In Silico and In Vitro Analysis of MAP3773c Protein from Mycobacterium avium subsp. Paratuberculosis
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
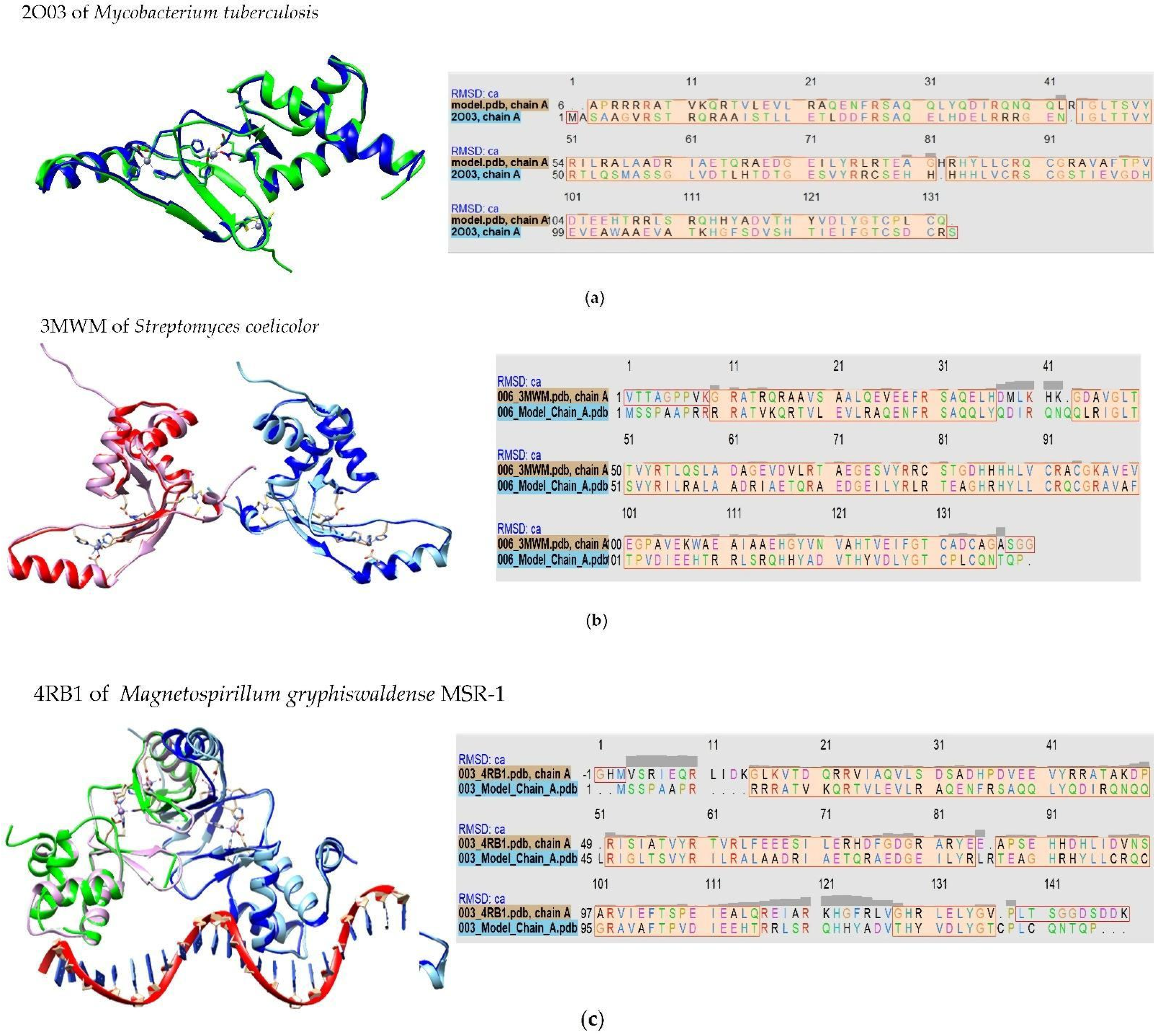
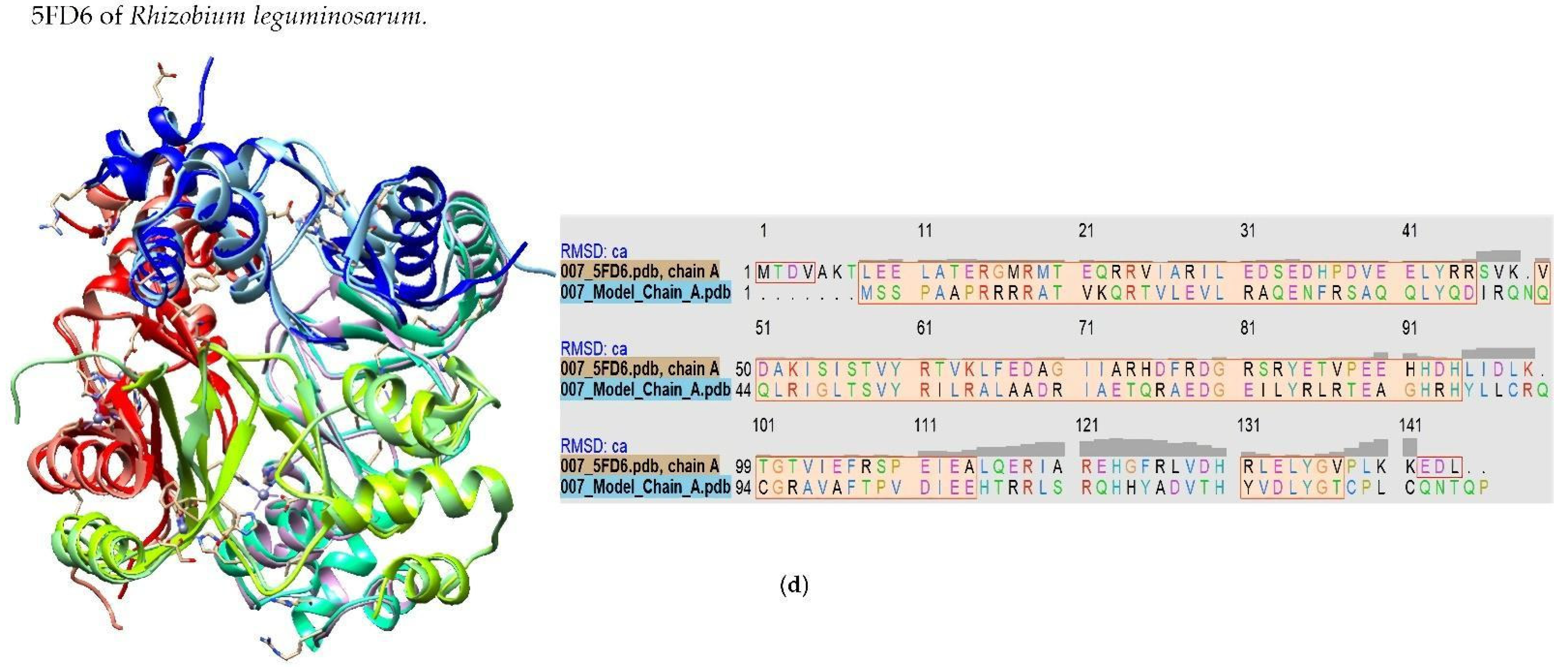
2.1. Model-Based Prediction of the Molecular Structure of MAP3773c
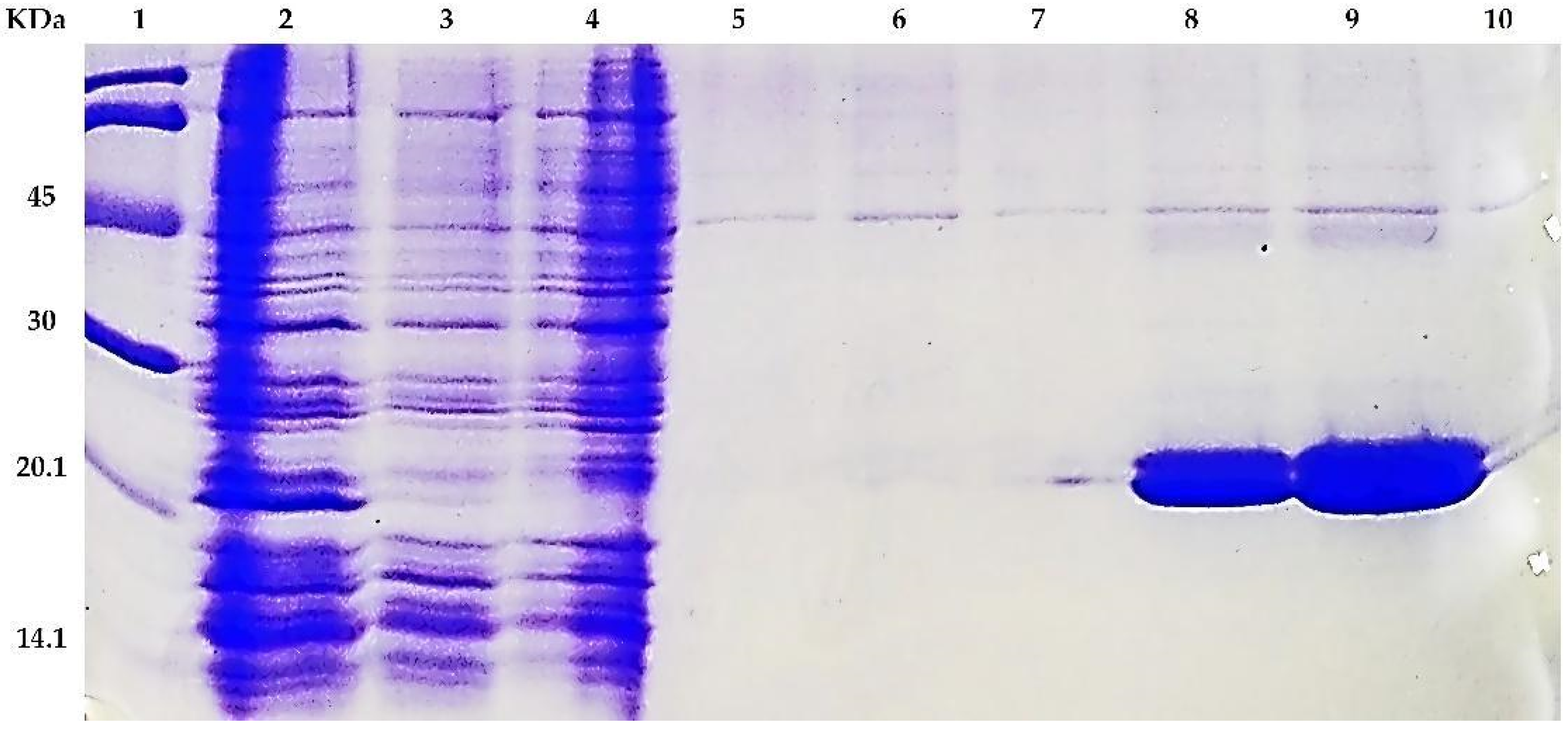
2.2. Cloning and Expression of map3773c
2.3. Protein Purification Conditions and Metal Oligomerization
2.4. Circular Dichroism (CD)
2.5. Cross-Linking and Structural Detection of Zinc
2.6. Western Blotting
2.7. BN-SDS PAGE and BN-PAGE Immunoblotting
2.8. Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS)
2.8.1. Optimization of the Mass Spectrometer (External Calibration)
2.8.2. Spectrometric Analysis
2.8.3. MALDI-TOF MS, (Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time of Flight) MS
3. Results and Discussion
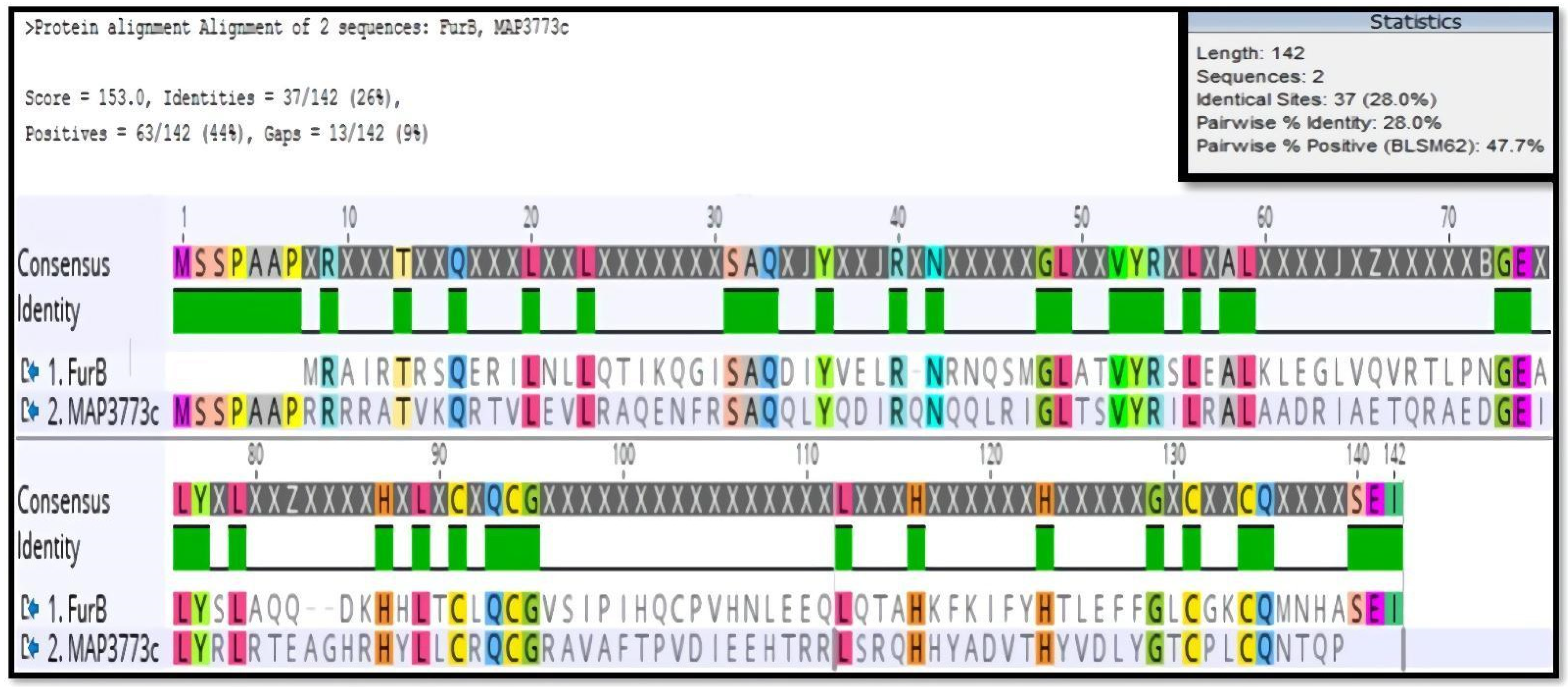
3.1. Homology of MAP3773c to Other Proteins of the FUR Family
3.2. Inferring Metal Binding Sites (Zn2+ and Mn2+) in MAP3773c Protein
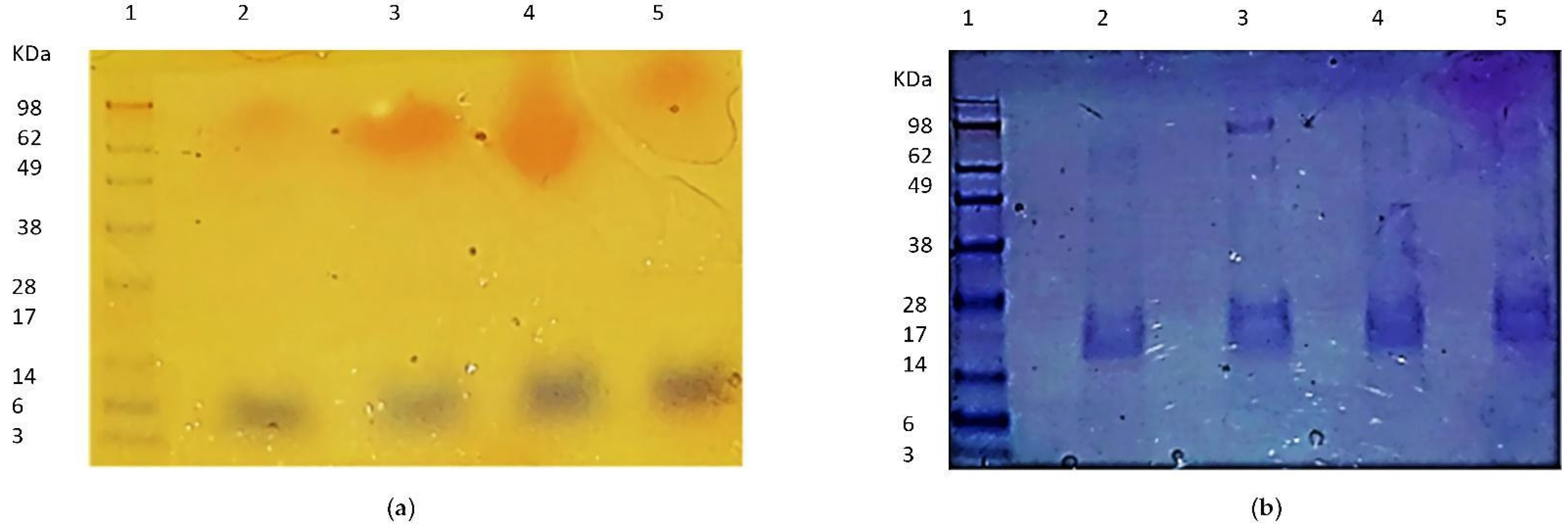
3.3. Expression, Purification and Oligomerization of MAP3773c
3.4. Circular Dichroism, Crosslinking, and PAR Staining
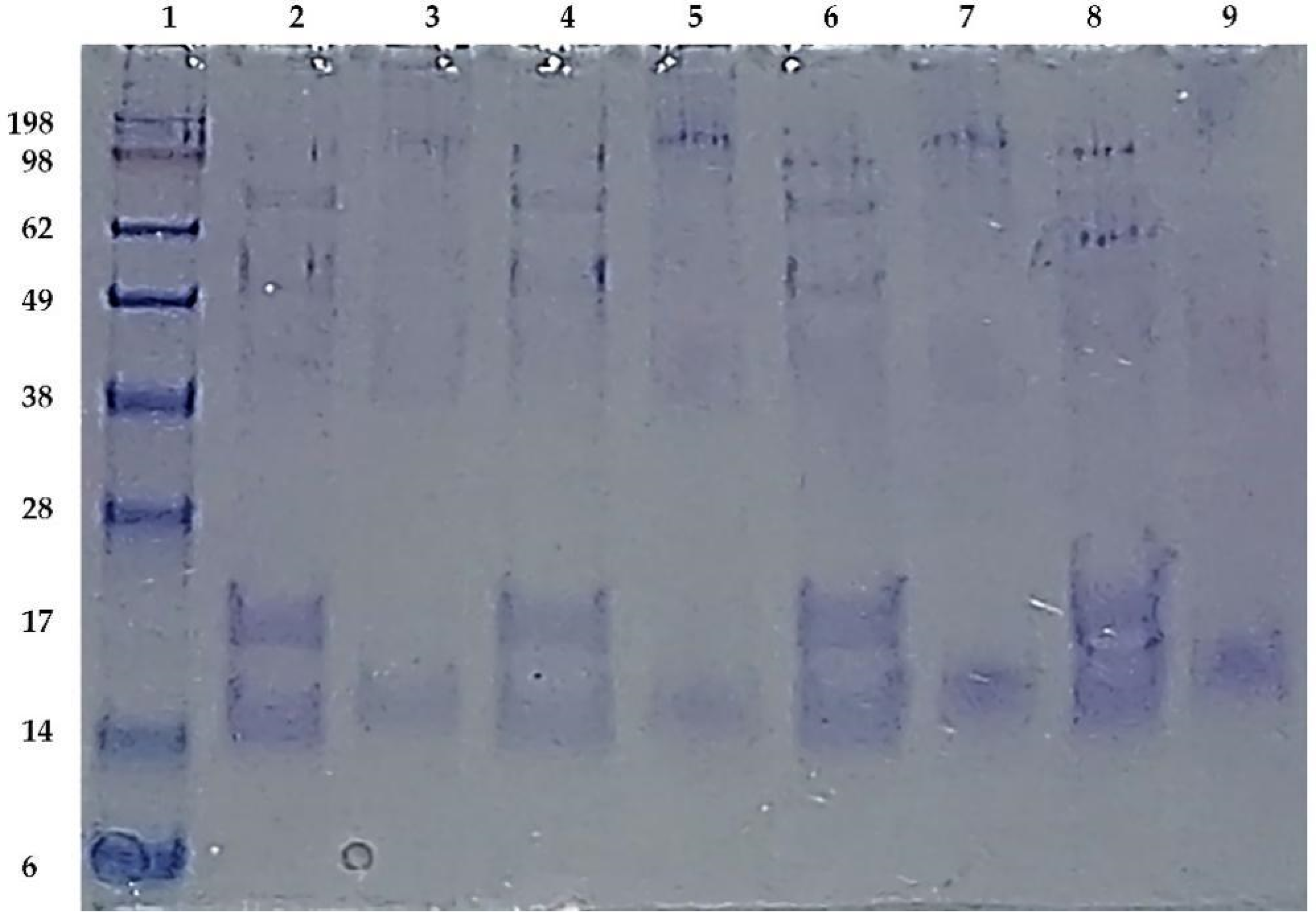
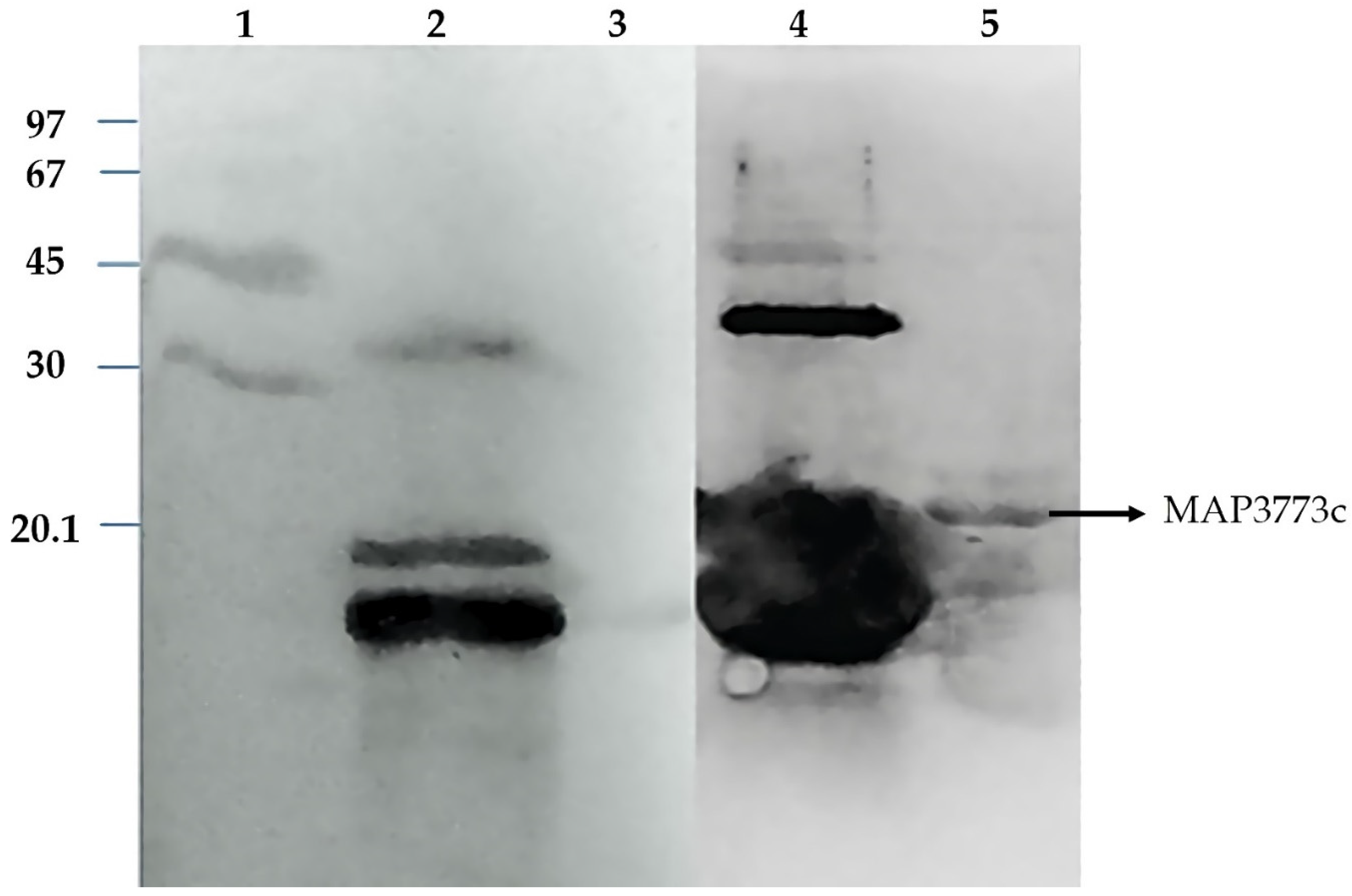
3.5. Western Blotting Analysis of Map3773c
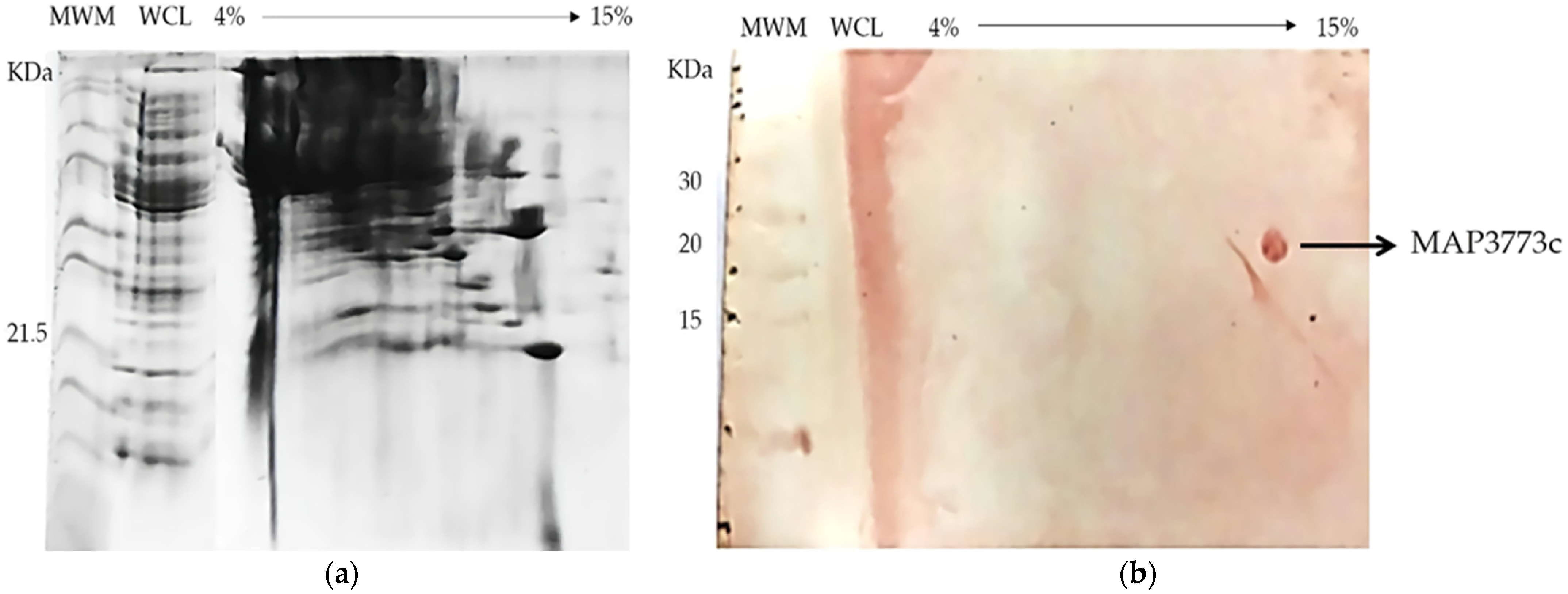
3.6. BN-SDS PAGE and BN PAGE Immunoblotting
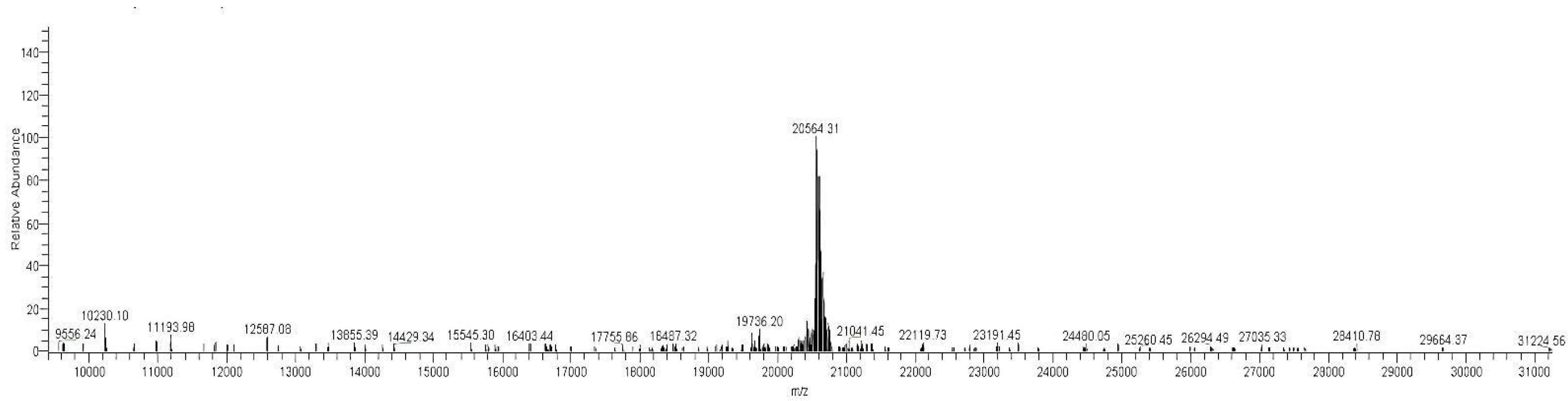
3.7. LC-MS of the Purified Monomer of MAP3773c
3.8. Oligomeric State of the Fur Protein, MALDI-TOF MS
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bannantine, J.P.; Barletta, R.G.; Stabel, J.R.; Paustian, M.L.; Kapur, V. Application of the Genome Sequence to Address Concerns That Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis. Might Be a Foodborne Pathogen. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2004, 1, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, J.E. Zinc proteins: Enzymes, storage proteins, transcription factors, and replication proteins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1992, 61, 897–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, L.D.; Skaar, E.P. Transition Metals and Virulence in Bacteria. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2016, 50, 67–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreini, C.; Bertini, I.; Cavallaro, G.; Holliday, G.L.; Thornton, J.M. Metal ions in biological catalysis: From enzyme databases to general principles. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 13, 1205–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zackular, J.P.; Chazin, W.J.; Skaar, E.P. Nutritional Immunity: S100 Proteins at the Host-Pathogen Interface. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 18991–18998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Helmann, J.D. Functional specialization within the Fur family of metalloregulators. Biometals 2007, 20, 485–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stratmann, J.; Strommenger, B.; Goethe, R.; Dohmann, K.; Gerlach, G.F.; Stevenson, K.; Li, L.L.; Zhang, Q.; Kapur, V.; Bull, T.J. A 38-Kilobase Pathogenicity Island Specific for Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis. Encodes Cell Surface Proteins Expressed in the Host. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escolar, L.; Pérez, M.J.; de Lorenzo, V. Opening the Iron Box: Transcriptional Metalloregulation by the Fur Protein. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 6223–6229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, B.M.; Whitmire, J.M.; Merrell, D.S. This Is Not Your Mother’s Repressor: The Complex Role of Fur in Pathogenesis. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 2590–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillat, M.F. The FUR (ferric uptake regulator) superfamily: Diversity and versatility of key transcriptional regulators. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 546, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hantke, K. Members of the Fur Protein Family Regulate Iron and Zinc Transport in E. coli and Characteristics of the Fur-Regulated FhuF Protein. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 4, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hantke, K. Cloning of the repressor protein gene of iron-regulated systems in Escherichia coli K12. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1984, 197, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litwin, C.M.; Boyko, S.A.; Calderwood, S.B. Cloning, sequencing, and transcriptional regulation of the Vibrio cholerae fur gene. J. Bacteriol. 1992, 174, 1897–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luna, B.M.; Hernández, J.A.; Bes, M.T.; Fillat, M.F.; Peleato, M.L. Identification of a Ferric uptake regulator from Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 254, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochsner, U.A.; Vasil, A.I.; Vasil, M.L. Role of the ferric uptake regulator of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the regulation of siderophores and exotoxin. An expression: Purification and activity on iron-regulated promoters. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 7194–7201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delany, I.; Spohn, G.; Rappuoli, R.; Scarlato, V. The Fur repressor controls transcription of iron-activated and -repressed genes in Helicobacter pylori. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 42, 1297–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkhoff-Schweizer, R.R.; Schryvers, A.B.; Schweizer, H.P. Cloning and sequence analysis of the fur gene encoding an iron-regulatory protein of Neisseria meningitidis. Gene 1994, 141, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, C.; Haentjens, S.; Bissinger, M.C.; Courcol, R.J. Characterization of the Acinetobacter baumannii Fur regulator: Cloning and sequencing of the fur homolog gene. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1999, 170, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledala, N.; Pearson, S.L.; Wilkinson, B.J.; Jayaswal, R.K. Molecular characterization of the Fur protein of Listeria monocytogenes. Microbiology 2007, 153, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janagama, H.K.; Senthilkumar, T.M.; Bannantine, J.P.; Rodriguez, G.M.; Smith, I.; Paustian, M.L.; McGarvey, J.A.; Sreevatsan, S. Identification and functional characterization of the iron-dependent regulator (IdeR) of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis. Microbiology 2009, 155, 3683–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Alexander, D.C.; Turenne, C.Y.; Behr, M.A. Insertion and deletion events that define the pathogen Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Moolji, J.; Dufort, A.; Staffa, A.; Domenech, P.; Reed, M.B.; Behr, M.A. Iron Acquisition in Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis. J. Bacteriol. 2016, 198, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoyama, F.M.; Janetanakit, T.; Bannantine, J.P.; Barletta, R.G.; Sreevatsan, S. Elucidating the Regulon of a Fur-like Protein in Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis (MAP). Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drozdetskiy, A.; Cole, C.; Procter, J.; Barton, G.J. JPred4: A protein secondary structure prediction server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W389–W394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Lasker, K.; Schneidman-Duhovny, D.; Webb, B.; Huang, C.C.; Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Meng, E.C.; Sali, A.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera, MODELLER, and IMP: An integrated modeling system. J. Struct. Biol. 2012, 179, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedretti, A.; Villa, L.; Vistoli, G. VEGA—An open platform to develop chemi- bio- informatics applications, using plug-in architecture and script programming. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2004, 18, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedretti, A.; Villa, L.; Vistoli, G. Vega: A versatile program to convert, handle and visualize molecular structure on windows-based PCs. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2002, 21, 47–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.F.; Cheng, C.W.; Shih, C.S.; Hwang, J.K.; Yu, C.S.; Lu, C.H. MIB: Metal Ion-Binding Site Prediction and Docking Server. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2016, 56, 2287–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quest CalculateTM Peptide and Protein Molecular Weight Calculator. AAT.Bioquest. Available online: https://www.aatbio.com/tools/calculate-peptide-and-protein-molecular-weight-mw (accessed on 23 June 2022).
- Pellicer, S.; Bes, M.T.; González, A.; Neira, J.L.; Peleato, M.L.; Fillat, M.F. High-recovery one-step purification of the DNA-binding protein Fur by mild guanidinium chloride treatment. Process Biochem. 2010, 45, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitmore, L.; Wallace, B.A. Protein secondary structure analyses from circular dichroism spectroscopy: Methods and reference databases. Biopolymers 2008, 89, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitmore, L.; Wallace, B.A. DICHROWEB, an online server for protein secondary structure analyses from circular dichroism spectroscopic data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W668–W673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchan, D.W.A.; Minneci, F.; Nugent, T.C.O.; Bryson, K.; Jones, D.T. Scalable web services for the PSIPRED Protein Analysis Workbench. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, W349–W357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Helmann, J.D. Biochemical characterization of the structural Zn2+ site in the Bacillus subtilis peroxide sensor PerR. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 23567–23578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towbin, H.; Staehelin, T.; Gordon, J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: Procedure and some applications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 4350–4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiala, G.J.; Schamel, W.W.; Blumenthal, B. Blue native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (BN-PAGE) for analysis of multiprotein complexes from cellular lysates. J. Vis. Exp. 2011, 48, e2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Wang, J.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, K.M.; Geer, C.R.; Gonzales, N.R.; Gwadz, M.; Hurwitz, I.D.; Marchler, H.G.; Song, S.J.; et al. CDD/SPARCLE: The conserved domain database in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D265–D268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucarelli, D.; Russo, S.; Garman, E.; Milano, A.; Meyer, W.; Pohl, E. Crystal structure and function of the zinc uptake regulator FurB from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 9914–9922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.H.; Jung, H.J.; An, Y.J.; Cho, Y.B.; Cha, S.S.; Roe, J.H. Graded expression of zinc-responsive genes through two regulatory zinc-binding sites in Zur. Proc Natl Acad Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5045–5050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Machado, A.C.; Chiu, T.P.; Feng, C.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, L.; Qi, L.; et al. Mechanistic insights into metal ion activation and operator recognition by the ferric uptake regulator. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protein Data Bank. Available online: https://www.rcsb.org/structure/5fd6 (accessed on 3 August 2021).
- Kaur, P.; Sharma, S.; Choudhury, S.D.; Singh, D.; Sharma, S.; Gadhave, K.; Garg, N.; Choudhury, D. Insulin-copper quantum clusters preparation and receptor targeted bioimaging. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 188, 110785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sein-Echaluce, V.C.; González, A.; Napolitano, M.; Luque, I.; Barja, F.; Peleato, M.L.; Fillat, M.F. Zur (FurB) is a key factor in the control of the oxidative stress response in Anabaena sp. PCC 7120. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 2006–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikhaylina, A.; Ksibe, A.Z.; Scanlan, D.J.; Blindauer, C.A. Bacterial zinc uptake regulator proteins and their regulons. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2018, 46, 983–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.H.; Lee, K.L.; Shin, J.H.; Cho, Y.B.; Cha, S.S.; Roe, J.H. Zinc-dependent regulation of zinc import and export genes by Zur. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delany, I.; Ieva, R.; Alaimo, C.; Rappuoli, R.; Scarlato, V. The Iron-Responsive Regulator Fur Is Transcriptionally Autoregulated and Not Essential in Neisseria meningitidis. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 6032–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, S.M.; Jess, T.J.; Price, N.C. How to study proteins by circular dichroism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2005, 1751, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupane, D.P.; Jacquez, B.; Sundararajan, A.; Ramaraj, T.; Schilkey, F.D.; Yukl, E.T. Zinc-Dependent Transcriptional Regulation in Paracoccus denitrificans. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenfield, N. Using circular dichroism spectra to estimate protein secondary structure. Nat Protoc. 2006, 1, 2876–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, M.C.; Siuzdak, G. Biochemical mass spectrometry: Worth the weight? Chem. Biol. 1996, 3, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]




| Secondary Structure of the Recombinant Protein MAP3773c | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Alpha helix | Folded Sheet-Beta | Twists | Disordered |
| 50% | 20% | 7% | 23% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernández-Guevara, E.; Gutiérrez-Pabello, J.A.; Quintero-Chávez, K.; Brito-Perea, M.D.C.; Hurtado-Ayala, L.A.; Ibarra-Molina, G.; Cortez-Hernández, O.; Dueñas-Mena, D.L.; Fernández-Otal, Á.; Fillat, M.F.; et al. In Silico and In Vitro Analysis of MAP3773c Protein from Mycobacterium avium subsp. Paratuberculosis. Biology 2022, 11, 1183. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11081183
Hernández-Guevara E, Gutiérrez-Pabello JA, Quintero-Chávez K, Brito-Perea MDC, Hurtado-Ayala LA, Ibarra-Molina G, Cortez-Hernández O, Dueñas-Mena DL, Fernández-Otal Á, Fillat MF, et al. In Silico and In Vitro Analysis of MAP3773c Protein from Mycobacterium avium subsp. Paratuberculosis. Biology. 2022; 11(8):1183. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11081183
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernández-Guevara, Esteban, José A. Gutiérrez-Pabello, Kaina Quintero-Chávez, Mirna Del Carmen Brito-Perea, Lilia Angélica Hurtado-Ayala, German Ibarra-Molina, Omar Cortez-Hernández, Dulce Liliana Dueñas-Mena, Ángela Fernández-Otal, María F. Fillat, and et al. 2022. "In Silico and In Vitro Analysis of MAP3773c Protein from Mycobacterium avium subsp. Paratuberculosis" Biology 11, no. 8: 1183. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11081183
APA StyleHernández-Guevara, E., Gutiérrez-Pabello, J. A., Quintero-Chávez, K., Brito-Perea, M. D. C., Hurtado-Ayala, L. A., Ibarra-Molina, G., Cortez-Hernández, O., Dueñas-Mena, D. L., Fernández-Otal, Á., Fillat, M. F., & Landeros-Sánchez, B. (2022). In Silico and In Vitro Analysis of MAP3773c Protein from Mycobacterium avium subsp. Paratuberculosis. Biology, 11(8), 1183. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11081183






