Molecular Mechanisms and Key Processes in Interstitial, Hemorrhagic and Radiation Cystitis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
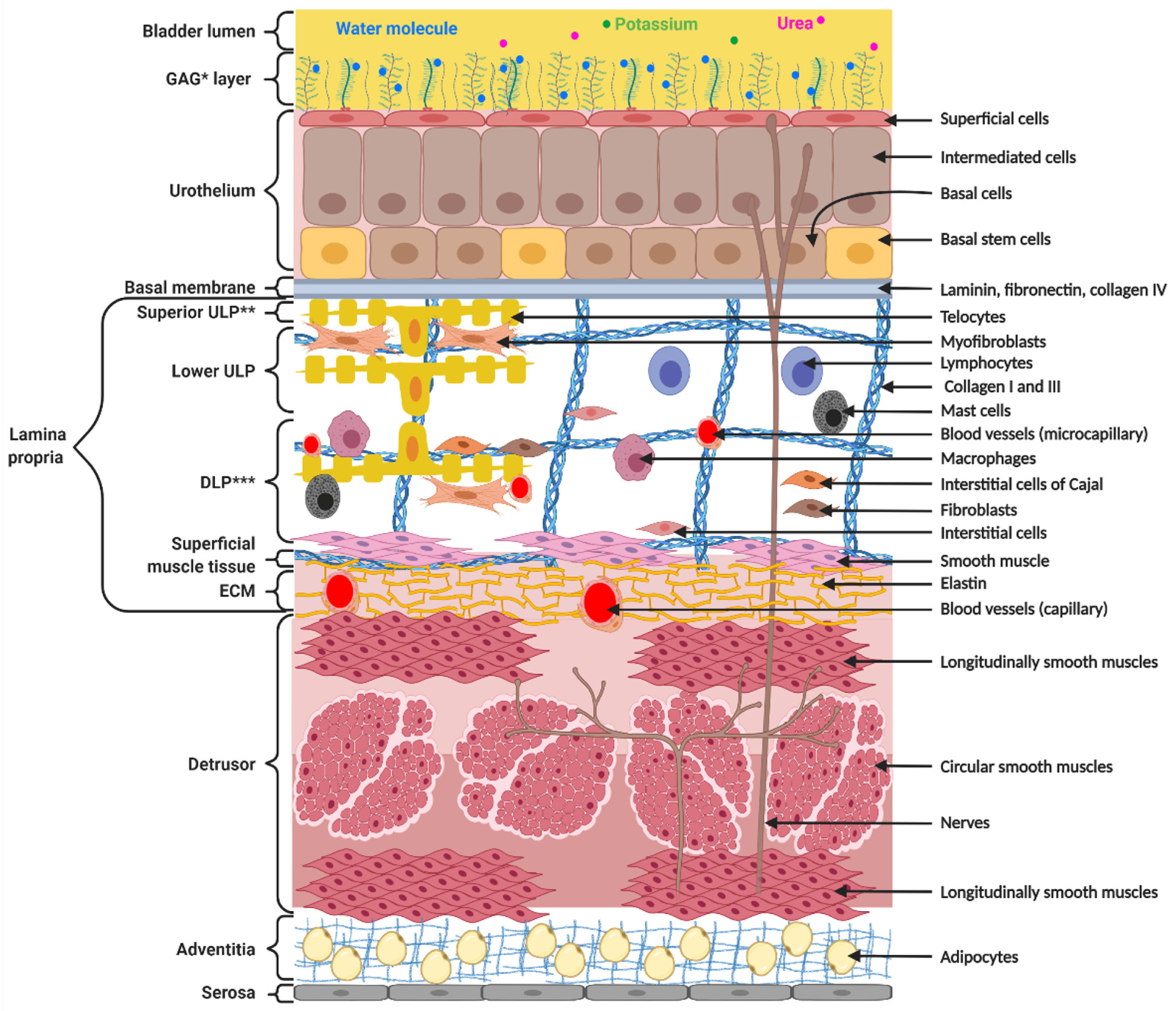
2. Structure and Function of the Bladder Wall
3. Discussion
3.1. Etiology, Prevalence and Clinical Features of Abacterial Cystitis
3.1.1. Interstitial Cystitis
3.1.2. Hemorrhagic Cystitis
3.1.3. Chronic Radiation Cystitis
4. Molecular Mechanisms in Cystitis
4.1. Bladder Mucosa Dysfunction
4.1.1. Common Mechanism
4.1.2. Specific Mechanisms
Interstitial Cystitis
Hemorrhagic Cystitis
Chronic Radiation Cystitis
4.2. Inflammation
4.2.1. Common Mechanism
4.2.2. Specific Mechanisms
Interstitial Cystitis
Hemorrhagic Cystitis
Chronic Radiation Cystitis
4.3. Vascular Response
4.3.1. Common Mechanism
4.3.2. Specific Mechanisms
Interstitial Cystitis
Hemorrhagic Cystitis
Chronic Radiation Cystitis
4.4. Fibrosis
4.4.1. Common Mechanism
4.4.2. Specific Mechanisms
Interstitial Cystitis
Hemorrhagic Cystitis
Chronic Radiation Cystitis
4.5. Assumptions Regarding Central Mechanisms in Interstitial, Hemorrhagic and Radiation Cystitis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Janssen, D.A.; van Wijk, X.M.; Jansen, K.C.; van Kuppevelt, T.H.; Heesakkers, J.P.; Schalken, J.A. The distribution and function of chondroitin sulfate and other sulfated glycosaminoglycans in the human bladder and their contribution to the protective bladder barrier. J. Urol. 2013, 189, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, K.; Lee, J.; Guo, N.; Kim, J.; Lim, A.; Qu, L.; Mysorekar, I.U.; Beachy, P.A. Hedgehog/Wnt feedback supports regenerative proliferation of epithelial stem cells in bladder. Nature 2011, 472, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, R.; Liu, G.; Shi, Y.; Bharadwaj, S.; Leng, X.; Zhou, X.; Liu, H.; Atala, A.; Zhang, Y. Self-renewal and differentiation capacity of urine-derived stem cells after urine preservation for 24 hours. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanno, P.M. Interstitial cystitis-epidemiology, diagnostic criteria, clinical markers. Rev. Urol. 2002, 4 (Suppl. S1), S3–S8. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, C.A.; Nyberg, L. Epidemiology of interstitial cystitis. Urology 1997, 49 (Suppl. S1), 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koziol, J.A.; Clark, D.C.; Gittes, R.F.; Tan, E.M. The natural history of interstitial cystitis: A survey of 374 patients. J. Urol. 1993, 149, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagiri, M.; Chottiner, S.; Ratner, V.; Slade, D.; Hanno, P.M. Interstitial cystitis: Unexplained associations with other chronic disease and pain syndromes. Urology 1997, 49 (Suppl. S1), 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, A.; Teichman, J.M. How do patients with interstitial cystitis present? J. Urol. 2001, 166, 2118–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Ueda, T.; Honma, Y.; Takei, M. Recent trends in patient characteristics and therapeutic choices for interstitial cystitis: Analysis of 282 Japanese patients. Int. J. Urol. Off. J. Jpn. Urol. Assoc. 2007, 14, 1068–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, K.M.; Killinger, K.A.; Mounayer, M.H.; Boura, J.A. Are ulcerative and nonulcerative interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome 2 distinct diseases? A study of coexisting conditions. Urology 2011, 78, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcu, I.; Campian, E.C.; Tu, F.F. Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome. Semin. Reprod. Med. 2018, 36, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payne, H.; Adamson, A.; Bahl, A.; Borwell, J.; Dodds, D.; Heath, C.; Huddart, R.; McMenemin, R.; Patel, P.; Peters, J.L.; et al. Chemical- and radiation-induced haemorrhagic cystitis: Current treatments and challenges. BJU Int. 2013, 112, 885–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigaud, J.; Hetet, J.F.; Bouchot, O. Management of radiation cystitis. Prog. Urol. J. L’Assoc. Fr. D’Urol. Soc. Fr. D’Urol. 2004, 14, 568–572. [Google Scholar]
- Traxer, O.; Desgrandchamps, F.; Sebe, P.; Haab, F.; Le Duc, A.; Gattegno, B.; Thibault, P. Hemorrhagic cystitis: Etiology and treatment. Prog. Urol. J. L’Assoc. Fr. D’Urol. Soc. Fr. D’Urol. 2001, 11, 591–601. [Google Scholar]
- Erard, V.; Kim, H.W.; Corey, L.; Limaye, A.; Huang, M.L.; Myerson, D.; Davis, C.; Boeckh, M. BK DNA viral load in plasma: Evidence for an association with hemorrhagic cystitis in allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant recipients. Blood 2005, 106, 1130–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, R.; Kumar, S.; Dorairajan, L.N. Hemorrhagic cystitis: A challenge to the urologist. Indian J. Urol. IJU J. Urol. Soc. India 2010, 26, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, C.R.; Freiha, F.S. Hemorrhagic cystitis: A review. J. Urol. 1990, 143, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugieres, L.; Hartmann, O.; Travagli, J.P.; Benhamou, E.; Pico, J.L.; Valteau, D.; Kalifa, C.; Patte, C.; Flamant, F.; Lemerle, J. Hemorrhagic cystitis following high-dose chemotherapy and bone marrow transplantation in children with malignancies: Incidence, clinical course, and outcome. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 1989, 7, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, K.; Biggs, J.; Noble, G.; Ashby, M.; Concannon, A.; Dodds, A. Preparative regimens for marrow transplantation containing busulphan are associated with haemorrhagic cystitis and hepatic veno-occlusive disease but a short duration of leucopenia and little oro-pharyngeal mucositis. Bone Marrow Transpl. 1987, 2, 385–394. [Google Scholar]
- Crew, J.P.; Jephcott, C.R.; Reynard, J.M. Radiation-induced haemorrhagic cystitis. Eur. Urol. 2001, 40, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, C.L.; Greene, R.A.; Chung, M.; Stanford, E.J.; Singh, G. Abnormal urinary potassium metabolism in patients with interstitial cystitis. J. Urol. 2005, 173, 1182–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patnaik, S.S.; Lagana, A.S.; Vitale, S.G.; Buttice, S.; Noventa, M.; Gizzo, S.; Valenti, G.; Rapisarda, A.M.C.; La Rosa, V.L.; Magno, C.; et al. Etiology, pathophysiology and biomarkers of interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2017, 295, 1341–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homma, Y.; Ueda, T.; Tomoe, H.; Lin, A.T.; Kuo, H.C.; Lee, M.H.; Oh, S.J.; Kim, J.C.; Lee, K.S. Clinical guidelines for interstitial cystitis and hypersensitive bladder updated in 2015. Int. J. Urol. Off. J. Jpn. Urol. Assoc. 2016, 23, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keay, S.; Warren, J.W.; Zhang, C.O.; Tu, L.M.; Gordon, D.A.; Whitmore, K.E. Antiproliferative activity is present in bladder but not renal pelvic urine from interstitial cystitis patients. J. Urol. 1999, 162, 1487–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.O.; Wang, J.Y.; Koch, K.R.; Keay, S. Regulation of tight junction proteins and bladder epithelial paracellular permeability by an antiproliferative factor from patients with interstitial cystitis. J. Urol. 2005, 174, 2382–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbadawi, A.E.; Light, J.K. Distinctive ultrastructural pathology of nonulcerative interstitial cystitis: New observations and their potential significance in pathogenesis. Urol. Int. 1996, 56, 137–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszewski, J.E.; Landis, J.R.; Russack, V.; Williams, T.M.; Wang, L.P.; Hardy, C.; Brensinger, C.; Matthews, Y.L.; Abele, S.T.; Kusek, J.W.; et al. Biopsy features are associated with primary symptoms in interstitial cystitis: Results from the interstitial cystitis database study. Urology 2001, 57 (Suppl. S1), 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, M.C.; Kuo, Y.C.; Kuo, H.C. Intravesical hyaluronic acid for interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome: A comparative randomized assessment of different regimens. Int. J. Urol. Off. J. Jpn. Urol. Assoc. 2013, 20, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keay, S.K.; Birder, L.A.; Chai, T.C. Evidence for bladder urothelial pathophysiology in functional bladder disorders. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 865463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, R.E.; Greenwood-Van Meerveld, B.; Wisniewski, A.B.; VanGordon, S.; Lin, H.; Kropp, B.P.; Towner, R.A. Increased bladder permeability in interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2015, 4, 563–571. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.T.; Shie, J.H.; Chen, S.H.; Wang, Y.S.; Kuo, H.C. Differences in mast cell infiltration, E-cadherin, and zonula occludens-1 expression between patients with overactive bladder and interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Urology 2012, 80, 225.e13–225.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.; Romih, R.; Zupancic, D. Cystitis: From urothelial cell biology to clinical applications. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 473536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, P.J. Cyclophosphamide cystitis--identification of acrolein as the causative agent. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1979, 28, 2045–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaal, J.; Dorr, W. Radiation-induced damage to mouse urothelial barrier. Radiother. Oncol. J. Eur. Soc. Ther. Radiol. Oncol. 2006, 80, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwaans, B.; Krueger, S.; Bartolone, S.N.; Chancellor, M.B.; Marples, B.; Lamb, L.E. Modeling of chronic radiation-induced cystitis in mice. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2016, 1, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kohler, M.; Eppenberger, H.M.; Cordt-Riehle, I.; Michel, C. Urination frequency and cystic pressure resistance after fractionated whole or partial irradiation of the rabbit urinary bladder. Acta Oncol. 1992, 31, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaganapathy, B.R.; Janicki, J.J.; Levanovich, P.; Tyagi, P.; Hafron, J.; Chancellor, M.B.; Krueger, S.; Marples, B. Intravesical Liposomal Tacrolimus Protects against Radiation Cystitis Induced by 3-Beam Targeted Bladder Radiation. J. Urol. 2015, 194, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.H.; Peng, C.H.; Liu, H.T.; Kuo, H.C. Increased pro-inflammatory cytokines, C-reactive protein and nerve growth factor expressions in serum of patients with interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, Q.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, G.; Chen, J.; Zhao, J.; Wu, P. Ketamine Analog Methoxetamine Induced Inflammation and Dysfunction of Bladder in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albulescu, R.; Tanase, C.; Codrici, E.; Popescu, D.I.; Cretoiu, S.M.; Popescu, L.M. The secretome of myocardial telocytes modulates the activity of cardiac stem cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2015, 19, 1783–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manole, C.G.; Cismasiu, V.; Gherghiceanu, M.; Popescu, L.M. Experimental acute myocardial infarction: Telocytes involvement in neo-angiogenesis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2011, 15, 2284–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cretoiu, D.; Cretoiu, S.M.; Simionescu, A.A.; Popescu, L.M. Telocytes, a distinct type of cell among the stromal cells present in the lamina propria of jejunum. Histol. Histopathol. 2012, 27, 1067–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, C.L.; Zupkas, P.; Parsons, J.K. Intravesical potassium sensitivity in patients with interstitial cystitis and urethral syndrome. Urology 2001, 57, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sant, G.R.; Kempuraj, D.; Marchand, J.E.; Theoharides, T.C. The mast cell in interstitial cystitis: Role in pathophysiology and pathogenesis. Urology 2007, 69, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theoharides, T.C.; Kempuraj, D.; Sant, G.R. Mast cell involvement in interstitial cystitis: A review of human and experimental evidence. Urology 2001, 57, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeker, R.; Enerback, L.; Fall, M.; Aldenborg, F. Recruitment, distribution and phenotypes of mast cells in interstitial cystitis. J. Urol. 2000, 163, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Walls, A.F. Human mast cell tryptase: A stimulus of microvascular leakage and mast cell activation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 328, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderwinden, J.M.; Rumessen, J.J.; de Kerchove d’Exaerde, A., Jr.; Gillard, K.; Panthier, J.J.; de Laet, M.H.; Schiffmann, S.N. Kit-negative fibroblast-like cells expressing SK3, a Ca2+-activated K+ channel, in the gut musculature in health and disease. Cell Tissue Res. 2002, 310, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevaert, T.; De Vos, R.; Everaerts, W.; Libbrecht, L.; Van Der Aa, F.; van den Oord, J.; Roskams, T.; De Ridder, D. Characterization of upper lamina propria interstitial cells in bladders from patients with neurogenic detrusor overactivity and bladder pain syndrome. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2011, 15, 2586–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevaert, T.; Moles Lopez, X.; Sagaert, X.; Libbrecht, L.; Roskams, T.; Rorive, S.; Decaestecker, C.; Salmon, I.; De Ridder, D. Morphometric and quantitative immunohistochemical analysis of disease-related changes in the upper (suburothelial) lamina propria of the human bladder dome. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannucchi, M.G.; Traini, C. The telocytes/myofibroblasts 3-D network forms a stretch receptor in the human bladder mucosa. Is this structure involved in the detrusor overactive diseases? Ann. Anat. = Anat. Anz. Off. Organ Anat. Ges. 2018, 218, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traini, C.; Fausssone-Pellegrini, M.S.; Guasti, D.; Del Popolo, G.; Frizzi, J.; Serni, S.; Vannucchi, M.G. Adaptive changes of telocytes in the urinary bladder of patients affected by neurogenic detrusor overactivity. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, C.H.; Vahabi, B. The Role of the Mucosa in Normal and Abnormal Bladder Function. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2016, 119 (Suppl. S3), 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, S.D.; Liu, H.T.; Lin, H.; Kuo, H.C. Elevation of serum c-reactive protein in patients with OAB and IC/BPS implies chronic inflammation in the urinary bladder. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2011, 30, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas, A.C.; Batista-Junior, F.F.; Macedo, L.F.; Mendes, M.N.; Azevedo, I.M.; Medeiros, A.C. Protective effect of simvastatin in the cyclophosphamide-induced hemorrhagic cystitis in rats. Acta Cir. Bras. 2010, 25, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, V.Y.; Malley, S.; Dattilio, A.; Folsom, J.B.; Zvara, P.; Vizzard, M.A. COX-2 and prostanoid expression in micturition pathways after cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis in the rat. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2003, 284, R574–R585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, A.; Topal, T.; Oter, S. Pathophysiological aspects of cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide induced hemorrhagic cystitis; implication of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species as well as PARP activation. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2007, 23, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virag, L.; Szabo, E.; Gergely, P.; Szabo, C. Peroxynitrite-induced cytotoxicity: Mechanism and opportunities for intervention. Toxicol. Lett. 2003, 140–141, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Salem, O.M. Uroprotective effect of pentoxifylline in cyclophosphamide-induced hemorrhagic cystitis in rats. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2013, 27, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornelas-Filho, A.F.; Pereira, V.B.M.; Wong, D.V.T.; Nobre, L.M.S.; Melo, A.T.; Silva, C.M.S.; Wanderley, C.W.S.; Nour, M.L.; Araujo, L.; Silva, R.O.; et al. Neutrophils contribute to the pathogenesis of hemorrhagic cystitis induced by ifosfamide. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 62, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, M.; Michel, C.; Zimmermann, A. Histological changes after fractionated whole or partial irradiation of the rabbit urinary bladder. Acta Oncol. 1995, 34, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaal, J.; Dorr, W. Radiation induced inflammatory changes in the mouse bladder: The role of cyclooxygenase-2. J. Urol. 2006, 175, 1529–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaki, M.; Saito, R.; Ogawa, O.; Yoshimura, N.; Ueda, T. Possible mechanisms inducing glomerulations in interstitial cystitis: Relationship between endoscopic findings and expression of angiogenic growth factors. J. Urol. 2004, 172, 945–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiuchi, H.; Tsujimura, A.; Takao, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Nakayama, J.; Miyagawa, Y.; Nonomura, N.; Takeyama, M.; Okuyama, A. Increased vascular endothelial growth factor expression in patients with bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis: Its association with pain severity and glomerulations. BJU Int. 2009, 104, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.D.; Lee, M.H. Increased expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and vascular endothelial growth factor associated with glomerulation formation in patients with interstitial cystitis. Urology 2011, 78, 971.e11–971.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, A.T.; Yoshimura, N.; Tyagi, V.; Jacobs, B.; Leng, W.; Tyagi, P. Mapping the cytokine profile of painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis in human bladder and urine specimens. World J. Urol. 2013, 31, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherif, I.O.; Nakshabandi, Z.M.; Mohamed, M.A.; Sarhan, O.M. Uroprotective effect of oleuropein in a rat model of hemorrhagic cystitis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 74, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auge, C.; Chene, G.; Dubourdeau, M.; Desoubzdanne, D.; Corman, B.; Palea, S.; Lluel, P.; Vergnolle, N.; Coelho, A.M. Relevance of the cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis model for pharmacological studies targeting inflammation and pain of the bladder. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 707, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, R.; Vianello, A.; Fullhase, C.; Wang, Z.; Atala, A.; Soker, S.; Yoo, J.J.; Koudywilliam, J. Vascular therapy for radiation cystitis. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2011, 30, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaal, J.; Dorr, W. Radiation induced late damage to the barrier function of small blood vessels in mouse bladder. J. Urol. 2006, 176, 2696–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwaans, B.M.M.; Wegner, K.A.; Bartolone, S.N.; Vezina, C.M.; Chancellor, M.B.; Lamb, L.E. Radiation cystitis modeling: A comparative study of bladder fibrosis radio-sensitivity in C57BL/6, C3H, and BALB/c mice. Physiol. Rep. 2020, 8, e14377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyagi, P.; Moon, C.H.; Janicki, J.; Kaufman, J.; Chancellor, M.; Yoshimura, N.; Chermansky, C. Recent advances in imaging and understanding interstitial cystitis. F1000Research 2018, 7, 1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.H.; Wang, S.C.; Wang, S.T.; Lin, S.M.; Wu, J.D.; Lin, C.T.; Liu, Y.W. Evaluation of urinary bladder fibrogenesis in a mouse model of long-term ketamine injection. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 1880–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, D.; Han, J.Y.; Shin, J.H.; Ryu, C.M.; Yu, H.Y.; Kim, A.; Lee, S.; Lim, J.; Shin, D.M.; Choo, M.S. Downregulation of WNT11 is associated with bladder tissue fibrosis in patients with interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome without Hunner lesion. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, P.; Tyagi, V.; Yoshimura, N.; Witteemer, E.; Barclay, D.; Loughran, P.A.; Zamora, R.; Vodovotz, Y. Gender-based reciprocal expression of transforming growth factor-beta1 and the inducible nitric oxide synthase in a rat model of cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis. J. Inflamm. 2009, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchelouche, K.; Nordling, J. Recent developments in the management of interstitial cystitis. Curr. Opin. Urol. 2003, 13, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanno, P.M.; Sant, G.R. Clinical highlights of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases/Interstitial Cystitis Association scientific conference on interstitial cystitis. Urology 2001, 57, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persu, C.; Cauni, V.; Gutue, S.; Blaj, I.; Jinga, V.; Geavlete, P. From interstitial cystitis to chronic pelvic pain. J. Med. Life 2010, 3, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kraft, M.; Oussoren, Y.; Stewart, F.A.; Dorr, W.; Schultz-Hector, S. Radiation-induced changes in transforming growth factor beta and collagen expression in the murine bladder wall and its correlation with bladder function. Radiat. Res. 1996, 146, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, Y.; Zabbarova, I.V.; Birder, L.A.; Wipf, P.; Getchell, S.E.; Tyagi, P.; Fry, C.H.; Drake, M.J.; Kanai, A.J. Relaxin-2 therapy reverses radiation-induced fibrosis and restores bladder function in mice. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2018, 37, 2441–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, F.A.; Michael, B.D.; Denekamp, J. Late radiation damage in the mouse bladder as measured by increased urination frequency. Radiat. Res. 1978, 75, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, F.A.; Randhawa, V.S.; Michael, B.D. Multifraction irradiation of mouse bladders. Radiother. Oncol. J. Eur. Soc. Ther. Radiol. Oncol. 1984, 2, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, F.A. The proliferative and functional response of mouse bladder to treatment with radiation and cyclophosphamide. Radiother. Oncol. J. Eur. Soc. Ther. Radiol. Oncol. 1985, 4, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, F.A.; Randhawa, V.S.; Michael, B.D.; Denekamp, J. Repair during fractionated irradiation of the mouse bladder. Br. J. Radiol. 1981, 54, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smit, S.G.; Heyns, C.F. Management of radiation cystitis. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2010, 7, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, G.; Patra, P.; Letourneau, R.; Jeudy, S.; Boucher, W.; Green, M.; Sant, G.R.; Theoharides, T.C. Pentosanpolysulfate inhibits mast cell histamine secretion and intracellular calcium ion levels: An alternative explanation of its beneficial effect in interstitial cystitis. J. Urol. 2000, 164, 2119–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, F.G.; Batezini, N.; Simoes, R.S.; Bernardo, W.M. Interstitial cystitis-intravesical treatment. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. (1992) 2019, 65, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascoe, C.; Duncan, C.; Lamb, B.W.; Davis, N.F.; Lynch, T.H.; Murphy, D.G.; Lawrentschuk, N. Current management of radiation cystitis: A review and practical guide to clinical management. BJU Int. 2019, 123, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teichman, J.M. The role of pentosan polysulfate in treatment approaches for interstitial cystitis. Rev. Urol. 2002, 4 (Suppl. S1), S21–S27. [Google Scholar]
- Parsons, C.L.; Lilly, J.D.; Stein, P. Epithelial dysfunction in nonbacterial cystitis (interstitial cystitis). J. Urol. 1991, 145, 732–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colemeadow, J.; Sahai, A.; Malde, S. Clinical Management of Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis: A Review on Current Recommendations and Emerging Treatment Options. Res. Rep. Urol. 2020, 12, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colaco, M.; Evans, R. Current guidelines in the management of interstitial cystitis. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2015, 4, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, R.A.; Freitas, H.C.; Campos, M.C.; Santos, C.C.; Figueiredo, F.C.; Brito, G.A.; Cunha, F.Q. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1beta mediate the production of nitric oxide involved in the pathogenesis of ifosfamide induced hemorrhagic cystitis in mice. J. Urol. 2002, 167, 2229–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, J.C.R.; Campelo, M.W.S.; Aragao, I.A.; de Moura, J.F.B.; Silva, L.F.G.; Oria, R.B. Treatment of Severe Refractory Hematuria due to Radiation-Induced Hemorrhagic Cystitis with Dexamethasone. Case Rep. Med. 2017, 2017, 1560363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoskes, D.A.; Radzinski, C.A.; Struthers, N.W.; Honey, R.J. Aluminum toxicity and death following intravesical alum irrigation in a patient with renal impairment. J. Urol. 1992, 147, 697–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavoussi, L.R.; Gelstein, L.D.; Andriole, G.L. Encephalopathy and an elevated serum aluminum level in a patient receiving intravesical alum irrigation for severe urinary hemorrhage. J. Urol. 1986, 136, 665–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dautruche, A.; Delouya, G. A contemporary review about the management of radiation-induced hemorrhagic cystitis. Curr. Opin. Supportive Palliat. Care 2018, 12, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinal, J.; Slade, A.; McFarland, M.; Keihani, S.; Hotaling, J.N.; Myers, J.B. Scoping Review and Meta-analysis of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for Radiation-Induced Hemorrhagic Cystitis. Curr. Urol. Rep. 2018, 19, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villeirs, L.; Tailly, T.; Ost, P.; Waterloos, M.; Decaestecker, K.; Fonteyne, V.; Van Praet, C.; Lumen, N. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for radiation cystitis after pelvic radiotherapy: Systematic review of the recent literature. Int. J. Urol. Off. J. Jpn. Urol. Assoc. 2020, 27, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oscarsson, N.; Muller, B.; Rosen, A.; Lodding, P.; Molne, J.; Giglio, D.; Hjelle, K.M.; Vaagbo, G.; Hyldegaard, O.; Vangedal, M.; et al. Radiation-induced cystitis treated with hyperbaric oxygen therapy (RICH-ART): A randomised, controlled, phase 2–3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1602–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, C.M.; Shin, J.H.; Yu, H.Y.; Ju, H.; Kim, S.; Lim, J.; Heo, J.; Lee, S.; Shin, D.M.; Choo, M.S. N-acetylcysteine prevents bladder tissue fibrosis in a lipopolysaccharide-induced cystitis rat model. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajasekaran, M.; Locke, K.W.; Parsons, C.L. MN-001, a novel oral anti-inflammatory agent, suppresses bladder hyperactivity in a rat model. BJU Int. 2006, 98, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawls, W.F.; Cox, L.; Rovner, E.S. Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) as intravesical therapy for interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: A review. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2017, 36, 1677–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazif, O.; Teichman, J.M.; Gebhart, G.F. Neural upregulation in interstitial cystitis. Urology 2007, 69, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Chai, T.C. Effects of dimethyl sulphoxide and heparin on stretch-activated ATP release by bladder urothelial cells from patients with interstitial cystitis. BJU Int. 2002, 90, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Generali, J.A.; Cada, D.J. Amitriptyline: Interstitial cystitis (painful bladder syndrome). Hosp. Pharm. 2014, 49, 809–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottem, D.P.; Teichman, J.M. What is the value of cystoscopy with hydrodistension for interstitial cystitis? Urology 2005, 66, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, L.E.; Dyer, J.E.; Haq, A.; Ockrim, J.; Greenwell, T.J. A systematic review of the literature on cystodistension in bladder pain syndrome. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2018, 29, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronsson-Kurttila, W.; Baygan, A.; Moretti, G.; Remberger, M.; Khoein, B.; Moll, G.; Sadeghi, B.; Ringden, O. Placenta-Derived Decidua Stromal Cells for Hemorrhagic Cystitis after Stem Cell Transplantation. Acta Haematol. 2018, 139, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringden, O.; Uzunel, M.; Sundberg, B.; Lonnies, L.; Nava, S.; Gustafsson, J.; Henningsohn, L.; Le Blanc, K. Tissue repair using allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells for hemorrhagic cystitis, pneumomediastinum and perforated colon. Leukemia 2007, 21, 2271–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voswinkel, J.; Francois, S.; Simon, J.M.; Benderitter, M.; Gorin, N.C.; Mohty, M.; Fouillard, L.; Chapel, A. Use of mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) in chronic inflammatory fistulizing and fibrotic diseases: A comprehensive review. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2013, 45, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Pathology | Interstitial Cystitis | Hemorrhagic Cystitis (Not a Distinct Form of Cystitis) | Chronic Radiation Cystitis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Causes | Idiopathic disease | Radiation, Chemotherapy (cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide), Infections (bacterial, viral, fungal and parasitic), Drugs, Toxins, Idiopathic diseases, Organ transplant | Pelvic radiation |
| Signs | Pain, Day and night pollakiuria, Urinary urgency | ||
| Dysuria, Incontinence, Hematuria (microscopic to severe macroscopic with clots) | |||
| Symptoms | Dyspareunia Digestive and/or gynecological disorders Glomerulations | Severe form: urinary obstruction and acute renal failure | |
| Diagnosis | Cytobacteriological examination, Physical examination, Biopsy | ||
| Urodynamic examination Cystomanometry Voiding diary Questionnaires | Ultrasound | ||
| Mechanism | Interstitial Cystitis | Hemorrhagic Cystitis * (* Not a Distinct Form of Cystitis) | Chronic Radiation Cystitis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urothelium dysfunction | Degradation of the GAG layer Alteration of permeability causing urinary potassium infiltration leading to activation of mast cells and depolarization of nerve and muscle fibers Alteration of the ATP/NO ratio Abnormal expression of APF inhibiting cell proliferation and the formation of tight junctions and preventing urothelium repair Cellular apoptosis | Urothelium degradation, subepithelial edema and ulceration Alteration of permeability | Decrease in the expression of uroplakin III and E-cadherin leading to a decrease in impermeability Hyperplasia, atrophy and/or erosion of urothelium Cellular edema (mainly in basal cells) |
| Inflammation | Production of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α | ||
| Production of SCF, IL-8 and CCL2 by urothelium SCF-stimulated proliferation and activation of mast cells Degranulation of mast cells releasing histamine, IL-6, IL-8, prostaglandins, VEGF, NGF and tryptases Microvascular leakage and tryptase activation of mast cells Vasodilatation and immature angiogenesis caused by VEGF Insufficient pericyte coverage resulting in hemorrhagic vessels and hypoxia Over-expression of HIF-1α Increased expression of IL-16, IL-18, SCGFβ, CTACK, TRAIL, ICAM-1, MCP-3 and VCAM-1 in the bladder wall | Increase in COX-2 at the urothelium level Oxidative stress, cell damage and apoptosis/necrosis due to overproduction of ROS and RNS Induction of NF-κB and AP-1 in resident bladder cells due to the production of ROS, IL-1β and TNF-α Induction of iNOS leading to overproduction of NO and production of ROS caused by NF-κB and AP-1 Neutrophil Recruitment | Increased number of mastocytes in tissue No study on molecular mechanisms | |
| Mechanisms | Interstitial Cystitis | Hemorrhagic Cystitis * (* Not a Distinct Form of Cystitis) | Chronic Radiation Cystitis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neural regulation | Release of substance P (SP) from C-fibers leading to vasodilation and degranulation of mast cells Increased nerve fiber proliferation caused by NGF Overexpression of SP receptor mRNA | Unknown | Unknown |
| Vascular lesions | High concentration of VEGF Overexpression of ICAM-1, VCAM-1 | Telangiectasias Albumin leakage Micro- and macro- hematuria | |
| Vasodilatation and immature angiogenesis Hypervascularization Glomerulations Overexpression of HIF-1α, IL-16, IL-18, SCGFβ,CTACK, TRAIL, MCP-3 | Overexpression of MCP-1 | ||
| Fibrosis | Increased TGF-β1expression Excessive deposition of ECM in the lamina propria (submucosa) and smooth muscle Positive regulation of collagen I and III, | ||
| Myofibroblast formation | |||
| Positive regulation of fibronectin Negative regulation of WNT11 Production of YKL-40 causing ECM accumulation Decreased contractile bladder capacity and bladder stiffening | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brossard, C.; Lefranc, A.-C.; Pouliet, A.-L.; Simon, J.-M.; Benderitter, M.; Milliat, F.; Chapel, A. Molecular Mechanisms and Key Processes in Interstitial, Hemorrhagic and Radiation Cystitis. Biology 2022, 11, 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11070972
Brossard C, Lefranc A-C, Pouliet A-L, Simon J-M, Benderitter M, Milliat F, Chapel A. Molecular Mechanisms and Key Processes in Interstitial, Hemorrhagic and Radiation Cystitis. Biology. 2022; 11(7):972. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11070972
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrossard, Clément, Anne-Charlotte Lefranc, Anne-Laure Pouliet, Jean-Marc Simon, Marc Benderitter, Fabien Milliat, and Alain Chapel. 2022. "Molecular Mechanisms and Key Processes in Interstitial, Hemorrhagic and Radiation Cystitis" Biology 11, no. 7: 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11070972
APA StyleBrossard, C., Lefranc, A.-C., Pouliet, A.-L., Simon, J.-M., Benderitter, M., Milliat, F., & Chapel, A. (2022). Molecular Mechanisms and Key Processes in Interstitial, Hemorrhagic and Radiation Cystitis. Biology, 11(7), 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11070972








