Identification and Functional Analyses of Host Proteins Interacting with the P3a Protein of Brassica Yellows Virus
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
2.2. Plasmid Construction
2.3. The MYTH Assay
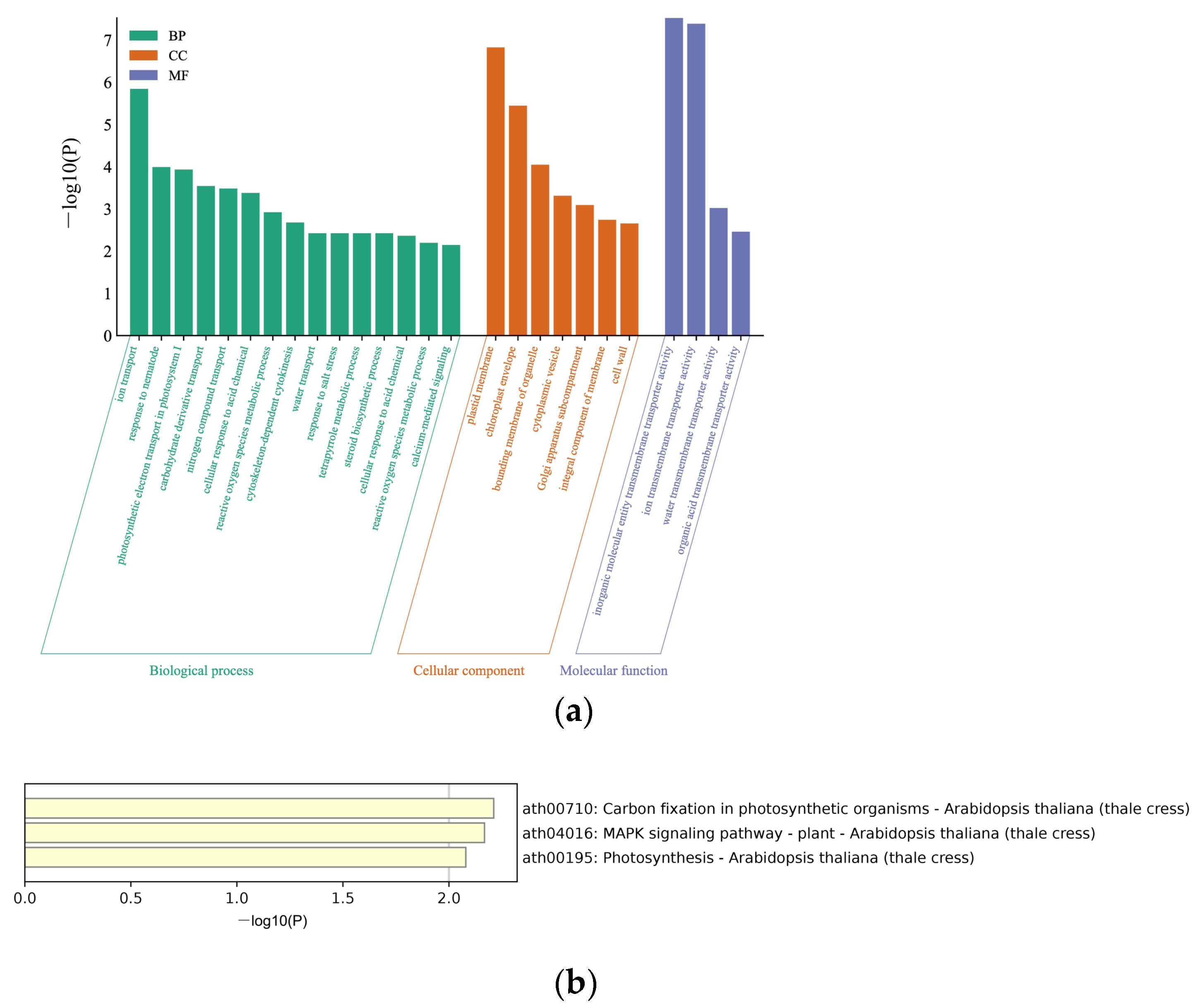
2.4. Bioinformatics
2.5. BiFC Assays and Subcellular Localization
2.6. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.7. Virus Inoculation by Insect Transmission
2.8. Agrobacterium-Mediated Transient Expression in N. benthamiana
2.9. Western Blotting Analysis
2.10. Accession Numbers
3. Results
3.1. Identifying BrYV P3a-Interacting Host Proteins by Yeast Library Screening
3.2. Validation of P3a-Interacting Proteins
3.3. P3a and BrYV hijack P3a-Interacting Proteins from the Plasma Membrane to Cytosol
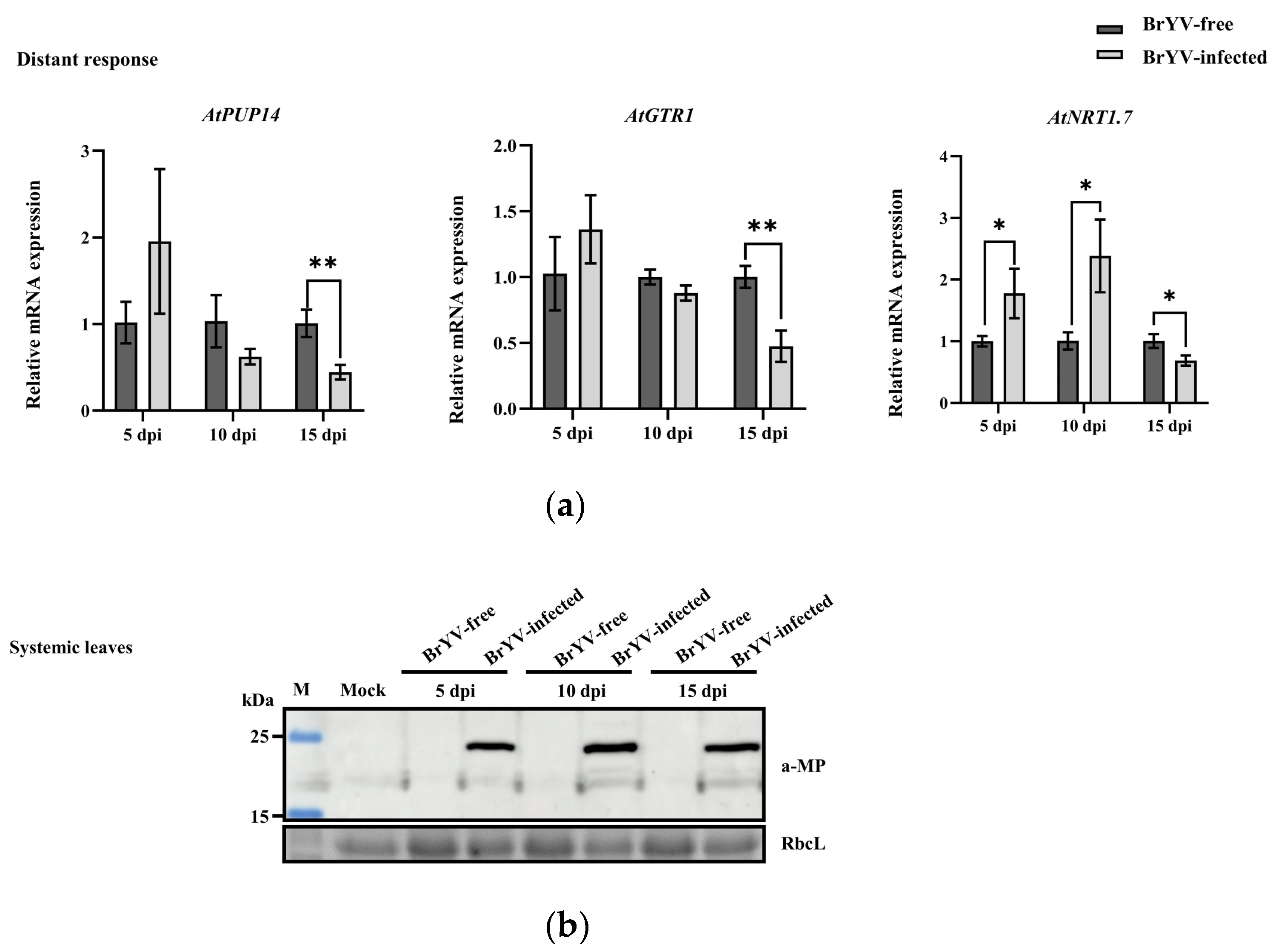
3.4. Expression Levels of AtPUP14, AtGTR1, and AtNRT1.7 in Response to BrYV
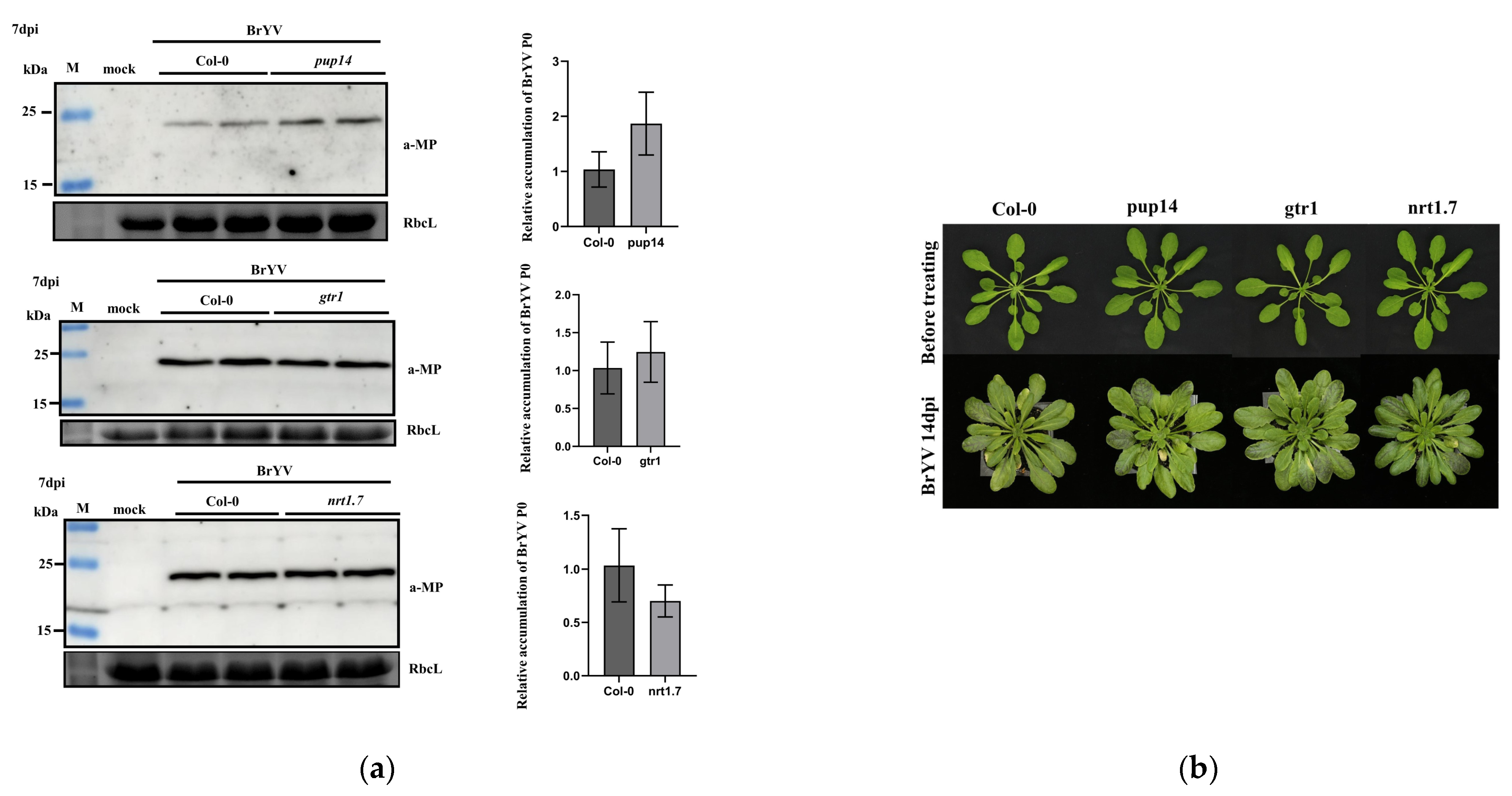
3.5. The Effects of A. thaliana T-DNA Insertion Mutants pup14, gtr1, and nrt1.7 on BrYV Infection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torrance, L.; Andreev, I.A.; Gabrenaite-Verhovskaya, R.; Cowan, G.; Makinen, K.; Taliansky, M.E. An unusual structure at one end of potato potyvirus particles. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 357, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittmann, S.; Chatel, H.; Fortin, M.G.; Laliberté, J.F. Interaction of the viral protein genome linked of turnip mosaic potyvirus with the translational eukaryotic initiation factor (iso) 4E of Arabidopsis thaliana using the yeast two-hybrid system. Virology 1997, 234, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Krishnaswamy, S. Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-mediated recessive resistance to plant viruses and its utility in crop improvement. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 13, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michon, T.; Estevez, Y.; Walter, J.; German-Retana, S.; Le Gall, O. The potyviral virus genome-linked protein VPg forms a ternary complex with the eukaryotic initiation factors eIF4E and eIF4G and reduces eIF4E affinity for a mRNA cap analogue. FEBS J. 2006, 273, 1312–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, D.; Yoshinari, S.; Dreher, T.W. eEF1A binding to aminoacylated viral RNA represses minus strand synthesis by TYMV RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Virology 2004, 321, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, A.; Wang, X.; Ahlquist, P. Membrane-shaping host reticulon proteins play crucial roles in viral RNA replication compartment formation and function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 16291–16296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, A.; Wang, X. Bromovirus-induced remodeling of host membranes during viral RNA replication. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2014, 9, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barajas, D.; Martin, I.F.; Pogany, J.; Risco, C.; Nagy, P.D. Noncanonical role for the host Vps4 AAA+ ATPase ESCRT protein in the formation of Tomato Bushy Stunt Virus replicase. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barajas, D.; Jiang, Y.; Nagy, P.D. A unique role for the host ESCRT proteins in replication of Tomato bushy stunt virus. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramaniam, M.; Kim, B.S.; Hutchens-Williams, H.M.; Loesch-Fries, L.S. The photosystem II oxygen-evolving complex protein PsbP interacts with the coat protein of Alfalfa mosaic virus and inhibits virus replication. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2014, 27, 1107–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mine, A.; Hyodo, K.; Tajima, Y.; Kusumanegara, K.; Taniguchi, T.; Kaido, M.; Mise, K.; Taniguchi, H.; Okuno, T. Differential roles of Hsp70 and Hsp90 in the assembly of the replicase complex of a positive-strand RNA plant virus. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 12091–12104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.W.; Hu, C.C.; Liou, M.R.; Chang, B.Y.; Tsai, C.H.; Meng, M.; Lin, N.S.; Hsu, Y.H. Hsp90 interacts specifically with viral RNA and differentially regulates replication initiation of Bamboo mosaic virus and associated satellite RNA. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Pogany, J.; Panavas, T.; Xu, K.; Esposito, A.M.; Kinzy, T.G.; Nagy, P.D. Translation elongation factor 1A is a component of the tombusvirus replicase complex and affects the stability of the p33 replication co-factor. Virology 2009, 385, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Pogany, J.; Tupman, S.; Esposito, A.M.; Kinzy, T.G.; Nagy, P.D. Translation elongation factor 1A facilitates the assembly of the tombusvirus replicase and stimulates minus-strand synthesis. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.S.; Nagy, P.D. Direct inhibition of tombusvirus plus-strand RNA synthesis by a dominant negative mutant of a host metabolic enzyme, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, in yeast and plants. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 9090–9102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.Y.; Nagy, P.D. Tomato bushy stunt virus co-opts the RNA-binding function of a host metabolic enzyme for viral genomic RNA synthesis. Cell Host Microbe 2008, 3, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaido, M.; Abe, K.; Mine, A.; Hyodo, K.; Taniguchi, T.; Taniguchi, H.; Mise, K.; Okuno, T. GAPDH-A recruits a plant virus movement protein to cortical virus replication complexes to facilitate viral cell-to-cell movement. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Wen, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Xiao, F.; Hong, N. The p23 of Citrus Tristeza Virus Interacts with Host FKBP-Type Peptidyl-Prolylcis-Trans Isomerase 17-2 and Is Involved in the Intracellular Movement of the Viral Coat Protein. Cells 2021, 10, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, S.; Spektor, R.; Natale, D.M.; Citovsky, V. ANK, a host cytoplasmic receptor for the Tobacco mosaic virus cell-to-cell movement protein, facilitates intercellular transport through plasmodesmata. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.D.; Lazarowitz, S.G. Arabidopsis synaptotagmin SYTA regulates endocytosis and virus movement protein cell-to-cell transport. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 2491–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunoyer, P.; Thomas, C.; Harrison, S.; Revers, F.; Maule, A. A cysteine-rich plant protein potentiates Potyvirus movement through an interaction with the virus genome-linked protein VPg. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 2301–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.H.; Sheng, J.S.; Hind, G.; Handa, A.K.; Citovsky, V. Interaction between the tobacco mosaic virus movement protein and host cell pectin methylesterases is required for viral cell-to-cell movement. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.H.; Citovsky, V. Systemic movement of a tobamovirus requires host cell pectin methylesterase. Plant J. 2003, 35, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisholm, S.T.; Parra, M.A.; Anderberg, R.J.; Carrington, J.C. Arabidopsis RTM1 and RTM2 Genes Function in Phloem to Restrict Long-Distance Movement of Tobacco Etch Virus. Plant Physiol. 2001, 127, 1667–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chisholm, S.T.; Mahajan, S.K.; Whitham, S.A.; Yamamoto, M.L.; Carrington, J.C. Cloning of the Arabidopsis RTM1 gene, which controls restriction of long-distance movement of tobacco etch virus. Plant Biol. 1999, 97, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, S.K.; Chisholm, S.T.; Whitham, S.A.; Carrington, J.C. Identification and characterization of a locus (RTM1) that restricts long-distance movement of tobacco etch virus in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 1998, 14, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosson, P.; Sofer, L.; Le, Q.H.; Leger, V.; Schurdi-Levraud, V.; Whitham, S.A.; Yamamoto, M.L.; Gopalan, S.; Le Gall, O.; Candresse, T.; et al. RTM3, which controls long-distance movement of potyviruses, is a member of a new plant gene family encoding a meprin and TRAF homology domain-containing protein. Plant Physiol. 2010, 154, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, M.; Freeman, B.; Liu, H.Y.; Herrbach, E.; Lemaire, O. Beet poleroviruses: Close friends or distant relatives? Mol. Plant Pathol. 2005, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taliansky, M.; Mayo, M.A.; Barker, H. Potato leafroll virus: A classic pathogen shows some new tricks. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2003, 4, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaTourrette, K.; Holste, N.M.; Garcia-Ruiz, H. Polerovirus genomic variation. Virus Evol. 2021, 7, veab102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hipper, C.; Brault, V.; Ziegler-Graff, V.; Revers, F. Viral and cellular factors involved in Phloem transport of plant viruses. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, J.; Stussi-Garaud, C.; Tacke, E.; Prüfer, D.; Rohde, W.; Rohfritsch, O. In situ localization of the putative movement protein (pr17) from potato leafroll luteovirus (PLRV) in infected and transgenic potato plants. Virology 1997, 235, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutterer, J.D.; Stussi-Garaud, C.; Michler, P.; Richards, K.E.; Jonard, G.; Ziegler-Graff, V. Role of the beet western yellows virus readthrough protein in virus movement in Nicotiana clevelandii. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80 Pt 10, 2771–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusaro, A.F.; Barton, D.A.; Nakasugi, K.; Jackson, C.; Kalischuk, M.L.; Kawchuk, L.M.; Vaslin, M.F.S.; Correa, R.L.; Waterhouse, P.M. The Luteovirus P4 Movement Protein Is a Suppressor of Systemic RNA Silencing. Viruses 2017, 9, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smirnova, E.; Firth, A.E.; Miller, W.A.; Scheidecker, D.; Brault, V.; Reinbold, C.; Rakotondrafara, A.M.; Chung, B.Y.W.; Ziegler-Graff, V. Discovery of a Small Non-AUG-Initiated ORF in Poleroviruses and Luteoviruses That Is Required for Long-Distance Movement. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBlasio, S.L.; Xu, Y.; Johnson, R.S.; Rebelo, A.R.; MacCoss, M.J.; Gray, S.M.; Heck, M. The Interaction Dynamics of Two Potato Leafroll Virus Movement Proteins Affects Their Localization to the Outer Membranes of Mitochondria and Plastids. Viruses 2018, 10, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Yoo, R.H.; Igori, D.; Zhao, F.; Kim, K.H.; Moon, J.S. Genome sequence of a recombinant brassica yellows virus infecting Chinese cabbage. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 597–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamitani, M.; Nagano, A.J.; Honjo, M.N.; Kudoh, H. RNA-Seq reveals virus-virus and virus-plant interactions in nature. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2016, 92, fiw176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-Y.; Peng, Y.-M.; Xiang, H.-U.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.-W.; Yu, J.-L.; Han, C.-G. Incidence and prevalence levels of three aphid-transmitted viruses in crucifer crops in China. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, N.; Tamada, T. Host range and molecular analysis of Beet leaf yellowing virus, Beet western yellows virus-JP and Brassica yellows virus in Japan. Plant Pathol. 2019, 68, 1045–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.Y.; Dong, S.W.; Shang, Q.X.; Zhou, C.J.; Li, D.W.; Yu, J.L.; Han, C.G. Molecular characterization of two genotypes of a new polerovirus infecting brassicas in China. Arch. Virol. 2011, 156, 2251–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Peng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, D.; Yu, J.; Han, C. Simultaneous detection and differentiation of three genotypes of Brassica yellows virus by multiplex reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Virol. J. 2016, 13, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.R.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H.H.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, X.B.; Li, D.W.; Yu, J.L.; Han, C.G. Brassica yellows virus’ movement protein upregulates anthocyanin accumulation, leading to the development of purple leaf symptoms on Arabidopsis thaliana. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Zhao, T.Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Xiang, H.Y.; Dong, S.W.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.W.; Yu, J.L.; Han, C.G. The Conserved Proline18 in the Polerovirus P3a Is Important for Brassica Yellows Virus Systemic Infection. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, M.; Chaban, C.; Schutze, K.; Batistic, O.; Weckermann, K.; Nake, C.; Blazevic, D.; Grefen, C.; Schumacher, K.; Oecking, C.; et al. Visualization of protein interactions in living plant cells using bimolecular fluorescence complementation. Plant J. 2004, 40, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodin, M.M.; Dietzgen, R.G.; Schichnes, D.; Ruzin, S.; Jackson, A.O. pGD vectors: Versatile tools for the expression of green and red fluorescent protein fusions in agroinfiltrated plant leaves. Plant J. 2002, 31, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, B.; Pache, L.; Chang, M.; Khodabakhshi, A.H.; Tanaseichuk, O.; Benner, C.; Chanda, S.K. Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, D.P.; He, M.J.; Chen, X.R.; Hu, R.J.; Zhao, T.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Peng, Y.M.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.W.; Yu, J.L.; et al. A Simple Method for the Acquisition and Transmission of Brassica Yellows Virus from Transgenic Plants and Frozen Infected Leaves by Aphids. Plants 2021, 10, 1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Li, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H.H.; Zhao, T.Y.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Li, D.W.; Yu, J.L.; Wang, X.B.; Zhang, Y.L.; et al. Brassica yellows virus P0 protein impairs the antiviral activity of NbRAF2 in Nicotiana benthamiana. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 3127–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, B.K.; Cai, X.; Nebenfuhr, A. A multicolored set of in vivo organelle markers for co-localization studies in Arabidopsis and other plants. Plant J. 2007, 51, 1126–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Mao, J.J.; Xiang, H.Y.; Dong, L.H.; Sun, Y.H.; Liu, G.S.; Liu, H.B. First Report of Brassica Yellows Virus on Tobacco in China. Plant Dis. 2015, 99, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, N.; Ben-Shem, A. The complex architecture of oxygenic photosynthesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahverdiyeva, Y.; Mamedov, F.; Suorsa, M.; Styring, S.; Vass, I.; Aro, E.M. Insights into the function of PsbR protein in Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1767, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glowacka, K.; Kromdijk, J.; Kucera, K.; Xie, J.; Cavanagh, A.P.; Leonelli, L.; Leakey, A.D.B.; Ort, D.R.; Niyogi, K.K.; Long, S.P. Photosystem II Subunit S overexpression increases the efficiency of water use in a field-grown crop. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.N.; Le, T.T.L.; Hwang, J.H.; Zulfugarov, I.S.; Kim, E.H.; Kim, H.U.; Jeon, J.S.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, C.H. High Light Acclimation Mechanisms Deficient in a PsbS-Knockout Arabidopsis Mutant. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Jia, Q.; Hong, Y.; Liu, Y. The rubisco small subunit is involved in tobamovirus movement and Tm-22-mediated extreme resistance. Plant Physiol. 2013, 161, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Huang, C.; He, Y.; Castillo-Gonzalez, C.; Gui, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, X. betaC1 protein encoded in geminivirus satellite concertedly targets MKK2 and MPK4 to counter host defense. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurcher, E.; Liu, J.; di Donato, M.; Geisler, M.; Muller, B. Plant development regulated by cytokinin sinks. Science 2016, 353, 1027–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nour-Eldin, H.H.; Andersen, T.G.; Burow, M.; Madsen, S.R.; Jorgensen, M.E.; Olsen, C.E.; Dreyer, I.; Hedrich, R.; Geiger, D.; Halkier, B.A. NRT/PTR transporters are essential for translocation of glucosinolate defence compounds to seeds. Nature 2012, 488, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, T.G.; Nour-Eldin, H.H.; Fuller, V.L.; Olsen, C.E.; Burow, M.; Halkier, B.A. Integration of biosynthesis and long-distance transport establish organ-specific glucosinolate profiles in vegetative Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 3133–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.C.; Lin, C.S.; Hsu, P.K.; Lin, S.H.; Tsay, Y.F. The Arabidopsis nitrate transporter NRT1.7, expressed in phloem, is responsible for source-to-sink remobilization of nitrate. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 2750–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ascencio-Ibanez, J.T.; Sozzani, R.; Lee, T.J.; Chu, T.M.; Wolfinger, R.D.; Cella, R.; Hanley-Bowdoin, L. Global analysis of Arabidopsis gene expression uncovers a complex array of changes impacting pathogen response and cell cycle during geminivirus infection. Plant Physiol. 2008, 148, 436–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Yeakley, J.M.; Garcia, E.W.; Holdridge, J.D.; Fan, J.B.; Whitham, S.A. Salicylic acid-dependent expression of host genes in compatible Arabidopsis-virus interactions. Plant Physiol. 2005, 137, 1147–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Buchwaldt, L.; Rimmer, S.R.; Sharpe, A.; McGregor, L.; Bekkaoui, D.; Hegedus, D. Patterns of differential gene expression in Brassica napus cultivars infected with Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2009, 10, 635–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.-Y.; Zuo, D.-P.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Han, C.-G. Identification and Functional Analyses of Host Proteins Interacting with the P3a Protein of Brassica Yellows Virus. Biology 2023, 12, 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12020202
Liu S-Y, Zuo D-P, Zhang Z-Y, Wang Y, Han C-G. Identification and Functional Analyses of Host Proteins Interacting with the P3a Protein of Brassica Yellows Virus. Biology. 2023; 12(2):202. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12020202
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Si-Yuan, Deng-Pan Zuo, Zong-Ying Zhang, Ying Wang, and Cheng-Gui Han. 2023. "Identification and Functional Analyses of Host Proteins Interacting with the P3a Protein of Brassica Yellows Virus" Biology 12, no. 2: 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12020202
APA StyleLiu, S.-Y., Zuo, D.-P., Zhang, Z.-Y., Wang, Y., & Han, C.-G. (2023). Identification and Functional Analyses of Host Proteins Interacting with the P3a Protein of Brassica Yellows Virus. Biology, 12(2), 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12020202






