Elevated Serum Levels of IgG4 in Patients with Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction: A Prospective Controlled Study
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Laboratory Measurements
2.3. Statistical Methods
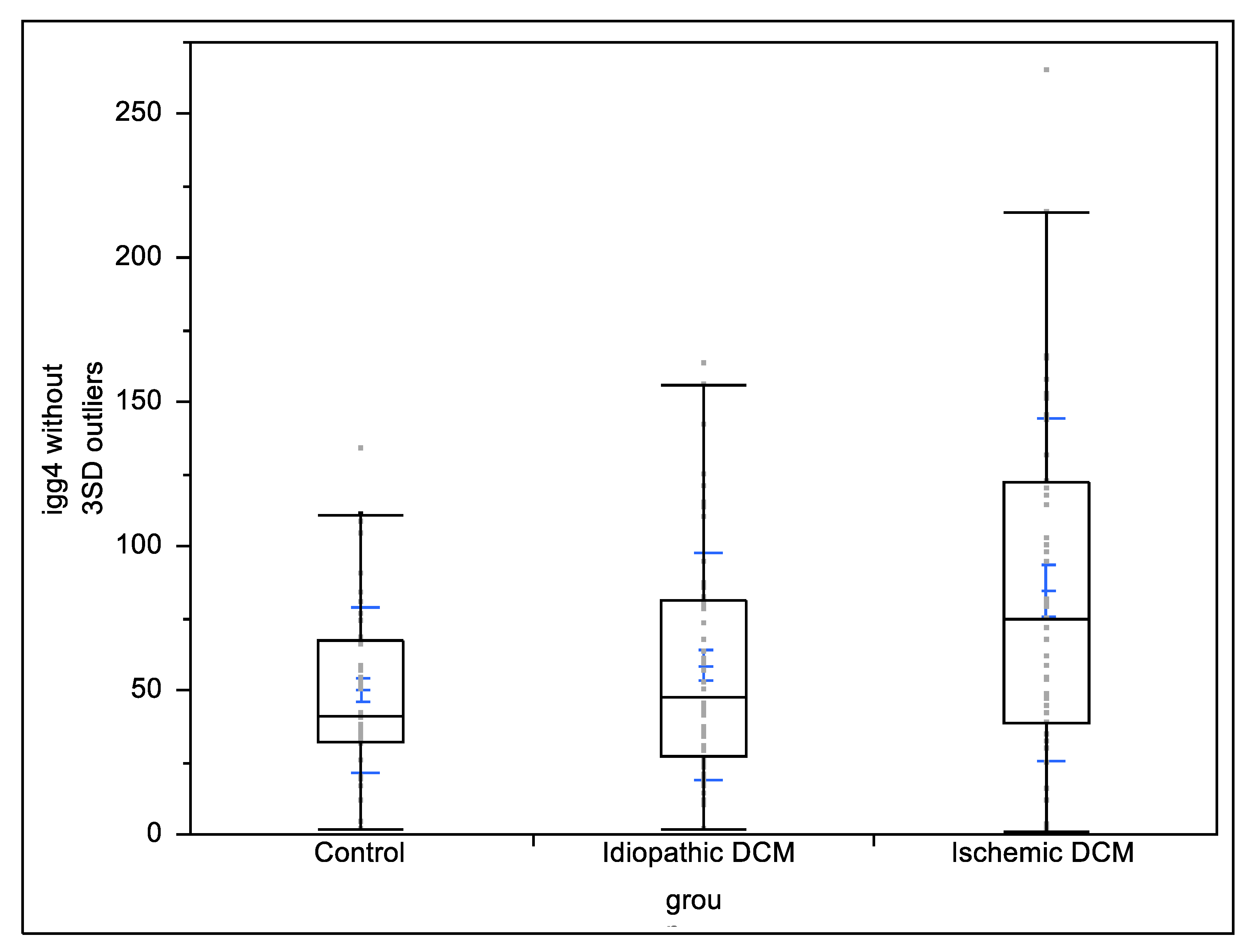
3. Results
The Results of the Study
4. Discussion
4.1. Discussion and Interpretation of the Results
4.2. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weintraub, R.G.; Semsarian, C.; Macdonald, P. Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Lancet 2017, 90, 400–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, P.; Andersson, B.; Arbustini, E.; Bilinska, Z.; Cecchi, F.; Charron, P.; Dubourg, O.; Kuhl, U.; Maisch, B.; McKenna, W.J.; et al. Classification of the cardiomyopathies: A position statement from the European Society of Cardiology Working Group on Myocardial and Pericardial Diseases. Eur. Heart J. 2008, 29, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.O.; Stehlik, J.; Edwards, L.B.; Aurora, P.; Christie, J.D.; Dobbels, F.; Kirk, R.; Kucheryavaya, A.Y.; Rahmel, A.O.; Hertz, M.I. Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: Twenty-sixth Official Adult Heart Transplant Report. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2009, 28, 1007–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codd, M.B.; Sugrue, D.D.; Gersh, B.J.; Melton, L.J., 3rd. Epidemiology of idiopathic dilated and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. A population-based study in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1975–1984. Circulation 1989, 80, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, L.T.; Virmani, R.; Chapman, N.M.; Frustaci, A.; Rodeheffer, R.J.; Cunningham, M.W.; McNamara, D.M. National Institutes of Health-sponsored workshop on inflammation and immunity in dilated cardiomyopathy. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2006, 81, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dec, G.W.; Palacios, I.F.; Fallon, J.T.; Aretz, H.T.; Mills, J.; Lee, D.C.; Johnson, R.A. Active myocarditis in the spectrum of acute dilated cardiomyopathies. N. Engl. J. Med. 1985, 312, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrillo, J.E.; Cunnion, R.E.; Epstein, S.E.; Parker, M.M.; Suffredini, A.F.; Brenner, M.; Schaer, G.L.; Palmeri, S.T.; Cannon, R.O.; Alling, D.; et al. A prospective, randomized, controlled trial of prednisone for dilated cardiomyopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 1989, 321, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, D.M.; Holubkov, R.; Starling, R.C.; Dec, G.W.; Loh, E.; Torre-Amione, G.; Gass, A.; Janosko, K.; Tokarczyk, T.; Kessler, P.; et al. A controlled trial of intravenous immune globulin in recent onset dilated cardiomyopathy. Circulation 2001, 103, 2254–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braunwald, E. Biomarkers in heart failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 2148–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, I.S.; Latini, R.; Florea, V.G.; Kuskowski, M.A.; Rector, T.; Masson, S.; Signorini, S.; Mocarelli, P.; Hester, A.; Glazer, R.; et al. C-reactive protein in heart failure: Prognostic value and the effect of valsartan. Circulation 2005, 112, 1428–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamisawa, T.; Zen, Y.; Pillai, S.; Stone, J.H. IgG4-related disease. Lancet 2015, 385, 1460–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasashima, S.; Zen, Y. IgG4-related inflammatory abdominal aortic aneurysm. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2011, 23, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, T.; Morita, Y.; Ishiki, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Uzu, T.; Kashiwagi, A.; Horie, M.; Asai, T. Constrictive pericarditis as an emerging manifestation of hyper-IgG4 disease. Int. J. Cardiol. 2008, 130, e100–e101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, A.; Nagai, R.; Saito, K.; Imai, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Hosoya, Y.; Takeda, N.; Hirano, K.; Koike, K.; Enomoto, Y.; et al. Idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis, inflammatory aortic aneurysm, and inflammatory pericarditis-retrospective analysis of 11 case histories. J. Cardiol. 2012, 59, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, M.N.; Langguth, D.; Hart, G.; Heiner, M.; Rafter, A.; Fleming, S.J.; Scalia, G.M. IgG4-related systemic disease with coronary arteritis and aortitis, causing recurring critical coronary ischemia. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 201, 33–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ruggio, A.; Iaconelli, A.; Panaioli, E.; Bernardini, F.; Tinelli, G.; Savino, G.; Infusino, F.; Leccisotti, L.; Manna, R.; Crea, F. Case Report Coronary Artery Aneurysms Presenting as Acute Coronary Syndrome: An Unusual Case of IgG4-Related Disease Vascular Involvement. Can. J. Cardiol. 2018, 34, 1088.e7–1088.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, J.; Takano, H.; Shimizu, W. IgG4-related periarteritis in the coronary artery and subclinical pericarditis assessed the presence and monitoring of therapy response by PET and CT scan. BMJ Case Rep. 2018, 2018, 225172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, H.; Satoh, H.; Yamashita, T.; Shinshi, Y.; Kikuchi, K.; Sasaki, S.; Matsui, Y. Immunoglobulin G4-Related Disease of the Heart Causing Aortic Regurgitation and Heart Block. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2013, 95, e151–e153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, B.J.; Delev, N.G.; Pasternack, G.R.; Halushka, M.K. Novel cause of sudden cardiac death in IgG4-related disease. Circulation 2012, 125, 2956–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, A.; Tanaka, T.; Hirano, K.; Koike, K.; Komuro, I. Immunoglobulin G4-related coronary periarteritis and luminal stenosis in a patient with a history of autoimmune pancreatitis. Intern. Med. 2017, 56, 2445–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sakamoto, A.; Ishizaka, N.; Saito, K.; Imai, Y.; Morita, H.; Koike, K.; Kohro, T.; Nagai, R. Serum levels of IgG4 and soluble interleukin-2 receptor in patients with coronary artery disease. Clin. Chim. Acta 2012, 413, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamano, H.; Kawa, S.; Horiuchi, A.; Unno, H.; Furuya, N.; Akamatsu, T.; Fukushima, M.; Nikaido, T.; Nakayama, K.; Usuda, N.; et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamisawa, T.; Egawa, N.; Nakajima, H. Autoimmune pancreatitis is a systemic autoimmune disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 98, 2811–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guma, M.; Firestein, G.S. IgG4-related diseases. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2012, 26, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, V.; Zen, Y.; Chan, J.K.; Yi, E.E.; Sato, Y.; Yoshino, T.; Klöppel, G.; Heathcote, J.G.; Khosroshahi, A.; Ferry, J.A.; et al. Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod. Pathol. 2012, 25, 1181–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umehara, H.; Okazaki KSatoh-Nakamura, T.; Nakajima, A.; Kawano, M.; Mimori, T.; Chiba, T. Current approach to the diagnosis of IgG4-related disease—Combination of comprehensive diagnostic and organ-specific criteria. Mod. Rheumatol. 2017, 27, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamisawa, T.; Shimosegawa, T.; Okazaki, K.; Nishino, T.; Watanabe, H.; Kanno, A.; Okumura, F.; Nishikawa, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Ichiya, T.; et al. Standard steroid treatment for autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut 2009, 58, 1504–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, J.H.; Zen, Y.; Deshpande, V. IgG4-related disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, T.; Hamasaki, A.; Kuroda, Y.; Sadahiro, M.; Tamazawa, N.; Ohe, R.; Yamakawa, M. Immunoglobulin G Subclass 4-Related Lymphoplasmacytic Thoracic Aortitis in a Patient with Acute Type a Aortic Dissection. Ann. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2018, 24, 208–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, V.; Connolly, C.; Stuklis, R. IgG4-Aortopathy: An Underappreciated Cause of Non-Infectious Thoracic Aortitis. Heart Lung Circ. 2017, 26, e79–e81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.Y.; Eun, Y.N.; Jeong, H.; Park, T.K.; Kim, H.G.; Lee, J.; Jang, S.Y.; Kim, J.-S.; Koh, E.-M.; Kim, D.-K.; et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of 61 patients with chronic periaortitis including IgG4-related and non-IgG4-related cases. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 20, 1751–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, K.; Yamada, K.; Konno, T.; Inoue, D.; Uno, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Okuda, M.; Oe, K.; Kawano, M.; Yamagishi, M. Pericardial Involvement in IgG4-related Disease. Intern. Med. 2015, 54, 1231–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.W.; Son, I.J.; Lee, S.; Jeong, H.J.; Kim, H.M.; Koh, B.S.; Park, S.H. A Case of Constrictive Pericarditis due to Immunoglobulin G4-Related Disease. Korean Circ. J. 2015, 45, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendo, S.; Saegusa, J.; Morinaga, Y.; Kawakami, F.; Kogata, Y.; Kageyama, G.; Morinobu, A. IgG4-related disease manifesting as pericarditis with elevated adenosine deaminase and IL-10 levels in pericardial fluid. Mod. Rheumatol. 2017, 27, 894–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibe, T.; Nakamura, T.; Taniguchi, Y.; Momomura, S.I. IgG4-related effusive constrictive pericarditis. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 17, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzic, B.; Spasic, M.; Djuric, P.; Vasilevic, V.; Radjen, S.; Mjuskovic, M. Retroperitoneal fibrosis and constrictive pericarditis-IgG4-related diseases: A case report. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 13, 3603–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, M.A.; Aubry, M.C.; Pflederer, B.R. A Case of IgG4-Related Aortitis and Pericarditis: Diagnostic Challenges and Natural History. Am. J. Case Rep. 2018, 19, 1232–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleszewski, H.J.; Tazelaar, H.D.; Horcher, H.M.; Hinkamp, T.J.; Conte, J.V.; Porterfield, J.K.; Halushka, M.K. IgG4-related disease of the aortic valve: A report of two cases and review of the literature. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2015, 24, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besik, J.; Pirk, J.; Netuka, I.; Szarszoi, O.; Marek, T.; Urban, M.; Honsova, E.; Laco, J. Aortic and Mitral Valve Replacement Due to Extensive Inflammatory Immunoglobulin G4–Related Pseudotumor. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2015, 100, 1439–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruls, S.; Courtois, A.; Delvenne, P.; Hustinx, R.; Moutschen, M.; Leval, L.; Defraigne, J.-O.; Sakalihasan, N. IgG4-Related Disease Causing Rapid Evolution of a Severe Aortic Valvular Stenosis. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2017, 103, e239–e240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Thiong, B.K.; Fishbein, G.A.; Brahn, E. IgG4-related disease of the mitral valve demonstrated by immunohistochemistry. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 1384–1385. [Google Scholar]
- Hourai, R.; Kasashima, S.; Fujita, S.I.; Sohmiya, K.; Daimon, M.; Hirose, Y.; Katsumata, T.; Kanki, S.; Ozeki, M.; Ishizaka, N. Case of Aortic Stenosis with Serum IgG4 Elevation, and IgG4-Positive Plasmacytic Infiltration in the Aortic Valve, Epicardium, and Aortic Adventitia. Int. Heart J. 2018, 59, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbajal, H.; Waters, L.; Popovich, J.; Boniuk, M.; Chevez-Barrios, P.; Marcus, D.M.; Sessoms, S. IgG4-related cardiac disease. Methodist DeBakey Cardiovasc. J. 2013, 9, 230–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.G.; Koh, M.J.; Yoon, N.Y.; Joung, B.Y.; Kim, S.H. IgG4-Related Sclerosing Disease Involving the Superior Vena Cava and the Atrial Septum of the Heart. Yonsei Med. J. 2013, 54, 1285–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, M.; Sakaguchi, T.; Miyagawa, S.; Nishi, H.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Fukushima, S.; Kawamura, A.; Ueno, T.; Ishibashi-Ueda, H.; Sawa, Y. Right Ventricular Outflow Tract Obstruction Due to Immunoglobulin G4-Related Disease. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2017, 103, e235–e237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yano, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Mochizuki, A.; Ogawa, T.; Nagano, N.; Fujito, T.; Nishida, J.; Nagahara, D.; Abe, K.; Miki, T.; et al. Successful Transcatheter Diagnosis and Medical Treatment of Right Atrial Involvement in IgG4-related Disease. Int. Heart J. 2018, 59, 1155–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, Z.; Peng, P.; Ruan, Y.; Jiang, W.; Wu, Z. Cardiac Mass, Aortic Intramural Hematoma, and IgG4-related Disease: A Case Report. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2016, 35, 208.e5–208.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Ansdell, D.; Brouha, S.; Yen, A. Coronary periarteritis in a patient with IgG4-related disease. J. Radiol. Case Rep. 2015, 9, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Keraliya, A.R.; Murphy, D.J.; Aghayev, A.; Steigner, M.L. IgG4-Related Disease with Coronary Arteritis. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 9, e004583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komiya, Y.; Soejima, M.; Tezuka, D.; Kohsaka, H. Detection and Intervention of Coronary Artery Involvement in Immunoglobulin G4-related Disease. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 57, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikutomi, M.; Matsumura, T.; Iwata, H.; Nishimura, G.; Ishizaka, N.; Hirata, Y.; Ono, M.; Nagai, R. Giant tumorous lesions surrounding the right coronary artery associated with immunoglobulin-G4-related systemic disease. Cardiology 2011, 120, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, N.R.; Anzalone, M.L.; Buja LMElghetany, M.T. Sudden Cardiac Death Due to Coronary Artery Involvement by IgG4-Related Disease a Rare, Serious Complication of a Rare Disease. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2014, 138, 833–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, P.S.; Schultz, T.; Siqueira, S.A.; de Figueiredo Borges, L. Sudden coronary death due to IgG4-related disease. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2013, 22, 505–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, Y.M.; Elliott, P.M.; Arbustini, E.; Adler, Y.; Anastasakis, A.; Bo, M.; Duboc, D.; Gimeno, J.; de Groote, P.; Imazio, M.; et al. Proposal for a revised definition of dilated cardiomyopathy, hypokinetic non-dilated cardiomyopathy, and its implications for clinical practice: Apposition statement of the ESC working group on myocardial and pericardial diseases. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 1850–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Joyce, J.; Margulies, K.B.; Tsuda, T. Enhanced bioactive myocardial transforming growth factor-β in advanced human heart failure. Circulation 2014, 78, 2711–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.; Chen-Tournoux, A.; Picard, M.; van Kimmenade, R.; Januzzi, J.L. Serum levels of the interleukin-1 receptor family member ST2, cardiac structure and function, and long-term mortality in patients with acute dyspnea. Circ. Heart Fail. 2009, 2, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, R.A.; Miller, A.M.; Murphy, G.E.; Clements, S.; Steedman, T.; Connell, J.M.; McInnes, I.B.; Dargie, H.J.; Mcmurray, J.J. Serum soluble ST2: A potential novel mediator in left ventricular and infarct remodeling after acute myocardial infarction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 55, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Januzzi, J.L., Jr.; Peacock, W.F.; Maisel, A.S.; Chae, C.U.; Jesse, R.L.; Baggish, A.L.; O’Donoghue, M.; Sakhuja, R.; Chen, A.A.; van Kimmenade, R.R.; et al. Measurement of the interleukin family member ST2 in patients with acute dyspnea: Results from the PRIDE (Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide Investigation of Dyspnea in the Emergency Department) Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 50, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, E.O.; Shimpo, M.; Hurwitz, S.; Tominaga, S.; Rouleau, J.L.; Lee, R.T. Identification of serum soluble ST2 receptor as a novel heart failure biomarker. Circulation 2003, 107, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felker, G.M.; Fiuzat, M.; Thompson, V.; Shaw, L.K.; Neely, M.L.; Adams, K.F. Soluble ST2 in ambulatory patients with heart failure: Association with functional capacity and long-term outcomes. Circ. Heart Fail. 2013, 6, 1172–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broch, K.; Ueland, T.; Nymo, S.H.; Kjekshus, J.; Hulthe, J.; Muntendam, P.; McMurray, J.J.; Wikstrand, J.; Cleland, J.G.; Aukrust, P.; et al. Soluble ST2 is associated with adverse outcome in patients with heart failure of ischaemic aetiology. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2012, 14, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Ruiz-Ortega, M.; Lorenzo, O.; Ruperez, M.; Esteban, V.; Egido, J. Inflammation and angiotensin II. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2003, 35, 881–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalbeth, N.; Edwards, J.; Fairchild, S.; Callan, M.; Hall, F.C. The non-thiol ACE inhibotr quinapril suppresses inflammatory arthritis. Rheumatology 2005, 44, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Idiopathic DCM | Ischemic DCM | Control | p-Value Idiopathic DCM vs. Ischemic DCM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N = 54 N (%) | N = 44 N (%) | N = 46 N (%) | ||
| Age (years) | 57.1 ± 12.3 | 57.5 ± 10.6 | 44.2 ± 8.6 | 0.9 |
| Gender (male %) | 34 (68%) | 40 (93%) | 20 (43.8%) | 0.01 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 14 (26%) | 21 (48%) | 0 (0%) | 0.03 |
| Hypertension | 32 (59%) | 36 (82%) | 11 (25%) | 0.03 |
| Dyslipidemia | 37 (69%) | 43 (98%) | 3 (6%) | <0.01 |
| Smoker | 15 (28%) | 21 (48%) | 3 (6%) | 0.06 |
| Atrial fibrillation | 6 (11%) | 1 (2%) | 0 (0%) | 0.13 |
| Implanted cardiodefibrillator | 10 (19%) | 13 (30%) | 0 (0%) | 0.23 |
| Resynchronization therapy | 16 (30%) | 13 (30%) | 0 (0%) | 0.99 |
| Diuretics | 40 (74%) | 40 (91%) | 0 (0%) | 0.04 |
| ACEI | 40 (74%) | 28 (64%) | 5 (11%) | 0.3 |
| ARB | 8 (15%) | 15 (34%) | 6 (13%) | 0.03 |
| Digitalis | 4 (7%) | 3 (7%) | 0 (0%) | 1 |
| Beta blockers | 50 (93%) | 43 (98%) | 0 (0%) | 0.4 |
| LVEF (%) | 33.1 ± 8.6 | 32.5 ± 7.0 | N/A | 0.7 |
| NYHA FC | 0.6 | |||
| NYHA FC I | 3 (5.6%) | 1 (2.2%) | 46 (100%) | 0.6 |
| NYHA FC II | 33 (61.1%) | 27 (62.4%) | 0 (0%) | 0.9 |
| NYHA FC III | 18 (33.3%) | 16 (36.4%) | 0 (0%) | 0.9 |
| Overall DCM | Ischemic Cardiomyopathy (n = 44) | Non-Ischemic DCM (n = 54) | Control (n = 46) | p Value Ischemic vs. Non-Ischemic | p Value Ischemic vs. Controls | p Value Non-Ischemic vs. Controls | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total IgG (g/dL) | 1.06 ± 0.78 | 1.19 ± 0.79 | 0.95 ± 0.58 | 1.1 ± 0.86 | 0.18 | 0.97 | 0.23 |
| IgG4 subclass (mg/dL) | 77.41 ± 63.69 | 89.77 ± 67.34 | 67.34 ± 59.94 | 50.28 ± 28.76 | 0.137 | <0.01 | 0.37 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Volodarsky, I.; Anton, A.; Zilberman, L.; Fugenfirov, I.; Neumark, E.; Malnick, S.; Levy, Y.; George, J.; Goland, S. Elevated Serum Levels of IgG4 in Patients with Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction: A Prospective Controlled Study. Biology 2022, 11, 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11081168
Volodarsky I, Anton A, Zilberman L, Fugenfirov I, Neumark E, Malnick S, Levy Y, George J, Goland S. Elevated Serum Levels of IgG4 in Patients with Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction: A Prospective Controlled Study. Biology. 2022; 11(8):1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11081168
Chicago/Turabian StyleVolodarsky, Igor, Anamaria Anton, Liaz Zilberman, Irina Fugenfirov, Eran Neumark, Stephen Malnick, Yair Levy, Jacob George, and Sorel Goland. 2022. "Elevated Serum Levels of IgG4 in Patients with Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction: A Prospective Controlled Study" Biology 11, no. 8: 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11081168
APA StyleVolodarsky, I., Anton, A., Zilberman, L., Fugenfirov, I., Neumark, E., Malnick, S., Levy, Y., George, J., & Goland, S. (2022). Elevated Serum Levels of IgG4 in Patients with Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction: A Prospective Controlled Study. Biology, 11(8), 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11081168





