Comparative Draft Genomes of Leishmania orientalis Isolate PCM2 (Formerly Named Leishmania siamensis) and Leishmania martiniquensis Isolate PCM3 from the Southern Province of Thailand
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Draft Genomes of L. orientalis Isolate PCM2 and L. martiniquensis Isolate PCM3
3.2. Comparative Functional Genomics of the Southern Isolates of L. orientalis and L. martiniquensis to Those of Other Leishmania
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, D.; Uzonna, J.E. The early interaction of Leishmania with macrophages and dendritic cells and its influence on the host immune response. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cotton, J.A. The Expanding World of Human Leishmaniasis. Trends Parasitol. 2017, 33, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steverding, D. The history of leishmaniasis. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alvar, J.; Vélez, I.D.; Bern, C.; Herrero, M.; Desjeux, P.; Cano, J.; Jannin, J.; Boer, M.D. Leishmaniasis Worldwide and Global Estimates of Its Incidence. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, S.; Frasca, K.; Scherrer, S.; Henao-Martínez, A.F.; Newman, S.; Ramanan, P.; Suarez, J.A. A Review of Leishmaniasis: Current Knowledge and Future Directions. Curr. Trop. Med. Rep. 2021, 8, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belo, V.S.; Struchiner, C.J.; Barbosa, D.S.; Nascimento, B.W.L.; Horta, M.A.P.; Da Silva, E.S.; Werneck, G.L. Risk Factors for Adverse Prognosis and Death in American Visceral Leishmaniasis: A Meta-analysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Conlan, J.V.; Sripa, B.; Attwood, S.; Newton, P.N. A review of parasitic zoonoses in a changing Southeast Asia. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 182, 22–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viroj, W. Leishmaniasis in Southeast Asia: The Story of the Emergence of an Imported Infection in a Non-Endemic Area of the World. J. Health Transl. Med. 2012, 15, 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Leelayoova, S.; Siripattanapipong, S.; Manomat, J.; Piyaraj, P.; Tan-Ariya, P.; Bualert, L.; Mungthin, M. Leishmaniasis in Thailand: A Review of Causative Agents and Situations. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 96, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wiwanitkit, S.; Wiwanitkit, V. Emerging Leishmania siamensis in Southern Thailand: Some facts and perspectives. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. 2015, 5, 502–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thisyakorn, U.; Jongwutiwes, S.; Vanichsetakul, P.; Lertsapcharoen, P. Visceral leishmaniasis: The first indigenous case report in Thailand. J. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1999, 93, 23–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pothirat, T.; Tantiworawit, A.; Chaiwarith, R.; Jariyapan, N.; Wannasan, A.; Siriyasatien, P.; Supparatpinyo, K.; Bates, M.D.; Kwakye-Nuako, G.; Bates, P.A. First Isolation of Leishmania from Northern Thailand: Case Report, Identification as Leishmania martiniquensis and Phylogenetic Position within the Leishmania enriettii Complex. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bualert, L.; Thongsuksai, P.; Siripattanapipong, S.; Charungkiattikul, W.; El Baidouri, F.; Mungthin, M.; Naaglor, T.; Ravel, C.; Leelayoova, S.; Khositnithikul, R. Autochthonous Disseminated Dermal and Visceral Leishmaniasis in an AIDS Patient, Southern Thailand, Caused by Leishmania siamensis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2012, 86, 821–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leelayoova, S.; Siripattanapipong, S.; Hitakarun, A.; Kato, H.; Tan-Ariya, P.; Siriyasatien, P.; Osatakul, S.; Mungthin, M. Multilocus characterization and phylogenetic analysis of Leishmania siamensis isolated from autochthonous visceral leishmaniasis cases, southern Thailand. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chanmol, W.; Jariyapan, N.; Somboon, P.; Bates, M.D.; Bates, P.A. Development of Leishmania orientalis in the sand fly Lutzomyia longipalpis (Diptera: Psychodidae) and the biting midge Culicoides soronensis (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae). Acta Trop. 2019, 199, 105157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manomat, J.; Leelayoova, S.; Bualert, L.; Tan-Ariya, P.; Siripattanapipong, S.; Mungthin, M.; Naaglor, T.; Piyaraj, P. Prevalence and risk factors associated with Leishmania infection in Trang Province, southern Thailand. PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0006095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ivens, A.C.; Peacock, C.S.; Worthey, E.A.; Murphy, L.; Aggarwal, G.; Berriman, M.; Sisk, E.; Rajandream, M.A.; Adlem, E.; Aert, R.; et al. The genome of the kinetoplastid parasite, Leishmania major. Science 2005, 309, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peacock, C.S.; Seeger, K.; Harris, D.; Murphy, L.; Ruiz, J.C.; Quail, M.A.; Peters, N.; Adlem, E.; Tivey, A.; Aslett, M.; et al. Comparative genomic analysis of three Leishmania species that cause diverse human disease. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- NCBI. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US), National Center for Biotechnology Information. 1988. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Almutairi, H.; Urbaniak, M.D.; Bates, M.D.; Jariyapan, N.; Kwakye-Nuako, G.; Thomaz Soccol, V.; Al-Salem, W.S.; Dillon, R.J.; Bates, P.A.; Gatherer, D. Chromosome-scale genome sequencing, assembly and annotation of six genomes from subfamily Leishmaniinae. Sci. Data 2021, 8, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.F.; Peacock, C.S.; Cruz, A.K. Comparative genomics: From genotype to disease phenotype in the leishmaniases. Int. J. Parasitol. 2007, 37, 1173–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laffitte, M.-C.N.; Leprohon, P.; Papadopoulou, B.; Ouellette, M. Plasticity of the Leishmania genome leading to gene copy number variations and drug resistance. F1000Research 2016, 5, 2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valdivia, H.O.; Reis-Cunha, J.L.; Rodrigues-Luiz, G.F.; Baptista, R.P.; Baldeviano, G.C.; Gerbasi, R.V.; Dobson, D.E.; Pratlong, F.; Bastien, P.; Lescano, A.G.; et al. Comparative genomic analysis of Leishmania (Viannia) peruviana and Leishmania (Viannia) braziliensis. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- FastQC: A Qality Control Tool for High Tthroughput Sequence Data. Available online: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Li, D.; Liu, C.-M.; Luo, R.; Sadakane, K.; Lam, T.-W. MEGAHIT: An ultra-fast single-node solution for large and complex metagenomics assembly via succinct de Bruijn graph. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1674–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darling, A.C.; Mau, B.; Blattner, F.R.; Perna, N.T. Mauve: Multiple alignment of conserved genomic sequence with rearrangements. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1394–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, L.; Zhang, H.; Tang, Z.; Xu, J.; Yin, D.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, X.; Zhu, M.; Zhao, S.; Li, X.; et al. rMVP: A Memory-efficient, Visualization-enhanced, and Parallel-accelerated tool for Genome-Wide Association Study. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoff, K.J.; Stanke, M. Predicting Genes in Single Genomes with AUGUSTUS. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2019, 65, e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Törönen, P.; Medlar, A.; Holm, L. PANNZER2: A rapid functional annotation web server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W84–W88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraga, J.; Montalvo, A.M.; De Doncker, S.; Dujardin, J.C.; Van der Auwera, G. Phylogeny of Leishmania species based on the heat-shock protein 70 gene. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2010, 10, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salloum, T.; Moussa, R.; Rahy, R.; Al Deek, J.; Khalifeh, I.; El Hajj, R.; Hall, N.; Hirt, R.P.; Tokajian, S. Expanded genome-wide comparisons give novel insights into population structure and genetic heterogeneity of Leishmania tropica complex. PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasanna, P.; Upadhyay, A. Heat Shock Proteins as the Druggable Targets in Leishmaniasis: Promises and Perils. Infect. Immun. 2021, 89, e00559-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaeffer, M.; de Miranda, A.; Mottram, J.C.; Coombs, G.H. Differentiation of Leishmania major is impaired by over-expression of pyroglutamyl peptidase I. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2006, 150, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, E.V.; Yoneyama, K.G.; Haapalainen, E.F.; Toledo, M.S.; Takahashi, H.K.; Straus, A.H. Myriocin, a serine palmitoyltransferase inhibitor, blocks cytokinesis in Leishmania (Viannia) braziliensis promastigotes. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2013, 60, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fyfe, P.K.; Oza, S.L.; Fairlamb, A.H.; Hunter, W.N. Leishmania Trypanothione Synthetase-Amidase Structure Reveals a Basis for Regulation of Conflicting Synthetic and Hydrolytic Activities. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 17672–17680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valdivia, H.O.; Scholte, L.L.S.; Oliveira, G.; Gabaldón, T.; Bartholomeu, D.C. The Leishmania metaphylome: A comprehensive survey of Leishmania protein phylogenetic relationships. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
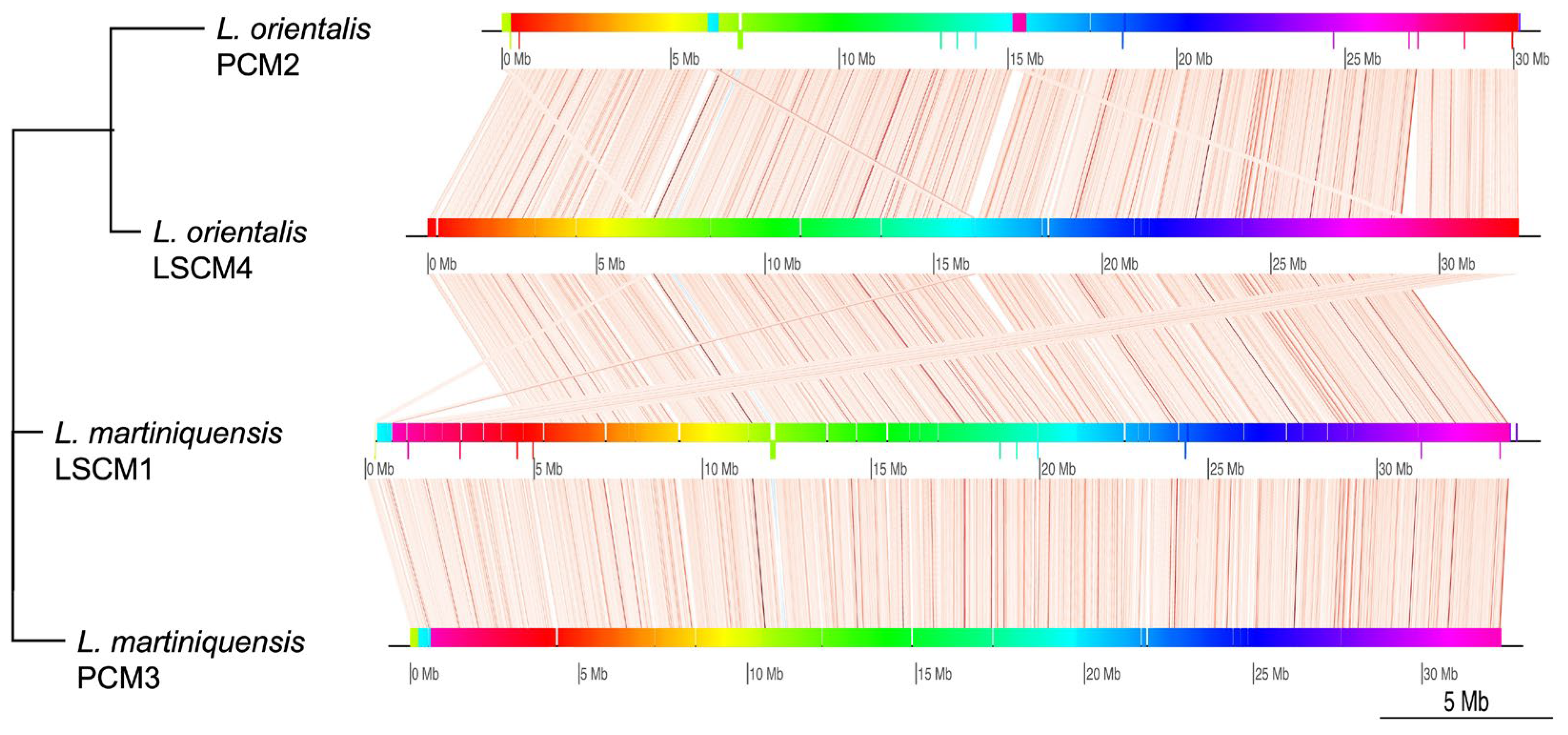
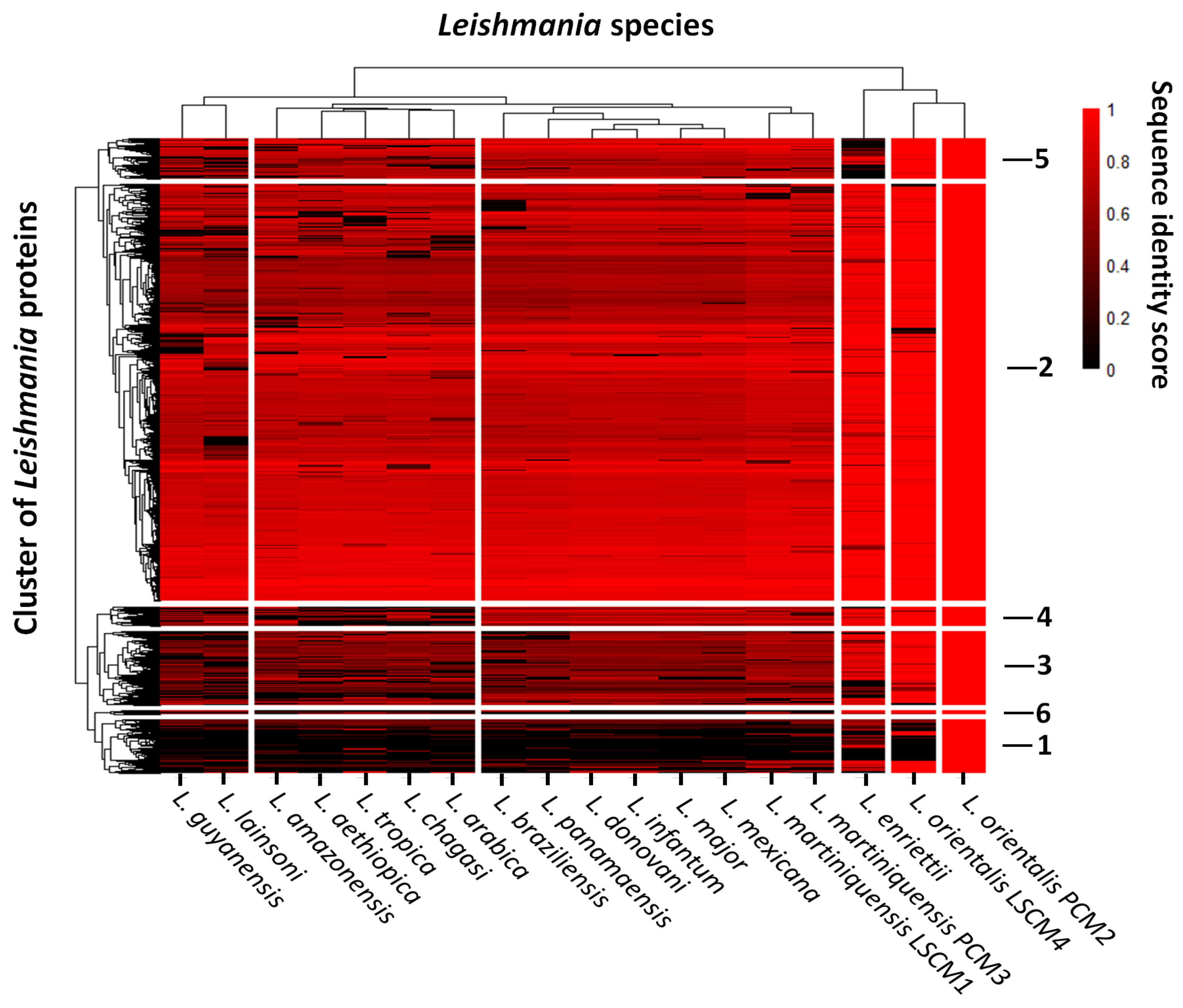
| Genome Characteristics | L. orientalis PCM2 | L. martiniquensis PCM3 |
|---|---|---|
| Contig number | 4399 | 42 |
| Total length | 30.01 Mbp | 32.39 Mbp |
| N50 | 14.03 Kbp | 1.05 Mbp |
| L50 | 651 | 11 |
| Number of coding genes | 8989 | 9577 |
| %GC | 59.02 | 59.92 |
| Protein Groups | Number of Uniquely Assigned GO Terms (Percentage of Annotated Proteins) | Total Number of Proteins in Each Group (Percentage of Overall Annotated Proteins) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biological Process | Cellular Component | Molecular Function | Enzymatic Function | ||
| 1 | 43 (13.58) | 23 (20.09) | 59 (16.47) | 30 (8.96) | 692 (21.24%) |
| 2 | 762 (53.81) | 378 (72.07) | 629 (54.85) | 474 (26.57) | 5371 (66.15%) |
| 3 | 119 (21.30) | 71 (36.10) | 125 (23.82) | 61 (10.07) | 953 (33.26%) |
| 4 | 77 (37.96) | 64 (57.55) | 65 (36.33) | 24 (11.84) | 245 (44.49%) |
| 5 | 136 (37.69) | 88 (64.04) | 109 (40.38) | 58 (14.81) | 520 (51.35%) |
| 6 | 5 (10.64) | 3 (23.40) | 6 (17.02) | 3 (8.51) | 47 (19.15%) |
| Total | 7828 (56.23%) | ||||
| Protein Cluster | Number of Unique Proteins Only Found in Either L. orientalis or L. martiniquensis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L. orientalis | L. martiniquensis | |||||
| Unique to PCM2 | Unique to LSCM4 | Found in Both Isolates | Unique to PCM3 | Unique to LSCM1 | Found in Both Isolates | |
| 1 | 3 | - | 28 | 7 | - | - |
| 2 | 47 | - | - | 67 | - | - |
| 3 | 3 | - | - | 21 | - | - |
| 4 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 5 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 6 | - | - | - | 2 | - | - |
| Total | 53 | - | 28 | 97 | - | - |
| No | Gene ID | Cluster | Protein Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | k59_7101.g4222 | 1 | Amastin surface glycofamily protein |
| 2 | k59_5884.g7963 | 1 | D-amastin |
| 3 | k59_5466.g3144 | 1 | Putative malic enzyme |
| 4 | k59_1669.g769 | 1+ | Receptor-type adenylate cyclase a |
| 5 | k59_10223.g2223 | 2+ | Aminoacyl-tRNA editing domain containing protein, putative |
| 6 | k59_6373.g6990 | 2 | Aminoacyl-tRNA editing domain containing protein, putative |
| 7 | k59_6105.g6831 | 2 | Ankyrin repeat family protein |
| 8 | k59_2596.g5206 | 2+ | Antiviral helicase |
| 9 | k59_4730.g7538 | 2 | ATP-dependent DNA helicase |
| 10 | k59_1985.g3871 | 2+ | Beta-lactamase, putative |
| 11 | k59_7875.g3627 | 2+ | C3H1-type domain-containing protein |
| 12 | k59_10386.g8210 | 2 | Cactus-binding C-terminus of cactin protein, putative |
| 13 | k59_3265.g2893 | 2 | Centromere/microtubule binding protein cbf5, putative |
| 14 | k59_10658.g8866 | 2+ | Chromatin assembly factor 1 subunit A, putative |
| 15 | k59_10459.g1059 | 2+ | CS domain-containing protein |
| 16 | k59_3314.g4482 | 2 | Cyclin dependent kinase-binding protein, putative |
| 17 | k59_5445.g2737 | 2 | D-3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase-like protein |
| 18 | k59_4821.g8945 | 2 | Endoplasmic Reticulum-Golgi Intermediate Compartment (ERGIC) |
| 19 | k59_2500.g2688 | 2 | Enkurin domain-containing protein |
| 20 | k59_10260.g4158 | 2+ | Essential nuclear protein 1 |
| 21 | k59_8350.g1377 | 2+ | Exosome-associated protein 1 |
| 22 | k59_9227.g4203 | 2 | Farnesyltransferase alpha subunit |
| 23 | k59_6707.g85 | 2+ | GB1/RHD3-type G domain-containing protein |
| 24 | k59_6854.g4013 | 2+ | Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase (Fragment) |
| 25 | k59_199.g4824 | 2+ | Glycosyltransferase (GlcNAc), putative |
| 26 | k59_10459.g1058 | 2 | GOLD domain-containing protein |
| 27 | k59_4463.g6091 | 2+ | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit beta-like protein |
| 28 | k59_1181.g5237 | 2+ | H(+)-exporting diphosphatase |
| 29 | k59_9085.g8550 | 2 | Heat shock protein DnaJ |
| 30 | k59_457.g6730 | 2+ | HECT domain-containing protein |
| 31 | k59_1395.g2084 | 2 | Intraflagellar transport protein 22 |
| 32 | k59_8474.g5391 | 2 | Intraflagellar transport protein D4 |
| 33 | k59_9119.g816 | 2 | MIZ/SP-RING zinc finger family protein |
| 34 | k59_7389.g5456 | 2 | mRNA processing protein, putative |
| 35 | k59_5206.g5478 | 2 | MRP-L46 domain-containing protein |
| 36 | k59_8917.g2151 | 2 | MYND zinc finger (ZnF) domain-like protein |
| 37 | k59_10044.g5171 | 2+ | NLE domain-containing protein |
| 38 | k59_7676.g6287 | 2 | NTF2 domain-containing protein |
| 39 | k59_5657.g997 | 2+ | Nuclease-related domain containing protein, putative |
| 40 | k59_5439.g2470 | 2+ | PAB-dependent poly(A)-specific ribonuclease subunit 3 |
| 41 | k59_660.g3683 | 2 | Palmitoyltransferase |
| 42 | k59_2880.g6470 | 2 | PHD domain-containing protein |
| 43 | k59_5927.g1098 | 2 | Phosphorylated CTD interacting factor 1 WW domain containing protein |
| 44 | k59_5927.g1098 | 2 | Phosphorylated CTD interacting factor 1 WW domain containing protein |
| 45 | k59_10222.g2044 | 2+ | Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase and DNA-Ligase Zn-finger region |
| 46 | k59_9477.g3999 | 2+ | PRK domain-containing protein |
| 47 | k59_8589.g1275 | 2 | Protein disulfide isomerase, putative |
| 48 | k59_5413.g1718 | 2 | Putative DNA repair protein RAD2 |
| 49 | k59_9374.g604 | 2+ | Putative flagellar radial spoke protein-like |
| 50 | k59_10153.g8013 | 2 | Putative Gamma-soluble NSF attachment protein (SNAP-gamma) |
| 51 | k59_2626.g6421 | 2 | Putative mitochondrial RNA binding complex 1 subunit |
| 52 | k59_7006.g1237 | 2+ | Putative prefoldin subunit 2 |
| 53 | k59_2660.g7703 | 2+ | Putative pre-mRNA branch site protein p14 |
| 54 | k59_10051.g5820 | 2 | Putative tRNA pseudouridine synthase A |
| 55 | k59_2665.g8021 | 2+ | Putative unspecified product |
| 56 | k59_2453.g835 | 2+ | Putative variant surface glycoprotein |
| 57 | k59_1240.g7057 | 2+ | Pyroglutamyl-peptidase I (PGP), putative |
| 58 | k59_10051.g5821 | 2 | Queuosine salvage protein |
| 59 | k59_1202.g6035 | 2 | Rab3 GTPase-activating protein catalytic subunit |
| 60 | k59_7391.g5855 | 2 | Rab-GTPase-TBC domain containing protein, putative |
| 61 | k59_3567.g2504 | 2 | Related to elongation factor-2 kinase efk-1b isoform-like protein |
| 62 | k59_1109.g2256 | 2+ | RNA recognition motif family protein |
| 63 | k59_4042.g1153 | 2+ | Roadblock/LC7 domain containing protein, putative |
| 64 | k59_3916.g6656 | 2+ | Secretory carrier membrane protein 3 |
| 65 | k59_3762.g682 | 2 | SNARE associated Golgi protein, putative |
| 66 | k59_1957.g3007 | 2+ | Sperm-tail PG-rich repeat family protein |
| 67 | k59_5678.g1713 | 2+ | Succinate dehydrogenase assembly factor 2, mitochondrial |
| 68 | k59_5098.g435 | 2+ | TFIIS central domain-containing protein |
| 69 | k59_8533.g7240 | 2+ | Translation initiation factor |
| 70 | k59_3506.g770 | 2+ | U5 snRNP-specific 40 kDa protein, putative |
| 71 | k59_6432.g50 | 2+ | WD domain, G-beta repeat family protein |
| 72 | k59_6901.g5645 | 3 | Alpha-1,3/1,6-mannosyltransferase ALG2 |
| 73 | k59_4782.g8504 | 3 | ATP-dependent DNA helicase |
| 74 | k59_6737.g659 | 3 | ATP-dependent helicase, putative |
| 75 | k59_7325.g3419 | 3 | N-terminal region of Chorein, a TM vesicle-mediated sorter family protein |
| 76 | k59_7204.g7945 | 3+ | Putative trypanothione synthetase |
| 77 | k59_5425.g1966 | 3 | RNA binding protein-like protein |
| 78 | k59_2661.g7832 | 3 | SAT domain-containing protein |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anuntasomboon, P.; Siripattanapipong, S.; Unajak, S.; Choowongkomon, K.; Burchmore, R.; Leelayoova, S.; Mungthin, M.; E-kobon, T. Comparative Draft Genomes of Leishmania orientalis Isolate PCM2 (Formerly Named Leishmania siamensis) and Leishmania martiniquensis Isolate PCM3 from the Southern Province of Thailand. Biology 2022, 11, 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040515
Anuntasomboon P, Siripattanapipong S, Unajak S, Choowongkomon K, Burchmore R, Leelayoova S, Mungthin M, E-kobon T. Comparative Draft Genomes of Leishmania orientalis Isolate PCM2 (Formerly Named Leishmania siamensis) and Leishmania martiniquensis Isolate PCM3 from the Southern Province of Thailand. Biology. 2022; 11(4):515. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040515
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnuntasomboon, Pornchai, Suradej Siripattanapipong, Sasimanas Unajak, Kiattawee Choowongkomon, Richard Burchmore, Saovanee Leelayoova, Mathirut Mungthin, and Teerasak E-kobon. 2022. "Comparative Draft Genomes of Leishmania orientalis Isolate PCM2 (Formerly Named Leishmania siamensis) and Leishmania martiniquensis Isolate PCM3 from the Southern Province of Thailand" Biology 11, no. 4: 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040515
APA StyleAnuntasomboon, P., Siripattanapipong, S., Unajak, S., Choowongkomon, K., Burchmore, R., Leelayoova, S., Mungthin, M., & E-kobon, T. (2022). Comparative Draft Genomes of Leishmania orientalis Isolate PCM2 (Formerly Named Leishmania siamensis) and Leishmania martiniquensis Isolate PCM3 from the Southern Province of Thailand. Biology, 11(4), 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040515






