Calcium Prevents Enhanced Degradation of Factor VIII in the Condition of Motion
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Antibodies
2.2. Mouse Model
2.3. Coagulation Assays
2.4. SDS-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (PAGE) and Immunoblot Analysis
2.5. Immunohistochemistry
2.6. Alizarin Red Staining
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
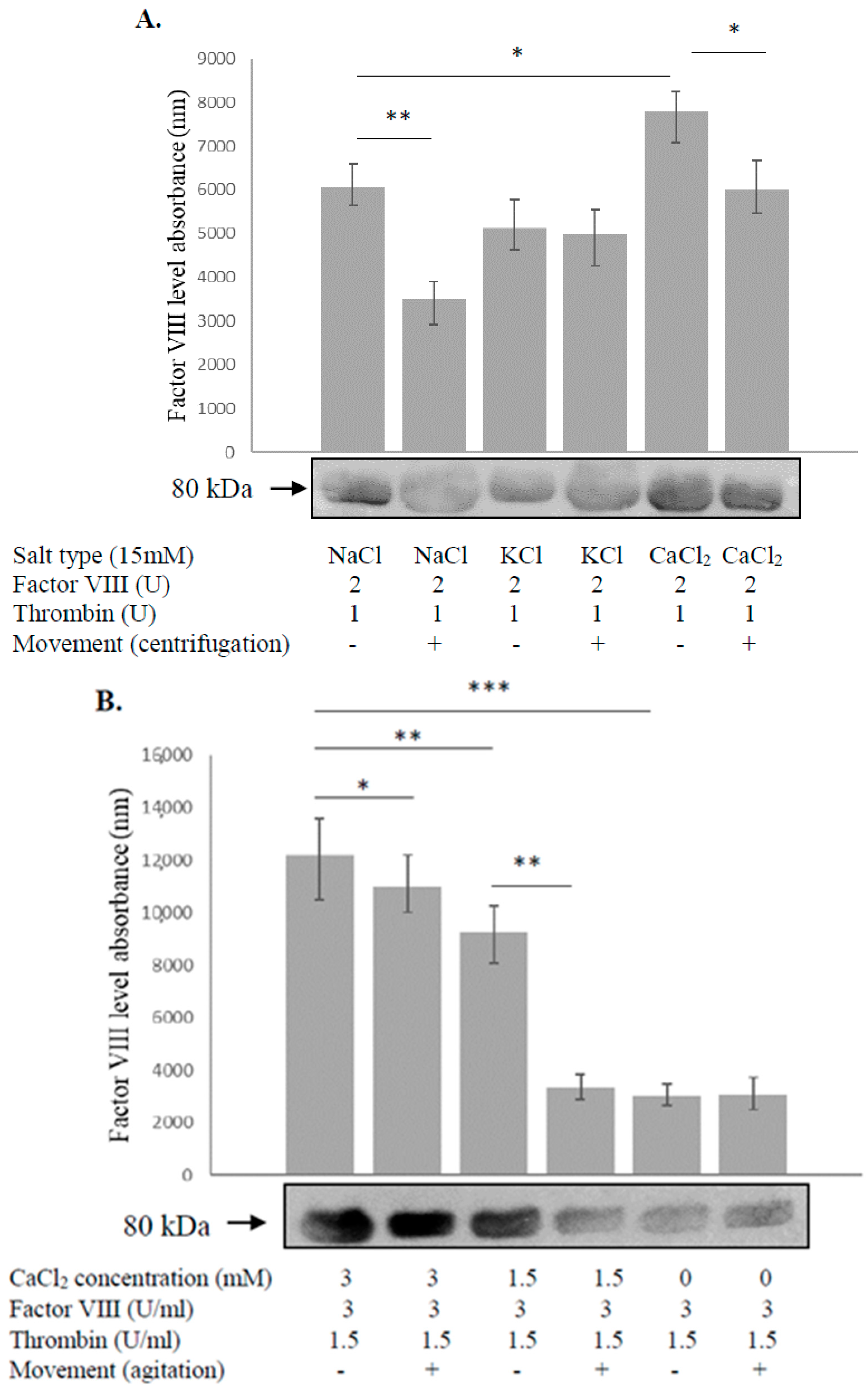
3.1. Calcium Prevents Degradation of Factor VIII during Intermittent Motion
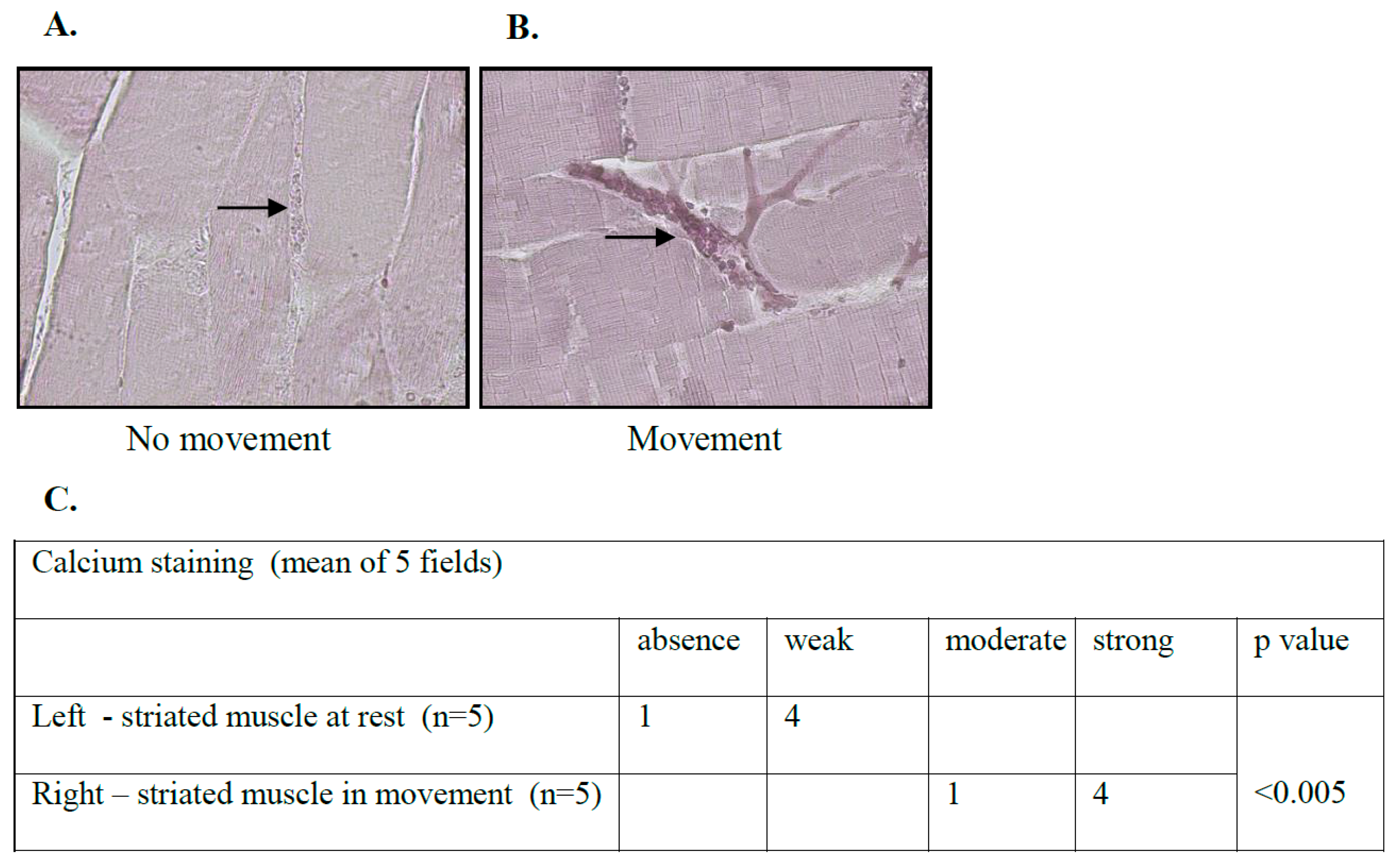
3.2. Calcium Levels in the Microcirculation of Skeletal Striated Muscles Are Elevated following Movement
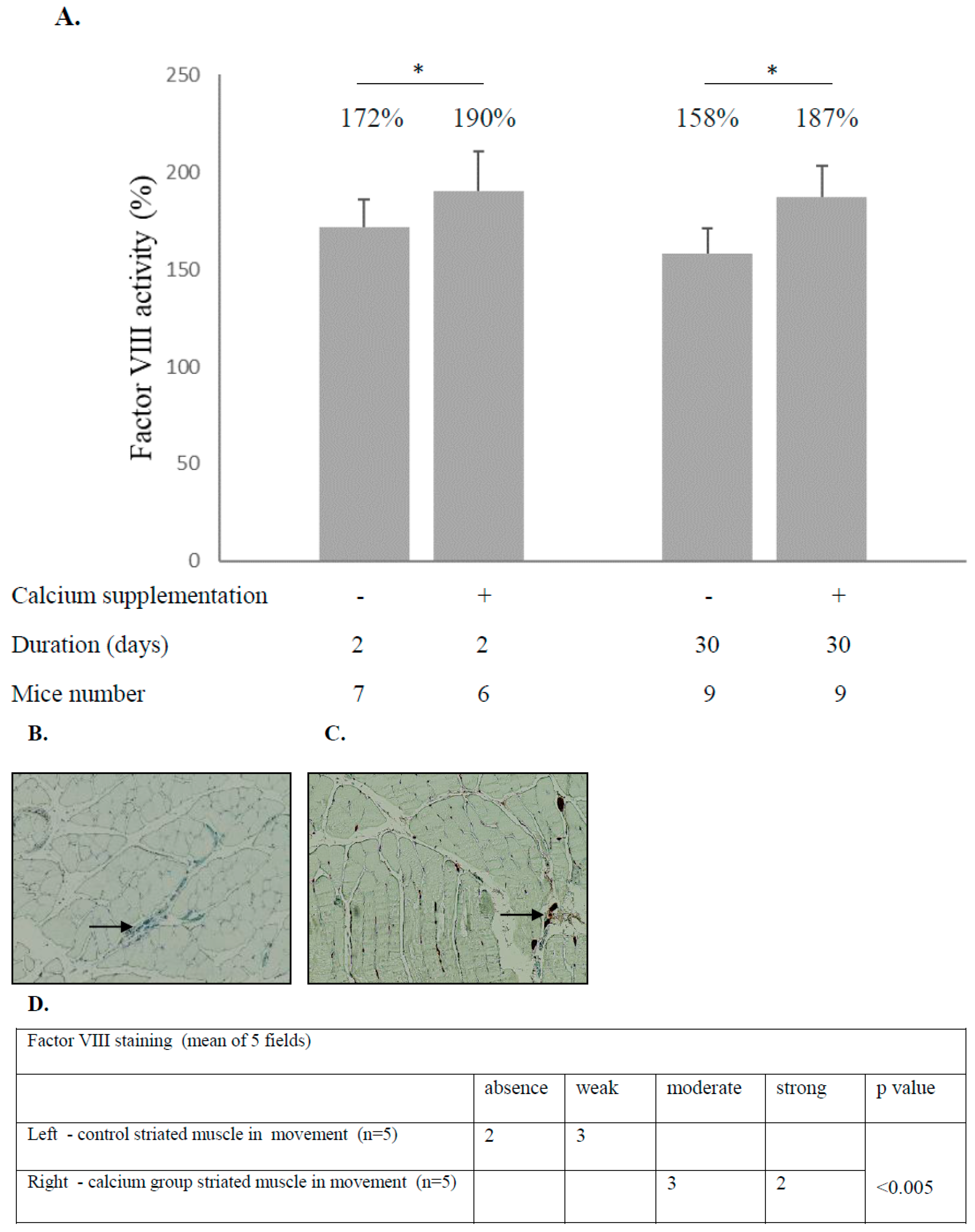
3.3. Calcium Supplementation in Drinking Water Raises the Level of Factor VIII in the Blood and Skeletal Striated Muscles
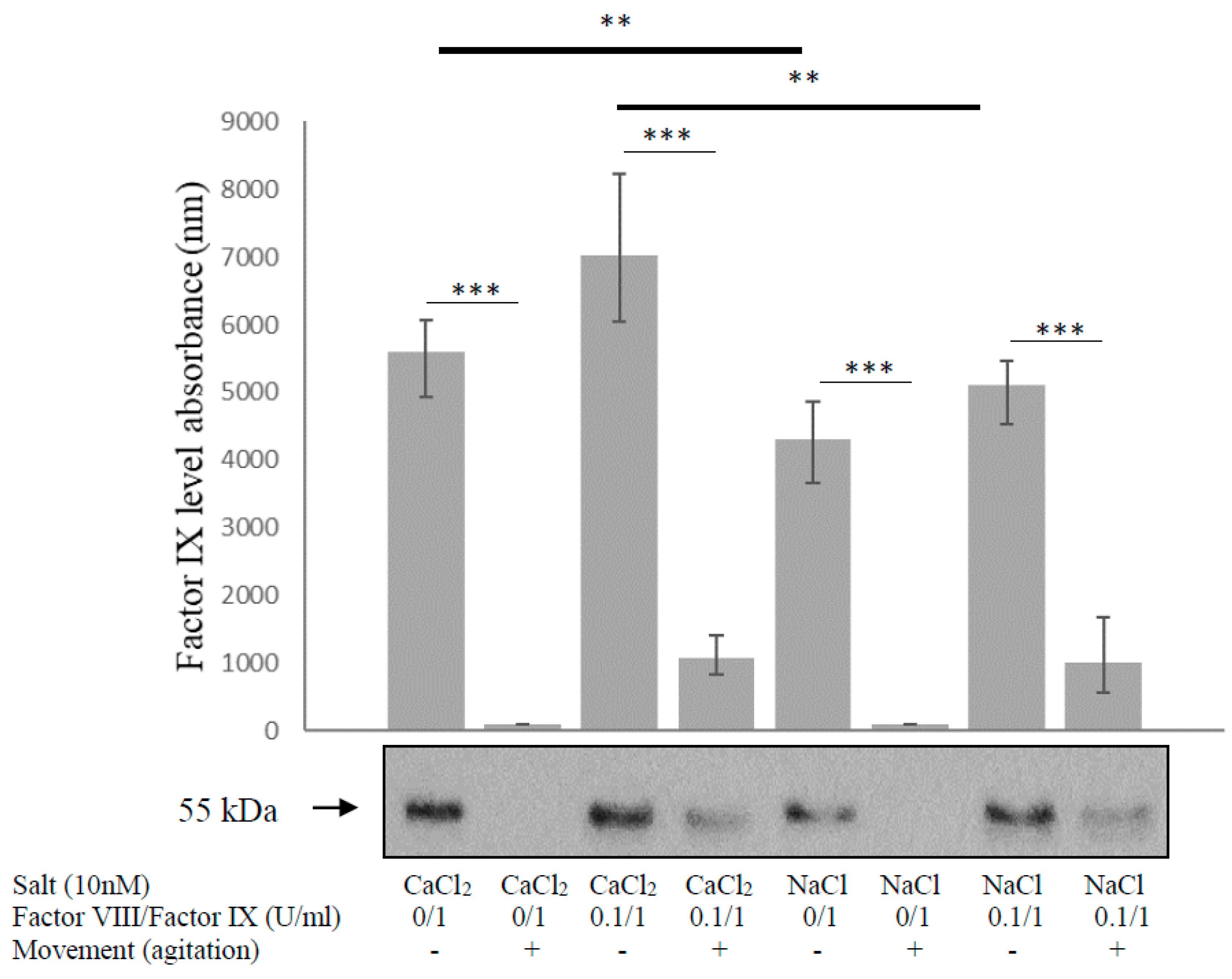
3.4. Calcium Solution Does Not Prevent Factor IX Degradation during Movement
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berntorp, E.; Fischer, K.; Hart, D.P.; Mancuso, M.E.; Stephensen, D.; Shapiro, A.D.; Blanchette, V. Haemophilia. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancuso, M.E.; Mahlangu, J.N.; Pipe, S.W. The changing treatment landscape in haemophilia: From standard half-life clotting factor concentrates to gene editing. Lancet 2021, 397, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soucie, J.M.; Miller, C.H.; Dupervil, B.; Le, B.; Buckner, T.W. Occurrence rates of haemophilia among males in the United States based on surveillance conducted in specialized haemophilia treatment centres. Haemophilia 2020, 26, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolton-Maggs, P.H.; Pasi, K.J. Haemophilias A and B. Lancet 2003, 361, 1801–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osooli, M.; Donfield, S.M.; Carlsson, K.S.; Baghaei, F.; Holmstrom, M.; Berntorp, E.; Astermark, J. Joint comorbidities among Swedish carriers of haemophilia: A register-based cohort study over 22 years. Haemophilia 2019, 25, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnsen, J.M.; Fletcher, S.N.; Huston, H.; Roberge, S.; Martin, B.K.; Kircher, M.; Josephson, N.C.; Shendure, J.; Ruuska, S.; Koerper, M.A.; et al. Novel approach to genetic analysis and results in 3000 hemophilia patients enrolled in the My Life, Our Future initiative. Blood Adv. 2017, 1, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyand, A.C.; Pipe, S.W. New therapies for hemophilia. Blood 2019, 133, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, H.; Keren-Politansky, A.; Crispel, Y.; Yanovich, C.; Asayag, K.; Nadir, Y. Augmented Degradation of Factors VIII and IX in the Intermittent Movement State. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Switzer, M.E.; McKee, P.A. Some effects of calcium on the activation of human factor VIII/Von Willebrand factor protein by thrombin. J. Clin. Investig. 1977, 60, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rock, G.A.; Cruickshank, W.H.; Tackaberry, E.S.; Ganz, P.R.; Palmer, D.S. Stability of VIII:C in plasma: The dependence on protease activity and calcium. Thromb. Res. 1983, 29, 521–535. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marlar, R.A.; Strandberg, K.; Shima, M.; Adcock, D.M. Clinical utility and impact of the use of the chromogenic vs one-stage factor activity assays in haemophilia A and B. Eur. J. Haematol. 2020, 104, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, B.J. SDS Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis of Proteins. Methods Mol. Biol. 1984, 1, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hagiwara, M. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and western blotting analyses via colored stacking gels. Anal. Biochem. 2022, 652, 114751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bristow, S.M.; Gamble, G.D.; Stewart, A.; Horne, A.M.; Reid, I.R. Acute effects of calcium supplements on blood pressure and blood coagulation: Secondary analysis of a randomised controlled trial in post-menopausal women. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 1868–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolland, M.J.; Grey, A.; Avenell, A.; Gamble, G.D.; Reid, I.R. Calcium supplements with or without vitamin D and risk of cardiovascular events: Reanalysis of the Women’s Health Initiative limited access dataset and meta-analysis. BMJ 2011, 342, d2040. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lerstad, G.; Brodin, E.E.; Svartberg, J.; Jorde, R.; Brox, J.; Braekkan, S.K.; Hansen, J.B. Associations between serum levels of calcium, parathyroid hormone and future risk of venous thromboembolism: The Tromso study. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 176, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kamphuisen, P.W.; Eikenboom, J.C.; Bertina, R.M. Elevated factor VIII levels and the risk of thrombosis. Arterioscler Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2001, 21, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyrle, P.A.; Minar, E.; Hirschl, M.; Bialonczyk, C.; Stain, M.; Schneider, B.; Weltermann, A.; Speiser, W.; Lechner, K.; Eichinger, S. High plasma levels of factor VIII and the risk of recurrent venous thromboembolism. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, P.V.; Rawley, O.; Smith, O.P.; O’Donnell, J.S. Elevated factor VIII levels and risk of venous thrombosis. Br. J. Haematol. 2012, 157, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavigne, G.; Mercier, E.; Quere, I.; Dauzat, M.; Gris, J.C. Thrombophilic families with inheritably associated high levels of coagulation factors VIII, IX and XI. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2003, 1, 2134–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cohen, H.; Keren-Politansky, A.; Crispel, Y.; Yanovich, C.; Asayag, K.; Nadir, Y. Calcium Prevents Enhanced Degradation of Factor VIII in the Condition of Motion. Biology 2023, 12, 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12111388
Cohen H, Keren-Politansky A, Crispel Y, Yanovich C, Asayag K, Nadir Y. Calcium Prevents Enhanced Degradation of Factor VIII in the Condition of Motion. Biology. 2023; 12(11):1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12111388
Chicago/Turabian StyleCohen, Haim, Anat Keren-Politansky, Yonatan Crispel, Chen Yanovich, Keren Asayag, and Yona Nadir. 2023. "Calcium Prevents Enhanced Degradation of Factor VIII in the Condition of Motion" Biology 12, no. 11: 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12111388
APA StyleCohen, H., Keren-Politansky, A., Crispel, Y., Yanovich, C., Asayag, K., & Nadir, Y. (2023). Calcium Prevents Enhanced Degradation of Factor VIII in the Condition of Motion. Biology, 12(11), 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12111388



