The Efficacy and Safety of Rituximab in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
- Studies on the eosinophilic granulomatous with polyangiitis (EGPA);
- Non-English studies;
- Any articles without clinical observations, such as review articles, conference abstracts, letters to the editor, and short communications.
2.3. Study Selection Process
2.4. Data Extraction
2.5. Data Synthesis
3. Results
3.1. Search Results and Studies’ Characteristics
3.2. Efficacy Reports Based on Randomized and Non-Randomized Studies
3.2.1. Randomized Studies
| No. | RCT Name | Country | Therapeutic Assessment | RTX Dosage | Number of Patients | Age | Sex | Outcome | Status | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | RITUXVAS | UK | RTX, CYC | 375 mg/BSA | 44 | 67.75 | 23M/21F | RTX is not superior to CYC | Completed | [17] |
| 2 | RAVE | US, The Netherlands | RTX, CYC | 375 mg/BSA | 197 | 52.75 | 98F/99M | RTX is not inferior to CYC | Completed | [19] |
| 3 | RITUXVAS * | UK | RTX plus CYC and GCs, CYC plus AZA | 375 mg/BSA | 44 | NG | NG | No significant difference between RTX plus CYC and CYC/AZA | Completed | [18] |
| 4 | RAVE * | US | RTX/GC, CYC/AZA | 375 mg/BSA | 102 | 55 | 48F/54M | A single course of RTX is similar to conventional therapies | Completed | [20] |
| 5 | RITAZAREM | US, Europe, Australia, Mexico | RTX, AZA | 1 g | 170 | 57.8 ± 14.5 | 86F/84M | RTX is superior to AZA in the prevention of relapse | Completed | [22] |
| 6 | SCOUT | US | RTX, GCs | 375 mg/BSA/w | 20 | 61.5 | 7F/13M | Combined RTX and GCs resulted in the same CR as the RAVE trial | Completed | [23] |
| 7 | MAINRITSAN | France | RTX, AZA | 500 mg | 115 | 55 ± 13 | 50F/65M | More serious relapse in AZA than RTX | Completed | [24] |
| 8 | MAINRITSAN2 | France | RTX, RTX | 500 mg | 162 | 60.5 | 68F/94M | No difference between adjusted infusion and organized infusion of RTX | Completed | [27] |
| 9 | MAINRITSAN3 | France | RTX, Placebo | 500 mg biannual | 97 | 63.9 | 34F/63M | Lower rate of relapse in RTX compared to placebo | Completed | [28] |
| 10 | MAINTANCAVAS | US | RTX | 2 × 1 g based on B cell repopulation | 200 | - | - | - | Recruiting | - |
| 11 | LoVAS | Japan | RTX+ low dose GC, RTX+ high dose GCs | 375 mg/BSA | 140 | 73.5 | 80F/54M | No significant difference between high-dose and low-dose GCs plus RTX regimens | Active | [29] |
| 12 | ENDURRANCE-1 | The Netherlands | RTX plus CYC, RTX | 2 × 1 g | 47 | - | - | No results available | Active, recruiting | - |
| 13 | RITUXGOPRO | France | RTX, Placebo | NG | 106 | - | - | - | Recruiting | - |
| 14 | COMBIVAS | UK | Belimumab, RTX | 2 × 1 g | 31 | - | - | No results available | Active, not recruiting | - |
| 15 | SATELITE | France | RTX, Tocilizumab, Abatacept | 375 mg/BSA, 500 mg | 42 | - | - | No results available | Not yet recruiting | - |
| 16 | RITUXGOPRO | France | RTX, placebo | 2 × 1 g | 106 | - | - | No results available | Recruiting | - |
3.2.2. Non-Randomized Studies
3.2.3. Case Reports
3.3. Pediatrics and Elderly
3.4. Dose
3.5. Comparing RTX to Conventional
3.6. Maintenance Regimen
3.7. Combination Therapies
3.8. Organ Involvement
3.8.1. Ear, Nose, and Throat (ENT)
3.8.2. Ocular
3.8.3. Renal
3.8.4. Respiratory Tract
| Author | Country | Type of Study | Number of Patients | Median Age | Sex | BVAS Score | Dose of RTX | Induction or Maintenance of RTX | Special Condition | CR or PR | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thietart et al., 2022 [144] | France | Prospective | 52 GPA 41 MPA | 79.4 | 51F/42M | NG | 4 × 375 mg/m2, 2 × 1 g (induction)/500 mg (maintenance) | Both | Elderly patients | 57/66 remission | RTX therapy achieves and maintains remission in most elderly patients |
| Brogan et al., 2022 [84] | Multicenter | Non-randomized uncontrolled clinical trial | 19 GPA, 6 MPA | 17 | 20F/5M | * PVAS: 8 | 4 × 375 mg/m2 | Induction | Pediatrics | All CR | RTX is effective and safe for children |
| Roccatello et al., 2022 [132] | Italy | Retrospective | 15 case: 11 MPA, 4 GPA; 10 control: 8 MPA, 2 GPA | 69 ± 11.6 (case), 72 ± 12.4 (control) | 15M/10F | 21 (case), 23 (control) | 6 × 375 mg/m2 | Induction | Renal involvement | 14/15 CR 7/15 CR | No significant difference between RTX+CYC+GC and CYC+GC+AZA in renal recovery |
| Moollan et al., 2022 [96] | Ireland | Retrospective | 20 MPA, 16 GPA | 63.5 | 23M/13F | 15 | NG | Induction | Renal involvement | NG | RTX is favored as an induction agent for relapsed AAV compared to CYC |
| Loftis et al., 2022 [82] | US | Retrospective | 12 MPA 7 GPA | 55 | 6M/13F | 25 | NG | Induction | Hispanic patients | 14 treated with RTX (10 remission, 4 died) | RTX is superior to CYC in preventing relapse |
| Besade et al., 2013 [106] | Norway | Retrospective | 35 GPA | 48 | 19M/16F | 9 | 2 × 1 g | Both | Maintenance therapy with RTX | 29 CR 4 PR | Long-term RTX was effective in prevention of relapse |
| Yusof et al., 2015 [90] | UK | Prospective | 35 AAV | 56 | 17M/18F | 10.5 | 2 × 1 g | Induction | Relapsing AAV | 20/35 CR 13/35 PR 2/35 NR | RTX provides long-term response |
| Baslund et al., 2012 [122] | Denmark | Prospective | 10 GPA | 50 | 3M/7F | NG | 2 × 1 g | Induction | Orbital inflammation | 10 remissions | RTX should be considered for dangerous ophthalmic patients |
| Wendt et al., 2011 [41] | Sweden | Retrospective | 14 GPA 1 MPA 1 EGPA | 60 | 9M/7F | 9.5 | 4 × 375 mg/m2, 2 × 1 g, 2 × 0.5 g | Induction | Relapsing or refractory AAV | 12/16 CR 3/16 PR 1/16 died | RTX provides long-term remission |
| Venhoff et al., 2014 [110] | Germany | Retrospective | 32 GPA 5 MPA | 62 | 21M/16F | 13 | 2 × 1 g, 2 × 0.5 g | Induction | Relapsing or refractory AAV | 19/37 CR 16/37 PR 1/37 NR 1/37 lost | RTX following conventional IST as maintenance therapy provided good response |
| Moog et al., 2014 [89] | Retrospective | 15 GPA 2 MPA | 58 | 10M/7F | 13 | 1 × 375 mg/m2 | Induction | Single-dose RTX therapy | 6/17 CR 11/17 PR | Single-dose RTX plus other IS are less effective than lymphoma protocol | |
| Wawrzycka-Adamczyk et al., 2014 [87] | Poland | Retrospective | 12 GPA | 50 | 5M/8F | 9.5 | Median 1 g | Induction | Refractory GPA | 11/12 remission | Low-dose RTX is effective for refractory AAV |
| Chasseur et al., 2020 [145] | Belgium | Retrospective | 48 GPA 9 MPA | 57 | 29M/28F | 6.2 ± 2.5 | - | Induction | RTX with and without GC therapy | 34 CR (GC and RTX) 0 CR (RTX) | Low CR rate using RTX without GC |
| Brihaye et al., 2007 [64] | France | Retrospective | 8 GPA | 49.6 | 5M/3F | 14.3 | 4 × 375 mg/m2, 2 × 1 g | Induction | Relapsing/refractory GPA | 3 CR 3 PR 2 NR | RTX plus steroid improved clinical outcome |
| Takeyama et al., 2021 [105] | Japan | Retrospective | 107 | 73 | 44M/79F | 13 | 375 mg/BSA | Both | Comparing RTX, other IST, and GC alone | 1- and 2-year relapse-free was 92.9% and 84.4% | RTX maintenance therapy is effective and provides lower dose of GCs |
| Asín et al., 2019 [127] | France | Retrospective | 63 | 46.1 | 33M/30F | NG | 375 mg/BSA | Induction | Ocular manifestation | 80.9% remission | RTX induced remission in refractory patients and was more effective than CYC |
| Caroti et al., 2019 [140] | Italy | Retrospective | 8 | 54 | 1M/7F | 14 | 4 × 375 mg/m2, 2 × 1 g | Both | Renal involvement | 8/8 remission | RTX was effective in partial renal function recovery |
| Mansfield et al., 2011 [138] | UK | Prospective | 13 GPA 10 MPA | 59 | 12M/11F | 21 | 2 × 1 g | Induction | Severe renal involvement | 23/23 Remission | RTX+low-dose CYC is effective in the induction of remission |
| P.McAdoo et al., 2019 [139] | UK | Prospective | 66 | 62 | 38M/28F | 19 | 2 × 1 g | Induction | Renal involvement | 94% remission | Combination of GC, RTX, CYC is better than previous regimen |
| Menthon et al., 2011 [99] | France | Prospective randomized | 17 (8 RTX, 9 IFX) | 52.9 ± 17 | 8M/9F | 12.6 | 4 × 375 mg/m2 | Both | Refractory WG | 3 CR 1 PR | RTX provides a higher rate of response and longer-lasting CR than Infliximab |
| Stasi et al., 2006 [31] | Italy | Prospective | 8 GPA 2 MPA | 53 | 5M/5F | 5.5 | 4 × 375 mg/m2 | Induction | Relapsing or refractory | 9 CR 1 PR | RTX was effective in severe patients or non-responders to standard treatment |
| Lally et al., 2014 [119] | US | Retrospective | 99 | 49.8 ± 15.1 | 31M/68F | NA | - | Maintenance | ENT manifestation | No ENT active disease in 92.4% | RTX results in 11-times lower rate of active symptoms than conventional therapies |
| Del Pero et al., 2009 [124] | UK | Retrospective | 34 GPA | 47.1 | 21M/13F | 11 | 4 × 375 mg/m2, 2 × 1 g | Induction | ENT manifestation | 21/34 CR 9/34 PR 4/34 NR | RTX provides 80% response, reduced exposure to other therapies |
| Casal Moura et al., 2020 [98] | US | Retrospective | 251 (64 RTX, 161 CYC) | 66 | 128M/123F | 8 | 4 × 375 mg/m2 | Induction | Severe renal disease | 54/64 remission | Risks and benefits of CYC and RTX were balanced; adding PLEX provides no benefit |
| Girard et al., 2015 [142] | France | Retrospective | 26 | 32 | 9M/17F | 8 | NG | Induction | Tracheobronchial stenosis | 80% remission in RTX group, 42% remission in CYC group | RTX was more successful in achieving remission than CYC |
| Miloslavsky et al., 2014 [40] | US | Retrospective | 24 GPA 2 MPA | NG | NG | 5.3 | 4 × 375 mg/m2 | Induction | Re-treatment of AAV relapse | 17/26 CR 8/26 PR 1/26 died | Re-treatment of relapsed patients with RTX/GC was effective |
| Lionaki et al., 2017 [113] | Greece | Retrospective | 29 GPA 6 MPA | 48.6 | 15M/20F | 15.1 | 4 × 375 mg/m2, 2 × 1 g | Induction | Refractory relapsing AAV | 21.4% CR 78.6% PR | CYC plus RTX provides prolonged remission and less CYC usage |
| Cartin-Ceba et al., 2012 [101] | US | Retrospective | 53 GPA | 46 | 25M/28F | 5 | 4 × 375 mg/m2, 2 × 1 g | Both | Chronic relapsing GPA | 52/53 CR 1/53 PR | RTX was effective for induction and maintenance |
| Calich et al., 2014 [103] | France | Retrospective | 66 GPA | 50 ± 17.4 | 32M/34F | 9.5 | 4 × 375 mg/m2, 2 × 1 g, 500 mg every 6 m | Both | Low-dose RTX as maintenance therapy | 25/66 CR 27/66 PR 14/66 NR | Low-dose RTX provides low-level rate of relapse |
| Lovric et al., 2009 [35] | Germany | Retrospective | 13 GPA 1 MPA 1 EGPA | 45 | 8M/7F | 12 | 4 × 375 mg/m2 | Induction | Refractory or relapsing AAV | 6/15 CR 8/15 PR 1/15 NR | RTX was effective to induce remission |
| Mittal et al., 2021 [43] | India | Retrospective | 77 GPA | 40 | 28M/49F | 12 | 2 × 1 g, 4 × 375 mg/m2, 0.5 g every 6 m | Both | RTX as induction and maintenance | 60% remission | RTX was effective as an induction and maintenance agent |
| Smith et al., 2012 [44] | UK | Retrospective | 61 GPA 12 MPA | 52 | 30M/43F | DEI = 4 | 2 × 1 g, 4 × 375 mg/m2, 0.5 g every 6 m | Both | Refractory or relapsing AAV | 61/73 CR 8/73 PR 4/73 NR | Fixed-interval RTX therapy reduces relapse risk |
| Ramos-Casals et al., 2010 [33] | Spain | Prospective | 17 GPA 2 MPA | 46.2 | 9M/10F | NG | - | - | Severe refractory patients | 10/19 CR 3/19 PR 6/19 NR | RTX can be used for severe refractory patients |
| Rees et al., 2011 [34] | UK | Retrospective | 15 (11 GPA) | 47.2 | 9M/6F | Median BVAS 13 | 4 × 375 mg/m2, 2 × 1 g | Induction | Refractory vasculitis | All CR | RTX was effective as an induction agent |
| Holle et al., 2012 [118] | Germany | Retrospective | 59 | 54 | 35M/24F | 16 | 4 × 375 mg/m2 | Induction | Comparing efficacy of RTX in granulomatous vs. vasculitis symptoms | 61.3% CR | RTX was more effective in vasculitis than granulomatous manifestations |
| Gulati et al., 2021 [114] | UK | Retrospective cohort | 64 | 66 | 39M/25F | 19 | 2 × 1 g | Induction | Combined therapy of severe AAV patients | 94% CR | Combined RTX, low-dose CYC, and GC resulted in early and sustained remission |
| Pepper et al., 2019 [109] | UK, Ireland | Prospective | 49 | 65.5 | 24M/25F | 16.4 | 2 × 1 g | Induction | GC-free regimen in severe AAV patients | 45/46 remission | Rapid GC discontinuation in severe AAV is effective as standard therapy with fewer adverse events |
| Puéchal et al., 2021 [102] | France | Retrospective | 434 | 53.4 | 252M/182F | 15.3 | NG | Both | 10 years follow-up to assess prolonged remission without treatment | - | Continual remission was significantly more achieved by RTX than conventional therapies |
| Joshi et al., 2015 [128] | UK | Retrospective cohort | 37 | 51.5 | - | - | 2 × 1 g | Induction | Ocular GPA | 31/37 CR 5/37 PR | RTX effectively induces remission of ocular manifestation in AAV patients |
| Malm et al., 2014 [120] | US | Retrospective | 11 | 30 | 5M/6F | 4 × 375 mg/m2 | Induction | Otolaryngologic manifestation | No improvement in otolaryngological manifestations | RTX did not provide improvement in ENT manifestations | |
| Kant et al., 2019 [85] | US | Retrospective | 9 | 63 | 3M/6F | 15 | 4 × 375 mg/m2 | Induction | AAV patients with GN | All remission | Consecutive therapy with GC and CYC followed by RTX was effective |
| Shah et al., 2015 [130] | US, Sweden, UK | Retrospective | 6 GPA 8 MPA | 61 | 8M/6F | NG | 4 × 375 mg/m2, 2 × 1 g | Induction | Severe renal disease | 14/14 responded | RTX plus GC regimen induced high-rate remission and dialysis withdrawal |
| Sorin et al., 2022 [111] | France | Retrospective | 17 GPA | - | - | - | - | Induction | Persistent active GPA with granulomatous manifestations | 88% remission | Combined RTX/MTX induced remission |
| Lower et al., 2012 [121] | US | Retrospective | 5 AAV 4 sarcoidosis | 54.3 | 2M/3F | NG | 375 mg/m2, 2 × 1 g | Both | Refractory ocular patients | 5/5 responded | RTX was effective in the treatment of patients with eye disease. |
| Taylor et al., 2009 [126] | UK | Retrospective | 10 GPA | 48.2 | 5M/5F | NG | 2 × 1 g | Induction | Refractory ocular patients | 10/10 Remission | prolonged remission was achieved using RTX |
| Pullerits et al., 2012 [133] | Sweden | Retrospective | 28 GPA 1 MPA | 49.3 | 15M/14F | 6 | 4 × 375 mg/m2 | Induction | Refractory AAV | 21% CR 41% PR 38% NR | RTX is an alternative option in conventional treatment-resistant patients |
| Chocova et al., 2015 [137] | Czech Republic | Prospective | 15 GPA 3 MPA | 37.5 | 11M/7F | 9.5 | 4 × 375 mg/m2, 2 × 1 g | Induction | Relapsing or refractory AAV | 8/18 CR 5/18 PR 2/18 NR 2/18 died 1/18 lost | RTX is associated with remission in 72% of patients |
| Keogh et al., 2006 [30] | US | Prospective | 10 GPA | 57 | 7M/3F | 6 | 4 × 375 mg/m2 | Induction | Severe refractory GPA | 10 CR | RTX was an effective induction agent for severe refractory GPA |
| Mc Gregor et al., 2015 [91] | US | Prospective | 56 GPA 52 MPA 3 EGPA 9 renal | 50 | 55M/64F | NG | 4 × 375 mg/m2, 2 × 1 g | Induction | - | 103 remissions | Two-dose and >2-dose RTX regimens were similar |
| Roccatello et al., 2011 [136] | Italy | Prospective | 5 GPA 4 MPA 2 EGPA | 57.5 | 6M/5F | 22 | 6 × 375 mg/m2 | Induction | Refractory patients | 11 remissions | RTX was effective in patients resistant to conventional IST |
| Roccatello et al., 2017 [93] | Italy | Prospective | 5 GPA 4 MPA 2 EGPA | 57.5 | 6M/5F | 22 | 6 × 375 mg/m2 | Induction | Long-term follow-up of refractory patients | 4/11 remained in remission 7/11 re-treated | RTX in 6 doses of 375 mg/m2 provides long-term remission |
| Ayan et al., 2018 [135] | Turkey | Retrospective | 21 GPA 4 idiopathic | 44 | 11M/14F | NG | 4 × 375 mg/m2, 2 × 1 g | Both | Untreated patients with conventional IST | 18 CR 1 died 6 ongoing diseases | RTX was effective in patients resistant to conventional IST |
| Knight et al., 2014 [39] | Sweden | Retrospective | 12 GPA | 52 | 5M/7F | 9 | 2 × 1 g | Maintenance | Severe relapsing AAV | 11/12 remission 1/12 NR | RTX therapy every six months is an effective maintenance treatment |
| B.Jones et al., 2009 [86] | UK | Retrospective | 46 GPA 10 MPA 5 EGPA 4 other | 47 | 34M/31F | DEI 4 | 4 × 375 mg/m2, 2 × 1 g | Induction | Comparing different regimes of RTX | 49/65 CR 15/65 PR 1/65 NR | No difference between the two regimes |
| Brihaye et al., 2007 [64] | France | Retrospective | 8 GPA | 49.6 | 5M/3F | 14.3 | 4 × 375 mg/m2, 2 × 1 g | Induction | Relapsing/refractory GPA | 3 CR 3 PR 2 NR | RTX plus steroids improved clinical outcome |
| Durel et al., 2019 [125] | France | Retrospective | 56 GPA 1 MPA 2 EGPA | 46 | 26M/33F | 9 | NG | Induction | Orbital mass | 64% remission with RTX vs. 26% with CYC | RTX was more effective than CYC |
| Timlin et al., 2015 [83] | US | Retrospective | 19 GPA 12 MPA | 71 ± 6 | 10M/21F | 4.4 | 4 × 375 mg/m2, 2 × 1 g | Induction | AAV patients older than 60 | 30/31 remission 1/31 NR | Elderly patients responded effectively to RTX |
| Puéchal X et al., 2019 [37] | France | Retrospective | 114 GPA | 52 | 40M/64F | 9 | 500 mg every 6 m | Maintenance | Low-dose RTX as maintenance therapy | 86% remission | Sustained remission using RTX for induction and low-dose maintenance |
| Azar et al., 2014 [112] | US | Retrospective | 105 GPA | 49 | 50M/55F | 4 | 4 × 375 mg/m2, 2 × 1 g | Induction | Evaluation of RTX with or without other maintenance therapies | 95/100 CR 1/100 PR 2/100 NR 1 died 1 lost | Conventional therapies plus RTX decrease relapse rate without increasing adverse events |
| Charles et al., 2013 [100] | France | Retrospective | 70 GPA 7 MPA 2 Renal restricted 1 EGPA | 54 ± 17 | NG | 7 | 4 × 375 mg/m2, 2 × 1 g | Both | Long-term follow-up | 66% CR 25% PR | RTX was more effective as a maintenance therapy |
| Roll et al., 2012 [38] | Germany | Retrospective | 50 GPA 8 MPA | 50.2 | 28M/30F | NG | 4 × 375 mg/m2, 2 × 1 g | Induction | Refractory AAV | 22/58 CR 29/58 PR 4/58 NR | RTX was effective in refractory AAV |
3.9. Resolving Rare Clinical Manifestations of GPA by Rituximab
3.10. Unsuccessful Reports in Rituximab Therapy for GPA Patients
3.11. Safety
3.11.1. Hypersensitivity
3.11.2. Hypogammaglobulinemia
3.11.3. Infection
3.11.4. Cancer
3.11.5. Cytopenia
3.11.6. Other Rare Side Effects
| Side Effects | Comment | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Infection | PCP, PJP, TB, UTI, salmonella, atypical mycobacterial infection, influenza, legionella, cutaneous abscess, GI infection, vulvovaginal pyoderma gangrenosome. CMV, HBV, HCV, JC virus, HSV, herpes zoster, varicella zoster, aspergillus. | [32,34,35,40,41,43,45,83,101,105,108,112,113,115,118,124,135,144,205,207,210,214,223,224,225,226,227,228,229,230,231,232,233,234,235] |
| Hypogammaglobulinemia | Hypogammaglobulinemia and severe hypogammaglobulinemia were reported in about 50% and 5% of patients. Hypogammaglobulinemia-induced infection is a controversial issue. Baseline Ig level is a substantial factor in the development of hypogammaglobulinemia. | [45,115,119,211,212,213,214,215,216,217,218,219,220,221] |
| Cancer | Breast cancer, colon, hepatocellular, hematologic, uterine, thyroid, peritoneal, renal, bladder, lung, SCC of the tongue and esophagus, basal cell carcinoma, melanoma, and non-melanoma skin cancer. | [19,32,90,91,112,124,138,236,237,238] |
| Cytopenia | Leucopenia (B-cell lymphopenia), which can be transient; thrombocytopenia; neutropenia, which can be late-onset. | [20,21,35,42,83,211,239,240,241] |
| Hypersensitivity | Hypersensitivity reaction is a first-onset complication developed in one-third of injected patients. Hypersensitivity can emerge as different symptoms such as rash and swelling. | [37,64,101,124,138] |
| Other side effects | CHF, AMI, VTE, bone fracture, herpes simplex osteomatitis, visual disturbance, vaginitis, pyomiosis pyoderma gangrenosome, anorexia nervosa, PML, pneumonitis, Crohn’s disease, PRES, ruptured aneurysm. | [20,32,43,88,90,108,128,135,144,210,211,222,229,232,235,243,244,245,246,247,248] |
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Constant Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RTX | Rituximab |
| CYC | Cyclophosphamide |
| GC | Glucocorticoids |
| AZA | Azathioprine |
| BSA | Body surface area |
| PR3 | Proteinase-3 |
| MPO | Myeloperoxidase |
| ANCA | Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody |
| AAV | ANCA-associated vasculitis |
| GPA | Granulomatosis with polyangiitis |
| MPA | Microscopic polyangiitis |
| EGPA | Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis |
| IST | Immunosuppressive therapy |
| GM-CSF | Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor |
References
- Kitching, A.R.; Anders, H.-J.; Basu, N.; Brouwer, E.; Gordon, J.; Jayne, D.R.; Kullman, J.; Lyons, P.A.; Merkel, P.A.; Savage, C.O.S.; et al. ANCA-associated vasculitis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2020, 6, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, R.A.; Mahr, A.; Mohammad, A.J.; Gatenby, P.; Basu, N.; Flores-Suárez, L.F. Classification, epidemiology and clinical subgrouping of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2015, 30 (Suppl. 1), i14–i22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, M.; Watts, R. ANCA-associated vasculitis. Clin. Med. 2017, 17, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, J.; Doll, H.; Suppiah, R.; Flossmann, O.; Harper, L.; Höglund, P.; Jayne, D.; Mahr, A.; Westman, K.; Luqmani, R. Damage in the anca-associated vasculitides: Long-term data from the European vasculitis study group (EUVAS) therapeutic trials. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, R.J.; Jennette, J.C. ANCA small-vessel vasculitis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1997, 8, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilhorst, M.; van Paassen, P.; Tervaert, J.W.C. Proteinase 3-ANCA Vasculitis versus Myeloperoxidase-ANCA Vasculitis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 2314–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Shen, C.; Zhong, Y.; Ooi, J.D.; Zhou, Y.-O.; Chen, J.-B.; Meng, T.; Xiao, Z.; Lin, W.; Ao, X.; et al. Differences between myeloperoxidase-antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody (ANCA) and proteinase 3-ANCA associated vasculitis: A retrospective study from a single center in China. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 21, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, M.; Watts, R.A.; Bajema, I.M.; Cid, M.C.; Crestani, B.; Hauser, T.; Hellmich, B.; Holle, J.U.; Laudien, M.; Little, M.A.; et al. EULAR/ERA-EDTA recommendations for the management of ANCA-associated vasculitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Yu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, M.H. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-associated vasculitis in older patients. Medicine 2008, 87, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsumata, Y.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Yamanaka, H. Interstitial Lung Disease with ANCA-associated Vasculitis. Clin. Med. Insights Circ. Respir. Pulm. Med. 2015, 9, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönermarck, U.; Gross, W.L.; de Groot, K. Treatment of ANCA-associated vasculitis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2014, 10, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faurschou, M.; Westman, K.; Rasmussen, N.; de Groot, K.; Flossmann, O.; Höglund, P.; Jayne, D.R. Brief Report: Long-term outcome of a randomized clinical trial comparing methotrexate to cyclophosphamide for remission induction in early systemic antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 3472–3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, R.I.; Gaffo, A.L. Rituximab in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2017, 19, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groh, M.; Pagnoux, C.; Baldini, C.; Bel, E.; Bottero, P.; Cottin, V.; Dalhoff, K.; Dunogué, B.; Gross, W.; Holle, J.; et al. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg–Strauss) (EGPA) Consensus Task Force recommendations for evaluation and management. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2015, 26, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, M.; McKenzie, J.E.; Sowden, A.; Katikireddi, S.V.; Brennan, S.E.; Ellis, S.; Hartmann-Boyce, J.; Ryan, R.; Shepperd, S.; Thomas, J.; et al. Synthesis without meta-analysis (SWiM) in systematic reviews: Reporting guideline. BMJ 2020, 368, l6890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.B.; Cohen Tervaert, J.W.; Hauser, T.; Luqmani, R.; Morgan, M.D.; Peh, C.A.; Savage, C.O.; Segelmark, M.; Tesar, V.; van Paassen, P.; et al. Rituximab versus Cyclophosphamide in ANCA-Associated Renal Vasculitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.B.; Furuta, S.; Tervaert, J.W.; Hauser, T.; Luqmani, R.; Morgan, M.D.; Peh, C.A.; Savage, C.O.; Segelmark, M.; Tesar, V.; et al. Rituximab versus cyclophosphamide in ANCA-associated renal vasculitis: 2-year results of a randomised trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1178–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, J.H.; Merkel, P.A.; Spiera, R.; Seo, P.; Langford, C.A.; Hoffman, G.S.; Kallenberg, C.G.; St Clair, E.W.; Turkiewicz, A.; Tchao, N.K.; et al. Rituximab versus cyclophosphamide for ANCA-associated vasculitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geetha, D.; Specks, U.; Stone, J.H.; Merkel, P.A.; Seo, P.; Spiera, R.; Langford, C.A.; Hoffman, G.S.; Kallenberg, C.G.M.; St Clair, E.W.; et al. Rituximab versus cyclophosphamide for ANCA-associated vasculitis with renal involvement. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2015, 26, 976–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Specks, U.; Merkel, P.A.; Seo, P.; Spiera, R.; Langford, C.A.; Hoffman, G.S.; Kallenberg, C.G.; St Clair, E.W.; Fessler, B.J.; Ding, L.; et al. Efficacy of remission-induction regimens for ANCA-associated vasculitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopaluni, S.; Smith, R.M.; Lewin, M.; McAlear, C.A.; Mynard, K.; Jones, R.B.; Specks, U.; Merkel, P.A.; Jayne, D.R. Rituximab versus azathioprine as therapy for maintenance of remission for anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibody-associated vasculitis (RITAZAREM): Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2017, 18, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miloslavsky, E.M.; Niles, J.L.; Wallace, Z.S.; Cortazar, F.B.; Fernandes, A.; Laliberte, K.; Stone, J.H. Reducing glucocorticoid duration in ANCA-associated vasculitis: A pilot trial. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2018, 48, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillevin, L.; Pagnoux, C.; Karras, A.; Khouatra, C.; Aumaître, O.; Cohen, P.; Maurier, F.; Decaux, O.; Ninet, J.; Gobert, P.; et al. Rituximab versus azathioprine for maintenance in ANCA-associated vasculitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1771–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugnet, G.; Pagnoux, C.; Terrier, B.; Perrodeau, E.; Puéchal, X.; Karras, A.; Khouatra, C.; Aumaître, O.; Cohen, P.; Maurier, F.; et al. Rituximab versus azathioprine for ANCA-associated vasculitis maintenance therapy: Impact on global disability and health-related quality of life. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2016, 34, S54–S59. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Terrier, B.; Pagnoux, C.; Perrodeau, É.; Karras, A.; Khouatra, C.; Aumaître, O.; Cohen, P.; Decaux, O.; Desmurs-Clavel, H.; Maurier, F.; et al. Long-term efficacy of remission-maintenance regimens for ANCA-associated vasculitides. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 1150–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, P.; Terrier, B.; Perrodeau, É.; Cohen, P.; Faguer, S.; Huart, A.; Hamidou, M.; Agard, C.; Bonnotte, B.; Samson, M.; et al. Comparison of individually tailored versus fixed-schedule rituximab regimen to maintain ANCA-associated vasculitis remission: Results of a multicentre, randomised controlled, phase III trial (MAINRITSAN2). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charles, P.; Perrodeau, É.; Samson, M.; Bonnotte, B.; Néel, A.; Agard, C.; Huart, A.; Karras, A.; Lifermann, F.; Godmer, P.; et al. Long-Term Rituximab Use to Maintain Remission of Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis: A Randomized Trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 173, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, S.; Nakagomi, D.; Kobayashi, Y.; Hiraguri, M.; Sugiyama, T.; Amano, K.; Umibe, T.; Kono, H.; Kurasawa, K.; Kita, Y.; et al. Effect of Reduced-Dose vs High-Dose Glucocorticoids Added to Rituximab on Remission Induction in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2021, 325, 2178–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keogh, K.A.; Ytterberg, S.R.; Fervenza, F.C.; Carlson, K.A.; Schroeder, D.R.; Specks, U. Rituximab for refractory Wegener’s granulomatosis: Report of a prospective, open-label pilot trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasi, R.; Stipa, E.; Del Poeta, G.; Amadori, S.; Newland, A.C.; Provan, D. Long-term observation of patients with anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis treated with rituximab. Rheumatology 2006, 45, 1432–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nagafuchi, H.; Atsumi, T.; Hatta, K.; Muso, E.; Takeno, M.; Yamada, H.; Ozaki, S. Long-term safety and efficacy of rituximab in 7 Japanese patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2015, 25, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Casals, M.; García-Hernández, F.J.; de Ramón, E.; Callejas, J.L.; Martínez-Berriotxoa, A.; Pallarés, L.; Caminal-Montero, L.; Selva-O’Callaghan, A.; Oristrell, J.; Hidalgo, C.; et al. Off-label use of rituximab in 196 patients with severe, refractory systemic autoimmune diseases. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2010, 28, 468–476. [Google Scholar]
- Rees, F.; Yazdani, R.; Lanyon, P. Long-term follow-up of different refractory systemic vasculitides treated with rituximab. Clin. Rheumatol. 2011, 30, 1241–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovric, S.; Erdbruegger, U.; Kümpers, P.; Woywodt, A.; Koenecke, C.; Wedemeyer, H.; Haller, H.; Haubitz, M. Rituximab as rescue therapy in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis: A single-centre experience with 15 patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2009, 24, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, N.; Matsudaira, R.; Hirashima, M.; Ikeda, M.; Tajima, M.; Nawata, M.; Morimoto, S.; Kaneda, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Hashimoto, H.; et al. Two cases of refractory Wegener’s granulomatosis successfully treated with rituximab. Intern. Med. 2007, 46, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puéchal, X.; Iudici, M.; Calich, A.L.; Vivot, A.; Terrier, B.; Régent, A.; Cohen, P.; Jeunne, C.L.; Mouthon, L.; Ravaud, P.; et al. Rituximab for induction and maintenance therapy of granulomatosis with polyangiitis: A single-centre cohort study on 114 patients. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roll, P.; Ostermeier, E.; Haubitz, M.; Lovric, S.; Unger, L.; Holle, J.; Kötter, I.; Henes, J.C.; Bergner, R.; Rubbert-Roth, A.; et al. Efficacy and safety of rituximab treatment in patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitides: Results from a German registry (GRAID). J. Rheumatol. 2012, 39, 2153–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, A.; Hallenberg, H.; Baecklund, E. Efficacy and safety of rituximab as maintenance therapy for relapsing granulomatosis with polyangiitis—A case series. Clin. Rheumatol. 2014, 33, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Miloslavsky, E.M.; Specks, U.; Merkel, P.A.; Seo, P.; Spiera, R.; Langford, C.A.; Hoffman, G.S.; Kallenberg, C.G.; St Clair, E.W.; Tchao, N.K.; et al. Rituximab for the treatment of relapses in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2014, 66, 3151–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendt, M.; Gunnarsson, I.; Bratt, J.; Bruchfeld, A. Rituximab in relapsing or refractory ANCA-associated vasculitis: A case series of 16 patients. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 41, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, E.P.; Laliberte, K.A.; Niles, J.L. Rituximab as maintenance therapy for anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 5, 1394–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mittal, S.; Naidu, G.; Jha, S.; Rathi, M.; Nada, R.; Minz, R.W.; Sharma, K.; Dhir, V.; Jain, S.; Sharma, A. Experience with similar biologic rituximab in 77 patients of granulomatosis with polyangiitis-a real-life experience. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.M.; Jones, R.B.; Guerry, M.J.; Laurino, S.; Catapano, F.; Chaudhry, A.; Smith, K.G.; Jayne, D.R. Rituximab for remission maintenance in relapsing antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 3760–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roubaud-Baudron, C.; Pagnoux, C.; Méaux-Ruault, N.; Grasland, A.; Zoulim, A.; Le Guen, J.; Prud’homme, A.; Bienvenu, B.; de Menthon, M.; Camps, S.; et al. Rituximab maintenance therapy for granulomatosis with polyangiitis and microscopic polyangiitis. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 39, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specks, U.; Fervenza, F.C.; McDonald, T.J.; Hogan, M.C. Response of Wegener’s granulomatosis to anti-CD20 chimeric monoclonal antibody therapy. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 2836–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallenbach, M.; Duan, H.; Ring, T. Rituximab induced remission in a patient with Wegener’s granulomatosis. Nephron. Clin. Pract. 2005, 99, c92–c96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalewska, B.; Szechiński, J.; Roszkowska, E. Wegener’s granulomatosis effectively treated with rituximab: A case study. Pol. Arch. Med. Wewn. 2008, 118, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recillas-Gispert, C.; Serna-Ojeda, J.C.; Flores-Suárez, L.F. Rituximab in the treatment of refractory scleritis in patients with granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener’s). Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2015, 253, 2279–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.; Ma, L.; Lasave, A.F.; Foster, C.S. Rituximab Induction and Maintenance Treatment in Patients with Scleritis and Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (Wegener’s). Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2018, 26, 1166–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, C.M.; Murray, P.I.; Savage, C.O. Successful treatment of Wegener’s granulomatosis associated scleritis with rituximab. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2005, 89, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ahmed, A.; Foster, C.S. Cyclophosphamide or Rituximab Treatment of Scleritis and Uveitis for Patients with Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis. Ophthalmic. Res. 2019, 61, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, X.; Iwata, D.; Namba, K.; Suzuki, K.; Mizuuchi, K.; Nakamura, H.; Atsumi, T.; Ishida, S. Posterior scleritis with anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis utilizing rituximab therapy to maintain remission: A case report. Am. J. Ophthalmol. Case Rep. 2022, 25, 101333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrada-Elena, M.; Ioana, T.T.; Mihaela, F.M.; Irina-Elena, C.; Andrei, T.I.; Florian, B. Wegener’s granulomatosis with orbital involvement: Case report and literature review. Rom. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 65, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avshovich, N.; Boulman, N.; Slobodin, G.; Zeina, A.R.; Rosner, I.; Rozenbaum, M. Refractory Wegener’s granulomatosis: Effect of rituximab on granulomatous bilateral orbital involvement. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 2009, 11, 566–568. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dalkilic, E.; Alkis, N.; Kamali, S. Rituximab as a new therapeutic option in granulomatosis with polyangiitis: A report of two cases. Mod. Rheumatol. 2012, 22, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dag, M.S.; Pehlivan, Y.; Tutar, E.; Kisacik, B. Rituximab seems a promising therapeutic option in granulomatosis with polyangiitis with intestinal perforation: A case report and literature review. BMJ Case Rep. 2013, 2013, bcr2012007518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memet, B.; Rudinskaya, A.; Krebs, T.; Oelberg, D. Wegener granulomatosis with massive intracerebral hemorrhage: Remission of disease in response to rituximab. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2005, 11, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawa, S.; Mukhtyar, C.; Edmonds, S.; Webley, M. Refractory Wegener’s meningitis treated with rituximab. J. Rheumatol. 2007, 34, 900–901. [Google Scholar]
- Benucci, M.; Li Gobbi, F.; Panconesi, P.; Manfredi, M.; Sarzi-Puttini, P.; Atzeni, F. Granulomatosis polyangiitis associated with meningeal involvement: Response to rituximab therapy after failure of cyclophosphamide. Reumatismo 2013, 65, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Freidlin, J.; Wong, I.G.; Acharya, N. Rituximab treatment for peripheral ulcerative keratitis associated with Wegener’s granulomatosis. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2007, 91, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ebrahimiadib, N.; Modjtahedi, B.S.; Roohipoor, R.; Anesi, S.D.; Foster, C.S. Successful Treatment Strategies in Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis-Associated Peripheral Ulcerative Keratitis. Cornea 2016, 35, 1459–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, J.; Song, J.W. Life-Threatening Subglottic Stenosis of Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis: A Case Report. Medicina 2021, 57, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brihaye, B.; Aouba, A.; Pagnoux, C.; Cohen, P.; Lacassin, F.; Guillevin, L. Adjunction of rituximab to steroids and immunosuppressants for refractory/relapsing Wegener’s granulomatosis: A study on 8 patients. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2007, 25, S23–S27. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Cano, D.; Callejas-Rubio, J.L.; Ortego-Centeno, N. Effect of rituximab on refractory Wegener granulomatosis with predominant granulomatous disease. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2008, 14, 92–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, A.J.; Day, C.J.; Drayson, M.T.; Savage, C.O. Effective therapeutic use of rituximab in refractory Wegener’s granulomatosis. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2005, 20, 622–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bachmeyer, C.; Cadranel, J.F.; Demontis, R. Rituximab is an alternative in a case of contra-indication of cyclophosphamide in Wegener’s granulomatosis. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2005, 20, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, P.; Specks, U.; Keogh, K.A. Efficacy of rituximab in limited Wegener’s granulomatosis with refractory granulomatous manifestations. J. Rheumatol. 2008, 35, 2017–2023. [Google Scholar]
- Omdal, R.; Wildhagen, K.; Hansen, T.; Gunnarsson, R.; Kristoffersen, G. Anti-CD20 therapy of treatment-resistant Wegener’s granulomatosis: Favourable but temporary response. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2005, 34, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aries, P.M.; Hellmich, B.; Voswinkel, J.; Both, M.; Nolle, B.; Holl-Ulrich, K.; Lamprecht, P.; Gross, W.L. Lack of efficacy of rituximab in Wegener’s granulomatosis with refractory granulomatous manifestations. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2006, 65, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oristrell, J.; Bejarano, G.; Jordana, R.; Monteagudo, M.; Marí, B.; Casanovas, A.; Tolosa, C. Effectiveness of rituximab in severe Wegener’s granulomatosis: Report of two cases and review of the literature. Open Respir. Med. J. 2009, 3, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tektonidou, M.G.; Skopouli, F.N. Sustained 3-year remission after rituximab treatment in a patient with refractory Wegener’s granulomatosis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2006, 24, S103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Henes, J.C.; Kanz, L.; Koetter, I. Rituximab and leflunomide for Wegener’s granulomatosis: A long-term follow-up. Rheumatol. Int. 2011, 31, 425–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.M.; Lehman, T.J. Rituximab for severe refractory pediatric Wegener granulomatosis. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2008, 14, 278–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plumb, L.A.; Oni, L.; Marks, S.D.; Tullus, K. Paediatric anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis: An update on renal management. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2018, 33, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermle, T.; Goestemeyer, A.K.; Sweny, P.; Burns, A. Successful therapeutic use of rituximab in refractory Wegener’s granulomatosis after renal transplantation. Clin. Nephrol. 2007, 68, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Lawson, C.A.; Quinn, M.A.; Isdale, A.H.; Green, M.J. Successful Treatment of ANCA-Negative Wegener’s Granulomatosis with Rituximab. Int. J. Rheumatol. 2010, 2010, 846063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooka, S.; Maeda, A.; Ito, H.; Omata, M.; Yamada, H.; Ozaki, S. Treatment of refractory retrobulbar granuloma with rituximab in a patient with ANCA-negative Wegener’s granulomatosis: A case report. Mod. Rheumatol. 2009, 19, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, K.; Fujii, Y.; Maekawa, M.; Tsukamoto, H. Successful rituximab treatment in a patient with ANCA-negative granulomatosis with polyangitis: A case report. Mod. Rheumatol. Case Rep 2022, 6, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoganson, D.D.; From, A.M.; Michet, C.J. ANCA vasculitis in the elderly. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2008, 14, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jariwala, M.P.; Laxer, R.M. Primary Vasculitis in Childhood: GPA and MPA in Childhood. Front. Pediatr. 2018, 6, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftis, C.E.; Dulgheru, E.C.; White, R. Disease Severity and Response to Induction Therapy in Hispanic Patients With Antineutrophilic Cytoplasmic Autoantibody-Associated Vasculitis-Related Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage. Cureus 2022, 14, e24470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timlin, H.; Lee, S.M.; Manno, R.L.; Seo, P.; Geetha, D. Rituximab for remission induction in elderly patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2015, 45, 67–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brogan, P.; Yeung, R.S.M.; Cleary, G.; Rangaraj, S.; Kasapcopur, O.; Hersh, A.O.; Li, S.; Paripovic, D.; Schikler, K.; Zeft, A.; et al. Phase IIa Global Study Evaluating Rituximab for the Treatment of Pediatric Patients With Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis or Microscopic Polyangiitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2022, 74, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kant, S.; Habbach, A.; Gapud, E.J.; Manno, R.L.; Gattu, R.; Seo, P.; Geetha, D. Sequential Therapy for Remission Induction in Severe Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Autoantibody-Associated Glomerulonephritis. Am. J. Nephrol. 2019, 50, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.B.; Ferraro, A.J.; Chaudhry, A.N.; Brogan, P.; Salama, A.D.; Smith, K.G.C.; Savage, C.O.S.; Jayne, D.R.W. A multicenter survey of rituximab therapy for refractory antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody–associated vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 2156–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wawrzycka-Adamczyk, K.; Zugaj, A.; Włudarczyk, A.; Kosałka, J.; Sznajd, J.; Bazan-Socha, S.; Musiał, J. Lower doses of rituximab in remission induction for refractory granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Przegl. Lek. 2014, 71, 663–665. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, A.; Takeuchi, Y.; Kagaya, S.; Ojima, Y.; Fukami, H.; Sato, H.; Matsuda, K.; Nagasawa, T. Remission Induction Therapy with Rituximab for Microscopic Polyangiitis: A Feasibility Study. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2017, 242, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moog, P.; Probst, M.; Kuechle, C.; Hauser, C.; Heemann, U.; Thuermel, K. Single-dose rituximab for remission induction and maintenance therapy in ANCA-associated vasculitis: A retrospective analysis of 17 patients. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2014, 43, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Md Yusof, M.Y.; Vital, E.M.; Das, S.; Dass, S.; Arumugakani, G.; Savic, S.; Rawstron, A.C.; Emery, P. Repeat cycles of rituximab on clinical relapse in ANCA-associated vasculitis: Identifying B cell biomarkers for relapse to guide retreatment decisions. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGregor, J.G.; Hogan, S.L.; Kotzen, E.S.; Poulton, C.J.; Hu, Y.; Negrete-Lopez, R.; Kidd, J.M.; Katsanos, S.L.; Bunch, D.O.; Nachman, P.H.; et al. Rituximab as an immunosuppressant in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc.–Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2015, 30 (Suppl. 1), i123–i131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keogh, K.A.; Wylam, M.E.; Stone, J.H.; Specks, U. Induction of remission by B lymphocyte depletion in eleven patients with refractory antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roccatello, D.; Sciascia, S.; Rossi, D.; Alpa, M.; Naretto, C.; Radin, M.; Fenoglio, R.; Baldovino, S.; Menegatti, E. The “4 plus 2” rituximab protocol makes maintenance treatment unneeded in patients with refractory ANCA-associated vasculitis: A 10 years observation study. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 52072–52077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaleshtori, M.T.; Farajzadegan, Z.; Salesi, M. A comparison of rituximab with cyclophosphamide in terms of efficacy and complications as induction therapy for treating granulomatosis with polyangiitis: A three-center study. Eur. J. Rheumatol. 2022, 9, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, P.; Karras, A.; Porcher, R.; Belenfant, X.; Audard, V.; Rafat, C.; Hanouna, G.; Beaudreuil, S.; Vilain, C.; Hummel, A.; et al. Management of severe renal disease in anti-neutrophil-cytoplasmic-antibody-associated vasculitis: Place of rituximab and plasma exchange? Rheumatology 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moollan, N.; Ahmed, A.R.; Denton, M. Management and Outcomes of ANCA-Associated Vasculitis at a Tertiary Healthcare Facility. Autoimmune. Dis. 2022, 2022, 4808806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, S. Rituximab has similar short-term safety and efficacy to cyclophosphamide in ANCA-associated vasculitis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2010, 6, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casal Moura, M.; Irazabal, M.V.; Eirin, A.; Zand, L.; Sethi, S.; Borah, B.J.; Winters, J.L.; Moriarty, J.P.; Cartin-Ceba, R.; Berti, A.; et al. Efficacy of Rituximab and Plasma Exchange in Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis with Severe Kidney Disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 31, 2688–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Menthon, M.; Cohen, P.; Pagnoux, C.; Buchler, M.; Sibilia, J.; Détrée, F.; Gayraud, M.; Khellaf, M.; Penalba, C.; Legallicier, B.; et al. Infliximab or rituximab for refractory Wegener’s granulomatosis: Long-term follow up. A prospective randomised multicentre study on 17 patients. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2011, 29, S63–S71. [Google Scholar]
- Charles, P.; Néel, A.; Tieulié, N.; Hot, A.; Pugnet, G.; Decaux, O.; Marie, I.; Khellaf, M.; Kahn, J.E.; Karras, A.; et al. Rituximab for induction and maintenance treatment of ANCA-associated vasculitides: A multicentre retrospective study on 80 patients. Rheumatology 2014, 53, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartin-Ceba, R.; Golbin, J.M.; Keogh, K.A.; Peikert, T.; Sánchez-Menéndez, M.; Ytterberg, S.R.; Fervenza, F.C.; Specks, U. Rituximab for remission induction and maintenance in refractory granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener’s): Ten-year experience at a single center. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 3770–3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puéchal, X.; Iudici, M.; Pagnoux, C.; Karras, A.; Cohen, P.; Maurier, F.; Quéméneur, T.; Lifermann, F.; Hamidou, M.; Mouthon, L.; et al. Sustained Remission of Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis After Discontinuation of Glucocorticoids and Immunosuppressant Therapy: Data From the French Vasculitis Study Group Registry. Arthritis Rheum. 2021, 73, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calich, A.L.; Puéchal, X.; Pugnet, G.; London, J.; Terrier, B.; Charles, P.; Mouthon, L.; Guillevin, L. Rituximab for induction and maintenance therapy in granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener’s). Results of a single-center cohort study on 66 patients. J. Autoimmun. 2014, 50, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charles, P.; Dechartres, A.; Terrier, B.; Cohen, P.; Faguer, S.; Huart, A.; Hamidou, M.; Agard, C.; Bonnotte, B.; Samson, M.; et al. Reducing the initial number of rituximab maintenance-therapy infusions for ANCA-associated vasculitides: Randomized-trial post-hoc analysis. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 2970–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeyama, Y.; Ono, N.; Shirahama, Y.; Inoue, Y.; Tanaka, A.; Ueda, N.; Nishimura, N.; Nagano, S.; Uchino, A.; Miyamura, T.; et al. Rituximab maintenance therapy for patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis in Japan. Mod. Rheumatol. 2021, 31, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besada, E.; Koldingsnes, W.; Nossent, J.C. Long-term efficacy and safety of pre-emptive maintenance therapy with rituximab in granulomatosis with polyangiitis: Results from a single centre. Rheumatology 2013, 52, 2041–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.M.; Jones, R.B.; Specks, U.; Bond, S.; Nodale, M.; Aljayyousi, R.; Andrews, J.; Bruchfeld, A.; Camilleri, B.; Carette, S.; et al. Rituximab as therapy to induce remission after relapse in ANCA-associated vasculitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 1243–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geetha, D.; Hruskova, Z.; Segelmark, M.; Hogan, J.; Morgan, M.D.; Cavero, T.; Eriksson, P.; Seo, P.; Manno, R.L.; Dale, J.; et al. Rituximab for treatment of severe renal disease in ANCA associated vasculitis. J. Nephrol. 2016, 29, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepper, R.J.; McAdoo, S.P.; Moran, S.M.; Kelly, D.; Scott, J.; Hamour, S.; Burns, A.; Griffith, M.; Galliford, J.; Levy, J.B.; et al. A novel glucocorticoid-free maintenance regimen for anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibody-associated vasculitis. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venhoff, N.; Niessen, L.; Kreuzaler, M.; Rolink, A.G.; Hässler, F.; Rizzi, M.; Voll, R.E.; Thiel, J. Reconstitution of the peripheral B lymphocyte compartment in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitides treated with rituximab for relapsing or refractory disease. Autoimmunity 2014, 47, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorin, B.; Samson, M.; Durel, C.A.; Diot, E.; Guichard, I.; Grados, A.; Limal, N.; Régent, A.; Cohen, P.; Dion, J.; et al. Rituximab plus methotrexate combination as a salvage therapy in persistently active granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 2619–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azar, L.; Springer, J.; Langford, C.A.; Hoffman, G.S. Rituximab with or without a conventional maintenance agent in the treatment of relapsing granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener’s): A retrospective single-center study. Arthritis Rheum. 2014, 66, 2862–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lionaki, S.; Fragoulis, G.E.; Venetsanopoulou, A.; Vlachoyiannopoulos, P.; Boletis, J.N.; Tzioufas, A.G. Cyclophosphamide followed by rituximab for aggressive multiple-relapsing antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2017, 35 (Suppl. 103), 155–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gulati, K.; Edwards, H.; Prendecki, M.; Cairns, T.D.; Condon, M.; Galliford, J.; Griffith, M.; Levy, J.B.; Tam, F.W.K.; Tanna, A.; et al. Combination treatment with rituximab, low-dose cyclophosphamide and plasma exchange for severe antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 1316–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rymarz, A.; Matyjek, A.; Sułek-Jakóbczyk, M.; Mosakowska, M.; Niemczyk, S. Impaired Kidney Function Associated with Increased Risk of Side Effects in Patients with Small Vessel Vasculitis Treated with Rituximab as an Induction Therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unizony, S.; Villarreal, M.; Miloslavsky, E.M.; Lu, N.; Merkel, P.A.; Spiera, R.; Seo, P.; Langford, C.A.; Hoffman, G.S.; Kallenberg, C.M.; et al. Clinical outcomes of treatment of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis based on ANCA type. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 1166–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miloslavsky, E.M.; Specks, U.; Merkel, P.A.; Seo, P.; Spiera, R.; Langford, C.A.; Hoffman, G.S.; Kallenberg, C.G.; St Clair, E.W.; Tchao, N.K.; et al. Outcomes of nonsevere relapses in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis treated with glucocorticoids. Arthritis Rheum. 2015, 67, 1629–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holle, J.U.; Dubrau, C.; Herlyn, K.; Heller, M.; Ambrosch, P.; Noelle, B.; Reinhold-Keller, E.; Gross, W.L. Rituximab for refractory granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener’s granulomatosis): Comparison of efficacy in granulomatous versus vasculitic manifestations. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lally, L.; Lebovics, R.S.; Huang, W.T.; Spiera, R.F. Effectiveness of rituximab for the otolaryngologic manifestations of granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener’s). Arthritis Care Res. 2014, 66, 1403–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malm, I.J.; Mener, D.J.; Kim, J.; Seo, P.; Kim, Y.J. Otolaryngological progression of granulomatosis with polyangiitis after systemic treatment with rituximab. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2014, 150, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lower, E.E.; Baughman, R.P.; Kaufman, A.H. Rituximab for refractory granulomatous eye disease. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2012, 6, 1613–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baslund, B.; Wiencke, A.K.; Rasmussen, N.; Faurschou, M.; Toft, P.B. Treatment of orbital inflammation with rituximab in Wegener’s granulomatosis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2012, 30, S7–S10. [Google Scholar]
- Pelegrin, L.; Jakob, E.; Schmidt-Bacher, A.; Schwenger, V.; Becker, M.; Max, R.; Lorenz, H.M.; Mackensen, F. Experiences with rituximab for the treatment of autoimmune diseases with ocular involvement. J. Rheumatol. 2014, 41, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez Del Pero, M.; Chaudhry, A.; Jones, R.B.; Sivasothy, P.; Jani, P.; Jayne, D. B-cell depletion with rituximab for refractory head and neck Wegener’s granulomatosis: A cohort study. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2009, 34, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durel, C.A.; Hot, A.; Trefond, L.; Aumaitre, O.; Pugnet, G.; Samson, M.; Abad, S.; Belot, A.; Blanchard-Delaunay, C.; Cohen, P.; et al. Orbital mass in ANCA-associated vasculitides: Data on clinical, biological, radiological and histological presentation, therapeutic management, and outcome from 59 patients. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 1565–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, S.R.; Salama, A.D.; Joshi, L.; Pusey, C.D.; Lightman, S.L. Rituximab is effective in the treatment of refractory ophthalmic Wegener’s granulomatosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 1540–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Jacoiste Asín, M.A.; Charles, P.; Rothschild, P.R.; Terrier, B.; Brézin, A.; Mouthon, L.; Guillevin, L.; Puéchal, X. Ocular involvement in granulomatosis with polyangiitis: A single-center cohort study on 63 patients. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, L.; Tanna, A.; McAdoo, S.P.; Medjeral-Thomas, N.; Taylor, S.R.; Sandhu, G.; Tarzi, R.M.; Pusey, C.D.; Lightman, S. Long-term Outcomes of Rituximab Therapy in Ocular Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis: Impact on Localized and Nonlocalized Disease. Ophthalmology 2015, 122, 1262–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Gasim, A.; Derebail, V.K.; Chung, Y.; McGregor, J.G.; Lionaki, S.; Poulton, C.J.; Hogan, S.L.; Jennette, J.C.; Falk, R.J.; et al. Predictors of treatment outcomes in ANCA-associated vasculitis with severe kidney failure. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. CJASN 2014, 9, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Hruskova, Z.; Segelmark, M.; Morgan, M.D.; Hogan, J.; Lee, S.K.; Dale, J.; Harper, L.; Tesar, V.; Jayne, D.R.; et al. Treatment of severe renal disease in ANCA positive and negative small vessel vasculitis with rituximab. Am. J. Nephrol. 2015, 41, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabris, J.L.; Jaramillo, G.; Torres, R.; Rosselli, C.; Olivares, C. Renal compromise in a patient with Wegener’s granulomatosis: Clinical case and literature review. Rev. Colomb. Nefrol. 2017, 4, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccatello, D.; Sciascia, S.; Murgia, S.; Quattrocchio, G.; Ferro, M.; De Simone, E.; Naretto, C.; Barreca, A.; Sammartino, A.; Rossi, D.; et al. Treating Patients With ANCA-Associated Vasculitis and Very Severe Renal Injury With an Intensified B Cell Depletion Therapy: Comparison With a Control Cohort Receiving a Conventional Therapy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 777134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pullerits, R.; Ljevak, M.; Vikgren, J.; Bokarewa, M. Off-trial evaluation of the B cell-targeting treatment in the refractory cases of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA)-associated vasculitis: Long-term follow-up from a single centre. Scand. J. Immunol. 2012, 76, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, P. Nine patients with anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-positive vasculitis successfully treated with rituximab. J. Intern. Med. 2005, 257, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayan, G.; Esatoglu, S.N.; Hatemi, G.; Ugurlu, S.; Seyahi, E.; Melikoglu, M.; Fresko, I.; Ozdogan, H.; Yurdakul, S.; Hamuryudan, V. Rituximab for anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies-associated vasculitis: Experience of a single center and systematic review of non-randomized studies. Rheumatol. Int. 2018, 38, 607–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roccatello, D.; Sciascia, S.; Rossi, D.; Alpa, M.; Naretto, C.; Russo, A.; Menegatti, E.; Baldovino, S. Long-term effects of rituximab added to cyclophosphamide in refractory patients with vasculitis. Am. J. Nephrol. 2011, 34, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chocova, Z.; Hruskova, Z.; Mareckova, H.; Svobodova, B.; Duskova, D.; Bednarova, V.; Jancova, E.; Rysava, R.; Tesar, V. Rituximab use in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis: Clinical efficacy and impact on immunological parameters. Clin. Rheumatol. 2015, 34, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfield, N.; Hamour, S.; Habib, A.M.; Tarzi, R.; Levy, J.; Griffith, M.; Cairns, T.; Cook, H.T.; Pusey, C.D.; Salama, A.D. Prolonged disease-free remission following rituximab and low-dose cyclophosphamide therapy for renal ANCA-associated vasculitis. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2011, 26, 3280–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAdoo, S.P.; Medjeral-Thomas, N.; Gopaluni, S.; Tanna, A.; Mansfield, N.; Galliford, J.; Griffith, M.; Levy, J.; Cairns, T.D.; Jayne, D.; et al. Long-term follow-up of a combined rituximab and cyclophosphamide regimen in renal anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibody-associated vasculitis. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2019, 34, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroti, L.; Cirami, C.L.; Di Maria, L.; Larti, A.; Carta, P.; Dervishi, E.; Farsetti, S.; Tsalouchos, A.; Novelli, L.; Minetti, E.E. Rituximab in relapsing and de novo MPO ANCA-associated vasculitis with severe renal involvement: A case series. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, K.; Watanabe, H.; Yamamura, Y.; Asano, Y.; Katayama, Y.; Hiramatsu-Asano, S.; Ohashi, K.; Morishita, M.; Narazaki, M.; Matsumoto, Y.; et al. Granulomatosis with polyangiitis with obstructive pneumonia progressing to hypertrophic pachymeningitis: A case report. Medicine 2021, 100, e24028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, C.; Charles, P.; Terrier, B.; Bussonne, G.; Cohen, P.; Pagnoux, C.; Cottin, V.; Cordier, J.F.; Guillevin, L. Tracheobronchial Stenoses in Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis (Wegener’s): A Report on 26 Cases. Medicine 2015, 94, e1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, S.R.; Copley, S.J.; Pusey, C.D.; Ind, P.W.; Salama, A.D. Prolonged B Cell Depletion With Rituximab is Effective in Treating Refractory Pulmonary Granulomatous Inflammation in Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis (GPA). Medicine 2014, 93, e229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thietart, S.; Karras, A.; Augusto, J.F.; Philipponnet, C.; Carron, P.L.; Delbrel, X.; Mesbah, R.; Blaison, G.; Duffau, P.; El Karoui, K.; et al. Evaluation of Rituximab for Induction and Maintenance Therapy in Patients 75 Years and Older With Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2220925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chasseur, P.; Blockmans, D.; von Frenckell, C.; Nicolas, J.B.; Regniers, C.; Vandergheynst, F. Rituximab prescription patterns and efficacy in the induction treatment of ANCA-Associated Vasculitis in a Belgian multicenter cohort. Acta Clin. Belg. 2020, 75, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Just, S.A.; Knudsen, J.B.; Nielsen, M.K.; Junker, P. Wegener’s Granulomatosis Presenting with Pachymeningitis: Clinical and Imaging Remission by Rituximab. ISRN Rheumatol. 2011, 2011, 608942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malina, M.; Schaefer, B.; Waldherr, R.; Wühl, E.; Schaefer, F.; Schmitt, C.P. Late recovery of renal function by rituximab in a patient with Wegener’s granulomatosis. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2013, 28, 511–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, C.; Manoharan, P.; Carter-Monroe, N.; Geetha, D. Rituximab for remission induction in recurrent ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis postkidney transplant. Transpl. Int. 2013, 26, 1225–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.; Barkhoudarian, G.; Ciarlini, P.; Laws, E.R.; Mody, E.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Woodmansee, W.W. Refractory pituitary granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener’s) treated with rituximab. Endocr. Pract. 2013, 19, e1–e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Gullo, A.; Bajocchi, G.; Cassone, G.; Cavazza, A.; Zanichelli, M.; Salvarani, C. Granulomatosis with polyangiitis presenting as a renal mass successfully treated with rituximab. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2014, 32, S138. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, M.; Ismail, M.; Pattanaik, D. Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis Presenting as Gastric Ulcer: An Unusual Initial Manifestation Successfully Treated With Rituximab. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 350, 338–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çakar, M.; Yilmaz, S.; Çinar, M. Successful treatment of PR3-ANCA positive vasculitis with pancreatitis as the first manifestation with rituximab. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 20, 2209–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez-Morrondo, C.; Pantoja, L.; Fernández, R.; Brañanova, P.; López, A.; Alexis, D. Good response to rituximab in a patient with granulomatosis with polyangiitis and pulmonary, renal manifestations and ophthalmoplegia. Acta Reumatol. Port. 2016, 41, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murthy, R.K.; Jackson, J.; Chatham, W.W.; Sami, N. Extensive Pyoderma Gangrenosum Associated with Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis with Both Responsive to Rituximab. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2016, 22, 393–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donmez, S.; Pamuk, O.N.; Gedik, M.; Ak, R.; Bulut, G. A case of granulomatosis with polyangiitis and pyoderma gangrenosum successfully treated with infliximab and rituximab. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 17, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, M.; Dogra, S.; Rathi, M.; Sharma, A. Successful treatment of large refractory pyoderma gangrenosum-like presentation of granulomatosis with polyangiitis by rituximab. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 20, 2200–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaukat, M.S.; Ocon, A.J.; Peredo, R.A.; Bhatt, B.D. Prostatitis, a rare presentation of granulomatosis with polyangiitis, successfully treated with rituximab and prednisone. BMJ Case Rep. 2018, 2018, bcr-2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda Bernal, L.; Bitencourt, N.; Batra, K.; Solow, E.B. Successful use of rituximab in granulomatosis with polyangiitis with aortic inflammation. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2019, 37 (Suppl. 117), 144–147. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, H.; Shima, K.; Sakata, H.; Ohtoh, T. Granulomatosis with polyangiitis with intestinal involvement successfully treated with rituximab and surgery. BMJ Case Rep. 2019, 12, e230355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Y.; Khudadah, M.; Alali, M.; George, S.; Abdulsalam, A. Treating Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis Presenting as Mastitis With Rituximab. Arch. Rheumatol. 2018, 34, 241–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skeik, N.; Hari, G.; Nasr, R. Aortitis caused by antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA)-associated vasculitis: A case-based review. Rheumatol. Int. 2019, 39, 1983–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, I.A.; Friesen, R.; McGaw, T.; Levin, L. Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis Mistaken as a Temporomandibular Joint Disorder: A Case Report. Clin. Adv. Periodontics. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewinter, K.E.; Cidon, M.; Warren, M.; Bansal, M. Successful Induction Treatment With Rituximab of Isolated Pauci-Immune Pulmonary Capillaritis Presenting as Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage in a Pediatric Patient. Chest 2020, 158, e225–e227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riancho-Zarrabeitia, L.; Peiró Callizo, E.; Drake-Pérez, M.; García Montesinos, B.; Terán, N.; Martínez-Taboada, V.M. Granulomatosis with polyangiitis with isolated orbital involvement in children: A case report successfully treated with Rituximab and review of literature. Acta Reumatol. Port. 2019, 44, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Horiuchi, K.; Oshima, Y.; Kudo, A. Successful Treatment with Rituximab for Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis and Multiple Cranial Neuropathies. Intern. Med. 2021, 60, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, S.I.; Shah, S.; Bagga, B.; Dudam, R. Rituximab therapy combined with methotrexate for severe necrotizing scleritis in a case of granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 68, 1981–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxton, L.; Champion De Crespigny, P.; Nicholls, K. Granulomatosis with polyangiitis complicated by genital involvement: Sustained response to rituximab. Intern. Med. J. 2021, 51, 444–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, M.; Kaieda, S.; Kawaguchi, A.; Tsutsumi, M.; Harada, Y.; Koga, T.; Akiba, J.; Hoshino, T.; Ida, H. Subcutaneous Cheek Nodule Associated with Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis. Intern. Med. 2021, 60, 3823–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitmehdi, R.; Moguelet, P.; Godot, S.; Chazerain, P.; Senet, P.; Barbaud, A.; Frances, C.; Chasset, F. Response to rituximab of pseudotumoral digital nodules in a patient with granulomatosis with polyangiitis with alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency: A case report. Dermatologic. Ther. 2020, 33, e13479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimojima, Y.; Kishida, D.; Hineno, A.; Yazaki, M.; Sekijima, Y.; Ikeda, S.I. Hypertrophic pachymeningitis is a characteristic manifestation of granulomatosis with polyangiitis: A retrospective study of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 20, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Kumar, S.; Wanchu, A.; Lal, V.; Singh, R.; Gupta, V.; Singh, S.; Gupta, A. Successful treatment of hypertrophic pachymeningitis in refractory Wegener’s granulomatosis with rituximab. Clin. Rheumatol. 2010, 29, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.R.; Tsai, Y.S.; Tsai, H.W. Acute Myocarditis in Patients with Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-positive Microscopic Polyangiitis and Receiving Rituximab Therapy. J. Rheumatol. 2019, 46, 1645–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wat, J.; Wat, M.; Honda, K. Granulomatosis with polyangiitis presenting as palpable purpura with sinusitis, hemoptysis, and lung cavitation. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2020, 47, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messmer, B.; Butts, M. Relapsing Primary Central Nervous System Vasculitis Treated With Rituximab. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 26, e206–e207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diegues, A.; Tavares, J.; Sá, D.; Oliveira, J.; Fernandes, D.; Santos, J.; Rocha, G. Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis: Recurrence or Treatment Consequences? Eur. J. Case Rep. Intern. Med. 2021, 8, 002448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Mancuso, E.; Armendi, I.; Krasinski, D.; Liu, L.; Tarsi, S.; Waz, W.R.; Abdul-Aziz, R.; Elenberg, E. Renal Involvement and Its Treatment in Pediatric Patients With Proteinase-3 Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody Positive Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis: A Case Series. Cureus 2021, 13, e18197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uijtterhaegen, G.; De Donder, L.; Ameloot, E.; Lefebvre, K.; Van Dorpe, J.; De Pauw, M.; François, K. Aortic valve replacement due to granulomatosis with polyangiitis: A case series. Eur. Heart J. Case Rep. 2020, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haridas, V.; Haridas, K. Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (GPA) Mimicking Tuberculosis. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2017, 65, 102–103. [Google Scholar]
- Bastone, P.; Squifflet, J.L.; Marbaix, E.; Houssiau, F. Successful treatment of gynaecological involvement of granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener’s granulomatosis) by rituximab. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2015, 33, S142–S144. [Google Scholar]
- Han, M.; Pan, C. A case of granulomatosis with polyangiitis mimicking lung malignancy. Respirol. Case Rep. 2021, 9, e0824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, T.; Maia, R.; Massano, J.; Mendonça, L.; Guimarães, J. From Kidney to Brain: An Uncommon Severe Relapse of Myeloperoxidase Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody (MPO-ANCA) Vasculitis. Cureus 2021, 13, e14205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moseley, I.; Greenberg, R.; Wasserman, M.; Thavaseelan, S.; Cancian, M. Leukocytoclastic vasculitis leading to penile necrosis and ischemia of the bladder and urethra. Urol. Case Rep. 2022, 40, 101902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja, A.; Afridi, S.M.; Noe, M.M.; Jain, A. Cytoplasmic Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies (C-ANCA) Vasculitis: An Uncommon Complication After Stem Cell Transplantation. Cureus 2022, 14, e25445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, H.A.; Bandhlish, A.; DeConde, R.P.; Humphreys, I.M.; Abuzeid, W.M.; Jafari, A. Initial Presentation of Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis as Progressive Skull Base Osteomyelitis. ORL J. Otorhinolaryngol. Relat. Spec. 2022, 84, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenen, L.; Elbelt, U.; Olze, H.; Zappe, S.; Dommerich, S. Granulomatosis with polyangiitis in a patient with polydipsia, facial nerve paralysis, and severe otologic complaints: A case report and review of the literature. J. Med. Case Rep. 2022, 16, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, T.; Suzuki, J.; Shirai, T.; Koizumi, S.; Tsuchiya, Y.; Hishinuma, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Katori, Y. Presence of Phlebitis in Aseptic Nasal Septal Abscess Complicated with Ulcerative Colitis; Possible Association with Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis: A Case Report. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2022, 258, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Salihi, M.O.; Dominguez, B.; Mohanlal, V.; Carlan, S.J. Oral and Lower Extremity Ulcers as the Initial Presentation of Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis. Case Rep. Med. 2022, 2022, 2737242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Hanai, S.; Nakagomi, D.; Kobayashi, K.; Takahashi, K.; Furuya, F. Membranous Nephropathy with Proteinase 3-ANCA-associated Vasculitis Successfully Treated with Rituximab. Intern. Med. 2021, 60, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, N.; Mushtaq, F.; Noor, N.; Ullah, Z.; Saleem, A.A. Role of Rituximab in miraculous cessation of ventricular tachycardia in Granulomatosis with polyangiitis: A case report. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2022, 72, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawneh, D.; Edrees, A. Hydralazine-Induced Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody (ANCA)-Associated Vasculitis: A Case Report and Literature Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e24132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alesaeidi, S.; Hashemi-Amir, S.Y.; Piri, S.M.; Tavakolpour, S. Fatal Outcome of Rituximab in an ANCA Negative Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis Patient with Acute Pancreatitis and Pancreatic Mass. Curr. Rheumatol. Rev. 2021, 17, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nili, A.; Tavakolpour, S.; Mahmoudi, H.; Noormohammadpour, P.; Balighi, K.; Daneshpazhooh, M. Paradoxical reaction to rituximab in patients with pemphigus: A report of 10 cases. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2020, 42, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudi, H.; Balighi, K.; Tavakolpour, S.; Daneshpazhooh, M. Unexpected worsening of pemphigus vulgaris after rituximab: A report of three cases. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 71, 40–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alesaeidi, S.; Piri, S.M.; Tavakolpour, S. The Paradoxical Reaction to Rituximab in Six Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis Patients: How Could it be Explained and Managed? Curr. Rheumatol. Rev. 2021, 17, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, K.; Dharmanand, B.G. Worsening of posterior scleritis and orbital pseudotumor in a patient with granulomatosis polyangiitis with rituximab-A case report. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 68, 1986–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, C.B.; Wang, Y.C.; Lai, C.C. Ocular and orbital exacerbation after rituximab therapy for granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Can. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 54, e237–e241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malviya, G.; Anzola, K.L.; Podestà, E.; Laganà, B.; Del Mastro, C.; Dierckx, R.A.; Scopinaro, F.; Signore, A. (99m)Tc-labeled rituximab for imaging B lymphocyte infiltration in inflammatory autoimmune disease patients. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2012, 14, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasi, P.M.; Tawbi, H.A.; Oddis, C.V.; Kulkarni, H.S. Clinical review: Serious adverse events associated with the use of rituximab—A critical care perspective. Crit. Care 2012, 16, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhler, E.B.; Lim, L.L.; Beardsley, R.M.; Giles, T.R.; Pasadhika, S.; Lee, S.T.; de Saint Sardos, A.; Butler, N.J.; Smith, J.R.; Rosenbaum, J.T. Rituximab therapy for refractory orbital inflammation: Results of a phase 1/2, dose-ranging, randomized clinical trial. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2014, 132, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarzi, R.M.; Pusey, C.D. Current and future prospects in the management of granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener’s granulomatosis). Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2014, 10, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Perry, S.R.; Rootman, J.; White, V.A. The clinical and pathologic constellation of Wegener granulomatosis of the orbit. Ophthalmology 1997, 104, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostri, C.; Heegaard, S.; Prause, J.U. Sclerosing Wegener’s granulomatosis in the orbit. Acta Ophthalmol. 2008, 86, 917–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fechner, F.P.; Faquin, W.C.; Pilch, B.Z. Wegener’s granulomatosis of the orbit: A clinicopathological study of 15 patients. Laryngoscope 2002, 112, 1945–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cambridge, G.; Stohl, W.; Leandro, M.J.; Migone, T.S.; Hilbert, D.M.; Edwards, J.C. Circulating levels of B lymphocyte stimulator in patients with rheumatoid arthritis following rituximab treatment: Relationships with B cell depletion, circulating antibodies, and clinical relapse. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thery-Casari, C.; Euvrard, R.; Mainbourg, S.; Durupt, S.; Reynaud, Q.; Durieu, I.; Belot, A.; Lobbes, H.; Cabrera, N.; Lega, J.C. Severe infections in patients with anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitides receiving rituximab: A meta-analysis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilal, T. Fatal cytomegalovirus disease after combination therapy with corticosteroids and rituximab for granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Case. Rep. Rheumatol. 2015, 2015, 538137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besada, E.; Nossent, J.C. Infection risks during longterm rituximab therapy change over time. J. Rheumatol. 2013, 40, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Merkel, P.A.; Niles, J.L.; Mertz, L.E.; Lehane, P.B.; Pordeli, P.; Erblang, F. Long-Term Safety of Rituximab in Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis and in Microscopic Polyangiitis. Arthritis Care Res. 2021, 73, 1372–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Vollenhoven, R.F.; Fleischmann, R.M.; Furst, D.E.; Lacey, S.; Lehane, P.B. Longterm Safety of Rituximab: Final Report of the Rheumatoid Arthritis Global Clinical Trial Program over 11 Years. J. Rheumatol. 2015, 42, 1761–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, Y.; Nakayamada, S.; Kubo, S.; Ishikawa, Y.; Yoshikawa, M.; Sakata, K.; Iwata, S.; Miyagawa, I.; Nakano, K.; Tanaka, Y. Favorable efficacy of rituximab in ANCA-associated vasculitis patients with excessive B cell differentiation. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberici, F.; Smith, R.M.; Jones, R.B.; Roberts, D.M.; Willcocks, L.C.; Chaudhry, A.; Smith, K.G.; Jayne, D.R. Long-term follow-up of patients who received repeat-dose rituximab as maintenance therapy for ANCA-associated vasculitis. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortazar, F.B.; Pendergraft, W.F., 3rd; Wenger, J.; Owens, C.T.; Laliberte, K.; Niles, J.L. Effect of Continuous B Cell Depletion with Rituximab on Pathogenic Autoantibodies and Total IgG Levels in Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2017, 69, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khojah, A.M.; Miller, M.L.; Klein-Gitelman, M.S.; Curran, M.L.; Hans, V.; Pachman, L.M.; Fuleihan, R.L. Rituximab-associated Hypogammaglobulinemia in pediatric patients with autoimmune diseases. Pediatr. Rheumatol. Online J. 2019, 17, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odler, B.; Windpessl, M.; Krall, M.; Steiner, M.; Riedl, R.; Hebesberger, C.; Ursli, M.; Zitt, E.; Lhotta, K.; Antlanger, M.; et al. The Risk of Severe Infections Following Rituximab Administration in Patients With Autoimmune Kidney Diseases: Austrian ABCDE Registry Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 4575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wade, S.D.; Kyttaris, V.C. Rituximab-associated hypogammaglobulinemia in autoimmune rheumatic diseases: A single-center retrospective cohort study. Rheumatol. Int. 2021, 41, 1115–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tieu, J.; Smith, R.M.; Gopaluni, S.; Kumararatne, D.S.; McClure, M.; Manson, A.; Houghton, S.; Jayne, D.R.W. Rituximab Associated Hypogammaglobulinemia in Autoimmune Disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 671503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besada, E.; Koldingsnes, W.; Nossent, J.C. Serum immunoglobulin levels and risk factors for hypogammaglobulinaemia during long-term maintenance therapy with rituximab in patients with granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Rheumatology 2014, 53, 1818–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, A.; Akenroye, A.; Azar, A.; Seo, P.; Geetha, D. Rituximab-associated hypogammaglobulinemia in ANCA-associated vasculitis: Incidence and time course. Eur. J. Rheumatol. 2022, 9, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besada, E. Low immunoglobulin levels increase the risk of severe hypogammaglobulinemia in granulomatosis with polyangiitis patients receiving rituximab. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2016, 17, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Besada, E.; Bader, L.; Nossent, H. Sustained hypogammaglobulinemia under rituximab maintenance therapy could increase the risk for serious infections: A report of two cases. Rheumatol. Int. 2013, 33, 1643–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melega, S.; Brogan, P.; Cleary, G.; Hersh, A.O.; Kasapcopur, O.; Rangaraj, S.; Yeung, R.S.M.; Zeft, A.; Cooper, J.; Pordeli, P.; et al. Evaluation of Serious Infection in Pediatric Patients with Low Immunoglobulin Levels Receiving Rituximab for Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis or Microscopic Polyangiitis. Rheumatol. Ther. 2022, 9, 721–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.; Jaggi, K.; Greenberg, K.; Geetha, D. Immunoglobulin levels and infection risk with rituximab induction for anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Clin. Kidney J. 2017, 10, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregersen, J.W.; Chaudhry, A.; Jayne, D.R. Rituximab for ANCA-associated vasculitis in the setting of severe infection. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2013, 42, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segelmark, L.; Flores-Suárez, L.; Mohammad, A. Severe infections in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis treated with rituximab. Rheumatology 2021, 61, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.Y.; Chen, M.; Zhao, M.H. Severe Infections following Rituximab Treatment in Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis. Kidney Dis. 2021, 7, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vollenhoven, R.F.; Emery, P.; Bingham, C.O., 3rd; Keystone, E.C.; Fleischmann, R.; Furst, D.E.; Macey, K.; Sweetser, M.; Kelman, A.; Rao, R. Longterm safety of patients receiving rituximab in rheumatoid arthritis clinical trials. J. Rheumatol. 2010, 37, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronbichler, A.; Kerschbaum, J.; Gopaluni, S.; Tieu, J.; Alberici, F.; Jones, R.B.; Smith, R.M.; Jayne, D.R.W. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole prophylaxis prevents severe/life-threatening infections following rituximab in antineutrophil cytoplasm antibody-associated vasculitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 1440–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun-Moscovici, Y.; Butbul-Aviel, Y.; Guralnik, L.; Toledano, K.; Markovits, D.; Rozin, A.; Nahir, M.A.; Balbir-Gurman, A. Rituximab: Rescue therapy in life-threatening complications or refractory autoimmune diseases: A single center experience. Rheumatol. Int. 2013, 33, 1495–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulkumaran, N.; Suleman, R.; Cecconi, M.; Kiely, P.; Chua, F. Rituximab associated pneumonitis in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2012, 18, 39–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugle, B.; Solomon, M.; Harvey, E.; James, A.; Wadhwa, A.; Amin, R.; Bell-Peter, A.; Benseler, S. Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia following rituximab treatment in Wegener’s granulomatosis. Arthritis Care Res. 2010, 62, 1661–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besada, E.; Nossent, J.C. Should Pneumocystis jiroveci prophylaxis be recommended with Rituximab treatment in ANCA-associated vasculitis? Clin. Rheumatol. 2013, 32, 1677–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nixon, A.; Ogden, L.; Woywodt, A.; Dhaygude, A. Infectious complications of rituximab therapy in renal disease. Clin. Kidney J. 2017, 10, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ishtiaq, R.; Wilhelm, D.M.; Ahmad, S. CMV gastric ulcer in a patient with pauci immune crescentic glomerulonephritis on rituximab—A rare combination. Postgrad. Med. 2019, 131, 619–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikse, J.; Rygh, A.; Kaisen, K.; Omdal, R. Life-threatening rituximab-induced pyoderma gangrenosum successfully treated with intravenous immunoglobulin. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2017, 46, 413–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viganò, M.; Mangia, G.; Lampertico, P. Management of patients with overt or resolved hepatitis B virus infection undergoing rituximab therapy. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2014, 14, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.S.; Han, M.; Yoo, J.; Jung, S.M.; Song, J.J.; Park, Y.-B.; Jung, I.; Lee, S.-W. Risk of Cancers in Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis: Results from the Korea National Health Insurance Claims Database 2010–2018. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, W.; Ning, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, M.; Guo, S.; Han, M.; Zeng, R.; Ge, S.; Xu, G. Incidence of Cancer in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Daalen, E.E.; Rizzo, R.; Kronbichler, A.; Wolterbeek, R.; Bruijn, J.A.; Jayne, D.R.; Bajema, I.M.; Rahmattulla, C. Effect of rituximab on malignancy risk in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1064–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, Y.; Koga, T.; Ishida, M.; Fujita, Y.; Tsuji, S.; Takatani, A.; Shimizu, T.; Sumiyoshi, R.; Igawa, T.; Umeda, M.; et al. Rituximab-induced Acute Thrombocytopenia in Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis. Intern. Med. 2018, 57, 2247–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, A.; Sundström, Y.; Börjesson, O.; Bruchfeld, A.; Malmström, V.; Gunnarsson, I. Late-onset neutropenia after rituximab in ANCA-associated vasculitis. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2016, 45, 404–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesfa, D.; Ajeganova, S.; Hägglund, H.; Sander, B.; Fadeel, B.; Hafström, I.; Palmblad, J. Late-onset neutropenia following rituximab therapy in rheumatic diseases: Association with B lymphocyte depletion and infections. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 2209–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molloy, E.S.; Calabrese, L.H. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy associated with immunosuppressive therapy in rheumatic diseases: Evolving role of biologic therapies. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 3043–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vikse, J.; Jonsdottir, K.; Kvaløy, J.T.; Wildhagen, K.; Omdal, R. Tolerability and safety of long-term rituximab treatment in systemic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Rheumatol. Int. 2019, 39, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yockey, L.; Dowst, S.; Zonozi, R.; Huizenga, N.; Murphy, P.; Laliberte, K.; Rosenthal, J.; Niles, J.L.; Mitchell, C.M. Inflammatory vaginitis in women on long-term rituximab treatment for autoimmune disorders. BMC Women’s Health 2021, 21, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, D.; Boyle, S.; Amft, N. Perianal Crohn Disease after Treatment with Rituximab for Active Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis. J. Rheumatol. 2016, 43, 2199–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gong, Y.; Lam, A.; Paul, V. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome after first rituximab transfusion for treatment of granulomatosis with polyangiitis. BMJ Case Rep. 2022, 15, e248864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakawa, S.; Arai, S.; Kawagoe, M.; Ohata, C.; Ono, W.; Murata, H.; Tamura, Y.; Uchida, S.; Shibata, S.; Fujigaki, Y. A Young Patient with Microscopic Polyangiitis Requiring Hemodialysis with Complications of Repeated Episodes of Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome Probably Due to Different Etiologies. Intern. Med. 2022, 61, 1423–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartin-Ceba, R.; Diaz-Caballero, L.; Al-Qadi, M.O.; Tryfon, S.; Fervenza, F.C.; Ytterberg, S.R.; Specks, U. Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage Secondary to Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis: Predictors of Respiratory Failure and Clinical Outcomes. Arthritis Rheum. 2016, 68, 1467–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
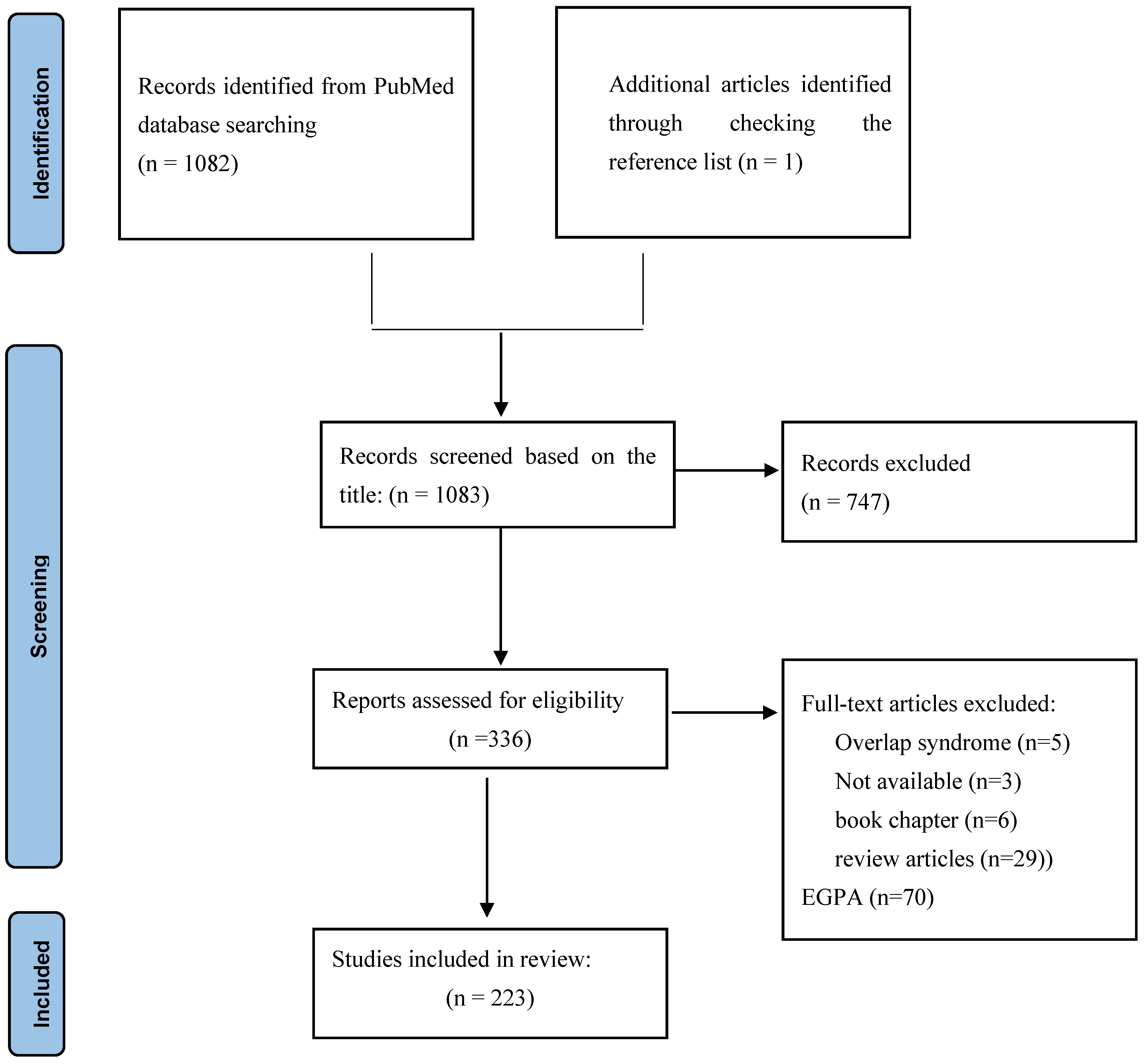
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Habibi, M.A.; Alesaeidi, S.; Zahedi, M.; Hakimi Rahmani, S.; Piri, S.M.; Tavakolpour, S. The Efficacy and Safety of Rituximab in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: A Systematic Review. Biology 2022, 11, 1767. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11121767
Habibi MA, Alesaeidi S, Zahedi M, Hakimi Rahmani S, Piri SM, Tavakolpour S. The Efficacy and Safety of Rituximab in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: A Systematic Review. Biology. 2022; 11(12):1767. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11121767
Chicago/Turabian StyleHabibi, Mohammad Amin, Samira Alesaeidi, Mohadeseh Zahedi, Samin Hakimi Rahmani, Seyed Mohammad Piri, and Soheil Tavakolpour. 2022. "The Efficacy and Safety of Rituximab in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: A Systematic Review" Biology 11, no. 12: 1767. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11121767
APA StyleHabibi, M. A., Alesaeidi, S., Zahedi, M., Hakimi Rahmani, S., Piri, S. M., & Tavakolpour, S. (2022). The Efficacy and Safety of Rituximab in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: A Systematic Review. Biology, 11(12), 1767. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11121767







