Bio-Ethology of Vespa crabro in Sardinia (Italy), an Area of New Introduction
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. European Hornet Foraging Activity
2.2. Predation Pressure of the European Hornet on Hives
2.3. Observations on European Hornet Free-Living Colonies
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
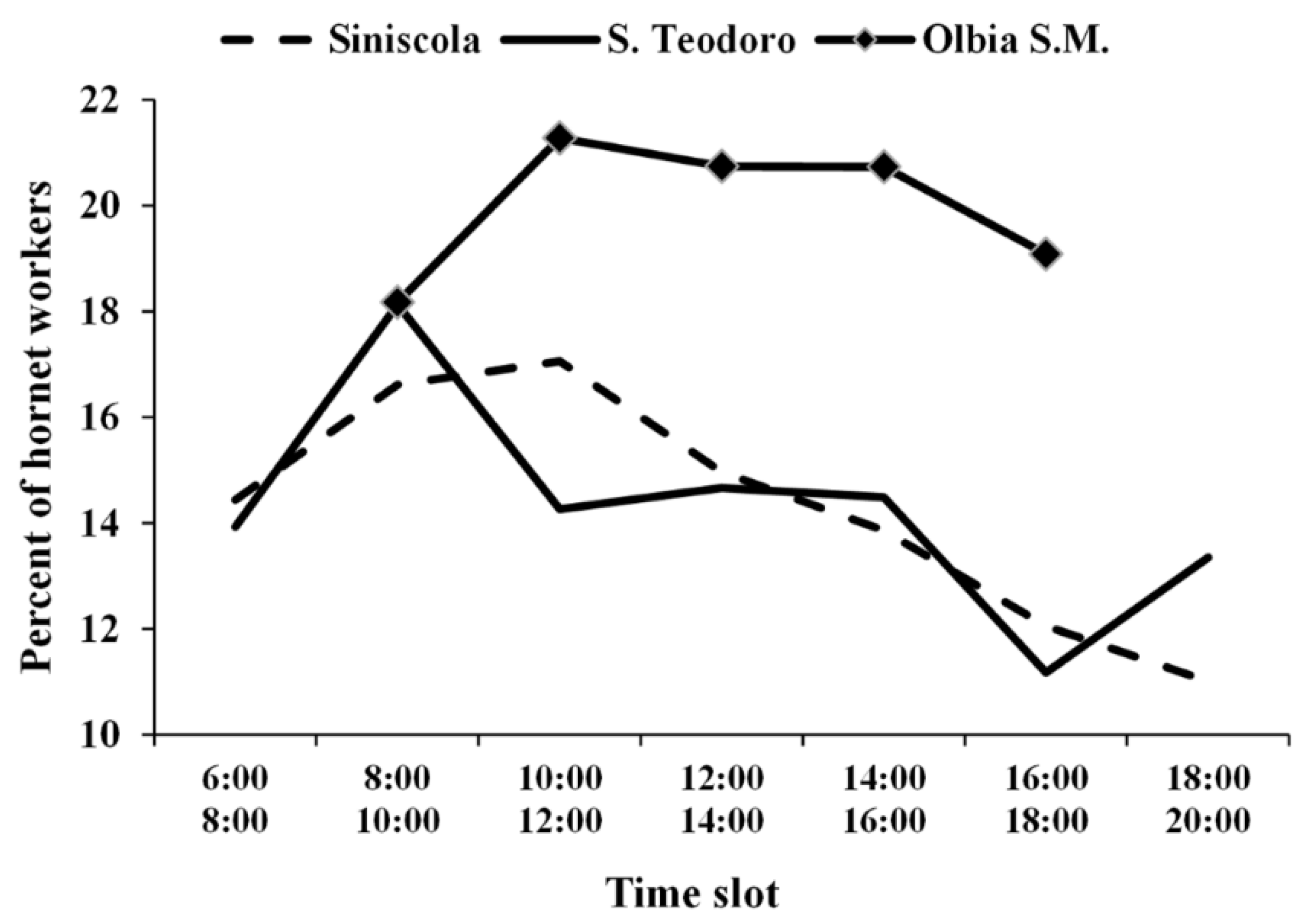
3.1. European Hornet Foraging Activity
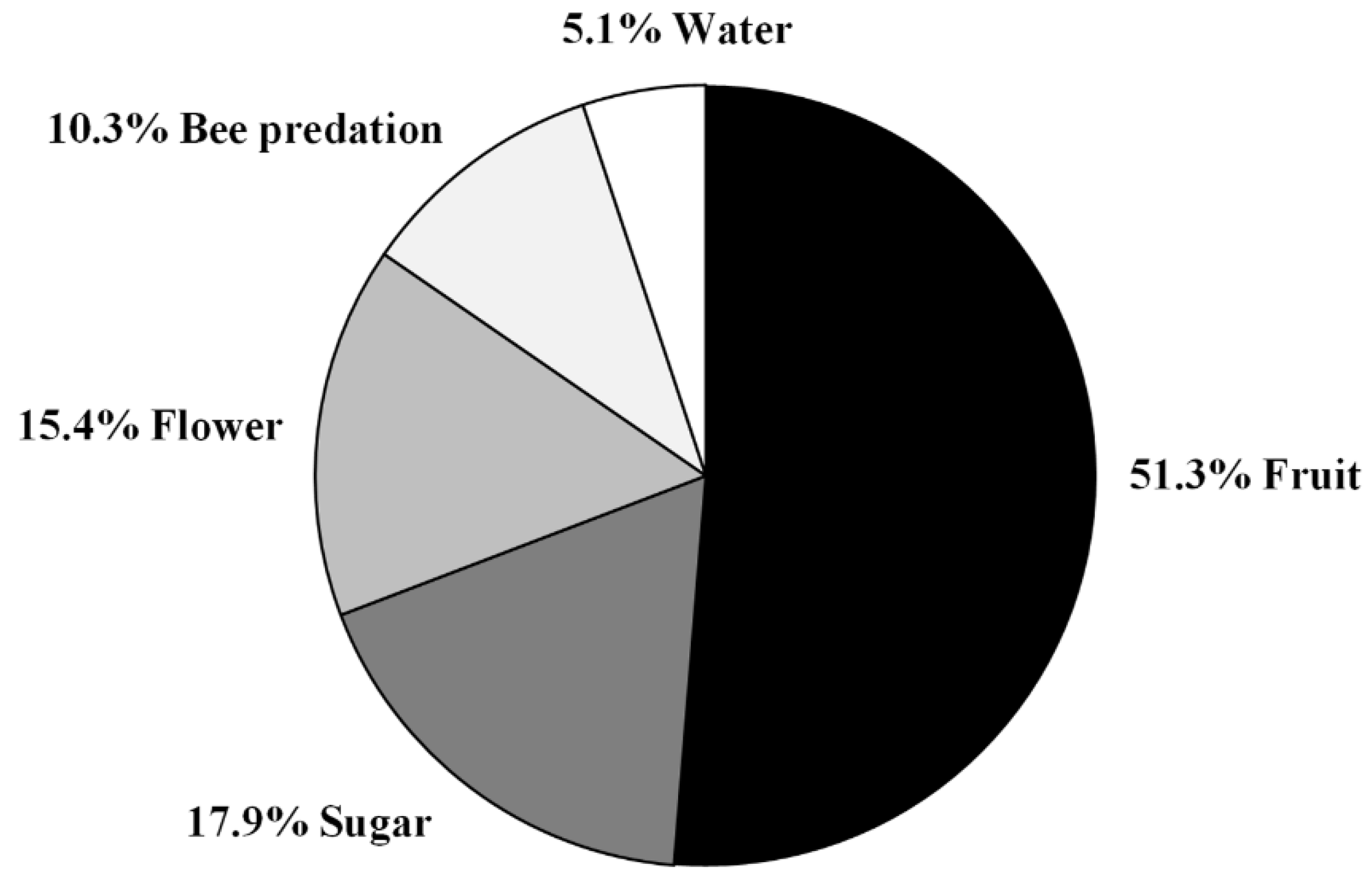
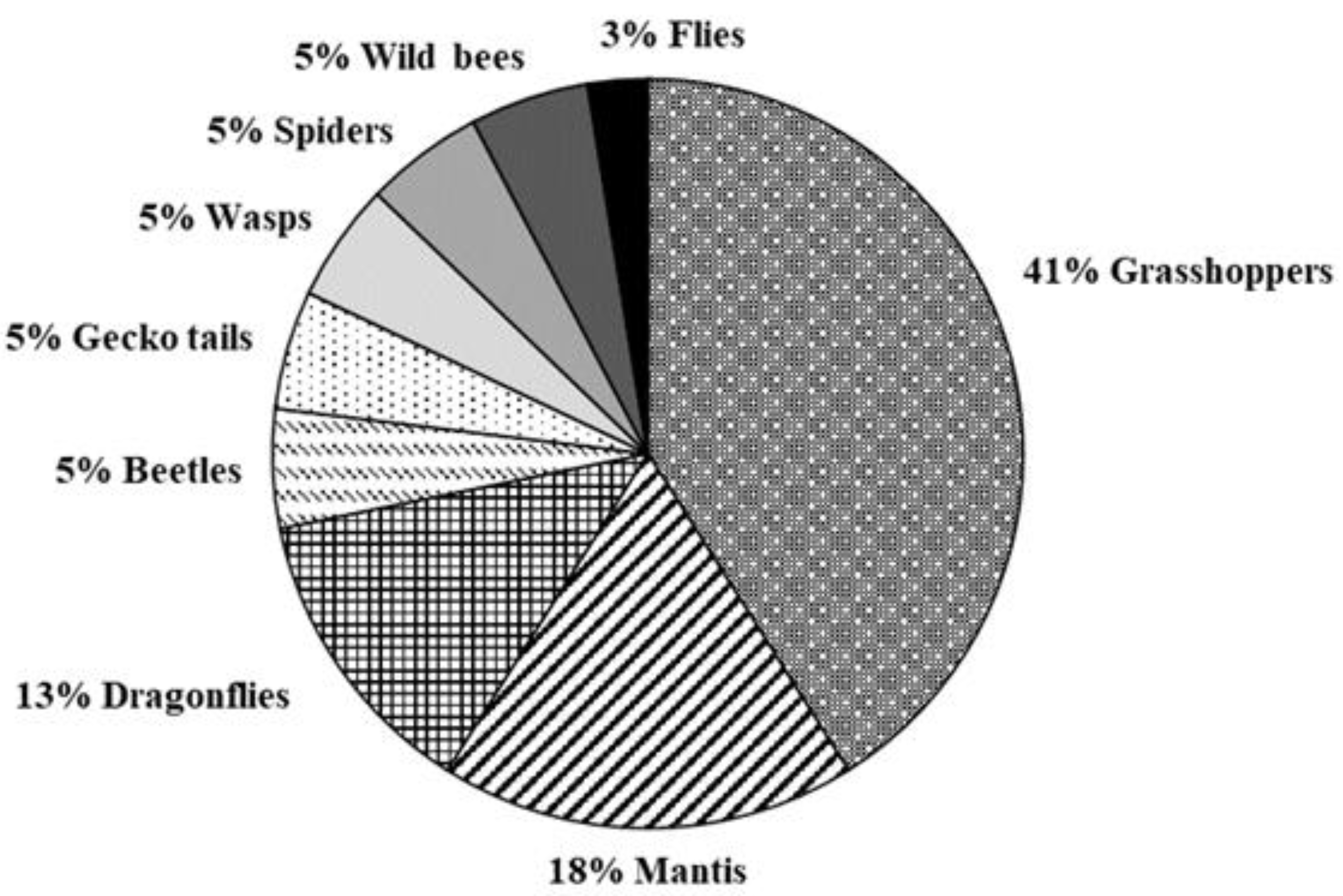
3.2. Predation Pressure of the European Hornet on Hives
3.3. Observations on European Hornet Free-Living Colonies
3.3.1. Hornet Ethogram
3.3.2. Intranidal and Extranidal Activity of the European Hornet Queen
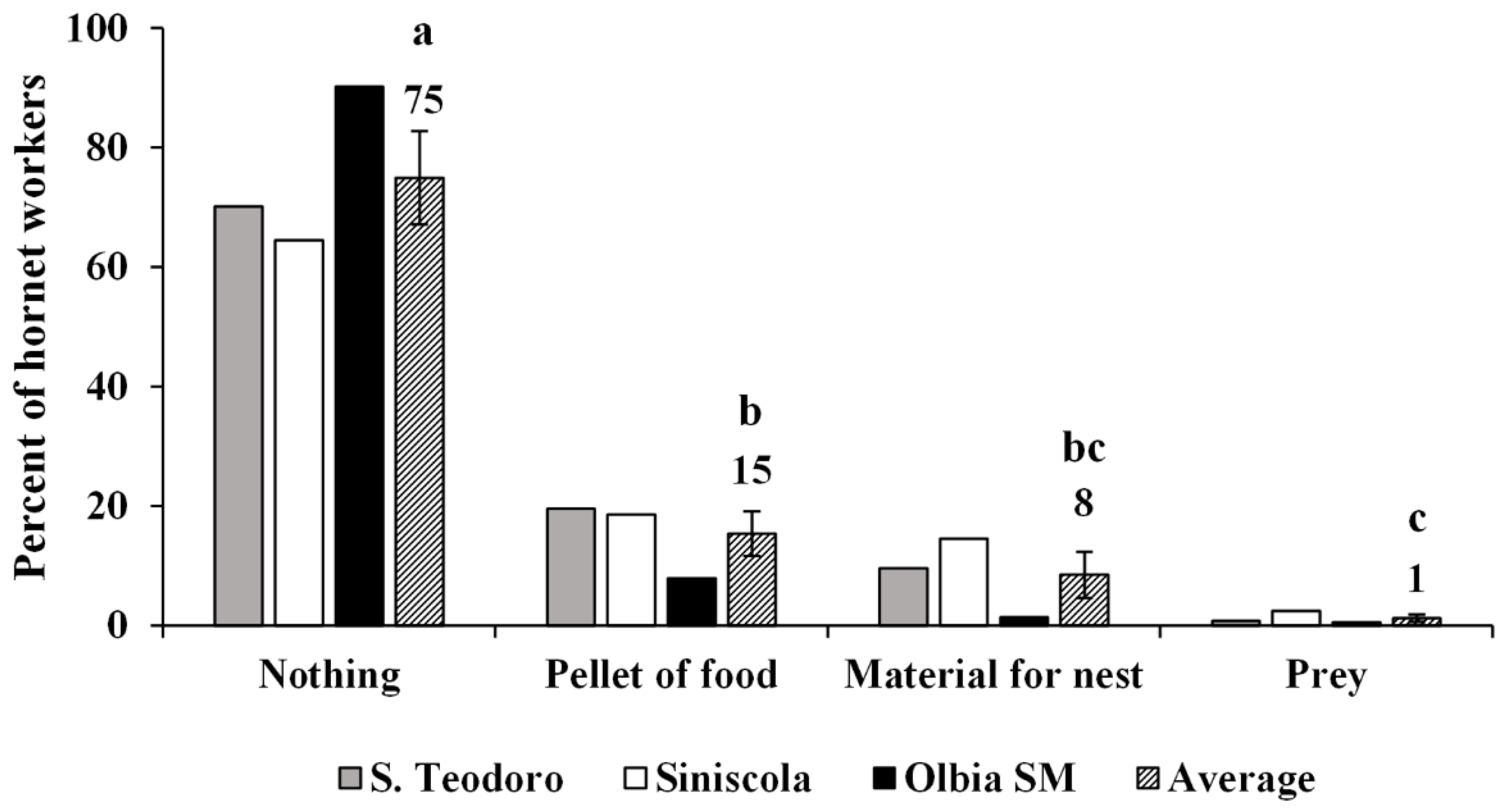
3.3.3. Foraging Activity of the Colonies and Tasks Performed Inside the Nest by Workers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carpenter, J.M.; Kojima, J.I. Checklist of the species in the subfamily Vespinae (Insecta: Hymenoptera: Vespidae). Nat. Hist. Bull. Ibaraki Univ. 1997, 1, 51–92. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, F.R.; Weidhaas, J., Jr. Distribution and habits of the giant hornet in North America. J. Econ. Entomol. 1956, 49, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landolt, P.J.; Monzon Sierra, J.; Unruh, T.R.; Zack, R.S. A new species of Vespula, and first record of Vespa crabro L. (Hymenoptera: Vespidae) from Guatemala, Central America. Zootaxa 2010, 2629, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, M.; Marshall, S.A.; Cheung, D.K. Identification atlas of the Vespidae (Hymenoptera, Aculeata) of the northeastern Nearctic region. Can. J. Arthropod Identif. 2008, 5, 1–492. [Google Scholar]
- Kimsey, L.; Carpenter, J. The Vespinae of North America (Vespidae, Hymenoptera). J. Hymenopt. Res. 2012, 28, 37–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pusceddu, M.; Floris, I.; Mannu, R.; Cocco, A.; Satta, A. Using verified citizen science as a tool for monitoring the European hornet (Vespa crabro) in the island of Sardinia (Italy). NeoBiota 2019, 50, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, M.; Yamane, S. Biology of the Vespine Wasps; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, M. Vespa and Provespa. In The Social Biology of Wasps; Ross, K.G., Matthews, R.W., Eds.; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 232–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, J.I.; Nakamura, J.; Akimoto, S.I.; Hasegawa, E. Kin structure and colony male reproduction in the hornet Vespa crabro (Hymenoptera: Vespidae). J. Ethol. 2004, 22, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monceau, K.; Maher, N.; Bonnard, O.; Thiéry, D. Evaluation of competition between a native and an invasive hornet species: Do seasonal phenologies overlap. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2015, 105, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edwards, R. Social Wasps. Their Biology and Control; Rentokil Limited: Sussex, UK, 1980; p. 398. [Google Scholar]
- Spradbery, J.P. Wasps. An Account of the Biology and Natural History of Social and Solitary Wasps, with Particular Reference to Those of the British Isles; University of Washington Press: Seattle, WA, USA, 1973; p. 408. [Google Scholar]
- Dijkstra, K.D.B.; Rivera, A.C.; Andrés, J.A. Repeated predation of Odonata by the hornet Vespa crabro (Hymenoptera: Vespidae). Int. J. Odonatol. 2001, 4, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, M. Comparative biology of the five Japanese species of the genus Vespa (Hymenoptera, Vespidae). Bull. Fac. Agric. Mie. Univ. 1984, 69, 1–131. [Google Scholar]
- Baracchi, D.; Cusseau, G.; Pradella, D.; Turillazzi, S. Defence reactions of Apis mellifera ligustica against attacks from the European hornet Vespa crabro. Ethol. Ecol. Evol. 2010, 22, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cini, A.; Cappa, F.; Petrocelli, I.; Pepiciello, I.; Bortolotti, L.; Cervo, R. Competition between the native and the introduced hornets Vespa crabro and Vespa velutina: A comparison of potentially relevant life-history traits. Ecol. Entomol. 2018, 43, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monceau, K.; Moreau, J.; Poidatz, J.; Bonnard, O.; Thiéry, D. Behavioral syndrome in a native and an invasive hymenoptera species. Insect Sci. 2015, 22, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusceddu, M.; Floris, I.; Buffa, F.; Salaris, E.; Satta, A. Agonistic interactions between the honeybee (Apis mellifera ligustica) and the European wasp (Vespula germanica) reveal context-dependent defense strategies. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pusceddu, M.; Mura, A.; Floris, I.; Satta, A. Feeding strategies and intraspecific competition in German yellowjacket (Vespula germanica). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lester, P.J.; Beggs, J.R. Invasion success and management strategies for social Vespula wasps. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2019, 64, 51–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buteler, M.; Yossen, M.B.; Alma, A.M.; Lozada, M. Interaction between Vespula germanica and Apis mellifera in Patagonia Argentina apiaries. Apidologie 2021, 52, 848–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmann, J. Observational study of behavior: Sampling methods. Behaviour 1974, 49, 227–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perrard, A.; Haxaire, J.; Rortais, A.; Villemant, C. Observations on the colony activity of the Asian hornet Vespa velutina Lepeletier 1836 (Hymenoptera: Vespidae: Vespinae) in France. Ann. Soc. Entomol. Fr. 2009, 45, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sokal, R.R.; Rohlf, F.J. Biometry, 2nd ed.; W.H. Freeman and Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1981; p. 859. [Google Scholar]
- Riabinin, K.; Kozhevnikov, M.; Ishay, J.S. Ventilating activity at the hornet nest entrance. J. Ethol. 2004, 22, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janet, C. Sur la Vespa crabro L.: Ponte: Conservation de la chaleur dans le nid. Société Zool. Fr. 1895. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, J.H.; Baker, I.; Baker, H.G. Similarity of amino acids in nectar and larval saliva: The nutritional basis for trophallaxis in social wasps. Evolution 1982, 36, 1318–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Miyazaki, H.; Kawasaki, Y.Y. Comparative study of the composition of hornet larval saliva, its effect on behaviour and role of trophallaxis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Comp. Pharmacol. 1991, 99, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Weyrauch, W. Dolichovespula und Vespa. Vergleichende Uebersicht iuber zwei wesentliche Leben- stypen bei sozialen Wespen. Mit Bezugrahme auf die Frage nach der Fortschnitlichkeit tierischer Organisation. Biol. Zent. 1935, 55, 484–524. [Google Scholar]
- Ishay, J.S.; Afek, A.B.; Brown, M.B. Allopurinol and theophylline: Their effect on longevity, fertility and behavior of hornets kept under different light and crowding conditions. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Comp. Pharmacol. 1982, 73, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamane, S. Morphological and taxonomic studies on vespine larvae, with reference to the phylogeny of the subfamily Vespinae (Hymenoptera: Vespidae). Insecta Matsumurana 1976, 8, 1–45. [Google Scholar]
- Zhukovskaya, M.; Yanagawa, A.; Forschler, B.T. Grooming behavior as a mechanism of insect disease defense. Insects 2013, 4, 609–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ertürk, Ö.; Sarikaya, A. Determination of some structural features of the nest paper materials of Vespa crabro germana Christ, 1791 (Hymenoptera: Vespidae) in Turkey. J. Kans. Entomol. Soc. 2020, 92, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhou, X. Corpse management in social insects. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 9, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spradbery, J.P.; Maywald, G.F. The distribution of the European or German wasp, Vespula germanica (F.) (Hymenoptera: Vespidae), in Australia: Past, present and future. Aust. J. Zool. 1992, 40, 495–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiewok, S.; Schmolz, E.; Ruther, J. Mating system of the European hornet Vespa crabro: Male seeking strategies and evidence for the involvement of a sex pheromone. J. Chem. Ecol. 2006, 32, 2777–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morse, R.A.; Nowogrodzki, R. Honey Bee Pests, Predators, and Diseases; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1990; p. 410. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, K.; Radloff, S.E.; Li, J.J.; Hepburn, H.R.; Yang, M.X.; Zhang, L.J.; Neumann, P. Bee-hawking by the wasp, Vespa velutina, on the honeybees Apis cerana and A. mellifera. Naturwissenschaften 2007, 94, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monceau, K.; Maher, N.; Bonnard, O.; Thiéry, D. Predation pressure dynamics study of the recently introduced honeybee killer Vespa velutina: Learning from the enemy. Apidologie 2013, 44, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monceau, K.; Bonnard, O.; Thiéry, D. Vespa velutina: A new invasive predator of honeybees in Europe. J. Pest Sci. 2014, 87, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurino, D.; Lioy, S.; Carisio, L.; Manino, A.; Porporato, M. Vespa velutina: An alien driver of honey bee colony losses. Diversity 2020, 12, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishay, J.; Schwartz, A. Acoustical communication between the members of the oriental hornet (Vespa orientalis) colony. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1973, 53, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandt, J.M.; Jeanne, R.L. German yellowjacket (Vespula germanica) foragers use odors inside the nest to find carbohydrate food sources. Ethology 2005, 111, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, B.J.; Jeanne, R.L. Gastral drumming: A nest-based food-recruitment signal in a social wasp. Sci. Nat. 2018, 105, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanini, I.; Dapporto, L.; Legras, J.L.; Calabretta, A.; Di Paola, M.; De Filippo, C.; Viola, R.; Capretti, P.; Polsinelli, M.; Turillazzi, S.; et al. Role of social wasps in Saccharomyces cerevisiae ecology and evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13398–13403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meriggi, N.; Di Paola, M.; Cavalieri, D.; Stefanini, I. Saccharomyces cerevisiae–insects association: Impacts, biogeography, and extent. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, D.M. Effects of long-term variation in pollinator abundance and diversity on reproduction of a generalist plant. J. Ecol. 2019, 107, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beggs, J. The ecological consequences of social wasps (Vespula spp.) invading an ecosystem that has an abundant carbohydrate resource. Biol. Conserv. 2001, 99, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resende, J.J.; Santos, G.M.d.M.; Bichara Filho, C.C.; Gimenes, M. Atividade diária de busca de recursos pela vespa social Polybia occidentalis occidentalis (Olivier, 1791) (Hymenoptera, Vespidae). Rev. Bras. Zooc. 2001, 3, 105–115. [Google Scholar]
- Schremmer, F. Wespen und Hornissen; A. Ziemsen Verlag: Wittenberg Lutherstadt, Germany, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Brodmann, J.; Twele, R.; Francke, W.; Hölzler, G.; Zhang, Q.H.; Ayasse, M. Orchids mimic green-leaf volatiles to attract prey-hunting wasps for pollination. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, 740–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sumner, S.; Law, G.; Cini, A. Why we love bees and hate wasps. Ecol. Entomol. 2018, 43, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, R.E.; Cini, A.; Sumner, S. Ecosystem services provided by aculeate wasps. Biol. Rev. 2021, 96, 1645–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beggs, J.R.; Brockerhoff, E.G.; Corley, J.C.; Kenis, M.; Masciocchi, M.; Muller, F.; Rome, Q.; Villemant, C. Ecological effects and management of invasive alien Vespidae. BioControl 2011, 56, 505–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Nest Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nest description | Social structure | Queen + brood | Queen + brood + workers | Queen + brood + workers | Queen + brood + workers | Queen + brood + workers | Queen + brood |
| Habitat | Rural | Urban | Urban | Rural | Rural | Rural | |
| Context | Inside an apiary with 40 hives | Near an apiary with 15 hives (500 m) | Street (no hives) | Near an apiary with 20 hives (700 m) | Garden (no hives) | Inside an apiary with 24 hives | |
| Placement | Polystyrene hive | Tree crown | Inside a wall | Box-house | Hole in the tree | Beekeeping hive | |
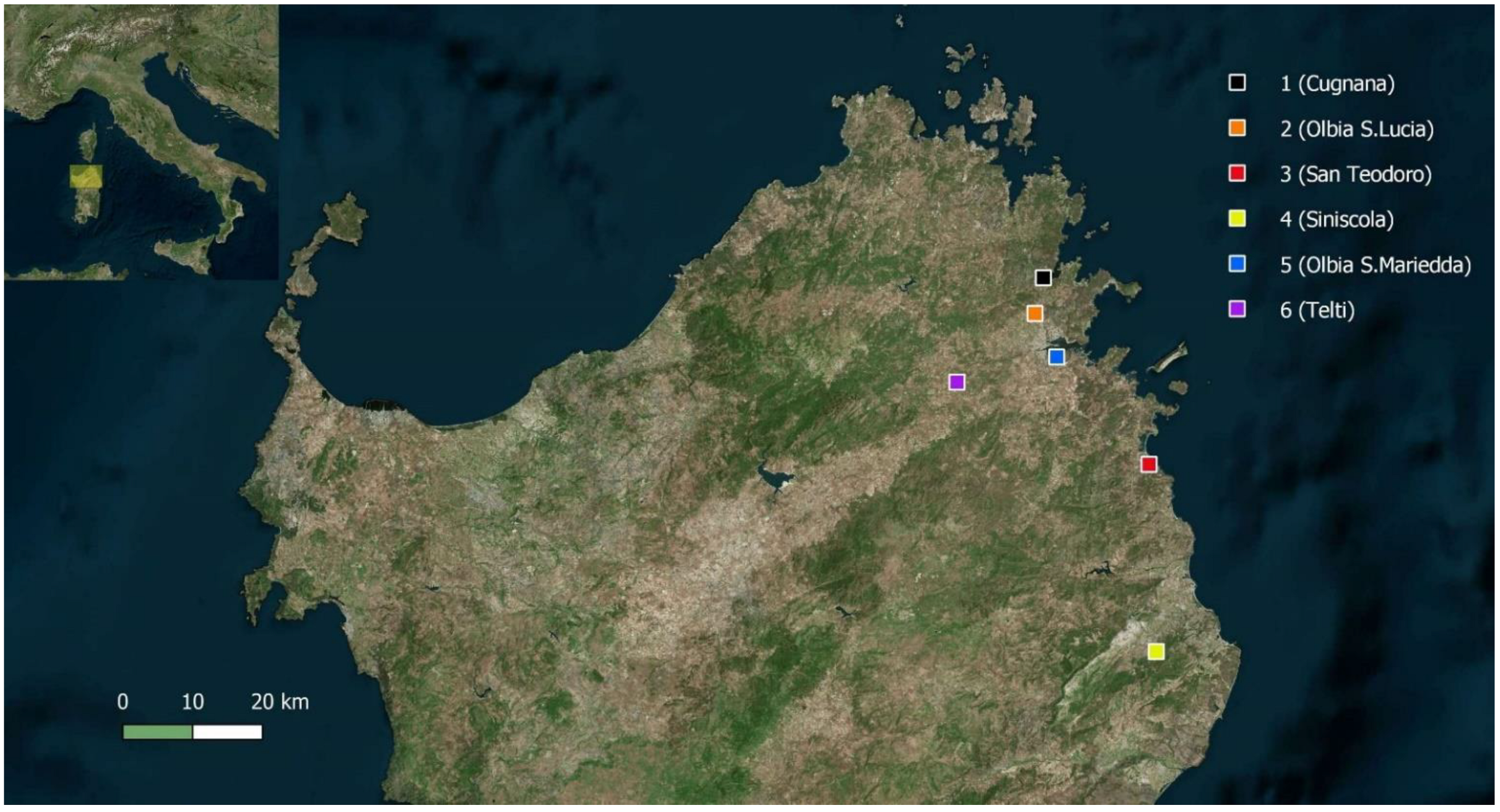
| Locality | Cugnana (Sassari) | Olbia Santa Lucia (Sassari) | San Teodoro (Sassari) | Siniscola (Nuoro) | Olbia Santa Mariedda (Sassari) | Telti (Sassari)$ | |
| Coordinates | 41°00′37.1″ N 9°29′57.5″ E | 40°57′51.40″ N 9°29′05.73″ E | 40°46′08.82″ N 9°40′36.26″ E | 40°31′40.66″ N 9°41′11.61″ E | 40°54′29.74″ N 9°31′17.29″ E | 40°52′35.14″ N 9°21′05.96″ E | |
| Altitude (m a.s.l.) | 9 | 77 | 40 | 158 | 6 | 329 | |
| Development | Number of capped brood cells = 3 Number of uncapped brood cells = 23 | Number of incoming foragers/h = 61.7 Number of outgoing foragers/h = 60.7 | Number of incoming foragers/h = 80.6 Number of outgoing foragers/h = 80.4 | Number of incoming foragers/h = 47.8 Number of outgoing foragers/h = 47.0 | Number of incoming foragers/h =544 Number of outgoing foragers/h =539 | Number capped brood cells = 4 Number of uncapped brood cells = 18 | |
| Nest observations | Start/end dates | 4 June 2018 8 June 2018 | 9 July 2019 9 July 2019 | 27 July 2019 29 July 2019 | 26 August 2019 28 August 2019 | 11 September 2019 13 September 2019 | 22 June 2020 22 June 2020 |
| Duration (days) | 5 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | |
| Duration (hours:min) | 40:00 | 08:00 | 22:05 | 28:10 | 26:28 | 07:00 | |
| Collected data | Task performed inside the nest | x | - | - | x | - | x |
| Daily foraging activity rate | x | x | x | x | x | x | |
| Predation pressure on hives | x | x | - | - | - | x |
| Behaviour | Locality and Actor | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cugnana (No. 1) Queen | Telti (No. 6) Queen | Siniscola (No. 4) Workers | |
| Nest building and maintenance | 8 | 5 | 639 |
| Pellet food preparation | 4 | 16 | 3 |
| Trophallaxis with larvae | 2 | 72 | 15 |
| Trophallaxis between adults | - | - | 871 |
| Antennation on capped brood | 0 | 18 | 0 |
| Self-grooming | 2 | 62 | 3 |
| Allo-grooming | - | - | 15 |
| Interaction with other species | 4 | 2 | 3 |
| Defecation | 0 | 0 | 496 |
| Ventilation | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Larval removal | 0 | 0 | 8 |
| Cannibalism | 0 | 0 | 9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pusceddu, M.; Lezzeri, M.; Cocco, A.; Floris, I.; Satta, A. Bio-Ethology of Vespa crabro in Sardinia (Italy), an Area of New Introduction. Biology 2022, 11, 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040518
Pusceddu M, Lezzeri M, Cocco A, Floris I, Satta A. Bio-Ethology of Vespa crabro in Sardinia (Italy), an Area of New Introduction. Biology. 2022; 11(4):518. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040518
Chicago/Turabian StylePusceddu, Michelina, Matteo Lezzeri, Arturo Cocco, Ignazio Floris, and Alberto Satta. 2022. "Bio-Ethology of Vespa crabro in Sardinia (Italy), an Area of New Introduction" Biology 11, no. 4: 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040518
APA StylePusceddu, M., Lezzeri, M., Cocco, A., Floris, I., & Satta, A. (2022). Bio-Ethology of Vespa crabro in Sardinia (Italy), an Area of New Introduction. Biology, 11(4), 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040518









