Determining Carina and Clavicular Distance-Dependent Positioning of Endotracheal Tube in Critically Ill Patients: An Artificial Intelligence-Based Approach
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Datasets
2.2. Data Preprocessing and Augmentation
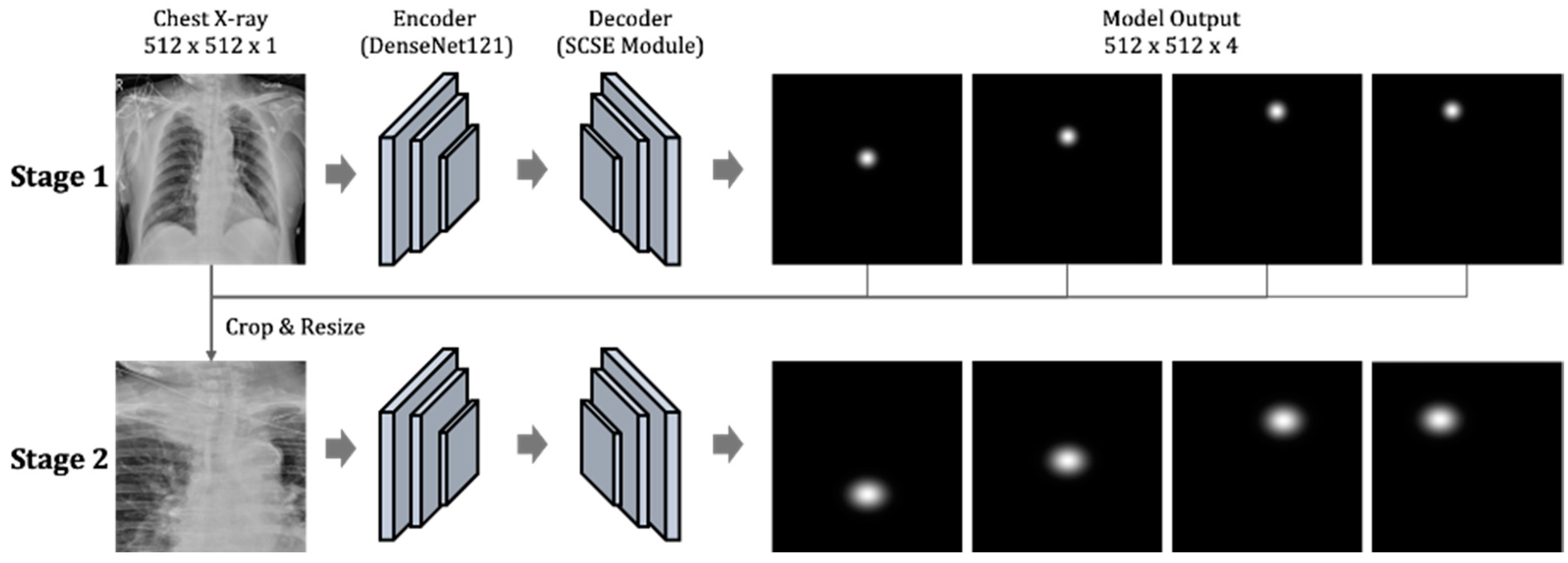
2.3. Modeling Framework
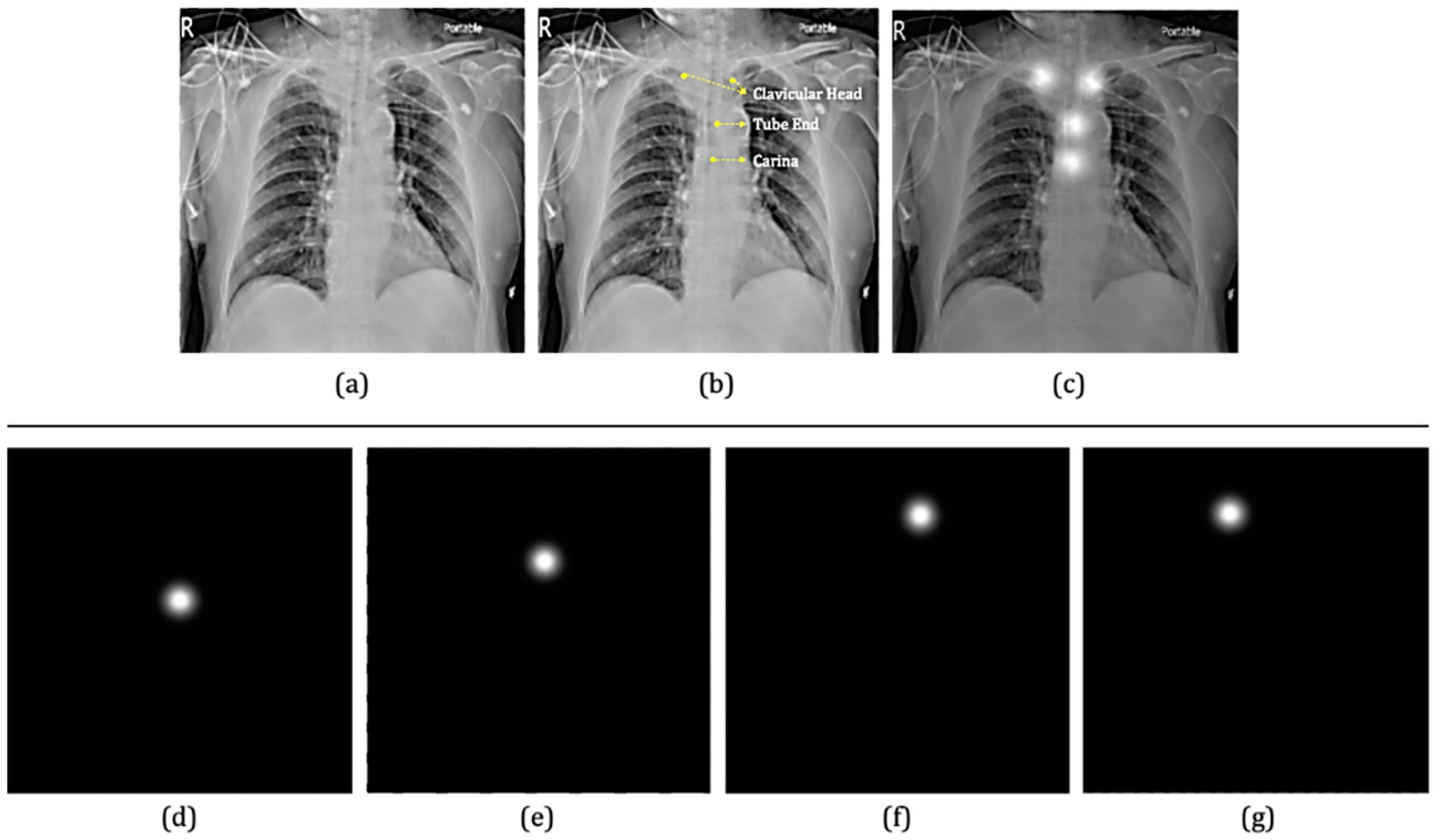
2.3.1. The First Component: Two-Stage Key Point Detection Model
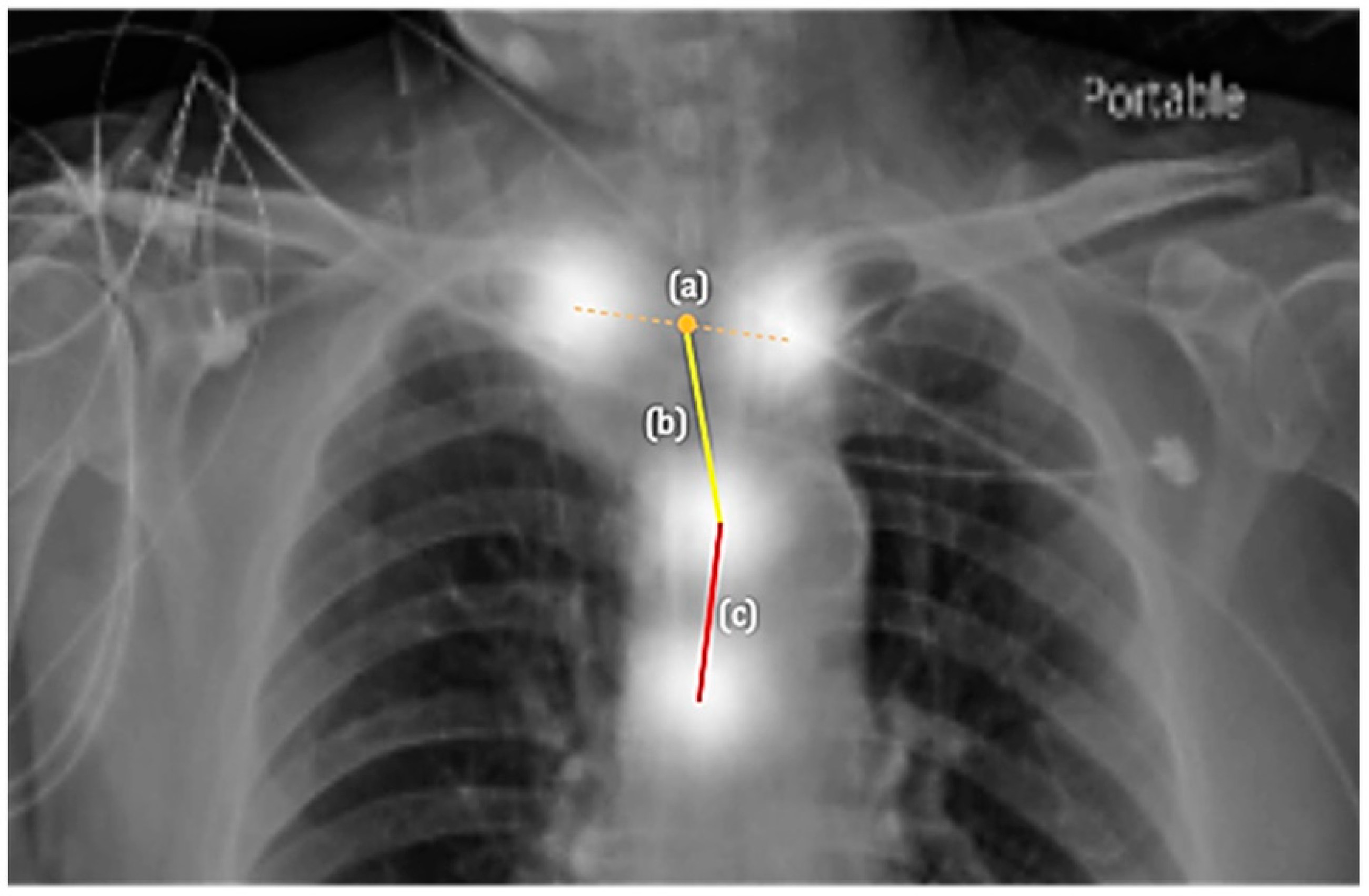
2.3.2. The Second Component: Appropriateness Prediction
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
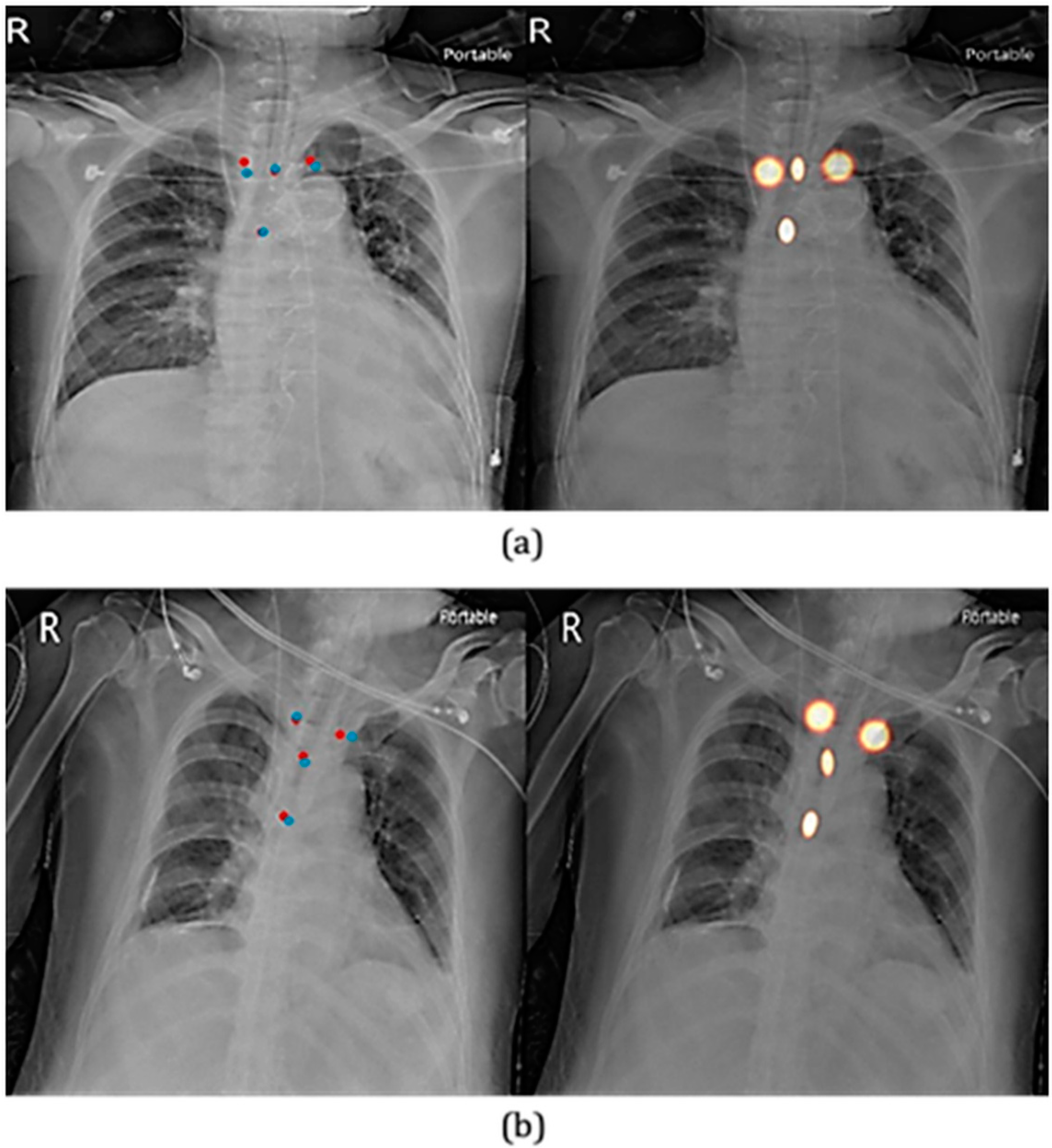
3.1. Key Point Detection
3.2. Appropriateness Prediction
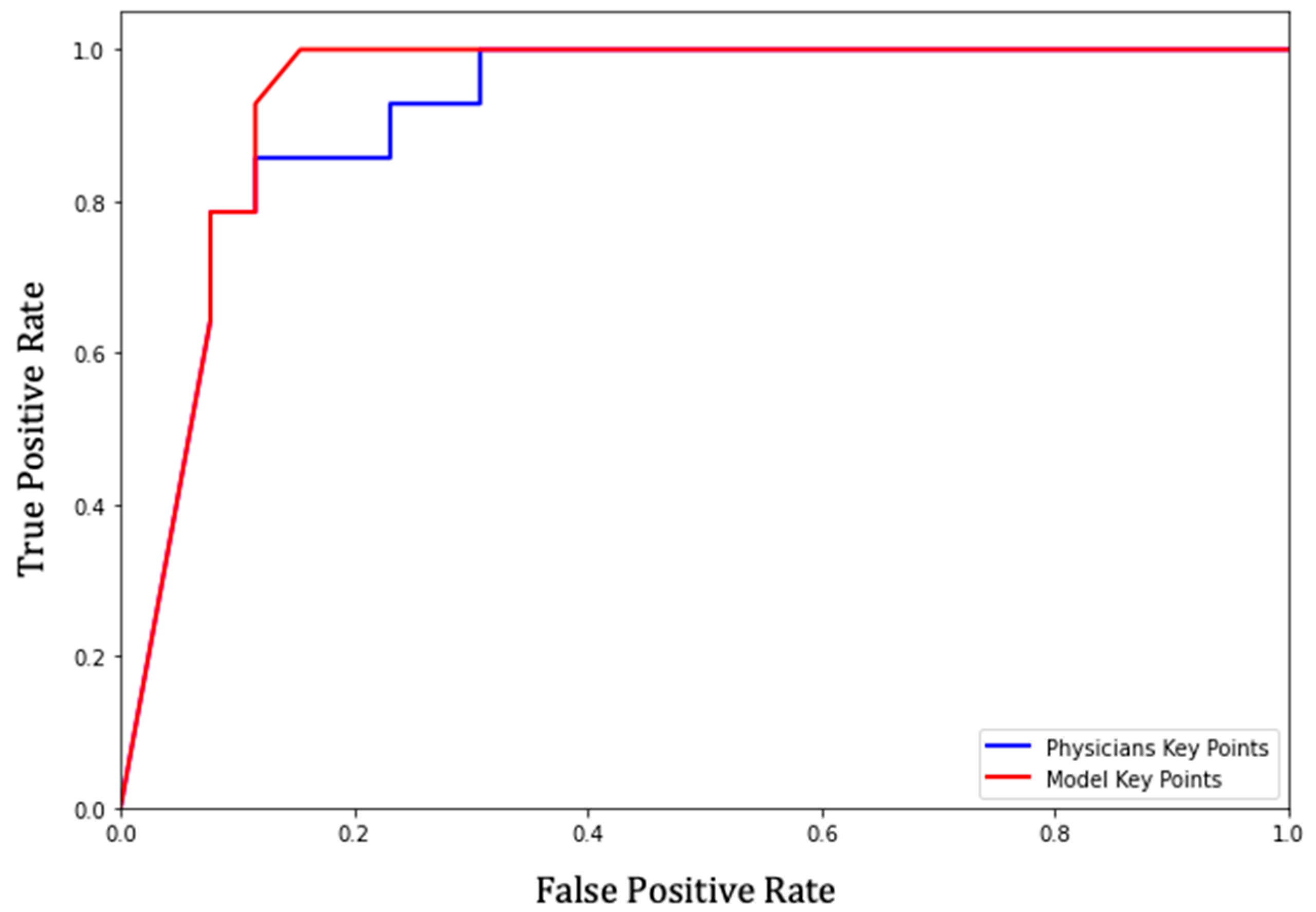
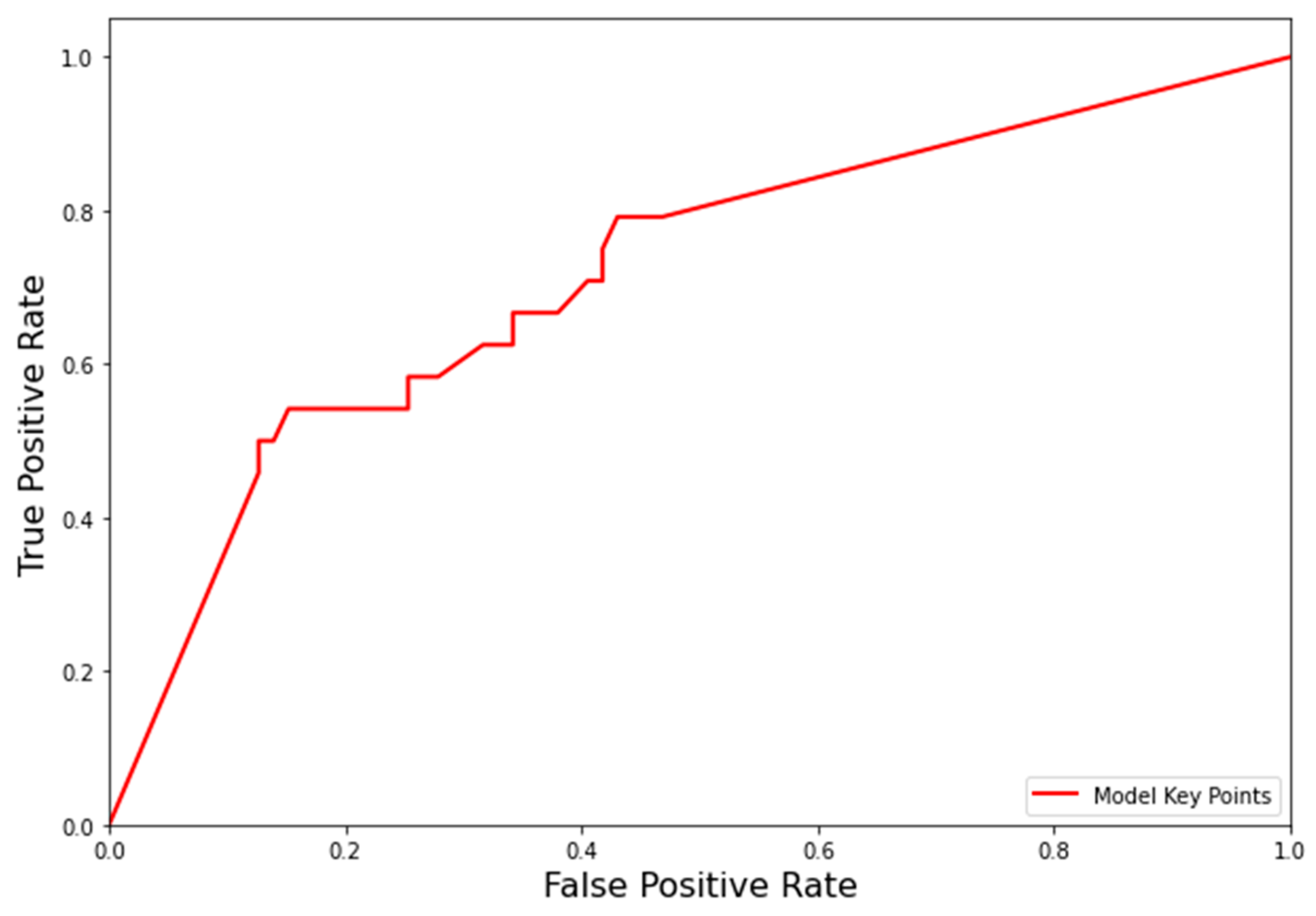
3.3. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) of the Prediction Model
3.4. Appropriateness Prediction on the Clinical Evaluation Dataset
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gupta, P.K.; Gupta, K.; Jain, M.; Garg, T. Postprocedural chest radiograph: Impact on the management in critical care unit. Anesth. Essays Res. 2014, 8, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco-Lopez, P.C.; Berkow, L.C.; Hillel, A.T.; Akst, L.M. Complications of airway management. Respir. Care 2014, 59, 1006–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.-W.; Lee, W.-T.; Chen, H.-L. Reexamining the ideal depth of endotracheal tube in neonates. Pediatrics Neonatol. 2018, 59, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, J.P.; Fisher, L.; Shun-Shin, M.J.; Keene, D.; Arnold, A.D.; Ahmad, Y.; Cook, C.M.; Moon, J.C.; Manisty, C.H.; Whinnett, Z.I.; et al. Cardiac Rhythm Device Identification Using Neural Networks. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2019, 5, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Danda, V.; Gorniak, R.; Flanders, A.; Lakhani, P. Assessment of Critical Feeding Tube Malpositions on Radiographs Using Deep Learning. J. Digit. Imaging 2019, 32, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normando, E.M.; Yap, T.E.; Maddison, J.; Miodragovic, S.; Bonetti, P.; Almonte, M.; Mohammad, N.G.; Ameen, S.; Crawley, L.; Ahmed, F.; et al. A CNN-aided method to predict glaucoma progression using DARC (Detection of Apoptosing Retinal Cells). Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 20, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soffer, S.; Ben-Cohen, A.; Shimon, O.; Amitai, M.M.; Greenspan, H.; Klang, E. Convolutional Neural Networks for Radiologic Images: A Radiologist’s Guide. Radiology 2019, 290, 590–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Yao, D.; Shi, Y.; Song, Z. Computer-aided detection in chest radiography based on artificial intelligence: A survey. Biomed. Eng. Online 2018, 17, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijaykumar, R.; Saboo, A. Review of Different Methods Used for Confirmation of Endotracheal Tube Placement in Newborns. J. Neonatal Biol. 2014, 3, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, A.; El-Feky, M. Evaluation of Endotracheal Tube Position. Available online: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/evaluation-of-endotracheal-tube-position (accessed on 16 March 2022).
- Wang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Luo, G.; Liu, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, W.; Cheng, J.-Z. Automated segmentation and diagnosis of pneumothorax on chest X-rays with fully convolutional multi-scale ScSE-DenseNet: A retrospective study. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2020, 20, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Prakash, S.; Mullick, P.; Guria, S.; Girdhar, K.K. Clinical Implications of Vocal Cord-Carina Distance and Tracheal Length in the Indian Population. Turk. J. Anaesthesiol. Reanim. 2019, 47, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.; Ray, M.; Pal, R. Bedside prediction of airway length by measuring upper incisor manubrio-sternal joint length. J. Anaesthesiol. Clin. Pharmacol. 2014, 30, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eagle, C.C. The relationship between a person’s height and appropriate endotracheal tube length. Anaesth Intensive Care 1992, 20, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saboo, A.R. Neonatal endotracheal intubation: What is the midtracheal position? Pediatr. Crit Care Med. 2013, 14, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.M. A new formula for estimating endotracheal tube insertion depth in neonates. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2018, 59, 225–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blayney, M.P.; Logan, D.R. First thoracic vertebral body as reference for endotracheal tube placement. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal. Ed. 1994, 71, F32–F35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, R.P.; Alexander, T.; Patel, V.; Low, G. Chest radiographs of cardiac devices (Part 1): Lines, tubes, non-cardiac medical devices and materials. SA J. Radiol. 2019, 23, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ong, K.C.; A’Court, G.D.; Eng, P.; Ong, Y.Y. Ideal endotracheal tube placement by referencing measurements on the tube. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 1996, 25, 550–552. [Google Scholar]
- Goodman, L.R.; Conrardy, P.A.; Laing, F.; Singer, M.M. Radiographic evaluation of endotracheal tube position. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1976, 127, 433–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evron, S.; Weisenberg, M.; Harow, E.; Khazin, V.; Szmuk, P.; Gavish, D.; Ezri, T. Proper insertion depth of endotracheal tubes in adults by topographic landmarks measurements. J. Clin. Anesth. 2007, 19, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitzwohl, C.; Langheinrich, A.; Schober, A.; Krafft, P.; Sessler, D.I.; Herkner, H.; Gonano, C.; Weinstabl, C.; Kettner, S.C. Endobronchial intubation detected by insertion depth of endotracheal tube, bilateral auscultation, or observation of chest movements: Randomised trial. BMJ 2010, 341, c5943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, M.; Balmer, C.; Dullenkopf, A.; Knirsch, W.; Gerber, A.; Bauersfeld, U.; Berger, F. Intubation depth markings allow an improved positioning of endotracheal tubes in children. Can J. Anaesth. 2005, 52, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhns, L.R.; Poznanski, A.K. Endotracheal tube position in the infant. J. Pediatr. 1971, 78, 991–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blayney, M.; Costello, S.; Perlman, M.; Lui, K.; Frank, J. A new system for location of endotracheal tube in preterm and term neonates. Pediatrics 1991, 87, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Os, S.; Cheung, P.Y.; Kushniruk, K.; O’Reilly, M.; Aziz, K.; Schmölzer, G.M. Assessment of endotracheal tube placement in newborn infants: A randomized controlled trial. J. Perinatol. 2016, 36, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, S.; Akers, J.Y.; Chang, P.D. Identification and Localization of Endotracheal Tube on Chest Radiographs Using a Cascaded Convolutional Neural Network Approach. J. Digit. Imaging 2021, 34, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Z.; Mao, H.; Zhang, J.; Sykes, A.M.; Munn, S.; Wandtke, J. Computer-aided detection of malpositioned endotracheal tubes in portable chest radiographs. In Proceedings of the Progress in Biomedical Optics and Imaging—Proceedings of SPIE, San Diego, CA, USA, 18–20 February 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Frid-Adar, M.; Amer, R.; Greenspan, H. Endotracheal Tube Detection and Segmentation in Chest Radiographs using Synthetic Data. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.07170. [Google Scholar]
- Tariqul Islam, M.; Aowal, M.A.; Tahseen Minhaz, A.; Ashraf, K. Abnormality Detection and Localization in Chest X-Rays using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.09850. [Google Scholar]
- Rajpurkar, P.; Irvin, J.; Zhu, K.; Yang, B.; Mehta, H.; Duan, T.; Ding, D.; Bagul, A.; Langlotz, C.; Shpanskaya, K.; et al. CheXNet: Radiologist-Level Pneumonia Detection on Chest X-Rays with Deep Learning. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.05225. [Google Scholar]
- Shillan, D.; Sterne, J.A.C.; Champneys, A.; Gibbison, B. Use of machine learning to analyse routinely collected intensive care unit data: A systematic review. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, G. Artificial Intelligence in the Intensive Care Unit. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleuren, L.M.; Klausch, T.L.T.; Zwager, C.L.; Schoonmade, L.J.; Guo, T.; Roggeveen, L.F.; Swart, E.L.; Girbes, A.R.J.; Thoral, P.; Ercole, A.; et al. Machine learning for the prediction of sepsis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 383–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.M.; Seo, J.B.; Yun, J.; Cho, Y.H.; Vogel-Claussen, J.; Schiebler, M.L.; Gefter, W.B.; van Beek, E.J.R.; Goo, J.M.; Lee, K.S.; et al. Deep Learning Applications in Chest Radiography and Computed Tomography: Current State of the Art. J. Thorac. Imaging 2019, 34, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, A.; Corke, C.; Joynt, G.M.; Griffith, J.; Lunn, D.; Tong, P. A comparative study of tracheal diameter in Caucasian and Chinese patients. Anaesth. Intensive Care 2016, 44, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauker, S.G.; Kassirer, J.P. The threshold approach to clinical decision making. N. Engl. J. Med. 1980, 302, 1109–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellamy, N.; Carette, S.; Ford, P.M.; Kean, W.F.; le Riche, N.G.; Lussier, A.; Wells, G.A.; Campbell, J. Osteoarthritis antirheumatic drug trials. III. Setting the delta for clinical trials--results of a consensus development (Delphi) exercise. J. Rheumatol. 1992, 19, 451–457. [Google Scholar]
- Rajpurkar, P.; Irvin, J.; Ball, R.L.; Zhu, K.; Yang, B.; Mehta, H.; Duan, T.; Ding, D.; Bagul, A.; Langlotz, C.P.; et al. Deep learning for chest radiograph diagnosis: A retrospective comparison of the CheXNeXt algorithm to practicing radiologists. PLoS Med. 2018, 15, e1002686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakhuja, P.; Finelli, M.; Hawes, J.; Whyte, H. Is It Time to Review Guidelines for ETT Positioning in the NICU? SCEPTIC-Survey of Challenges Encountered in Placement of Endotracheal Tubes in Canadian NICUs. Int. J. Pediatr. 2016, 2016, 7283179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| (n) Images in Test Dataset Normal/Abnormal | |
|---|---|
| Mandible above C7 | 26/14 |
| Mandible below C7 | 2/0 |
| Test Dataset (Normal/Abnormal) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mandible Above C7 (26/14) | Mandible Below C7 (2/0) | |||
| Parameters | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) |
| 30 ≤ Distance < 70 | 35.71 | 100.00 | N/A | 100.00 |
| 30 ≤ Distance < 60 | 57.14 | 100.00 | 100.00 | |
| 20 ≤ Distance < 60 | 57.14 | 100.00 | 100.00 | |
| 20 ≤ Distance < 55 | 71.42 | 92.30 | 100.00 | |
| Test Set (Normal/Abnormal) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mandible Above C7 (26/14) | Mandible Below C7 (2/0) | |||
| Parameters | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) |
| 30 ≤ Distance < 70 | 71.42 | 88.46 | N/A | 100.00 |
| 30 ≤ Distance < 60 | 85.71 | 88.46 | 100.00 | |
| 20 ≤ Distance < 60 | 85.71 | 88.46 | 100.00 | |
| 20 ≤ Distance < 55 | 92.85 | 84.62 | 100.00 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsai, L.-W.; Yuan, K.-C.; Hou, S.-K.; Wu, W.-L.; Hsu, C.-H.; Liu, T.-L.; Lee, K.-M.; Li, C.-H.; Chen, H.-C.; Tu, E.; et al. Determining Carina and Clavicular Distance-Dependent Positioning of Endotracheal Tube in Critically Ill Patients: An Artificial Intelligence-Based Approach. Biology 2022, 11, 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040490
Tsai L-W, Yuan K-C, Hou S-K, Wu W-L, Hsu C-H, Liu T-L, Lee K-M, Li C-H, Chen H-C, Tu E, et al. Determining Carina and Clavicular Distance-Dependent Positioning of Endotracheal Tube in Critically Ill Patients: An Artificial Intelligence-Based Approach. Biology. 2022; 11(4):490. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040490
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsai, Lung-Wen, Kuo-Ching Yuan, Sen-Kuang Hou, Wei-Lin Wu, Chen-Hao Hsu, Tyng-Luh Liu, Kuang-Min Lee, Chiao-Hsuan Li, Hann-Chyun Chen, Ethan Tu, and et al. 2022. "Determining Carina and Clavicular Distance-Dependent Positioning of Endotracheal Tube in Critically Ill Patients: An Artificial Intelligence-Based Approach" Biology 11, no. 4: 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040490
APA StyleTsai, L.-W., Yuan, K.-C., Hou, S.-K., Wu, W.-L., Hsu, C.-H., Liu, T.-L., Lee, K.-M., Li, C.-H., Chen, H.-C., Tu, E., Dubey, R., Yeh, C.-F., & Chen, R.-J. (2022). Determining Carina and Clavicular Distance-Dependent Positioning of Endotracheal Tube in Critically Ill Patients: An Artificial Intelligence-Based Approach. Biology, 11(4), 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040490






