Characterization and Genetic Diversity of Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae Isolates Associated with Rice Bacterial Leaf Spot in Heilongjiang, China
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Bacterial Isolates
2.2. Biochemical Characteristics
2.3. Pathogenicity Test
2.4. DNA Extraction
2.5. syrB Gene Detection
2.6. Phylogenetic Analysis of 16S rRNA
2.7. Multilocus Sequence Analysis
2.8. Repetitive PCR
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results
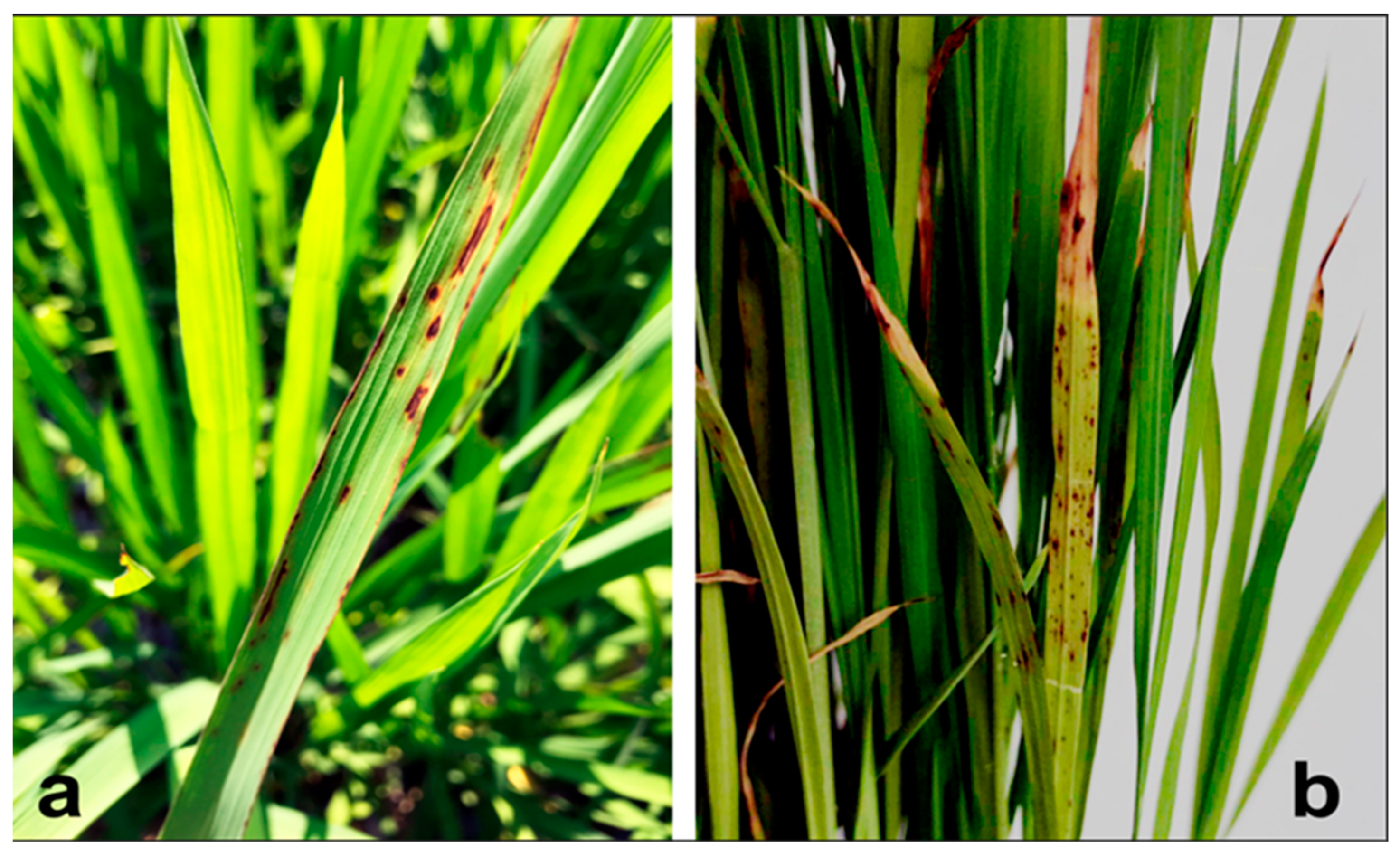
3.1. Identification and Characterization of Bacterial Strains
3.2. Pathogenicity Tests
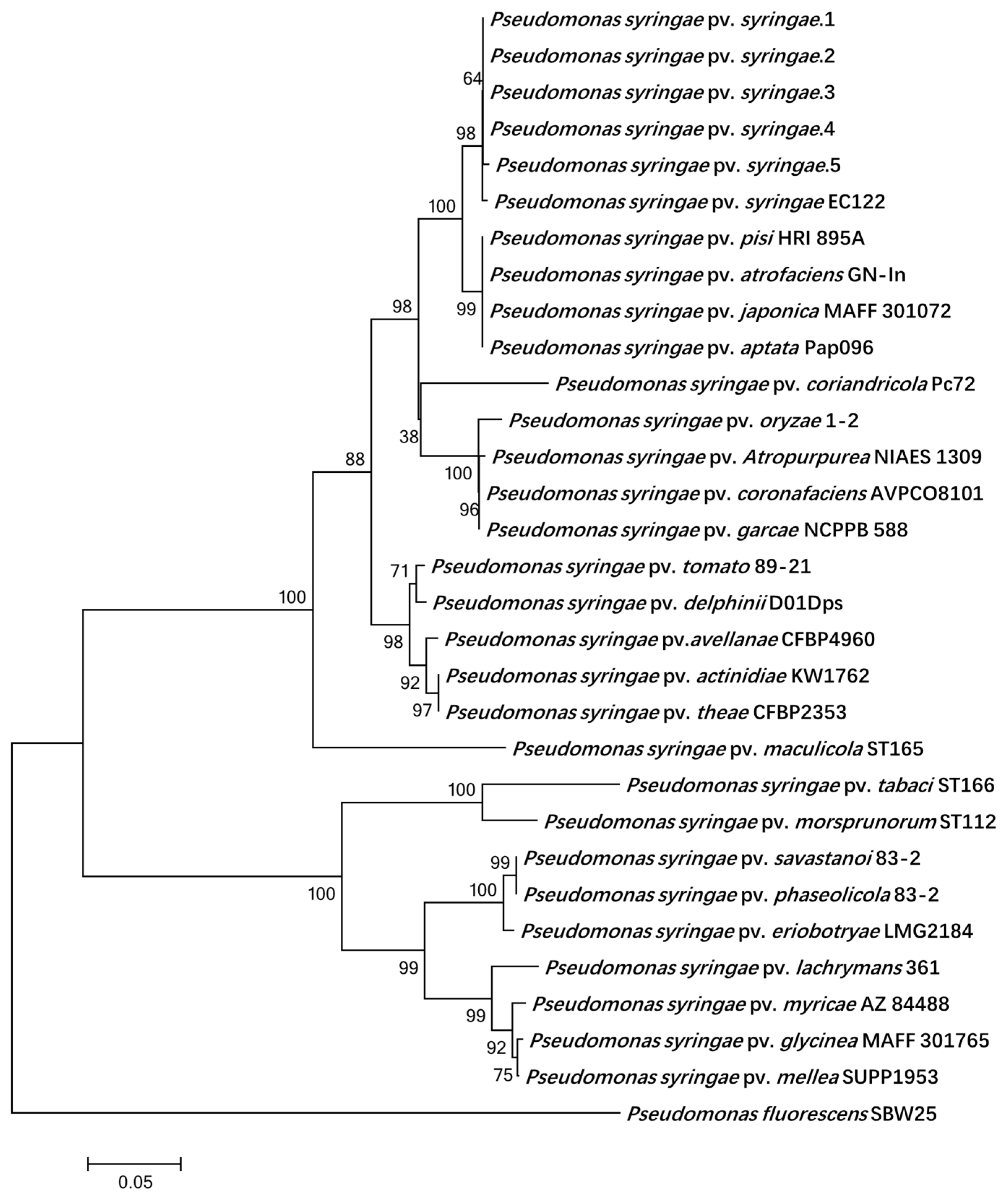
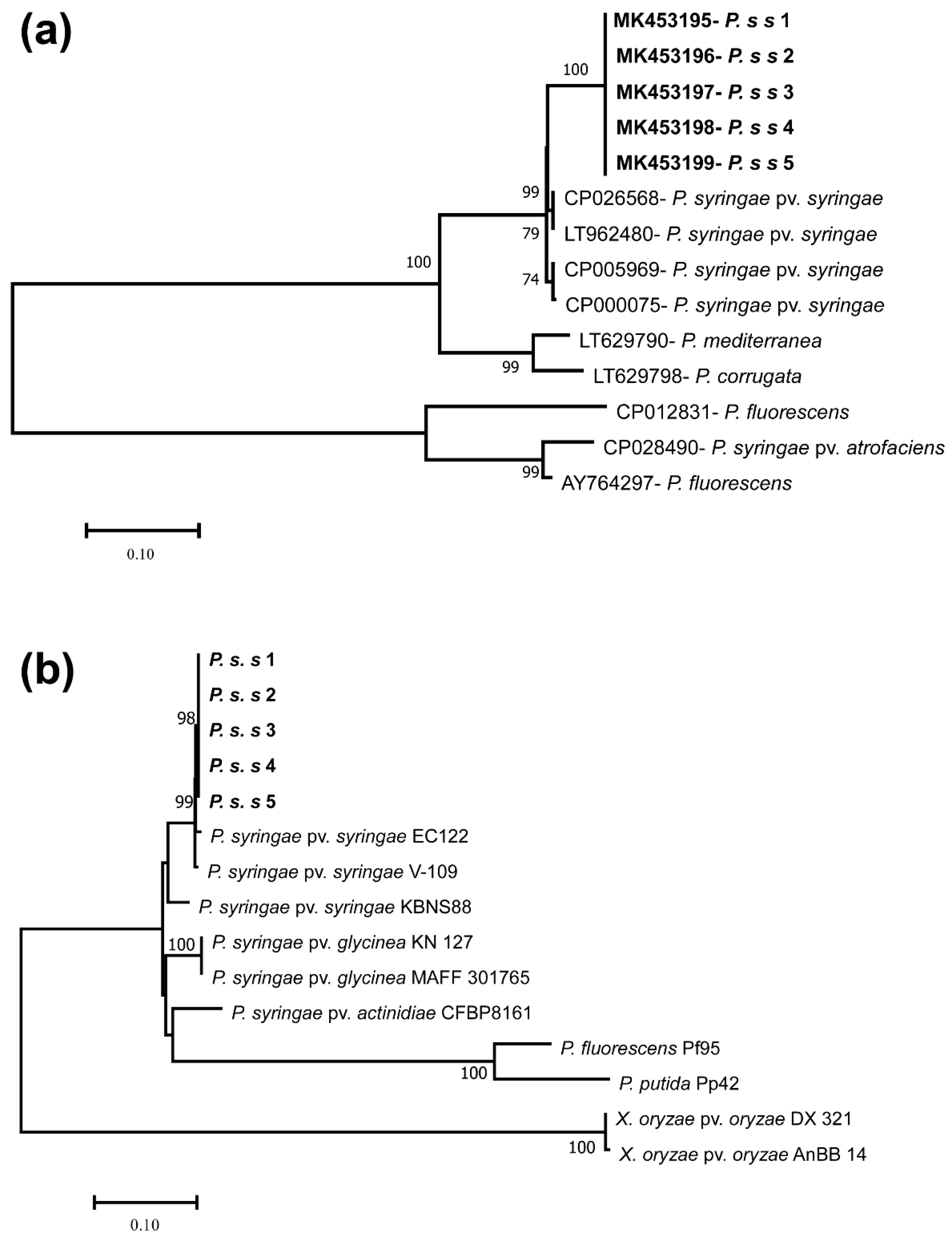
3.3. Molecular Characterization
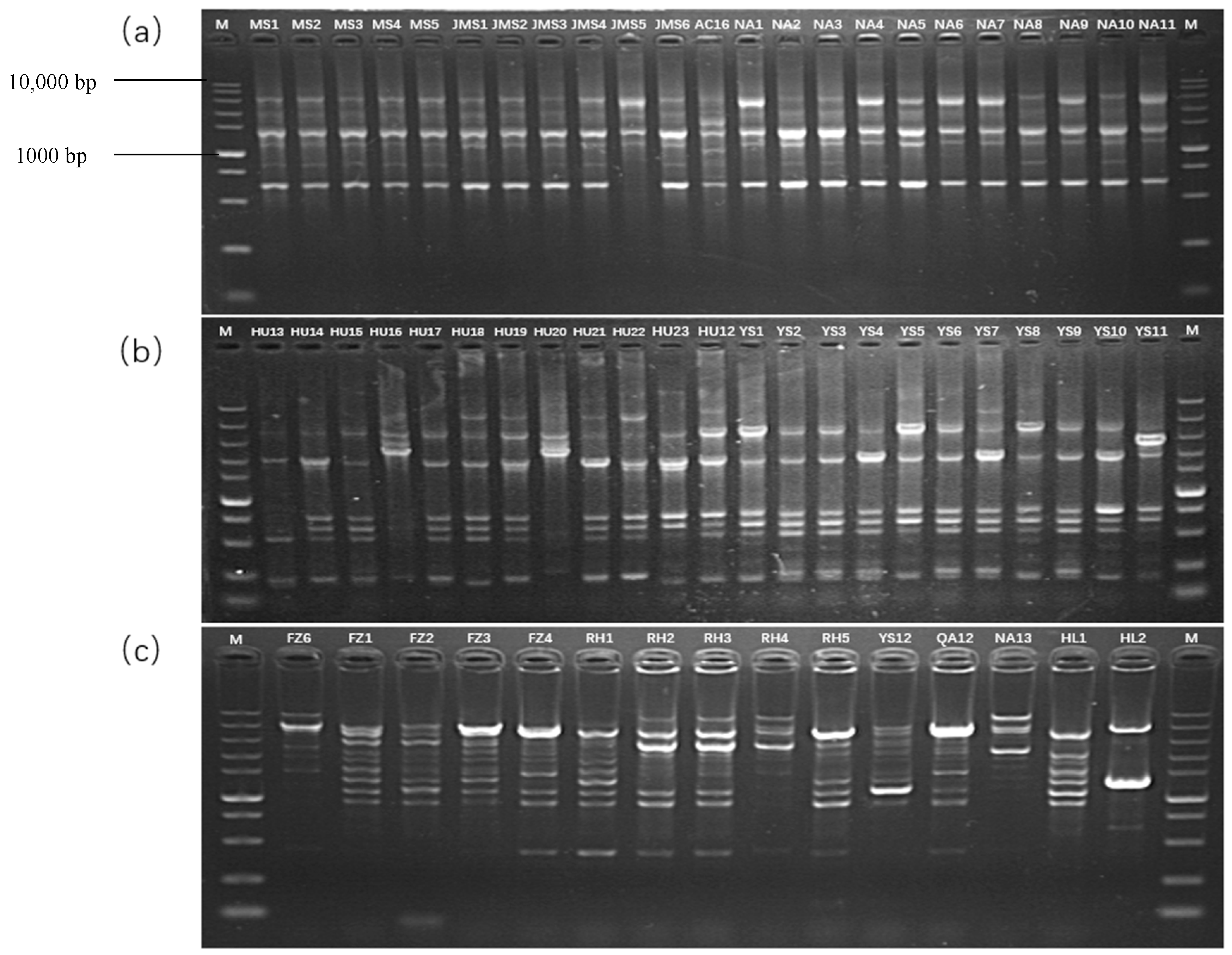
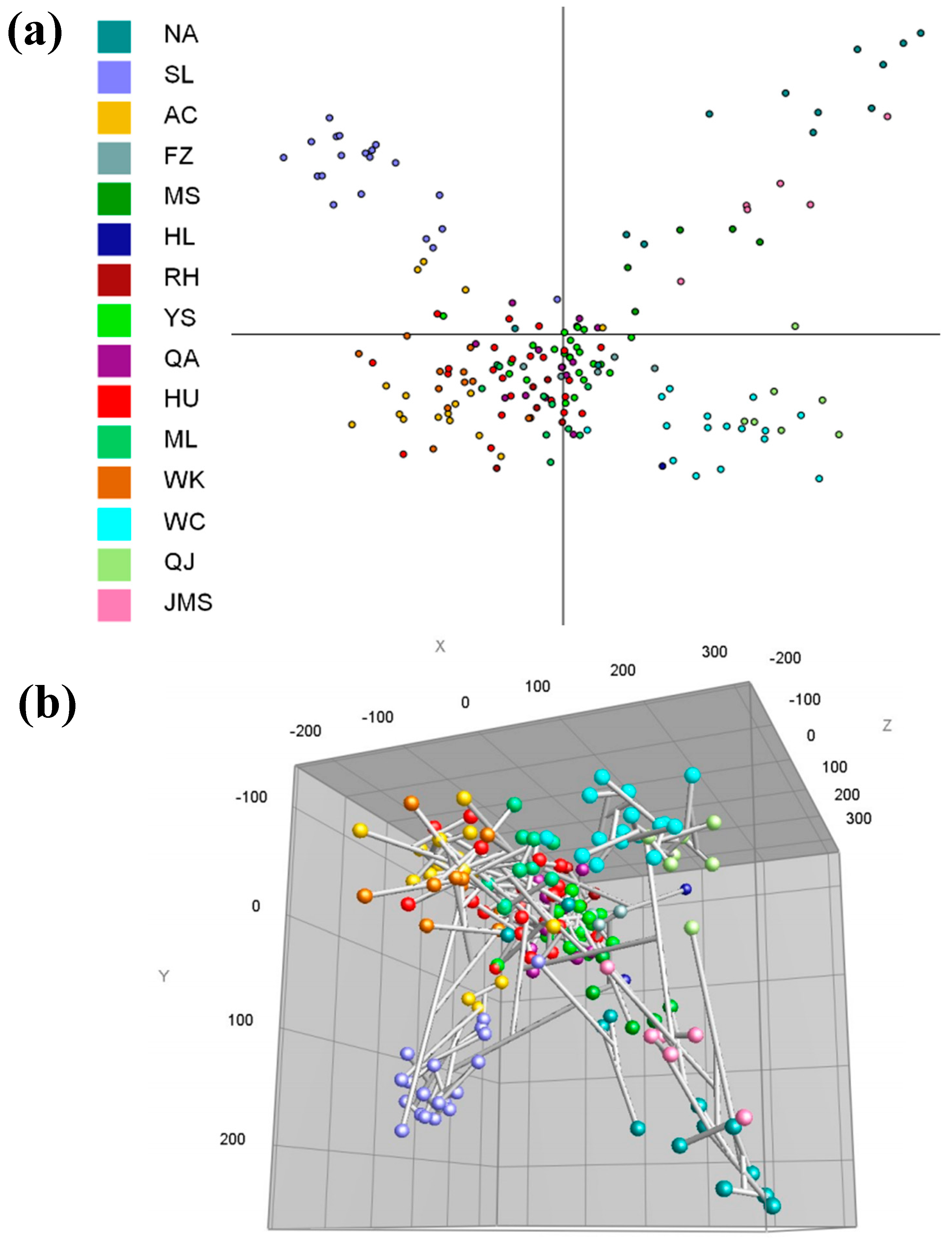
3.4. Rep-PCR Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- White, F.F.; Potnis, N.; Jones, J.B.; Koebnik, R. The Type III Effectors of Xanthomonas. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2009, 10, 749–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanneste, J.L. The Scientific, Economic, and Social Impacts of the New Zealand Outbreak of Bacterial Canker of Kiwifruit (Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae). Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2017, 55, 377–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Bentzmann, S.; Plésiat, P. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa Opportunistic Pathogen and Human Infections. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1655–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bull, C.T.; Clarke, C.R.; Cai, R.; Vinatzer, B.A.; Jardini, T.M.; Koike, S.T. Multilocus Sequence Typing of Pseudomonas syringae Sensu Lato Confirms Previously Described Genomospecies and Permits Rapid Identification of P. syringae pv. coriandricola and P. syringae pv. apii Causing Bacterial Leaf Spot on Parsley. Phytopathology 2011, 101, 847–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balaž, J.; Iličić, R.; Maširević, S.; Jošić, D.; Kojić, S. First Report of Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae Causing Bacterial Leaf Spots of Oil Pumpkin (Cucurbita Pepo) in Serbia. Plant Dis. 2014, 98, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanović, Ž.; Blagojević, J.; Nikolić, I. Leaf Spot Disease on Philodendron scandens, Ficus carica and Actinidia deliciosa Caused by Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae in Serbia. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2018, 151, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klement, Z. A New Bacterial Disease of Rice Caused by Pseudomonas oryzicola n. sp. Acta Microbiol. Acad. Sci. Hung. 1955, 2, 265–274. [Google Scholar]
- Young, J.M.; Dye, D.W.; Bradbury, J.F.; Panagopoulos, C.G.; Robbs, C.F. A Proposed Nomenclature and Classification for Plant Pathogenic Bacteria. N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 1978, 21, 153–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.T.; Ren, H.C. A Bacterial Disease of Rice New to China. Acta Phytopath 1960, 6, 90–92. [Google Scholar]
- Khu, T.C.; Bai, T.K. Investigations on a New Bacterial Disease of Rice, Brown Spot. Preliminary Communication (Distribution, Symptoms, and Determination of the Genus of the Causal Agent of the Disease). Acta Phytopath 1960, 6, 93–105. [Google Scholar]
- Funayama, H.; Hirano, T. A sheath brown rot of rice caused by Pseudomonas. Ann. Phytopathol. Soc. Jpn. 1963, 28, 67–68. [Google Scholar]
- Roach, R.; Mann, R.; Gambley, C.G.; Shivas, R.G.; Rodoni, B. Identification of Xanthomonas Species Associated with Bacterial Leaf Spot of Tomato, Capsicum and Chilli Crops in Eastern Australia. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2018, 150, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larrea-Sarmiento, A.; Dhakal, U.; Boluk, G.; Fatdal, L.; Alvarez, A.; Strayer-Scherer, A.; Paret, M.; Jones, J.; Jenkins, D.; Arif, M. Development of a Genome-Informed Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay for Rapid and Specific Detection of Xanthomonas euvesicatoria. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gironde, S.; Manceau, C. Housekeeping Gene Sequencing and Multilocus Variable-Number Tandem-Repeat Analysis to Identify Subpopulations within Pseudomonas syringae pv. maculicola and Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato That Correlate with Host Specificity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 3266–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hilario, E.; Buckley, T.R.; Young, J.M. Improved Resolution on the Phylogenetic Relationships among Pseudomonas by the Combined Analysis of atpD, carA, recA and 16S rDNA. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2004, 86, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, K.N.; Kim, K.-H.; Takemoto, J.Y. PCR Detection of Cyclic Lipodepsinonapeptide-Producing Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae and Similarity of Strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- King, E.O.; Ward, M.K.; Raney, D.E. Two Simple Media for the Demonstration of Pyocyanin and Fluorescin. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1954, 44, 301–307. [Google Scholar]
- Lelliott, R.A.; Stead, D.E. Methods for the Diagnosis of Bacterial Diseases of Plants; Methods in Plant Pathology; Blackwell Scientific Publication: Boston, MA, USA, 1987; ISBN 978-0-632-01233-6. [Google Scholar]
- Schaad, N.W.; Jones, J.B.; Chun, W. Laboratory Guide for Identifiction of Plant Pathogenic Bacteria, 3rd ed.; American Phytopathological Society: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2001; ISBN 978-0-89054-263-7. [Google Scholar]
- Klement, Z.; Rudolph, K.; Sands, D.C. Methods in Phytobacteriology; Akadémiai Kiadó: Budapest, Hungary, 1990; ISBN 978-963-05-4955-4. [Google Scholar]
- Scortichini, M.; Rossi, M.P.; Loreti, S.; Bosco, A.; Fiori, M.; Jackson, R.W.; Stead, D.E.; Aspin, A.; Marchesi, U.; Zini, M.; et al. Pseudomonas syringae pv. coryli, the Causal Agent of Bacterial Twig Dieback of Corylus avellana. Phytopathology 2005, 95, 1316–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altschul, S. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A New Generation of Protein Database Search Programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lupski, J.R.; Weinstock, G.M. Short, Interspersed Repetitive DNA Sequences in Prokaryotic Genomes. J. Bacteriol. 1992, 174, 4525–4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Versalovic, J.; Schneider, M.; Bruijn, F.J.D.; Lupski, J.R. Genomic fingerprinting of bacteria using repetitive sequence-based polymerase chain reaction. Method Mol. Cell Biol. 1994, 5, 25–40. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, F.; Amadoro, C.; Conficoni, D.; Giaccone, V.; Colavita, G. Occurrence, Diversity of Listeria Spp. Isolates from Food and Food-Contact Surfaces and the Presence of Virulence Genes. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gardan, L.; Shafik, H.; Belouin, S.; Broch, R.; Grimont, F.; Grimont, P.A.D. DNA Relatedness among the Pathovars of Pseudomonas syringae and Description of Pseudomonas tremae sp. nov. and Pseudomonas cannabina sp. nov. (Ex Sutic and Dowson 1959). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1999, 49, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balestra, G.M.; Varvaro, L. Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae Causal Agent of Disease on Floral Buds of Actinidia deliciosa (A. Chev) Liang et Ferguson in Italy. J. Phytopathol. 1997, 145, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirvilleri, G.; Bonaccorsi, A.; Scuderi, G.; Scortichini, M. Potential Biological Control Activity and Genetic Diversity of Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae Strains. J. Phytopathol. 2005, 153, 654–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natalini, U.; Rossi, M.P.; Barionovi, D.; Scortichini, M. Genetic and Pathogenic Diversity of Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae Isolates Associated with Bud Necrosis and Leaf Spot of Pear in a Single Orchard. J. Plant Pathol. 2006, 88, 219–223. [Google Scholar]
- Scortichini, M.; Marchesi, U.; Dettori, M.T.; Rossi, M.P. Genetic Diversity, Presence of the syrB Gene, Host Preference and Virulence of Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae Strains from Woody and Herbaceous Host Plants. Plant Pathol. 2003, 52, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, E.L.; Bostock, R.M.; Kirkpatrick, B.C. Genetic Characterization of Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae Strains from Stone Fruits in California. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 3818–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cirvilleri, G.; Scuderi, G.; Bonaccorsi, A.; Scortichini, M. Molecular characterization of Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae strains from different host plants using fluorescent amplified fragment length polymorphism. J. Plant Pathol. 2006, 88, 329–333. [Google Scholar]
- Manceau, C.; Brin, C. Pathovars of Pseudomonas syringae Are Structured in Genetic Populations Allowing the Selection of Specific Markers for Their Detection in Plant Samples. In Pseudomonas Syringae and Related Pathogens; Iacobellis, N.S., Collmer, A., Hutcheson, S.W., Mansfield, J.W., Morris, C.E., Murillo, J., Schaad, N.W., Stead, D.E., Surico, G., Ullrich, M.S., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 503–512. ISBN 978-90-481-6267-3. [Google Scholar]
- Young, J.M. Pathogenicity and Identification of the Lilac Pathogen, Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringa van Hall 1902. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1991, 118, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, C.E.; Kinkel, L.L.; Xiao, K.; Prior, P.; Sands, D.C. Surprising Niche for the Plant Pathogen Pseudomonas syringae. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2007, 7, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoshkdaman, M.; Ebadi, A.A.; Mossanejad, S.; Pedramfar, H. Identification of causal agents of foot and sheath rot of rice in the field of Guilan province of Iran. Agric. Trop. Subtrop. 2008, 41, 17–20. [Google Scholar]


| Characteristics | Reaction | |
|---|---|---|
| Growth at 41 °C | − | |
| Detection of syrB | + | |
| Gram staining | − | |
| Hydrolysis gelatin | − | |
| Nitrate reductase | − | |
| LOPAT Test | Levan formation | + |
| Oxidase | − | |
| Potato rot | − | |
| Arginine dihydrolase | + | |
| Tobacco hypersensitivity | + | |
| Utilization as carbon source | Glucose | + |
| Mannose | + | |
| Lactose | + | |
| Maltose | − | |
| Sucrose | + | |
| Trehalose | − | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, L.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Haseeb, Y.; Song, S.; Xu, X.; Yang, M.; Zhang, J. Characterization and Genetic Diversity of Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae Isolates Associated with Rice Bacterial Leaf Spot in Heilongjiang, China. Biology 2022, 11, 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11050720
Peng L, Yang S, Zhang Y, Haseeb Y, Song S, Xu X, Yang M, Zhang J. Characterization and Genetic Diversity of Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae Isolates Associated with Rice Bacterial Leaf Spot in Heilongjiang, China. Biology. 2022; 11(5):720. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11050720
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Lili, Songrun Yang, Yao Zhang, Younis Haseeb, Shuang Song, Xiaofeng Xu, Mingxiu Yang, and Junhua Zhang. 2022. "Characterization and Genetic Diversity of Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae Isolates Associated with Rice Bacterial Leaf Spot in Heilongjiang, China" Biology 11, no. 5: 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11050720
APA StylePeng, L., Yang, S., Zhang, Y., Haseeb, Y., Song, S., Xu, X., Yang, M., & Zhang, J. (2022). Characterization and Genetic Diversity of Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae Isolates Associated with Rice Bacterial Leaf Spot in Heilongjiang, China. Biology, 11(5), 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11050720






