Simple Summary
Acetaminophen overdose causes acute liver injury by excessive oxidative stress. The present study examines the mechanisms underlying the protective effect of corilagin against acetaminophen-induced liver injury. Our results showed that corilagin attenuates the liver injury through its anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Corilagin may be a therapeutic agent for acute liver injury.
Abstract
Acetaminophen (APAP) overdose causes acute liver injury via oxidative stress, uncontrolled inflammatory response, and subsequent hepatocyte death. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase (NOX) is a potent source of cellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) and may contribute to oxidative stress in many inflammatory processes. Corilagin, a component of Phyllanthus urinaria, possesses antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and hepatoprotective effects. We evaluated the mechanisms underlying the protective effect of corilagin against acetaminophen-induced liver injury. Mice were intraperitoneally administrated 300 mg/kg APAP or equal volume of saline (control), with or without various concentrations of corilagin (0, 1, 5, or 10 mg/kg) administered after 30 min. All animals were sacrificed 16 h after APAP administration, and serum and liver tissue assays including histology, immunohistochemistry, and Western blot assay were performed. Corilagin post-treatment significantly attenuated APAP-induced liver injury (p < 0.005), inflammatory cell infiltration, hepatic proinflammatory cytokine levels, and hepatic oxidative stress. Furthermore, corilagin attenuated the protein levels of NOX1, NOX2, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) in APAP-induced liver injury. These results indicated that the antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and protective effects of corilagin in APAP-induced liver injury might involve the regulation of interleukin (IL)-6/STAT3 and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/NF-κB signaling pathways through NOX-derived ROS.
1. Introduction
Acetaminophen, N-acetyl-p-aminophenol (APAP), is commonly used for antipyretics and analgesics globally [1]. APAP is considered safe at proper therapeutic doses; however, accidental or unintentional overdose may lead to acute liver injury [2,3]. APAP is metabolized to its inactive glucuronide and sulfate conjugates in liver [4]. Only a small amount of APAP is oxidized to the metabolite N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI), which is inactivated to form non-toxic compounds [5,6]. Excessive NAPQI formation can result in oxidative stress and uncontrolled inflammatory response [3,7,8].
Oxidative stress is critical for APAP-induced organ injury [9,10]. Briefly, protein adducts formed through the reactive intermediate NAPQI augment mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) production [11,12]. Excess ROS production can promote mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) including c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) [13,14]. Previous studies demonstrated that JNK activation could also amplify ROS formation [15]. Moreover, sustained activation of MAPK was shown to contribute to inflammatory response and cell death [16,17].
Corilagin, an important major component of Phyllanthus urinaria, possesses antioxidant and hepatoprotective effects [18,19,20]. In sepsis, corilagin was shown to ameliorate an inflammatory response through the toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) [21]. In a recent study, corilagin protected against cerebral ischemic injury [22]. In hemorrhagic shock, corilagin was hepatoprotective [23]. Furthermore, we recently demonstrated that corilagin was protective against acute lung injury [24]. We also demonstrated that corilagin was protective through the suppression of inflammation; however, mechanisms underlying the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory roles of corilagin were unclear [25]. Therefore, we aimed to elucidate these mechanisms in the present study.
2. Methods
2.1. Mice
Adult male C57BL/6C mice were used. All experimental procedures were approved by Chang Gung Memorial Hospital.
2.2. Animal Model
Mice were assigned to one of six groups, in which acetaminophen was dissolved. In four of the six groups, mice received 300 mg/kg acetaminophen, followed by intraperitoneal administration of corilagin (Sigma Chemical, St. Louis, MO, USA) (0, 1, 5, or 10 mg/kg). In the remaining two groups, mice were intraperitoneally injected with normal saline, then the intraperitoneal was injected with phosphate-buffered saline or corilagin (10 mg/kg). After 16 h, the animals were sacrificed and tissue and blood samples were collected.
2.3. Serum Alanine Transaminase (ALT) and Aspartate Transaminase (AST) Measurement
Serum ALT and AST concentrations were measured and blood samples were collected. Then, the collected supernatants were analyzed.
2.4. Histology and Immunohistochemistry
At the end of the experiments, left liver lobes were harvested and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde. For histological examination, the samples were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. For immunohistochemistry, the samples were incubated with antibodies for the neutrophil marker Ly6G, the macrophage marker Mac-2, or nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase (NOX) 2.
2.5. Interleukin (IL)-6 and Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF)-α Levels
Liver tissues were homogenized. The supernatants were used to measure IL-6 and TNF-α concentrations with a spectrometer (absorbance of 450 nm) using ELISA Kits (R&D Systems Minneapolis, MN, USA).
2.6. Myeloperoxidase (MPO) Activity, Malondialdehyde (MDA), and Glutathione (GSH) in Liver
Supernatants were used to measure malondialdehyde levels and to determine glutathione levels. For myeloperoxidase activity, liver tissues were homogenized. Absorbance of the samples was measured over 5 min.
2.7. Western Blot
Membranes were incubated with antibodies to NOX1, NOX2, IL-6, ERK, phospho-ERK, JNK, phospho-JNK, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB).
2.8. Statistical Analysis
Data were presented as means ± standard error of the mean. One-way analysis of variance and Tukey’s multiple comparison test were used to analyze the results. A p-value of <0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Corilagin on APAP-Induced Liver Injury
ALT and AST levels were increased in the APAP group (p < 0.005), whereas no difference was observed between the control and 10 mg/kg corilagin groups. Treatment with 5 and 10 mg/kg corilagin significantly reduced serum ALT and AST levels. However, serum ALT and AST concentrations were not decreased significantly following the treatment with 1 mg/kg corilagin (Figure 1A,B).
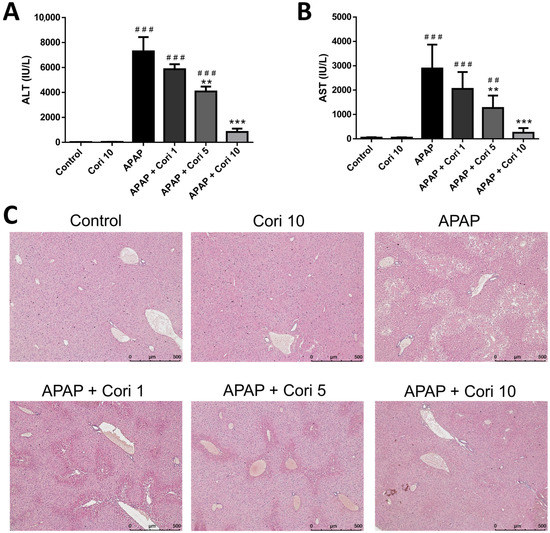
Figure 1.
The effects of corilagin on serum ALT levels (A), AST levels (B), and histopathological changes (C) in acetaminophen-induced hepatic injury. Mice were injected with APAP (300 mg/kg) or equal volume of saline (control), and treated with corilagin (0, 1, 5, or 10 g/kg) after 30 min. Each value represents mean ± SEM; n = 6 for each group. ## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.005 vs. control group; ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.005 vs. APAP group (50×).
Histological examination demonstrated severe centrilobular hepatic necrosis in the APAP group. Clearly, the treatment with 5 and 10 mg/kg corilagin attenuated the pathological changes (Figure 1C).
3.2. Effects of Corilagin on Hepatic Accumulation of Neutrophils and Macrophages in APAP-Induced Hepatic Injury
Immunohistochemistry of liver tissue sections using an antibody to Ly6G, a granulocyte-specific marker, revealed overt neutrophil infiltration of the necrotic areas in the APAP group (Figure 2). The groups treated with corilagin following APAP administration exhibited significantly decreased neutrophil infiltration in liver parenchyma.
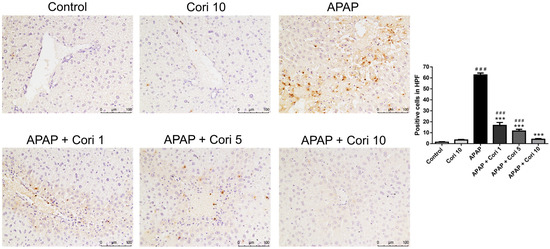
Figure 2.
The effects of corilagin on neutrophil infiltration in acetaminophen-induced hepatic injury. Animals were injected with APAP (300 mg/kg) or equal volume of saline (control), and treated with corilagin (0, 1, 5, or 10 g/kg) (200×). Each value represents mean ± SEM; n = 6 for each group. ### p < 0.005 vs. control group; *** p < 0.005 vs. APAP group.
To evaluate macrophage infiltration following APAP-induced injury, the liver tissue sections were immunohistochemically stained using an antibody to Mac-2. The APAP group exhibited increased macrophage infiltration of the necrotic areas, whereas the groups treated with corilagin following APAP administration exhibited significantly decreased macrophage infiltration in liver parenchyma (Figure 3).
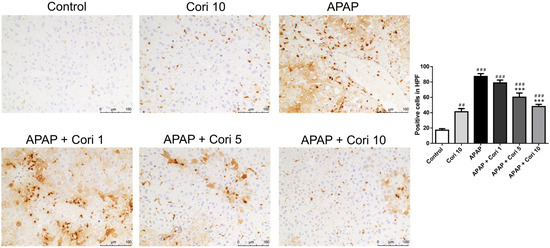
Figure 3.
The effects of corilagin on macrophage infiltration in acetaminophen-induced hepatic injury. Animals were injected with APAP (300 mg/kg) or equal volume of saline (control), and treated with corilagin (0, 1, 5, or 10 g/kg) (200×). Each value represents mean ± SEM; n = 6 for each group. ## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.005 vs. control group; *** p < 0.005 vs. APAP group.
3.3. Effects of Corilagin on Hepatic IL-6 and TNF-α Levels
Hepatic IL-6 and TNF-α levels, which were increased in the APAP group, did not differ between the control and 10 mg/kg corilagin alone groups (Figure 4A). Importantly, treatment with 5 mg/kg corilagin significantly reduced hepatic IL-6 levels (p < 0.01). Moreover, IL-6 and TNF-α were lower in the group treated with 10 mg/kg corilagin following APAP administration (Figure 4B).
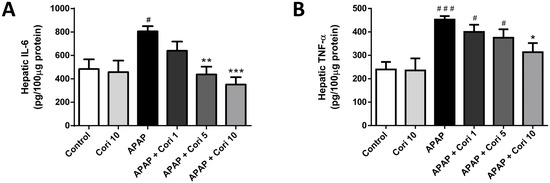
Figure 4.
The effects of corilagin on IL-6 (A) and TNF-α (B) concentrations in acetaminophen-induced hepatic injury. Animals were intraperitoneally injected with APAP (300 mg/kg) or equal volume of saline (control), and administrated with various concentrations of corilagin (0, 1, 5, or 10 g/kg) after 30 min. # p < 0.05, ### p < 0.005 vs. control group; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.005 vs. APAP group.
3.4. Corilagin on Hepatic MDA and GSH Levels and MPO Activity
In Figure 5, MDA, a lipid peroxidation marker, which was markedly increased in the APAP group, was reduced after the treatment with 5 and 10 mg/kg corilagin. Moreover, hepatic levels of GSH, a cellular antioxidant marker, which was significantly lower in the APAP group, was significantly higher after the treatment with 1, 5, and 10 mg/kg corilagin. Finally, MPO activity, used as a marker for neutrophil infiltration and oxidant levels, which was increased in the APAP group, was decreased after the treatment with corilagin.
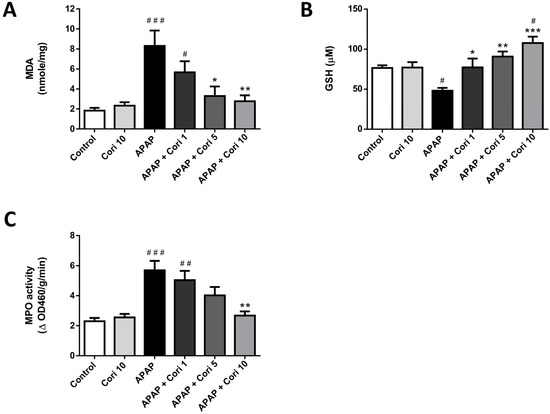
Figure 5.
The effects of corilagin on MDA (A), GSH (B) levels, and MPO activity (C) in acetaminophen-induced hepatic injury. Animals were injected with APAP (300 mg/kg) or equal volume of saline (control), and treated with corilagin (0, 1, 5, or 10 g/kg). # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.005 vs. control group; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.005 vs. APAP group.
3.5. Effects of Corilagin on Hepatic NOX1 and NOX2 Expressions
We measured NOX1 and NOX2 levels in liver tissue using Western blotting. Hepatic NOX1 and NOX2 levels, which were comparable between the control and 10 mg/kg corilagin alone groups, were higher in the APAP group (Figure 6A,B). Notably, the treatment with corilagin significantly reduced hepatic NOX1 and NOX2 levels (p < 0.005 for both). Furthermore, immunohistochemical staining revealed increased hepatic NOX2 levels in the APAP group (Figure 7), which were clearly reduced after administration with 5 and 10 mg/kg corilagin following APAP administration (Figure 7).
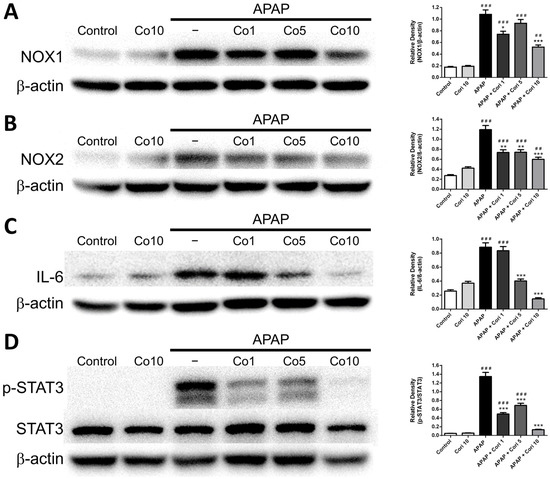
Figure 6.
The effects of corilagin on NOX1 (A), NOX2 (B), IL-6 (C), and STAT3 (D) expression. Animals were injected with APAP (300 mg/kg) or equal volume of saline (control), and treated with corilagin (0, 1, 5, or 10 g/kg) after 30 min. ## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.005 vs. control group; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.005 vs. APAP group. Figures S1–S4 Uncropped Western blots.
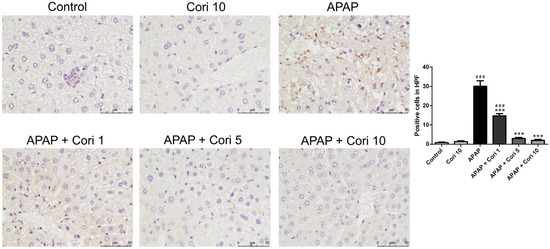
Figure 7.
The effects of corilagin on NOX2 expression. Animals were injected with APAP (300 mg/kg) or equal volume of saline (control), and treated with corilagin (0, 1, 5, or 10 g/kg) (400×). Each value represents mean ± SEM; n = 6 for each group. ### p < 0.005 vs. control group; *** p < 0.005 vs. APAP group.
3.6. Effects of Corilagin on IL-6 and STAT3 Concentrations
We measured hepatic IL-6 and STAT3 concentrations using Western blotting. Hepatic IL-6 and STAT3 levels, which were not different between the control and 10 mg/kg corilagin alone groups, were significantly higher in the APAP group (Figure 6C,D). Additionally, administration with corilagin following APAP administration significantly reduced hepatic IL-6 and STAT3 levels (p < 0.005 for both).
3.7. Hepatic NF-κB, Phospho-JNK, and Phospho-ERK Levels
Finally, we determined changes in NF-κB, phospho-JNK, and phospho-ERK. NF-κB, phospho-JNK, and phospho-ERK were not significantly different between the control and 10 mg/kg corilagin alone groups. However, hepatic levels of all three parameters were increased in the APAP group (Figure 8A–C). Administration with 5 mg/kg corilagin significantly reduced hepatic phospho-ERK and NF-κB levels (Figure 8A,C). Furthermore, administration with corilagin significantly reduced hepatic phospho-ERK, phospho-JNK, and NF-κB levels (p < 0.005 for all) (Figure 8A–C).
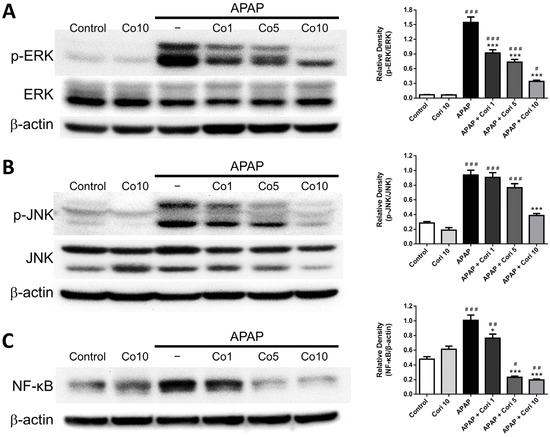
Figure 8.
The effects of corilagin on ERK (A), JNK (B), and NF-kB (C) expression. Animals were injected with APAP (300 mg/kg) or equal volume of saline (control), and administered with corilagin (0, 1, 5, or 10 g/kg). # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.005 vs. control group; * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.005 vs. APAP group. Figures S5–S7: Uncropped Western blots.
4. Discussion
Our analyses revealed that corilagin post-treatment reduced APAP-induced hepatic injury, inflammation, and oxidation. Moreover, corilagin post-treatment significantly reduced hepatic NOX1, NOX2, IL-6, STAT3, phospho-ERK, phospho-JNK, and NF-κB levels. Altogether, these results show the protection of corilagin against APAP-induced hepatic injury and suggest that its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effect occurs through NOX-derived ROS-mediated regulation of the IL-6/STAT3 and MAPK/NF-κB.
Innate immune system is important for APAP-induced hepatic injury [26,27,28]. Hepatocyte apoptosis or necrosis activate Kupffer cells through recognition by TLR [29,30,31]. Hepatic recruitment of monocytes and neutrophils secrete proinflammatory cytokines that contribute to an extensive inflammatory response and the subsequent severe liver damage [32,33,34,35]. Consistent with our previous work, we herein demonstrate that corilagin post-treatment ameliorates APAP-induced hepatic injury and reduces inflammatory cell infiltration and proinflammatory cytokine levels, confirming that corilagin exhibits protective effects for APAP-induced hepatic injury.
Progressive oxidative stress is characterized for APAP-induced hepatic injury [36,37]. Oxidative stress is a function of ROS overproduction in the setting of relative deficiency in antioxidant defenses [38,39]. Imbalanced ROS generation and consequent free radical production may result in injury [40]. Malondialdehyde is the main final product of lipid peroxidation in cells, and malondialdehyde levels frequently serve as an indicator of oxidative stress [41]. Myeloperoxidase represents the degree of neutrophil infiltration, and myeloperoxidase levels are a common biomarker of oxidative damage [42]. A recent study demonstrated that corilagin reduced oxidative stress in APAP-induced hepatic injury [43]. In agreement, we found that corilagin post-treatment led to reductions in malondialdehyde and myeloperoxidase levels, indicating reduced ROS production. Moreover, we found that corilagin post-treatment led to increased glutathione levels, indicating enhanced antioxidant capacity. Altogether, the results show that corilagin exerts protection against APAP-induced liver injury through antioxidant mechanisms.
A previous study demonstrated that excess ROS production mediated through NOX activation played a vital role in neutrophil-mediated inflammatory response and liver injury in a hemorrhagic shock model [44]. A recent study reported that NOX1-derived ROS played a critical role in liver disease [45]. Moreover, NOX2, primarily expressed in Kupffer cells, macrophages, and neutrophils, plays an important role in inflammation through ROS release in many inflammatory conditions [46]. Furthermore, we recently reported that corilagin post-treatment attenuated lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury through the inhibition of NOX2 pathway [24]. We found that the marked increase in hepatic NOX1 and NOX2 levels was attenuated with corilagin post-treatment, suggesting that the antioxidant effect of corilagin was, at least partially, through the downregulation of NOX1 and NOX2 levels in liver.
STAT3, a transcription factor activated by several proinflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6, regulates diverse cellular functions, such as inflammation, survival, differentiation, and proliferation [47]. STAT3 signaling is associated with liver injury, fibrosis, inflammatory response, and oncogenesis [48]. Previous studies have shown the significant role of STAT3 in hepatic injury [49]. A recent study demonstrated that treatment with a STAT3 inhibitor attenuated acute liver injury by regulating macrophages and reducing proinflammatory cytokine levels [50]. Corilagin post-treatment reduced IL-6 and STAT3 levels, suggesting that the anti-inflammatory effect of corilagin might occur via the regulation of IL-6/STAT3.
MAPK family members, including ERK and JNK, play essential roles in differentiation, inflammation, and oxidative stress [51]. MAPK activation can lead to the induction of NF-κB pathway and subsequent increases in proinflammatory cytokine secretion and augmentation of inflammation [52]. Consistent with our previous work, we found that APAP challenge led to significant increases in phospho-JNK, phospho-ERK, and NF-κB, which were significantly reduced with corilagin post-treatment, suggesting that the anti-inflammation of corilagin was through MAPK signaling pathway.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, corilagin was beneficial for APAP-induced hepatic injury through its antioxidation and anti-inflammation. The underlying mechanisms might involve the regulation of IL-6/STAT3 and MAPK/NF-κB mediated with NOX-derived ROS.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/biology12020334/s1, Figure S1: Uncropped Western blots from Figure 6A.; Figure S2: Uncropped Western blots from Figure 6B; Figure S3. Uncropped Western blots from Figure 6C; Figure S4. Uncropped Western blots from Figure 6D; Figure S5. Uncropped Western blots from Figure 8A. Figure S6. Uncropped Western blots from Figure 8B. Figure S7. Uncropped Western blots from Figure 8C.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.-C.L. and A.-H.C.; methodology, A.-H.C. and H.-P.Y.; formal analysis, H.-C.L. and C.-C.L.; writing—original draft preparation, H.-C.L. and C.-C.L.; writing—review and editing, F.-C.L. and H.-P.Y.; project administration, F.-C.L. and H.-C.L.; funding acquisition, F.-C.L. and H.-P.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST 110-2314-B-182A-085-MY2) and Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (CMRPG3L1661-3) to Fu-Chao Liu, and the Ministry of Science and Technology (110-2314-B-182A-083-MY3) and Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (CMRPG3L0611-3, CMRPG3L1311-3) to Huang-Ping Yu.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at the Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (protocol code 2020061601).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ghanem, C.I.; Perez, M.J.; Manautou, J.E.; Mottino, A.D. Acetaminophen from liver to brain: New insights into drug pharmacological action and toxicity. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 109, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lancaster, E.M.; Hiatt, J.R.; Zarrinpar, A. Acetaminophen hepatotoxicity: An updated review. Arch. Toxicol. 2015, 89, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.; Huo, Y.; Yin, S.; Hu, H. Mechanisms of acetaminophen-induced liver injury and its implications for therapeutic interventions. Redox Biol. 2018, 17, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunchorntavakul, C.; Reddy, K.R. Acetaminophen-related hepatotoxicity. Clin. Liver Dis. 2013, 17, 587–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letelier, M.E.; Lopez-Valladares, M.; Peredo-Silva, L.; Rojas-Sepulveda, D.; Aracena, P. Microsomal oxidative damage promoted by acetaminophen metabolism. Toxicol. Vitr. 2011, 25, 1310–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgman, M.J.; Garrard, A.R. A review of acetaminophen poisoning. Crit. Care Clin. 2012, 28, 499–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Briede, J.J.; Jennen, D.G.; Van Summeren, A.; Saritas-Brauers, K.; Schaart, G.; Kleinjans, J.C.; de Kok, T.M. Increased mitochondrial ROS formation by acetaminophen in human hepatic cells is associated with gene expression changes suggesting disruption of the mitochondrial electron transport chain. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 234, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenderink, J.B.; van den Heuvel, J.; Bilos, A.; Vredenburg, G.; Vermeulen, N.P.E.; Russel, F.G.M. Human multidrug resistance protein 4 (MRP4) is a cellular efflux transporter for paracetamol glutathione and cysteine conjugates. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 3027–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moles, A.; Torres, S.; Baulies, A.; Garcia-Ruiz, C.; Fernandez-Checa, J.C. Mitochondrial-Lysosomal Axis in Acetaminophen Hepatotoxicity. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Feng, J.; Du, J.; Zhuo, Z.; Yang, S.; Zhang, W.; Wang, W.; Zhang, S.; Iwakura, Y.; Meng, G.; et al. Macrophage-derived IL-1alpha promotes sterile inflammation in a mouse model of acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 15, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Ramachandran, A.; Jaeschke, H. Oxidative stress during acetaminophen hepatotoxicity: Sources, pathophysiological role and therapeutic potential. Redox Biol. 2016, 10, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rada, P.; Pardo, V.; Mobasher, M.A.; Garcia-Martinez, I.; Ruiz, L.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, A.; Sanchez-Ramos, C.; Muntane, J.; Alemany, S.; James, L.P.; et al. SIRT1 Controls Acetaminophen Hepatotoxicity by Modulating Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 28, 1187–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, Y.; Kim, S.; Chung, H.T.; Pae, H.O. Reactive oxygen species in the activation of MAP kinases. Method. Enzymol. 2013, 528, 27–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takata, T.; Araki, S.; Tsuchiya, Y.; Watanabe, Y. Oxidative Stress Orchestrates MAPK and Nitric-Oxide Synthase Signal. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Wang, C.; Luo, T.; Lu, B.; Ma, H.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, D.; Chi, G.; Ge, P.; Luo, Y. JNK Activation Contributes to Oxidative Stress-Induced Parthanatos in Glioma Cells via Increase of Intracellular ROS Production. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 3492–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.; Lopez, J.M. Understanding MAPK Signaling Pathways in Apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westenberger, G.; Sellers, J.; Fernando, S.; Junkins, S.; Han, S.M.; Min, K.; Lawan, A. Function of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases in Hepatic Inflammation. J. Cell. Signal. 2021, 2, 172–180. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.T.; Pang, J.H.; Yang, R.C. Anti-cancer effects of Phyllanthus urinaria and relevant mechanisms. Chang Gung Med. J. 2010, 33, 477–487. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, F.; Cheng, D.; Tao, J.Y.; Zhang, S.L.; Pang, R.; Guo, Y.J.; Ye, P.; Dong, J.H.; Zhao, L. Anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative effects of corilagin in a rat model of acute cholestasis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2013, 13, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Deng, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Huang, W.; Chen, L.; Tong, Q.; Ming, Y. Corilagin, a promising medicinal herbal agent. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 99, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.R.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S.L.; Luo, T.; Wu, F.; Dong, J.H.; Guo, Y.J.; Zhao, L. Corilagin ameliorates the extreme inflammatory status in sepsis through TLR4 signaling pathways. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Ren, D.; Xu, H.; Liu, W.; Liu, T.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Wen, A. Antioxidant and pro-angiogenic effects of corilagin in rat cerebral ischemia via Nrf2 activation. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 114816–114828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.C.; Chaudry, I.H.; Yu, H.P. Hepatoprotective Effects of Corilagin Following Hemorrhagic Shock are through Akt-Dependent Pathway. Shock 2017, 47, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.C.; Liao, C.C.; Lee, H.C.; Chou, A.H.; Yu, H.P. Effects of Corilagin on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury via Regulation of NADPH Oxidase 2 and ERK/NF-kappaB Signaling Pathways in a Mouse Model. Biology 2022, 11, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.C.; Yu, H.P.; Chou, A.H.; Lee, H.C.; Liao, C.C. Corilagin reduces acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity through MAPK and NF-kappaB signaling pathway in a mouse model. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 5597–5607. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.X.; Kaplowitz, N. Role of innate immunity in acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2006, 2, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeschke, H. Innate immunity and acetaminophen-induced liver injury: Why so many controversies? Hepatology 2008, 48, 699–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, E.; Babar, A.; Choudhary, M.; Kutner, M.; Pyrsopoulos, N. Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity: A Comprehensive Update. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2016, 4, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.E.; McKenzie, T.J.; Lillegard, J.B.; Yu, Y.; Juskewitch, J.E.; Nedredal, G.I.; Brunn, G.J.; Yi, E.S.; Malhi, H.; Smyrk, T.C.; et al. Role of Kupffer cells and toll-like receptor 4 in acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure. J. Surg. Res. 2013, 180, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, M.; Elgamal, M.; Abdelaziz, A.; Ellithy, M.; Magdy, D.; Ali, L.; Fekry, E.; Mohsen, Z.; Mostafa, M.; Elgamal, H.; et al. Toll-like receptor 4 blocker as potential therapy for acetaminophen-induced organ failure in mice. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 10, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Ge, K.; Mu, J.; Rong, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, B.; Wan, J.; Xia, G. Ferulic acid attenuated acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity though down-regulating the cytochrome P 2E1 and inhibiting toll-like receptor 4 signaling-mediated inflammation in mice. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 4205–4214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marques, P.E.; Amaral, S.S.; Pires, D.A.; Nogueira, L.L.; Soriani, F.M.; Lima, B.H.; Lopes, G.A.; Russo, R.C.; Avila, T.V.; Melgaco, J.G.; et al. Chemokines and mitochondrial products activate neutrophils to amplify organ injury during mouse acute liver failure. Hepatology 2012, 56, 1971–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mossanen, J.C.; Krenkel, O.; Ergen, C.; Govaere, O.; Liepelt, A.; Puengel, T.; Heymann, F.; Kalthoff, S.; Lefebvre, E.; Eulberg, D.; et al. Chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 2-positive monocytes aggravate the early phase of acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury. Hepatology 2016, 64, 1667–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mossanen, J.C.; Tacke, F. Acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury in mice. Lab. Anim. 2015, 49, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcondes-Alves, L.; Fattori, V.; Borghi, S.M.; Lourenco-Gonzalez, Y.; Bussmann, A.J.C.; Hirooka, E.Y.; Casagrande, R.; Verri, W.A., Jr.; Arakawa, N.S. Kaurenoic acid extracted from Sphagneticola trilobata reduces acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity through inhibition of oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory cytokine production in mice. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 921–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeschke, H.; McGill, M.R.; Ramachandran, A. Oxidant stress, mitochondria, and cell death mechanisms in drug-induced liver injury: Lessons learned from acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Drug Metab. Rev. 2012, 44, 88–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeschke, H.; McGill, M.R. Cytochrome P450-derived versus mitochondrial oxidant stress in acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 235, 216–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; He, T.; Farrar, S.; Ji, L.; Liu, T.; Ma, X. Antioxidants Maintain Cellular Redox Homeostasis by Elimination of Reactive Oxygen Species. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 44, 532–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi-Rad, M.; Kumar, N.V.A.; Zucca, P.; Varoni, E.M.; Dini, L.; Panzarini, E.; Rajkovic, J.; Fokou, P.V.T.; Azzini, E.; Peluso, I.; et al. Lifestyle, Oxidative Stress, and Antioxidants: Back and Forth in the Pathophysiology of Chronic Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.J.; Zhang, J.H.; Gomez, H.; Murugan, R.; Hong, X.; Xu, D.; Jiang, F.; Peng, Z.Y. Reactive Oxygen Species-Induced Lipid Peroxidation in Apoptosis, Autophagy, and Ferroptosis. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 5080843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Wei, J.G.; Tu, M.J.; Gu, J.G.; Zhang, W. Fucoidan Alleviates Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity via Oxidative Stress Inhibition and Nrf2 Translocation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.C.; Yu, H.P.; Liao, C.C.; Chou, A.H.; Liu, F.C. Escin protects against acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice via attenuating inflammatory response and inhibiting ERK signaling pathway. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 5170–5182. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lv, H.; Hong, L.; Tian, Y.; Yin, C.; Zhu, C.; Feng, H. Corilagin alleviates acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity via enhancing the AMPK/GSK3beta-Nrf2 signaling pathway. Cell Commun. Signal. 2019, 17, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Li, Y.; Levy, R.M.; Fan, J.J.; Hackam, D.J.; Vodovotz, Y.; Yang, H.; Tracey, K.J.; Billiar, T.R.; Wilson, M.A. Hemorrhagic shock induces NAD(P)H oxidase activation in neutrophils: Role of HMGB1-TLR4 signaling. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 6573–6580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Jiang, J.X.; Yamaguchi, K.; Taruno, A.; Katsuyama, M.; Iwata, K.; Ibi, M.; et al. The NOX1 isoform of NADPH oxidase is involved in dysfunction of liver sinusoids in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 115, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.X.; Torok, N.J. NADPH Oxidases in Chronic Liver Diseases. Adv. Hepatol. 2014, 2014, 742931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fielding, C.A.; McLoughlin, R.M.; McLeod, L.; Colmont, C.S.; Najdovska, M.; Grail, D.; Ernst, M.; Jones, S.A.; Topley, N.; Jenkins, B.J. IL-6 regulates neutrophil trafficking during acute inflammation via STAT3. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 2189–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lafdil, F.; Kong, X.; Gao, B. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 in liver diseases: A novel therapeutic target. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 7, 536–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, B.; Xu, X.; Wu, X.; Guo, M.; Wang, F. Effect of JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway on liver injury associated with severe acute pancreatitis in rats. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 2013–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akcora, B.O.; Gabriel, A.V.; Ortiz-Perez, A.; Bansal, R. Pharmacological inhibition of STAT3 pathway ameliorates acute liver injury in vivo via inactivation of inflammatory macrophages and hepatic stellate cells. FASEB Bioadv. 2020, 2, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braicu, C.; Buse, M.; Busuioc, C.; Drula, R.; Gulei, D.; Raduly, L.; Rusu, A.; Irimie, A.; Atanasov, A.G.; Slaby, O.; et al. A Comprehensive Review on MAPK: A Promising Therapeutic Target in Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorrington, M.G.; Fraser, I.D.C. NF-κB Signaling in Macrophages: Dynamics, Crosstalk, and Signal Integration. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).