Origin of Neuroblasts in the Avian Otic Placode and Their Distributions in the Acoustic and Vestibular Ganglia
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Processing of the Tissue
2.2. Grafting Experiments
2.3. Immunohistochemical Staining Procedure
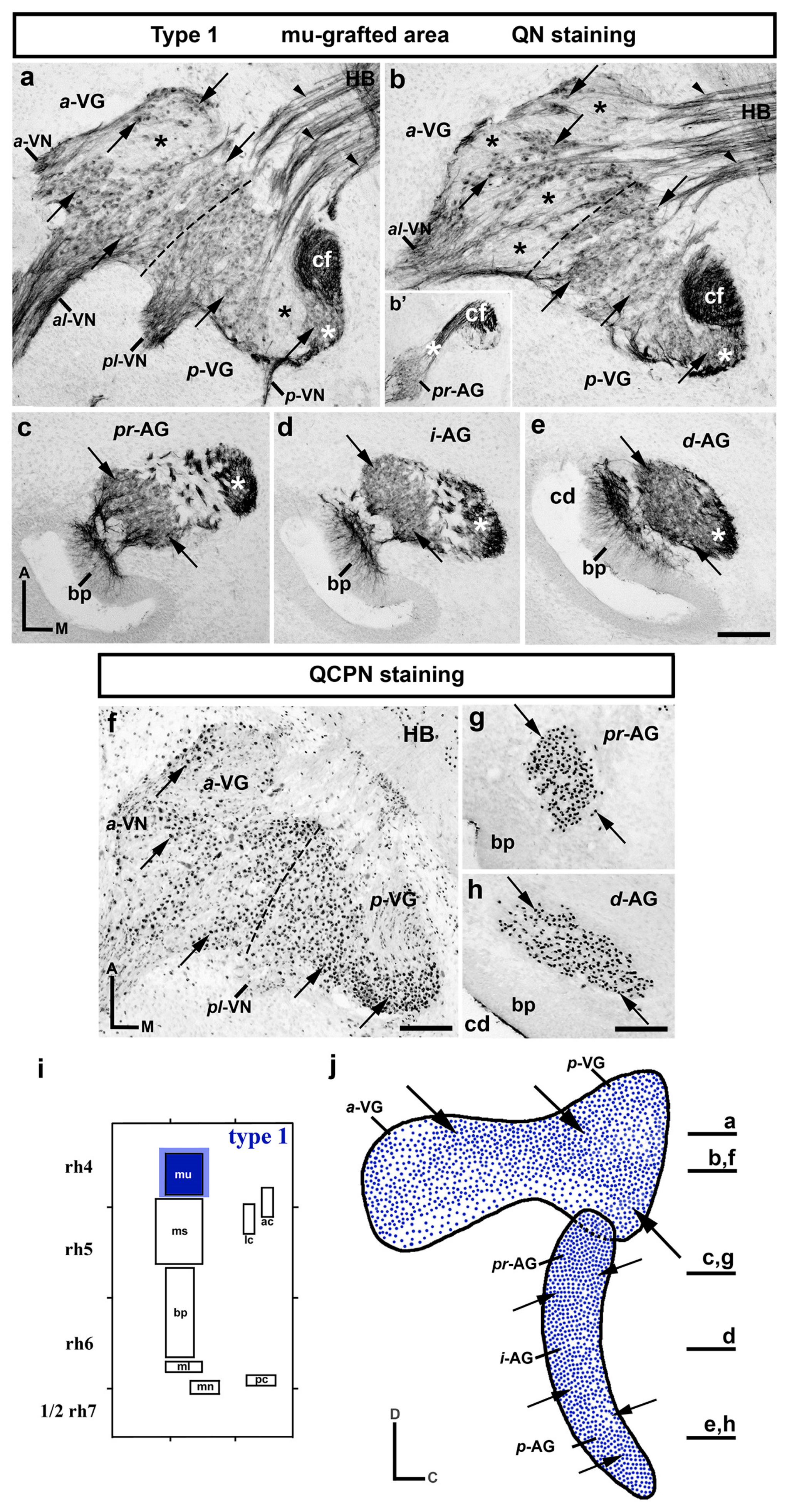
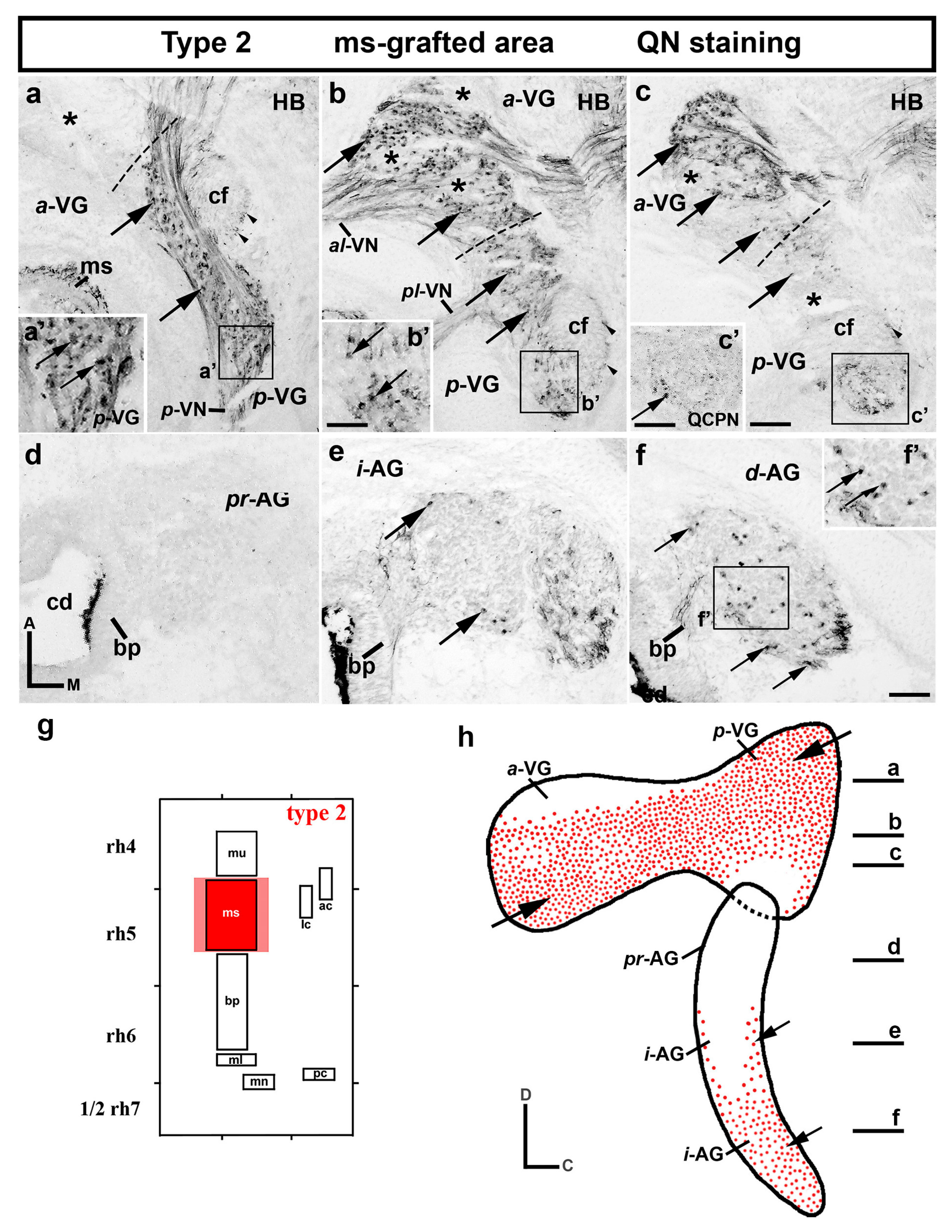
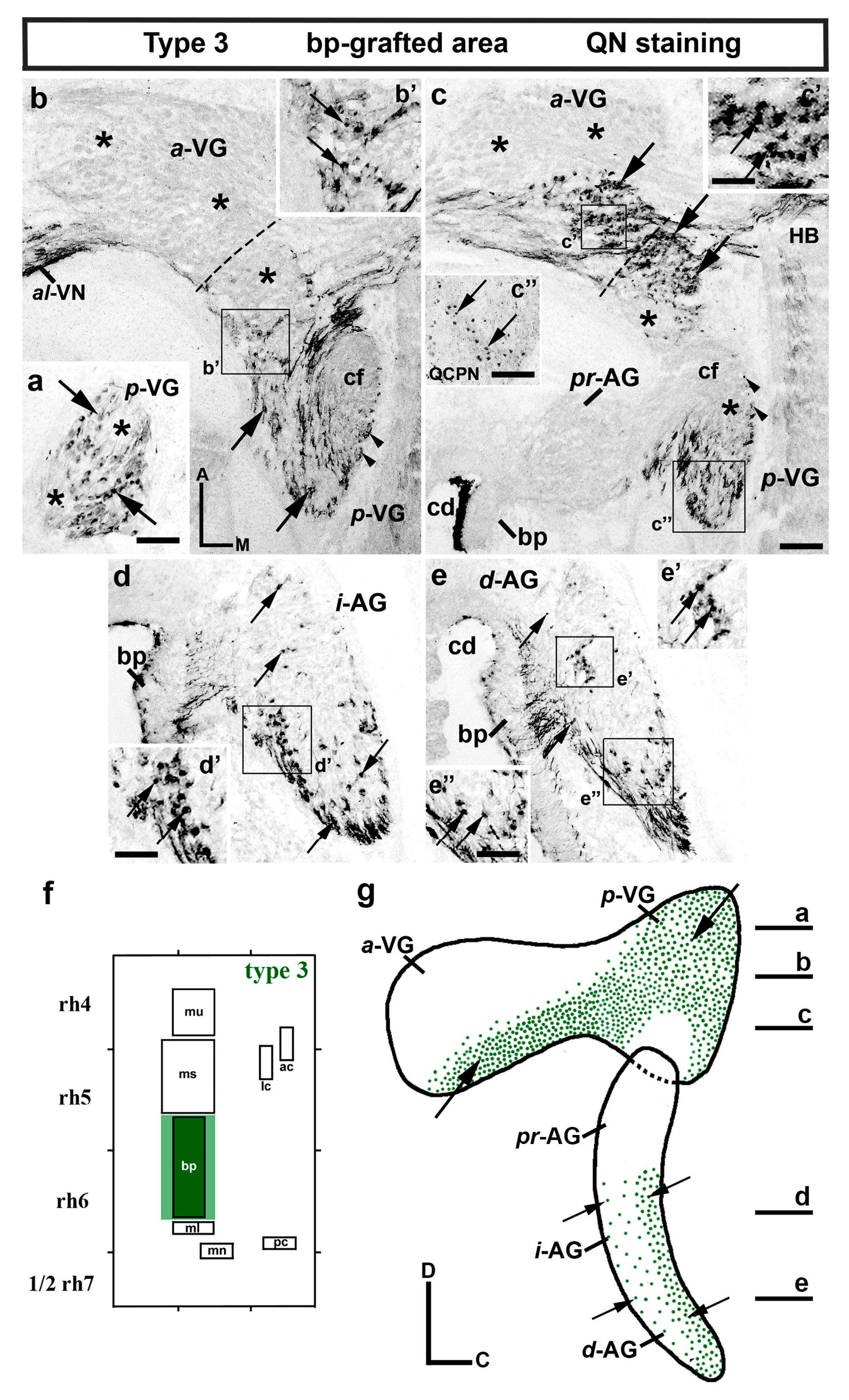
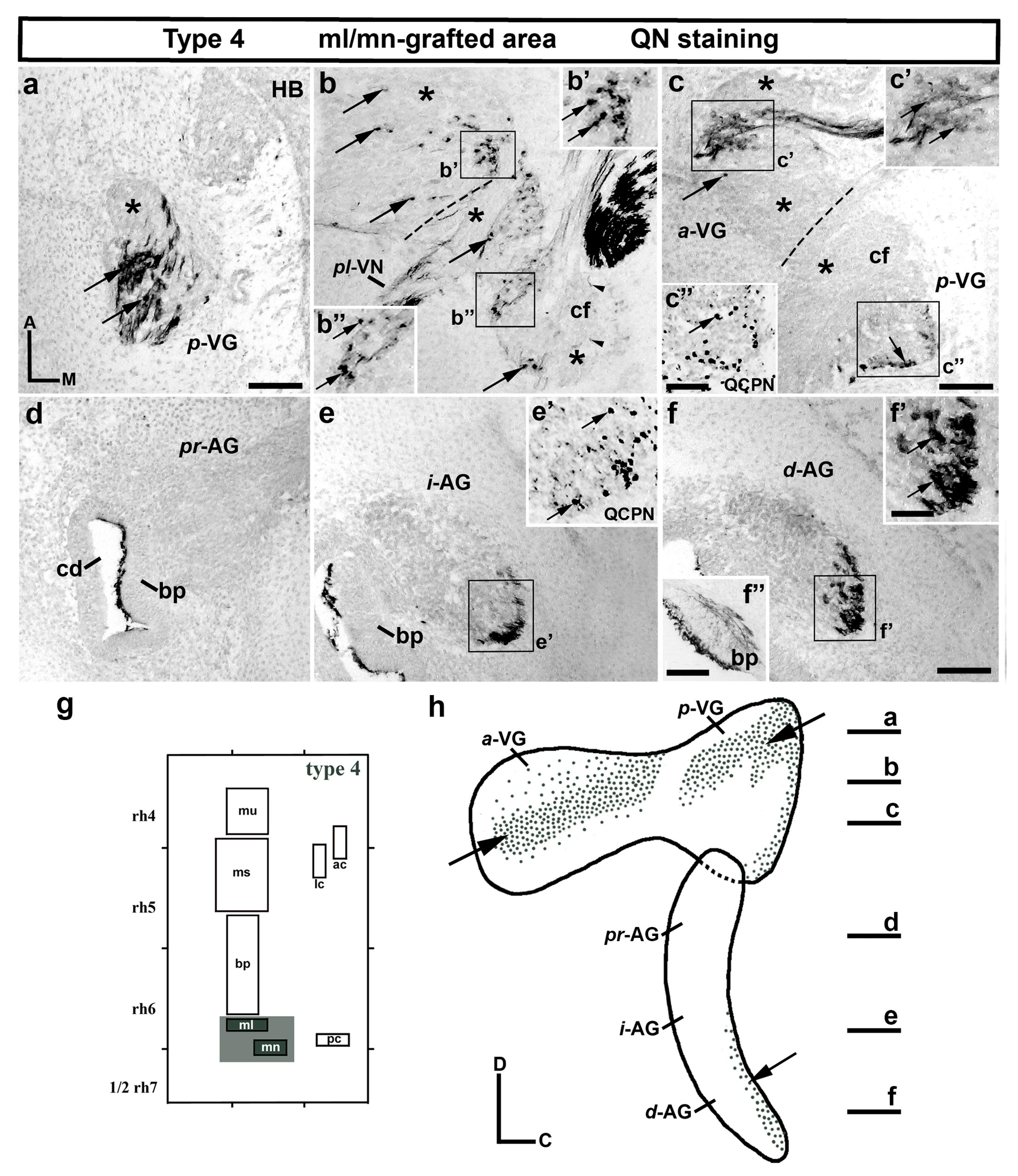
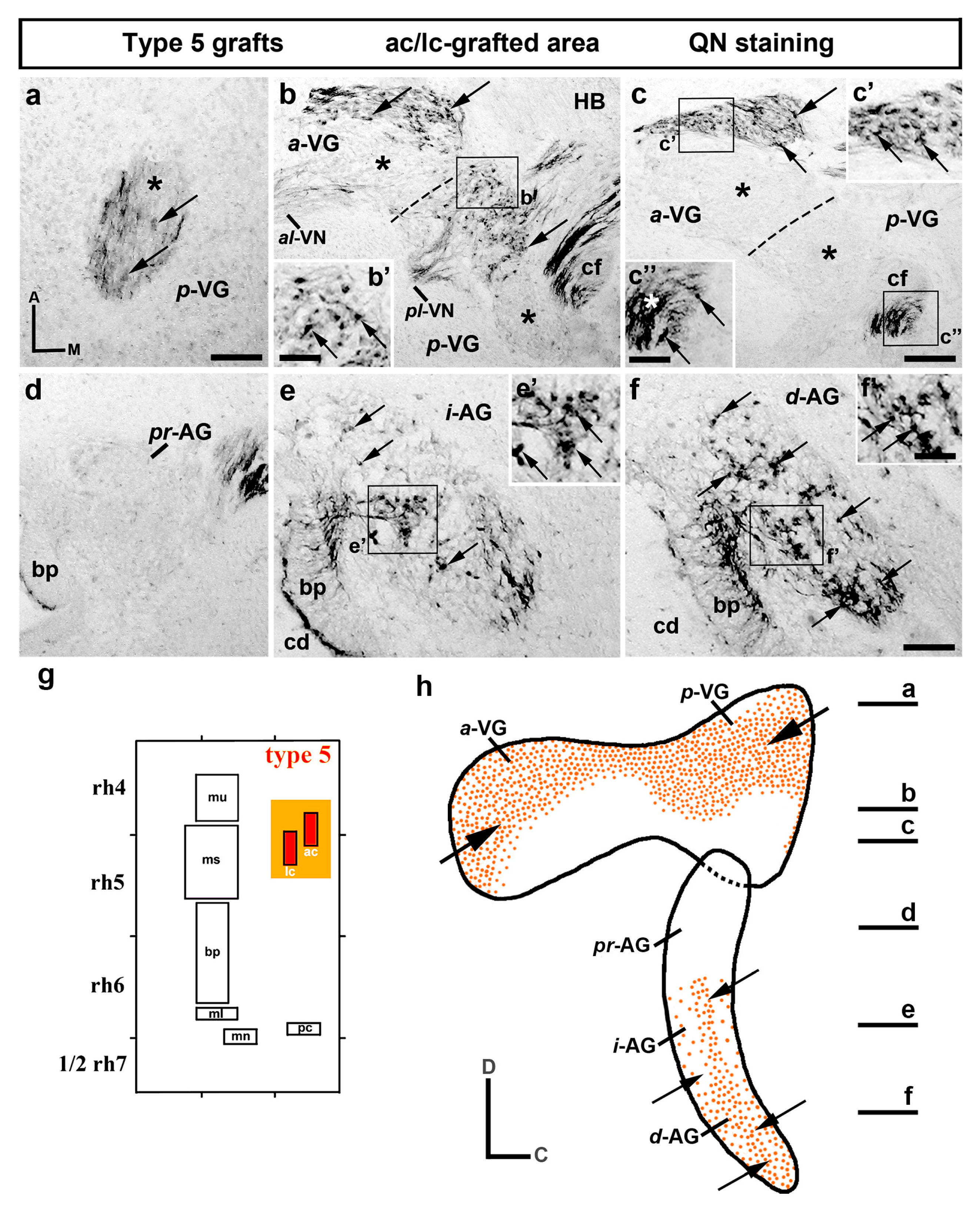
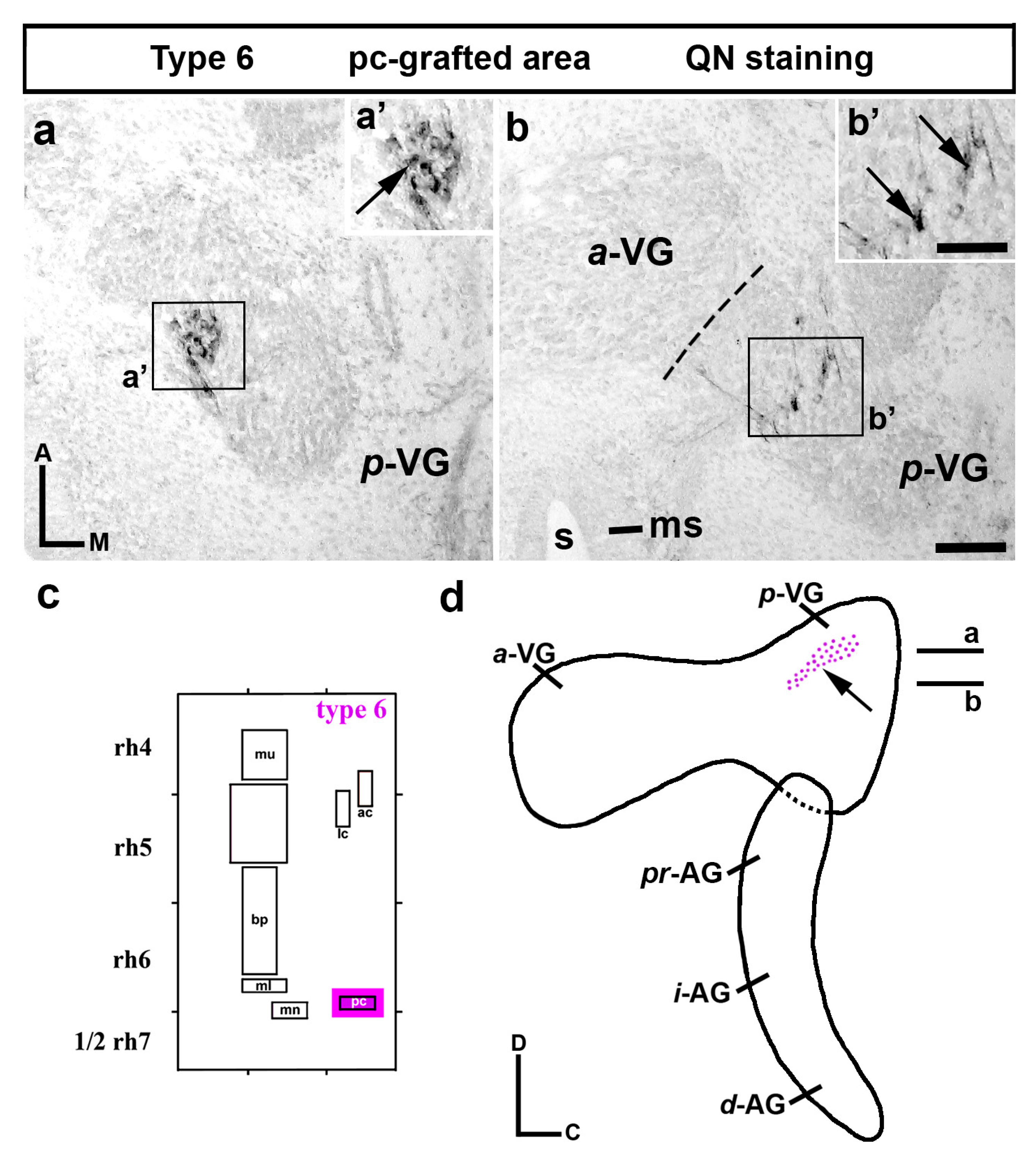
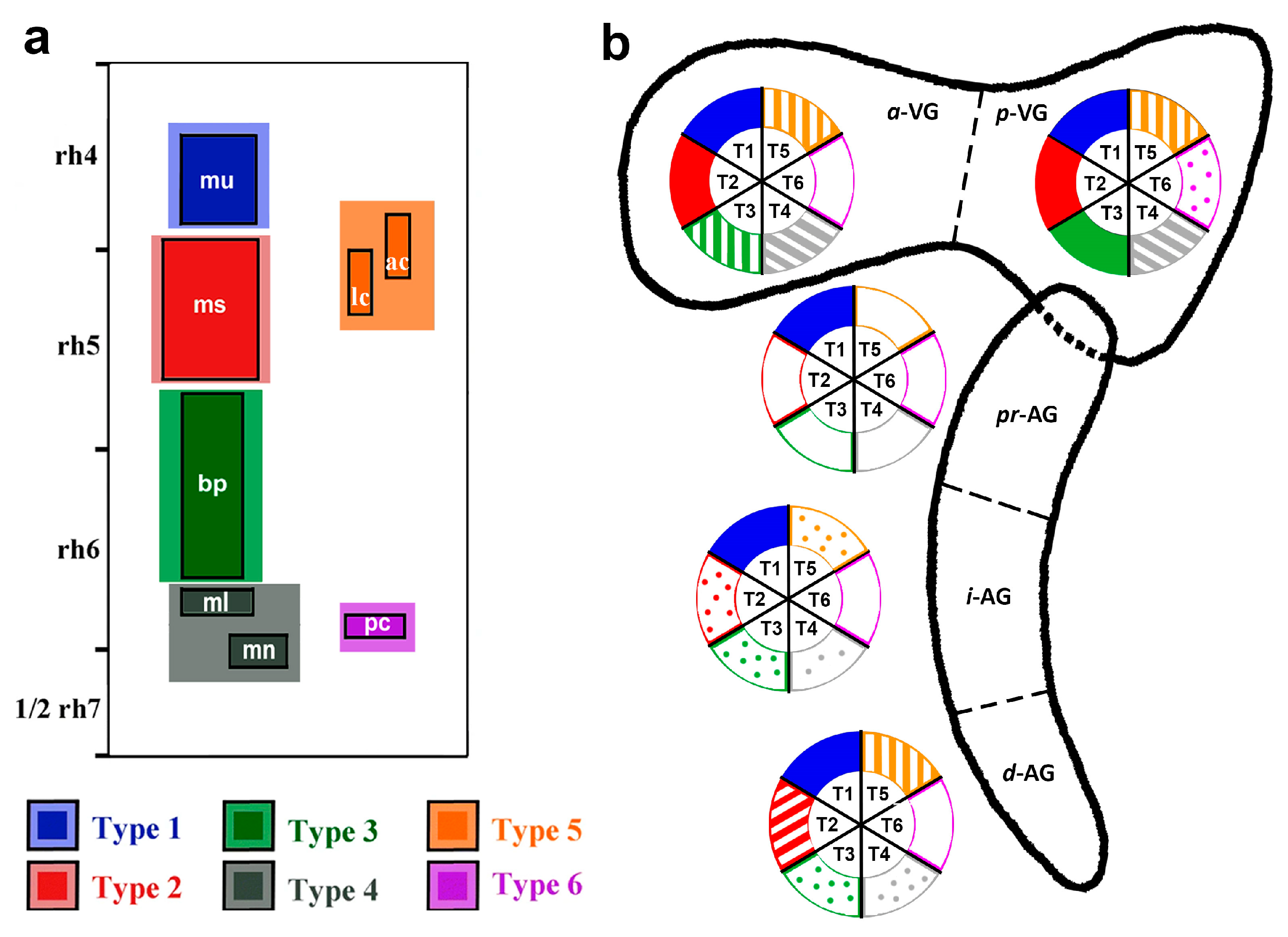
3. Results
3.1. Neuroblast Generation from the Maculae and Basilar Papilla Presumptive Domains of the Otic Placode
3.2. Neuroblast Generation from the Cristae Presumptive Domains of the Otic Placode
4. Discussion
4.1. The Pro-Sensory Domain of the Otic Placode
4.2. Segregation of Acoustic and Vestibular Neuronal Precursors by Otic Vesicle Stage
4.3. No Segregation of Acoustic and Vestibular Neuronal Precursors at the Otic Placode Stage
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abreviations
| ac | anterior crista |
| AG | acoustic ganglion |
| AVG | acoustic-vestibular ganglion |
| a-VG | anterior vestibular ganglion |
| a-VN | anterior vestibular nerve |
| al-VN | anterior-lateral vestibular nerve |
| bp | basilar papilla |
| cd | cochlear duct |
| cf | cochlea nerve fascicle |
| d-AG | distal acoustic ganglion |
| HB | hindbrain |
| i-AG | intermediate acoustic ganglion |
| lc | lateral crista |
| ml | macula lagena |
| mn | macula neglecta |
| ms | macula sacculi |
| mu | macula utriculi |
| pc | posterior crista |
| p-VG | posterior vestibular ganglion |
| p-VN | posterior vestibular nerve |
| pl-VN | posterior-lateral vestibular nerve |
| pr-AG | proximal acoustic ganglion |
References
- Streit, A. Extensive Cell Movements Accompany Formation of the Otic Placode. Dev. Biol. 2002, 249, 237–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohyama, T.; Groves, A.K.; Martin, K. The First Steps towards Hearing: Mechanisms of Otic Placode Induction. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2007, 51, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladher, R.K.; O′Neill, P.; Begbie, J. From Shared Lineage to Distinct Functions: The Development of the Inner Ear and Epibranchial Placodes. Development 2010, 137, 1777–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Streit, A. Induction of the Inner Ear: Stepwise Specification of Otic Fate from Multipotent Progenitors. Hear. Res. 2013, 297, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Guardado, L.Ó.; Puelles, L.; Hidalgo-Sánchez, M. Fate Map of the Chicken Otic Placode. Development 2014, 141, 2302–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritzsch, B.; Pauley, S.; Beisel, K.W. Cells, Molecules and Morphogenesis: The Making of the Vertebrate Ear. Brain Res. 2006, 1091, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritzsch, B.; Eberl, D.F.; Beisel, K.W. The Role of BHLH Genes in Ear Development and Evolution: Revisiting a 10-Year-Old Hypothesis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 3089–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubel, E.W.; Fritzsch, B. Auditory System Development: Primary Auditory Neurons and Their Targets. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2002, 25, 51–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maklad, A.; Kamel, S.; Wong, E.; Fritzsch, B. Development and Organization of Polarity-Specific Segregation of Primary Vestibular Afferent Fibers in Mice. Cell Tissue Res. 2010, 340, 303–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.; Reed, C.; Maklad, A. Central Projections of Lagenar Primary Neurons in the Chick. J. Comp. Neurol. 2013, 521, 3524–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straka, H.; Baker, R. Vestibular Blueprint in Early Vertebrates. Front. Neural Circuits 2013, 7, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoh, T.; Fekete, D.M. Clonal Analysis of the Relationships between Mechanosensory Cells and the Neurons That Innervate Them in the Chicken Ear. Development 2005, 132, 1687–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raft, S.; Koundakjian, E.J.; Quinones, H.; Jayasena, C.S.; Goodrich, L.V.; Johnson, J.E.; Segil, N.; Groves, A.K. Cross-Regulation of Ngn1 and Math1 Coordinates the Production of Neurons and Sensory Hair Cells during Inner Ear Development. Development 2007, 134, 4405–4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bok, J.; Chang, W.; Wu, D.K. Patterning and Morphogenesis of the Vertebrate Inner Ear. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2007, 51, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fekete, D.M.; Campero, A.M. Axon Guidance in the Inner Ear. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2007, 51, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, T.T.; Hammond, K.L. Axial Patterning in the Developing Vertebrate Inner Ear. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2007, 51, 507–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groves, A.K.; Fekete, D.M. Shaping Sound in Space: The Regulation of Inner Ear Patterning. Development 2012, 139, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.K.; Kelley, M.W. Molecular Mechanisms of Inner Ear Development. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a008409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raft, S.; Groves, A.K. Segregating Neural and Mechanosensory Fates in the Developing Ear: Patterning, Signaling, and Transcriptional Control. Cell Tissue Res. 2015, 359, 315–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsina, B.; Whitfield, T.T. Sculpting the Labyrinth: Morphogenesis of the Developing Inner Ear. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 65, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D′Amico-Martel, A. Temporal Patterns of Neurogenesis in Avian Cranial Sensory and Autonomic Ganglia. Am. J. Anat. 1982, 163, 351–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, I.S.; Martín-Partido, G.; Rodríguez-Gallardo, L.; González-Ramos, C.; Navascués, J. Cell Proliferation during Early Development of the Chick Embryo Otic Anlage: Quantitative Comparison of Migratory and Nonmigratory Regions of the Otic Epithelium. J. Comp. Neurol. 1989, 290, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemond, S.G.; Morest, D.K. Ganglion Formation from the Otic Placode and the Otic Crest in the Chick Embryo: Mitosis, Migration, and the Basal Lamina. Anat. Embryol. 1991, 184, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsina, B.; Abelló, G.; Ulloa, E.; Henrique, D.; Pujades, C.; Giraldez, F. FGF Signaling Is Required for Determination of Otic Neuroblasts in the Chick Embryo. Dev. Biol. 2004, 267, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, J.; Myat, A.; Le Roux, I.; Eddison, M.; Henrique, D.; Ish-Horowicz, D.; Lewis, J. Cell Fate Choices and the Expression of Notch, Delta and Serrate Homologues in the Chick Inner Ear: Parallels with Drosophila Sense-Organ Development. Development 1998, 125, 4645–4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritzsch, B. Development of Inner Ear Afferent Connections: Forming Primary Neurons and Connecting Them to the Developing Sensory Epithelia. Brain Res. Bull. 2003, 60, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Calderon, H.; Milo, M.; Leon, Y.; Varela-Nieto, I. A Network of Growth and Transcription Factors Controls Neuronal Differentation and Survival in the Developing Ear. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2007, 51, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsina, B.; Giraldez, F.; Pujades, C. Patterning and Cell Fate in Ear Development. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2009, 53, 1503–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coate, T.M.; Kelley, M.W. Making Connections in the Inner Ear: Recent Insights into the Development of Spiral Ganglion Neurons and Their Connectivity with Sensory Hair Cells. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2013, 24, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassiter, R.N.T.; Stark, M.R.; Zhao, T.; Zhou, C.J. Signaling Mechanisms Controlling Cranial Placode Neurogenesis and Delamination. Dev. Biol. 2014, 389, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, K.L.; Pavlínková, G.; Chizhikov, V.V.; Yamoah, E.N.; Fritzsch, B. Development in the Mammalian Auditory System Depends on Transcription Factors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldez, F. Regionalized Organizing Activity of the Neural Tube Revealed by the Regulation of Lmx1 in the Otic Vesicle. Dev. Biol. 1998, 203, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abello, G.; Alsina, B. Establishment of a Proneural Field in the Inner Ear. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2007, 51, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fekete, D.M.; Wu, D.K. Revisiting Cell Fate Specification in the Inner Ear. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2002, 12, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carney, P.R.; Silver, J. Studies on Cell Migration and Axon Guidance in the Developing Distal Auditory System of the Mouse. J. Comp. Neurol. 1983, 215, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begbie, J.; Ballivet, M.; Graham, A. Early Steps in the Production of Sensory Neurons by the Neurogenic Placodes. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2002, 21, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, J.; Kamaid, A.; Alsina, B.; Giraldez, F. Differential Expression of Sox2 and Sox3 in Neuronal and Sensory Progenitors of the Developing Inner Ear of the Chick. J. Comp. Neurol. 2007, 503, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez-Echeverría, C.; Dominguez-Frutos, E.; Charnay, P.; Schimmang, T.; Pujades, C. Analysis of Mouse Kreisler Mutants Reveals New Roles of Hindbrain-Derived Signals in the Establishment of the Otic Neurogenic Domain. Dev. Biol. 2008, 322, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radosevic, M.; Robert-Moreno, A.; Coolen, M.; Bally-Cuif, L.; Alsina, B. Her9 Represses Neurogenic Fate Downstream of Tbx1 and Retinoic Acid Signaling in the Inner Ear. Development 2011, 138, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapède, D.; Dyballa, S.; Pujades, C. Cell Lineage Analysis Reveals Three Different Progenitor Pools for Neurosensory Elements in the Otic Vesicle. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 16424–16434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Wu, D.K. Temporal Coupling between Specifications of Neuronal and Macular Fates of the Inner Ear. Dev. Biol. 2016, 414, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyballa, S.; Savy, T.; Germann, P.; Mikula, K.; Remesikova, M.; Špir, R.; Zecca, A.; Peyriéras, N.; Pujades, C. Distribution of Neurosensory Progenitor Pools during Inner Ear Morphogenesis Unveiled by Cell Lineage Reconstruction. Elife 2017, 6, e22268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evsen, L.; Sugahara, S.; Uchikawa, M.; Kondoh, H.; Wu, D.K. Progression of Neurogenesis in the Inner Ear Requires Inhibition of Sox2 Transcription by Neurogenin1 and Neurod1. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 3879–3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fariñas, I.; Jones, K.R.; Tessarollo, L.; Vigers, A.J.; Huang, E.; Kirstein, M.; de Caprona, D.C.; Coppola, V.; Backus, C.; Reichardt, L.F.; et al. Spatial Shaping of Cochlear Innervation by Temporally Regulated Neurotrophin Expression. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 6170–6180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matei, V.; Pauley, S.; Kaing, S.; Rowitch, D.; Beisel, K.W.; Morris, K.; Feng, F.; Jones, K.; Lee, J.; Fritzsch, B. Smaller Inner Ear Sensory Epithelia in Neurog 1 Null Mice Are Related to Earlier Hair Cell Cycle Exit. Dev. Dyn. 2005, 234, 633–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Kersigo, J.; Jahan, I.; Pan, N.; Fritzsch, B. The Molecular Basis of Making Spiral Ganglion Neurons and Connecting Them to Hair Cells of the Organ of Corti. Hear. Res. 2011, 278, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritzsch, B.; Pan, N.; Jahan, I.; Elliott, K.L. Inner Ear Development: Building a Spiral Ganglion and an Organ of Corti out of Unspecified Ectoderm. Cell Tissue Res. 2015, 361, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Guardado, L.Ó.; Puelles, L.; Hidalgo-Sánchez, M. Origin of Acoustic-Vestibular Ganglionic Neuroblasts in Chick Embryos and Their Sensory Connections. Brain Struct. Funct. 2019, 224, 2757–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivolta, M.N.; Holley, M.C. GATA3 Is Downregulated during Hair Cell Differentiation in the Mouse Cochlea. J. Neurocytol. 1998, 27, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karis, A.; Pata, I.; van Doorninck, J.H.; Grosveld, F.; de Zeeuw, C.I.; de Caprona, D.; Fritzsch, B. Transcription Factor GATA-3 Alters Pathway Selection of Olivocochlear Neurons and Affects Morphogenesis of the Ear. J. Comp. Neurol. 2001, 429, 615–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawoko-Kerali, G.; Rivolta, M.N.; Holley, M. Expression of the Transcription Factors GATA3 and Pax2 during Development of the Mammalian Inner Ear. J. Comp. Neurol. 2002, 442, 378–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawoko-Kerali, G.; Rivolta, M.N.; Lawlor, P.; Cacciabue-Rivolta, D.I.; Langton-Hewer, C.; van Doorninck, J.H.; Holley, M.C. GATA3 and NeuroD Distinguish Auditory and Vestibular Neurons during Development of the Mammalian Inner Ear. Mech. Dev. 2004, 121, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koundakjian, E.J.; Appler, J.L.; Goodrich, L.V. Auditory Neurons Make Stereotyped Wiring Decisions before Maturation of Their Targets. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 14078–14088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, D.; Streit, A.; Gorospe, I.; Varela-Nieto, I.; Alsina, B.; Giraldez, F. Spatial and Temporal Segregation of Auditory and Vestibular Neurons in the Otic Placode. Dev. Biol. 2008, 322, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Guardado, L.O.; Ferran, J.L.; Mijares, J.; Puelles, L.; Rodríguez-Gallardo, L.; Hidalgo-Sánchez, M. Raldh3 Gene Expression Pattern in the Developing Chicken Inner Ear. J. Comp. Neurol. 2009, 514, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Guardado, L.Ó.; Ferran, J.L.; Rodríguez-Gallardo, L.; Puelles, L.; Hidalgo-Sánchez, M. Meis Gene Expression Patterns in the Developing Chicken Inner Ear. J. Comp. Neurol. 2011, 519, 125–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardeña-Núñez, S.; Sánchez-Guardado, L.Ó.; Corral-San-Miguel, R.; Rodríguez-Gallardo, L.; Marín, F.; Puelles, L.; Aroca, P.; Hidalgo-Sánchez, M. Expression Patterns of Irx Genes in the Developing Chick Inner Ear. Brain Struct. Funct. 2017, 222, 2071–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaya-Sánchez, D.; Sánchez-Guardado, L.Ó.; Ohta, S.; Chapman, S.C.; Schoenwolf, G.C.; Puelles, L.; Hidalgo-Sánchez, M. Fgf3 and Fgf16 Expression Patterns Define Spatial and Temporal Domains in the Developing Chick Inner Ear. Brain Struct. Funct. 2017, 222, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferran, J.L.; Ayad, A.; Merchán, P.; Morales-Delgado, N.; Sánchez-Arrones, L.; Alonso, A.; SandovalSandoval, J.E.; Bardet, S.M.; Corral-San-Miguel, R.; Sánchez-Guardado, L.Ó.; et al. Exploring Brain Genoarchitecture by Single and Double Chromogenic In Situ Hybridization (ISH) and Immunohistochemistry (IHC) on Cryostat, Paraffin, or Floating Sections. In In Situ Hybridization Methods; Hauptmann, G., Ed.; Neuromethods; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 83–107. ISBN 978-1-4939-2303-8. [Google Scholar]
- Hamburger, V.; Hamilton, H.L. A Series of Normal Stages in the Development of the Chick Embryo. J. Morphol. 1951, 88, 49–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado-Mallart, R.M.; Sotelo, C. Homotopic and Heterotopic Transplantations of Quail Tectal Primordia in Chick Embryos: Organization of the Retinotectal Projections in the Chimeric Embryos. Dev. Biol. 1984, 103, 378–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D′Amico-Martel, A.; Noden, D.M. Contributions of Placodal and Neural Crest Cells to Avian Cranial Peripheral Ganglia. Am. J. Anat. 1983, 166, 445–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M.; Jayabalan, S.; Machnicki, M.; Sohal, G.S. Ventrally Emigrating Neural Tube Cells Migrate into the Developing Vestibulocochlear Nerve and Otic Vesicle. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2003, 21, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freyer, L.; Aggarwal, V.; Morrow, B.E. Dual Embryonic Origin of the Mammalian Otic Vesicle Forming the Inner Ear. Development 2011, 138, 5403–5414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Calderón, H.; Martín-Partido, G.; Hidalgo-Sánchez, M. Otx2, Gbx2, and Fgf8 Expression Patterns in the Chick Developing Inner Ear and Their Possible Roles in Otic Specification and Early Innervation. Gene Expr. Patterns 2004, 4, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Calderón, H.; Martín-Partido, G.; Hidalgo-Sánchez, M. Pax2 Expression Patterns in the Developing Chick Inner Ear. Gene Expr. Patterns 2005, 5, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Calderón, H.; Francisco-Morcillo, J.; Martín-Partido, G.; Hidalgo-Sánchez, M. Fgf19 Expression Patterns in the Developing Chick Inner Ear. Gene Expr. Patterns 2007, 7, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Guardado, L.Ó.; Puelles, L.; Hidalgo-Sánchez, M. Fgf10 Expression Patterns in the Developing Chick Inner Ear. J. Comp. Neurol. 2013, 521, 1136–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Kinutani, M.; Agata, A.; Takashima, Y.; Obata, K. Pathfinding during Spinal Tract Formation in the Chick-Quail Chimera Analysed by Species-Specific Monoclonal Antibodies. Development 1990, 110, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millet, S.; Bloch-Gallego, E.; Simeone, A.; Alvarado-Mallart, R.M. The Caudal Limit of Otx2 Gene Expression as a Marker of the Midbrain/Hindbrain Boundary: A Study Using in Situ Hybridisation and Chick/Quail Homotopic Grafts. Development 1996, 122, 3785–3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, H.; Fekete, D.M. Lineage Analysis in the Chicken Inner Ear Shows Differences in Clonal Dispersion for Epithelial, Neuronal, and Mesenchymal Cells. Dev. Biol. 2001, 234, 120–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Sánchez, M.; Millet, S.; Bloch-Gallego, E.; Alvarado-Mallart, R.-M. Specification of the Meso-Isthmo-Cerebellar Region: The Otx2/Gbx2 Boundary. Brain Res. Rev. 2005, 49, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maklad, A.; Fritzsch, B. Incomplete Segregation of Endorgan-Specific Vestibular Ganglion Cells in Mice and Rats. J. Vestib. Res. 1999, 9, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maklad, A.; Fritzsch, B. The Developmental Segregation of Posterior Crista and Saccular Vestibular Fibers in Mice: A Carbocyanine Tracer Study Using Confocal Microscopy. Dev. Brain Res. 2002, 135, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornaro, M.; Geuna, S.; Fasolo, A.; Giacobini-Robecchi, M.G. HuC/D Confocal Imaging Points to Olfactory Migratory Cells as the First Cell Population That Expresses a Post-Mitotic Neuronal Phenotype in the Chick Embryo. Neuroscience 2003, 122, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, C.V.; Bronner-Fraser, M. Vertebrate Cranial Placodes I. Embryonic Induction. Dev. Biol. 2001, 232, 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Dude, C.M.; Baker, C.V.H. Fine-Grained Fate Maps for the Ophthalmic and Maxillomandibular Trigeminal Placodes in the Chick Embryo. Dev. Biol. 2008, 317, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakamatsu, Y.; Endo, Y.; Osumi, N.; Weston, J.A. Multiple Roles of Sox2, an HMG-Box Transcription Factor in Avian Neural Crest Development. Dev. Dyn. 2004, 229, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, A.C.Y.; Szeto, I.Y.Y.; Fritzsch, B.; Cheah, K.S.E. Differential and Overlapping Expression Pattern of SOX2 and SOX9 in Inner Ear Development. Gene Expr. Patterns 2009, 9, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, A.; Manley, G.A. Brainstem Connections of the Macula Lagenae in the Chicken. J. Comp. Neurol. 1996, 374, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, Y. Signaling Regulating Inner Ear Development: Cell Fate Determination, Patterning, Morphogenesis, and Defects. Congenit. Anom. 2015, 55, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noden, D.M.; Van de Water, T.R. The Developing Ear: Tissue Origins and Interactions. In The Biology of Change in Otolaryngology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1986; pp. 15–46. [Google Scholar]
- Abelló, G.; Khatri, S.; Giráldez, F.; Alsina, B. Early Regionalization of the Otic Placode and Its Regulation by the Notch Signaling Pathway. Mech. Dev. 2007, 124, 631–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abelló, G.; Khatri, S.; Radosevic, M.; Scotting, P.J.; Giráldez, F.; Alsina, B. Independent Regulation of Sox3 and Lmx1b by FGF and BMP Signaling Influences the Neurogenic and Non-Neurogenic Domains in the Chick Otic Placode. Dev. Biol. 2010, 339, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Sánchez, M.; Alvarado-Mallart, R.; Alvarez, I.S. Pax2, Otx2, Gbx2 and Fgf8 Expression in Early Otic Vesicle Development. Mech. Dev. 2000, 95, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bok, J.; Bronner-Fraser, M.; Wu, D.K. Role of the Hindbrain in Dorsoventral but Not Anteroposterior Axial Specification of the Inner Ear. Development 2005, 132, 2115–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruben, R.J. Development of the Inner Ear of the Mouse: A Radioautographic Study of Terminal Mitoses. Acta. Otolaryngol. 1967, 220 (Suppl. S220), 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Lilleväli, K.; Matilainen, T.; Karis, A.; Salminen, M. Partially Overlapping Expression of Gata2 and Gata3 during Inner Ear Development. Dev. Dyn. 2004, 231, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.M.; Warchol, M.E. Expression of the Gata3 Transcription Factor in the Acoustic Ganglion of the Developing Avian Inner Ear. J. Comp. Neurol. 2009, 516, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.C.; Appler, J.M.; Houseman, E.A.; Goodrich, L.V. Developmental Profiling of Spiral Ganglion Neurons Reveals Insights into Auditory Circuit Assembly. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 10903–10918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Pereira, F.A.; Price, S.D.; Chu, M.J.; Shope, C.; Himes, D.; Eatock, R.A.; Brownell, W.E.; Lysakowski, A.; Tsai, M.J. Essential Role of BETA2/NeuroD1 in Development of the Vestibular and Auditory Systems. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 2839–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.Y.; Fritzsch, B.; Serls, A.; Bakel, L.A.; Huang, E.J.; Reichardt, L.F.; Barth, D.S.; Lee, J.E. NeuroD-Null Mice Are Deaf Due to a Severe Loss of the Inner Ear Sensory Neurons during Development. Development 2001, 128, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Chen, Z.; del Barco Barrantes, I.; de la Pompa, J.L.; Anderson, D.J. Neurogenin1 Is Essential for the Determination of Neuronal Precursors for Proximal Cranial Sensory Ganglia. Neuron 1998, 20, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kersigo, J.; Fritzsch, B. Inner Ear Hair Cells Deteriorate in Mice Engineered to Have No or Diminished Innervation. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2015, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvorakova, M.; Jahan, I.; Macova, I.; Chumak, T.; Bohuslavova, R.; Syka, J.; Fritzsch, B.; Pavlinkova, G. Incomplete and Delayed Sox2 Deletion Defines Residual Ear Neurosensory Development and Maintenance. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, N.; Nichols, D.H.; Zhang, W.J.; Fritzsch, B.; He, D.Z.Z. Organ of Corti and Stria Vascularis: Is There an Interdependence for Survival? PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hidalgo-Sánchez, M.; Callejas-Marín, A.; Puelles, L.; Sánchez-Guardado, L. Origin of Neuroblasts in the Avian Otic Placode and Their Distributions in the Acoustic and Vestibular Ganglia. Biology 2023, 12, 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030453
Hidalgo-Sánchez M, Callejas-Marín A, Puelles L, Sánchez-Guardado L. Origin of Neuroblasts in the Avian Otic Placode and Their Distributions in the Acoustic and Vestibular Ganglia. Biology. 2023; 12(3):453. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030453
Chicago/Turabian StyleHidalgo-Sánchez, Matías, Antuca Callejas-Marín, Luis Puelles, and Luis Sánchez-Guardado. 2023. "Origin of Neuroblasts in the Avian Otic Placode and Their Distributions in the Acoustic and Vestibular Ganglia" Biology 12, no. 3: 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030453
APA StyleHidalgo-Sánchez, M., Callejas-Marín, A., Puelles, L., & Sánchez-Guardado, L. (2023). Origin of Neuroblasts in the Avian Otic Placode and Their Distributions in the Acoustic and Vestibular Ganglia. Biology, 12(3), 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12030453





