Simple Summary
In vitro-induced differentiation of sperm cells is a key technology for genetic resource conservation. In the past ten years, Opsariichthys bidens has become a famous and excellent aquatic species in some areas in China. However, its genetic resources have reduced dramatically. To protect against the decline of O. bidens, a long-term-cultured spermatogonial stem cell line (ObSSC) of adult O. bidens was successfully established. The result of our study showed that ObSSC had a diploid karyotype and stable growth over more than 2 years, with SSC-typical gene expression patterns. Furthermore, our research demonstrates the potential and regulation mechanism of fish spermatogonial stem cell differentiation into different cells of three germ layers. Our findings will assist further research on the genetic resource conservation of germplasm in a commercially and ecologically valuable fish species.
Abstract
Opsariichthys bidens belongs to the family Cyprinidae and is a small freshwater economic fish widely distributed in China. In recent years, the natural resources of O. bidens have been drastically reduced due to overfishing and the destruction of the water environment. The in vitro culture and long-term preservation of germ stem cells are the key technologies to keep genetic resources from degeneration. However, except for the establishment of the first long-term cultured medaka spermatogonia cell line (SSC) capable of producing sperm in vitro in 2004, no other long-term cultured SSC line has been found in other fish species. In this study, we successfully established another long-term-cultured spermatogonial stem cell line from Opsariichthys bidens (ObSSC). After more than 2 years of culture, ObSSC had a diploid karyotype and stable growth, with the typical gene expression patterns of SSC. Under in vitro culture, ObSSC could be induced to differentiate into sperm and other different types of somatic cells. In vivo, ObSSC could differentiate into different cells of three germ layers upon being transplanted into zebrafish embryos. Our research helps to explore the potential and regulation mechanism of fish SSC differentiation and spermatogenesis in vitro, provides a new way for solving the problem of fish genetic resource degradation and lays a foundation for further research on fish germ cell transplantation.
1. Introduction
Fish have the utmost diversity of all vertebrates, with over 32,000 species recorded, which is half the number of vertebrates on earth. Several fish species are facing extinction due to rapid population declines []. As a result, the long-term preservation of fish genetic resources is becoming extremely important for the protection of fish species with declining populations []. Due to the limitation of available methods for cryopreservation of fish eggs and embryos [], cryopreservation of germline stem cells (GSCs) and its successive transplantation into donor fish is an alternative option to retain the genetic resources of endangered fish [,].
The establishment of germline stem cell (GSC) cultures, such as primordial germ cells (PGCs), spermatogonia stem cells (SSCs) in the testis, and oogonia stem cells (OSCs) in the ovary, have attracted considerable interest [,]. SSCs are abundant in immature testis during all phases of testis development, and a method for efficiently isolating SSCs in many species has been developed. In contrast, PGCs and OSCs are difficult to isolate [].
Currently, many culture systems have been designed to imitate the germ cell niche and give various supplementary factors for SSCs to make haploid sperm []. In mice, the establishment of in vitro-derived gametes was performed by stepwise differentiation from pluripotent stem cells after exposure to morphogens and hormones in coculture systems [,,]. In zebrafish, early-stage spermatogonia and Sertoli-like cells were cocultured in adherent culture systems to produce functional sperm []. In the cyprinid honmoroko (Gnathopogon caerulescens), from dissociated testicular cells in suspension culture, functional sperm were obtained []. In swamp eel (Monopterus Albus), enriched SSCs were isolated and cultured in vitro from the testis []. In marine four-eyed sleepers (Bostrychus sinensis), premeiotic spermatogonia were obtained and further flagellated sperm from spermatogonia in a 3D culture system []. Our laboratory previously successfully established a normal SSC line (SG3) from the adult testis of medaka (Oryzias latipes), which can be cultured for a long time in vitro, and successfully made the SG3 cell line recapitulate the spermatogenesis process and produce motile sperm in vitro []. However, due to the lack of an efficient culture technique that supports continuous SSC proliferation in vitro, stable SSC lines in other fish species have not been recorded []. Therefore, establishing a culture system for long-term in vitro SSC lines in aquaculture fish remains a key challenge.
O. bidens is becoming an increasingly important small aquaculture species in China, with high economic value and wide distribution. O. bidens wild stocks have declined due to environmental changes and overfishing. Its reproductive biology research should be carried out to protect the diversity of O. bidens genetic resources. Recently, we performed an analytical study on the O. bidens gonad transcriptome []. In the present study, we successfully established a long-term-cultured spermatogonia cell line capable of sperm production from the adult testis of O. bidens in vitro. O. bidens SSCs can be induced to differentiate into a variety of somatic cells in vitro and in vivo. This study helps to provide a new model for the study of fish SSCs and lays the foundation for further studies on the reproduction of O. bidens. It also provides a donor for further research on germ cell transplantation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish
Fry fish were obtained at Jinhua Hengyuan Agricultural Science and Technology Co., Ltd. (Jinhua, China) and were transported to Shanghai. They were raised (26 °C) in an automated breeder with a 14 h:10 h light/dark cycle at the Shanghai Ocean University Opsariichthys bidens Center (Shanghai, China). The study was performed following the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Shanghai Ocean University Animal Care and Use Committee with Approval Number SHOU-2021-118.
2.2. Preparation of Culture Medium
Preparation of culture media ESM2 and EMS4 was carried out as described []. The basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF; Gibco, Carlsbad, CA, USA) and medaka embryo extract (MEE) content of ESM2 is higher than ESM4. For ESM4, each 1 L of DMEM/HEPES (pH 7.8; Gibco, New York, NY, USA) contains the following components: FBS (150 mL; Gibco, NSW, Australia), MEE (1 mL; 400 medaka embryos/mL; 2.5 mL for ESM2), fish serum (10 mL; Seabass; serum extraction method as described []), bFGF (20 µL; 0.1 mg/mL; 100 µL for ESM2), L-glutamine, nonessential amino acids, sodium pyruvate, and pen/strep (all 100×; 10 mL; Gibco, New York, NY, USA), 2-mercaptoethanol (4 mL; stock 50 mM; Sigma, Burlington, MA, USA) and sodium selenite (1 mL; stock 2 µM; Sigma). The culture medium was filtered using a filter (0.22 µm) and stored (4 °C) for up to 6 months.
2.3. Primary Culture and Subculture
All equipment used in the experiment was sterilized before use. The 6-month-old fish were placed on ice for 15 min and sterilized with 75% ethanol. The testis was dissected carefully and washed 3 times in phosphate-buffered solution (PBS) containing 1% penicillin/streptomycin. After being finely minced, the testicular tissues were subjected to 1 h dissociation (28 °C) in a solution including 5% trypsin (25 μL; Worthington, OH, USA; dissolved in L-15 medium), 40 mg/mL collagenase H (50 μL; Roche, Mannheim, Germany; dissolved in L-15 medium), FBS (25 μL) and 1% DNase I (25 μL; Roche, Mannheim, Germany; dissolved in L-15 sterile water) in 500 μL L-15 for 1 h at 28 °C. Next, the dissociated cells were transferred to gelatin-coated 6-well plates and cultured (28 °C) in a culture medium (1.5 mL). Cells were cultured at 28 °C in air. Cell subcultures were performed as described []. Briefly, dissociated cells were cultured in EMS2 medium for several weeks, passaged to Passage 15, and stably proliferating ObSSCs were obtained. From Passage 15 of the culture, ObSSCs were cultured in fresh ESM4 medium, and the cells were passaged to 50 passages and named the ObSSC line, which has more than 100 passages in 2 years of culture.
2.4. Chromosome Analysis
ObSSCs (at Passages 20 and 60) were used for chromosomal analysis. The ObSSCs were seeded into a 6 cm culture dish for culturing (24 h, 28 °C). Cells with active growth were cultured (4 h, 28 °C) in colchicine solution (20 μg/mL) to accumulate metaphases. After 2 PBS washes, cells were treated with 0.25% trypsin/EDTA solution (Gibco, NY, USA) for 30 s for dissociation, which was then removed, followed by the addition of PBS (1 mL). Cells were put into microcentrifuge tubes (1.5 mL) and gradually added with hypotonic solution (1 mL, 2.98 mg/mL KCl) for 30 min incubation for cell swelling. After that, the hypotonic treatment was terminated by adding fresh fixative (0.2 mL, 3:1 methanol/acetic acid). Next, following resuspension in 1 mL fixative, the cells underwent 30–60 min fixing after two fixative changes. After cell centrifugation and resuspension in fixative (0.1–0.5 mL), cells were loaded onto clean glass slides; 5% Giemsa solution was used for chromosome staining (15 min, room temperature). Slides were photographed and examined through a Nikon Eclipse 80I fluorescence microscope.
2.5. Cryopreservation, Recovery, and Alkaline Phosphatase (AP) Staining of ObSSC
The 4 × 105 ObSSCs were resuspended in 1.5 mL medium containing 15% FBS and 10% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). Cells were transferred into 2 mL cryogenic vials (Corning, Reynosa, Mexic) and placed in a cell freezing container (Corning, Reynosa, Mexic), where they were incubated at (−80 °C, 48 h) before storage in liquid nitrogen. To recover the cells, they were immediately thawed (37 °C, 2 min) in a water bath being centrifugation (1000 g, 10 min). Next, cells were seeded into a gelatin-coated 24-well plate cell after being suspended in fresh subculture medium. After 24 h of incubation (28 °C), the medium was replaced. Part of the cells was taken and placed into a gelatin-coated 24-well plate, and AP staining was prepared after the cells adhered to the wall. AP staining was performed as described [].
2.6. Extraction of Total RNA and RT-PCR
To isolate RNA, cells were collected from 4 wells of a 24-well plate and treated with Trizol (Sigma, Burlington, MA, USA). Total RNA was precipitated in isopropanol after chloroform extraction, followed by 75% ethanol washing and then dissolution in 10 μL nuclease-free water for cDNA synthesis. cDNA was synthesized from 1 µg total RNA (TaKaRa, Kusatsu, Japan) using the M-MLV Reverse Transcription Kit (TaKaRa, Kusatsu, Japan). To obtain cDNA fragments, O. bidens gonad raw sequence data were used []. Primer sequences are shown in Table 1. PCR amplification conditions were: 95 °C for 5 min, and then 35 cycles of 95 °C for 20 s, 58 °C for 20 s, and 72 °C for 30–60 s in a 20 μL system, followed by 72 °C for 10 min. β-Actin was used as an internal reference.

Table 1.
Primers used for reverse transcription polymerase chain reactions (RT-PCR).
2.7. Immunofluorescence Staining of ObSSCs
The round 24-well cell climbing slices were soaked overnight in 75% alcohol before being covered with gelatin. ObSSCs were seeded on 24-well climbing slices, and the media were removed after the cells reached 70% confluence. After 2 PBS washes, cells were fixed (10 min) in 4% paraformaldehyde. Following PBS washing, the cell climbing slides were transferred to a new 24-well plate with the cell-covered side facing up. Cells were subjected to 10 min 0.1% Triton-X 100 (200 μL) treatment and then 2 PBS washes. Next, cells were blocked (30 min) with 3% bovine serum albumin (BSA, 200 μL, Sigma) and washed with 500 μL PBS once. Next, the cells in one well were incubated with 200 μL Vasa antibody (1:200 dilution with 3% BSA; Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA, PA5-30749; this antibody corresponds to a recombinant fragment of human DDX4; Gene ID: 54514), while the cells in another well were added with 200 μL proliferating cell nuclear antigen antibody (PCNA; 1:200 dilution with 3% BSA; Sigma, P8825; this antibody is derived from the PC10 hybridoma created by the fusion of mouse myeloma cells and splenocytes from a BALB/c mouse immunized with PCNA–Protein A fusion protein; Gene ID: 18538) at 4 °C overnight. After 3 washes with 500 μL PBS, cells were incubated (room temperature, 1.5 h) with 200 μL goat anti-rabbit-FITC (1:250 dilution with 3% BSA; Sigma, F1262) and 200 μL anti-mouse-TRITC (1:250 dilution with 3% BSA; Sigma, T5393), respectively, and rinsed with PBS 3 times. Subsequently, each well was subjected to 200 μL DAPI (1:500 dilution with PBS; Sigma, D9542) treatment (room temperature, 15 min) and PBST washing once. Finally, the gold antifade reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) was used for cell climbing slide mounting.
2.8. Cell Transfection
pCVpr plasmid DNA (1 μg) was transfected into ObSSCs in gelatin-coated 24-well plates at 60% confluence using the GeneJuice reagent (Novagen, Darmstadt, Germany) according to a previous description []. Briefly, cells were seeded; after growing to 60–70% confluence, cells were transfected with plasmids following the instructions of the GeneJuice reagent. After 6 h of incubation at 28 °C, 1 mL EMS4 was added, and the transfection efficiency was observed after culturing in the cell incubator at 28 °C for 24–48 h. Puromycin (10–15 μg/mL) was administered to cell cultures after 48 h for drug selection. A single cell with strong red fluorescent protein (RFP) expression was selected and cultured in a new 96-well, and then a monoclonal ObSSC line stably expressing RFP was obtained.
2.9. Induced Differentiation
RFP-positive ObSSCs were seeded on 24-well plates for suspension culture with all-trans retinoic acid (10 μM) to generate embryoid bodies (EBs), as previously described []. Following 7 days of suspension culture, single cells were separated from EBs and seeded on gelatin-coated 24-well plates to allow cells to adhere overnight.
2.10. Cell Transplantation
Cell transplantation was carried out essentially as reported [,]. Trypsinization resulted in a single RFP-positive ObSSC. Dechorionated zebrafish embryos (treated with 5 mg/mL pronase E at the blastula stage for 4 min) were collected and arranged in balanced salt saline (0.3% Instant Ocean Salt) with 2 ppm of methylene blue. Each midblastula recipient received 100–200 ObSSCs, which were injected into the deep cell layer. The embryos were cultured (28 °C) in zebrafish egg water (0.3% Instant Ocean Salt containing 2 ppm of methylene blue) and were periodically checked.
2.11. Coculture and Flow Cytometry
After trypsinization, the ESM4, gelatin-coated 24-well plates were seeded with 104 RFP-positive ObSSCs and 104 O. bidens testicular cells (ObCTs) at 4 passages. During two weeks of continuous induction, half of the medium was replaced every two days for coculturing of cells at 28 °C.
For flow cytometry, RFP-positive ObSSCs (p70) and ObCTs (p4) were collected by trypsinization. After fixing in 70% ethanol, cells underwent 15 min incubation (37 °C) in PBS supplemented with 200 μg/mL RNase A and 20 μg/mL propidium iodide for DNA staining. BD Accuri C6 flow cytometer and ModFitWinTrial software were used for analysis.
3. Results
3.1. Establishment of a Spermatogonial Stem Cell Line
The feeder-free culture system developed in medaka was successful for embryonic stem cells [], SSCs [], and haploid stem cell derivation [], which was adopted for the establishment of an ObSSC line (Figure 1). Briefly, dissociated testicular cells from 6-month-old O. bidens were seeded into gelatin-coated 24-well plates in the culture medium (Figure 2A). A large number of testicular cells were attached to the cell plate (about 50–60%) on the third day, and many embryoid bodies (EBs) formed (Figure 2B). The number of spermatogonial stem cells around EBs was identified by immunofluorescence (Figure S1A–F), and the cells were selected from the surrounding EBs for subculture.
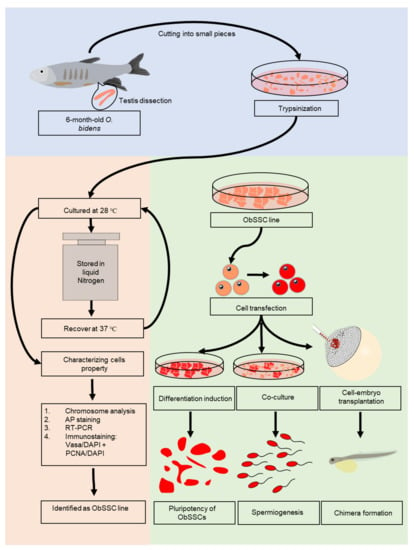
Figure 1.
Flowchart of experiments. In total, seven 6-month-old male adult fish with a length of about 10 cm were used. Live fish were placed on ice, and there was no response to mechanical stimulation. Testicular tissues were dissected and washed two times with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) containing 1% penicillin/streptomycin. All testes were minced and dissociated by trypsin and collagenase. A stable ObSSC line was obtained by appropriate culturing and then cryopreserved. We verified that these cells were SSCs by chromosomal analysis, RT-PCR and immunofluorescence. ObSSCs were identified in vitro and in vivo with pluripotent stem cell properties. Importantly, ObSSCs were induced to sperm by coculture with testis cells.
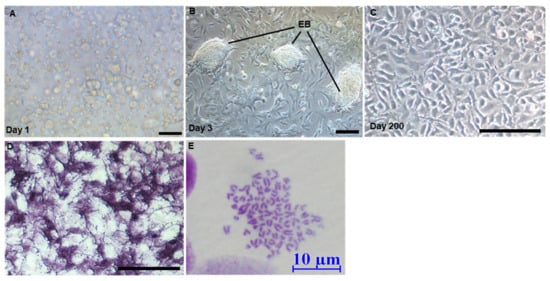
Figure 2.
Derivation of ObSSCs. (A) Testicular cells after enzymatic dissociation. (B) O. bidens primary testis cells were cultured on the 3rd day. (C) Morphology of ObSSCs at Passage 78 and Day 200. (D) Alkaline phosphatase staining. EB, embryoid bodies. (E) Diploid metaphase of ObSSCs. (Bars = 100 μm unless indicated).
Alkaline phosphatase (AP) staining is effective in identifying embryonic germ cells, embryonic stem cells, and other pluripotent stem cell types []. In medaka, AP is highly expressed in embryonic stem cells and SSCs [,,]. In our study, when testicular cells from O. bidens were stably subcultured for 20 days (Figure S2A), 60% of adherent cells were found to be strongly positive for AP staining, while the remaining adherent cells were negative for AP staining (Figure S2B). With the passage, the number of AP-negative cells gradually decreased. A spermatogonial stem cell line was obtained from the testis of male O. bidens, which had been subcultured for more than 70 passages in 200 days without any senescence, termed O. bidens spermatogonial stem cells (ObSSCs). ObSSCs were smooth in outline and oval in shape with sparse cytoplasm and uniform morphology (Figure 2C), and they consistently maintained high AP activity (Figure 2D).
3.2. Characterization of the Spermatogonial Property of ObSSCs
The chromosomal morphology of ObSSCs is shown in (Figure 2E). Most cells exhibited a diploid karyotype of 76 chromosomes, which is the characteristic of this organism []. Flow cytometry analysis also revealed the diploid structure (see below). Moreover, a small number of haploid cells were also observed (Figure S2E). These results indicated that ObSSCs exhibited genetic stability during long-term culture.
The identity of ObSSCs was further analyzed by using germ cell markers. Dazl is specifically expressed in the germ cells of medaka and Coilia nasus and is highly expressed in spermatogonia [,]. Dnd has been characterized as a germ cell marker in a variety of vertebrates. Dnd is expressed in the spermatogenic cells of the four-eyed sleeper and highly expressed in the spermatogonia of Oryzias celebensis and medaka [,]. Vasa showed high expression in spermatogonia and spermatocytes of medaka and swamp eel [,]. Gfra1, as a molecular marker of rodent SSCs, is also expressed in SSCs of Nile tilapia, medaka, swamp eel, and rainbow trout [,,]. Nanog is a molecular marker of stem cells, which is abundantly expressed in SSCs of some fish such as medaka, zebrafish, and rainbow trout [,]. Dmrt1 is often used as a somatic marker gene, as in the identification of large yellow croaker gonadal somatic cell lines and gonadal Sertoli cells of medaka [,]. According to the in situ hybridization expression pattern of O. bidens gonad sections, dmrt1 is expressed in both germ cells and somatic cells (data not shown). Our results showed that the reproductive-specific genes dazl, dnd, vasa, and gfra1 and stem cell marker gene nanog were highly expressed in ObSSCs, while the somatic marker gene dmrt1 was relatively poorly expressed (Figure 3A).
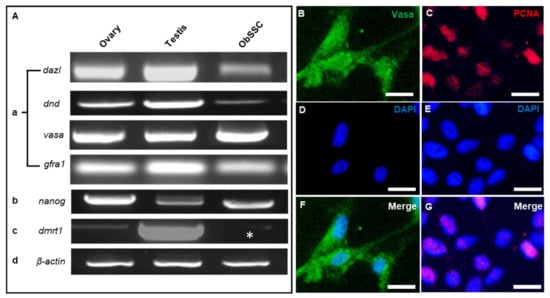
Figure 3.
PCR and immunofluorescence analysis of ObSSCs. (A) Expression of germ cell markers by RT-PCR of total RNA from ObSSCs and adult gonads with primers for dazl, dnd, vasa, and gfra1. (B) Expression of stem cell marker by RT-PCR with primers for nanog. (C) Expression of Sertoli cell marker by RT-PCR with primers for dmrt1 (asterisk). (D) Actin expression was determined for calibration. (B–G) Immunofluorescence of Vasa (green) and PCNA (red) in ObSSCs. (Bars = 20 µm).
ObSSCs showed a high proliferation rate. When the passage ratio was 1:2 or 1:3, the number of cells nearly doubled in 2 days, and the cells maintained rapid growth for more than 1 year. Through immunostaining, ObSSCs were characterized and mitotic activity was determined. The ObSSCs showed a strong proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) signal, and almost all cells exhibited positive expression for germ cell marker VASA (Figure 3B–G). After ObSSCs (at Passage 80) were subjected to 2 weeks of cryopreservation and recovered, most cells still had strong AP activity (Figure S2C,D).
3.3. Differentiation Induction of ObSSCs In Vitro
To unambiguously identify the ObSSCs, we transfected the plasmid pCVpr into ObSSCs at Passage 40. A satisfactory efficiency (15–20%) was achieved with the GeneJuice reagent. The red fluorescent protein (RFP)-expressing ObSSCs were clonally expanded for 2 months (Figure 4A–C). The RFP-expressing ObSSCs still maintained the same high growth rate and high AP activity as untransfected ObSSCs (Figure S2F). ObSSCs formed three-dimensional EBs in suspension culture. After continuous treatment with retinoic acid for one week, the types of terminally differentiated cells from EBs were identified, including neurons, astrocytes, and epithelial cells, suggesting the pluripotency ability of ObSSCs in vivo (Figure 4G–I).
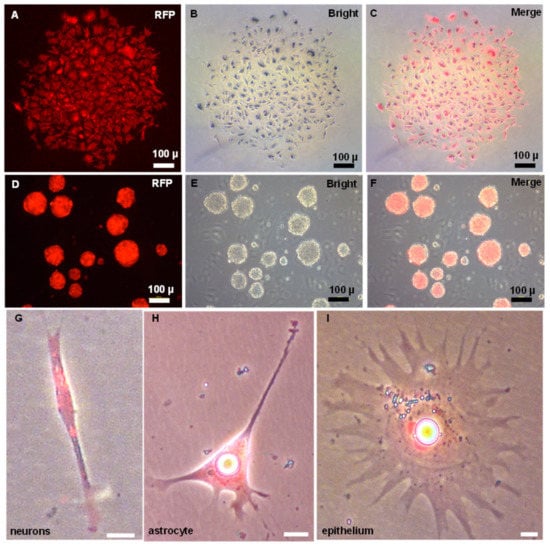
Figure 4.
Pluripotency of ObSSCs in vitro. (A–C) Single colony of ObSSCs expressed with RFP by transfection with pCVpr at Passage 40. (D–F) Embryoid bodies formed by suspension culture of ObSSCs labeled with RFP. (G–I) The types of terminally differentiated cells from EBs. (Bars = 10 µm unless indicated).
3.4. Pluripotency of ObSSCs In Vivo
Furthermore, the in vivo pluripotency of ObSSCs was tested by cell-embryo transplantation. With RFP-expressing ObSSCs as transplant donors, 100–200 cells were transplanted into zebrafish blastocysts. A total of 80 zebrafish embryos were transferred, of which 11 were found to be positive (13.75%). Among the transfer-positive embryos, five embryos were able to develop normally, and the remaining embryos died due to excessive mechanical damage during transfer. To explore the development of ObSSCs in the zebrafish host, we observed the recipients for one week after transplantation. ObSSCs were not rejected in the zebrafish host but followed the embryonic development of zebrafish to form chimeras, showing normal proliferation and differentiation ability in zebrafish (Figure 5). Due to the different positions of the blastocyst transplanted, ObSSCs differentiated into a variety of tissues, such as vascular epithelial cells, skin cells, and muscle tissues (Figure S4). The results show that ObSSCs adopted the developmental program of the zebrafish host and proliferated and differentiated into various tissues from three germ layers in zebrafish.
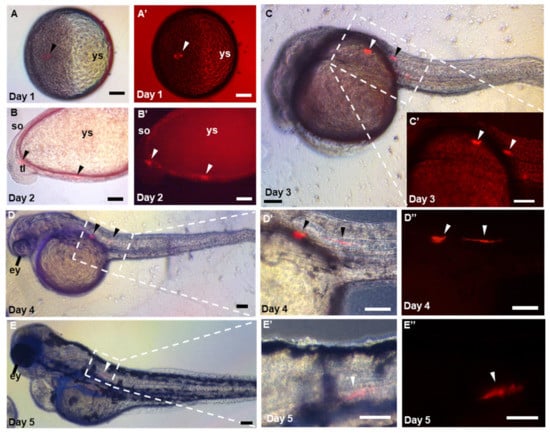
Figure 5.
Pluripotency of ObSSCs in vivo. (A–E) Different stages of embryo, in which the chimeras were observed by microscopy at 1 to 5 days post-fertilization. (A–D,D′,E,E′) Merge of bright and fluorescent fields. (A′–C′,D″,E″) Red fluorescent micrograph. ys, yolk sac; ey, eye; so; somite; tl; tail; ht; heart. (Scale bars, 100 µm).
3.5. Sperm Production of ObSSC In Vitro
SSCs reside in a specialized microenvironment in the testis of vertebrates and maintain spermatogenesis homeostasis by providing growth factors and cell-to-cell interactions [,]. To simulate the process of meiosis in vitro, we co-cultured ObSSCs with ObCTs (at Passage 4). We collected RFP-expressing ObSSCs and ObCTs separately for chromosome examination by flow cytometry. ObCTs contain three peaks of haploid, diploid, and tetraploid DNA content, indicating that the cells can enter and complete meiosis to produce haploid products (Figure 6O). ObSSCs exhibit two peaks of diploid and tetraploid DNA content (Figure 6P).
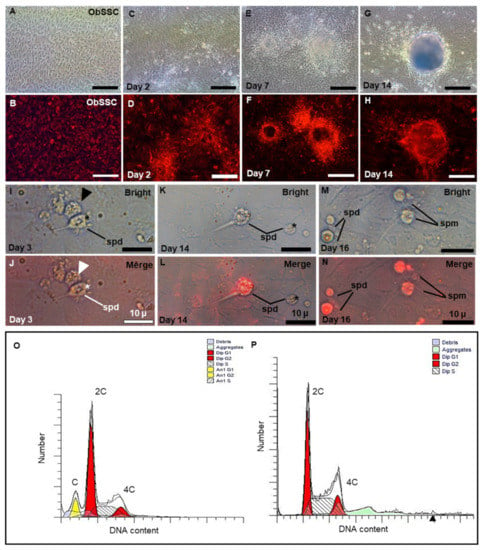
Figure 6.
Sperm production of ObSSCs in vivo. (A,B) The RFP-expressing ObSSCs were evenly distributed in the culture wells. (C–H) Coculture of O. bidens primary testicular cells and ObSSCs at Passage 70 were maintained at confluence without subculture for 2 weeks. (I–N) After coculture of O. bidens primary testicular cells and ObSSCs, sperm production can be observed in the culture medium. (I,J) Sperm from O. bidens primary testis cells. A cluster of four sperm from a tetrad is indicated by an arrow. (K–N) RFP-positive, spermatid, and sperm with a thin and long tail. (O) Primary testicular cells showing a prominent haploid peak in addition to diploid and tetraploid peaks. (P) ObSSCs at Passage 70 were maintained under normal culture conditions for undifferentiated proliferation, showing diploid and tetraploid peaks. c, 2c, and 4c, haploid, diploid, and tetraploid DNA contents, respectively. (Scale bars, 100 µm in (A–H); 10 µm in (I–N)).
From Day 1 of coculture, we exposed cells to the EMS4 medium containing fetal bovine serum (FBS), basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), fish serum, and medaka embryo extract (MEM). It can be observed that RFP-expressing ObSSCs that grow uniformly before coculture are clustered under coculture with ObCTs (Figure 6A–D). After one week, ObSSCs and ObCT together formed EBs (Figure 6E–H). The volume of the EB increased after two weeks and did not increase significantly in the third week (Figure S3).
During spermatogenesis, four round spermatids from a single primary spermatocyte are connected into a tetrad through cytoplasmic bridges []. On Day 3 of coculture, a clustered tetrad consisting of four round cells from ObCT was observed in the medium (Figure 6I,J). On Day 14, RFP-expressing sperm cells were observed in the cultured medium, showing that ObSSCs were gradually induced into immature sperm cells (Figure 6K,L). After 16 days of coculture, it was observed that RFP-expressing ObSSCs were differentiated into more mature sperm with slight wobbling behavior in their tails; however, they could not swim normally (Figure 6M,N). Briefly, these findings suggested that, under suitable induction conditions, ObSSCs could enter the spermatogenesis stage to produce sperm cells.
4. Discussion
In this study, a normal SSC line was established for the first time in farmed fish, Chinese hook snout carp, and it was verified that the ObSSC line could produce sperm by coculture with testicular cells. ObSSCs were identified by various methods, including AP activity staining, identification of germ stem cell marker genes, cellular immunohistochemistry, and its potential spermatogenesis ability. ObSSCs underwent cryopreservation and resuscitation in vitro, followed by more than 2 years of subculture. ObSSCs had a stable growth rate and a uniform oval shape. The results confirmed that ObSSCs stably showed the characteristics of SSCs, indicating the successful establishment of the O. bidens spermatogonial stem cell line.
An appropriate culture system is a key to successfully establishing a spermatogonial stem cell line. A previous study reported that high-level FBS not only promoted the proliferation of germ cells in rainbow trout, but also promoted the rapid proliferation of somatic cells, which was not conducive to the continued growth of germ cells []. Zebrafish SSCs cultured with FBS were also unable to maintain their normal proliferation []. In salmon, FBS was replaced by bovine serum (BSA) and salmon serum to inhibit somatic cell growth and maintain the biological properties of cultured salmon SSCs in a short time []. The growth factors in medaka embryo extracts are also important for maintaining the properties of medaka embryonic stem cells and SSCs [,]. The medium used in this study was partially modified on the basis of the EMS4 medium. We mixed FBS with sea bass serum in an appropriate ratio and added medaka embryo extract and bFGF. Interestingly, although medaka and O. bidens are cross-order species, the requirement for stable growth of ObSSCs under feeder-free conditions is very similar to that of medaka. Showing that the growth factors in medaka embryos still play an important role in maintaining ObSSCs’ biological characteristics.
Recent studies have shown that SSCs have the potential to differentiate into various cells after induction. For example, mouse male SSCs can be transformed into oocyte-like cells in culture []. Embryonic stem-like cells from mouse SSCs can be transformed into retinal ganglion cells with morphological and functional characteristics []. Human SSCs can generate biologically functional neurons in vitro []. Notably, we found that retinoic acid induced ObSSCs to differentiate into nerve cells, epithelial cells, and other somatic cells. In medaka, a previous study reported that the spermatogonial cell line (SG3) differentiates into four different ectodermal and mesodermal somatic cell types in vitro []. After microinjection of ObSSCs into zebrafish embryos at the blastula stage, ObSSCs proliferated and differentiated with the development of zebrafish embryos to form chimeras, and the differentiative capacity of donor cells into multiple tissues in zebrafish embryos represented the most convincing demonstration of their pluripotency both in vitro and in vivo.
Spermatogenesis goes through three main stages: self-renewal of spermatogonia, meiosis, and sperm production. During meiosis, round sperm cells are formed to further generate mature sperm. Previous studies have shown that in lower vertebrates, spermatogenesis can be performed in vitro. In medaka, coculture of the SG3 cell line with gonadal somatic cells from rainbow trout or Coilia nasus [] can induce sperm in vitro []. Recently, the whole spermatogenesis process of mice was reproduced in vitro by combining IPS induction technology and 3D culture technology, and the generated organoids formed a structure similar to seminiferous tubules, in which spermatogenesis was performed and functional sperm was obtained [,]. In the current study, flow cytometry results revealed that long-term-cultured ObSSCs could not spontaneously enter the spermatogenesis program. Interestingly, coculture by simulating the testicular environment in vivo not only facilitated the production of sperm by ObSSCs, but also induced them to re-form larger gonadal organoids. Whether spermatogenesis can be performed inside the organoids generated in this experiment requires further research.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, SSCs have unique advantages over other types of stem cells, which are excellent models for stem cell biology. Especially in recent years, the widespread application of SSCs in fish germ cell transplantation has gradually become an important aspect of fish reproductive development. In Chinese rare minnow (Gobiocypris rarus), gene-edited sperm derived from different subfamily species were obtained by transplanting SSCs into zebrafish []. The establishment of the O. bidens SSC line contributes to exploring the potential and regulatory mechanism of fish SSC differentiation and also lays a foundation for further research on fish germ cell transplantation, which is of great importance to the protection of the endangered fish species and the optimization of fish resources and confers novel insight into fish breeding. Further studies are needed to determine whether the SSC of O. bidens can differentiate into functional gametes and produce offspring of O. bidens upon transplantation to surrogate fish.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/biology11071069/s1. Figure S1. Immunofluorescence analysis of primary cultured testis cells of O. bidens. Green fluorescence is for Vasa protein, and blue is the nuclear staining with DAPI. (A–C) View under low magnification. (D–F) View under high magnification. EB, embryoid body. Scale bars, 100 µm; Figure S2. Derivation and characterization of ObSSCs. (A,B) Brightfield observation and alkaline phosphatase staining analysis of ObSSC cells at Passage 6 (Day 20). (C,D) ObSSCs were recovered and stained by alkaline phosphatase after cryopreservation. (E) Haploid metaphase of ObSSCs. (F) AP staining analysis of RFP-expressing ObSSCs. Scale bars, 100 µm; Figure S3. Gonadal-like organoids formed after coculture of ObSSCs and ObTCs for 20 days. (A) Bright field. (B) Fluorescence field. Scale bars, 100 µm; Figure S4. Pluripotency of ObSSCs in vivo. The RFP-expressing ObSSCs were transplanted into zebrafish embryos at blastula stage. (A–I) Micrograph of a zebrafish chimera in the side view from 2 dpf to 5 dpf. (A–C, D–F, and G–I) Three representative chimeras at different developmental days. Showing wide distribution of ObSSCs in zebrafish embryos, including blood vessel wall epithelial tissue, skin, muscle tissue, etc. The photomicrograph is a merger of red fluorescence and bright fields. ey, eye; ht, heart; so, somite; tl, tail; ys, yolk sac. Scale bars, 100 µm.
Author Contributions
Methodology, investigation data curation, analysis, and writing: X.C., Y.K. and Y.Z.; visualization: Y.K. and X.C.; resources: K.G. and W.W.; writing—review and editing: L.G. and M.J.; funding, writing—review and editing: M.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFD0901205) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31672700).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Shanghai Ocean University Animal Care and Use Committee with Approval Number SHOU-2021-118.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Not Applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gui, J.-F.; Zhou, L.; Li, X.-Y. Rethinking fish biology and biotechnologies in the challenge era for burgeoning genome resources and strengthening food security. Water Biol. Secur. 2022, 1, 100002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.-Y.; Hong, X.-Y.; Zhong, C.-Y.; Wu, X.-L.; Zhu, X.-P. Restoring Genetic Resource through In Vitro Culturing Testicular Cells from the Cryo-Preserved Tissue of the American Shad (Alosa sapidissima). Biology 2022, 11, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazur, P.; Leibo, S.; Seidel, G.E., Jr. Cryopreservation of the germplasm of animals used in biological and medical research: Importance, impact, status, and future directions. Biol. Reprod. 2008, 78, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoshizaki, G.; Lee, S. Production of live fish derived from frozen germ cells via germ cell transplantation. Stem Cell Res. 2018, 29, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizaki, G.; Yazawa, R. Application of surrogate broodstock technology in aquaculture. Fish. Sci. 2019, 85, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dunlop, C.E.; Telfer, E.E.; Anderson, R.A. Ovarian germline stem cells. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2014, 5, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, X.; Nobrega, R.; Psenicka, M. Spermatogonial Stem Cells in Fish: Characterization, Isolation, Enrichment, and Recent Advances of In Vitro Culture Systems. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dias, G.C.M.; Batlouni, S.R.; Cassel, M.; Chehade, C.; De Jesus, L.W.O.; Branco, G.S.; Camargo, M.P.; Borella, M.I. Isolation, in vitro study, and stem cell markers for type A spermatogonia in a Characiformes species. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2020, 87, 783–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, K.; Nayernia, K.; Maier, L.S.; Wagner, S.; Dressel, R.; Lee, J.H.; Nolte, J.; Wolf, F.; Li, M.; Engel, W.; et al. Pluripotency of spermatogonial stem cells from adult mouse testis. Nature 2006, 440, 1199–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikura, Y.; Ohta, H.; Sato, T.; Murase, Y.; Yabuta, Y.; Kojima, Y.; Yamashiro, C.; Nakamura, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Ogawa, T.; et al. In vitro reconstitution of the whole male germ-cell development from mouse pluripotent stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2021, 28, 2167–2179.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Wang, M.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, X.; Fu, R.; Wan, H.; Xie, M.; Liu, M.; Guo, X.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Complete Meiosis from Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Germ Cells In Vitro. Cell Stem Cell 2016, 18, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawasaki, T.; Siegfried, K.R.; Sakai, N. Differentiation of zebrafish spermatogonial stem cells to functional sperm in culture. Development 2016, 143, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Higaki, S.; Shimada, M.; Kawamoto, K.; Todo, T.; Kawasaki, T.; Tooyama, I.; Fujioka, Y.; Sakai, N.; Takada, T. In vitro differentiation of fertile sperm from cryopreserved spermatogonia of the endangered endemic cyprinid honmoroko (Gnathopogon caerulescens). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, X.; Tao, B.; Wang, Y.; Hu, W.; Sun, Y. Isolation and Characterization of Germline Stem Cells in Protogynous Hermaphroditic Monopterus albus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, W.W.; Mo, C.Y.; Dong, M.D.; Jia, K.T.; Liu, W.; Yi, M.S. Production of functional sperm from in vitro-cultured premeiotic spermatogonia in a marine fish. Zool. Res. 2022, 43, 537–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhao, H.; Xu, H.; Wang, W.; Liu, R.; Chen, T.; Deng, J.; Gui, J. Establishment of a normal medakafish spermatogonial cell line capable of sperm production in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 8011–8016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawasaki, T.; Saito, K.; Sakai, C.; Shinya, M.; Sakai, N. Production of zebrafish offspring from cultured spermatogonial stem cells. Genes Cells 2012, 17, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Zhu, Y.; Gan, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, Z.; Ren, J.; Li, M. De novo transcriptome analysis of gonads reveals the sex-associated genes in Chinese hook snout carp Opsariichthys bidens. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 23, 101068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.; Hong, N.; Hong, Y. Derivation and characterization of haploid embryonic stem cell cultures in medaka fish. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 1418–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Winkler, C.; Schartl, M. Pluripotency and differentiation of embryonic stem cell lines from the medakafish (Oryzias latipes). Mech. Dev. 1996, 60, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Hong, N.; Lu, W.; Zeng, H.; Song, J.; Hong, Y. Fusion gene vectors allowing for simultaneous drug selection, cell labeling, and reporter assay in vitro and in vivo. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.; Hong, N.; Hong, Y. Generation of medaka fish haploid embryonic stem cells. Science 2009, 326, 430–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Hong, N.; Xu, H.; Song, J.; Hong, Y. Germline replacement by blastula cell transplantation in the fish medaka. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, N.; Chen, S.; Ge, R.; Song, J.; Yi, M.; Hong, Y. Interordinal chimera formation between medaka and zebrafish for analyzing stem cell differentiation. Stem Cells Dev. 2012, 21, 2333–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hong, Y.; Winkler, C.; Schartl, M. Production of medakafish chimeras from a stable embryonic stem cell line. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 3679–3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, U.; Quintanilla, R.H.; Grecian, S.; Gee, K.R.; Rao, M.S.; Lakshmipathy, U. Novel live alkaline phosphatase substrate for identification of pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2012, 8, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y. Karyotype study of Opsariichthys bidens and Misgurnus anguillicaudatus, and the relationship between polymorphism and taxonomy of fish chromosomes. J. Wuhan Univ. 1987, 1, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Song, P.; Xia, J.; Guo, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Li, M. Evolutionarily conserved boule and dazl identify germ cells of Coilia nasus. Aquac. Fish. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhu, F.; Li, Z.; Hong, N.; Hong, Y. Dazl is a critical player for primordial germ cell formation in medaka. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, N.; Li, M.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, T.; Yi, M.; Xu, H.; Zeng, H.; Song, J.; Hong, Y. Dnd Is a Critical Specifier of Primordial Germ Cells in the Medaka Fish. Stem Cell Rep. 2016, 6, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Hong, N.; Xu, H.; Yi, M.; Li, C.; Gui, J.; Hong, Y. Medaka vasa is required for migration but not survival of primordial germ cells. Mech. Dev. 2009, 126, 366–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacerda, S.M.; Costa, G.M.; de Franca, L.R. Biology and identity of fish spermatogonial stem cell. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2014, 207, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, J.; Liu, L.; Fan, Z.; Hong, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, L.; Wang, D. Identification, Prokaryote Expression of Medaka gdnfa/b and Their Biological Activity in a Spermatogonial Cell Line. Stem Cells Dev. 2017, 26, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellaiche, J.; Lareyre, J.J.; Cauty, C.; Yano, A.; Allemand, I.; Le Gac, F. Spermatogonial stem cell quest: nanos2, marker of a subpopulation of undifferentiated A spermatogonia in trout testis. Biol. Reprod. 2014, 90, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Sánchez, A.V.; Camp, E.; Mullor, J.L. Fishing pluripotency mechanisms in vivo. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 7, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, L.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Y. Establishment and characterization of the gonadal cell lines derived from large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) for gene expression studies. Aquaculture 2021, 546, 737300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rooij, D.G. Proliferation and differentiation of spermatogonial stem cells. Reproduction 2001, 121, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, B.T.; Gassei, K.; Orwig, K.E. Spermatogonial stem cell regulation and spermatogenesis. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 1663–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hecht, N.B. Molecular mechanisms of male germ cell differentiation. Bioessays 1998, 20, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikina, S.; Ihara, S.; Yoshizaki, G. Culture conditions for maintaining the survival and mitotic activity of rainbow trout transplantable type A spermatogonia. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2008, 75, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurita, K.; Burgess, S.M.; Sakai, N. Transgenic zebrafish produced by retroviral infection of in vitro-cultured sperm. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 1263–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shikina, S.; Yoshizaki, G. Improved in vitro culture conditions to enhance the survival, mitotic activity, and transplantability of rainbow trout type a spermatogonia. Biol. Reprod. 2010, 83, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Cao, J.; Ji, P.; Zhang, D.; Ma, L.; Dym, M.; Yu, Z.; Feng, L. Oocyte-like cells induced from mouse spermatogonial stem cells. Cell Biosci. 2012, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suen, H.C.; Qian, Y.; Liao, J.; Luk, C.S.; Lee, W.T.; Ng, J.K.W.; Chan, T.T.H.; Hou, H.W.; Li, I.; Li, K.; et al. Transplantation of Retinal Ganglion Cells Derived from Male Germline Stem Cell as a Potential Treatment to Glaucoma. Stem Cells Dev. 2019, 28, 1365–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Hao, D.; Liu, C.; Huang, D.; Chen, B.; Fan, H.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.; An, J.; et al. Generation of functional dopaminergic neurons from human spermatogonial stem cells to rescue parkinsonian phenotypes. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thoma, E.C.; Wagner, T.U.; Weber, I.P.; Herpin, A.; Fischer, A.; Schartl, M. Ectopic expression of single transcription factors directs differentiation of a medaka spermatogonial cell line. Stem Cells Dev. 2011, 20, 1425–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Jawad, M.; Chen, X.; Liu, D.; Ren, M.; Xu, G.; Gui, L.; Li, M. Establishment of a Coilia nasus gonadal somatic cell line capable of sperm induction in vitro. Biology 2022, 11, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Hao, Y.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Ye, D.; Zhang, R.; Wang, X.; He, M.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Z.; et al. Surrogate production of genome-edited sperm from a different subfamily by spermatogonial stem cell transplantation. Sci. China Life Sci. 2022, 65, 969–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).