Acute Changes in Heart Rate Variability to Glucose and Fructose Supplementation in Healthy Individuals: A Double-Blind Randomized Crossover Placebo-Controlled Trial
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Assessment of Eligibility
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Study Design
2.4. Trial Visits
2.5. HRV Measurement
2.6. Blood Glucose Stratification
2.7. Blood Sampling
2.8. Randomization Procedure
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Type of Carbohydrates
3.2. Glucose Range Stratification
3.3. Glucose Rate of Change Stratification
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trimmel, K.; Sacha, J.; Huikuri, H.V. Heart Rate Variability: Clinical Applications and Interaction between HRV and Heart Rate; Trimmel, K., Sacha, J., Huikuri, H.V., Eds.; Frontiers Research Topics; Frontiers Media SA: Lausanne, Switzerland, 2015; ISBN 9782889196524. [Google Scholar]
- Kleiger, R.E.; Miller, J.P.; Bigger, J.T.; Moss, A.J. Decreased Heart Rate Variability and Its Association with Increased Mortality After Acute Myocardial Infarction. Am. J. Cardiol. 1987, 59, 258–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.P.; Larson, M.G.; O’Donnell, C.J.; Wilson, P.F.; Tsuji, H.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Levy, D. Association of hyperglycemia with reduced heart rate variability (The Framingham Heart Study). Am. J. Cardiol. 2000, 86, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandercock, G.R.H.; Brodie, D.A. The use of heart rate variability measures to assess autonomic control during exercise. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sport. 2006, 16, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Rovere, M.T.; Pinna, G.D.; Maestri, R.; Mortara, A.; Capomolla, S.; Febo, O.; Ferrari, R.; Franchini, M.; Gnemmi, M.; Opasich, C.; et al. Short-term heart rate variability strongly predicts sudden cadiac death in chronic heart failure patients. Circulation 2003, 107, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.A.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Shantsila, A. Heart rate variability in atrial fibrillation: The balance between sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 49, e13174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boyett, M.; Wang, Y.; D’Souza, A. CrossTalk opposing view: Heart rate variability as a measure of cardiac autonomic responsiveness is fundamentally flawed. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 2599–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinik, A.I.; Ziegler, D. Diabetic cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy. Circulation 2007, 115, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, D.J.; Borsey, D.Q.; Bellavere, F.; Clarke, B.F. Cardiac autonomic neuropathy in diabetes: Comparison of measures of R-R interval variation. Diabetologia 1981, 21, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, D.R.; Tesfaye, S.; Chaturvedi, N.; Eaton, S.E.M.; Kempler, P.; Fuller, J.H. Risk factors for cardiac autonomic neuropathy in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 2005, 48, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaiswal, M.; Fingerlin, T.E.; Urbina, E.M.; Wadwa, R.P.; Talton, J.W.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Hamman, R.F.; Daniels, S.R.; Marcovina, S.M.; Dolan, L.M.; et al. Impact of Glycemic Control on Heart Rate Variability in Youth with Type 1 Diabetes: The SEARCH CVD Study. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2013, 15, 977–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bekkink, M.O.; Koeneman, M.; De Galan, B.E.; Bredie, S.J. Early detection of hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes using heart rate variability measured by a wearable device. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 689–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernjak, A.; Chow, E.; Robinson, E.J.; Freeman, J.; Marques, J.L.B.; Macdonald, I.A.; Sheridan, P.J.; Heller, S.R. Influence of cardiac autonomic neuropathy on cardiac repolarisation during incremental adrenaline infusion in type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Battelino, T.; Danne, T.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Amiel, S.A.; Beck, R.; Biester, T.; Bosi, E.; Buckingham, B.A.; Cefalu, W.T.; Close, K.L.; et al. Clinical Targets for Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data Interpretation: Recommendations From the International Consensus on Time in Range. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 1593–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eckstein, M.L.; Moser, O.; Tripolt, N.J.; Pferschy, P.N.; Obermayer, A.A.M.; Kojzar, H.; Mueller, A.; Abbas, F.; Sourij, C.; Sourij, H. Rapid glucose rise reduces heart rate variability in adults with type 1 diabetes—A prospective secondary outcome analysis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 4, 14287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, V.L.; Tahrani, A.A. Cardiac autonomic neuropathy in patients with diabetes mellitus: Current perspectives. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2017, 10, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eckstein, M.L.; Brockfeld, A.; Haupt, S.; Schierbauer, J.R.; Zimmer, R.T.; Wachsmuth, N.; Zunner, B.; Zimmermann, P.; Obermayer-Pietsch, B.; Moser, O. Acute Metabolic Responses to Glucose and Fructose Supplementation in Healthy Individuals: A Double-Blind Randomized Crossover Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, T.K.; Tadi, P. Blood Glucose Monitoring; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, S.; Graham, K.S.; Davis Oam, G.M. Cardiac Autonomic Responses during Exercise and Post-exercise Recovery Using Heart Rate Variability and Systolic Time Intervals—A Review. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teixeira, L.; Ritti-Dias, R.M.; Tinucci, T.; Mion Júnior, D.; de Moraes Forjaz, C.L. Post-concurrent exercise hemodynamics and cardiac autonomic modulation. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 111, 2069–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Miyachi, M.; Saitoh, T.; Yoshioka, A.; Onodera, S. Effects of endurance training on resting and post-exercise cardiac autonomic control. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2001, 33, 1496–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benichou, T.; Pereira, B.; Mermillod, M.; Tauveron, I.; Pfabigan, D.; Maqdasy, S.; Dutheil, F. Heart rate variability in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urbaniak, G.C.; Plous, S. Research Randomizer (Version 4.0) [Computer Software]. Available online: https://randomizer.org/about/ (accessed on 27 September 2021).
- Rodero, A.B.; de Souza Rodero, L.; Azoubel, R. Toxicity of Sucralose in Humans: A Review. Int. J. Morphol. 2009, 27, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Task force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Standards of measurement, physiological interpretation and clinical use. Circulation 1996, 93, 1043–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, C.S.; Ko, C.W.; Lien, H.C.; Chou, M.C. Varying postprandial abdominovagal and cardiovagal activity in normal subjects. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2010, 22, 546-e119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Mey, C.; Hansen-Schmidt, S.; Enterling, D.; Meineke, I. Time course and nature of postprandial haemodynamic changes in normal man. Clin. Physiol. 1989, 9, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heseltine, D.; Potter, J.F.; Hartley, G.; Macdonald, I.A.; James, O.F.W. Blood pressure, heart rate and neuroendocrine responses to a high carbohydrate and a high fat meal in healthy young subjects. Clin. Sci. 1990, 79, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sauder, K.A.; Johnston, E.R.; Skulas-Ray, A.C.; Campbell, T.S.; West, S.G. Effect of meal content on heart rate variability and cardiovascular reactivity to mental stress. Psychophysiology 2012, 49, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mcneilly, A.D.; Mccrimmon, R.J. Impaired hypoglycaemia awareness in type 1 diabetes: Lessons from the lab. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Young, C.N.; Deo, S.H.; Chaudhary, K.; Thyfault, J.P.; Fadel, P.J. Insulin enhances the gain of arterial baroreflex control of muscle sympathetic nerve activity in humans. J. Physiol. 2010, 588, 3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brognara, F.; Castania, J.A.; Dias, D.P.M.; Kanashiro, A.; Salgado, H.C. Time course of hemodynamic responses to different doses of lipopolysaccharide in unanesthetized Male rats. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippi, G.; Montagnana, M.; Salvagno, G.L.; Franchini, M.; Guidi, G.C. Glycaemic control in athletes. Int. J. Sports Med. 2008, 29, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
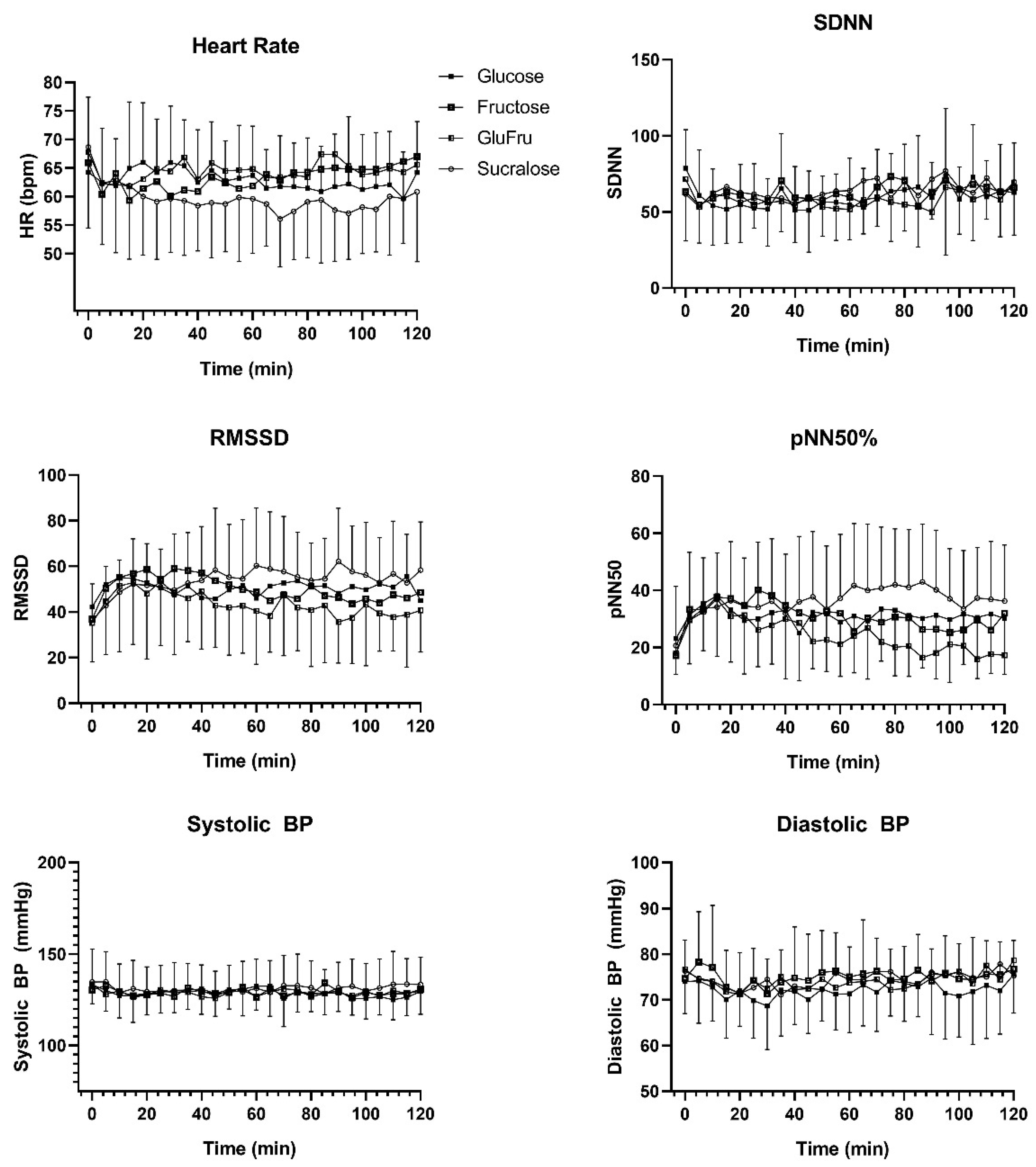
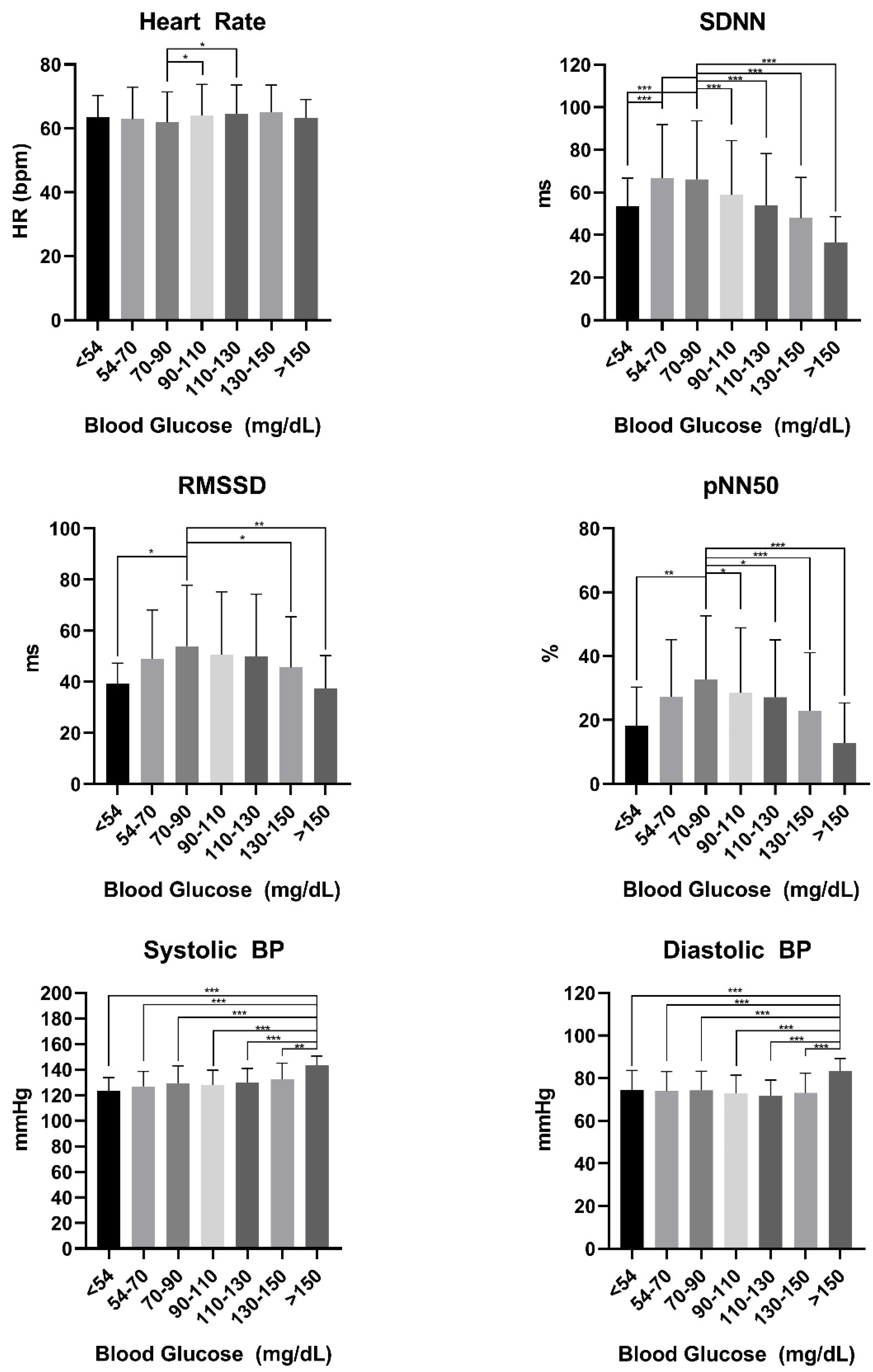
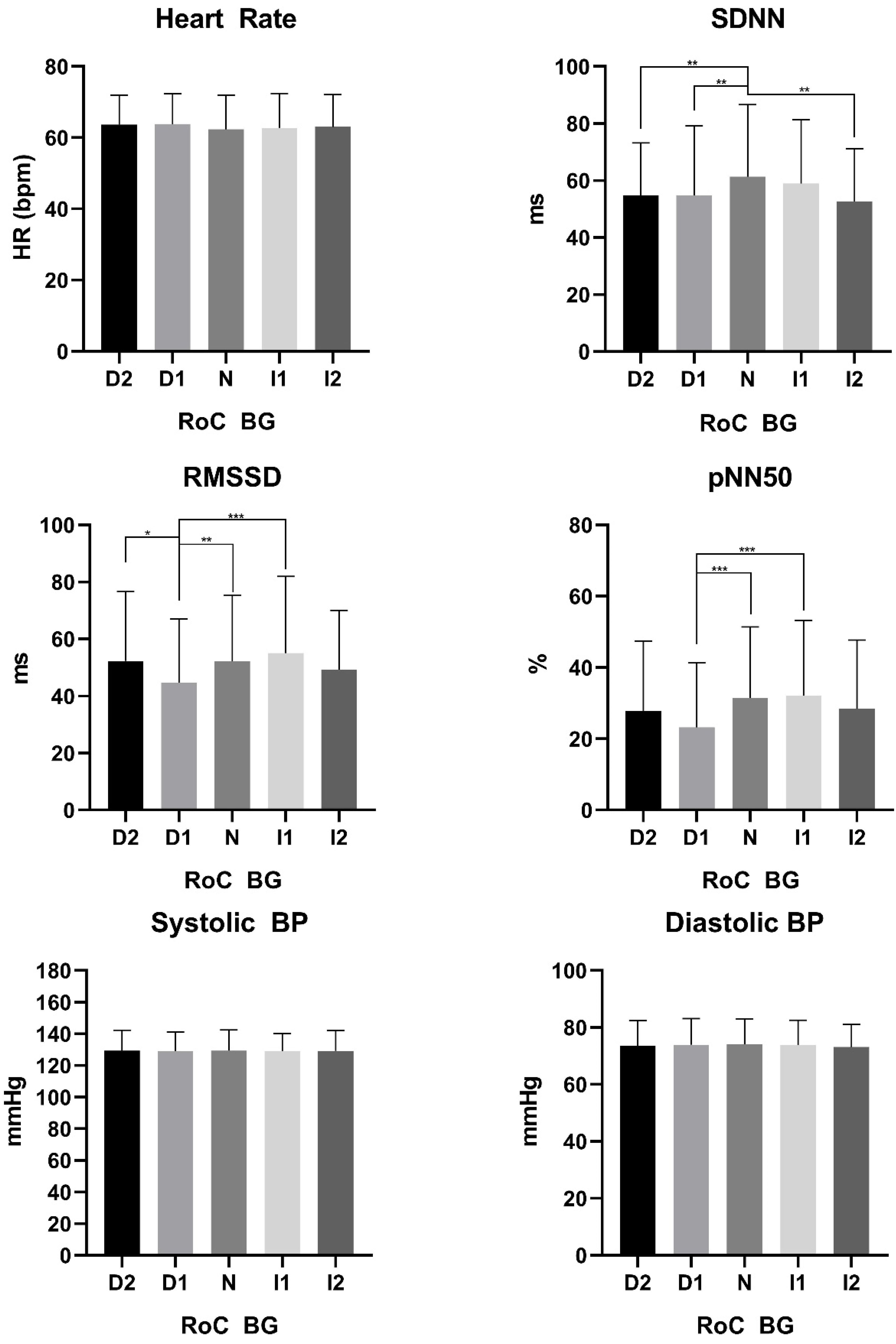
| <54 | 54–70 | 70–90 | 90–110 | 110–130 | 130–150 | >150 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heart Rate | 63 ± 7 | 63 ± 10 | 61 ± 10 | 64 ± 10 | 65 ± 9 | 65 ± 8 | 66 ± 5 | 0.001 |
| SDNN | 53.4 ± 13.3 | 66.7± 25.2 | 66.1 ± 27.6 | 58.8 ± 25.6 | 53.9 ± 24.2 | 47.9 ± 19.2 | 36.5 ± 12.1 | <0.001 |
| RMSSD | 39.3 ± 7.8 | 48.9 ± 19.2 | 53.9 ± 23.8 | 50.5 ± 24.7 | 50.0 ± 24.3 | 45.6 ± 19.9 | 37.4 ± 12.9 | <0.001 |
| pNN50 | 18.2 ± 12.0 | 27.3 ± 17.9 | 32.6 ± 19.9 | 28.52 ± 20.4 | 27.2 ± 17.9 | 22.9 ± 18.1 | 12.8 ± 12.5 | <0.001 |
| Systolic BP | 124 ± 10 | 127 ± 12 | 130 ± 13 | 128 ± 12 | 130 ± 11 | 133 ± 12 | 143 ± 7 | <0.001 |
| Diastolic BP | 74 ± 10 | 74 ± 9 | 73 ± 8 | 72 ± 7 | 72 ± 7 | 73 ± 9 | 83 ± 5 | <0.001 |
| D2 | D1 | N | I1 | I2 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heart Rate | 64 ± 8 | 64 ± 9 | 62 ± 10 | 63 ± 10 | 63 ± 9 | 0.25 |
| SDNN | 54.7 ± 18.5 | 54.8 ± 24.4 | 61.4 ± 25.3 | 58.9 ± 22.4 | 52.7 ± 18.5 | <0.001 |
| RMSSD | 52.4 ± 24.3 | 44.7 ± 22.3 | 52.2 ± 23.0 | 55.1 ± 26.8 | 49.3 ± 20.8 | <0.001 |
| pNN50 | 27.9 ± 19.5 | 23.2 ± 18.2 | 31.5 ± 19.9 | 32.2 ± 21.0 | 28.4 ± 19.3 | <0.001 |
| Systolic BP | 129 ± 13 | 129 ± 12 | 129 ± 13 | 129 ± 11 | 129 ± 12 | 0.99 |
| Diastolic BP | 74 ± 9 | 74 ± 9 | 74 ± 9 | 73 ± 9 | 73 ± 7 | 0.80 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eckstein, M.L.; Brockfeld, A.; Haupt, S.; Schierbauer, J.R.; Zimmer, R.T.; Wachsmuth, N.B.; Zunner, B.E.M.; Zimmermann, P.; Erlmann, M.; Obermayer-Pietsch, B.; et al. Acute Changes in Heart Rate Variability to Glucose and Fructose Supplementation in Healthy Individuals: A Double-Blind Randomized Crossover Placebo-Controlled Trial. Biology 2022, 11, 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020338
Eckstein ML, Brockfeld A, Haupt S, Schierbauer JR, Zimmer RT, Wachsmuth NB, Zunner BEM, Zimmermann P, Erlmann M, Obermayer-Pietsch B, et al. Acute Changes in Heart Rate Variability to Glucose and Fructose Supplementation in Healthy Individuals: A Double-Blind Randomized Crossover Placebo-Controlled Trial. Biology. 2022; 11(2):338. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020338
Chicago/Turabian StyleEckstein, Max Lennart, Antonia Brockfeld, Sandra Haupt, Janis Ramon Schierbauer, Rebecca Tanja Zimmer, Nadine Bianca Wachsmuth, Beate Elisabeth Maria Zunner, Paul Zimmermann, Maximilian Erlmann, Barbara Obermayer-Pietsch, and et al. 2022. "Acute Changes in Heart Rate Variability to Glucose and Fructose Supplementation in Healthy Individuals: A Double-Blind Randomized Crossover Placebo-Controlled Trial" Biology 11, no. 2: 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020338
APA StyleEckstein, M. L., Brockfeld, A., Haupt, S., Schierbauer, J. R., Zimmer, R. T., Wachsmuth, N. B., Zunner, B. E. M., Zimmermann, P., Erlmann, M., Obermayer-Pietsch, B., Aberer, F., & Moser, O. (2022). Acute Changes in Heart Rate Variability to Glucose and Fructose Supplementation in Healthy Individuals: A Double-Blind Randomized Crossover Placebo-Controlled Trial. Biology, 11(2), 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020338







