Knockdown of Ecdysone-Induced Protein 93F Causes Abnormal Pupae and Adults in the Eggplant Lady Beetle
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect
2.2. Molecular Cloning and Bioinformatic Analysis
2.3. Synthesis of dsRNA Molecules
2.4. Introduction of dsRNA
2.5. Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
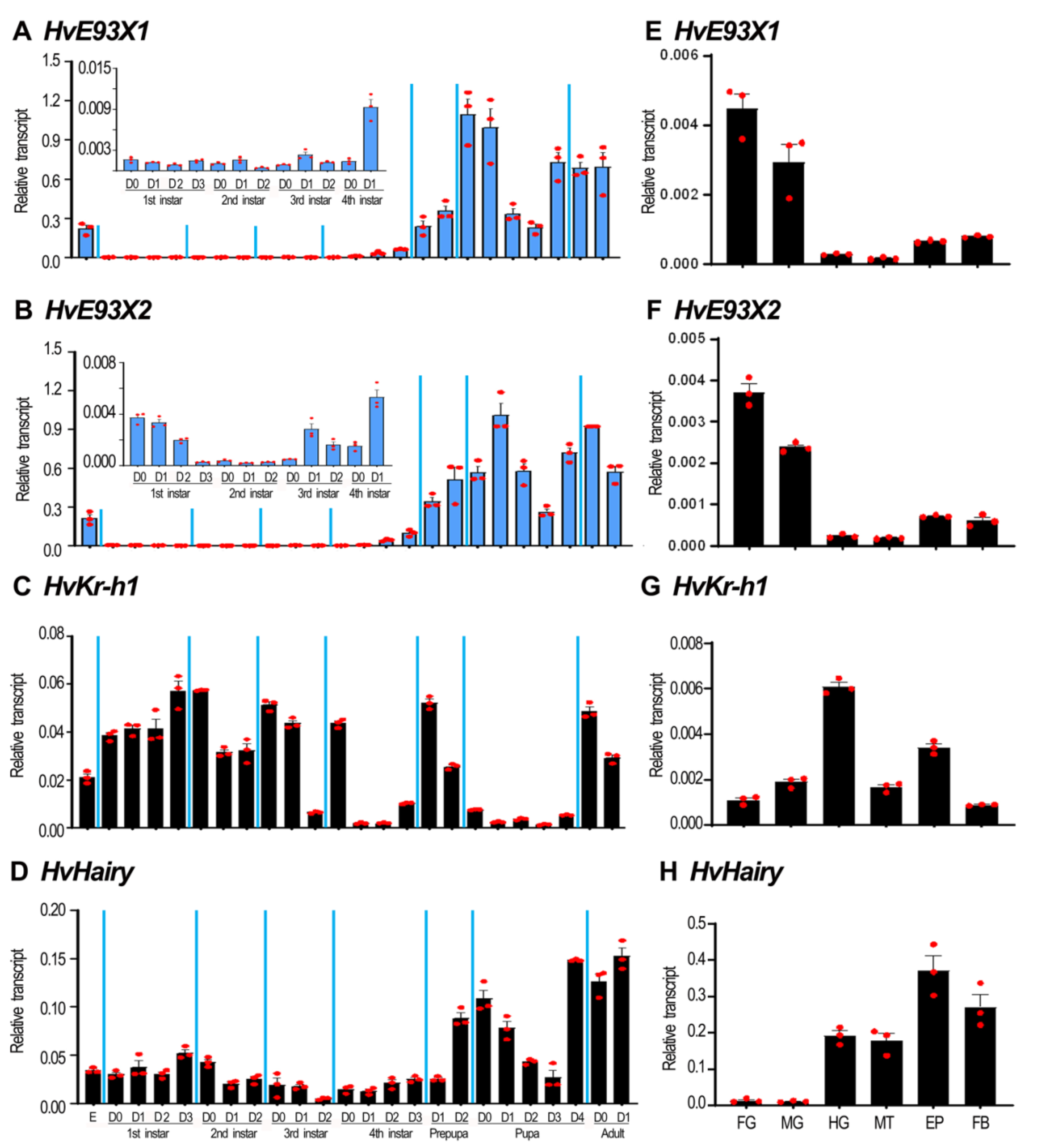
3.1. Identification of E93 Isoforms in H. vigintioctopunctata
3.2. The Expression Profiles of HvE93, HvKr-h1 and HvHairy
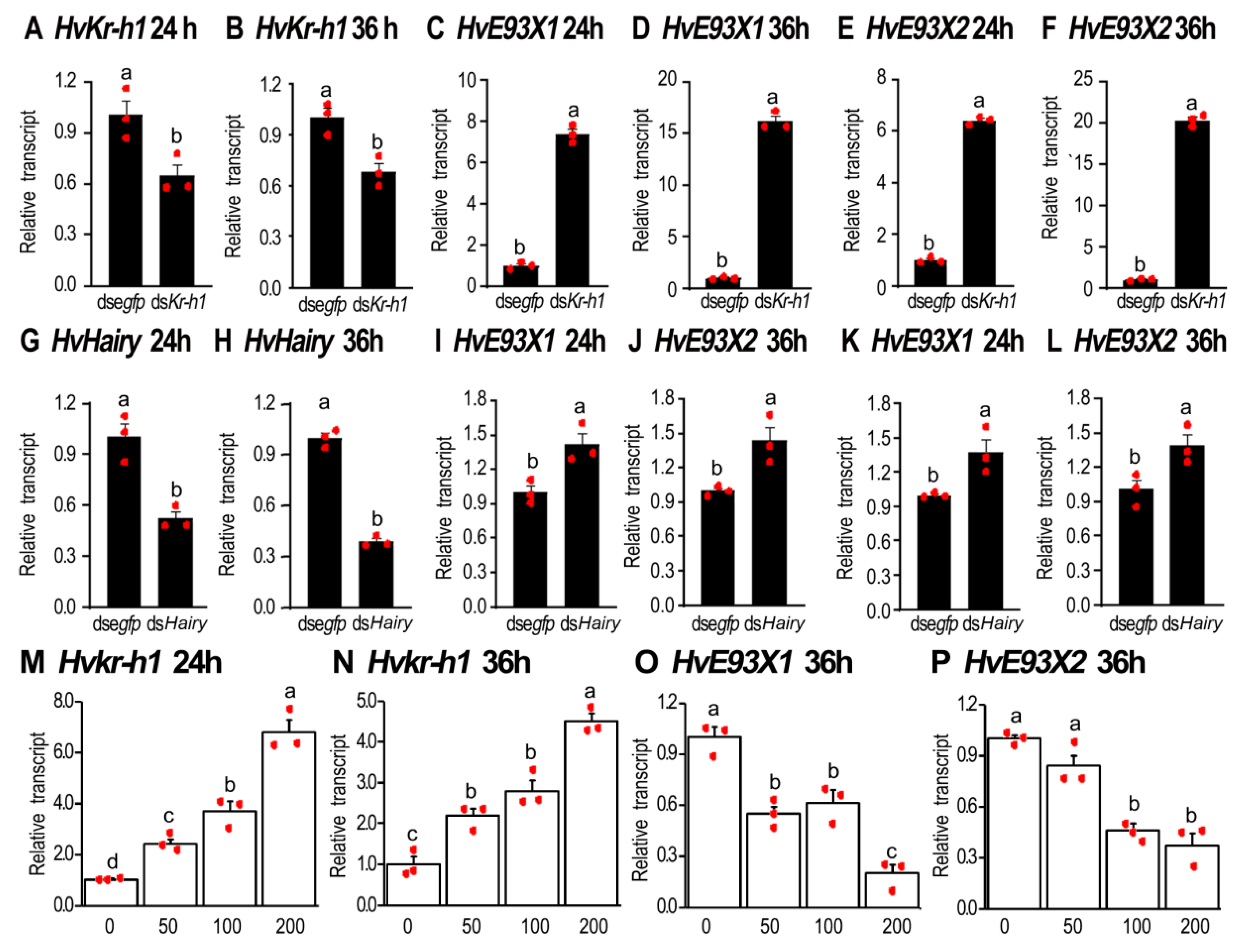
3.3. JH signal Inhibits the Expression of HvE93
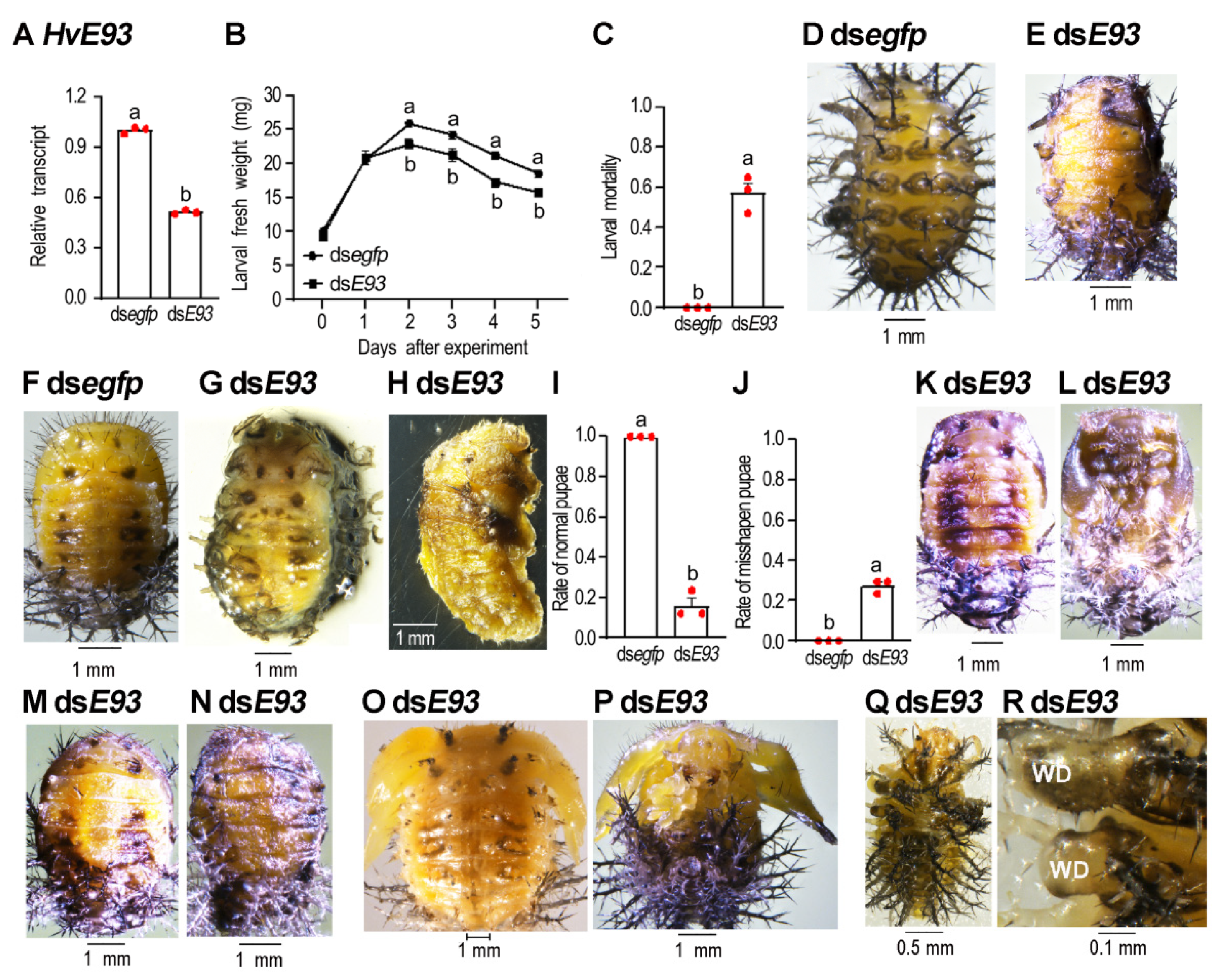
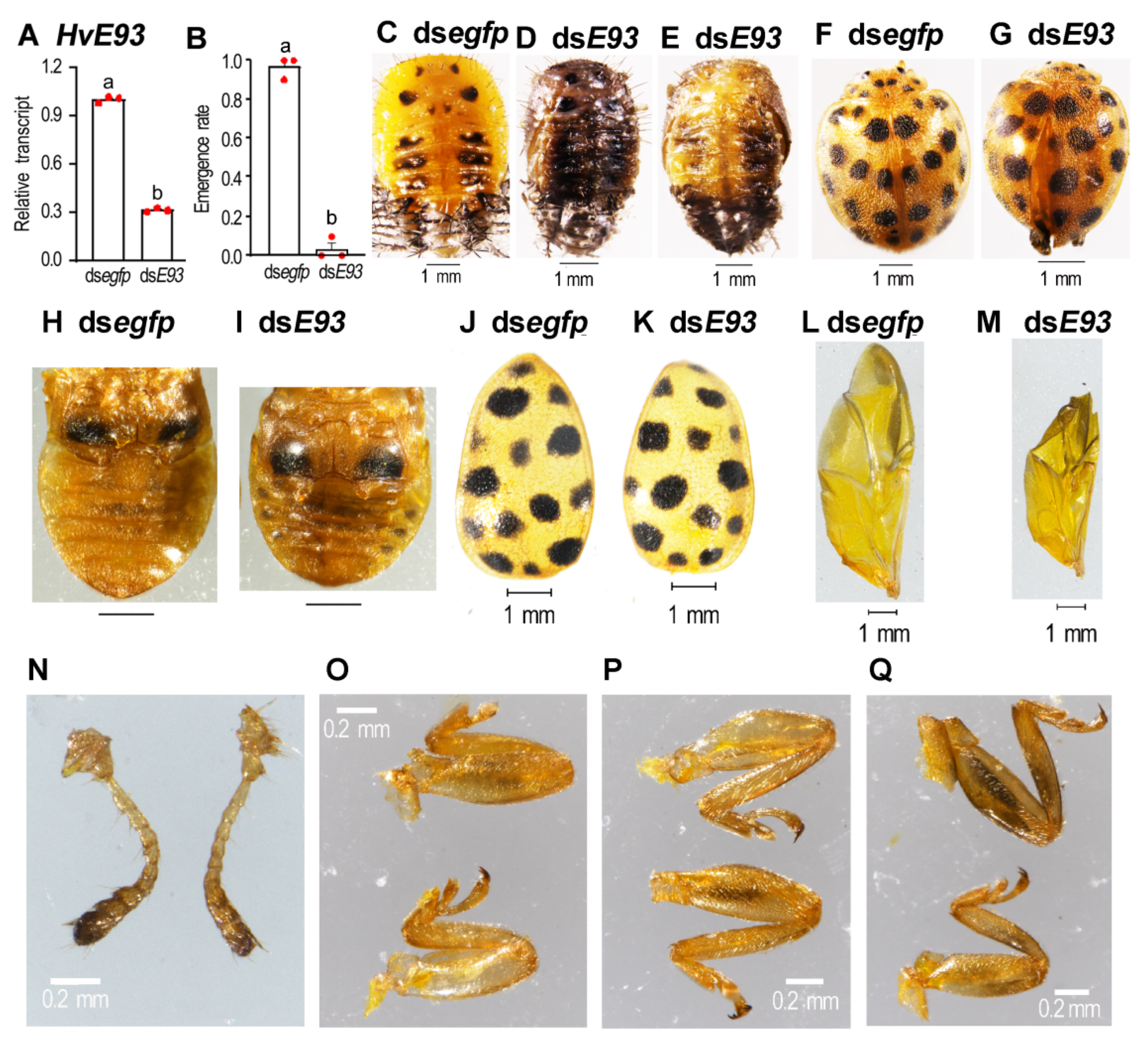
3.4. HvE93 Depletion in the Third Instar Larva Affects Larval-Pupal Transition
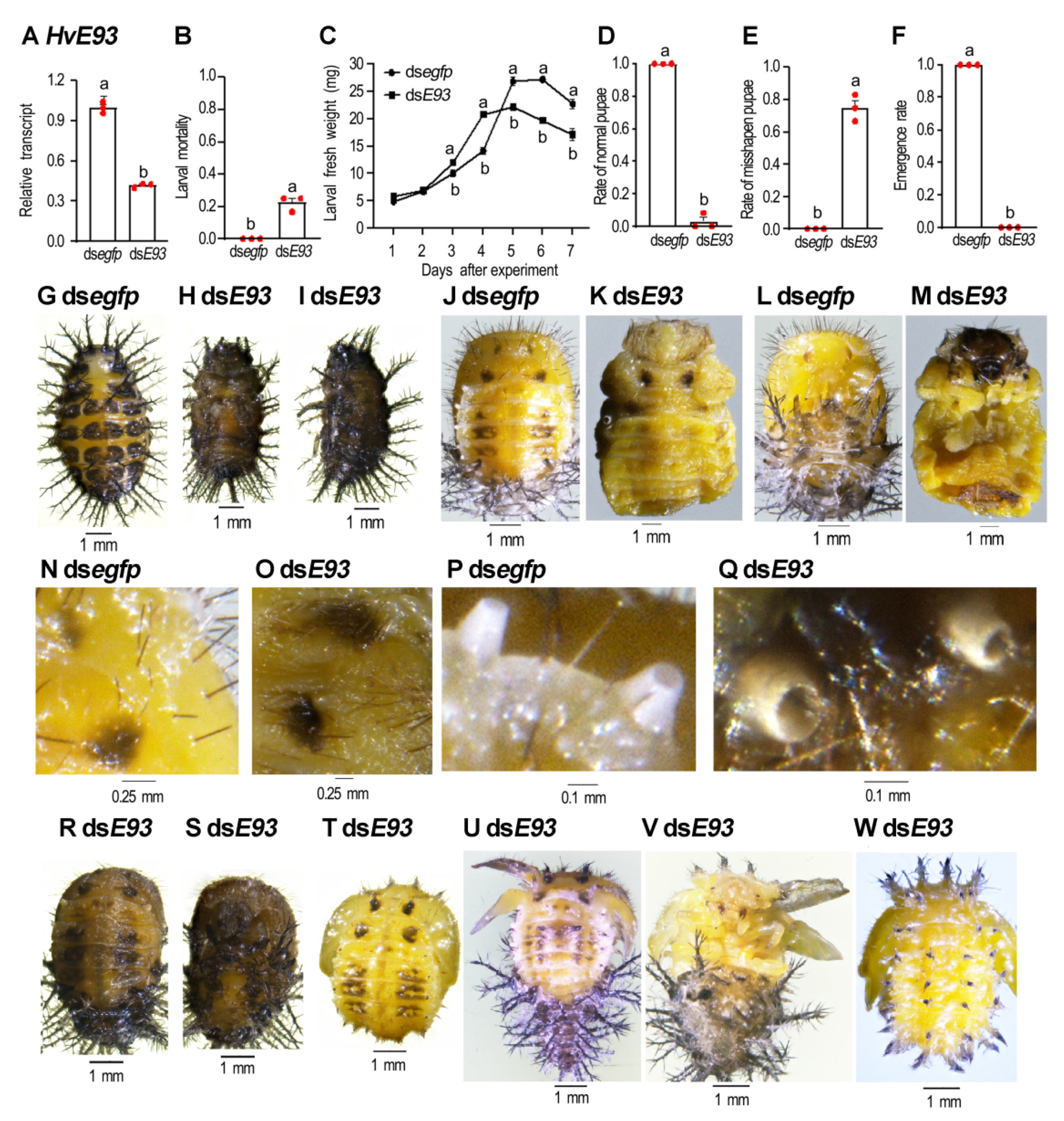
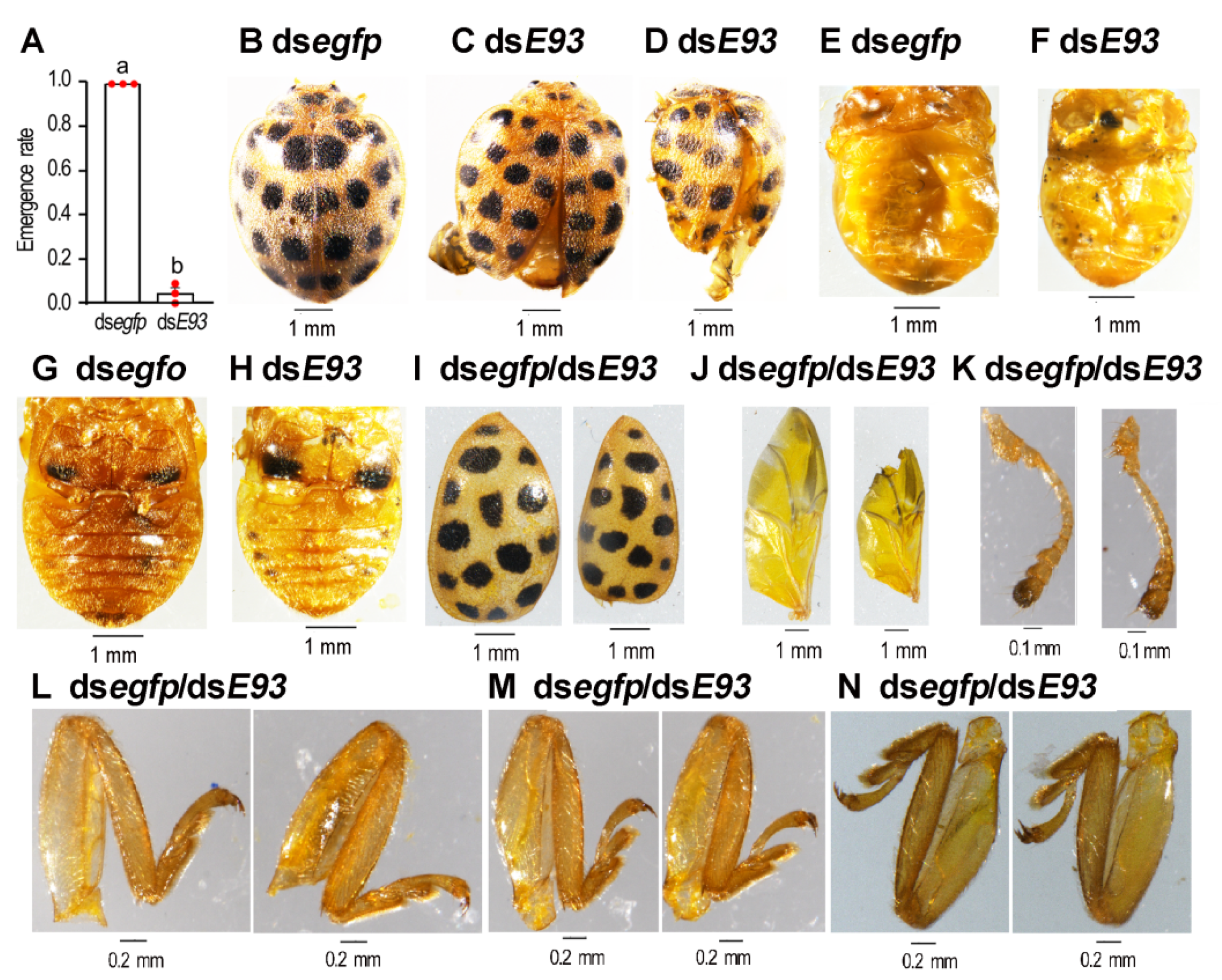
3.5. HvE93 Knockdown in the Fourth-Instar Larvae Impairs Larval–Pupal–Adult Transition
3.6. HvE93 RNAi in the Prepupae Mimicks the Impairment of Metamorphosis
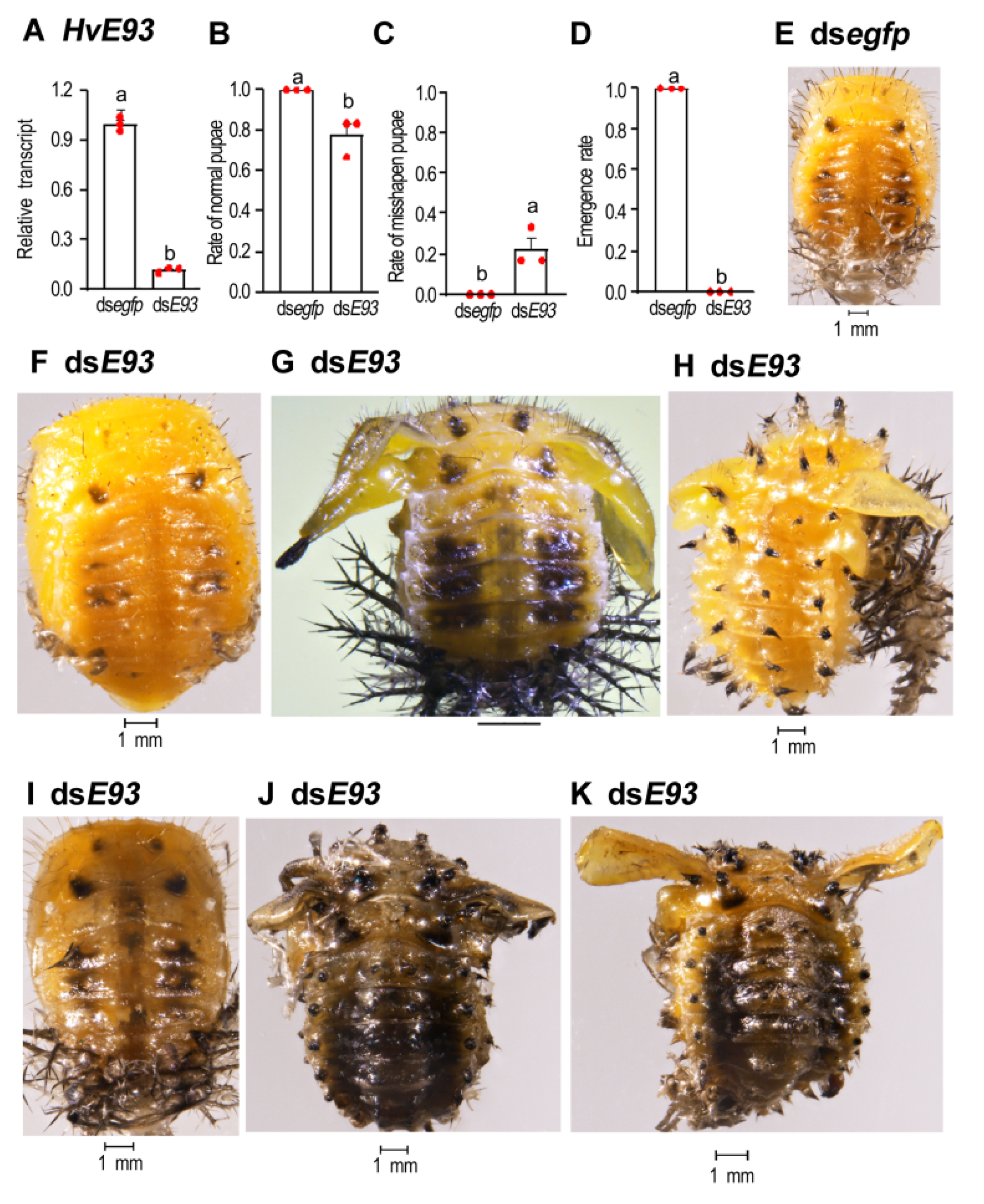
3.7. Depletion of HvE93 in the Pupae
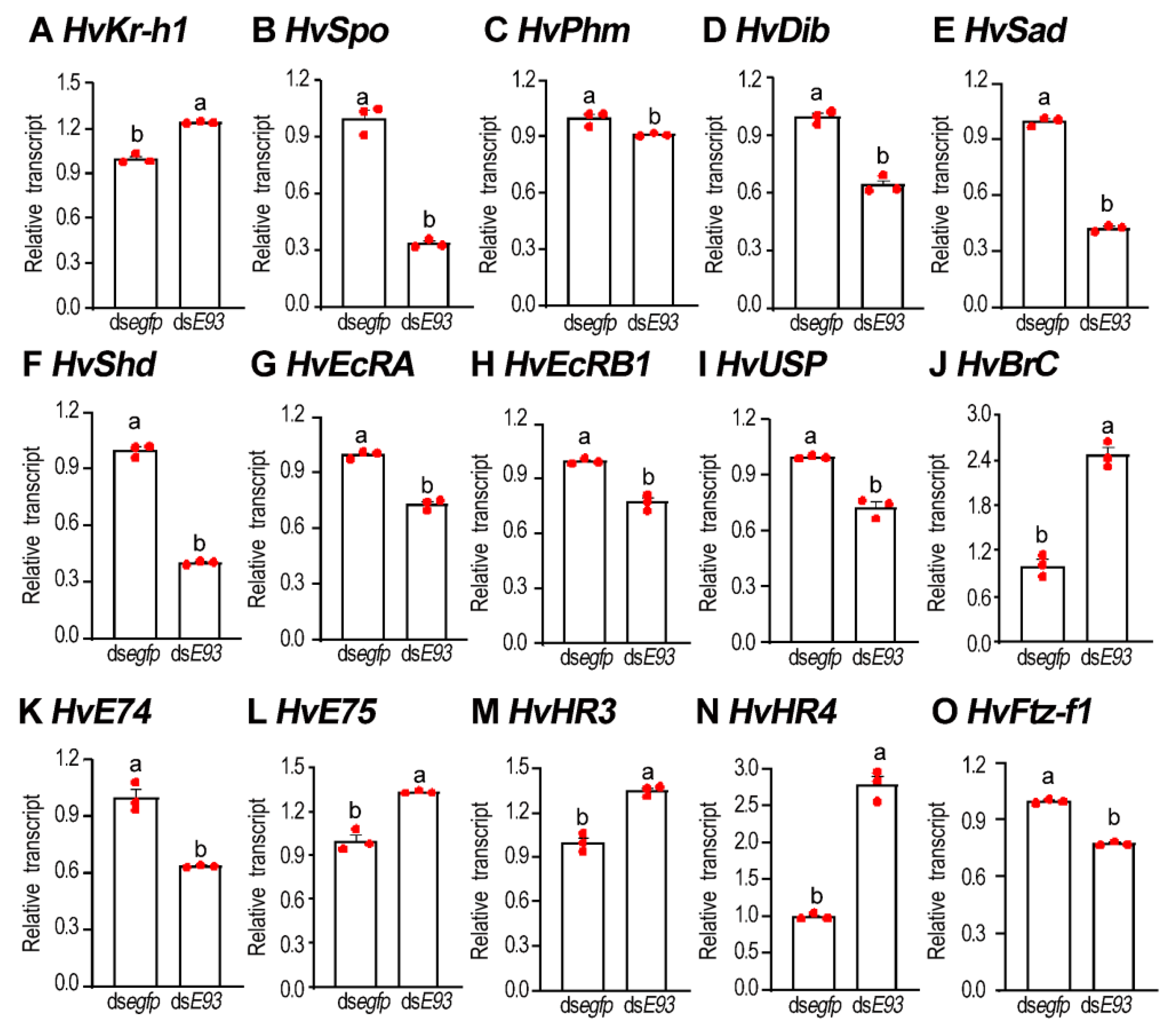
3.8. RNAi of HvE93 Disrupts 20E and JH Signals
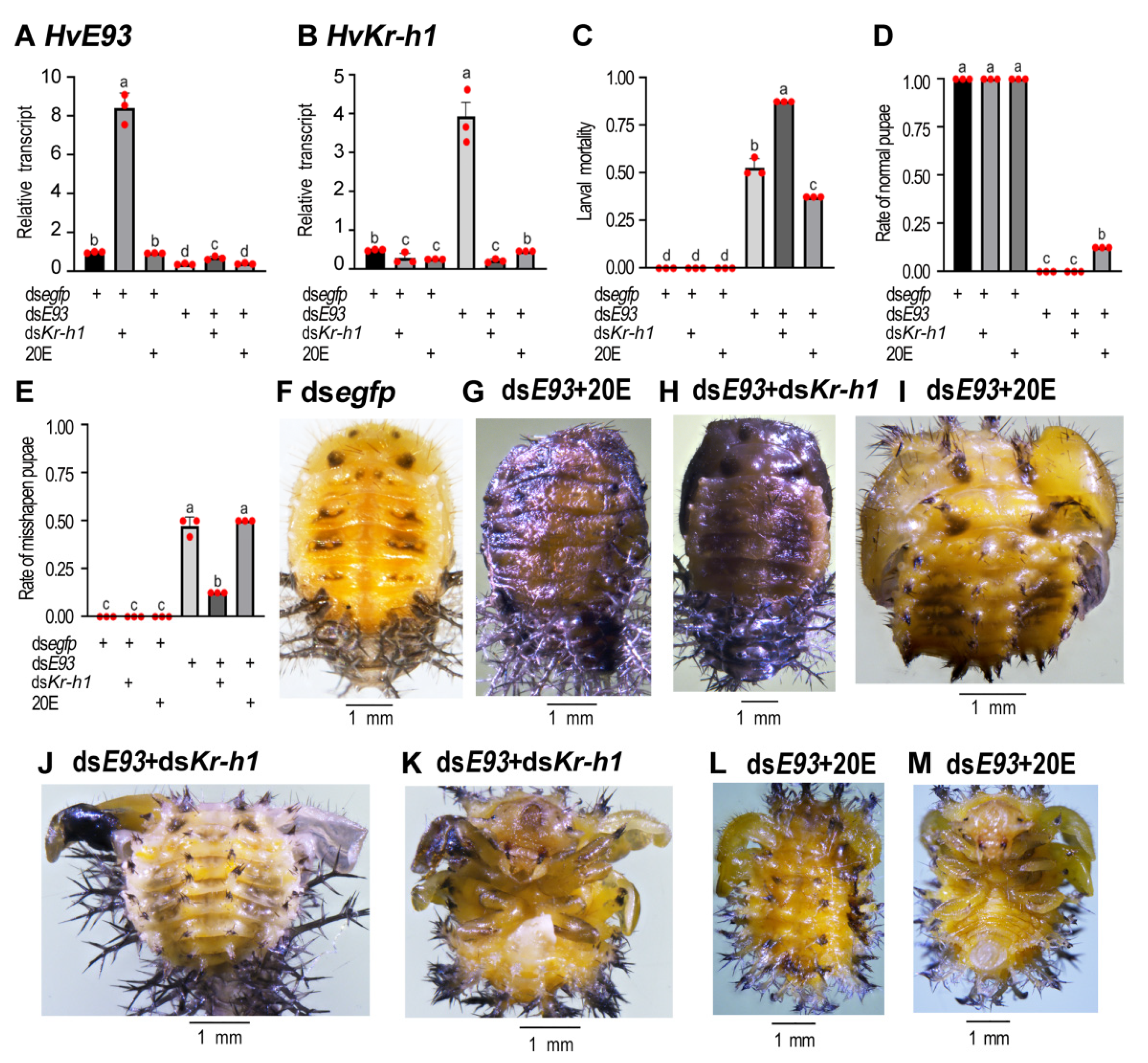
3.9. Rescuing Experiments with 20E or a Combination of dsE93 + dsKr-h1
4. Discussion
4.1. The Number of Larval Instars Is Fixed in H. vigintioctopunctata
4.2. E93 Acts as a Repressor of Larval Scoli during Metamorphosis
4.3. E93 Specifies Adult Differentiation
4.4. Mechanism of E93 Controlling Larval Metamorphosis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vea, I.M.; Minakuchi, C. Atypical insects: Molecular mechanisms of unusual life history strategies. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2021, 43, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y.; Shiotsuki, T.; Jouraku, A.; Miura, K.; Minakuchi, C. Characterization of E93 in neometabolous thrips Frankliniella occidentalis and Haplothrips brevitubus. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederhuber, M.J.; McKay, D.J. Mechanisms underlying the control of dynamic regulatory element activity and chromatin accessibility during metamorphosis. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2021, 43, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, G.; Nam, H.J.; Velentzas, P.D.; Baehrecke, E.H.; Thummel, C.S. Drosophila E93 promotes adult development and suppresses larval responses to ecdysone during metamorphosis. Dev. Biol. 2022, 481, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, D.; Chafino, S.; Franch-Marro, X. How stage identity is established in insects: The role of the Metamorphic Gene Network. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2021, 43, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanaka, N.; Rewitz, K.F.; O’Connor, M.B. Ecdysone control of developmental transitions: Lessons from Drosophila research. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 497–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jindra, M.; Palli, S.R.; Riddiford, L.M. The juvenile hormone signaling pathway in insect development. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 181–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truman, J.W. The evolution of insect metamorphosis. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, R1252–R1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ureña, E.; Chafino, S.; Manjón, C.; Franch-Marro, X.; Martín, D. The occurrence of the holometabolous pupal stage requires the interaction between E93, Krüppel-Homolog 1 and Broad-Complex. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saha, T.T.; Shin, S.W.; Dou, W.; Roy, S.; Zhao, B.; Hou, Y.; Wang, X.L.; Zou, Z.; Girke, T.; Raikhel, A.S. Hairy and Groucho mediate the action of juvenile hormone receptor methoprene-tolerant in gene repression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E735–E743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, T.T.; Roy, S.; Pei, G.; Dou, W.; Zou, Z.; Raikhel, A.S. Synergistic action of the transcription factors Krüppel homolog 1 and Hairy in juvenile hormone/Methoprene-tolerant-mediated gene-repression in the mosquito Aedes aegypti. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1008443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Okude, G.; Moriyama, M.; Kawahara-Miki, R.; Yajima, S.; Fukatsu, T.; Futahashi, R. Molecular mechanisms underlying metamorphosis in the most-ancestral winged insect. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2114773119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chafino, S.; Ureña, E.; Casanova, J.; Casacuberta, E.; Franch-Marro, X.; Martín, D. Upregulation of E93 gene expression acts as the trigger for metamorphosis independently of the threshold size in the beetle Tribolium castaneum. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishimaru, Y.; Tomonari, S.; Watanabe, T.; Noji, S.; Mito, T. Regulatory mechanisms underlying the specification of the pupal-homologous stage in a hemimetabolous insect. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 374, 20190225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gujar, H.; Palli, S.R. Kruppel homolog 1 and E93 mediate Juvenile hormone regulation of metamorphosis in the common bed bug, Cimex lectularius. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.L.; Yuan, S.Y.; Nanda, S.; Wang, W.X.; Lai, F.X.; Fu, Q.; Wan, P.J. The roles of E93 and Kr-h1 in metamorphosis of Nilaparvata lugens. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kayukawa, T.; Jouraku, A.; Ito, Y.; Shinoda, T. Molecular mechanism underlying juvenile hormone-mediated repression of precocious larval-adult metamorphosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belles, X.; Santos, C.G. The MEKRE93 (Methoprene tolerant-Kruppel homolog 1-E93) pathway in the regulation of insect metamorphosis, and the homology of the pupal stage. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 52, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, J.P.; Iwema, T.; Epa, V.C.; Takaki, K.; Rynes, J.; Jindra, M. Ligand-binding properties of a juvenile hormone receptor, Methoprene-tolerant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 21128–21133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Mead, E.A.; Zhu, J. Heterodimer of two bHLH-PAS proteins mediates juvenile hormone-induced gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jindra, M.; Uhlirova, M.; Charles, J.P.; Smykal, V.; Hill, R.J. Genetic evidence for function of the bHLH-PAS protein Gce/Met as a Juvenile hormone receptor. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kayukawa, T.; Minakuchi, C.; Namiki, T.; Togawa, T.; Yoshiyama, M.; Kamimura, M.; Mita, K.; Imanishi, S.; Kiuchi, M.; Ishikawa, Y.; et al. Transcriptional regulation of juvenile hormone-mediated induction of Kruppel homolog 1, a repressor of insect metamorphosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 11729–11734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cui, Y.; Sui, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhu, F.; Palli, S.R. Juvenile hormone regulates Aedes aegypti Kruppel homolog 1 through a conserved E box motif. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 52, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Konopova, B.; Smykal, V.; Jindra, M. Common and distinct roles of juvenile hormone signaling genes in metamorphosis of holometabolous and hemimetabolous insects. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lozano, J.; Belles, X. Conserved repressive function of Kruppel homolog 1 on insect metamorphosis in hemimetabolous and holometabolous species. Sci. Rep. 2011, 1, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ureña, E.; Manjón, C.; Franch-Marro, X.; Martín, D. Transcription factor E93 specifies adult metamorphosis in hemimetabolous and holometabolous insects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7024–7029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gijbels, M.; Marchal, E.; Verdonckt, T.W.; Bruyninckx, E.; Vanden Broeck, J. RNAi-mediated knockdown of transcription factor E93 in nymphs of the desert locust (Schistocerca gregaria) inhibits adult morphogenesis and results in supernumerary juvenile stages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.J.; Jun, G.; Liang, X.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhang, T.T.; Liu, W.M.; Zhang, J.Z.; Zhang, M. Silencing of transcription factor E93 inhibits adult morphogenesis and disrupts cuticle, wing and ovary development in Locusta migratoria. Insect Sci. 2022, 29, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minakuchi, C.; Namiki, T.; Shinoda, T. Kruppel homolog 1, an early juvenile hormone-response gene downstream of Methoprene-tolerant, mediates its anti-metamorphic action in the red flour beetle Tribolium castaneum. Dev. Biol. 2009, 325, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kayukawa, T.; Murata, M.; Kobayashi, I.; Muramatsu, D.; Okada, C.; Uchino, K.; Sezutsu, H.; Kiuchi, M.; Tamura, T.; Hiruma, K.; et al. Hormonal regulation and developmental role of Kruppel homolog 1, a repressor of metamorphosis, in the silkworm Bombyx mori. Dev. Biol. 2014, 388, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Dai, F.; Guo, E.; Li, K.; Ma, L.; Tian, L.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Palli, S.R.; Li, S. 20-Hydroxyecdysone (20E) primary response gene E93 modulates 20E signaling to promote Bombyx larval-pupal metamorphosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 27370–27383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Belles, X. Kruppel homolog 1 and E93: The doorkeeper and the key to insect metamorphosis. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2020, 103, e21609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mou, X.; Duncan, D.M.; Baehrecke, E.H.; Duncan, I. Control of target gene specificity during metamorphosis by the steroid response gene E93. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 2949–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.Y.; Wendel, D.P.; Reid, P.; Lam, G.; Thummel, C.S.; Baehrecke, E.H. E93 directs steroid-triggered programmed cell death in Drosophila. Mol. Cell 2000, 6, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Baehrecke, E.H. Steroid regulation of autophagic programmed cell death during development. Development 2001, 128, 1443–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Li, S. E93 predominantly transduces 20-hydroxyecdysone signaling to induce autophagy and caspase activity in Drosophila fat body. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 45, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, S.; Tapadia, M.G. Transcriptome profiling identifies multistep regulation through E93, Forkhead and Ecdysone Oxidase in survival of Malpighian tubules during metamorphosis in Drosophila. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2020, 64, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, D.M.; Kiefel, P.; Duncan, I. Mutants for Drosophila isocitrate dehydrogenase 3b are defective in mitochondrial function and larval cell death. G3 2017, 7, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pecasse, F.; Beck, Y.; Ruiz, C.; Richards, G. Kruppel-homolog, a stage-specific modulator of the prepupal ecdysone response, is essential for Drosophila metamorphosis. Dev. Biol. 2000, 221, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beck, Y.; Pecasse, F.; Richards, G. Kruppel-homolog is essential for the coordination of regulatory gene hierarchies in early Drosophila development. Dev. Biol. 2004, 268, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdou, M.A.; He, Q.; Wen, D.; Zyaan, O.; Wang, J.; Xu, J.; Baumann, A.A.; Joseph, J.; Wilson, T.G.; Li, S.; et al. Drosophila Met and Gce are partially redundant in transducing juvenile hormone action. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 41, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.L.; Wang, F.; Guo, J.; Deng, X.Y.; Chen, J.Y.; Lin, L.B. Characterization of ladybird Henosepilachna vigintioctopunctata transcriptomes across various life stages. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.-J.; Cheng, M.-D.; Ze, L.-J.; Shen, C.-H.; Jin, L.; Li, G.-Q. Dissecting the isoform-specific roles of FTZ-F1 in the larval-larval and larval-pupal ecdyses in Henosepilachna vigintioctopunctata. Insects 2022, 13, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.-J.; Mu, L.-L.; Kang, W.-N.; Ze, L.-J.; Shen, C.-H.; Jin, L.; Anjum, A.A.; Li, G.-Q. RNA interference targeting ecdysone receptor blocks the larval-pupal transition in Henosepilachna vigintioctopunctata. Insect Sci. 2021, 28, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ze, L.-J.; Xu, P.; Kang, W.-N.; Wu, J.-J.; Jin, L.; Anjum, A.A.; Li, G.-Q. Disruption of kynurenine pathway reveals physiological importance of tryptophan catabolism in Henosepilachna vigintioctopunctata. Amino Acids 2021, 53, 1091–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Ze, L.-J.; Kang, W.-N.; Wu, J.-J.; Jin, L.; Ali, A.A.; Li, G.-Q. Functional divergence of white genes in Henosepilachna vigintioctopunctata revealed by RNA interference. Insect Mol. Biol. 2020, 29, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, J.; Chen, S.; Guo, M.; Ye, C.; Qiu, B.; Wu, J.; Yang, C.; Pan, H. Selection and validation of reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis of the ladybird beetle Henosepilachna vigintioctomaculata. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L.; et al. The MIQE guidelines: Minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siegmund, T.; Lehmann, M. The Drosophila Pipsqueak protein defines a new family of helix-turn-helix DNA-binding proteins. Dev. Gene Evol. 2002, 212, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Peng, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, P.; Guo, M.; Zhang, T.; Qian, W.; Xia, Q.; Cheng, D. Transcription factor E93 regulates wing development by directly promoting Dpp signaling in Drosophila. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 513, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, T.; Li, Z.; Qian, W.; Peng, J.; Wei, L.; Yuan, D.; Li, Y.; Xia, Q.; Cheng, D. Histone H3K27 methylation-mediated repression of Hairy regulates insect developmental transition by modulating ecdysone biosynthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2101442118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Song, W.; Li, Z.; Qian, W.; Wei, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhou, X.; Meng, M.; Peng, J.; et al. Krüppel homolog 1 represses insect ecdysone biosynthesis by directly inhibiting the transcription of steroidogenic enzymes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 3960–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.Y.; Fu, D.Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, L.J.; Chen, H. Roles of Krüppel homolog 1 and Broad-Complex in the development of Dendroctonus armandi (Coleoptera: Scolytinae). Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 865442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uyehara, C.M.; Nystrom, S.L.; Niederhuber, M.J.; Leatham-Jensen, M.; Ma, Y.; Buttitta, L.A.; McKay, D.J. Hormone-dependent control of developmental timing through regulation of chromatin accessibility. Genes Dev. 2017, 31, 862–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nystrom, S.L.; Niederhuber, M.J.; McKay, D.J. Expression of E93 provides an instructive cue to control dynamic enhancer activity and chromatin accessibility during development. Development 2020, 147, dev181909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.-J.; Chen, F.; Yang, R.; Shen, C.-H.; Ze, L.-J.; Jin, L.; Li, G.-Q. Knockdown of Ecdysone-Induced Protein 93F Causes Abnormal Pupae and Adults in the Eggplant Lady Beetle. Biology 2022, 11, 1640. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111640
Wu J-J, Chen F, Yang R, Shen C-H, Ze L-J, Jin L, Li G-Q. Knockdown of Ecdysone-Induced Protein 93F Causes Abnormal Pupae and Adults in the Eggplant Lady Beetle. Biology. 2022; 11(11):1640. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111640
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jian-Jian, Feng Chen, Rui Yang, Chen-Hui Shen, Long-Ji Ze, Lin Jin, and Guo-Qing Li. 2022. "Knockdown of Ecdysone-Induced Protein 93F Causes Abnormal Pupae and Adults in the Eggplant Lady Beetle" Biology 11, no. 11: 1640. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111640
APA StyleWu, J.-J., Chen, F., Yang, R., Shen, C.-H., Ze, L.-J., Jin, L., & Li, G.-Q. (2022). Knockdown of Ecdysone-Induced Protein 93F Causes Abnormal Pupae and Adults in the Eggplant Lady Beetle. Biology, 11(11), 1640. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111640





