Potential Impact of Polymorphisms in Toll-like Receptors 2, 3, 4, 7, 9, miR-146a, miR-155, and miR-196a Genes on Osteoarthritis Susceptibility
Abstract
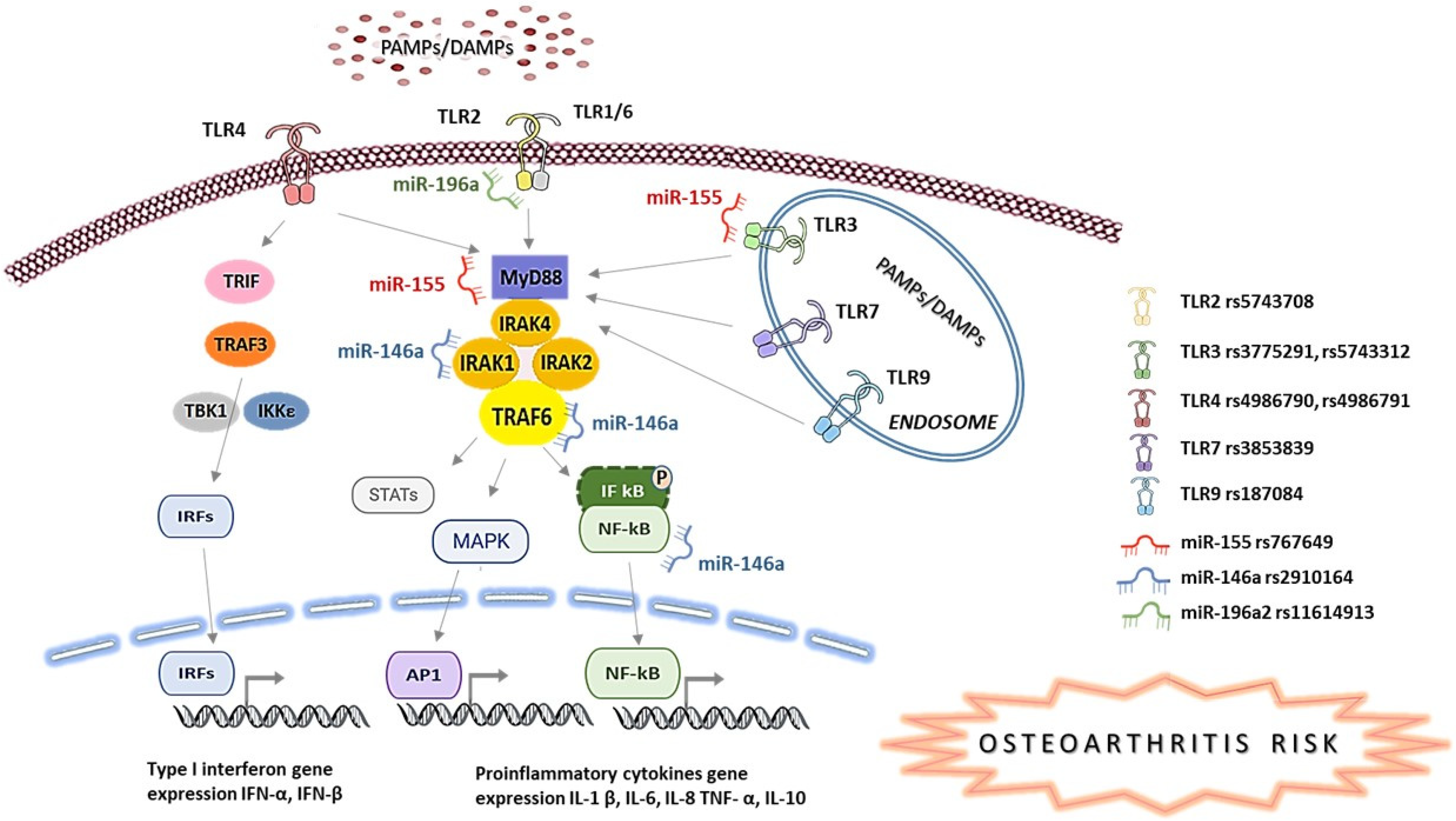
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants and Biological Samples
2.2. Biological Samples, DNA Isolation, and Polymorphism Genotyping
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mobasheri, A.; Batt, M. An Update on the Pathophysiology of Osteoarthritis. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2016, 59, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramoff, B.; Caldera, F.E. Osteoarthritis. Med. Clin. North Am. 2020, 104, 293–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreto, G.; Manninen, M.; Eklund, K.K. Osteoarthritis and Toll-Like Receptors: When Innate Immunity Meets Chondrocyte Apoptosis. Biology 2020, 9, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. TLR Signaling. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 816–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, Y.Y.; Chin, K.-Y. The Role of Inflammation in the Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 2020, 8293921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raisch, J.; Darfeuille-Michaud, A.; Nguyen, H.T.T. Role of MicroRNAs in the Immune System, Inflammation and Cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 2985–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Abak, A.; Shoorei, H.; Talebi, S.F.; Mohaqiq, M.; Sarabi, P.; Taheri, M.; Mokhtari, M. Interaction between Non-Coding RNAs and Toll-like Receptors. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 140, 111784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, U.; Pelosi, E.; Castelli, G.; Labbaye, C. MiR-146 and MiR-155: Two Key Modulators of Immune Response and Tumor Development. Noncoding RNA 2017, 3, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.A.; Ramadan, A.; Wahby, A.A.; Hassan, M.; Soliman, H.M.; Abdel Hamid, T.A. Micro-RNA 196a2 Expression and MiR-196a2 (Rs11614913) Polymorphism in T1DM: A Pilot Study. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 32, 1171–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xiong, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, B.; Liu, T.; Xie, W. Association of Three Polymorphisms Rs11614913, Rs2910146, and Rs3746444 in MiRNA-196a2, MiRNA-146a, and MiRNA-499 with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterol. Res. Pr. 2018, 2018, 7295131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisch, K.M.; Saito, M.; Akagi, R.; Duffy, S.; Alvarez-Garcia, O.; Grogan, S.; D’Lima, D.; Su, A.I.; Lotz, M.K. Integrative Omics Profiling of Osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2014, 22, S231–S232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayraktar, R.; Bertilaccio, M.T.S.; Calin, G.A. The Interaction Between Two Worlds: MicroRNAs and Toll-Like Receptors. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.-G.; Xia, Y. The Rs5743708 Gene Polymorphism in the TLR2 Gene Contributes to the Risk of Tuberculosis Disease. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 11921–11928. [Google Scholar]
- Ranjith-Kumar, C.T.; Miller, W.; Sun, J.; Xiong, J.; Santos, J.; Yarbrough, I.; Lamb, R.J.; Mills, J.; Duffy, K.E.; Hoose, S.; et al. Effects of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms on Toll-like Receptor 3 Activity and Expression in Cultured Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 17696–17705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohto, U.; Yamakawa, N.; Akashi-Takamura, S.; Miyake, K.; Shimizu, T. Structural Analyses of Human Toll-like Receptor 4 Polymorphisms D299G and T399I. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 40611–40617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.; Fu, Q.; Deng, Y.; Qian, X.; Zhao, J.; Kaufman, K.M.; Wu, Y.L.; Yu, C.Y.; Tang, Y.; Chen, J.-Y.; et al. Sex-Specific Association of X-Linked Toll-like Receptor 7 (TLR7) with Male Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 15838–15843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, X.; Mehmood, A.; Niu, P.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Han, X.; Ma, L.; Jin, S.; Wu, Y. Association of X-Linked TLR-7 Gene Polymorphism with the Risk of Knee Osteoarthritis: A Case-Control Study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Xu, E.; Xiao, Y.; Cai, X. Evaluation of the Relationship Between Common Variants in the TLR-9 Gene and Hip Osteoarthritis Susceptibility. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2019, 23, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, S.R.; Shaker, O.G.; Mohammed, A.A.; Fouad, N.A.; Hussein, H.A.; Ahmed, N.A.; Ahmed, O.M.; Ali, D.Y.; Mohamed, M.M.; Ibrahim, A.A. Impact of MiR-155 (Rs767649 A>T) and MiR-146a (Rs57095329 A>G) Polymorphisms in System Lupus Erythematosus Susceptibility in an Egyptian Cohort. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 1425–1435. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, A.E.; Zheng, T.; Yi, C.; Leaderer, D.; Weidhaas, J.; Slack, F.; Zhang, Y.; Paranjape, T.; Zhu, Y. MicroRNA MiR-196a-2 and Breast Cancer: A Genetic and Epigenetic Association Study and Functional Analysis. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 5970–5977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boer, C.G.; Hatzikotoulas, K.; Southam, L.; Stefánsdóttir, L.; Zhang, Y.; Coutinho de Almeida, R.; Wu, T.T.; Zheng, J.; Hartley, A.; Teder-Laving, M.; et al. Deciphering Osteoarthritis Genetics across 826,690 Individuals from 9 Populations. Cell 2021, 184, 4784–4818.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Q.; Chen, G.; Li, X.; Yang, Q.; Du, Z.; Ren, M.; Song, Y.; Zhang, G. Integration of Gene Expression Profile Data to Screen and Verify Hub Genes Involved in Osteoarthritis. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 9482726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildirim, İ.H.; Uzen, R. Investigation of the Asp299Gly and Thr399Ile Polymorphisms of TLR4 Gene in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Dicle Tıp Derg. 2019, 46, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulic, M.K.; Hurrelbrink, R.J.; Prêle, C.M.; Laing, I.A.; Upham, J.W.; Le Souef, P.; Sly, P.D.; Holt, P.G. TLR4 Polymorphisms Mediate Impaired Responses to Respiratory Syncytial Virus and Lipopolysaccharide. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakawa, N.; Ohto, U.; Akashi-Takamura, S.; Takahashi, K.; Saitoh, S.-I.; Tanimura, N.; Suganami, T.; Ogawa, Y.; Shibata, T.; Shimizu, T.; et al. Human TLR4 Polymorphism D299G/T399I Alters TLR4/MD-2 Conformation and Response to a Weak Ligand Monophosphoryl Lipid A. Int. Immunol. 2013, 25, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, L.; Xiong, Y.; Song, C.; Piao, W.; Vogel, S.N.; Medvedev, A.E. The Asp299Gly Polymorphism Alters TLR4 Signaling by Interfering with Recruitment of MyD88 and TRIF. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 4506–4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hold, G.L.; Berry, S.; Saunders, K.A.; Drew, J.; Mayer, C.; Brookes, H.; Gay, N.J.; El-Omar, E.M.; Bryant, C.E. The TLR4 D299G and T399I SNPs Are Constitutively Active to Up-Regulate Expression of Trif-Dependent Genes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabroe, I.; Whyte, M.; Wilson, A.; Dower, S.; Hubbard, R.; Hall, I. Toll-like Receptor (TLR) 4 Polymorphisms and COPD. Thorax 2004, 59, 81. [Google Scholar]
- Balistreri, C.; Grimaldi, M.; Chiappelli, M.; Licastro, F.; Castiglia, L.; Listi, F.; Vasto, S.; Lio, D.; Caruso, C.; Candore, G. Association between the Polymorphisms of TLR4 and CD14 Genes and Alzheimers Disease. CPD 2008, 14, 2672–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raafat, I.I.; El Guindy, N.; Shahin, R.M.H.; Samy, L.A.; El Refai, R.M. Toll-like Receptor 7 Gene Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms and the Risk for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Case-Control Study. Z. Für Rheumatol. 2018, 77, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.-L.; Yang, H.-Y.; Lee, C.-H.; Huang, G.-S.; Salter, D.M.; Lee, H.-S. The (-1486T/C) Promoter Polymorphism of the TLR-9 Gene Is Associated with End-Stage Knee Osteoarthritis in a Chinese Population. J. Orthop. Res. 2012, 30, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbaloglu, O.; Sabah Ozcan, S.; Korkmaz, M.; Yılmaz, N. Promoter Polymorphism (T-1486C) of TLR-9 Gene Is Associated with Knee Osteoarthritis in a Turkish Population: TLR-9 GENE PROMOTER POLYMORPHISM (T-1486C) AND KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS. J. Orthop. Res. 2017, 35, 2484–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Shi, S.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, Y.; Ying, X.; Jin, Y. Association between TLR-9 Gene Rs187084 Polymorphism and Knee Osteoarthritis in a Chinese Population. Biosci. Rep. 2017, 37, BSR20170844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillat, T.; Barreto, G.; Clarijs, P.; Soininen, A.; Ainola, M.; Pajarinen, J.; Korhonen, M.; Konttinen, Y.T.; Sakalyte, R.; Hukkanen, M.; et al. Toll-like Receptors in Human Chondrocytes and Osteoarthritic Cartilage. Acta Orthop. 2013, 84, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, M. The Role of Toll-Like Receptors in Osteoclastogenesis. J. Bone Metab. 2020, 27, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlowsky, E.W.; Kraus, V.B. The Role of Innate Immunity in Osteoarthritis: When Our First Line of Defense Goes on the Offensive. J. Rheumatol. 2015, 42, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, J.H.; Rai, V.; Dilisio, M.F.; Sekundiak, T.D.; Agrawal, D.K. Increased Expression of Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns (DAMPs) in Osteoarthritis of Human Knee Joint Compared to Hip Joint. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 436, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platanitis, E.; Decker, T. Regulatory Networks Involving STATs, IRFs, and NFκB in Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venugopal, P.; Lavu, V.; RangaRao, S.; Venkatesan, V. Evaluation of a Panel of Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms in MiR-146a and MiR-196a2 Genomic Regions in Patients with Chronic Periodontitis. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2017, 21, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjha, R.; Meena, N.K.; Singh, A.; Ahuja, V.; Paul, J. Association of MiR-196a-2 and MiR-499 Variants with Ulcerative Colitis and Their Correlation with Expression of Respective MiRNAs. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toraih, E.A.; Ismail, N.M.; Toraih, A.A.; Hussein, M.H.; Fawzy, M.S. Precursor MiR-499a Variant but Not MiR-196a2 Is Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis Susceptibility in an Egyptian Population. Mol. Diagn. 2016, 20, 279–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemán-Ávila, I.; Jiménez-Morales, M.; Beltrán-Ramírez, O.; Barbosa-Cobos, R.E.; Jiménez-Morales, S.; Sánchez-Muñoz, F.; Valencia-Pacheco, G.; Amezcua-Guerra, L.M.; Juárez-Vicuña, Y.; Razo-Blanco Hernández, D.M.; et al. Functional Polymorphisms in Pre-MiR146a and Pre-MiR499 Are Associated with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus but Not with Rheumatoid Arthritis or Graves’ Disease in Mexican Patients. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 91876–91886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De La Cruz-Castillejos, J.; Barbosa-Cobos, R.; Becerril-Mendoza, L.; Lugo-Zamudio, G.; Ramírez-Bello, J.; Matias-Carmona, M.; Alemán-Άvila, I. AB0242 Evaluation of Variants in MIR-146A, MIR-196A-2 and MIR-499 and Their Association with Susceptibility for Rheumatoid Arthritis and Its Extra-Articular Manifestations. In Proceedings of the Abstracts Accepted for Publication; BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.: London, UK; European League Against Rheumatism: Zürich, Switzerland, 2017; p. 1133. [Google Scholar]
- Taganov, K.D.; Boldin, M.P.; Chang, K.-J.; Baltimore, D. NF-KappaB-Dependent Induction of MicroRNA MiR-146, an Inhibitor Targeted to Signaling Proteins of Innate Immune Responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 12481–12486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saba, R.; Sorensen, D.L.; Booth, S.A. MicroRNA-146a: A Dominant, Negative Regulator of the Innate Immune Response. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasi, S.; Ea, H.-K.; Chobaz, V.; van Lent, P.; Lioté, F.; So, A.; Busso, N. Dispensable Role of Myeloid Differentiation Primary Response Gene 88 (MyD88) and MyD88-Dependent Toll-like Receptors (TLRs) in a Murine Model of Osteoarthritis. Jt. Bone Spine 2014, 81, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelttari, K.; Barbero, A.; Martin, I. A Potential Role of Homeobox Transcription Factors in Osteoarthritis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2015, 3, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, Y.; Okabe, T.; Larmour, C.; Di Rocco, A.; Maijenburg, M.W.; Phillips, A.; Speck, N.A.; Wakitani, S.; Nakamura, T.; Yamada, Y.; et al. Articular Cartilage Endurance and Resistance to Osteoarthritic Changes Require Transcription Factor Erg: Erg IN LONG-TERM JOINT MAINTENANCE. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 2679–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAlinden, A.; Varghese, N.; Wirthlin, L.; Chang, L.-W. Differentially Expressed MicroRNAs in Chondrocytes from Distinct Regions of Developing Human Cartilage. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WANG, X.; ZHU, Y.; XU, B.; WANG, J.; LIU, X. Identification of TLR2 and TLR4-Induced MicroRNAs in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Their Possible Roles in Regulating TLR Signals. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 4969–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Fang, F.; Yu, X.; Yang, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhu, L.; Shao, K.; Zhu, T. Knockdown of H19 Inhibits the Pathogenesis of Acne Vulgaris by Targeting the MiR-196a/TLR2/NF-ΚB Axis. Inflammation 2020, 43, 1936–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, K.; Nakasa, T.; Miyaki, S.; Ishikawa, M.; Deie, M.; Adachi, N.; Yasunaga, Y.; Asahara, H.; Ochi, M. Expression of MicroRNA-146 in Osteoarthritis Cartilage. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Zhao, J.; Jing, W.; Yan, S.; Wang, X.; Xiao, C.; Ma, B. Role of MiR-146a in Human Chondrocyte Apoptosis in Response to Mechanical Pressure Injury in Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 34, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papathanasiou, I.; Balis, C.; Trachana, V.; Mourmoura, E.; Tsezou, A. The Synergistic Function of MiR-140–5p and MiR-146a on TLR4-Mediated Cytokine Secretion in Osteoarthritic Chondrocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 522, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Ye, J.; Qin, A.; Zou, H.; Shao, H.; Qian, K. Both MicroRNA-155 and Virus-Encoded MiR-155 Ortholog Regulate TLR3 Expression. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran-Moguel, M.C.; Petarra-del Rio, S.; Mayorquin-Galvan, E.E.; Zavala-Cerna, M.G. Rheumatoid Arthritis and MiRNAs: A Critical Review through a Functional View. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 2474529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Dong, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, C. Acetylbritannilactone Modulates MicroRNA-155-Mediated Inflammatory Response in Ischemic Cerebral Tissues. Mol. Med. 2015, 21, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, S.; Margulies, B.S.; Kerr, W.G. Role of SHIP1 in Bone Biology: Role of SHIP1 in Bone Biology. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2013, 1280, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Q.; Yang, H. Inhibition of Toll-Like Receptor Signaling as a Promising Therapy for Inflammatory Diseases: A Journey from Molecular to Nano Therapeutics. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grässel, S.; Muschter, D. Recent Advances in the Treatment of Osteoarthritis. F1000Res 2020, 9, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshikawa, N.; Sakai, A.; Takai, S.; Suzuki, H. Targeting Extracellular MiR-21-TLR7 Signaling Provides Long-Lasting Analgesia in Osteoarthritis. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2020, 19, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyhan, A.A.; Carini, C. Are Innovation and New Technologies in Precision Medicine Paving a New Era in Patients Centric Care? J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patron, A.; Annala, L.; Lainiala, O.; Paloneva, J.; Äyrämö, S. An Automatic Method for Assessing Spiking of Tibial Tubercles Associated with Knee Osteoarthritis. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Kuang, L.; Chen, C.; Yang, J.; Zeng, W.-N.; Li, T.; Chen, H.; Huang, S.; Fu, Z.; Li, J.; et al. MiR-100-5p-Abundant Exosomes Derived from Infrapatellar Fat Pad MSCs Protect Articular Cartilage and Ameliorate Gait Abnormalities via Inhibition of MTOR in Osteoarthritis. Biomaterials 2019, 206, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | Location | rs Number | SNP Change | Variant Type, Region | Amino Acid Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TLR2 | 4q31.3 | rs5743708 | G2258A | Exon 3 | Arg753Gln, R753Q |
| TLR3 | 4q35.1 | rs3775291 | G13909A | Exon 4 | Leu412Phe, L412F |
| rs5743312 | C9948T | Intron 3 | - | ||
| TLR4 | 9q33.1 | rs4986790 | A896G | Exon 3 | Asp299Gly, D299G |
| rs4986791 | C1196T | Exon 4 | Thr399Ile, T399I | ||
| TLR7 | Xp22.2 | rs3853839 | C/G | 3′ UTR | - |
| TLR9 | 3p21.2 | rs187084 | A/G | Promoter | - |
| miR-196a2 | 12q13.13 | rs11614913 | C/T | 3′ UTR | - |
| miR-146a | 5q33.3 | rs2910164 | C/G | Promoter | - |
| miR-155 | 21q21.3 | rs767649 | A/T | Promoter | - |
| Demographic and Risk Factors | N | TLR2 rs5743708 | TLR3 rs3775291 | TLR3 rs5743312 | TLR4 rs4986790 | TLR4 rs4986791 | TLR7 rs3853839 | TLR9 rs187084 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GG/AG/AA | GG/GA/AA | CC/CT/TT | AA/AG/GG | CC/CT/TT | CC/CG/GG | AA/AG/GG | |||
| Sex | Male | 35 | 26/8/1 | 14/20/1 | 21/14/0 | 26/9/0 | 12/20/3 | 26/0/9 | 10/17/8 |
| Female | 60 | 40/20/0 | 21/36/3 | 39/19/2 | 44/16/0 | 24/35/1 | 36/6/18 | 21/25/14 | |
| p | 0.256 | 0.810 | 0.428 | 1.000 | 0.259 | 0.115 | 0.771 | ||
| Localization | Hip | 61 | 42/18/1 | 24/36/1 | 38/21/2 | 45/16/0 | 22/37/2 | 36/6/19 | 20/28/13 |
| Knee | 34 | 24/10/0 | 11/20/3 | 22/12/0 | 25/9/0 | 14/18/2 | 26/0/8 | 11/14/9 | |
| p | 0.753 | 0.227 | 0.566 | 1.000 | 0.695 | 0.090 | 0.834 | ||
| Age median | <70 | 46 | 33/13/0 | 17/26/3 | 29/16/1 | 33/13/0 | 19/25/2 | 29/3/14 | 16/18/12 |
| >70 | 49 | 33/15/1 | 18/30/1 | 31/17/1 | 37/12/0 | 17/30/2 | 33/3/13 | 15/24/10 | |
| p | 0.592 | 0.543 | 0.999 | 0.816 | 0.790 | 0.905 | 0.613 | ||
| BMI | ≤25 | 2 | 1/1/0 | 1/1/0 | 2/0/0 | 2/0/0 | 0/2/0 | 1/0/1 | 2/0/0 |
| 25–30 | 77 | 52/24/1 | 27/47/3 | 50/25/2 | 56/21/0 | 30/43/4 | 53/5/19 | 26/31/20 | |
| >30 | 16 | 13/3/0 | 7/8/1 | 8/8/0 | 12/4/0 | 6/10/0 | 8/1/7 | 3/11/2 | |
| p | 0.793 | 0.920 | 0.516 | 0.682 | 0.655 | 0.566 | 0.072 | ||
| Smoking | Yes | 17 | 12/4/1 | 6/10/1 | 12/5/0 | 15/2/0 | 4/13/0 | 10/2/5 | 7/5/5 |
| No | 78 | 54/24/0 | 29/46/3 | 48/28/2 | 55/23/0 | 32/42/4 | 52/4/22 | 24/37/17 | |
| p | 0.089 | 0.927 | 0.675 | 0.223 | 0.199 | 0.573 | 0.399 | ||
| Physical activity | Yes | 20 | 17/3/0 | 8/11/1 | 15/5/0 | 17/3/0 | 5/13/2 | 14/0/6 | 7/8/5 |
| No | 75 | 49/25/1 | 27/45/3 | 45/28/2 | 53/22/0 | 31/42/2 | 48/6/21 | 24/34/17 | |
| p | 0.229 | 0.917 | 0.409 | 0.259 | 0.187 | 0.425 | 0.913 | ||
| History of injury | Yes | 33 | 21/11/1 | 12/19/2 | 24/8/1 | 26/7/0 | 12/18/3 | 20/2/11 | 10/17/6 |
| No | 62 | 45/17/0 | 23/37/2 | 36/25/1 | 44/18/0 | 24/37/1 | 42/4/16 | 21/25/16 | |
| p | 0.304 | 0.806 | 0.281 | 0.471 | 0.224 | 0.740 | 0.539 | ||
| Family history | No | 56 | 29/9/1 | 15/22/2 | 26/12/1 | 31/8/0 | 13/24/2 | 23/3/13 | 11/20/8 |
| Yes | 39 | 37/19/0 | 20/34/2 | 34/21/1 | 39/17/0 | 23/31/2 | 39/3/14 | 20/22/14 | |
| p | 0.275 | 0.882 | 0.781 | 0.347 | 0.723 | 0.560 | 0.510 | ||
| Early OA onset | <55 | 52 | 38/13/1 | 18/32/2 | 33/19/0 | 39/13/0 | 18/32/2 | 36/1/15 | 14/24/14 |
| >55 | 43 | 28/15/0 | 17/24/2 | 27/14/2 | 31/12/0 | 18/23/2 | 26/5/12 | 17/18/8 | |
| p | 0.402 | 0.851 | 0.283 | 0.817 | 0.731 | 0.150 | 0.377 | ||
| Menopause | Yes | 56 | 40/16/0 | 19/34/3 | 36/18/2 | 42/14/0 | 21/34/1 | 33/5/18 | 19/23/14 |
| No | 4 | 0/4/0 | 2/2/0 | 3/1/0 | 2/2/0 | 3/1/0 | 3/1/0 | 2/2/0 | |
| p | 0.003 | 0.755 | 0.874 | 0.275 | 0.333 | 0.300 | 0.510 | ||
| Early menopause | Yes | 15 | 11/4/0 | 5/10/0 | 7/8/0 | 11/4/0 | 6/9/0 | 9/2/4 | 6/6/3 |
| No | 45 | 29/16/0 | 16/26/3 | 32/11/2 | 33/12/0 | 18/26/1 | 27/4/14 | 15/19/11 | |
| p | 0.753 | 0.559 | 0.097 | 1.000 | 0.842 | 0.862 | 0.882 | ||
| Swelling | Yes | 32 | 22/10/0 | 10/19/3 | 20/12/0 | 23/9/0 | 13/17/2 | 24/0/8 | 11/12/9 |
| No | 63 | 44/18/1 | 25/37/1 | 40/21/2 | 47/16/0 | 23/38/2 | 38/6/19 | 20/30/13 | |
| p | 0.755 | 0.177 | 0.570 | 0.808 | 0.683 | 0.139 | 0.591 | ||
| Demographic and Risk Factors | Total N | miR-196a2 rs11614913 | miR-146a rs2910164 | miR-155 rs767649 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC/CT/TT | GG/GC/CC | TT/TA/AA | |||
| Sex | Male | 35 | 11/13/11 | 18/13/4 | 34/1/0 |
| Female | 60 | 5/28/27 | 40/17/3 | 51/9/0 | |
| p | 0.014 | 0.269 | 0.086 | ||
| Localization | Hip | 61 | 13/26/22 | 38/19/4 | 55/6/0 |
| Knee | 34 | 3/15/16 | 20/11/3 | 30/4/0 | |
| p | 0.260 | 0.902 | 0.742 | ||
| Age median | <70 | 46 | 7/21/18 | 26/16/4 | 39/7/0 |
| >70 | 49 | 9/20/20 | 32/14/3 | 46/3/0 | |
| p | 0.867 | 0.669 | 0.190 | ||
| BMI | ≤25 | 2 | 0/0/2 | 1/0/1 | 2/0/0 |
| 25–30 | 77 | 10/37/30 | 47/24/6 | 69/8/0 | |
| >30 | 16 | 6/4/6 | 10/6/0 | 14/2/0 | |
| p | 0.051 | 0.136 | 0.859 | ||
| Smoking | Yes | 17 | 2/9/6 | 11/5/1 | 16/1/0 |
| No | 78 | 14/32/32 | 47/25/6 | 69/9/0 | |
| p | 0.641 | 0.933 | 0.684 | ||
| Physical activity | Yes | 20 | 5/6/9 | 11/7/2 | 19/1/0 |
| No | 75 | 11/35/29 | 47/23/5 | 66/9/0 | |
| p | 0.337 | 0.785 | 0.683 | ||
| History of injury | Yes | 33 | 10/9/14 | 18/11/4 | 30/3/0 |
| No | 62 | 6/32/24 | 40/19/3 | 55/7/0 | |
| p | 0.014 | 0.377 | 1.000 | ||
| Family history | Yes | 56 | 9/14/16 | 23/12/4 | 36/3/0 |
| No | 39 | 7/27/22 | 35/18/3 | 49/7/0 | |
| p | 0.308 | 0.667 | 0.518 | ||
| Early OA onset | <55 | 52 | 9/22/21 | 30/18/4 | 47/5/0 |
| >55 | 43 | 7/19/17 | 28/12/3 | 38/5/0 | |
| p | 0.981 | 0.754 | 0.751 | ||
| Menopause | Yes | 56 | 4/26/26 | 38/15/3 | 47/9/0 |
| No | 4 | 1/2/1 | 2/2/0 | 4/0/0 | |
| p | 0.403 | 0.576 | 1.000 | ||
| Early menopause | Yes | 15 | 0/8/7 | 10/5/0 | 10/5/0 |
| No | 45 | 5/20/20 | 30/12/3 | 41/4/0 | |
| p | 0.393 | 0.555 | 0.036 | ||
| Swelling | Yes | 32 | 2/14/16 | 18/11/3 | 28/4/0 |
| No | 63 | 14/27/22 | 40/19/4 | 57/6/0 | |
| p | 0.109 | 0.754 | 0.728 | ||
| TLRs Gene Variants | Genotype | Controls | OA Patients | p * | Adjusted OR ** [95% CI] | p *** | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N = 104 | % | N = 95 | % | |||||
| TLR2 rs5743708 | GG | 71 | 68.27 | 66 | 69.47 | 0.877 | 0.930 [0.532–1.627] | 0.800 |
| AG | 31 | 29.81 | 28 | 29.47 | ||||
| AA | 2 | 1.92 | 1 | 1.05 | ||||
| TLR3 rs3775291 | GG | 43 | 41.35 | 35 | 36.84 | 0.400 | 1.038 [0.644–1.674] | 0.878 |
| GA | 53 | 50.96 | 56 | 58.95 | ||||
| AA | 8 | 7.69 | 4 | 4.21 | ||||
| TLR3 rs5743312 | CC | 78 | 75.00 | 60 | 63.16 | 0.186 | 1.587 [0.910–2.768] | 0.104 |
| CT | 24 | 23.08 | 33 | 34.74 | ||||
| TT | 2 | 1.92 | 2 | 2.11 | ||||
| TLR4 rs4986790 | AA | 93 | 89.42 | 70 | 73.68 | 0.004 | 2.964 [1.364–6.442] | 0.006 |
| AG | 11 | 10.58 | 25 | 26.32 | ||||
| GG | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | ||||
| TLR4 rs4986791 | CC | 90 | 86.54 | 36 | 37.89 | 0.0001 | 8.766 [4.435–17.328] | 0.00001 |
| CG | 13 | 12.50 | 55 | 57.89 | ||||
| GG | 1 | 0.96 | 4 | 4.21 | ||||
| TLR7 rs3853839 | CC | 83 | 79.81 | 63 | 66.32 | 0.033 | 1.579 [1.106–2.255] | 0.012 |
| CG | 7 | 6.73 | 5 | 5.26 | ||||
| GG | 14 | 13.46 | 27 | 28.42 | ||||
| TLR9 rs1870840 | AA | 35 | 33.65 | 31 | 32.63 | 0.186 | 1.253 [0.839–1.871] | 0.271 |
| AG | 55 | 52.88 | 42 | 44.21 | ||||
| GG | 14 | 13.46 | 22 | 23.16 | ||||
| miR-196a2 rs11614913 | CC | 4 | 3.85 | 16 | 16.84 | 0.010 | 0.619 [0.397–0.964] | 0.034 |
| CT | 52 | 50.00 | 41 | 43.16 | ||||
| TT | 48 | 46.15 | 38 | 40.00 | ||||
| miR-146a rs2910164 | GG | 68 | 65.38 | 58 | 61.05 | 0.344 | 1.328 [0.821–2.146] | 0.248 |
| GC | 33 | 31.73 | 30 | 31.58 | ||||
| CC | 3 | 2.88 | 7 | 7.37 | ||||
| miR-155 rs767649 | TT | 94 | 90.38 | 85 | 89.47 | 0.831 | 1.119 [0.439–2.850] | 0.813 |
| TA | 10 | 9.62 | 10 | 10.53 | ||||
| AA | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stefik, D.; Vranic, V.; Ivkovic, N.; Velikic, G.; Maric, D.M.; Abazovic, D.; Vojvodic, D.; Maric, D.L.; Supic, G. Potential Impact of Polymorphisms in Toll-like Receptors 2, 3, 4, 7, 9, miR-146a, miR-155, and miR-196a Genes on Osteoarthritis Susceptibility. Biology 2023, 12, 458. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030458
Stefik D, Vranic V, Ivkovic N, Velikic G, Maric DM, Abazovic D, Vojvodic D, Maric DL, Supic G. Potential Impact of Polymorphisms in Toll-like Receptors 2, 3, 4, 7, 9, miR-146a, miR-155, and miR-196a Genes on Osteoarthritis Susceptibility. Biology. 2023; 12(3):458. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030458
Chicago/Turabian StyleStefik, Debora, Vladimir Vranic, Nemanja Ivkovic, Gordana Velikic, Dusan M. Maric, Dzihan Abazovic, Danilo Vojvodic, Dusica L. Maric, and Gordana Supic. 2023. "Potential Impact of Polymorphisms in Toll-like Receptors 2, 3, 4, 7, 9, miR-146a, miR-155, and miR-196a Genes on Osteoarthritis Susceptibility" Biology 12, no. 3: 458. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030458
APA StyleStefik, D., Vranic, V., Ivkovic, N., Velikic, G., Maric, D. M., Abazovic, D., Vojvodic, D., Maric, D. L., & Supic, G. (2023). Potential Impact of Polymorphisms in Toll-like Receptors 2, 3, 4, 7, 9, miR-146a, miR-155, and miR-196a Genes on Osteoarthritis Susceptibility. Biology, 12(3), 458. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030458











