Comparison of the Impact between Classical and Novel Strains of Rabbit Haemorrhagic Disease on Wild Rabbit Populations in Spain
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
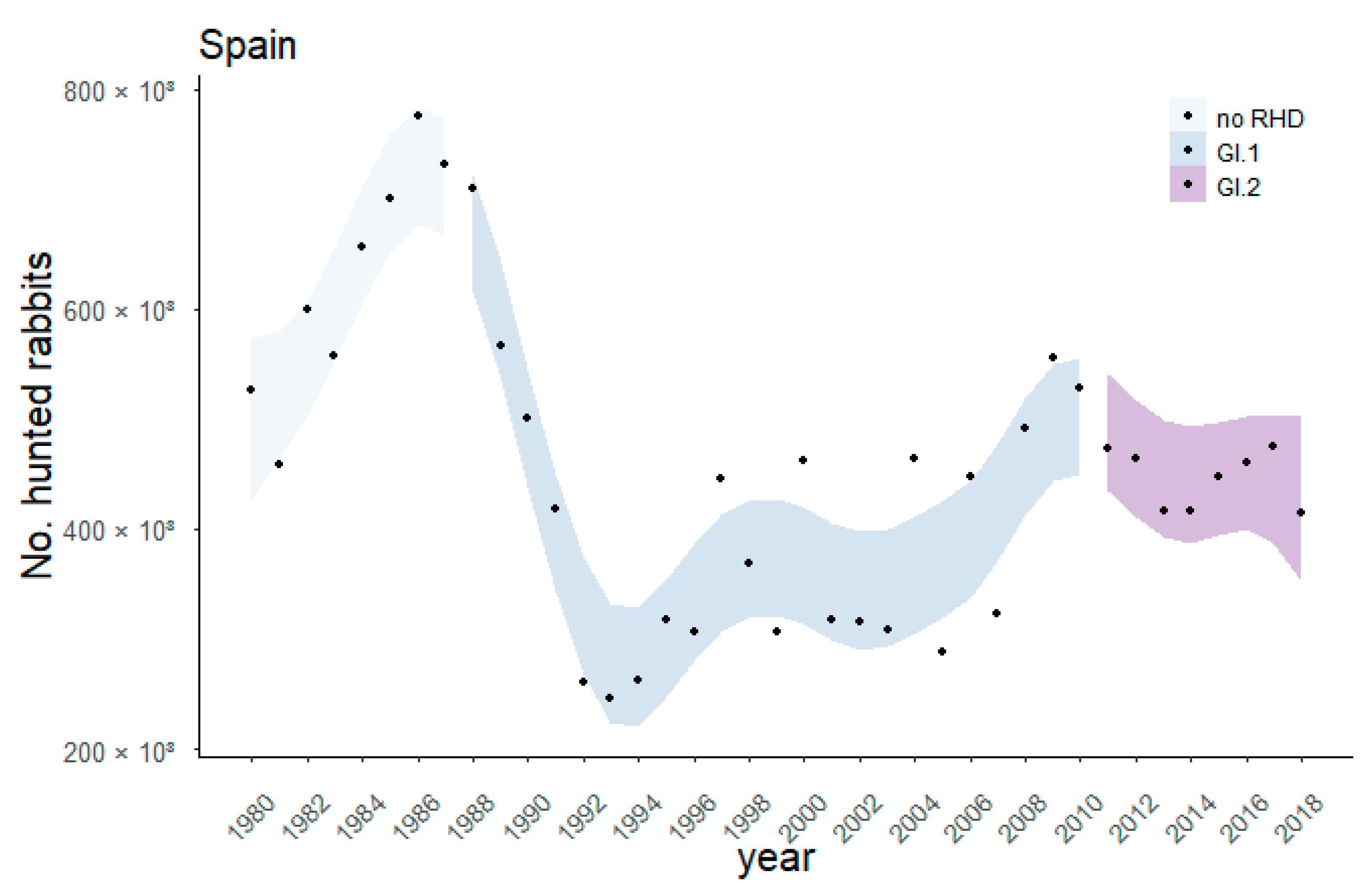
3.1. Nationwide Effect
3.2. Regionwide Effect
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Delibes-Mateos, M.; Delibes, M.; Ferreras, P.; Villafuerte, R. Key role of European rabbits in the conservation of the western Mediterranean Basin hotspot. Conserv. Biol. 2008, 22, 1106–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministerio para la Transición Ecológica y el Reto Demográfico (2023). Estadística Anual de caza. Available online: https://www.miteco.gob.es/es/biodiversidad/estadisticas/Est_Anual_Caza.aspx (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Delibes-Mateos, M.; Ferreras, P.; Villafuerte, R. European rabbit population trends and associated factors: A review of the situation in the Iberian Peninsula. Mamm. Rev. 2009, 39, 124–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouco, C.; Abrantes, J.; Serronha, A.; Lopes, A.M.; Maio, E.; Magalhães, M.J.; Blanco, E.; Bárcena, J.; Esteves, P.J.; Santos, N.; et al. Epidemiology of RHDV2 (Lagovirus europaeus/GI.2) in free-living wild European rabbits in Portugal. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, e373–e382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouco, C.; Abrantes, J.; Delibes-Mateos, M. Lessons from viruses that affect lagomorphs. Science 2020, 369, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delibes-Mateos, M.; Ferreira, C.; Carro, F.; Escudero, M.A.; Gortázar, C. Ecosystem Effects of Variant Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease Virus, Iberian Peninsula. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 2166–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monterroso, P.; Garrote, G.; Serronha, A.; Santos, E.; Delibes-Mateos, M.; Abrantes, J.; De Ayala, R.; Silvestre, F.; Carvalho, J.; Vasco, I.; et al. Disease-mediated bottom-up regulation: An emergent virus affects a keystone prey, and alters the dynamics of trophic webs. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villafuerte, R.; Delibes-Mateos, M.; Oryctolagus cuniculus. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019: e.T41291A45189779. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/41291/170619657 (accessed on 15 April 2023).
- Le Pendu, J.; Abrantes, J.; Bertagnoli, S.; Guitton, J.S.; Le Gall-Reculé, G.; Lopes, A.M.; Marchandeau, S.; Alda, F.; Almeida, T.; Célio, A.P.; et al. Proposal for a unified classification system and nomenclature of lagoviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 1658–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.J.; Xue, H.P.; Pu, B.Q.; Qian, N.H. A new viral disease in rabbits. Xumu Yu Shouyi 1984, 16, 253–255. [Google Scholar]
- Abrantes, J.; Van Der Loo, W.; Le Pendu, J.; Esteves, P.J. Rabbit haemorrhagic disease (RHD) and rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus (RHDV): A review. Vet. Res. 2012, 43, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguayo-Adán, J.A.; Rouco, C.; Delibes-Mateos, M.; Santoro, S. Lack of evidence for differences in spread of classic (Lagovirus europaeus/GI.1) and novel (Lagovirus europaeus/GI.2) rabbit haemorrhagic disease viruses in Europe and North Africa. Vet. Rec. 2022, 190, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvete, C. Modeling the effect of population dynamics on the impact of rabbit hemorrhagic disease. Conserv. Biol. 2006, 20, 1232–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Gall-Reculé, G.; Zwingelstein, F.; Boucher, S.; Le Normand, B.; Plassiart, G.; Portejoie, Y.; Decors, A.; Bertagnoli, S.; Guérin, J.L.; Marchandeau, S. Detection of a new variant of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus in France. Vet. Rec. 2011, 168, 137–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Gall-Recule, G.; Lavazza, A.; Marchandeau, S.; Bertagnoli, S.; Zwingelstein, F.; Cavadini, P.; Martinelli, N.; Lombardi, G.; Guérin, J.L.; Lemaitre, E.; et al. Emergence of a new lagovirus related to Rabbit Haemorrhagic Disease Virus. Vet. Res. 2013, 44, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, K.P.; Nicieza, I.; Balseiro, A.; Muguerza, M.A.; Rosell, J.M.; Casais, R.; Álvarez, A.L.; Parra, F. Variant Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease Virus in Young Rabbits, Spain. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 2009–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouco, C.; Aguayo-Adán, J.A.; Santoro, S.; Abrantes, J.; Delibes-Mateos, M. Worldwide rapid spread of the novel rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus (GI.2/RHDV2/b). Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 1762–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capucci, L.; Cavadini, P.; Schiavitto, M.; Lombardi, G.; Lavazza, A. Increased pathogenicity in rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus type 2 (RHDV2). Vet. Rec. 2017, 180, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velarde, R.; Abrantes, J.; Lopes, A.M.; Estruch, J.; Côrte-Real, J.V.; Esteves, P.J.; García-Bocanegra, I.; Ruiz-Olmo, J.; Rouco, C. Spillover event of recombinant Lagovirus europaeus/GI.2 into the Iberian hare (Lepus granatensis) in Spain. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 3187–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puggioni, G.; Cavadini, P.; Maestrale, C.; Scivoli, R.; Botti, G.; Ligios, C.; Le Gall-Reculé, G.; Lavazza, A.; Capucci, L. The new French 2010 Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease Virus causes an RHD-like disease in the Sardinian Cape hare (Lepus capensis mediterraneus). Vet. Res. 2013, 44, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camarda, A.; Pugliese, N.; Cavadini, P.; Circella, E.; Capucci, L.; Caroli, A.; Legretto, M.; Mallia, E.; Lavazza, A. Detection of the new emerging rabbit haemorrhagic disease type 2 virus (RHDV2) in Sicily from rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus) and Italian hare (Lepus corsicanus). Res. Vet. Sci. 2014, 97, 642–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velarde, R.; Cavadini, P.; Neimanis, A.; Cabezón, O.; Chiari, M.; Gaffuri, A.; Lavín, S.; Grilli, G.; Gavier-Widén, D.; Lavazza, A.; et al. Spillover Events of Infection of Brown Hares (Lepus europaeus) with Rabbit Haemorrhagic Disease Type 2 Virus (RHDV2) Caused Sporadic Cases of an European Brown Hare Syndrome-Like Disease in Italy and Spain. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 1750–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abade Dos Santos, F.A.; Pinto, A.; Burgoyne, T.; Dalton, K.P.; Carvalho, C.L.; Ramilo, D.W.; Carneiro, C.; Carvalho, T.; Peleteiro, M.C.; Parra, F.; et al. Spillover events of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus 2 (recombinant GI.4P-GI.2) from Lagomorpha to Eurasian badger. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 1030–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, A.M.; Dalton, K.P.; Magalhães, M.J.; Parra, F.; Esteves, P.J.; Holmes, E.C.; Abrantes, J. Full genomic analysis of new variant rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus revealed multiple recombination events. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvério, D.; Lopes, A.M.; Melo-Ferreira, J.; Magalhães, M.J.; Monterroso, P.; Serronha, A.; Maio, E.; Alves, P.C.; Esteves, P.J.; Abrantes, J. Insights into the evolution of the new variant rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus (GI.2) and the identification of novel recombinant strains. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, K.P.; Nicieza, I.; Abrantes, J.; Esteves, P.J.; Parra, F. Spread of new variant RHDV in domestic rabbits on the Iberian Peninsula. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 21, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villafuerte, R.; Calvete, C.; Blanco, J.C.; Lucientes, J. Incidence of viral hemorrhagic disease in wild rabbit populations in Spain. Mammalia 1995, 59, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvete, C.; Pelayo, E.; Sampietro, F.J. Habitat factors related to wild rabbit population trends after initial impact of rabbit haemorrhagic disease. Wildl. Res. 2006, 33, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, S.; Beltrán, J.F.; Cotilla, I.; Kuffner, B.; Laffite, R.; Jordan, G.; Ayala, J.; Quintero, C.; Jiménez, A.; Castro, F.; et al. Long-term decline of European wild rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus) in south-western Spain. Wildl. Res. 2007, 34, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delibes-Mateos, M.; Ferreras, P.; Villafuerte, R. Rabbit populations and game management: The situation after 15 years of rabbit haemorrhagic disease in central-southern Spain. Biodivers. Conserv. 2008, 17, 559–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, S.; Pacios, I.; Moreno, S.; Bertó-Moran, A.; Rouco, C. Multi-event capture–recapture modeling of host–pathogen dynamics among European rabbit populations exposed to myxoma and Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease Viruses: Common and heterogeneous patterns. Vet. Res. 2014, 45, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Casado, J.; Carpio, A.J.; Tortosa, F.S. Recent negative trends of wild rabbit populations in southern Spain after the arrival of the new variant of the rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus RHDV2. Mamm. Biol. 2016, 81, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvete, C.; Capucci, L.; Lavazza, A.; Sarto, M.P.; Calvo, A.J.; Monroy, F.; Calvo, J.H. Changes in European wild rabbit population dynamics and the epidemiology of rabbit haemorrhagic disease in response to artificially increased viral transmission. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 2682–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-de-Simon, J.; Díaz-Ruiz, F.; Cirilli, F.; Tortosa, F.S.; Villafuerte, R.; Delibes-Mateos, M.; Ferreras, P. Towards a standardized index of European rabbit abundance in Iberian Mediterranean habitats. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2011, 57, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouco, C.; Santoro, S.; Delibes-Mateos, M.; Villafuerte, R. Optimization and accuracy of faecal pellet count estimates of population size: The case of European rabbits in extensive breeding nuclei. Ecol. Ind. 2016, 64, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouco, C.; Villafuerte, R.; Aguayo-Adán, J.A.; Carrasco-Expósito, D.; Inigo-Lopez, S.; Jeblaoui, H.; Jiménez-Fernández, J.; Jiménez-Uceda, J.C.; Limones-Ceballos, D.; López-Luengo, M.C.; et al. Persistence of wild rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus) latrines and its implication for monitoring programs. J. Nat. Conserv. 2021, 62, 126021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virgós, E.; Cabezas-Díaz, S.; Lozano, J. Is the wild rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus) a threatened species in Spain? Sociological constraints in the conservation of species. Biodivers. Conserv. 2007, 16, 3489–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Classification and Regression by randomForest. R News 2002, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, F.; Ishwaran, H. Random forest missing data algorithms. Stat. Anal. Data Min. 2007, 10, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyndman, R.; Athanasopoulos, G.; Bergmeir, C.; Caceres, G.; Chhay, L.; O’Hara-Wild, M.; Petropoulos, F.; Razbash, S.; Wang, E.; Yasmeen, F. Forecast: Forecasting Functions for Time Series and Linear Models, R Package Version 8.18; 2022. Available online: https://pkg.robjhyndman.com/forecast/ (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Exploring the Nature of Covariate Effects in the Proportional Hazards Model. Biometrics 1990, 46, 1005–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belgrano, A.; Lima, M.; Stenseth, N.C. Non-linear dynamics in marine-phytoplankton population systems. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2004, 273, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.N. Fast stable restricted maximum likelihood and marginal likelihood estimation of semiparametric generalised linear models. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 2011, 73, 3–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R Version 4.2.1: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Delibes-Mateos, M.; Rödel, H.G.; Rouco, C.; Alves, C.P.; Carneiro, M.; Villafuerte, R. European rabbit Oryctolagus cuniculus Linnaeus, 1758. In Handbook of the Mammals of Europe: Primates and Lagomorpha; Hacklander, K., Alves, P.C., Eds.; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; p. 220. ISBN 978–3–030–34042–1. [Google Scholar]
- Cooke, B.D.; Fenner, F. Rabbit haemorrhagic disease and the biological control of wild rabbits, Oryctolagus cuniculus, in Australia and New Zealand. Wildl. Res. 2002, 29, 689–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, H.V.; King, C. The European Rabbit—The History and Biology of a Successful Colonizer; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1994; 245p, ISBN 0 19 857611 0. [Google Scholar]
- Peiró, V.; SEvA, E. Le lapin de garenne daos la province d’Alícante (sud-est de I’Espagne). Bull. Mens. Off. Nat. Chase 1991, 182, 189–196. [Google Scholar]
- Blanco, J.C.; Villafuerte, R. Factores Ecológicos que Influyen Sobre las Poblaciones de Conejos: Incidencia de la Enfermedad Hemorrágica; Empresa de Transformación Agraria, S.A.: Madrid, Spain, 1993; 123p. [Google Scholar]
- Mutze, G.; Bird, P.; Jennings, S.; Peacock, D.; de Preu, N.; Kovaliski, J.; Cooke, B.; Capucci, L. Recovery of South Australian rabbit populations from the impact of rabbit haemorrhagic disease. Wil. Res. 2015, 41, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvete, C.; Estrarda, R. Epidemiología de Enfermedad Hemorrágica (VHD) y Mixomatosis en el Conejo Silvestre en el Vallemedio del Ebro; Herramientas de Gestión; Consejo de la Protección de la Naturaleza de Aragón: Zaragoza, Spain, 2000; 175p. [Google Scholar]
- Capucci, L.; Nardin, A.; Lavazza, A. Seroconversion in an industrial unit of rabbits infected with a non-pathogneic rabbit haemorrhagic disease-like virus. Vet. Rec. 1997, 140, 647–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gall-Reculé, G.; Zwingelstein, F.; Fages, M.P.; Bertagnoli, S.; Gelfi, J.; Aubineau, J.; Roobrouck, A.; Botti, G.; Lavazza, A.; Marchandeau, S. Characterisation of a non-pathogenic and non-protective infectious rabbit lagovirus related to RHDV. Virology 2011, 410, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strive, T.; Elsworth, P.; Liu, J.; Wright, J.D.; Kovaliski, J.; Capucci, L. The non-pathogenic Australian rabbit calicivirus RCV-A1 provides temporal and partial cross protection to lethal Rabbit Haemorrhagic Disease Virus infection which is not dependent on antibody titres. Vet. Res. 2013, 44, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delibes-Mateos, M.; Farfán, M.A.; Rouco, C.; Olivero, J.; Márquez, A.L.; Fa, J.; Vargas, J.M.; Villafuerte, R. A large-scale assessment of European rabbit damage to agriculture in Spain. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delibes-Mateos, M.; Ferreira, C.; Rouco, C.; Villafuerte, R.; Barrio, I.C. Conservationists, hunters and farmers: The European rabbit Oryctolagus cuniculus management conflict in the Iberian Peninsula. Mamm. Rev. 2014, 44, 190–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho-Sillero, L.; Caballero-Gómez, J.; Gómez-Guillamón, F.; Martínez-Padilla, A.; Agüero, M.; San Miguel, E.; Zorrilla, I.; Rayas, E.; Talavera, V.; García-Bocanegra, I. Monitoring of the novel rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus type 2 (GI. 2) epidemic in European wild rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus) in southern Spain, 2013–2017. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 237, 108361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AEMET, Agencia estatal de Meteorología Series Centenarias. Ministerio para la Transición Ecológica y el Reto Demográfico. Gobierno de España. 2023. Available online: https://www.aemet.es/es/serviciosclimaticos/datosclimatologicos/series-centenarias/izana/temperatura (accessed on 15 April 2023).
- Calvete, C.; Mendoza, M.; Alcaraz, A.; Sarto, M.P.; Jiménez-de-Bagüéss, M.P.; Calvo, A.J.; Monroy, F.; Clavo, J.H. Rabbit haemorrhagic disease: Cross-protection and comparative pathogenicity of GI.2/RHDV2/b and GI.1b/RHDV lagoviruses in a challenge trial. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 219, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begon, M.; Townsend, C.R. Parasites and Disease. Ecology: From Individuals to Ecosystems; John Wiley & Sons: Oxford, UK, 2022; pp. 378–415. [Google Scholar]
- Kerr, P.J.; Cattadori, I.M.; Liu, J.; Derek, G.S.; Dodds, J.F.; Brooks, J.W.; Kennet, M.J.; Holmes, E.C.; Read, A.F. Next step in the ongoing arms race between myxoma virus and wild rabbits in Australia is a novel disease phenotype. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 9397–9402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giallonardo, F.; Holmes, E.C. Viral biocontrol: Grand experiments in disease emergence and evolution. Trends Microbiol. 2015, 23, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| GI.1 | GI.2 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Community | Slope | Std. Error | t-Value | p-Value | Slope | Std. Error | t-Value | p-Value |
| Andalusia | −0.25 | 0.07 | −3.38 | 0.014 | −0.06 | 0.01 | −8.21 | 0.0001 |
| Aragon | −0.01 | 0.1 | −0.95 | 0.38 | 0.13 | 0.01 | 10.25 | >0.0001 |
| Balearic Islands | −0.24 | 0.04 | −5.34 | 0.0017 | −0.03 | 0.04 | −0.74 | 0.489 |
| Valencian Community | −0.01 | 0.01 | −1.68 | 0.145 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 3.46 | 0.0134 |
| Castille La Mancha | −0.09 | 0.03 | −2.75 | 0.033 | −0.003 | 0.02 | −0.19 | 0.854 |
| Castille and Leon | −0.28 | 0.06 | −4.94 | 0.002 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 2.45 | 0.05 |
| Catalonia | −0.06 | 0.01 | −5.51 | 0.002 | 0.005 | 0.02 | 0.28 | 0.784 |
| Extremadura | 0.03 | 0.02 | 1.95 | 0.098 | −0.18 | 0.03 | −5.26 | 0.001 |
| Galicia | −0.003 | 0.02 | −0.16 | 0.876 | −0.06 | 0.04 | −1.52 | 0.178 |
| La Rioja | −0.001 | 0.009 | −0.12 | 0.912 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.78 | 0.461 |
| Madrid | −0.283 | 0.06 | −4.93 | 0.002 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 2.44 | 0.05 |
| Navarra | −0.06 | 0.05 | −1.32 | 0.233 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.373 | 0.722 |
| Basque Country | −0.13 | 0.03 | −3.99 | 0.007 | 0.72 | 0.204 | 3.54 | 0.012 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santoro, S.; Aguayo-Adán, J.A.; Rouco, C. Comparison of the Impact between Classical and Novel Strains of Rabbit Haemorrhagic Disease on Wild Rabbit Populations in Spain. Biology 2023, 12, 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12050728
Santoro S, Aguayo-Adán JA, Rouco C. Comparison of the Impact between Classical and Novel Strains of Rabbit Haemorrhagic Disease on Wild Rabbit Populations in Spain. Biology. 2023; 12(5):728. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12050728
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantoro, Simone, Juan Antonio Aguayo-Adán, and Carlos Rouco. 2023. "Comparison of the Impact between Classical and Novel Strains of Rabbit Haemorrhagic Disease on Wild Rabbit Populations in Spain" Biology 12, no. 5: 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12050728
APA StyleSantoro, S., Aguayo-Adán, J. A., & Rouco, C. (2023). Comparison of the Impact between Classical and Novel Strains of Rabbit Haemorrhagic Disease on Wild Rabbit Populations in Spain. Biology, 12(5), 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12050728