Advanced Proteomic and Bioinformatic Tools for Predictive Analysis of Allergens in Novel Foods
Abstract
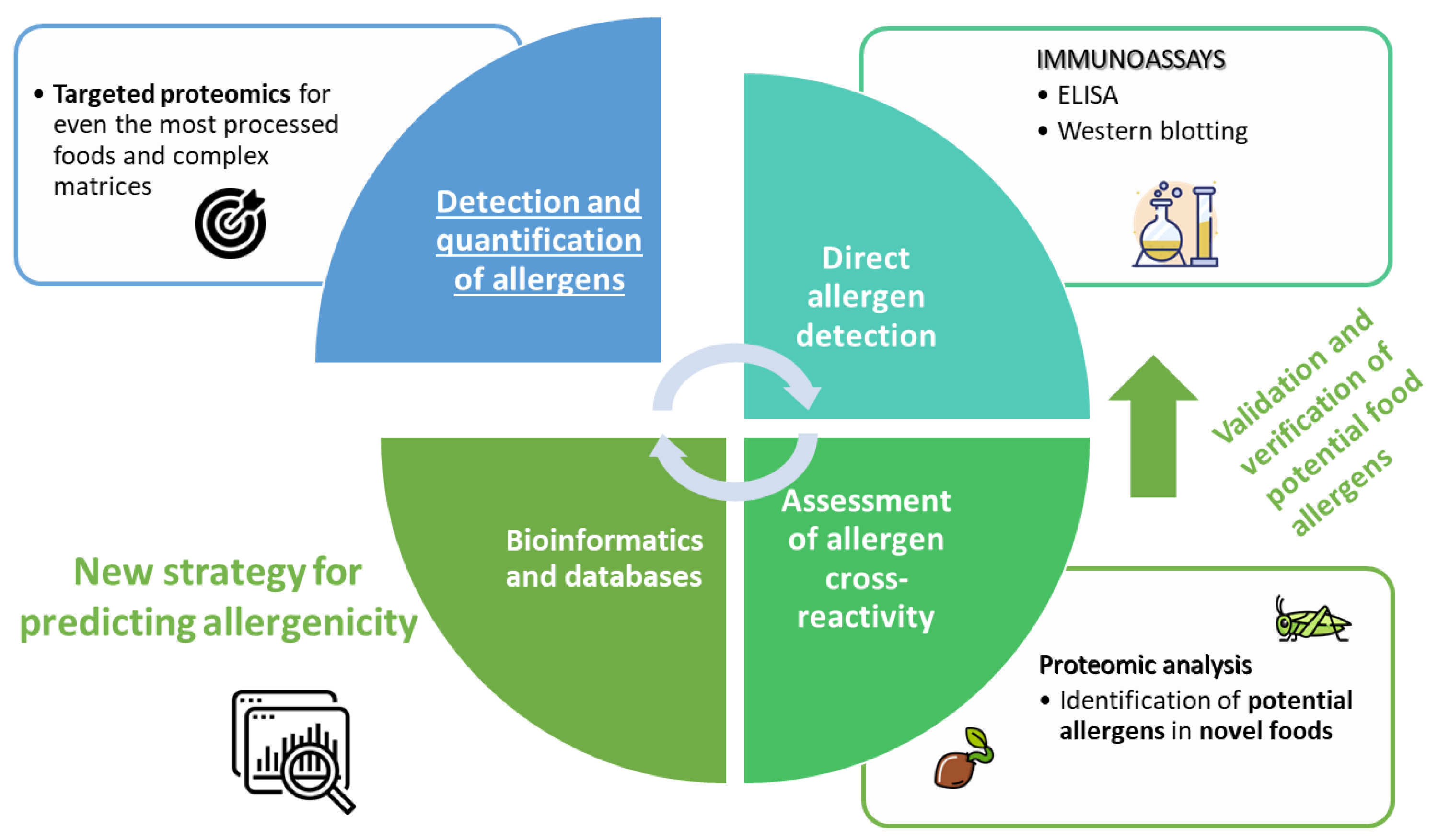
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Allergens of Traditional Food
3. Allergens of Novel Foods
| Novel Food | Protein Name/Allergen | Specie | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microalgae | C-phycocyanin Thioredoxins Superoxide dismutase Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase Triosephosphate isomerase | Microalgae spirulina (A. platensis) | [35,37] |
| Microalgae | viz. calmodulin Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase | Microalgae chlorella (C. vulgaris) | [37] |
| Insects | Tropomyosin, myosin, actin, troponin C (muscle proteins) Tubulin (cellular proteins) Hemocyanin, defensin (circulating proteins) Arginine kinase, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), triosephosphate isomerase, α-amylase, trypsin, phospholipase A, hyaluronidase (enzymes) | [38,39] |
4. Current Prevalent Methods Used to Assess the Presence of Allergens in Foods
5. Proteomic Approach to Identify Allergens in Novel Foods
6. Targeted Proteomics for Quantification of Food Allergens
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- EFSA. Scientific Opinion on the Evaluation of Allergenic Foods and Food Ingredients for Labelling Purposes. 2014. Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/es/efsajournal/pub/3894 (accessed on 12 February 2023).
- Shroba, J.; Das, R.; Bilaver, L.; Vincent, E.; Brown, E.; Polk, B.; Ramos, A.; Russell, A.F.; Bird, J.A.; Ciaccio, C.E.; et al. Food Insecurity in the Food Allergic Population: A Work Group Report of the AAAAI Adverse Reactions to Foods Committee. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2022, 10, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Xie, M.; Qian, Y.; Fu, L. Application of in vitro and in vivo models in the study of food allergy. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2018, 7, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenta, R.; Hochwallner, H.; Linhart, B.; Pahr, S. Food allergies: The basics. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 1120–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tordesillas, L.; Berin, M.C.; Sampson, H.A. Immunology of Food Allergy. Immunity 2017, 47, 32–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, F.J.; Nieto-Fontarigo, J.J.; González-Barcala, F.J. Proteomic analysis of food allergens. In Food Proteomics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 225–300. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, F.; He, S.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Advances in epitope mapping technologies for food protein allergens: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 107, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huby, R.D.; Dearman, R.J.; Kimber, I. Why are some proteins allergens? Toxicol. Sci. 2000, 55, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monaci, L.; Pilolli, R.; De Angelis, E.; Crespo, J.F.; Novak, N.; Cabanillas, B. Food allergens: Classification, molecular properties, characterization, and detection in food sources. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2020, 93, 113–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raheem, D.; Raposo, A.; Oluwole, O.B.; Nieuwland, M.; Saraiva, A.; Carrascosa, C. Entomophagy: Nutritional, ecological, safety and legislation aspects. Food Res. Int. 2019, 126, 108672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Zhu, R. Allergen Preparation in AIT, Now and in the Future. Curr. Treat. Options Allergy 2021, 8, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, C.; Costa, J.; Oliveira, M.B.P.; Mafra, I. Bovine Milk Allergens: A Comprehensive Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 137–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dona, D.W.; Suphioglu, C. Egg allergy: Diagnosis and immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, M.F.; Lopata, A.L. Fish allergy: In review. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2014, 46, 258–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Raghavan, V. A comprehensive overview of emerging processing techniques and detection methods for seafood allergens. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 3540–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozias-Akins, P.; Breiteneder, H. The functional biology of peanut allergens and possible links to their allergenicity. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 74, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Jin, Y.; Cerny, R.; Ballmer-Weber, B.; Goodman, R.E. Combining 2-DE immunoblots and mass spectrometry to identify putative soybean (Glycine max) allergens. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 116, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quirce, S.; Boyano-Martínez, T.; Díaz-Perales, A. Clinical presentation, allergens, and management of wheat allergy. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 12, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa, C.; Costa, J.; Mafra, I. Sesame as a source of food allergens: Clinical relevance, molecular characterization, cross-reactivity, stability toward processing and detection strategies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasolin, L.H.; Pereira, R.N.; Pinheiro, A.C.; Martins, J.T.; Andrade CC, P.; Ramos, O.L.; Vicente, A.A. Emergent food proteins—Towards sustainability, health and innovation. Food Res. Int. 2019, 125, 108586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.; Bavaro, S.L.; Benedé, S.; Diaz-Perales, A.; Bueno-Diaz, C.; Gelencser, E.; Klueber, J.; Larré, C.; Lozano-Ojalvo, D.; Lupi, R.; et al. Are Physicochemical Properties Shaping the Allergenic Potency of Plant Allergens? Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2022, 62, 37–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albunni, B.A.; Wessels, H.; Paschke-Kratzin, A.; Fischer, M. Antibody Cross-Reactivity between Proteins of Chia Seed (Salvia hispanica L.) and Other Food Allergens. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 7475–7484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; McFarland, M.A.; Pirone, C.; Parker, C.H. Selection of tree nut allergen peptide markers: A need for improved protein sequence databases. J. AOAC Int. 2019, 102, 1263–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, J.; Villa, C.; Verhoeckx, K.; Cirkovic-Velickovic, T.; Schrama, D.; Roncada, P.; Rodrigues, P.M.; Piras, C.; Martín-Pedraza, L.; Monaci, L.; et al. Are Physicochemical Properties Shaping the Allergenic Potency of Animal Allergens? Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2022, 62, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Gier, S.; Verhoeckx, K. Insect (food) allergy and allergens. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 100, 82–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinroch, C.; Srisomsap, C.; Chokchaichamnankit, D.; Punyarit, P.; Phiriyangkul, P. Identification of novel allergen in edible insect, Gryllus bimaculatus and its cross-reactivity with Macrobrachium spp. Allergens. Food Chem. 2015, 184, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broekman, H.; Verhoeckx, K.C.; den Hartog Jager, C.F.; Kruizinga, A.G.; Pronk-Kleinjan, M.; Remington, B.C.; Bruijnzeel-Koomen, C.A.; Houben, G.F.; Knulst, A.C. Majority of shrimp-allergic patients are allergic to mealworm. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 1261–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, F.; Doyen, V.; Debaugnies, F.; Mazzucchelli, G.; Caparros, R.; Alabi, T.; Blecker, C.; Haubruge, E.; Corazza, F. Limited cross reactivity among arginine kinase allergens from mealworm and cricket edible insects. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 714–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garino, C.; Mielke, H.; Knüppel, S.; Selhorst, T.; Broll, H.; Braeuning, A. Quantitative allergenicity risk assessment of food products containing yellow mealworm (Tenebrio molitor). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 142, 111460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murefu, T.R.; Macheka, L.; Musundire, R.; Manditsera, F.A. Safety of wild harvested and reared edible insects: A review. Food Control 2019, 101, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pali-Schöll, I.; Meinlschmidt, P.; Larenas-Linnemann, D.; Purschke, B.; Hofstetter, G.; Rodríguez-Monroy, F.A.; Einhorn, L.; Mothes-Luksch, N.; Jensen-Jarolim, E.; Jäger, H. Edible insects: Cross-recognition of IgE from crustacean- and house dust mite allergic patients, and reduction of allergenicity by food processing. World Allergy Organ. J. 2019, 12, 100006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, F.; Johnson, P.E.; Liceaga, A. Effect of enzymatic hydrolysis on bioactive properties and allergenicity of cricket (Gryllodes sigillatus) protein. Food Chem. 2018, 262, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso Alves, S.; Díaz-Ruiz, E.; Lisboa, B.; Sharma, M.; Mussatto, S.I.; Thakur, V.K.; Kalaskar, D.M.; Gupta, V.K.; Chandel, A.K. Microbial meat: A sustainable vegan protein source produced from agri-waste to feed the world. Food Res. Int. 2023, 166, 112596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.M.; Knulst, A.C.; Röckmann, H. Anaphylaxis to Spirulina confirmed by skin prick test with ingredients of Spirulina tablets. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 74, 309–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrus, M.; Culerrier, R.; Campistron, M.; Barre, A.; Rougé, P. First case report of anaphylaxis to spirulin: Identification of phycocyanin as responsible allergen. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 65, 924–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, H.E.; Yoo, K.H.; Seo, W.H.; Won, N.H.; Hong, Y.S.; Lee, J.W. Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis following ingestion of Chlorella tablets. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2007, 22, 887–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, M.; Ventura, G.; Calvano, C.D.; Losito, I.; Cataldi, T.R. A new paradigm to search for allergenic proteins in novel foods by integrating proteomics analysis and in silico sequence homology prediction: Focus on spirulina and chlorella microalgae. Talanta 2022, 240, 123188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlüter, O.; Rumpold, B.; Holzhauser, T.; Roth, A.; Vogel, R.F.; Quasigroch, W.; Vogel, S.; Heinz, V.; Jäger, H.; Bandick, N.; et al. Safety aspects of the production of foods and food ingredients from insects. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, J.C.; Cunha, L.M.; Sousa-Pinto, B.; Fonseca, J. Allergic risks of consuming edible insects: A systematic review. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1700030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanga, S.K.; Jain, M.; Raghavan, V. Significance of fruit and vegetable allergens: Possibilities of its reduction through processing. Food Rev. Int. 2018, 34, 103–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Wang, J.; Raghavan, V. Critical reviews and recent advances of novel non-thermal processing techniques on the modification of food allergens. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 62, 196–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Vanga, S.K.; McCusker, C.; Raghavan, V. A Comprehensive Review on Kiwifruit Allergy: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, Management, and Potential Modification of Allergens Through Processing. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 500–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suriyamoorthy, P.; Madhuri, A.; Tangirala, S.; Michael, K.R.; Sivanandham, V.; Rawson, A.; Anandharaj, A. Comprehensive Review on Banana Fruit Allergy: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, Management, and Potential Modification of Allergens through Food Processing. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2022, 77, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Pedrouso, M.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Gagaoua, M.; Franco, D. Current trends in proteomic advances for food allergen analysis. Biology 2020, 9, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koeberl, M.; Sharp, M.F.; Tian, R.; Buddhadasa, S.; Clarke, D.; Roberts, J. Lupine allergen detecting capability and cross-reactivity of related legumes by ELISA. Food Chem. 2018, 256, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruethers, T.; Taki, A.C.; Khangurha, J.; Roberts, J.; Buddhadasa, S.; Clarke, D.; Hedges, C.E.; Campbell, D.E.; Kamath, S.D.; Lopata, A.L.; et al. Commercial fish ELISA kits have a limited capacity to detect different fish species and their products. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 4353–4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Auria, G.; Nitride, C.; Nicolai, M.A.; Mamone, G.; Montesano, D.; Mills, E.N.C.; Ferranti, P. Identification of allergen encoding sequences in a novel food ingredient from Moringa oleifera leaves. Food Chem. 2023, 401, 134185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, K.Y.; Lee, J.S.; Yuk, J.E.; Song, H.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, K.J.; Kim, B.J.; Lim, K.J.; Park, K.H.; Lee, J.H.; et al. Allergenic characterization of Bomb m 4, a 30-kDa Bombyx mori lipoprotein 6 from silkworm pupa. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2022, 52, 888–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Yin, S.; Fu, L.; Wang, M.; Meng, L.; Li, F.; Xue, X.; Wu, L.; Li, Q. Identification of allergens and allergen hydrolysates by proteomics and metabolomics: A comparative study of natural and enzymolytic bee pollen. Food Res. Int. 2022, 158, 111572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, T.L.; Han, X.Y.; Li, M.S.; Yang, Y.; Liu, M.; Ji, N.R.; Yu, C.C.; Lai, D.; Cao, M.J.; Liu, G.M. Effects of the Maillard reaction on the epitopes and immunoreactivity of tropomyosin, a major allergen in: Chlamys nobilis. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 5096–5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Qi, Q.; Wang, C.; Qian, Y.; Liu, G.; Wang, Y.; Fu, L. Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) biosensors for food allergen detection in food matrices. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 142, 111449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilolli, R.; Monaci, L.; Visconti, A. Advances in biosensor development based on integrating nanotechnology and applied to food-allergen management. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 47, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, J.; Hubel, P.; Pfannstiel, J.; Afzal, M.; Longin, C.F.H.; Hitzmann, B.; Götz, H.; Bischoff, S.C. Comprehensive proteome analysis of bread deciphering the allergenic potential of bread wheat, spelt and rye. J. Proteom. 2021, 247, 104318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Downs, M.L. Proteomic Analysis of Oil-Roasted Cashews Using a Customized Allergen-Focused Protein Database. J. Proteome Res. 2022, 21, 1694–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, S.; Luís, I.M.; Oliveira, M.M.; Abreu, I.A.; Batista, R. Goji berries superfood–contributions for the characterisation of proteome and IgE-binding proteins. Food Agric. Immunol. 2019, 30, 262–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rost, J.; Muralidharan, S.; Lee, N.A. A label-free shotgun proteomics analysis of macadamia nut. Food Res. Int. 2020, 129, 108838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakhlef, M.; Giangrieco, I.; Ciardiello, M.A.; Fiume, I.; Mari, A.; Souiki, L.; Pocsfalvi, G. Potential allergenicity of Medicago sativa investigated by a combined IgE-binding inhibition, proteomics and in silico approach. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 1182–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, N.; Halima, O.; Akhter, K.T.; Nuzhat, N.; Rao, R.S.P.; Wilson, R.S.; Ahsan, N. Proteomic characterization of low molecular weight allergens and putative allergen proteins in lentil (Lens culinaris) cultivars of Bangladesh. Food Chem. 2019, 297, 124936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.; Zhao, Z.; Che, H. Identification of Allergens in White-and Red-Fleshed Pitaya (Selenicereus undatus and Selenicereus costaricensis) Seeds Using Bottom-Up Proteomics Coupled with Immunoinformatics. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varunjikar, M.S.; Belghit, I.; Gjerde, J.; Palmblad, M.; Oveland, E.; Rasinger, J.D. Shotgun proteomics approaches for authentication, biological analyses, and allergen detection in feed and food-grade insect species. Food Control 2022, 137, 108888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, F.G.; Liceaga, A.M. Isolation and proteomic characterization of tropomyosin extracted from edible insect protein. Food Chem. Mol. Sci. 2021, 3, 100049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bose, U.; Broadbent, J.A.; Juhász, A.; Karnaneedi, S.; Johnston, E.B.; Stockwell, S.; Byrne, K.; Limviphuvadh, V.; Maurer-Stroh, S.; Lopata, A.L.; et al. Protein extraction protocols for optimal proteome measurement and arginine kinase quantitation from cricket Acheta domesticus for food safety assessment. Food Chem. 2021, 348, 129110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leni, G.; Tedeschi, T.; Faccini, A.; Pratesi, F.; Folli, C.; Puxeddu, I.; Migliorini, P.; Gianotten, N.; Jacobs, J.; Depraetere, S.; et al. Shotgun proteomics, in-silico evaluation and immunoblotting assays for allergenicity assessment of lesser mealworm, black soldier fly and their protein hydrolysates. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochanowski, M.; Dąbrowska, J.; Różycki, M.; Karamon, J.; Sroka, J.; Cencek, T. Proteomic Profiling Reveals New Insights into the Allergomes of Anisakis simplex, Pseudoterranova decipiens, and Contracaecum osculatum. J. Parasitol. 2020, 106, 572–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pali-Schöll, I.; Verhoeckx, K.; Mafra, I.; Bavaro, S.L.; Mills, E.C.; Monaci, L. Allergenic and novel food proteins: State of the art and challenges in the allergenicity assessment. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 84, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomés, A.; Davies, J.M.; Gadermaier, G.; Hilger, C.; Holzhauser, T.; Lidholm, J.; Lopata, A.L.; Mueller, G.A.; Nandy, A.; Radauer, C.; et al. WHO/IUIS Allergen Nomenclature: Providing a common language. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 100, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, K.; Karbhal, R.; Jayaraman, V.K.; Sawant, S.; Kulkarni-Kale, U. AllerBase: A comprehensive allergen knowledgebase. Database 2017, 2017, bax066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer-Stroh, S.; Krutz, N.L.; Kern, P.S.; Gunalan, V.; Nguyen, M.N.; Limviphuvadh, V.; Eisenhaber, F.; Frank Gerberick, G. AllerCatPro-prediction of protein allergenicity potential from the protein sequence. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 3020–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, R.E.; Ebisawa, M.; Ferreira, F.; Sampson, H.A.; van Ree, R.; Vieths, S.; Baumert, J.L.; Bohle, B.; Lalithambika, S.; Wise, J.; et al. AllergenOnline: A peer-reviewed, curated allergen database to assess novel food proteins for potential cross-reactivity. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 1183–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mari, A.; Scala, E.; Palazzo, P.; Ridolfi, S.; Zennaro, D.; Carabella, G. Bioinformatics applied to allergy: Allergen databases, from collecting sequence information to data integration. The Allergome platform as a model. Cell. Immunol. 2006, 244, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ree, R.; Sapiter Ballerda, D.; Berin, M.C.; Beuf, L.; Chang, A.; Gadermaier, G.; Guevera, P.A.; Hoffmann-Sommergruber, K.; Islamovic, E.; Koski, L.; et al. The COMPARE Database: A Public Resource for Allergen Identification, Adapted for Continuous Improvement. Front. Allergy 2021, 2, 700533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radauer, C.; Bublin, M.; Wagner, S.; Mari, A.; Breiteneder, H. Allergens are distributed into few protein families and possess a restricted number of biochemical functions. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 121, 847–852.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, B.; Sidney, J.; Bourne, P.; Bui, H.H.; Buus, S.; Doh, G.; Fleri, W.; Kronenberg, M.; Kubo, R.; Lund, O.; et al. The immune epitope database and analysis resource: From vision to blueprint. PLoS Biol. 2005, 3, e91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanciuc, O.; Schein, C.H.; Braun, W. SDAP: Database and computational tools for allergenic proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monaci, L.; De Angelis, E.; Montemurro, N.; Pilolli, R. Comprehensive overview and recent advances in proteomics MS based methods for food allergens analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 106, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzano, V.; Tilocca, B.; Fiocchi, A.G.; Vernocchi, P.; Levi Mortera, S.; Urbani, A.; Roncada, P.; Putignani, L. Perusal of food allergens analysis by mass spectrometry-based proteomics. J. Proteom. 2020, 215, 103636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aalberse, R.C. Structural biology of allergens. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 106, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmoteleb, M.; Zhang, C.; Furey, B.; Kozubal, M.; Griffiths, H.; Champeaud, M.; Goodman, R.E. Evaluating potential risks of food allergy of novel food sources based on comparison of proteins predicted from genomes and compared to www.AllergenOnline.org. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 147, 111888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagdonas, H.; Fogarty, C.A.; Fadda, E.; Agirre, J. The case for post-predictional modifications in the AlphaFold Protein Structure Database. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2021, 28, 869–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Yu, N.; Tang, R.; Sun, X.; Wei, L.; Sun, J.; Chen, Y. Quantification of major allergens in peach based on shotgun proteomics using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Lwt 2022, 160, 113234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yang, C.; Downs, M. Targeted mass spectrometry quantification of total soy protein residues from commercially processed ingredients for food allergen management. J. Proteom. 2021, 239, 104194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, M.; Calvano, C.D.; Ventura, G.; Losito, I.; Cataldi, T.R.I. Determination of hidden milk allergens in meat-based foodstuffs by liquid chromatography coupled to electrospray ionization and high-resolution tandem mass spectrometry. Food Control 2022, 131, 108443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neethirajan, S.; Weng, X.; Tah, A.; Cordero, J.O.; Ragavan, K.V. Nano-biosensor platforms for detecting food allergens—New trends. Sens. BioSens. Res. 2018, 18, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Food | Protein Name | Specie | Allergen | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Milk | Caseins α S1-casein (23.6 kDa) α S2-casein (25.2 kDa) β -casein (24 kDa) κ-casein (19 kDa) β-lactoglobulin (18.3 kDa) α-lactalbumin (14.2 kDa) Serum albumin (66.3 kDa) Immunoglobulin (160 kDa) | Bos taurus | Bos d 9 Bos d 10 Bos d 11 Bos d 12 Bos d 5 Bos d 4 Bos d 6 Bos d 7 | [12] |
| Eggs | Ovomucoid (28 kDa) Ovalbumin (44 kDa) Ovotransferrin (78 kDa) Lysozyme (14 kDa) α-livetin (69 kDa) YGP42 (35 kDa) | Gallus domesticus | Gal d 1 Gal d 2 Gal d 3 Gal d 3 Gal d 5 Gal d 6 | [13] |
| Fish | Parvalbumin α-parvalbumin (13 kDa) β-parvalbumin (11.6 kDa) | Gadius callarias (Baltic cod) | Gad p 2 Gad p 1 | [14] |
| Shellfish | Tropomyosin (34 kDa) | Metapenaeus ensis (Shrimp) | Met e 1 | [15] |
| Peanuts/tree nuts | 7 S seed storage globulin, vicilins (64 kDa) 2 S albumin (17 kDa) Nonspecific lipid transfer proteins Oleosins Defensins Profilins Plant pathogenesis-related proteins PR-10 | Arachis hypogaea | Ara h 1 Ara h 2, Ara h 6, Ara h 7 Ara h 9, Ara h 16, Ara h 17 Ara h 10, Ara h 11, Ara h 14, Ara h 15 Ara h 12, Ara h 13 Ara h 5 Ara h 8 | [16] |
| Soy | 7 S seed storage globulin, β-conglycinin 11 S seed storage globulin, glycinin | Glycine max | Gly m 5 Gly m 6 | [17] |
| Wheat | α-amylase inhibitor (13 kDa) Gamma gliadin (88 kDa) Elongation factor 1 | Triticum aestivum | Tri a 28 Tri a 20 Tri a 45 | [18] |
| Sesame | 2 S albumins 7 S vicilin-type globulin (45 kDa) Oleosins 11 S globulin, legumins Profilin | Sesamum indicum | Ses i 1, Ses i 2 Ses i 3. Ses i 4, Ses i 5 Ses i 6, Ses i 7 Ses i 8 | [19] |
| Novel Food | Bioinformatic Tool | Goal/Main Achievements | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vegetables | |||
| Bread wheat spelt and rye | Database of Allergen Families-AllFam AllergenOnline Allergome | Comparison of allergenicity in cereal products | [53] |
| Cashews | BLASTP Search against AllergenOnline sequence | Analysis of allergen stability under heat treatment | [54] |
| Goji berries | AlgPred software hybrid approach | Identification of 11 IgE-binding proteins | [55] |
| Macadamia nut | AllergenOnline Immune Epitope Database Analysis Resource (IEDB) | Analysis of homology and linear epitope similarities to known allergens | [56] |
| Medicago sativa | COMPARE allergen database | Identification of three allergenic protein families | [57] |
| Lentil (Lens culinaris) | Blast2GO—Functional Annotation and Genomics | Quantification of major allergen proteins | [58] |
| White- and red-fleshed pitaya seeds | AllermatchTM webtool Algpred 2.0 AllerCatPro web server | Identification of five potential allergens | [59] |
| Seaweeds | |||
| Spirulina and chlorella microalgae | AllergenOnline | Six proteins exhibit significant homology with food allergens | [37] |
| Insects | |||
| Black soldier fly, yellow mealworm, lesser mealworm, house cricket and Morio Worms | Allergen nomenclature (WHO/IUIS) | Detection of arginine kinase and tropomyosin | [60] |
| Cricket | Allermatch TM webtool AlgPred 2.0 ABCPred Bepipred | Description of the impact of processing on allergenic reactivity of insect proteins. | [61] |
| Cricket Acheta domesticus | Database of Allergen Families-AllFam Allergen nomenclatura (WHO/IUIS) CLC Genomics Workbench 20.0.4. AllerCatPro web server | Identification of 20 putative allergens | [62] |
| Lesser mealworms, black soldier flies and their protein hydrolysate | AllermatchTM webtool | Identification of potential allergens by similarity to known allergens | [63] |
| Parasites | |||
| Anisakis simplex, Pseudoterranova decipiens, and Contracaecum osculatum | Blast2GO—Functional Annotation and Genomics AllergenOnline AllerTOP web server ver. 2.0 PREAL web server | Prediction of 53 probable allergens in three species | [64] |
| Name | Link (Website) | Description | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Allergen nomenclature | http://www.allergen.org (accessed on 12 February 2023) | Official site for the systematic allergen nomenclature provided by the World Health Organization and International Union of Immunological Societies (WHO/IUIS) | [66] |
| AllerBase | http://bioinfo.unipune.ac.in/AllerBase/Home.html (accessed on 12 February 2023) | Database of allergens detected as IgE-binding epitopes, IgE antibodies and cross reactivity. Allergen data such as experimental information on its allergenic activity and food source is compiled, resulting in a curated database. | [67] |
| AllerCatPro | https://allercatpro.bii.a-star.edu.sg/ (accessed on 12 February 2023) | Provides protein allergenicity potential prediction based on the similarity of amino acid sequence and 3D protein structure | [68] |
| AllergenOnline | http://www.allergenonline.org (accessed on 12 February 2023) | Provides sequence database of allergens to identify proteins and assess the potential risk of allergenic cross-reactivity. This database offers 2233 peer-reviewed sequences from 912 taxonomic protein groups (February 2021) | [69] |
| Allergome | http://www.allergome.org (accessed on 12 February 2023) | A website with detailed information on Allergenic Molecules (Allergens) causing an IgE-mediated (allergic, atopic) disease (anaphylaxis, asthma, atopic dermatitis, conjunctivitis, rhinitis, urticaria). | [70] |
| Comprehensive protein allergen resource (COMPARE allergen database) | https://comparedatabase.org/ (accessed on 12 February 2023 | A database comprised of protein sequences of known allergens | [71] |
| Database of Allergen Families-AllFam | http://www.meduniwien.ac.at/allfam/ (accessed on 12 February 2023) | Comprises a resource for classifying allergens into protein families as well as biochemical properties and allergology significance | [72] |
| Immune Epitope Database and analysis resource (IEDB) | https://www.iedb.org (accessed on 12 February 2023) | Provides experimental data on antibody and T-cell epitopes to identify allergens and to assist in the prediction and analysis of allergenicity | [73] |
| Structural Database of Allergenic Proteins (SDAP) | https://fermi.utmb.edu (accessed on 12 February 2023) | Tool for testing the FAO/WHO allergenicity rules in new proteins and investigating cross reactivity, also offering information about protein sequence and structure | [74] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
López-Pedrouso, M.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Alché, J.d.D.; Moreira, R.; Franco, D. Advanced Proteomic and Bioinformatic Tools for Predictive Analysis of Allergens in Novel Foods. Biology 2023, 12, 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12050714
López-Pedrouso M, Lorenzo JM, Alché JdD, Moreira R, Franco D. Advanced Proteomic and Bioinformatic Tools for Predictive Analysis of Allergens in Novel Foods. Biology. 2023; 12(5):714. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12050714
Chicago/Turabian StyleLópez-Pedrouso, María, José M. Lorenzo, Juan de Dios Alché, Ramón Moreira, and Daniel Franco. 2023. "Advanced Proteomic and Bioinformatic Tools for Predictive Analysis of Allergens in Novel Foods" Biology 12, no. 5: 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12050714
APA StyleLópez-Pedrouso, M., Lorenzo, J. M., Alché, J. d. D., Moreira, R., & Franco, D. (2023). Advanced Proteomic and Bioinformatic Tools for Predictive Analysis of Allergens in Novel Foods. Biology, 12(5), 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12050714










