NF-kB Regulation and the Chaperone System Mediate Restorative Effects of the Probiotic Lactobacillus fermentum LF31 in the Small Intestine and Cerebellum of Mice with Ethanol-Induced Damage
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
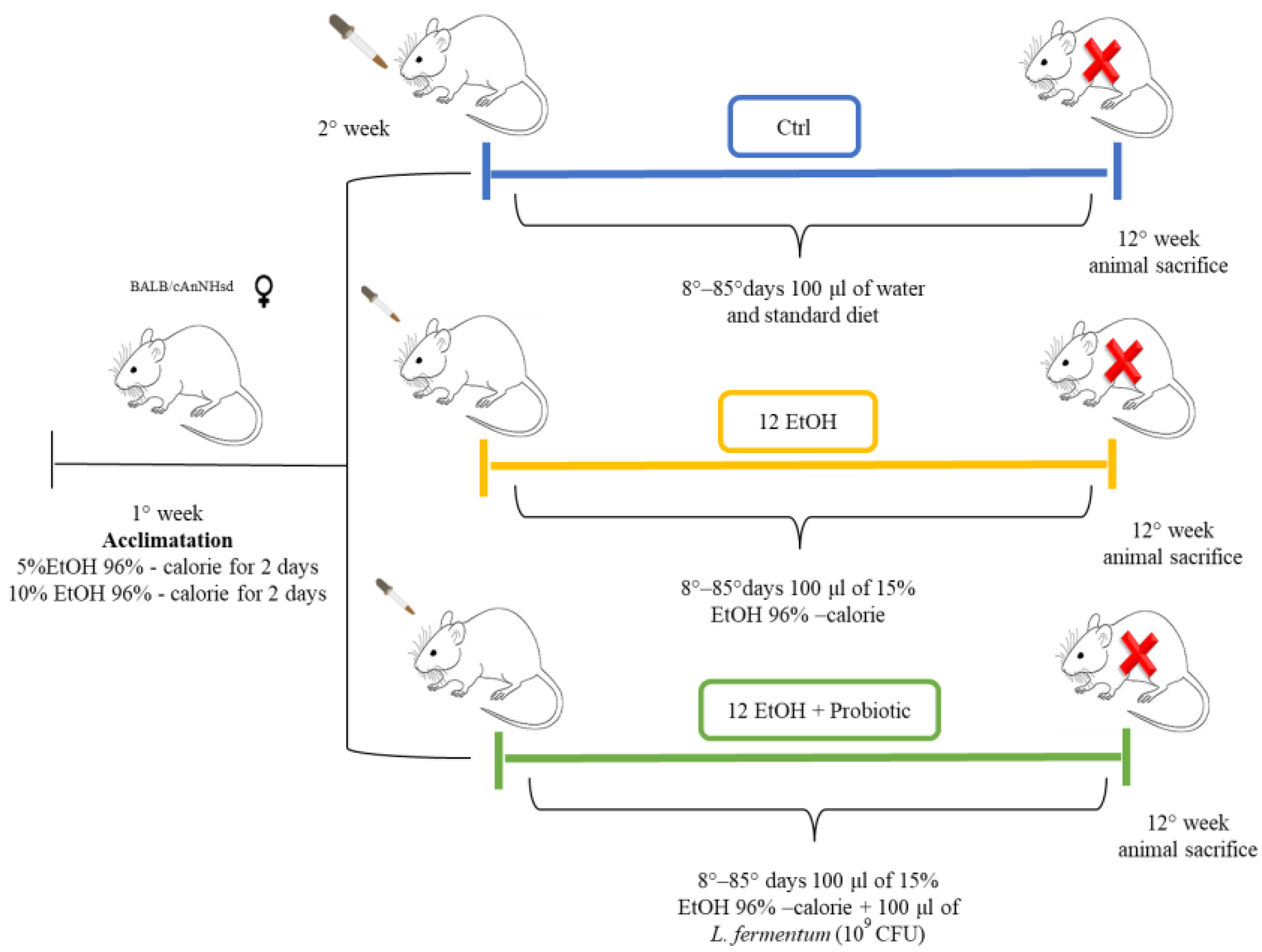
2.1. Animal Model
2.2. Histopatology
2.3. Immunofluorescence
2.4. Immunohistochemistry
2.5. RNA Preparation and Quantitative Real Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) Assay
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
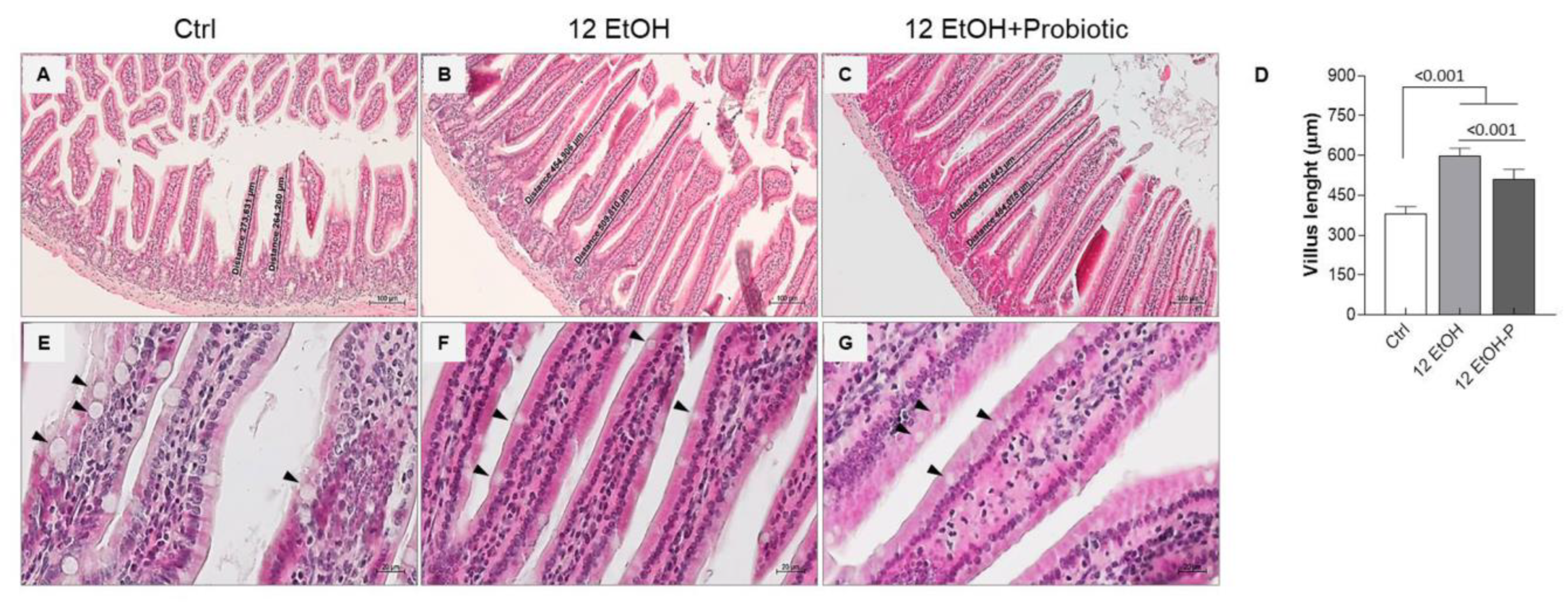
3.1. Small Intestinal Histomorphometry
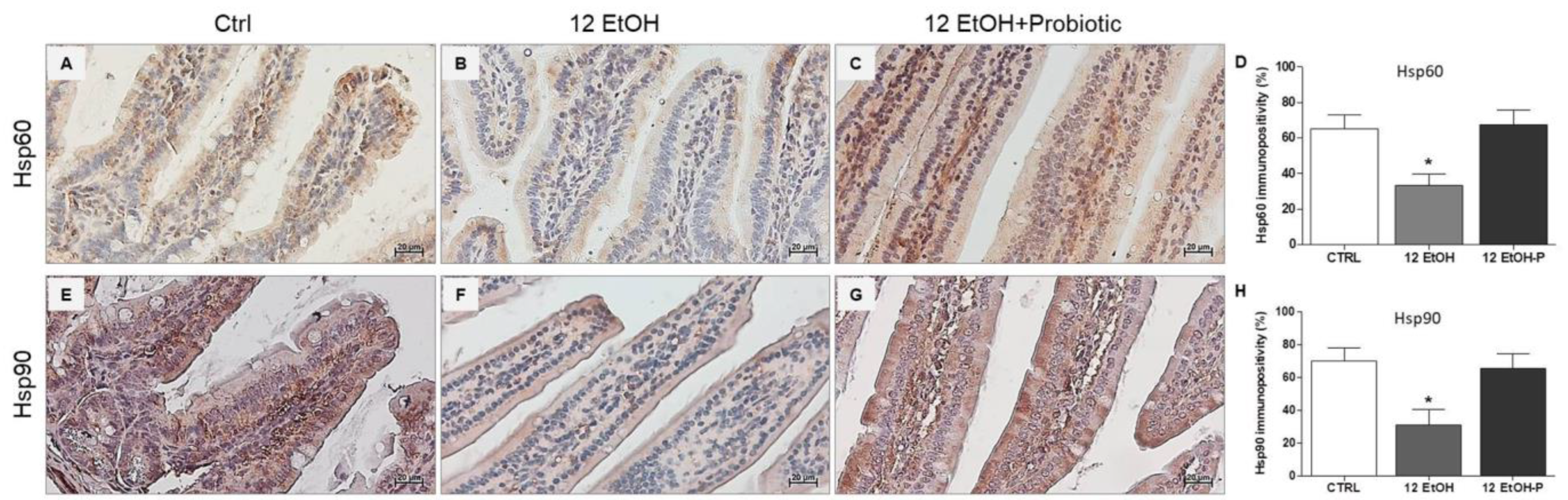
3.2. Effects of L. fermentum Administration on Hsp60 and Hsp90 Immunoreactivity in the Jejunum
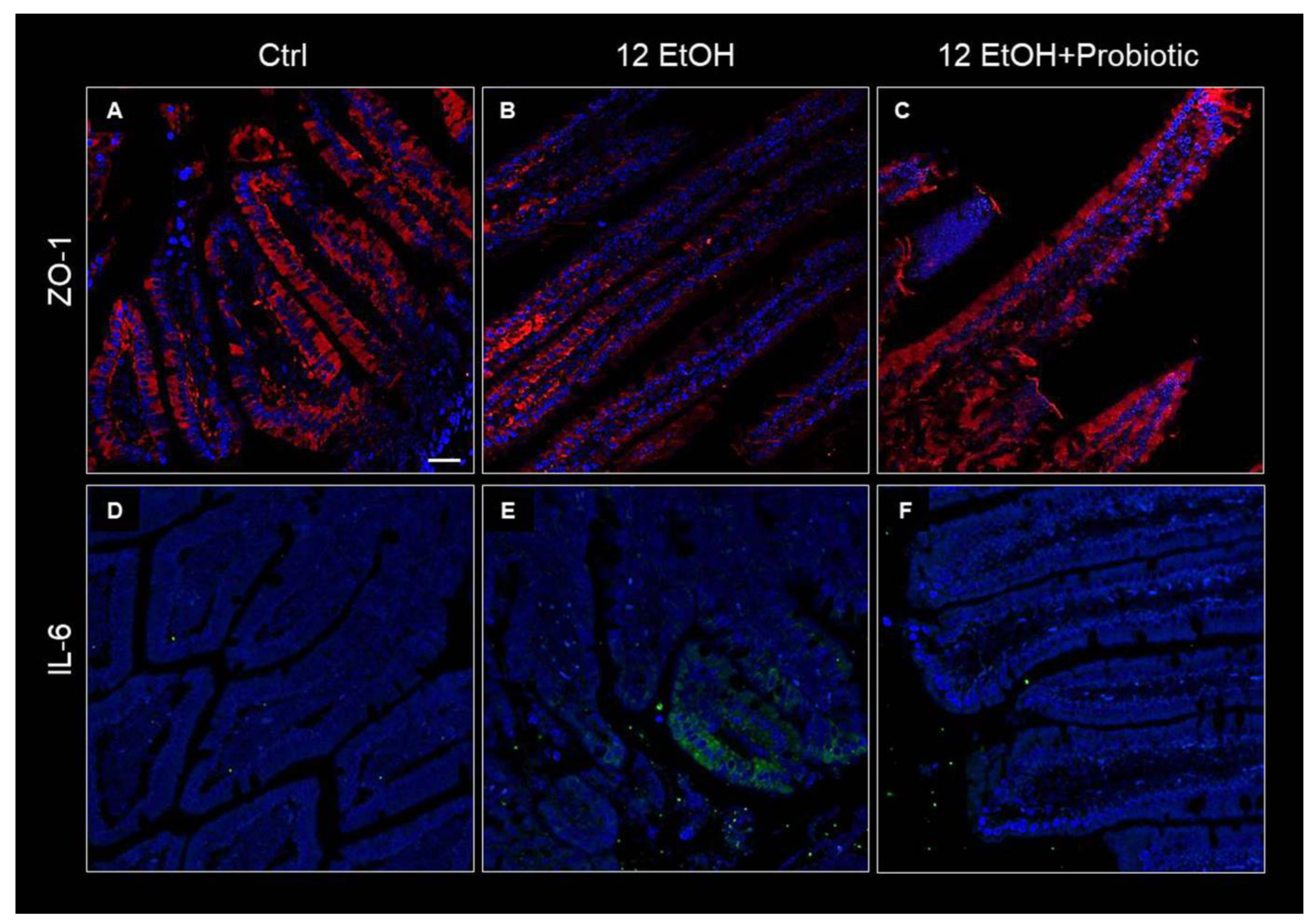
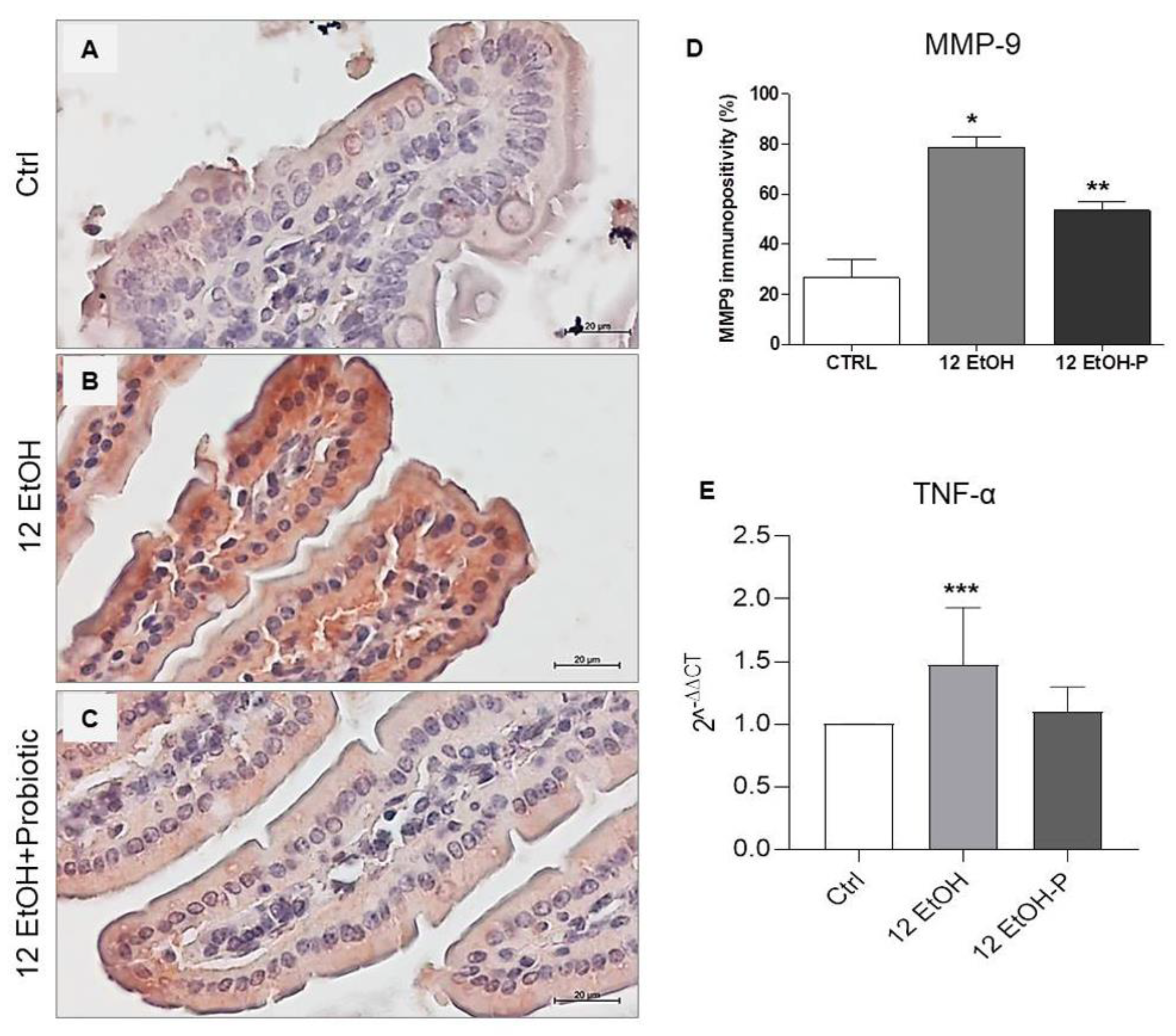
3.3. Effects of Ethanol Consumption and L. fermentum Administration on the Intestinal Barrier Integrity and Permeability
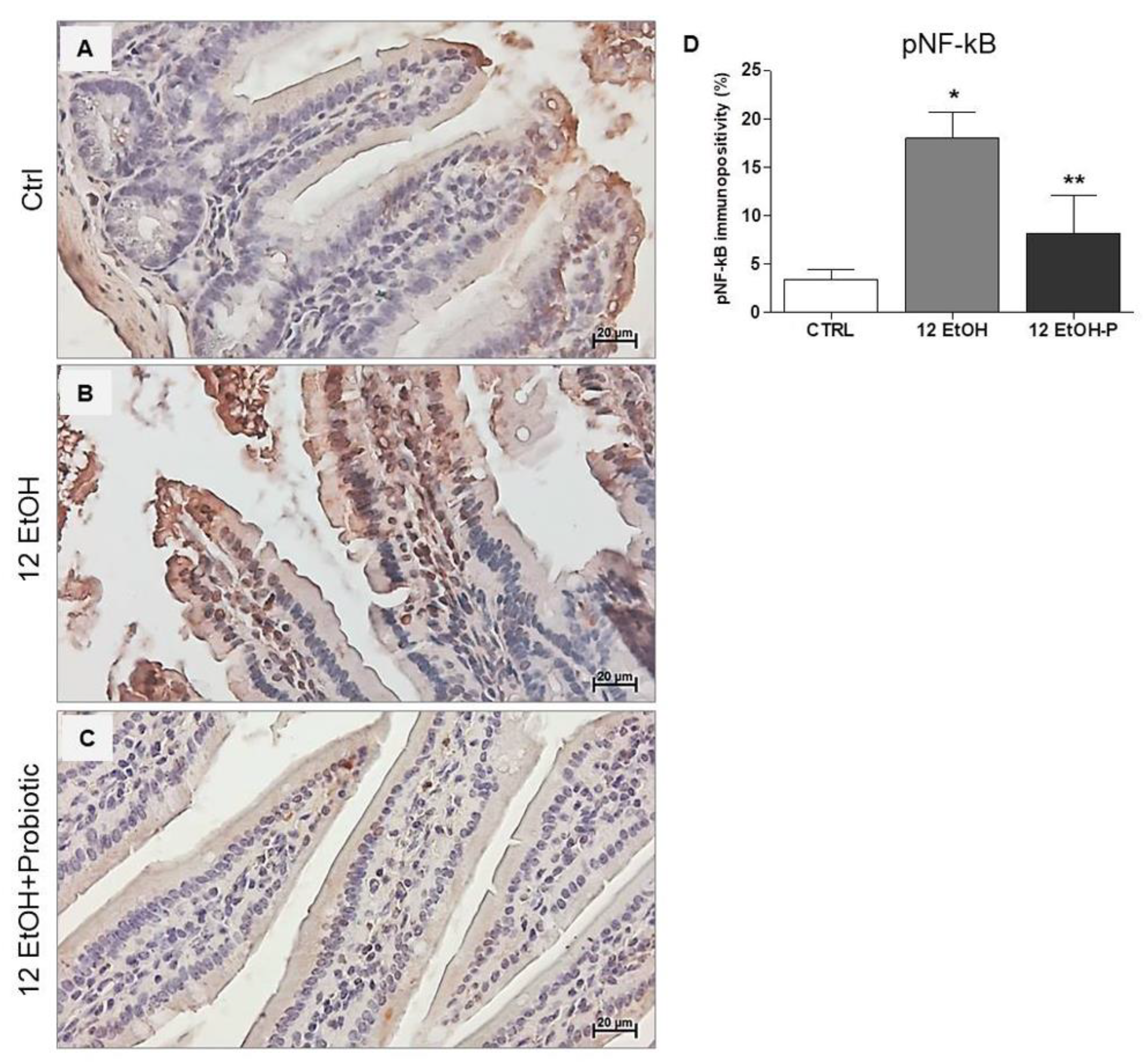
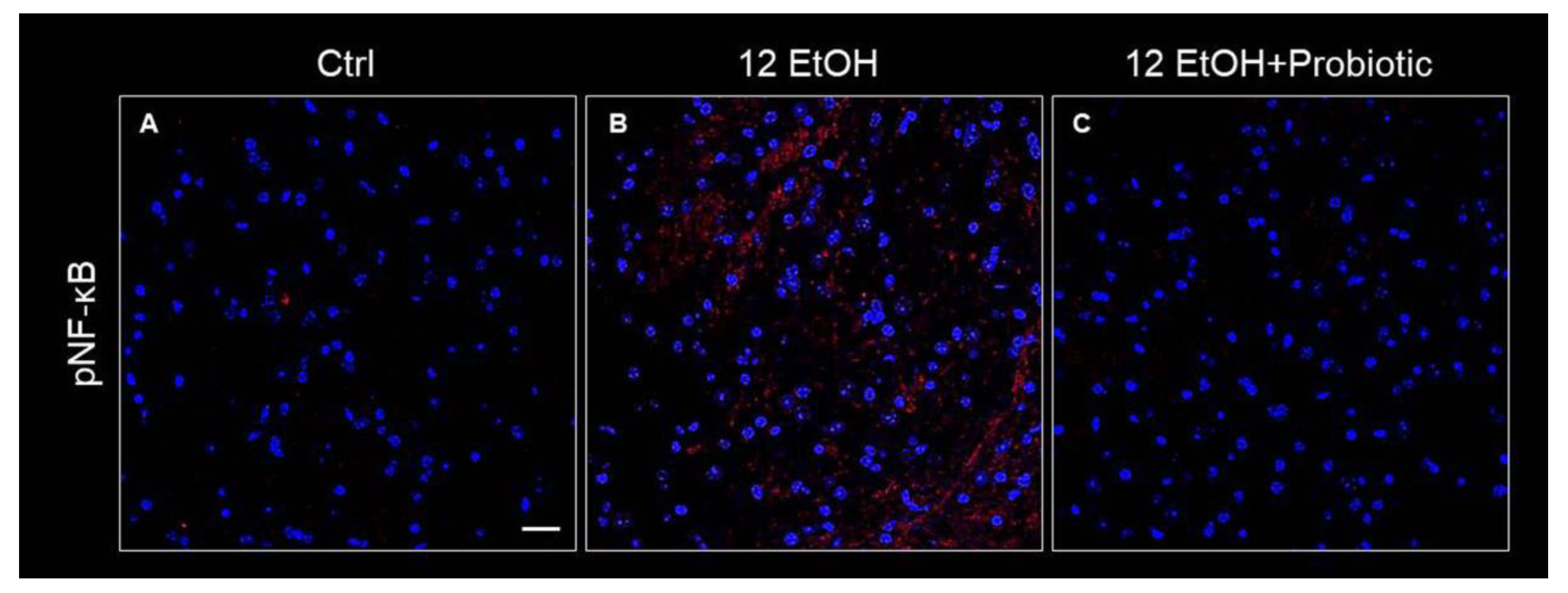
3.4. Effect of L. fermentum on pNF-kB and IkB-α Tissue Distribution
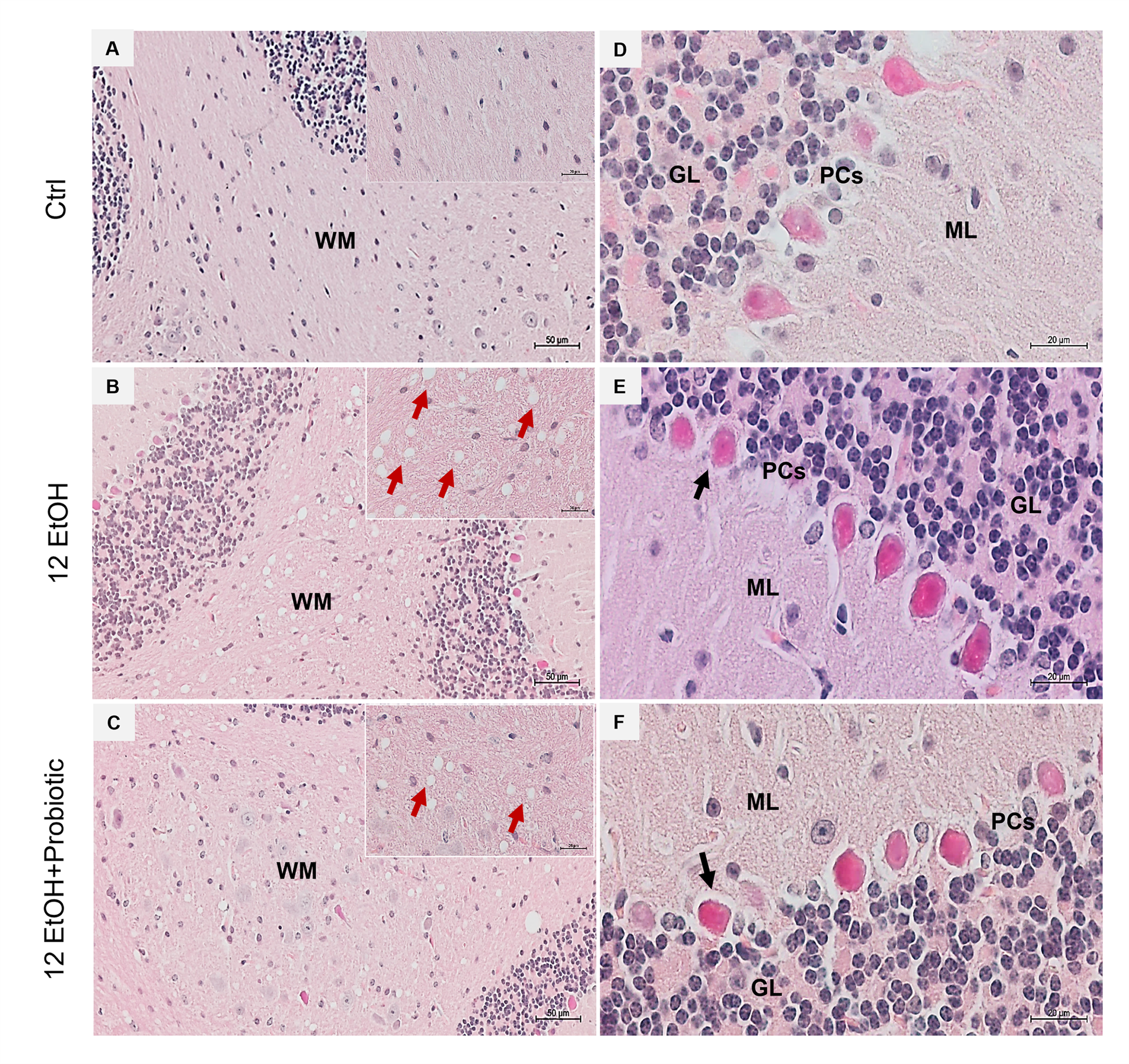
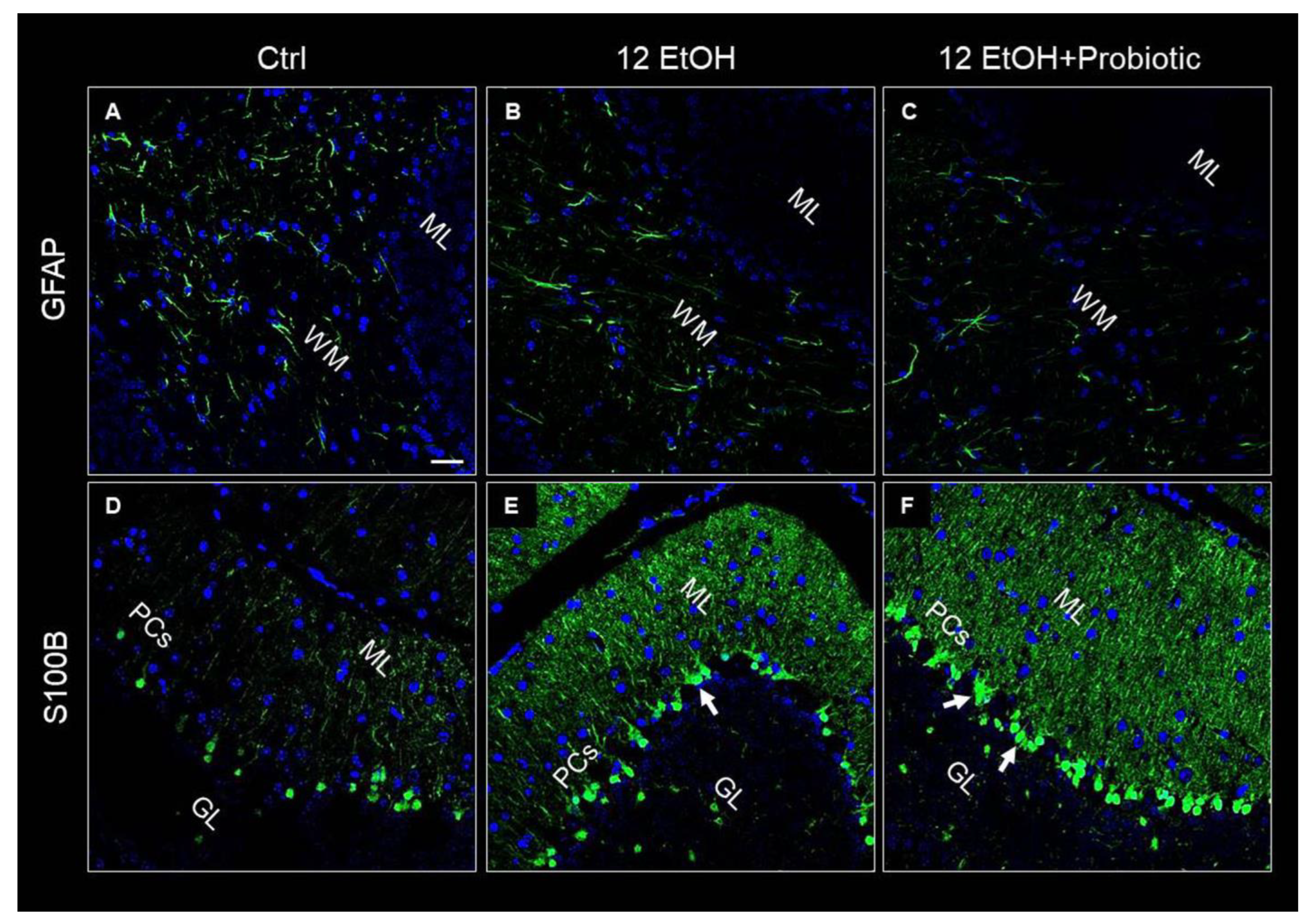
3.5. Effects of Ethanol Consumption and L. fermentum Administration on the Cerebellum: Morphological Observations and Determination of Astrocyte Activation
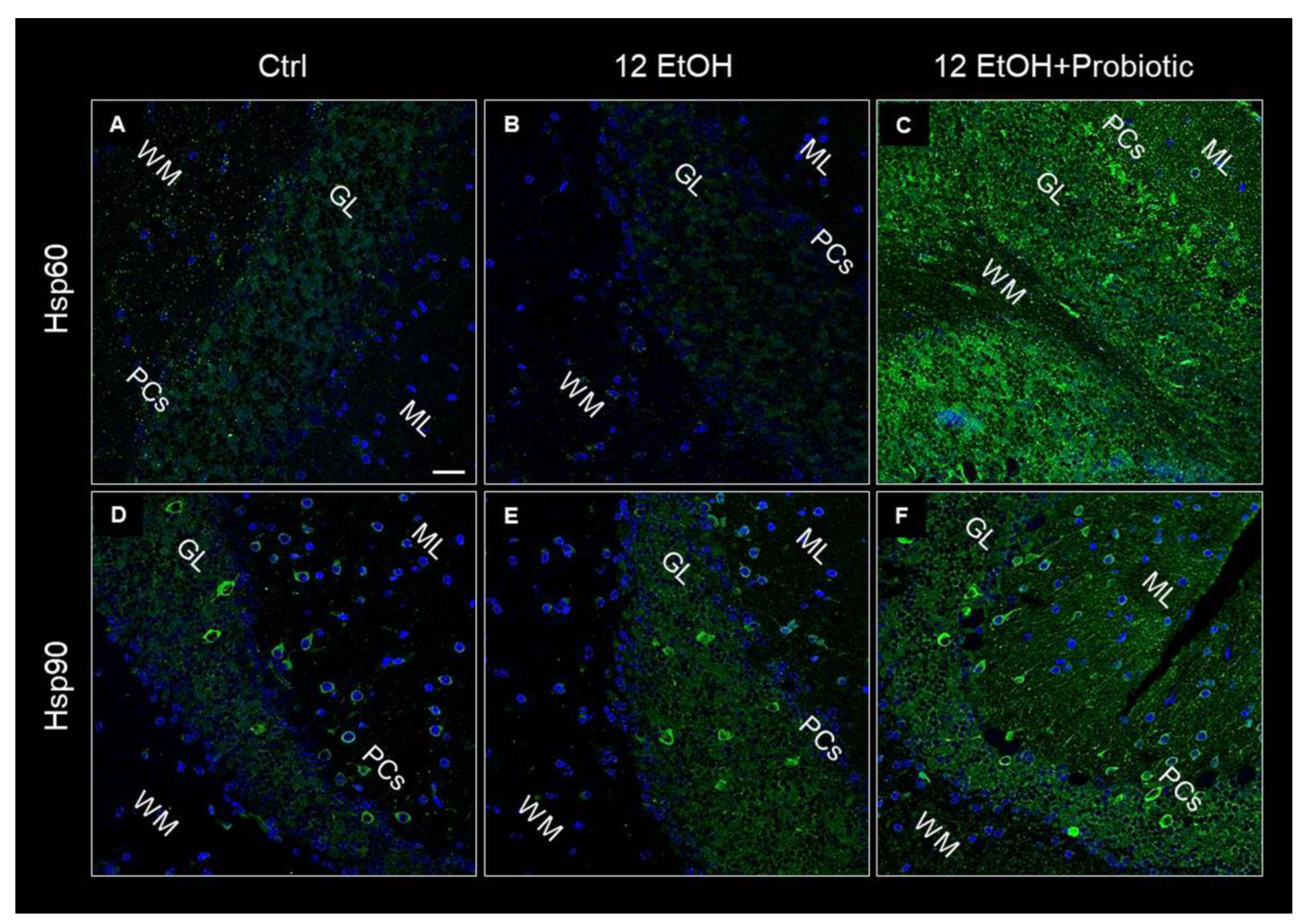
3.6. In L. fermentum-fed Mice the Cerebellum Showed Increased Hsp60 and Hsp90 and Decreased pNF-κB Immunoreactivity
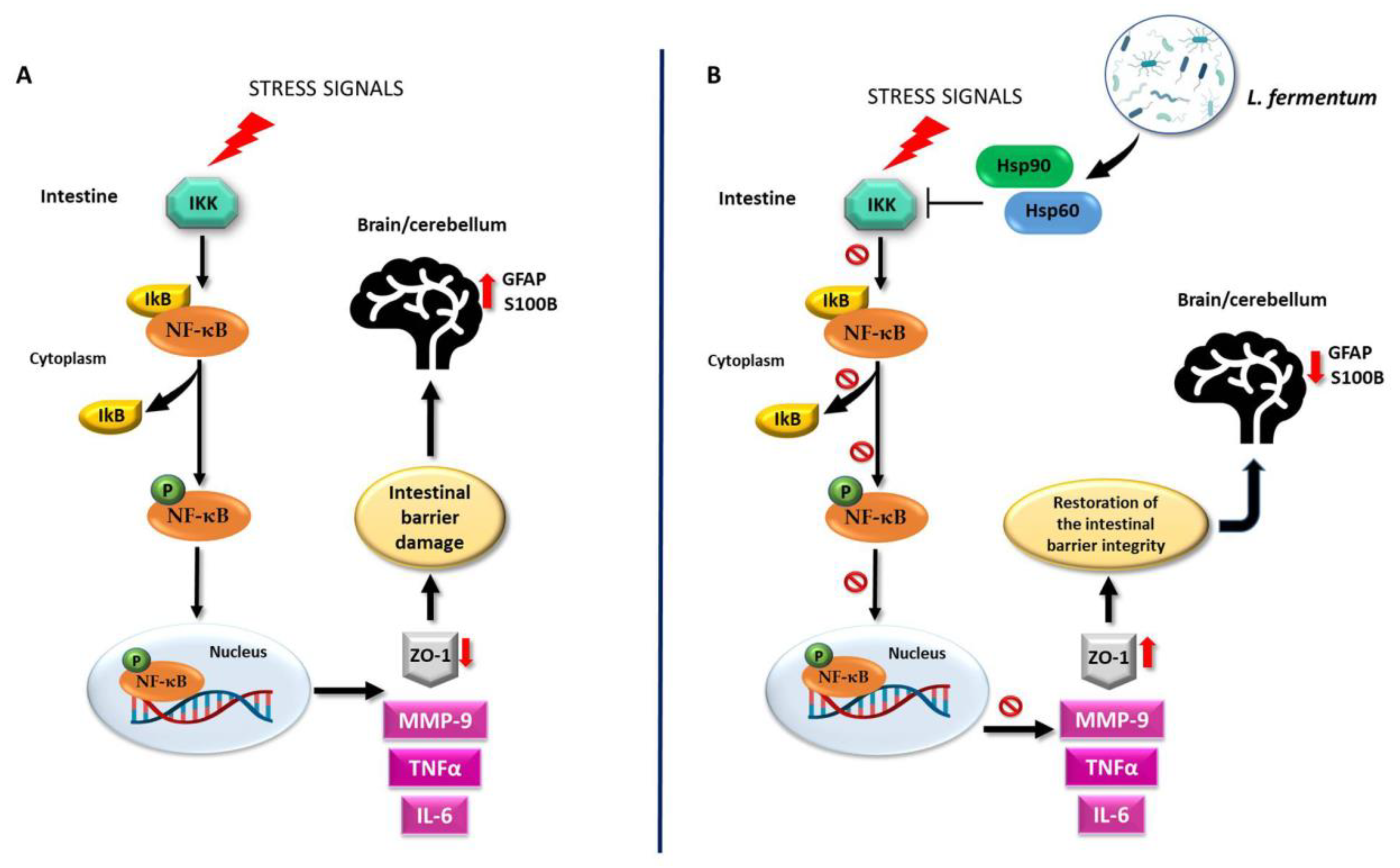
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| EtOH | Ethanol |
| GFAP | Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein |
| GL | Granular Layer |
| Hsps | Heat Shock Proteins |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and Eosin |
| IECs | Intestinal Epithelial Cells |
| IκB-α | NF kappa B inhibitor-α |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| ML | Molecular Layer |
| MMP-9 | Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 |
| NF-κB | Pro-inflammatory Nuclear Factor kappa B |
| PCs | Purkinje cells |
| PGN | Peptidoglycan |
| pNF-κB | Phosphorylated NF-κB |
| S100B | Calcium-Binding Protein |
| TJs | Tight Junctions |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor alpha |
| WM | Subcerebellar White Matter |
| ZO-1 | Zonula Occludens-1 |
References
- Obrenovich, M.E.M. Leaky Gut, Leaky Brain? Microorganisms 2018, 6, 107. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kelly, J.R.; Kennedy, P.J.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G.; Clarke, G.; Hyland, N.P. Breaking down the barriers: The gut microbiome, intestinal permeability and stress-related psychiatric disorders. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 392. [Google Scholar]
- Rutsch, A.; Kantsjö, J.B.; Ronchi, F. The Gut-Brain Axis: How Microbiota and Host Inflammasome Influence Brain Physiology and Pathology. Front Immunol. 2020, 11, 604179. [Google Scholar]
- Alberti, G.; Vergilio, G.; Paladino, L.; Barone, R.; Cappello, F.; Conway de Macario, E.; Macario, A.J.L.; Bucchieri, F.; Rappa, F. The Chaperone System in Breast Cancer: Roles and Therapeutic Prospects of the Molecular Chaperones Hsp27, Hsp60, Hsp70, and Hsp90. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7792. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pitruzzella, A.; Paladino, L.; Vitale, A.M.; Martorana, S.; Cipolla, C.; Graceffa, G.; Cabibi, D.; David, S.; Fucarino, A.; Bucchieri, F.; et al. Quantitative Immunomorphological Analysis of Heat Shock Proteins in Thyroid Follicular Adenoma and Carcinoma Tissues Reveals Their Potential for Differential Diagnosis and Points to a Role in Carcinogenesis. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4324. [Google Scholar]
- Rappa, F.; Pitruzzella, A.; Marino Gammazza, A.; Barone, R.; Mocciaro, E.; Tomasello, G.; Carini, F.; Farina, F.; Conway de Macario, E.; Macario, A.J.L.; et al. Quantitative patterns of Hsps in tubular adenoma compared with normal and tumor tissues reveal the value of Hsp10 and Hsp60 in early diagnosis of large bowel cancer. Cell Stress Chaperones 2016, 21, 927–933. [Google Scholar]
- Moura, C.S.; Lollo, P.C.B.; Morato, P.N.; Amaya-Farfan, J. Dietary nutrients and bioactive substances modulate heat shock protein (HSP) expression: A Review. Nutrients 2018, 10, 683. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Drabik, K.A.; Waypa, T.S.; Musch, M.W.; Alverdy, J.C.; Schneewind, O.; Chang, E.B.; Petrof, E.O. Soluble factors from Lactobacillus GG activate MAPKs and induce cytoprotective heat shock proteins in intestinal epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2006, 290, C1018–C1030. [Google Scholar]
- Bishehsari, F.; Magno, E.; Swanson, G.; Desai, V.; Voigt, R.M.; Forsyth, C.B.; Keshavarzian, A. Alcohol and gut-derived inflammation. Alcohol Res. 2017, 38, 163–171. [Google Scholar]
- Naghmouchi, K.; Belguesmia, Y.; Bendali, F.; Spano, G.; Seal, B.S.; Drider, D. Lactobacillus fermentum: A bacterial species with potential for food preservation and biomedical applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 3387–3399. [Google Scholar]
- Tenorio-Jiménez, C.; Martínez-Ramírez, M.J.; Gil, Á.; Gómez-Llorente, C. Effects of Probiotics on Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review of Randomized Clinical Trials. Nutrients 2020, 12, 124. [Google Scholar]
- He, M.; Shi, B. Gut microbiota as a potential target of metabolic syndrome: The role of probiotics and prebiotics. Cell Biosci. 2017, 7, 54. [Google Scholar]
- Peran, L.; Camuesco, D.; Comalada, M.; Nieto, A.; Concha, A.; Adrio, J.L.; Olivares, M.; Xaus, J.; Galvez, J. Lactobacillus fermentum, a probiotic capable to release glutathione, prevents colonic inflammation in the TNBS model of rat colitis. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2006, 21, 737–746. [Google Scholar]
- Barone, R.; Rappa, F.; Macaluso, F.; Caruso Bavisotto, C.; Sangiorgi, C.; Di Paola, G.; Tomasello, G.; Di Felice, V.; Marcianò, V.; Farina, F.; et al. Alcoholic liver disease: A mouse model reveals protection by Lactobacillus fermentum. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2016, 7, e138. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carr, R.M.; Peralta, G.; Yin, X.; Ahima, R.S. Absence of perilipin 2 prevents hepatic steatosis, glucose intolerance and ceramide accumulation in alcohol-fed mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97118. [Google Scholar]
- Carr, R.M.; Dhir, R.; Yin, X.; Agarwal, B.; Ahima, R.S. Temporal effects of ethanol consumption on energy homeostasis, hepatic steatosis, and insulin sensitivity in mice. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2013, 37, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar]
- D’Amico, D.; Marino Gammazza, A.; Macaluso, F.; Paladino, L.; Scalia, F.; Spinoso, G.; Dimauro, I.; Caporossi, D.; Barone, R. Sex-based differences after a single bout of exercise on PGC1α isoforms in skeletal muscle: A pilot study. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21328. [Google Scholar]
- Nennig, S.E.; Schank, J.R. The Role of NFκB in Drug Addiction: Beyond Inflammation. Alcohol Alcohol. 2017, 52, 172–179. [Google Scholar]
- Nowak, A.J.; Relja, B. The impact of acute or chronic alcohol intake on the NF-κB signaling pathway in alcohol-related liver disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9407. [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishnan, S.K.; Zhang, H.; Ma, X.; Jung, I.; Schwartz, A.J.; Triner, D.; Devenport, S.N.; Das, N.K.; Xue, X.; Zeng, M.Y.; et al. Intestinal non-canonical NFκB signaling shapes the local and systemic immune response. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 660. [Google Scholar]
- Llopis, M.; Cassard, A.M.; Wrzosek, L.; Boschat, L.; Bruneau, A.; Ferrere, G.; Puchois, V.; Martin, J.C.; Lepage, P.; Le Roy, T.; et al. Intestinal microbiota contributes to individual susceptibility to alcoholic liver disease. Gut 2016, 65, 830–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sadi, R.; Guo, S.; Ye, D.; Ma, T.Y. TNF-α modulation of intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier is regulated by ERK1/2 activation of Elk-1. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 183, 1871–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruder, B.; Atreya, R.; Becker, C. Tumour necrosis factor alpha in intestinal homeostasis and gut related diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, P.P.; Gyongyosi, B.; Satishchandran, A.; Iracheta-Vellve, A.; Cho, Y.; Ambade, A.; Szabo, G. Reduced gut microbiome protects from alcohol-induced neuroinflammation and alters intestinal and brain inflammasome expression. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, R. Endotoxemia and gut barrier dysfunction in alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology 2009, 50, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclercq, S.; Matamoros, S.; Cani, P.D.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Jamar, F.; Stärkel, P.; Windey, K.; Tremaroli, V.; Bäckhed, F.; Verbeke, K.; et al. Intestinal permeability, gut-bacterial dysbiosis, and behavioral markers of alcohol-dependence severity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E4485–E4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huf, F.; Bandiera, S.; Müller, C.B.; Gea, L.; Carvalho, F.B.; Rahmeier, F.L.; Reiter, K.C.; Tortorelli, L.S.; Gomez, R.; da Cruz Fernandes, M. Comparative study on the effects of cigarette smoke exposure, ethanol consumption and association: Behavioral parameters, apoptosis, glial fibrillary acid protein and S100β immunoreactivity in different regions of the rat hippocampus. Alcohol 2019, 77, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakopoulou, A. Neuronal vacuolation and spinocerebellar degeneration associated with altered neurotransmission. Folia Neuropathol. 2017, 55, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel-Hidalgo, J.J. Molecular neuropathology of astrocytes and oligodendrocytes in alcohol use disorders. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanella, C.; Marino Gammazza, A.; Mularoni, L.; Cappello, F.; Zummo, G.; Di Felice, V. A comparative analysis of the products of GROEL-1 gene from Chlamydia trachomatis serovar D and the HSP60 var1 transcript from Homo sapiens suggests a possible autoimmune response. Int. J. Immunogenet. 2009, 36, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalia, F.; Marino Gammazza, A.; Conway de Macario, E.; Macario, A.J.L.; Cappello, F. Myelin Pathology: Involvement of Molecular Chaperones and the Promise of Chaperonotherapy. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, K.; Musch, M.W.; Ren, H.; Boone, D.L.; Hendrickson, B.A.; Ma, A.; Chang, E.B. Enteric flora and lymphocyte-derived cytokines determine expression of heat shock proteins in mouse colonic epithelial cells. Gastroenterology 2003, 124, 1395–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrof, E.O.; Kojima, K.; Ropeleski, M.J.; Musch, M.W.; Tao, Y.; De Simone, C.; Chang, E.B. Probiotics inhibit nuclear factor-kappaB and induce heat shock proteins in colonic epithelial cells through proteasome inhibition. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 1474–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.M.; Versalovic, J. Probiotics-host communication: Modulation of signaling pathways in the intestine. Gut Microbes. 2010, 1, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Mei, X.; Yu, D.; Wang, Y.; Li, W. Antioxidant properties of probiotic bacteria. Nutrients 2017, 9, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrof, E.O.; Claud, E.C.; Sun, J.; Abramova, T.; Guo, Y.; Waypa, T.S.; He, S.M.; Nakagawa, Y.; Chang, E.B. Bacteria-free solution derived from Lactobacillus plantarum inhibits multiple NF-κB pathways and inhibits proteasome function. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2009, 15, 1537–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, N.D. Integrating cell-signalling pathways with NF-κB and IKK function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Bai, L.; Chen, W.; Xu, S. The NF-κB activation pathways, emerging molecular targets for cancer prevention and therapy. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2010, 14, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, T. The nuclear factor NF-kappaB pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a001651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Lin, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Hu, H. Targeting NF-κB pathway for the therapy of diseases: Mechanism and clinical study. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, M.S.; Matthew, S. Shared principles in NF-κB signaling. Cell 2008, 132, 344–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.W.; Myers, L.E.; Ray, L.; Song, S.C.; Nasr, T.R.; Berardinelli, A.J.; Kundu, K.; Murthy, N.; Hansen, J.M.; Neish, A.S. Lactobacillus rhamnosus blocks inflammatory signaling in vivo via reactive oxygen species generation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 47, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.; Forsythe, P.; Bienenstock, J. Live Lactobacillus rhamnosus [corrected] is essential for the inhibitory effect on tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced interleukin-8 expression. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 5308–5314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, N.; Caicedo, R.; Neu, J. Alive and dead Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG decrease tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced interleukin-8 production in Caco-2 cells. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 1752–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resta-Lenert, S.; Barrett, K.E. Live probiotics protect intestinal epithelial cells from the effects of infection with enteroinvasive Escherichia coli (EIEC). Gut 2003, 52, 988–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaza-Díaz, J.; Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; Vilchez-Padial, L.M.; Gil, A. Evidence of the Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Probiotics and Synbiotics in Intestinal Chronic Diseases. Nutrients 2017, 9, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillippi, D.T.; Daniel, S.; Nguyen, K.N.; Penaredondo, B.A.; Lund, A.K. Probiotics Function as Immunomodulators in the Intestine in C57Bl/6 Male Mice Exposed to Inhaled Diesel Exhaust Particles on a High-Fat Diet. Cells 2022, 11, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Primary Antibody | Source and Type | Supplier | Dilution | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IHC 1 | IF | |||
| Glial Fibrillary Acid Protein (GFAP) | Mouse monoclonal | Sc-33673—Santa Cruz, Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, USA | - | 1:50 |
| S100B-calcium-binding-protein (S100B) | Rabbit polyclonal | Z0311–Dako, Santa Clara, CA, USA | - | 1:250 |
| Phospho-proinflammatory nuclear factor (pNFκB) | Rabbit polyclonal | Sc-33020—Santa Cruz, Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, USA | 1:100 | 1:50 |
| Heat Shock Protein 60 (Hsp60) | Mouse monoclonal | Ab-13532—Abcam, Cambridge, UK | 1:300 | 1:50 |
| Heat Shock Protein 90 α/β (Hsp90 α/β) | Mouse monoclonal | Sc-13119—Santa Cruz, Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, USA. | 1:200 | 1:50 |
| Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) | Rabbit polyclonal | Sc-10737—Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, USA | 1:100 | - |
| Tight Junction Protein 1 (TJP1) | Rabbit polyclonal | C82740—Sigma Aldrich, Hamburg, Germany | - | 1:50 |
| NF-kappa-B inhibitor alpha (IκBα) | Rabbit polyclonal | Sc-203—Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, USA | - | 1:50 |
| Interleukin 6 (IL-6) | Rabbit polyclonal | P620—Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA | - | 1:50 |
| Primer | Sequence |
|---|---|
| Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GADPH) | F: 5′-CAAGGACACTGAGCAAGAGA-3′ |
| R: 5′-GCCCCTCCTGTTATTATGGG-3′ | |
| Tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α) | F: 5′-CCCCCAGTCTGTATCCTTCT-3′ |
| R: 5′-TTTGAGTCCTTGATGGTGGT-3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paladino, L.; Rappa, F.; Barone, R.; Macaluso, F.; Zummo, F.P.; David, S.; Szychlinska, M.A.; Bucchieri, F.; Conway de Macario, E.; Macario, A.J.L.; et al. NF-kB Regulation and the Chaperone System Mediate Restorative Effects of the Probiotic Lactobacillus fermentum LF31 in the Small Intestine and Cerebellum of Mice with Ethanol-Induced Damage. Biology 2023, 12, 1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12111394
Paladino L, Rappa F, Barone R, Macaluso F, Zummo FP, David S, Szychlinska MA, Bucchieri F, Conway de Macario E, Macario AJL, et al. NF-kB Regulation and the Chaperone System Mediate Restorative Effects of the Probiotic Lactobacillus fermentum LF31 in the Small Intestine and Cerebellum of Mice with Ethanol-Induced Damage. Biology. 2023; 12(11):1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12111394
Chicago/Turabian StylePaladino, Letizia, Francesca Rappa, Rosario Barone, Filippo Macaluso, Francesco Paolo Zummo, Sabrina David, Marta Anna Szychlinska, Fabio Bucchieri, Everly Conway de Macario, Alberto J. L. Macario, and et al. 2023. "NF-kB Regulation and the Chaperone System Mediate Restorative Effects of the Probiotic Lactobacillus fermentum LF31 in the Small Intestine and Cerebellum of Mice with Ethanol-Induced Damage" Biology 12, no. 11: 1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12111394
APA StylePaladino, L., Rappa, F., Barone, R., Macaluso, F., Zummo, F. P., David, S., Szychlinska, M. A., Bucchieri, F., Conway de Macario, E., Macario, A. J. L., Cappello, F., & Marino Gammazza, A. (2023). NF-kB Regulation and the Chaperone System Mediate Restorative Effects of the Probiotic Lactobacillus fermentum LF31 in the Small Intestine and Cerebellum of Mice with Ethanol-Induced Damage. Biology, 12(11), 1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12111394














