Identification of N6-Methyladenosine-Related Factors and the Prediction of the Regulatory Mechanism of Hair Follicle Development in Rex and Hycole Rabbits
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Hair Index Determination
2.3. Hematoxylin–Eosin (HE) Staining
2.4. RNA Fragmentation
2.5. M6A IP and Library Construction
2.6. RT-qPCR
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
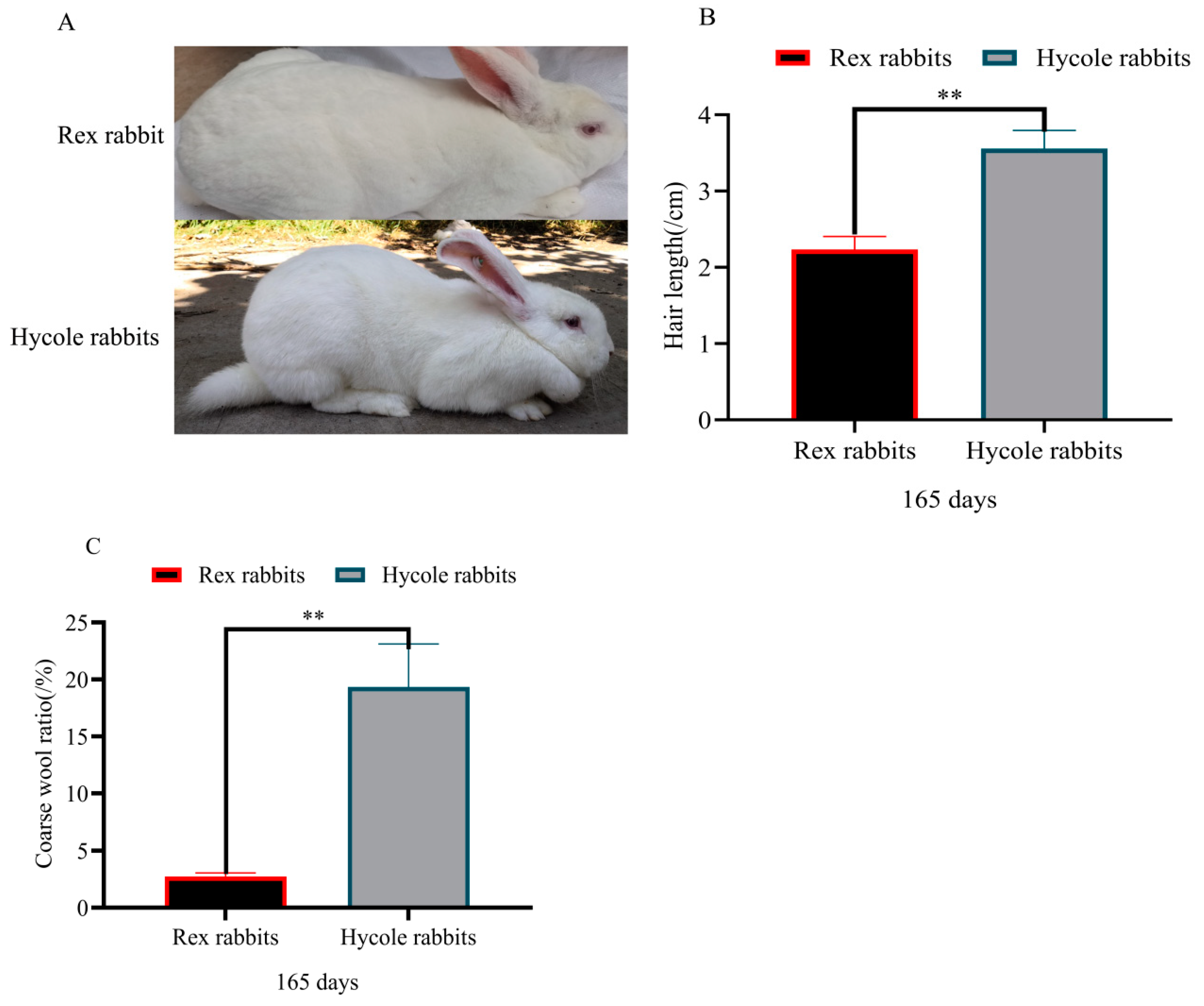
3.1. Difference in Hair Follicles between Rex and Hycole Rabbits
3.2. Summary and Quality Control of Rabbit m6A Sequencing Data
3.3. General Features of Rabbit m6A Methylation
3.4. KEGG Pathway, Methylases, and Methylation Modifying Genes in Rex Rabbit Skin and Hycole Rabbit Skin
3.5. Regulation of Methylation Modified Genes by Methylase
3.6. The Connection between Differential Pathways and Differential Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Epstein, F.H.; Paus, R.; Cotsarelis, G. The biology of hair follicles. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 491–497. [Google Scholar]
- Stenn, K.S.; Paus, R. Controls of Hair Follicle Cycling. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 449–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paus, R.; Müller-Rver, S.; Veen, C.V.D.; Maurer, M.; Handjiski, B. A Comprehensive Guide for the Recognition and Classification of Distinct Stages of Hair Follicle Morphogenesis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1999, 113, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Zhao, H.; Cheng, G.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Qi, Y.; Huang, D. Analyses of histological and transcriptome differences in the skin of short-hair and long-hair rabbits. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Chen, Y.; Yan, X.; Hao, Y.; Zhu, J.; Weng, Q.; Wu, X. Gene Expression Profiling Analysis Reveals Fur Development in Rex Rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus). Genome 2017, 60, 1060–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Cheng, G.; Leng, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, H. Analysis of histological and microRNA profiles changes in rabbit skin development. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rishikaysh, P.; Dev, K.; Diaz, D.; Qureshi, W.; Filip, S.; Mokry, J. Signaling Involved in Hair Follicle Morphogenesis and Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 1647–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roundtree, I.A.; Evans, M.E.; Pan, T.; He, C. Dynamic RNA Modifications in Gene Expression Regulation. Cell 2017, 169, 1187–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhan, V.T.; Ernst, F.; Hawley, B.R.; Christiane, Z.; Nathalie, U.; Philipp, H.; Bohnsack, K.E.; Bohnsack, M.T.; Jaffrey, S.R.; Marc, G. The human 18S rRNA m6A methyltransferase METTL5 is stabilized by TRMT112. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 49, 7719–7733. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Hsu, P.J.; Chen, Y.S.; Yang, Y.G. Dynamic transcriptomic m6A decoration: Writers, erasers, readers and functions in RNA metabolism. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, Y.T.; Koh, C.; Sim, D.Y.; Roca, X.; Goh, W. METTL4 catalyzes m6Am methylation in U2 snRNA to regulate pre-mRNA splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 9250–9261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Kennedy, S.; Hajian, T.; Gibson, E.; Seitova, A.; Xu, C.; Arrowsmith, C.H.; Vedadi, M. A Radioactivity-Based Assay for Screening Human m6A-RNA Methyltransferase, METTL3-METTL14 Complex, and Demethylase ALKBH5. J. Biomol. Screen. Off. J. Soc. Biomol. Screen. 2016, 21, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, K.D.; Jaffrey, S.R. Rethinking m6A Readers, Writers, and Erasers. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 33, 319–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, L.; Mason, C.E. The Pivotal Regulatory Landscape of RNA Modifications. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2013, 15, 127–150. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, K.D.; Jaffrey, S.R. The dynamic epitranscriptome: N6-methyladenosine and gene expression control. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2014, 15, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, S.; Pandya-Jones, A.; Saito, Y.; Fak, J.J.; Vågbø, C.B.; Geula, S.; Hanna, J.H.; Black, D.L.; Darnell, J.E.; Darnell, R.B. m6A mRNA modifications are deposited in nascent pre-mRNA and are not required for splicing but do specify cytoplasmic turnover. Genes Dev. 2017, 31, 990–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slobodin, B.; Han, R.; Calderone, V.; Vrielink, J.; Loayza-Puch, F.; Elkon, R.; Agami, R. Transcription Impacts the Efficiency of mRNA Translation via Co-transcriptional N6-adenosine Methylation. Cell 2017, 169, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xing, Y.; Gao, W.; Yang, L.; Shi, J.; Song, W.; Li, T. N-6-methyladenosine (m6A) reader IGF2BP2 promotes gastric cancer progression via targeting SIRT1. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 11541–11550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Vásquez, E.; Jimenez, N.A.; Vázquez, N.; Strobl-Mazzulla, P.H. Emerging role of dynamic RNA modifications during animal development. Mech. Dev. 2018, 154, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sun, B.; Jiang, Q.; Wu, R.; Cai, M.; Yao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Shi, H.; Feng, J.; Wang, Y. mRNA m6A plays opposite role in regulating UCP2 and PNPLA2 protein expression in adipocytes. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 42, 1912–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Hsu, P.J.; Xing, X.; Fang, J.; Lu, Z.; Zou, Q.; Zhang, K.J.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, T. Mettl3-/Mettl14-mediated mRNA N6-methyladenosine modulates murine spermatogenesis. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 1216–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.; Davies, J.J.; Wittig, D.; Oakeley, E.J.; Haase, M.; Lam, W.L.; Schübeler, D. Chromosome-wide and promoter-specific analyses identify sites of differential DNA methylation in normal and transformed human cells. Nat. Genet. 2005, 38, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gbolagunte, G. Fibrocartilage embedding hair follicles on the skin of the knee of the camel (Camelus dromedarius): An ideal structure for its comfort. J. Sci. Res. Stud. 2016, 3, 30–33. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 274100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siren, J.; Valimaki, N.; Makinen, V. Indexing Graphs for Path Queries with Applications in Genome Research. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2014, 11, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Lu, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Y.; Rao, M.K.; Huang, Y. A protocol for RNA methylation differential analysis with MeRIP-Seq data and exomePeak R/Bioconductor package. Methods 2014, 69, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, R.; Brown, G. DiffBind differential binding analysis of ChIP-Seq peak data. R Package Version 2011, 100, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millar, S.E. Molecular mechanisms regulating hair follicle development. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2002, 118, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taha, E.; Hekal, S.; Nasr, A.I. Evaluating skin quality of some rabbit breeds under Egyptian conditions. World Rabbit Sci. 2017, 25, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, D.; Xavier, M.; Céline, C.-D.; Anne, V.; Gérard, A.; Stéphan, B.; Séverine, D.; Edmond-Paul, C.; Hubert, D.R.; Daniel, A. A deletion in exon 9 of the LIPH gene is responsible for the Rex hair coat phenotype in rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus). PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19281. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, H.C.; Wei, L.H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Lu, Z.; Chen, P.R.; He, C.; Jia, G. ALKBH10B is An RNA N6-Methyladenosine Demethylase Affecting Arabidopsis Floral Transition. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 2995–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominissini, D.; Moshitch-Moshkovitz, S.; Schwartz, S.; Salmon-Divon, M.; Ungar, L.; Osenberg, S.; Cesarkas, K.; Jacob-Hirsch, J.; Amariglio, N.; Kupiec, M.; et al. Topology of the human and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-seq. Nature 2012, 485, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Guo, D.; Zhang, X.; Bai, W. m6A Methylation Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes in Skin Tissues of Coarse and Fine Type Liaoning Cashmere Goats. Front. Genet. 2020, 10, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, G.; Yuan, Y.; He, M.; Gong, R.; Yang, L. m6A Methylation of Precursor-miR-320/RUNX2 Controls Osteogenic Potential of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 19, 421–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, W.; Chen, J.; Jia, L.; Ma, J.; Song, D. The m6A methyltransferase METTL3 promotes osteosarcoma progression by regulating the m6A level of LEF1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 516, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Tang, H.; Yang, J.; Yao, Z.; Bai, L.; Xie, Y.; Li, Q.; Xiao, J. METTL3-m6A methylase regulates the osteogenic potential of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in osteoporotic rats via the Wnt signalling pathway. Cell Prolif. 2022, 55, e13234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, K.; Xu, R.; Wang, Q.; Xiong, Q.; Zhou, X.; Li, Q.; Seriwatanachai, D.; Lin, S.; Zhou, C.; Yuan, Q. METTL5 regulates cranial suture fusion via Wnt signaling. Fundam. Res. 2022, 5, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, W.; Guttentag, S.; Wang, Z.; Andl, T.; Ballard, P.; Min, M.L.; Piccolo, S.; Birchmeier, W.; Whitsett, J.A.; Millar, S.E. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling acts upstream of N-myc, BMP4, and FGF signaling to regulate proximal-distal patterning in the lung. Dev. Biol. 2005, 283, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tomann, P.; Andl, T.; Gallant, N.M.; Schmidt-Ullrich, R. Reciprocal Requirements for EDA/EDAR/NF-κB and Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathways in Hair Follicle Induction. Dev. Cell 2009, 17, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, S.; Satoh, K.; Hirota, M.; Kimura, K.; Kanno, A.; Masamune, A.; Shimosegawa, T. Bone morphogenetic protein 4 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition through MSX2 induction on pancreatic cancer cell line. J. Cell. Physiol. 2010, 213, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.B.; Man, Z.T.; Li, W.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.Q.; Sun, S. Calcitonin protects chondrocytes from lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis and inflammatory response through MAPK/Wnt/NF-κB pathways. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 87, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.U.; Zhang, A.L.; Xiao, G.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Z.M.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.-Q. p53 and NFκB regulate microRNA-34c expression in porcine ovarian granulosa cells. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 15, 1816–1824. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, F.; Wu, N.; Tian, X.; Fan, J.; Liu, J.; Song, T.; Fu, H. MicroRNA-34c promotes osteoclast differentiation through targeting LGR4. Gene 2017, 610, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Guo, J.; Zhou, J.; Wang, D.; Zhou, L. NF-κB maintains the stemness of colon cancer cells by downregulating miR-195-5p/497-5p and upregulating MCM2. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2020, 39, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Su, K.; Cao, W. Circ_LDLR promoted the development of papillary thyroid carcinoma via regulating miR-195-5p/LIPH axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, T.; Du, Q. Regulation of Adipocyte Differentiation by METTL4, a 6 mA Methylase. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, F.; Wang, S.; Wang, D.B.; Xu, J.; Yang, G.Z. Triterpenoid Saponins from Stauntonia chinensis Ameliorate Insulin Resistance via the AMP-Activated Protein Kinase and IR/IRS-1/PI3K/Akt Pathways in Insulin-Resistant HepG2 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 10446–10458. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Ge, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, W. MiR-129 inhibits cell proliferation and metastasis by targeting ETS1 via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in prostate cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 96, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Tsuyada, A.; Ren, X.; Wu, X.; Stubblefield, K.; Rankin-Gee, E.K.; Wang, S.E. Transforming growth factor-beta regulates the sphereinitiating stem cell like feature in breast cancer through miRNA-181 and ATM. Oncogene 2011, 30, 1470–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moroney, J.B.; Vasudev, A.; Pertsemlidis, A.; Zan, H.; Casali, P. Integrative transcriptome and chromatin landscape analysis reveals distinct epigenetic regulations in human memory B cells. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Hu, Y.; Qi, K.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, R. Dihydromyricetin improves LPS-induced sickness and depressive-like behaviors in mice by inhibiting the TLR4/Akt/HIF1a/NLRP3 pathway. Behav. Brain Res. 2022, 423, 113775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Peng, R.; Guo, P.; Zhang, H.; Liao, Y. A HIF1A/miR-485-5p/SRPK1 axis modulates the aggressiveness of glioma cells upon hypoxia. Exp. Cell Res. 2021, 402, 112547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Fu, J.; Jiao, G.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z. LINC00659 Regulates Colorectal Cancer Migration and Invasion by Targeting miR-485-5p/HOXC13 Axis. Res. Sq. 2021, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, L.; Akinyi, M.; Li, Y.; Fan, G. Danshensu protects isolated heart against ischemia reperfusion injury through activation of Akt/ERK1/2/Nrf2 signaling. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 14793–14804. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Bao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, K.; Zhi, T.; Dong, W.; Fan, L.; Ning, L.; Jing, J. PBX3/MEK/ERK1/2/LIN28/let-7b positive feedback loop enhances mesenchymal phenotype to promote glioblastoma migration and invasion. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.D.; Shen, Y.; Liu, N.; Cao, J.; Yu, X.J.; Dong, C.S.; He, X.Y. Alpaca fiber growth is mediated by microRNA let-7b via down-regulation of target gene FGF5. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 13754–13763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Mu, Q.; Huang, H. The Roles of Insulin-Like Growth Factor 2 mRNA-Binding Protein 2 in Cancer and Cancer Stem Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 4217259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruchat, S.M.; Elks, C.E.; Loos, R.J.F.; Vohl, M.C.; Weisnagel, S.J.; Rankinen, T.; Bouchard, C.; Pérusse, L. Association between insulin secretion, insulin sensitivity and type 2 diabetes susceptibility variants identified in genome-wide association studies. Acta Diabetol. 2009, 46, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, C.K.; Lee, K.S.; Lyu, J. Insulin Enhances Cell Migration Through EGFR in Human Corneal Epithelial Cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 5031. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Valades, A.G.; Mendez-Lucas, A.; Vidal-Alabro, A.; Blasco, F.X.; Chillon, M.; Bartrons, R.; Bermudez, J.; Perales, J.C. Pck1 Gene Silencing in the Liver Improves Glycemia Control, Insulin Sensitivity, and Dyslipidemia in db/db Mice. Diabetes 2008, 57, 2199–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Lim, C.Y.; Li, C.; Xiao, X.; Radda, G.K.; Li, C.; Cao, X.; Han, W. FoxO1 Inhibits Leptin Regulation of Pro-opiomelanocortin Promoter Activity by Blocking STAT3 Interaction with Specificity Protein 1. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 3719–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, A.; Padmanaban, S. A synergy of estradiol with leptin modulates the long non-coding RNA NEAT1/ mmu-miR-204-5p/IGF1 axis in the uterus of high-fat-diet-induced obese ovariectomized mice. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 209, 105843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, W.; Imamura, T.; Sonoda, N.; Sears, D.D.; Patsouris, D.; Kim, J.J.; Olefsky, J.M. FOXO1 transrepresses PPARγ transactivation, coordinating an insulin-induced feed-forward response in adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 12188–12197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Luo, G.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Wu, J.; Peng, Y. PPAR gamma inhibits HMGB1 expression through upregulation of miR-142-3p in vitro and in vivo. Cell. Signal. 2016, 28, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.M.; Tembhurne, P.A.; Raja, P.; Ingle, V.C. Deciphering the role of gga-miR-142-3p on target gene CD200 and its contribution towards signal transduction and immune response. Appl. Biol. Res. 2017, 19, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, G.; Yan, L.; Chen, D.; Ji, L.; Hua, Z.C. FAK regulates E-cadherin expression via p-SrcY416/p-ERK1/2/p-Stat3Y705 and PPARγ/miR-125b/Stat3 signaling pathway in B16F10 melanoma cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 13898–13908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, N.; Brodin, P.; Wei, T.; Meisgen, F.; Eidsmo, L.; Nagy, N.; Kemeny, L.; Ståhle, M.; Sonkoly, E.; Pivarcsi, A. MiR-125b, a microRNA downregulated in psoriasis, modulates keratinocyte proliferation by targeting FGFR2. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 1521–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Ge, S.; Li, M. MiR-451a promotes cell growth, migration and EMT in osteosarcoma by regulating YTHDC1-mediated m6A methylation to activate the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. J. Bone Oncol. 2022, 33, 100412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Uchiyama, Y.; Hiyama, A.; Gajghate, S.; Shapiro, I.M.; Risbud, M.V. PI3K/AKT regulates aggrecan gene expression by modulating Sox9 expression and activity in nucleus pulposus cells of the intervertebral disc. J. Cell. Physiol. 2009, 221, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Z.; Pu, Q.H.; Lin, X.H.; Liu, M.Y.; Wu, L.R.; Wu, Q.Q.; Chen, Y.H.; Liao, F.F.; Zhu, J.Y.; Jin, X.B. Silencing of miR-21 sensitizes CML CD34+ stem/progenitor cells to imatinib-induced apoptosis by blocking PI3K/AKT pathway. Leuk. Res. 2015, 39, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomann, P.; Paus, R.; Millar, S.E.; Scheidereit, C.; Schmidt-Ullrich, R. Lhx2 is a direct NF-kappa B target gene that promotes primary hair follicle placode down-growth. Development 2016, 143, 1512–1522. [Google Scholar]
- Günschmann, C.; Stachelscheid, H.; Akyüz, M.; Schmitz, A.; Missero, C.; Brüning, J.; Niessen, C. Insulin/IGF-1 Controls Epidermal Morphogenesis via Regulation of FoxO-Mediated p63 Inhibition. Dev. Cell 2013, 26, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Q.; Wang, H.; Chen, H.; Li, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Xing, Y.; Liu, F.; Yu, D.; et al. Essential Role of Sptan1 in Cochlear Hair Cell Morphology and Function Via Focal Adhesion Signaling. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 386–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Feng, C.; Ma, G.; Fu, S.; Chen, M.; Zhang, W.; Li, J. Time-course RNA-seq analysis reveals stage-specific and melatonin-triggered gene expression patterns during the hair follicle growth cycle in Capra hircus. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Kim, S.R.; Choi, Y.H.; Shin, J.Y.; Lee, S. Quercitrin Stimulates Hair Growth with Enhanced Expression of Growth Factors via Activation of MAPK/CREB Signaling Pathway. Molecules 2020, 25, 4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.H.; Ho, J.K.; Eun, K.J.; Kang, H. Various Wavelengths of Light-Emitting Diode Light Regulate the Proliferation of Human Dermal Papilla Cells and Hair Follicles via Wnt/β-Catenin and the Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase Pathways. Ann. Dermatol. 2017, 29, 747–754. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Shi, C.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Yang, T. Regulatory effect of β-catenin on proliferation of hair follicle stem cells involves PI3K/Akt pathway. J. Appl. Biomed. 2013, 11, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harel, S.; Higgins, C.A.; Cerise, J.E.; Dai, Z.; Chen, J.C.; Clynes, R.; Christiano, A.M. Pharmacologic inhibition of JAK-STAT signaling promotes hair growth. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risek, B.; Klier, F.G.; Gilula, N.B. Multiple gap junction genes are utilized during rat skin and hair development. Development 1992, 116, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, R.; Eicheler, W.; Wenzel, E.; Happle, R. Interleukin-1beta-Induced Inhibition of Hair Growth In Vitro Is Mediated by Cyclic AMP. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1997, 108, 40–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botchkarev, V.A.; Komarova, E.A.; Siebenhaar, F.; Botchkareva, N.V.; Sharov, A.A.; Komarov, P.G.; Maurer, M.; Gudkov, A.V.; Gilchrest, B.A. p53 Involvement in the Control of Murine Hair Follicle Regression. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 158, 1913–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Gene Name | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | Tm (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | GGAGATCGTGCGGGACAT | 60 |
| GTTGAAGGTGGTCTCGTGGAT | ||
| IGF1 | ACCCACCCTAACCTGCTGTA | 60 |
| TCCTGTGGGCTTGTTGAAAT | ||
| EGFR | ACCTTGTCATTCAGGGGGATG | 60 |
| ACACAAGCCATGGTGGAACT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, G.; Gong, R.; Ai, Y.; Zhu, T.; Ren, Z. Identification of N6-Methyladenosine-Related Factors and the Prediction of the Regulatory Mechanism of Hair Follicle Development in Rex and Hycole Rabbits. Biology 2023, 12, 1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12111448
Luo G, Gong R, Ai Y, Zhu T, Ren Z. Identification of N6-Methyladenosine-Related Factors and the Prediction of the Regulatory Mechanism of Hair Follicle Development in Rex and Hycole Rabbits. Biology. 2023; 12(11):1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12111448
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Gang, Ruiguang Gong, Yaotian Ai, Tongyan Zhu, and Zhanjun Ren. 2023. "Identification of N6-Methyladenosine-Related Factors and the Prediction of the Regulatory Mechanism of Hair Follicle Development in Rex and Hycole Rabbits" Biology 12, no. 11: 1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12111448
APA StyleLuo, G., Gong, R., Ai, Y., Zhu, T., & Ren, Z. (2023). Identification of N6-Methyladenosine-Related Factors and the Prediction of the Regulatory Mechanism of Hair Follicle Development in Rex and Hycole Rabbits. Biology, 12(11), 1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12111448





