preprocessing
2.2. Identification of the ICD Level in TCGA-LUAD Samples
2.3. WGCNA and Construction of a Scoring System to Assess Single-Sample Immunogenic Cell Death (ICD) Patterns
2.4. Functional and Pathway Enrichment Analysis
2.5. Detecting Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs) and Protein-Protein Interaction (PPIs)
2.6. Establishment and Verification of an ICDrisk Model
2.7. Extraction of RNA and qRT-PCR
2.8. Human Protein Atlas Database Analysis
2.9. Tumor Mutation Status in the Low- and High-ICDrisk Subtypes
2.10. Estimation of Immune Infiltration and Functional Enrichment for the ICDrisk
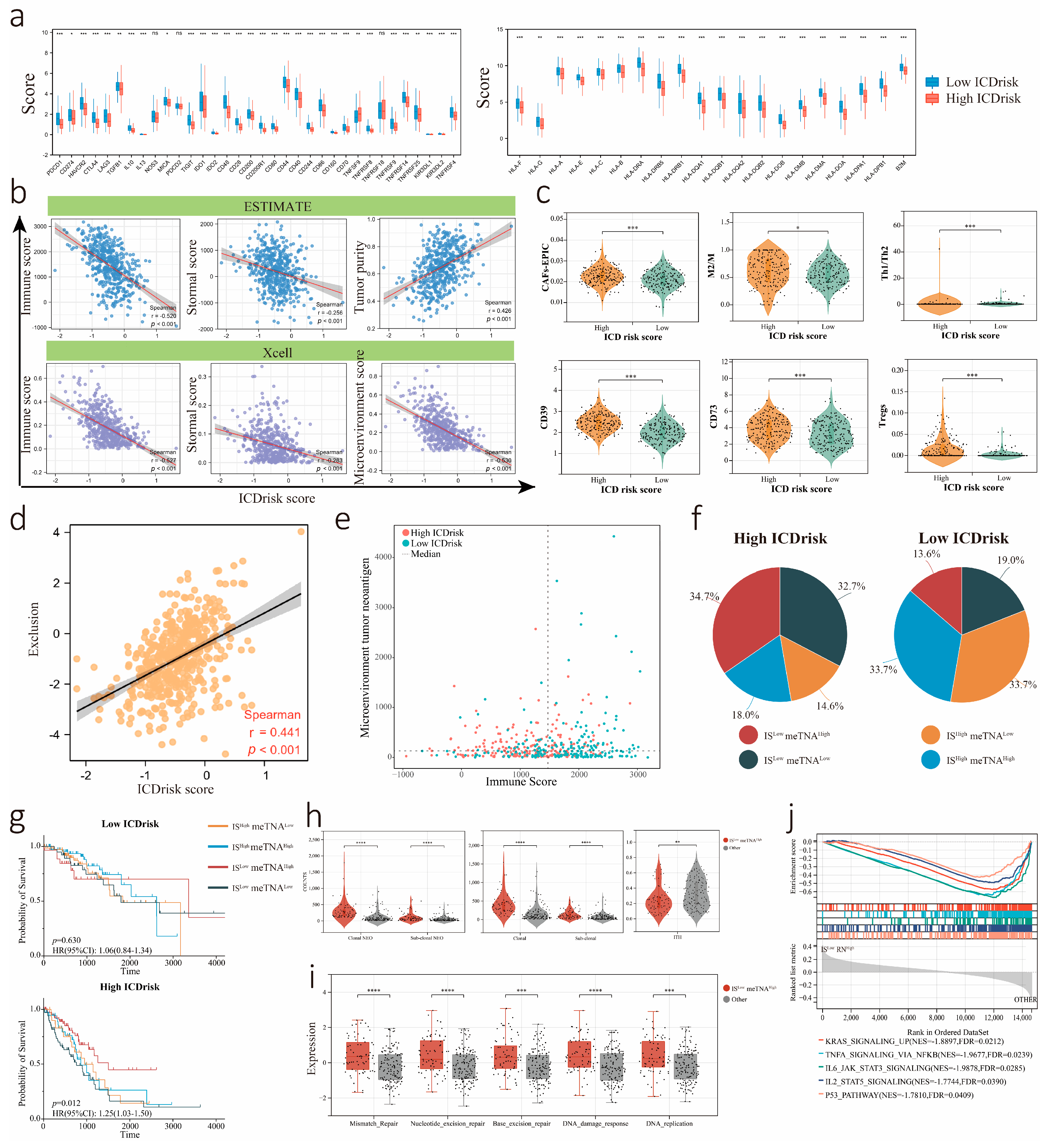
2.11. TIDE (Tumor Immune Dysfunction and Exclusion) Analysis
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
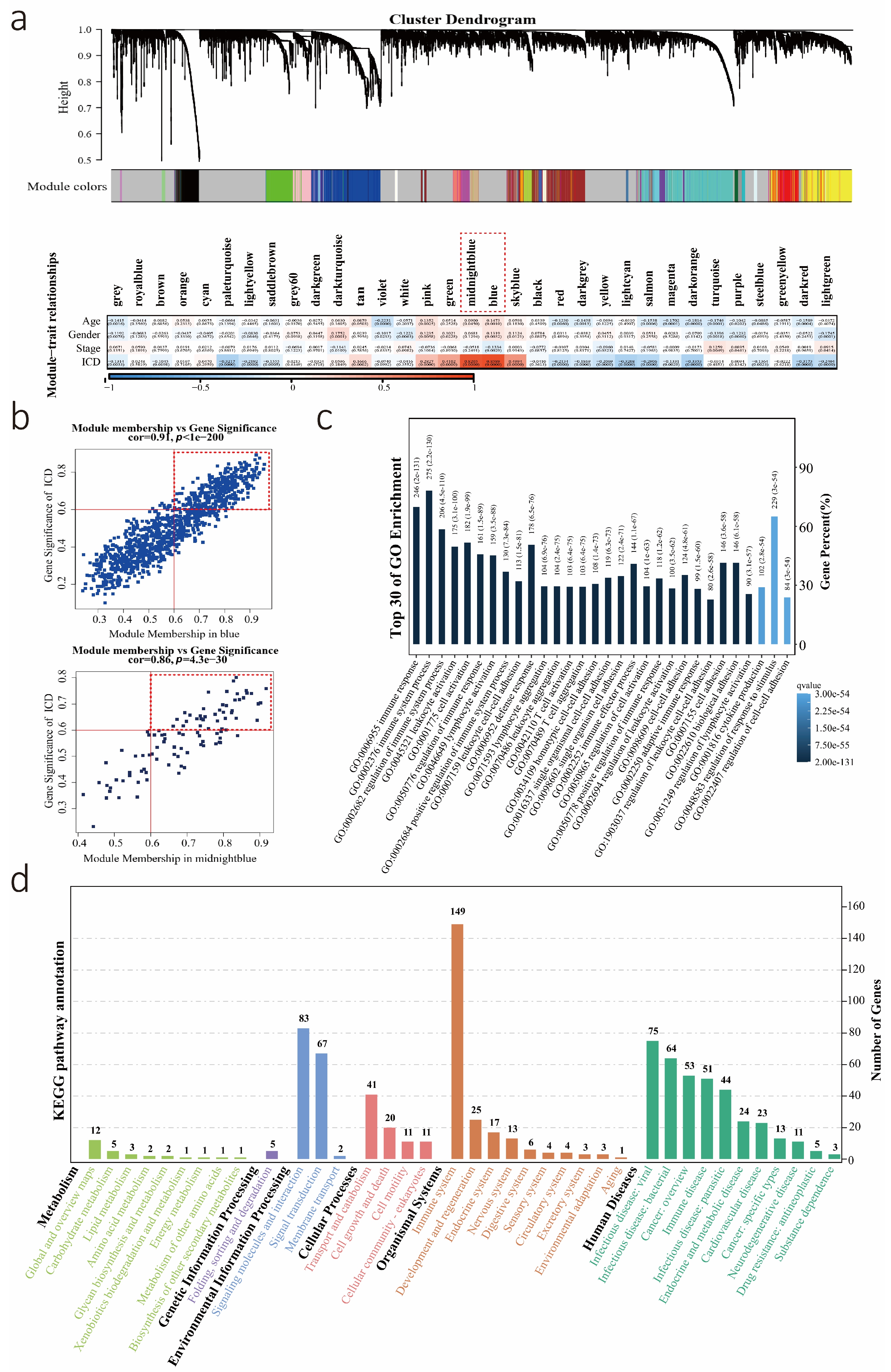
3.1. Calculation of the ICD Level, Performance of WGCNA, and Identification of Key Modules
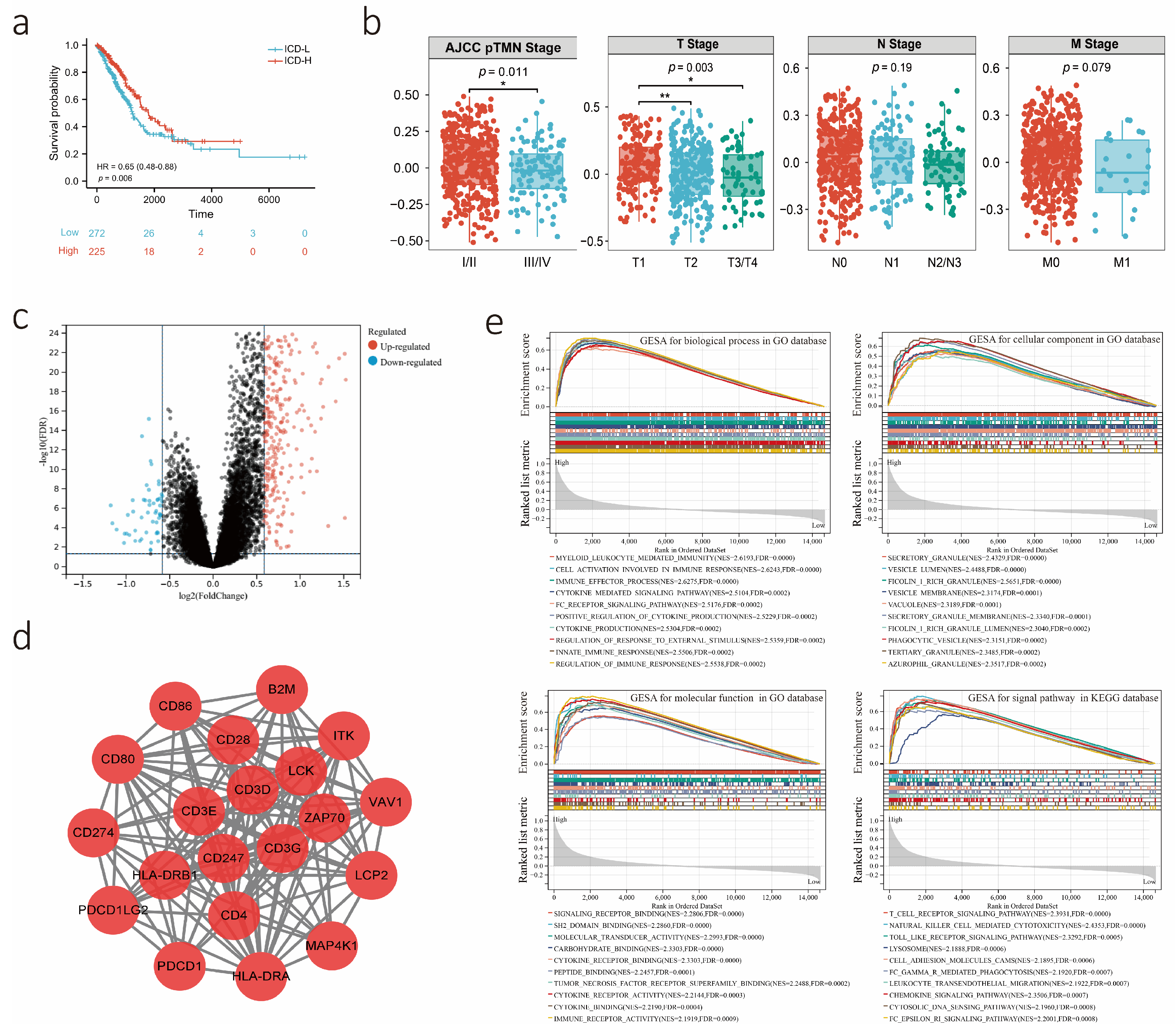
3.2. Potential Biological Role of the ICD Score as a Predictor
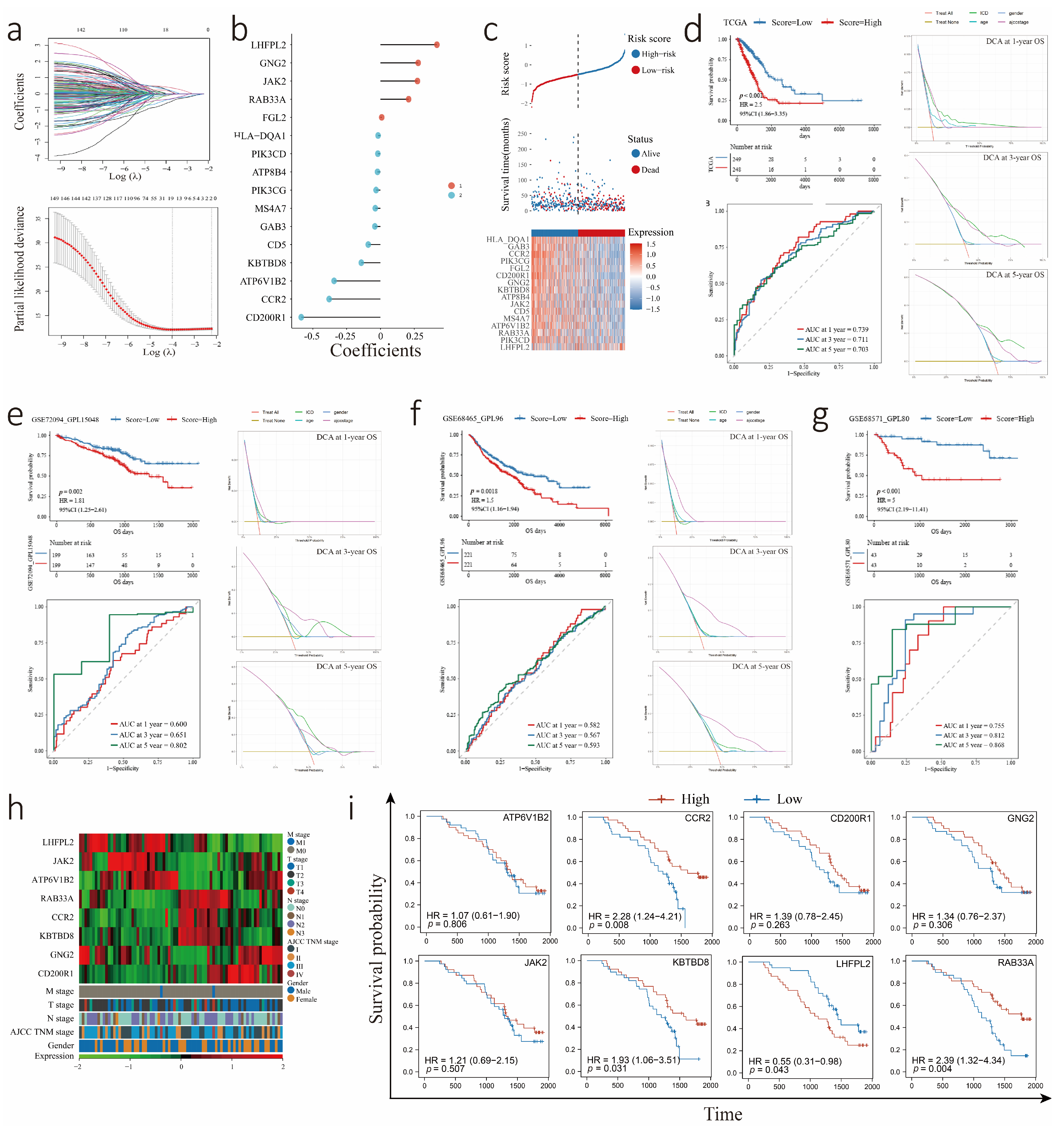
3.3. Construction and Validation of the ICDrisk Score Model
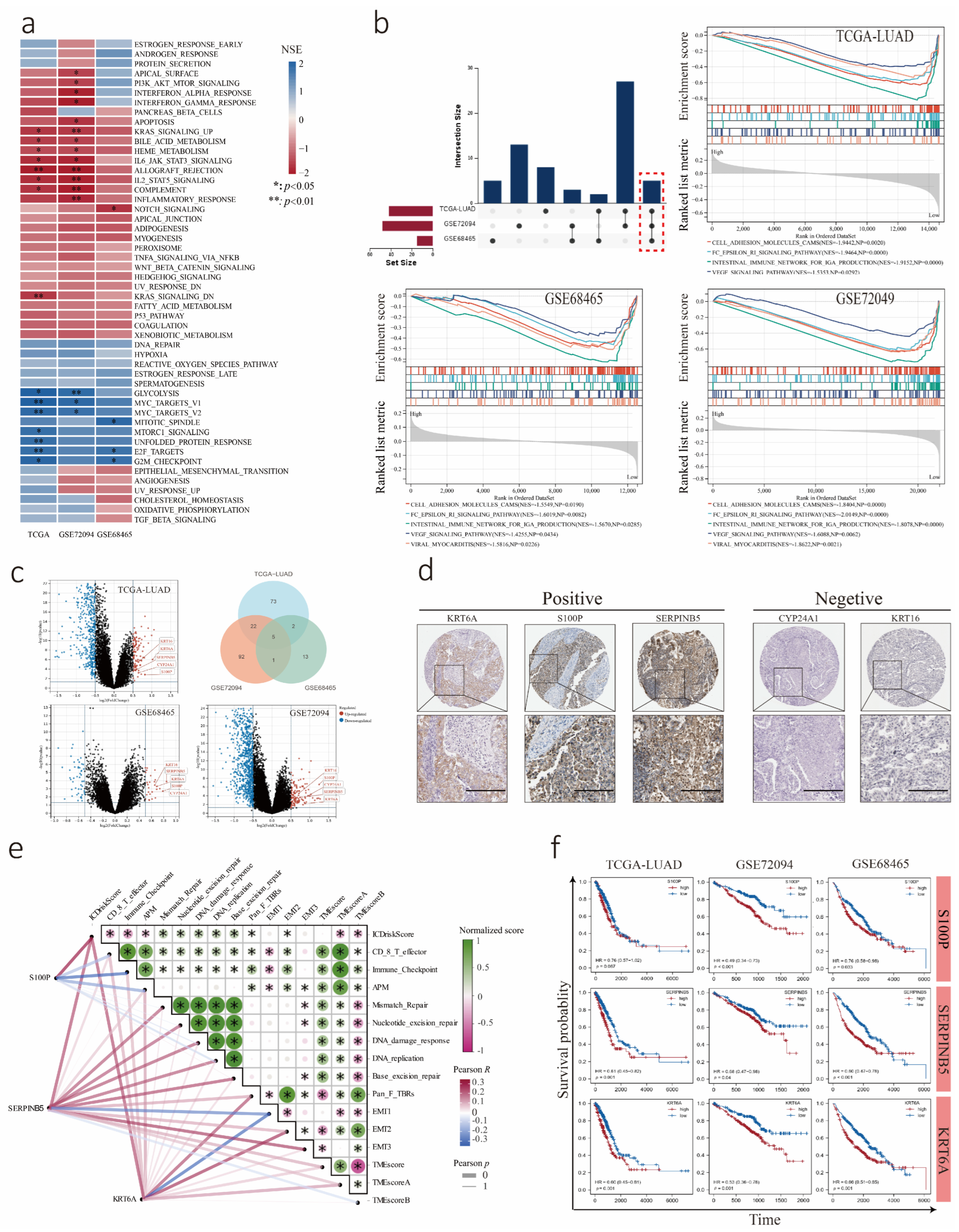
3.4. Transcriptome Analysis of LUAD Cohorts Divided into Low and High ICDrisk Subtypes
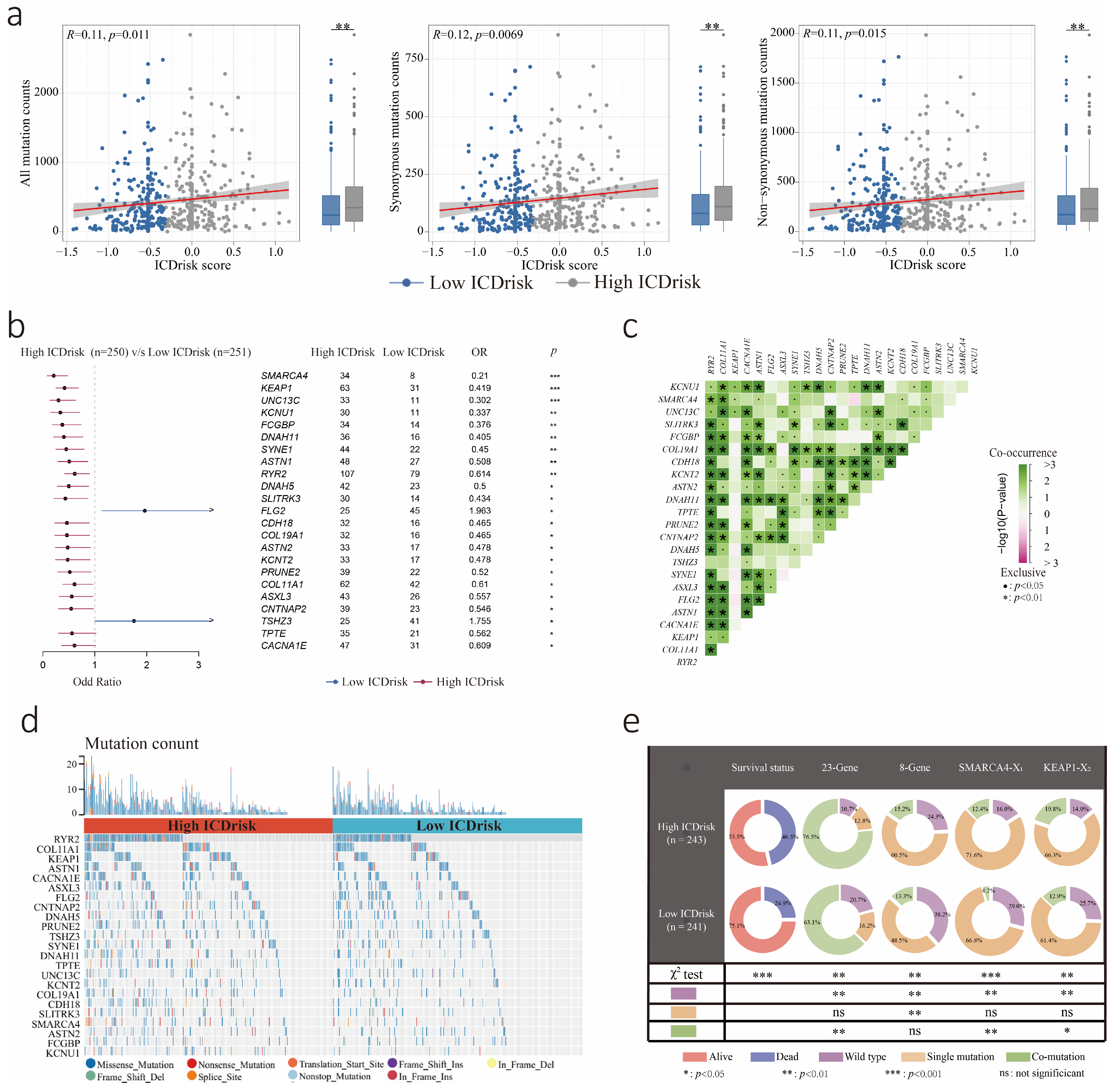
3.5. Mutation Statuses of LUAD Patients with Different ICDrisk Subtypes
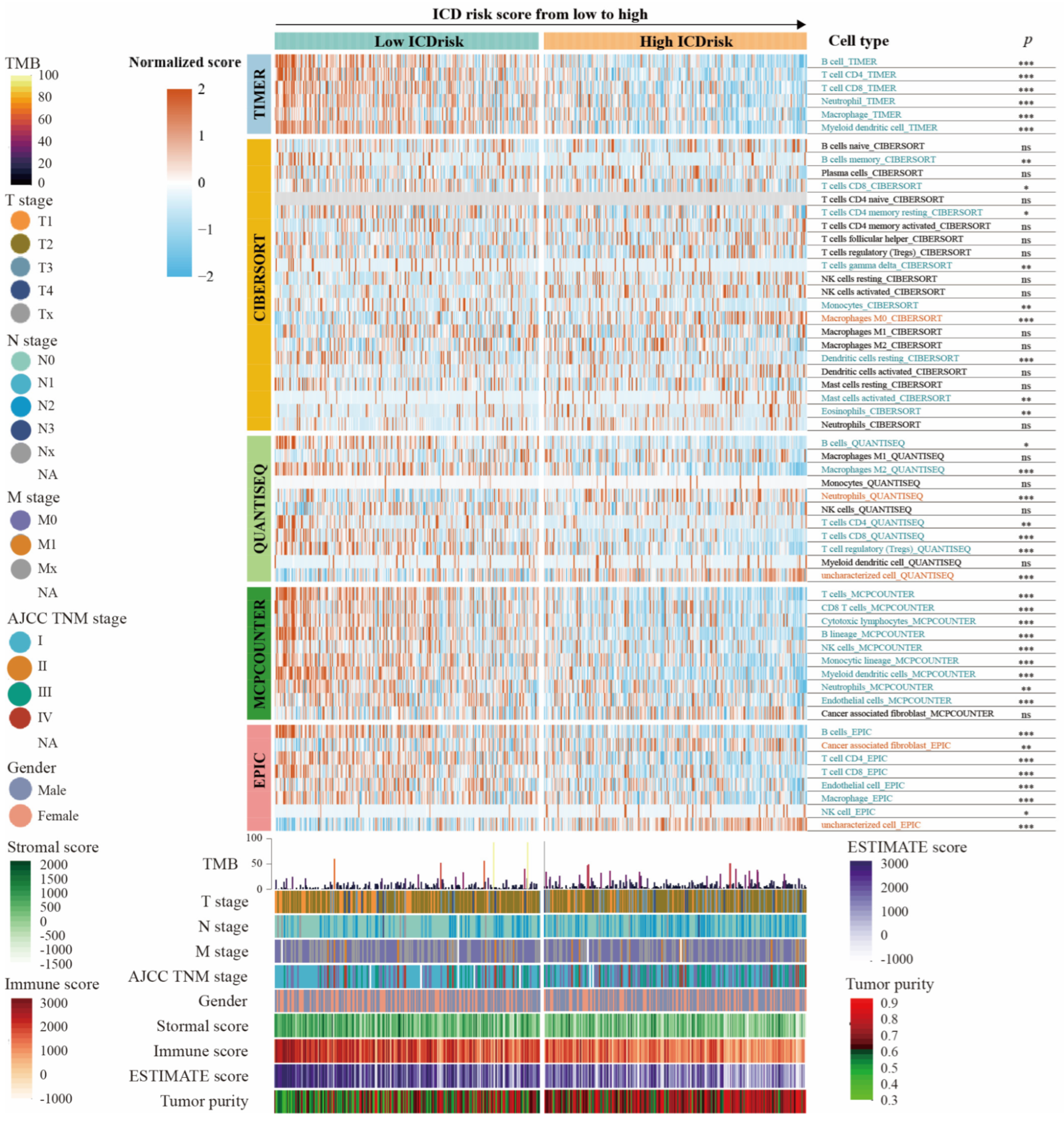
3.6. Relationship between Immune Cells Infiltration and ICDrisk Subtypes
3.7. Association between the LUAD Immune Signature and ICDrisk Score
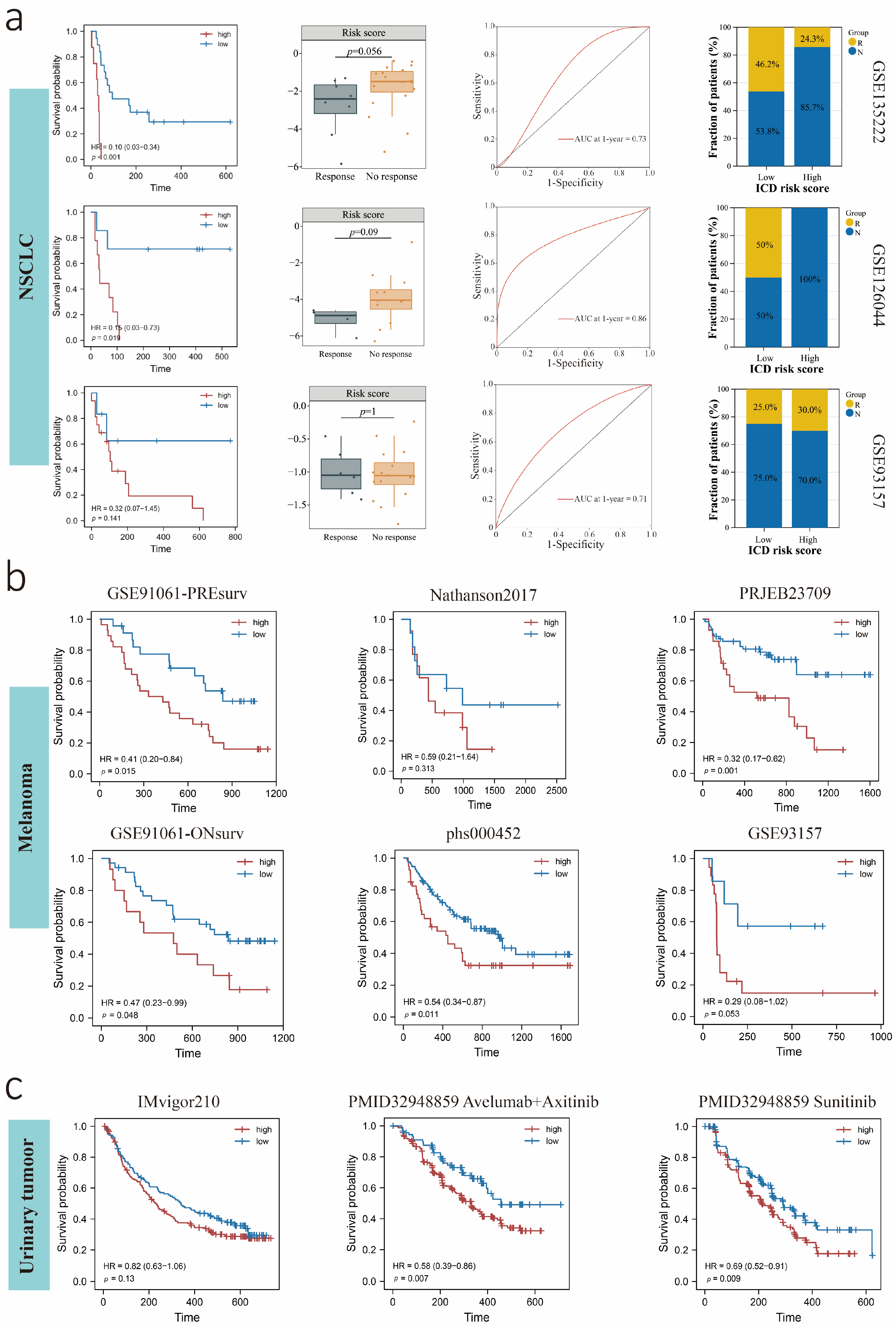
3.8. Predictive Value of the ICDrisk for Response to Immunotherapy and Prognosis of LUAD Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travis, W.D.; Brambilla, E.; Noguchi, M.; Nicholson, A.G.; Geisinger, K.R.; Yatabe, Y.; Beer, D.G.; Powell, C.A.; Riely, G.J.; Van Schil, P.E.; et al. International association for the study of lung cancer/american thoracic society/european respiratory society international multidisciplinary classification of lung adenocarcinoma. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2011, 6, 244–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, X.; Zhao, W.; Pesatori, A.C.; Consonni, D.; Caporaso, N.E.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, B.; Wang, M.; Jones, K.; Hicks, B.; et al. Genetic and epigenetic intratumor heterogeneity impacts prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Succony, L.; Rassl, D.M.; Barker, A.P.; McCaughan, F.M.; Rintoul, R.C. Adenocarcinoma spectrum lesions of the lung: Detection, pathology and treatment strategies. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2021, 99, 102237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, M.; Jiao, D.; Xu, H.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, W.; Han, X.; Wu, K. Biomarkers for predicting efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoenfeld, A.J.; Rizvi, H.; Bandlamudi, C.; Sauter, J.L.; Travis, W.D.; Rekhtman, N.; Plodkowski, A.J.; Perez-Johnston, R.; Sawan, P.; Beras, A.; et al. Clinical and molecular correlates of PD-L1 expression in patients with lung adenocarcinomas. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoulidis, F.; Goldberg, M.E.; Greenawalt, D.M.; Hellmann, M.D.; Awad, M.M.; Gainor, J.F.; Schrock, A.B.; Hartmaier, R.J.; Trabucco, S.E.; Gay, L.; et al. STK11/LKB1 Mutations and PD-1 Inhibitor Resistance in KRAS-Mutant Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 822–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardoll, D.M. The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.; Hodgins, J.J.; Marathe, M.; Nicolai, C.J.; Bourgeois-Daigneault, M.C.; Trevino, T.N.; Azimi, C.S.; Scheer, A.K.; Randolph, H.E.; Thompson, T.W.; et al. Contribution of NK cells to immunotherapy mediated by PD-1/PD-L1 blockade. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 4654–4668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Wu, X.; Ma, S.; Wang, Y.; Nalin, A.P.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Benson, D.M.; He, K.; Caligiuri, M.A.; et al. The Mechanism of Anti-PD-L1 Antibody Efficacy against PD-L1-Negative Tumors Identifies NK Cells Expressing PD-L1 as a Cytolytic Effector. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 1422–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaes, T.L.; Vandenabeele, P. The intrinsic immunogenic properties of cancer cell lines, immunogenic cell death, and how these influence host antitumor immune responses. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 843–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, D.R.; Ferguson, T.; Zitvogel, L.; Kroemer, G. Immunogenic and tolerogenic cell death. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galluzzi, L.; Humeau, J.; Buqué, A.; Zitvogel, L.; Kroemer, G. Immunostimulation with chemotherapy in the era of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 725–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deutsch, E.; Chargari, C.; Galluzzi, L.; Kroemer, G. Optimising efficacy and reducing toxicity of anticancer radioimmunotherapy. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, e452–e463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Gunti, S.; Allen, C.T.; Hong, Y.; Clavijo, P.E.; Van Waes, C.; Schmitt, N.C. ASTX660, an antagonist of cIAP1/2 and XIAP, increases antigen processing machinery and can enhance radiation-induced immunogenic cell death in preclinical models of head and neck cancer. Oncoimmunology 2020, 9, 1710398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fucikova, J.; Kepp, O.; Kasikova, L.; Petroni, G.; Yamazaki, T.; Liu, P.; Zhao, L.; Spisek, R.; Kroemer, G.; Galluzzi, L. Detection of immunogenic cell death and its relevance for cancer therapy. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoentong, P.; Finotello, F.; Angelova, M.; Mayer, C.; Efremova, M.; Rieder, D.; Hackl, H.; Trajanoski, Z. Pan-cancer Immunogenomic Analyses Reveal Genotype-Immunophenotype Relationships and Predictors of Response to Checkpoint Blockade. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 248–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.D.; De Ruysscher, D.; Agostinis, P. Immunological metagene signatures derived from immunogenic cancer cell death associate with improved survival of patients with lung, breast or ovarian malignancies: A large-scale meta-analysis. Oncoimmunology 2016, 5, e1069938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänzelmann, S.; Castelo, R.; Guinney, J. GSVA: Gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. WGCNA: An R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gene Ontology Consortium: Going forward. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D1049–D1056. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M. KEGG as a reference resource for gene and protein annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D457–D462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colwill, K.; Gräslund, S. A roadmap to generate renewable protein binders to the human proteome. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becht, E.; Giraldo, N.A.; Lacroix, L.; Buttard, B.; Elarouci, N.; Petitprez, F.; Selves, J.; Laurent-Puig, P.; Sautès-Fridman, C.; Fridman, W.H.; et al. Estimating the population abundance of tissue-infiltrating immune and stromal cell populations using gene expression. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossarizza, A.; Chang, H.D.; Radbruch, A.; Acs, A.; Adam, D.; Adam-Klages, S.; Agace, W.W.; Aghaeepour, N.; Akdis, M.; Allez, M.; et al. Guidelines for the use of flow cytometry and cell sorting in immunological studies (second edition). Eur. J. Immunol. 2019, 49, 1457–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, A.M.; Liu, C.L.; Green, M.R.; Gentles, A.J.; Feng, W.; Xu, Y.; Hoang, C.D.; Diehn, M.; Alizadeh, A.A. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racle, J.; Gfeller, D. EPIC: A Tool to Estimate the Proportions of Different Cell Types from Bulk Gene Expression Data. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2120, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aran, D.; Hu, Z.; Butte, A.J. xCell: Digitally portraying the tissue cellular heterogeneity landscape. Genome Biol. 2017, 18, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshihara, K.; Shahmoradgoli, M.; Martínez, E.; Vegesna, R.; Kim, H.; Torres-Garcia, W.; Treviño, V.; Shen, H.; Laird, P.W.; Levine, D.A.; et al. Inferring tumour purity and stromal and immune cell admixture from expression data. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wu, S.; Xu, B. A risk model developed based on tumor microenvironment predicts overall survival and associates with tumor immunity of patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 2021, 40, 4413–4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, P.; Gu, S.; Pan, D.; Fu, J.; Sahu, A.; Hu, X.; Li, Z.; Traugh, N.; Bu, X.; Li, B.; et al. Signatures of T cell dysfunction and exclusion predict cancer immunotherapy response. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1550–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galluzzi, L.; Buqué, A.; Kepp, O.; Zitvogel, L.; Kroemer, G. Immunogenic cell death in cancer and infectious disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopecka, J.; Salaroglio, I.C.; Righi, L.; Libener, R.; Orecchia, S.; Grosso, F.; Milosevic, V.; Ananthanarayanan, P.; Ricci, L.; Capelletto, E.; et al. Loss of C/EBP-β LIP drives cisplatin resistance in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Lung Cancer 2018, 120, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesniere, A.; Schlemmer, F.; Boige, V.; Kepp, O.; Martins, I.; Ghiringhelli, F.; Aymeric, L.; Michaud, M.; Apetoh, L.; Barault, L.; et al. Immunogenic death of colon cancer cells treated with oxaliplatin. Oncogene 2010, 29, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Zhao, L.; Pol, J.; Levesque, S.; Petrazzuolo, A.; Pfirschke, C.; Engblom, C.; Rickelt, S.; Yamazaki, T.; Iribarren, K.; et al. Crizotinib-induced immunogenic cell death in non-small cell lung cancer. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzi, C.; Cuomo, A.; Spadoni, I.; Magni, E.; Silvola, A.; Conte, A.; Sigismund, S.; Ravenda, P.S.; Bonaldi, T.; Zampino, M.G.; et al. The EGFR-specific antibody cetuximab combined with chemotherapy triggers immunogenic cell death. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.C.; Holl, E.K.; Boczkowski, D.; Dobrikova, E.; Mosaheb, M.; Chandramohan, V.; Bigner, D.D.; Gromeier, M.; Nair, S.K. Cancer immunotherapy with recombinant poliovirus induces IFN-dominant activation of dendritic cells and tumor antigen-specific CTLs. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaan4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fend, L.; Yamazaki, T.; Remy, C.; Fahrner, C.; Gantzer, M.; Nourtier, V.; Préville, X.; Quéméneur, E.; Kepp, O.; Adam, J.; et al. Immune Checkpoint Blockade, Immunogenic Chemotherapy or IFN-α Blockade Boost the Local and Abscopal Effects of Oncolytic Virotherapy. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 4146–4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siurala, M.; Bramante, S.; Vassilev, L.; Hirvinen, M.; Parviainen, S.; Tähtinen, S.; Guse, K.; Cerullo, V.; Kanerva, A.; Kipar, A.; et al. Oncolytic adenovirus and doxorubicin-based chemotherapy results in synergistic antitumor activity against soft-tissue sarcoma. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragale, A.; Romagnoli, G.; Licursi, V.; Buoncervello, M.; Del Vecchio, G.; Giuliani, C.; Parlato, S.; Leone, C.; De Angelis, M.; Canini, I.; et al. Antitumor Effects of Epidrug/IFNα Combination Driven by Modulated Gene Signatures in Both Colorectal Cancer and Dendritic Cells. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2017, 5, 604–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fucikova, J.; Moserova, I.; Truxova, I.; Hermanova, I.; Vancurova, I.; Partlova, S.; Fialova, A.; Sojka, L.; Cartron, P.F.; Houska, M.; et al. High hydrostatic pressure induces immunogenic cell death in human tumor cells. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 1165–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golden, E.B.; Frances, D.; Pellicciotta, I.; Demaria, S.; Helen Barcellos-Hoff, M.; Formenti, S.C. Radiation fosters dose-dependent and chemotherapy-induced immunogenic cell death. Oncoimmunology 2014, 3, e28518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riganti, C.; Lingua, M.F.; Salaroglio, I.C.; Falcomatà, C.; Righi, L.; Morena, D.; Picca, F.; Oddo, D.; Kopecka, J.; Pradotto, M.; et al. Bromodomain inhibition exerts its therapeutic potential in malignant pleural mesothelioma by promoting immunogenic cell death and changing the tumor immune-environment. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1398874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Nelson, M.; Basu, M.; Srinivasan, P.; Lazarski, C.; Zhang, P.; Zheng, P.; Sandler, A.D. MYC oncogene is associated with suppression of tumor immunity and targeting Myc induces tumor cell immunogenicity for therapeutic whole cell vaccination. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e001388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.L.; Pillai, S.; Pernazza, D.; Sebti, S.M.; Lawrence, N.J.; Chellappan, S.P. Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase genes by E2F transcription factors: Rb-Raf-1 interaction as a novel target for metastatic disease. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshi, M.; Takahashi, H.; Tokumaru, Y.; Yan, L.; Rashid, O.M.; Matsuyama, R.; Endo, I.; Takabe, K. G2M Cell Cycle Pathway Score as a Prognostic Biomarker of Metastasis in Estrogen Receptor (ER)-Positive Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beauchemin, N.; Arabzadeh, A. Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecules (CEACAMs) in cancer progression and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2013, 32, 643–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molfetta, R.; Quatrini, L.; Gasparrini, F.; Zitti, B.; Santoni, A.; Paolini, R. Regulation of fc receptor endocytic trafficking by ubiquitination. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariathasan, S.; Turley, S.J.; Nickles, D.; Castiglioni, A.; Yuen, K.; Wang, Y.; Kadel, E.E., III; Koeppen, H.; Astarita, J.L.; Cubas, R.; et al. TGFβ attenuates tumour response to PD-L1 blockade by contributing to exclusion of T cells. Nature 2018, 554, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojahn, T.B.; Vorstandlechner, V.; Krausgruber, T.; Bauer, W.M.; Alkon, N.; Bangert, C.; Thaler, F.M.; Sadeghyar, F.; Fortelny, N.; Gernedl, V.; et al. Single-cell transcriptomics combined with interstitial fluid proteomics defines cell type-specific immune regulation in atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 1056–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouboulis, C.C.; Nogueira da Costa, A.; Makrantonaki, E.; Hou, X.X.; Almansouri, D.; Dudley, J.T.; Edwards, H.; Readhead, B.; Balthasar, O.; Jemec, G.B.E.; et al. Alterations in innate immunity and epithelial cell differentiation are the molecular pillars of hidradenitis suppurativa. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. JEADV 2020, 34, 846–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloy, N.; Garcia, P.; Laumont, C.M.; Pitt, J.M.; Sistigu, A.; Stoll, G.; Yamazaki, T.; Bonneil, E.; Buqué, A.; Humeau, J.; et al. Immunogenic stress and death of cancer cells: Contribution of antigenicity vs adjuvanticity to immunosurveillance. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 280, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, A.D.; Galluzzi, L.; Apetoh, L.; Baert, T.; Birge, R.B.; Bravo-San Pedro, J.M.; Breckpot, K.; Brough, D.; Chaurio, R.; Cirone, M.; et al. Molecular and Translational Classifications of DAMPs in Immunogenic Cell Death. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krysko, D.V.; Garg, A.D.; Kaczmarek, A.; Krysko, O.; Agostinis, P.; Vandenabeele, P. Immunogenic cell death and DAMPs in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 860–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Paulete, A.R.; Teijeira, A.; Cueto, F.J.; Garasa, S.; Pérez-Gracia, J.L.; Sánchez-Arráez, A.; Sancho, D.; Melero, I. Antigen cross-presentation and T-cell cross-priming in cancer immunology and immunotherapy. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, xii44–xii55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfirschke, C.; Engblom, C.; Rickelt, S.; Cortez-Retamozo, V.; Garris, C.; Pucci, F.; Yamazaki, T.; Poirier-Colame, V.; Newton, A.; Redouane, Y.; et al. Immunogenic Chemotherapy Sensitizes Tumors to Checkpoint Blockade Therapy. Immunity 2016, 44, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voorwerk, L.; Slagter, M.; Horlings, H.M.; Sikorska, K.; van de Vijver, K.K.; de Maaker, M.; Nederlof, I.; Kluin, R.J.C.; Warren, S.; Ong, S.; et al. Immune induction strategies in metastatic triple-negative breast cancer to enhance the sensitivity to PD-1 blockade: The TONIC trial. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, D.; Margolis, C.A.; Vokes, N.I.; Liu, D.; Taylor-Weiner, A.; Wankowicz, S.M.; Adeegbe, D.; Keliher, D.; Schilling, B.; Tracy, A.; et al. Genomic correlates of response to immune checkpoint blockade in microsatellite-stable solid tumors. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1271–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumal, D.; Imai, N.; Laganà, A.; Finnigan, J.; Melnekoff, D.; Leshchenko, V.V.; Solovyov, A.; Madduri, D.; Chari, A.; Cho, H.J.; et al. Mutation-derived Neoantigen-specific T-cell Responses in Multiple Myeloma. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 450–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGranahan, N.; Furness, A.J.; Rosenthal, R.; Ramskov, S.; Lyngaa, R.; Saini, S.K.; Jamal-Hanjani, M.; Wilson, G.A.; Birkbak, N.J.; Hiley, C.T.; et al. Clonal neoantigens elicit T cell immunoreactivity and sensitivity to immune checkpoint blockade. Science 2016, 351, 1463–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGranahan, N.; Swanton, C. Clonal Heterogeneity and Tumor Evolution: Past, Present, and the Future. Cell 2017, 168, 613–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DuPage, M.; Mazumdar, C.; Schmidt, L.M.; Cheung, A.F.; Jacks, T. Expression of tumour-specific antigens underlies cancer immunoediting. Nature 2012, 482, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Lu, Z.; McCadden, J.D.; Levitsky, H.I.; Marson, A.L. Reciprocal changes in tumor antigenicity and antigen-specific T cell function during tumor progression. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 200, 1581–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumacher, T.N.; Schreiber, R.D. Neoantigens in cancer immunotherapy. Science 2015, 348, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vesely, M.D.; Kershaw, M.H.; Schreiber, R.D.; Smyth, M.J. Natural innate and adaptive immunity to cancer. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 235–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.A.; Yarchoan, M.; Jaffee, E.; Swanton, C.; Quezada, S.A.; Stenzinger, A.; Peters, S. Development of tumor mutation burden as an immunotherapy biomarker: Utility for the oncology clinic. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenfeld, A.J.; Bandlamudi, C.; Lavery, J.A.; Montecalvo, J.; Namakydoust, A.; Rizvi, H.; Egger, J.; Concepcion, C.P.; Paul, S.; Arcila, M.E.; et al. The Genomic Landscape of SMARCA4 Alterations and Associations with Outcomes in Patients with Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 5701–5708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalera, S.; Mazzotta, M.; Corleone, G.; Sperati, F.; Terrenato, I.; Krasniqi, E.; Pizzuti, L.; Barba, M.; Vici, P.; Gallo, E.; et al. KEAP1 and TP53 Frame Genomic, Evolutionary, and Immunologic Subtypes of Lung Adenocarcinoma With Different Sensitivity to Immunotherapy. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2021, 16, 2065–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, J.M.; Marabelle, A.; Eggermont, A.; Soria, J.C.; Kroemer, G.; Zitvogel, L. Targeting the tumor microenvironment: Removing obstruction to anticancer immune responses and immunotherapy. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 1482–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Cao, N.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, S.; Chen, D.; Li, L.; He, Y.; Dong, X.; et al. NFE2L2/KEAP1 Mutations Correlate with Higher Tumor Mutational Burden Value/PD-L1 Expression and Potentiate Improved Clinical Outcome with Immunotherapy. Oncologist 2020, 25, e955–e963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinelli, D.; Mazzotta, M.; Scalera, S.; Terrenato, I.; Sperati, F.; D’Ambrosio, L.; Pallocca, M.; Corleone, G.; Krasniqi, E.; Pizzuti, L.; et al. KEAP1-driven co-mutations in lung adenocarcinoma unresponsive to immunotherapy despite high tumor mutational burden. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1746–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, X.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, R.; Huang, Z.; Wang, G.; Guo, G.; Wang, W.; Wen, Y.; et al. Intrinsic Immunogenic Tumor Cell Death Subtypes Delineate Prognosis and Responsiveness to Immunotherapy in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Biology 2023, 12, 808. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060808
He X, Zhao D, Zhang X, Ma Y, Zhang R, Huang Z, Wang G, Guo G, Wang W, Wen Y, et al. Intrinsic Immunogenic Tumor Cell Death Subtypes Delineate Prognosis and Responsiveness to Immunotherapy in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Biology. 2023; 12(6):808. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060808
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Xiaotian, Dechang Zhao, Xuewen Zhang, Yiyang Ma, Rusi Zhang, Zirui Huang, Gongming Wang, Guangran Guo, Weidong Wang, Yingsheng Wen, and et al. 2023. "Intrinsic Immunogenic Tumor Cell Death Subtypes Delineate Prognosis and Responsiveness to Immunotherapy in Lung Adenocarcinoma" Biology 12, no. 6: 808. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060808
APA StyleHe, X., Zhao, D., Zhang, X., Ma, Y., Zhang, R., Huang, Z., Wang, G., Guo, G., Wang, W., Wen, Y., & Zhang, L. (2023). Intrinsic Immunogenic Tumor Cell Death Subtypes Delineate Prognosis and Responsiveness to Immunotherapy in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Biology, 12(6), 808. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12060808


_Kwok.png)

