Detection and Quantification of Acrylamide in Second Trimester Amniotic Fluid Using a Novel LC-MS/MS Technique to Determine Whether High Acrylamide Content during Pregnancy Is Associated with Fetal Growth
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Amniotic Fluid Samples
2.1.1. Amniotic Fluid Collection
2.1.2. Amniotic Fluid Samples Preparation and Storage
2.1.3. Determination of Study Groups
2.2. Novel Quantification Technique for Acrylamide Based on Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry
2.2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2.2. Sample Preparation
2.2.3. LC-MS/MS Measurements
LC-MS/MS Optimization
LC-MS/MS Conditions
2.2.4. Method Validation
3. Results
3.1. Novel Method Performance
3.2. Detection of Acrylamide
4. Discussion—Clinical Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Does Burnt Food Give You Cancer? University of Birmingham: Birmingham, UK, 2022; Available online: https://www.birmingham.ac.uk/research/perspective/does-burnt-food-give-you-cancer.aspx (accessed on 30 September 2022).
- Can Burnt Toast Cause Cancer? Healthline: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2021; Available online: https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/burnt-toast-cancer (accessed on 30 September 2022).
- Pantalone, S.; Verardo, V.; Zafra-Gómez, A.; Guerra-Hernández, E.; Cichelli, A.; D’Alessandro, N.; Gómez-Caravaca, A.M. Evaluation of the effects of intermittent frying in French fries and frying oil on monochloropropanediols, glycidols and acrylamide. Food Control 2023, 150, 109771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogurschi, E.N.; Zugravu, C.A.; Ranga, I.N.; Trifunschi, S.; Munteanu, M.F.; Popa, D.C.; Tudorache, M.; Custura, I. Determination of Acrylamide in Selected Foods from the Romanian Market. Foods 2021, 10, 2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tölgyesi, Á.; Sharma, V.K. Determination of acrylamide in gingerbread and other food samples by HILIC-MS/MS: A dilute-and-shoot method. J. Chromatogr. B 2020, 1136, 121933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schettino, L.; García-Juan, A.; Fernández-Lozano, L.; Benedé, J.L.; Chisvert, A. Trace determination of prohibited acrylamide in cosmetic products by vortex-assisted reversed-phase dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2023, 1687, 463651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acrylamide and Cancer Risk; American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019; Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/risk-prevention/chemicals/acrylamide.html (accessed on 11 February 2019).
- Cantrell, M.S.; McDougal, O.M. Biomedical rationale for acrylamide regulation and methods of detection. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 2176–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can Eating Burnt Foods Cause Cancer? Cancer Research UK: London, UK, 2021; Available online: https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/causes-of-cancer/cancer-myths/can-eating-burnt-foods-cause-cancer (accessed on 15 October 2021).
- BS EN 16618:2015; Food Analysis—Determination of Acrylamide in Food by Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-ESI-MS/MS). iTeh, Inc.: Newark, DE, USA, 2015. Available online: https://standards.iteh.ai/catalog/standards/cen/cf79df49-9418-4fbe-a129-dfae52a4d9e4/en-16618-2015 (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- Granby, K. Guidance Document on Analyses of Acrylamide in Food Including Analyses in the Low Concentration Range; Technical University of Denmark: Kongens Lyngby, Denmark, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Desmarchelier, A.; Hamel, J.; Delatour, T. Sources of overestimation in the analysis of acrylamide-in coffee by liquid chromatography mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1610, 460566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrachnis, N.; Loukas, N.; Vrachnis, D.; Antonakopoulos, N.; Zygouris, D.; Kοlialexi, A.; Pergaliotis, V.; Iavazzo, C.; Mastrakos, G.; Iliodromiti, Z. A Systematic Review of Bisphenol A from Dietary and Non-Dietary Sources during Preg-nancy and Its Possible Connection with Fetal Growth Restriction: Investigating Its Potential Effects and the Window of Fetal Vulnerability. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrachnis, N.; Loukas, N.; Vrachnis, D.; Antonakopoulos, N.; Christodoulaki, C.; Tsonis, O.; George, M.; Iliodromiti, Z. Phthalates and fetal growth velocity: Tracking down the suspected links. J. Matern. Neonatal. Med. 2021, 35, 4985–4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldawood, N.; Jalouli, M.; Alrezaki, A.; Nahdi, S.; Alamri, A.; Alanazi, M.; Manoharadas, S.; Alwasel, S.; Harrath, A.H. Fetal programming: In utero exposure to acrylamide leads to intergenerational disrupted ovarian function and accelerated ovarian aging. Aging 2022, 14, 6887–6904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaides, K.H.; Wright, D.; Syngelaki, A.; Wright, A.; Akolekar, R. Fetal Medicine Foundation fetal and neonatal population weight charts. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 52, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonakopoulos, N.; Iliodromiti, Z.; Mastorakos, G.; Iavazzo, C.; Valsamakis, G.; Salakos, N.; Papageorghiou, A.; Margeli, A.; Kalantaridou, S.; Creatsas, G.; et al. Association between Brain-Derived Neu-rotrophic Factor (BDNF) Levels in 2nd Trimester Amniotic Fluid and Fetal Development. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 8476217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrachnis, D.; Antonakopoulos, N.; Fotiou, A.; Pergialiotis, V.; Loukas, N.; Valsamakis, G.; Iavazzo, C.; Stavros, S.; Maroudias, G.; Panagopoulos, P.; et al. Is There a Correlation between Apelin and Insulin Concentrations in Early Second Trimester Amniotic Fluid with Fetal Growth Disorders? J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Guan, T.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, Y. Relationship between gestational acrylamide exposure and offspring’s growth: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Public Health Nutr. 2020, 23, 1791–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Underwood, M.; Gilbert, W.; Sherman, M. Amniotic Fluid: Not Just Fetal Urine Anymore. J. Perinatol. 2005, 25, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyl, R.W.; Friedman, M.A. Effects of acrylamide on rodent reproductive performance. Reprod. Toxicol. 2003, 17, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manson, J.; Brabac, M.J.; Buelke-Sam, J.; Carlson, G.P.; Chapin, R.E.; Favor, J.B.; Fischer, L.J.; Hattis, D.; Lees, P.S.; Perreault-Darney, S.; et al. NTP-CERHR expert panel report on the reproductive and developmental toxicity of acrylamide. Birth Defects Res. Part B: Dev. Reprod. Toxicol. 2005, 74, 17–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Sayyad, H.I.; Abou-Egla, M.H.; Al Sayyad, F.I.; El-Ghawet, H.A.; Gaur, R.L.; Fernando, A.; Raj, A.H.G.; Ouhtit, A. Effects of fried potato chip supplementation on mouse pregnancy and fetal development. Nutrition 2011, 27, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, J.M. The carcinogenicity of acrylamide. Mutat. Res. 2005, 580, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, M.; von Stedingk, H.; Botsivali, M.; Agramunt, S.; Alexander, J.; Brunborg, G.; Chatzi, L.; Fleming, S.; Fthenou, E.; Granum, B.; et al. Birth weight, head circumference, and prenatal exposure to acrylamide from maternal diet: The European prospective mother-child study (NewGeneris). Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 1739–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, C.R.; O’Callaghan, F.J.; Bredow, M.; Martyn, C.N. The influence of head growth in fetal life, infancy, and childhood on intelligence at the ages of 4 and 8 years. Pediatrics 2008, 118, 1486–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogervorst, J.; Vesper, H.W.; Madhloum, N.; Gyselaers, W.; Nawrot, T. Cord blood acrylamide levels and birth size, and interactions with genetic variants in acrylamide-metabolising genes. Environ. Health 2021, 20, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
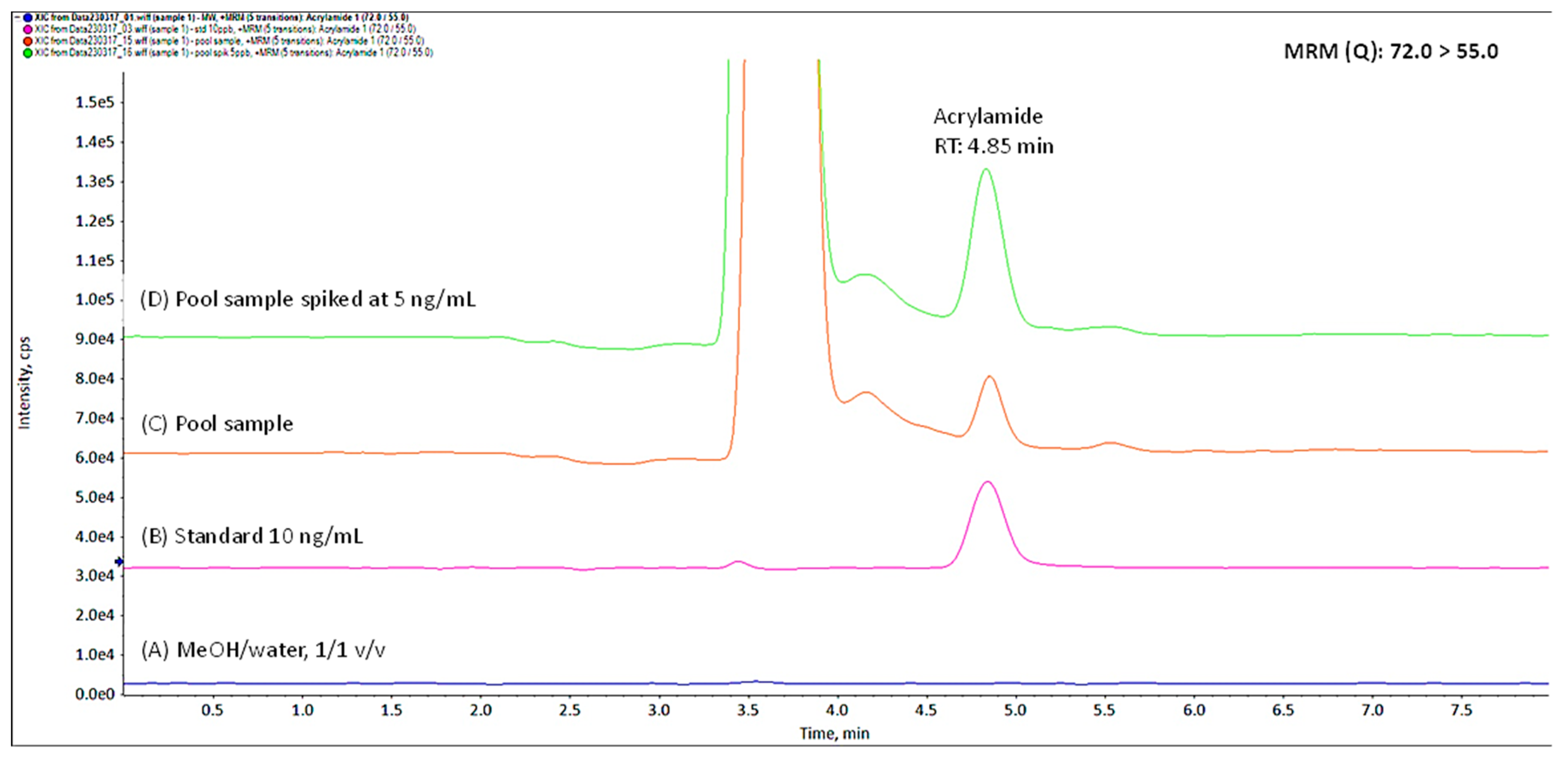
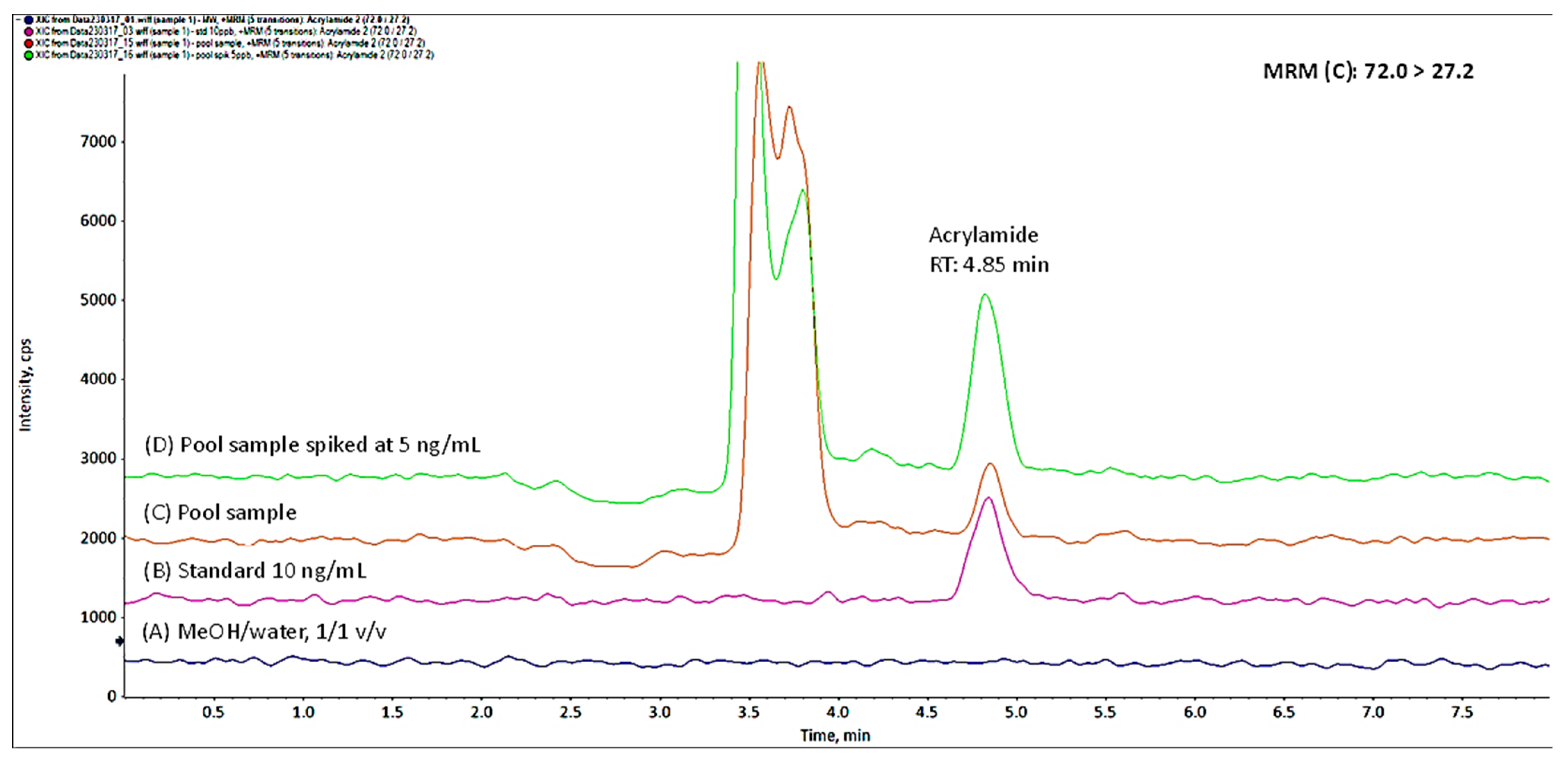
| Matrix | Calibration Curve (× 10−4) | LOD (ng/mL) | LOQ (ng/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard solutions | y = (2.70 ± 0.09) × C + (7.95 ± 4.66) r = 0.998 | 0.7 | 2.3 |
| Amniotic fluid | y = (3.33 ± 0.05) × C + (12.18 ± 2.34) r = 0.993 | 1.4 | 4.6 |
| Fortification Level (ng/mL) (Number of Replicates) | Average Recovery (%) | %RSD |
|---|---|---|
| 5 ppb (n = 4) | 127 | 14 |
| 10 ppb (n = 7) | 144 | 12 |
| 50 ppb (n = 3) | 132 | 11 |
| 100 ppb (n = 3) | 136 | 14 |
| Sample Number | Fetal Birth Weight Centile | Acrylamide Concentration (ng/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| 6 | 18 | 1468 |
| 7 | 20 | 71 |
| 15 | 36 | 7.6 |
| 16 | 38 | 47.8 |
| 20 | 49 | 8.1 |
| 33 | 79 | 122 |
| 1–5, 8–14, 17–19, 21–32, 34–40 | Various | Not detected |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vrachnis, N.; Loukas, N.; Antonakopoulos, N.; Maragou, N.; Kostakis, M.; Tsakni, A.; Vrachnis, D.; Vougiouklaki, D.; Machairiotis, N.; Chatzilazarou, A.; et al. Detection and Quantification of Acrylamide in Second Trimester Amniotic Fluid Using a Novel LC-MS/MS Technique to Determine Whether High Acrylamide Content during Pregnancy Is Associated with Fetal Growth. Biology 2023, 12, 1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12111425
Vrachnis N, Loukas N, Antonakopoulos N, Maragou N, Kostakis M, Tsakni A, Vrachnis D, Vougiouklaki D, Machairiotis N, Chatzilazarou A, et al. Detection and Quantification of Acrylamide in Second Trimester Amniotic Fluid Using a Novel LC-MS/MS Technique to Determine Whether High Acrylamide Content during Pregnancy Is Associated with Fetal Growth. Biology. 2023; 12(11):1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12111425
Chicago/Turabian StyleVrachnis, Nikolaos, Nikolaos Loukas, Nikolaos Antonakopoulos, Niki Maragou, Marios Kostakis, Aliki Tsakni, Dionysios Vrachnis, Despina Vougiouklaki, Nikolaos Machairiotis, Arhodoula Chatzilazarou, and et al. 2023. "Detection and Quantification of Acrylamide in Second Trimester Amniotic Fluid Using a Novel LC-MS/MS Technique to Determine Whether High Acrylamide Content during Pregnancy Is Associated with Fetal Growth" Biology 12, no. 11: 1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12111425
APA StyleVrachnis, N., Loukas, N., Antonakopoulos, N., Maragou, N., Kostakis, M., Tsakni, A., Vrachnis, D., Vougiouklaki, D., Machairiotis, N., Chatzilazarou, A., Houhoula, D., Sokou, R., Stavros, S., Drakakis, P., Mastorakos, G., & Iliodromiti, Z. (2023). Detection and Quantification of Acrylamide in Second Trimester Amniotic Fluid Using a Novel LC-MS/MS Technique to Determine Whether High Acrylamide Content during Pregnancy Is Associated with Fetal Growth. Biology, 12(11), 1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12111425








