PIP2 Interacts Electrostatically with MARCKS-like Protein-1 and ENaC in Renal Epithelial Cells
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
MLP-1 Associates with PIP2
2. Methods
2.1. Tissue Culture Models
2.2. Fluorescent Immunohistochemistry
2.3. Data Analysis and Statistics
2.4. Co-Localization Analysis
2.5. Western Blots
2.6. Single-Channel Patch-Clamp Studies
2.7. Chemicals
3. Results
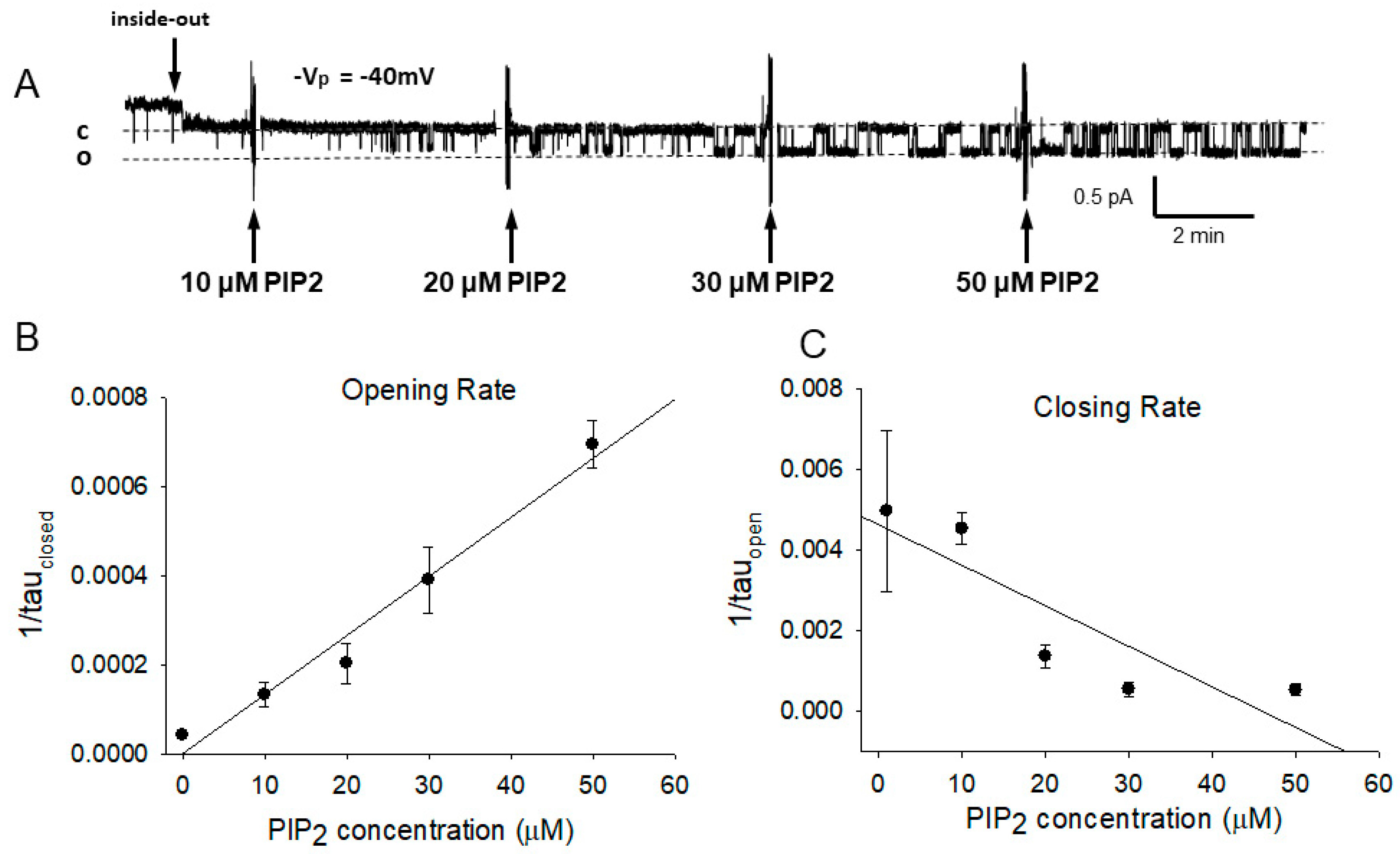
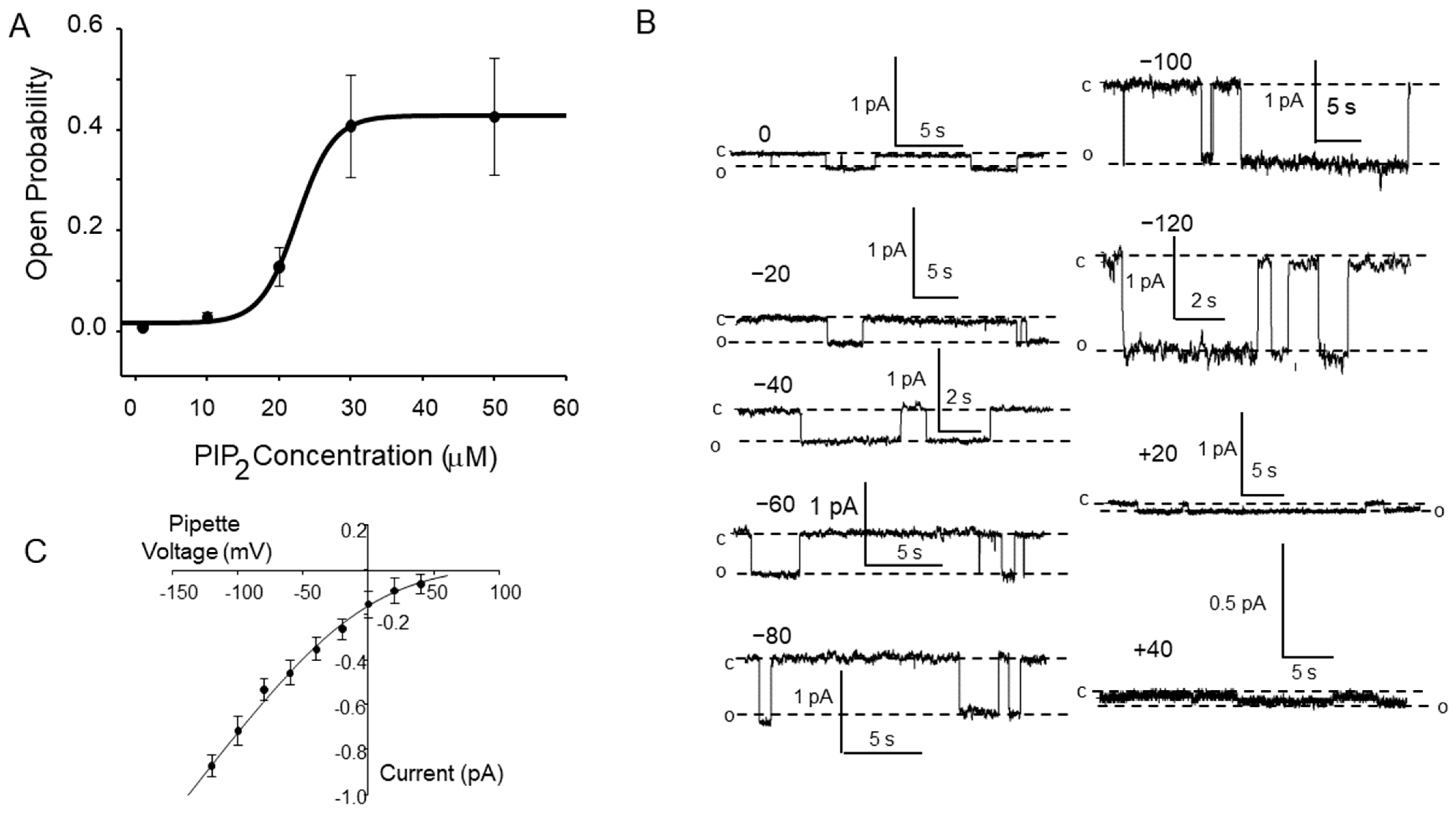
3.1. PIP2 Activates ENaC
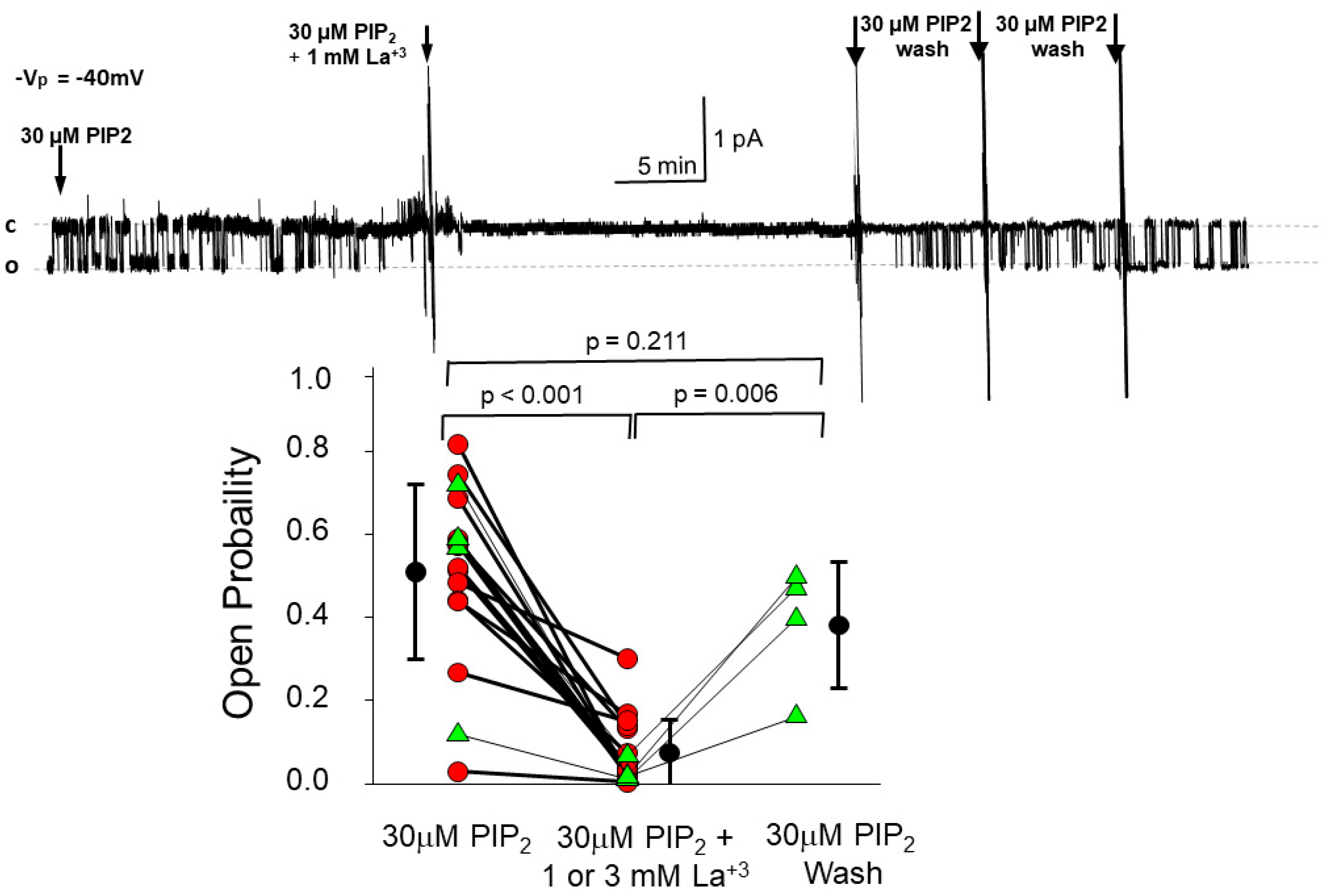
3.2. PIP2’s Interaction with ENaC Is Consistent with an Electrostatic Interaction
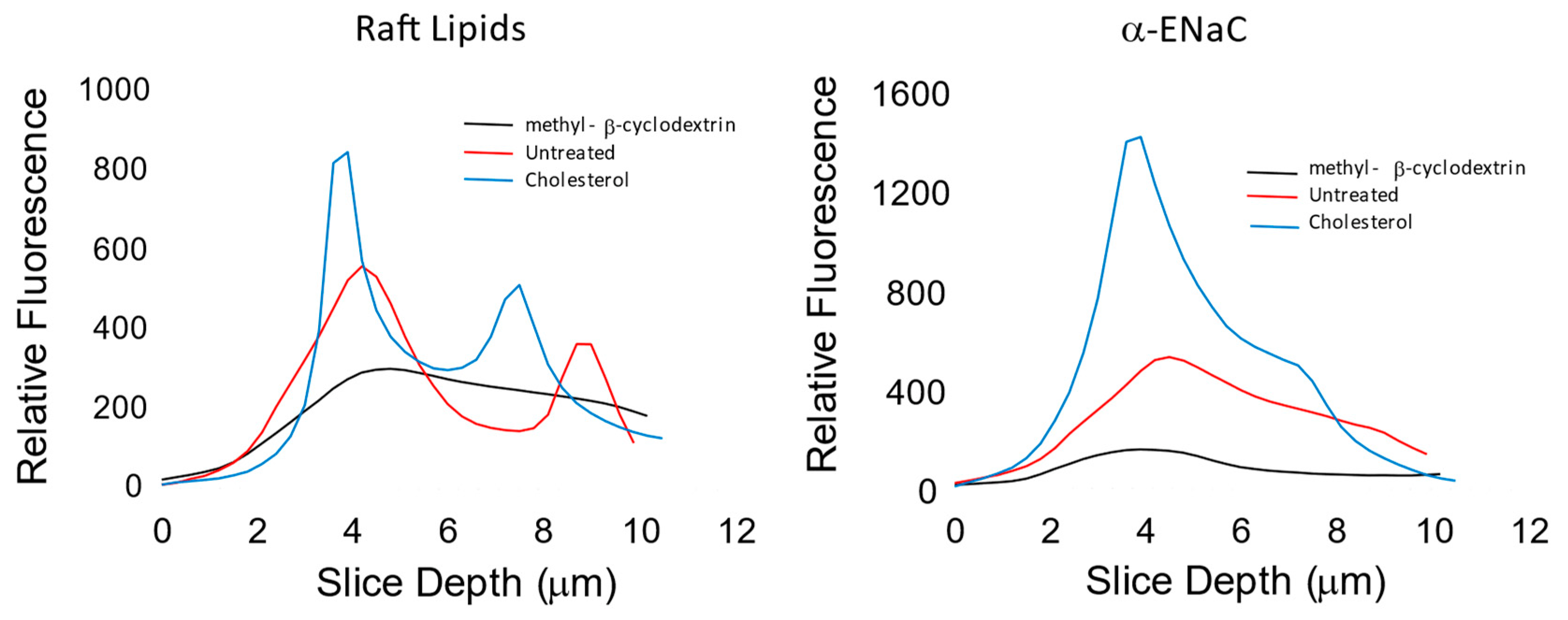
3.3. ENaC Is in Lipid Domains Enriched in Inositol Lipid Phosphates
3.4. MLP-1 Is Necessary for ENaC-PIP2 Interaction
3.5. Altering the Charge Structure of β or γ ENaC Changes ENaC Open Probability




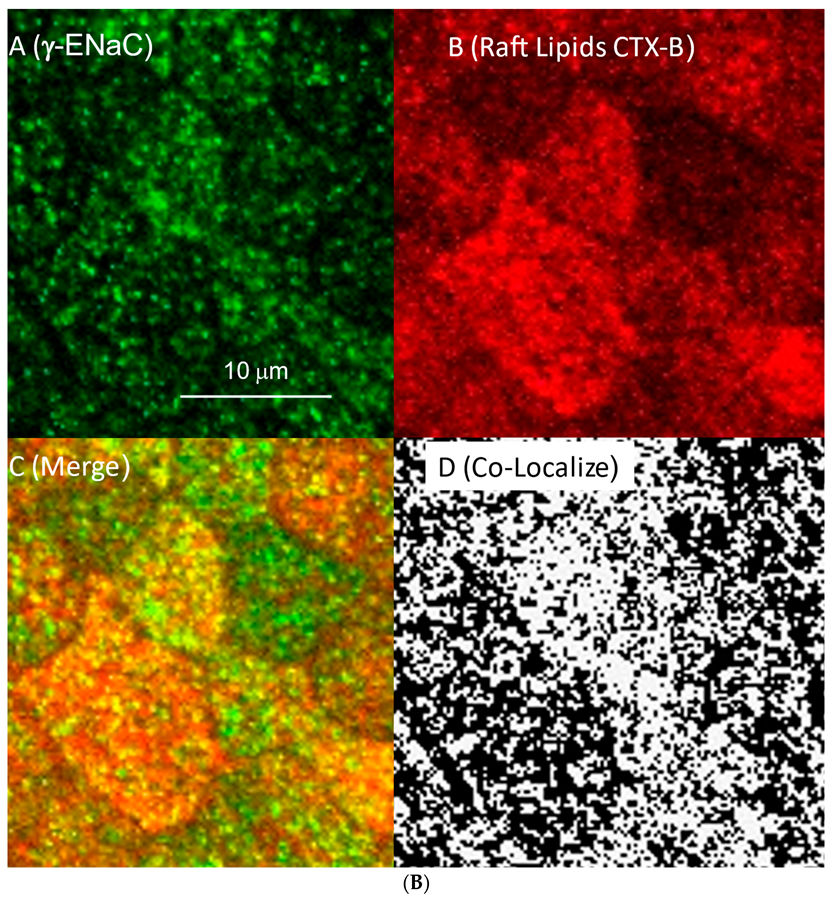
| αENaC | βENaC | γENaC | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pearson’s correlation coefficient | 0.194 | 0.198 | 0.190 |
| ENaC channel (green) threshold | 61 | 66 | 64 |
| Raft lipids channel (red) threshold | 33 | 31 | 32 |
| Overlap coefficient (R—pixels above threshold) | 0.761 | 0.731 | 0.802 |
| Overlap coefficient (R—pixels below threshold) | 0.0030 | 0.0029 | 0.0029 |
| ENaC channel overlap coefficient (k1) | 0.976 | 0.944 | 0.952 |
| Raft lipids channel overlap coefficient (k2) | 0.999 | 0.960 | 0.972 |
| Slope of the correlation function | 0.685 | 0.673 | 0.706 |
| Intercept of the correlation function | −9 | −8 | −9 |
| ENaC channel threshold | 61 | 66 | 64 |
| Raft lipids channel threshold | 33 | 31 | 32 |
| Number of colocalized pixels (red and green > threshold) | 19,366 | 18,362 | 20,041 |
| Total green pixels above the threshold | 128,935 | 115,122 | 136,799 |
| Total red pixels above the threshold | 138,626 | 151,502 | 100,005 |
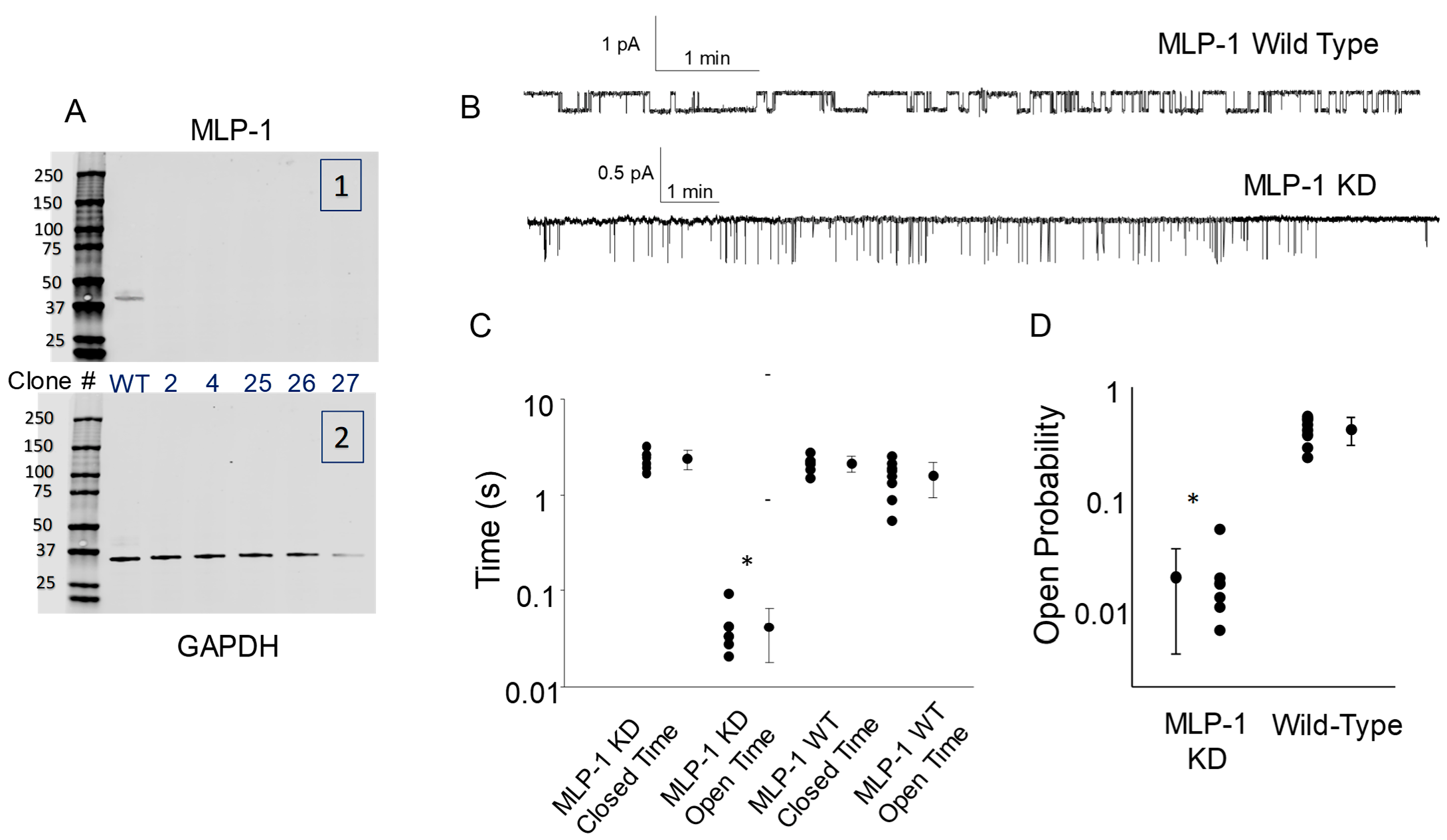

4. Discussion
MLP-1 Promotes ENaC-PIP2 Interaction
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yue, G.; Malik, B.; Yue, G.; Eaton, D.C. Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) stimulates epithelial sodium channel activity in A6 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 11965–11969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.P.; Saxena, S.; Warnock, D.G. Anionic phospholipids regulate native and expressed ENaC. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 7641–7644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pochynyuk, O.; Bugaj, V.; Stockand, J.D. Physiologic regulation of the epithelial sodium channel by phosphatidylinositides. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2008, 17, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pochynyuk, O.; Tong, Q.; Medina, J.; Vandewalle, A.; Staruschenko, A.; Bugaj, V.; Stockand, J.D. Molecular Determinants of PI(4,5)P2 and PI(3,4,5)P3 Regulation of the Epithelial Na+ Channel. J. Gen. Physiol. 2007, 130, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pochynyuk, O.; Tong, Q.; Staruschenko, A.; Ma, H.-P.; Stockand, J.D. Regulation of the epithelial Na+ channel (ENaC) by phosphatidylinositides. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2006, 290, F949–F957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Q.; Gamper, N.; Medina, J.L.; Shapiro, M.S.; Stockand, J. Direct Activation of the Epithelial Na+ Channel by Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-Trisphosphate and Phosphatidylinositol 3,4-Bisphosphate Produced by Phosphoinositide 3-OH Kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 22654–22663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Yue, Q.; Moseley, A.; Al-Khalili, O.; Wynne, B.M.; Ma, H.; Wang, L.; Eaton, D.C. Myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate-like protein-1 regulates epithelial sodium channel activity in renal distal convoluted tubule cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2020, 319, C589–C604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pochynyuk, O.; Tong, Q.; Staruschenko, A.; Stockand, J.D. Binding and direct activation of the epithelial Na+ channel (ENaC) by phosphatidylinositides. J. Physiol. 2007, 580 Pt 2, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alli, A.A.; Bao, H.-F.; Alli, A.A.; Aldrugh, Y.; Song, J.Z.; Ma, H.-P.; Yu, L.; Al-Khalili, O.; Eaton, D.C. Phosphatidylinositol phosphate-dependent regulation of Xenopus ENaC by MARCKS protein. Am. J. Physiol.-Renal Physiol. 2012, 303, F800–F811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helms, M.N.; Liu, L.; Liang, Y.-Y.; Al-Khalili, O.; Vandewalle, A.; Saxena, S.; Eaton, D.C.; Ma, H.-P. Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-Trisphosphate Mediates Aldosterone Stimulation of Epithelial Sodium Channel (ENaC) and Interacts with γ-ENaC. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 40885–40891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.-P.; Chou, C.-F.; Wei, S.-P.; Eaton, D.C. Regulation of the epithelial sodium channel by phosphatidylinositides: Experiments, implications, and speculations. Pflugers Arch. 2007, 455, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-R.; Chou, C.-F.; Wang, J.; Liang, Y.-Y.; Ma, H.-P. Anionic phospholipids differentially regulate the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) by interacting with alpha, beta, and gamma ENaC subunits. Pflugers Arch. 2010, 459, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pochynyuk, O.; Bugaj, V.; Rieg, T.; Insel, P.A.; Mironova, E.; Vallon, V.; Stockand, J.D. Paracrine Regulation of the Epithelial Na+ Channel in the Mammalian Collecting Duct by Purinergic P2Y2 Receptor Tone. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 36599–36607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pochynyuk, O.; Bugaj, V.; Vandewalle, A.; Stockand, J.D. Purinergic control of apical plasma membrane PI(4,5)P2levels sets ENaC activity in principal cells. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2008, 294, F38–F46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mullane, L.M.; Cook, D.I.; Dinudom, A. Purinergic regulation of the epithelial Na+ channel. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2009, 36, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marunaka, Y.; Eaton, D.C. Effects of vasopressin and cAMP on single amiloride-blockable Na channels. Am. J. Physiol. 1991, 260 Pt 1, C1071–C1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, K. Review of PIP2 in Cellular Signaling, Functions and Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macháň, R.; Hof, M. Lipid diffusion in planar membranes investigated by fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1798, 1377–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.-F.; Thai, T.L.; Yue, Q.; Ma, H.-P.; Eaton, A.F.; Cai, H.; Klein, J.D.; Sands, J.M.; Eaton, D.C. ENaC activity is increased in isolated, split-open cortical collecting ducts from protein kinase Calpha knockout mice. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2014, 306, F309–F320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gambhir, A.; Hangyás-Mihályné, G.; Zaitseva, I.; Cafiso, D.S.; Wang, J.; Murray, D.; Pentyala, S.N.; Smith, S.O.; McLaughlin, S. Electrostatic Sequestration of PIP2 on Phospholipid Membranes by Basic/Aromatic Regions of Proteins. Biophys. J. 2004, 86, 2188–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbuzova, A.; Wang, J.; Murray, D.; Jacob, J.; Cafiso, D.S.; McLaughlin, S. Kinetics of Interaction of the Myristoylated Alanine-rich C Kinase Substrate, Membranes, and Calmodulin. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 27167–27177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin, S.; Murray, D. Plasma membrane phosphoinositide organization by protein electrostatics. Nature 2005, 438, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin, S.; Aderem, A. The myristoyl-electrostatic switch: A modulator of reversible protein-membrane interactions. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1995, 20, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusu, L.; Gambhir, A.; McLaughlin, S.; Rädler, J. Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy Studies of Peptide and Protein Binding to Phospholipid Vesicles. Biophys. J. 2004, 87, 1044–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Gambhir, A.; Hangyás-Mihályneá, G.; Murray, D.; Golebiewska, U.; McLaughlin, S. Lateral Sequestration of Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-Bisphosphate by the Basic Effector Domain of Myristoylated Alanine-rich C Kinase Substrate Is Due to Nonspecific Electrostatic Interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 34401–34412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gambhir, A.; McLaughlin, S.; Murray, D. A Computational Model for the Electrostatic Sequestration of PI(4,5)P2 by Membrane-Adsorbed Basic Peptides. Biophys. J. 2004, 86, 1969–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bens, M.; Vallet, V.; Cluzeaud, F.; Pascual-Letallec, L.; Kahn, A.; Rafestin-Oblin, M.E.; Rossier, B.C.; Vandewalle, A. Corticosteroid-dependent sodium transport in a novel immortalized mouse collecting duct principal cell line. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1999, 10, 923–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, B.; Mistry, A.C.; Hanson, L.; Mallick, R.; Cooke, L.L.; Hack, B.K.; Cunningham, P.; Hoover, R.S. A new model of the distal convoluted tubule. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2012, 303, F700–F710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Bao, H.-F.; Self, J.L.; Eaton, D.C.; Helms, M.N. Aldosterone-induced increases in superoxide production counters nitric oxide inhibition of epithelial Na channel activity in A6 distal nephron cells. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2007, 293, F1666–F1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Eaton, D.C.; Helms, M.N. Effect of divalent heavy metals on epithelial Na+ channels in A6 cells. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2007, 293, F236–F244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, K.W.; Kamocka, M.M.; McDonald, J.H. A practical guide to evaluating colocalization in biological microscopy. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2011, 300, C723–C742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manders, E.M.M.; Verbeek, F.J.; Aten, J.A. Measurement of co-localization of objects in dual-colour confocal images. J. Microsc. 1993, 169, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 Years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, D.E. Potential, impedance, and rectification in membranes. J. Gen. Physiol. 1943, 27, 37–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Aziz, T.M.; Kaur, A.; Shapiro, M.S.; Stockand, J.D.; Archer, C.R. Optogenetic Control of PIP2 Interactions Shaping ENaC Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, C.R.; Enslow, B.T.; Carver, C.M.; Stockand, J.D. Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate directly interacts with the beta and gamma subunits of the sodium channel ENaC. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 7958–7969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, W.G.; An, B.; Johnson, J.P. Endogenously Expressed Epithelial Sodium Channel Is Present in Lipid Rafts in A6 Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 33541–33544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, W.G.; Butterworth, M.B.; Wang, H.; Edinger, R.S.; Lebowitz, J.; Peters, K.W.; Frizzell, R.A.; Johnson, J.P. The Epithelial Sodium Channel (ENaC) Traffics to Apical Membrane in Lipid Rafts in Mouse Cortical Collecting Duct Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 37402–37411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugh, J.M.; Wells, A.; Lauffenburger, D.A. Mathematical modeling of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling through the phospholipase C pathway: Mechanistic insights and predictions for molecular interventions. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2000, 70, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, C.; Ott, M.; Klingel, K.; Beck, S.; Friedrich, B.; Wild, K.-N.; Bröer, S.; Moschen, I.; Albers, A.; Waldegger, S.; et al. Effects of the Serine/Threonine Kinase SGK1 on the Epithelial Na(+) Channel (ENaC) and CFTR: Implications for Cystic Fibrosis. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2001, 11, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alli, A.A.; Bao, H.F.; Alli, A.A.; Aldrugh, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, L.; Eaton, D.C. Calmodulin and CaM kinase II govern MARCKS-mediated PIP2-dependent regulation of ENaC. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 867.15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.-J.; Wu, M.-M.; Linck, V.A.; Zou, L.; Yue, Q.; Wei, S.-P.; Song, C.; Zhang, S.; Williams, C.R.; Song, B.-L.; et al. Intracellular cholesterol stimulates ENaC by interacting with phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate and mediates cyclosporine A-induced hypertension. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2019, 1865, 1915–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.J.; Liu, B.C.; Wei, S.P.; Chou, C.F.; Wu, M.M.; Song, B.L.; Linck, V.A.; Zou, L.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.Q.; et al. Depletion of Cholesterol Reduces ENaC Activity by Decreasing Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-Bisphosphate in Microvilli. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 47, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Z.; Xiao, J.; Chen, X.; Hu, X.; Li, R.; Chen, S.; Feng, X.; Shen, S.; Ma, H.P.; Zhuang, J. G protein pathway suppressor 2 enhanced the renal large-conductance Ca(2+)-activated potassium channel expression via inhibiting ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2018, 315, F503–F511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.-P.; Li, X.-Q.; Chou, C.-F.; Liang, Y.-Y.; Peng, J.-B.; Warnock, D.G.; Ma, H.-P. Membrane Tension Modulates the Effects of Apical Cholesterol on the Renal Epithelial Sodium Channel. J. Membr. Biol. 2007, 220, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuna, K.M.; Liu, B.-C.; Yue, Q.; Ghazi, Z.M.; Ma, H.-P.; Eaton, U.C.; Alli, A.A. Mal protein stabilizes luminal membrane PLC-β3 and negatively regulates ENaC in mouse cortical collecting duct cells. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2019, 317, F986–F995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larionov, A.; Dahlke, E.; Kunke, M.; Rodriguez, L.Z.; Schiessl, I.M.; Magnin, J.; Kern, U.; Alli, A.A.; Mollet, G.; Schilling, O.; et al. Cathepsin B increases ENaC activity leading to hypertension early in nephrotic syndrome. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 6543–6553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, V.D.; Jella, K.K.; Ragheb, R.R.T.; Denslow, N.D.; Alli, A.A. Lipidomic and proteomic analysis of exosomes from mouse cortical collecting duct cells. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 5399–5408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alli, A.A.; Bao, H.-F.; Liu, B.-C.; Yu, L.; Aldrugh, S.; Montgomery, D.S.; Ma, H.-P.; Eaton, D.C. Calmodulin and CaMKII modulate ENaC activity by regulating the association of MARCKS and the cytoskeleton with the apical membrane. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2015, 309, F456–F463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, B.; Haerteis, S.; Yang, L.; Hartner, A.; Rauh, R.; Korbmacher, C.; Diakov, A. Cholesterol Depletion of the Plasma Membrane Prevents Activation of the Epithelial Sodium Channel (ENaC) by SGK1. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 24, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, W.; Selmi, C.; Ridgway, W.M.; Leung, P.S.; Zhang, F.; Gershwin, M.E. The myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrates (MARCKS): A membrane-anchored mediator of the cell function. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin, S.; Wang, J.; Gambhir, A.; Murray, D. PIP2 and Proteins: Interactions, Organization, and Information Flow. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 2002, 31, 151–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamper, N.; Shapiro, M.S. Target-specific PIP2signalling: How might it work? J. Physiol. 2007, 582 Pt 3, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Amri, M.; Fitzgerald, U.; Schlosser, G. MARCKS and MARCKS-like proteins in development and regeneration. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018, 25, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cebecauer, M.; Amaro, M.; Jurkiewicz, P.; Sarmento, M.J.; Šachl, R.; Cwiklik, L.; Hof, M. Membrane Lipid Nanodomains. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 11259–11297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golebiewska, U.; Kay, J.G.; Masters, T.; Grinstein, S.; Im, W.; Pastor, R.W.; Scarlata, S.; McLaughlin, S. Evidence for a fence that impedes the diffusion of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate out of the forming phagosomes of macrophages. Mol. Biol. Cell 2011, 22, 3498–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Richards, D.A. Segregation of PIP2 and PIP3 into distinct nanoscale regions within the plasma membrane. Biol. Open 2012, 1, 857–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pochynyuk, O.; Staruschenko, A.; Tong, Q.; Medina, J.; Stockand, J. Identification of a Functional Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-Trisphosphate Binding Site in the Epithelial Na+ Channel. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 37565–37571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staruschenko, A.; Pochynyuk, O.; Vandewalle, A.; Bugaj, V.; Stockand, J.D. Acute Regulation of the Epithelial Na+ Channel by Phosphatidylinositide 3-OH Kinase Signaling in Native Collecting Duct Principal Cells. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 1652–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmento, M.J.; Coutinho, A.; Fedorov, A.; Prieto, M.; Fernandes, F. Ca(2+) induces PI(4,5)P2 clusters on lipid bilayers at physiological PI(4,5)P2 and Ca(2+) concentrations. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2014, 1838, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmento, M.J.; Coutinho, A.; Fedorov, A.A.; Prieto, M.; Fernandes, F. Membrane Order Is a Key Regulator of Divalent Cation-Induced Clustering of PI(3,5)P2 and PI(4,5)P2. Langmuir 2017, 33, 12463–12477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yue, Q.; Al-Khalili, O.; Moseley, A.; Yoshigi, M.; Wynne, B.M.; Ma, H.; Eaton, D.C. PIP2 Interacts Electrostatically with MARCKS-like Protein-1 and ENaC in Renal Epithelial Cells. Biology 2022, 11, 1694. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11121694
Yue Q, Al-Khalili O, Moseley A, Yoshigi M, Wynne BM, Ma H, Eaton DC. PIP2 Interacts Electrostatically with MARCKS-like Protein-1 and ENaC in Renal Epithelial Cells. Biology. 2022; 11(12):1694. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11121694
Chicago/Turabian StyleYue, Qiang, Otor Al-Khalili, Auriel Moseley, Masaaki Yoshigi, Brandi Michele Wynne, Heping Ma, and Douglas C. Eaton. 2022. "PIP2 Interacts Electrostatically with MARCKS-like Protein-1 and ENaC in Renal Epithelial Cells" Biology 11, no. 12: 1694. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11121694
APA StyleYue, Q., Al-Khalili, O., Moseley, A., Yoshigi, M., Wynne, B. M., Ma, H., & Eaton, D. C. (2022). PIP2 Interacts Electrostatically with MARCKS-like Protein-1 and ENaC in Renal Epithelial Cells. Biology, 11(12), 1694. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11121694







