Maturation Selection Biases and Relative Age Effect in Italian Soccer Players of Different Levels
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Study Design
2.2. Anthropometry
2.3. Bioelectric Impedance Vector Analysis
2.4. Maturity Status
2.5. Relative Age Effect (RAE)
2.6. Motor Tests
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Maturity Status (MS)
3.2. Relative Age Effect (RAE)
3.3. Bioimpedance Vector Analysis (BIVA)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Campa, F.; Semprini, G.; Júdice, P.B.; Messina, G.; Toselli, S. Anthropometry, Physical and Movement Features, and Repeated-Sprint Ability in Soccer Players. Int. J. Sports Med. 2019, 40, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cossio-Bolaños, M.; Vidal-Espinoza, R.; Urra Albornoz, C.; Leite Portella, D.; Vega-Novoa, S.; Mendez-Cornejo, J.; Fuentes Lopez, J.; Gomez-Campos, R. A Systematic Review of Intervention Programs That Produced Changes in Speed and Explosive Strength in Youth Footballers. Eur. J. Transl. Myol. 2021, 31, 9692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohr, M.; Nólsøe, E.L.; Krustrup, P.; Fatouros, I.G.; Jamurtas, A.Z. Improving Hydration in Elite Male Footballers during a National Team Training Camp—An Observational Case Study. Phys. Act. Nutr. 2021, 25, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akpinar, S. Participation of Soccer Training Improves Lower Limb Coordination and Decreases Motor Lateralization. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 7525262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokstej, J. The Relationship between Fundamental Motor Skills and Game Specific Skills in Elite Young Soccer Players. J. Phys. Educ. Sport 2019, 19, 249–254. [Google Scholar]
- Rommers, N.; Mostaert, M.; Goossens, L.; Vaeyens, R.; Witvrouw, E.; Lenoir, M.; D’Hondt, E. Age and Maturity Related Differences in Motor Coordination among Male Elite Youth Soccer Players. J. Sports Sci. 2019, 37, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radnor, J.M.; Staines, J.; Bevan, J.; Cumming, S.P.; Kelly, A.L.; Lloyd, R.S.; Oliver, J.L. Maturity Has a Greater Association than Relative Age with Physical Performance in English Male Academy Soccer Players. Sports 2021, 9, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meylan, C.; Cronin, J.; Oliver, J.; Hughes, M. Talent Identification in Soccer: The Role of Maturity Status on Physical, Physiological and Technical Characteristics. Int. J. Sports Sci. Coach. 2010, 5, 571–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, R.; Hirose, N. Relationship Among Biological Maturation, Physical Characteristics, and Motor Abilities in Youth Elite Soccer Players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2020, 34, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.; Scott, S.; Malina, R.M.; McGee, D.; Cumming, S.P. Relative Age and Maturation Selection Biases in Academy Football. J. Sports Sci. 2020, 38, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubajczyk, K.; Rokita, A. The Relative Age Effect in Poland’s Elite Youth Soccer Players. J. Hum. Kinet. 2018, 64, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skorski, S.; Skorski, S.; Faude, O.; Hammes, D.; Meyer, T. The Relative Age Effect in German Elite Youth Soccer: Implications for a Successful Career. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2016, 11, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, J.E.; Alves, A.R.; Ferraz, R.; Forte, P.; Leal, M.; Ribeiro, J.; Silva, A.J.; Barbosa, T.M.; Monteiro, A.M. Effects of Chronological Age, Relative Age, and Maturation Status on Accumulated Training Load and Perceived Exertion in Young Sub-Elite Football Players. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 832202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helsen, W.F.; van Winckel, J.; Williams, A.M. The Relative Age Effect in Youth Soccer across Europe. J. Sports Sci. 2005, 23, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simmons, C.; Paull, G.C. Season-of-Birth Bias in Association Football. J. Sports Sci. 2001, 19, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattie, N.; Cobley, S.; Baker, J. Towards a Unified Understanding of Relative Age Effects. J. Sports Sci. 2008, 26, 1403–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorme, N.; Boiche, J.; Raspaud, M. Relative Age and Dropout in French Male Soccer. J. Sports Sci. 2010, 28, 717–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malina, R.M.; Eisenmann, J.C.; Cumming, S.P.; Ribeiro, B.; Aroso, J. Maturity-Associated Variation in the Growth and Functional Capacities of Youth Football (Soccer) Players 13–15 Years. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 91, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towlson, C.; Salter, J.; Ade, J.D.; Enright, K.; Harper, L.D.; Page, R.M.; Malone, J.J. Maturity-Associated Considerations for Training Load, Injury Risk, and Physical Performance in Youth Soccer: One Size Does Not Fit All. J. Sport Health Sci. 2021, 10, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campa, F.; Silva, A.M.; Iannuzzi, V.; Mascherini, G.; Benedetti, L.; Toselli, S. The Role of Somatic Maturation on Bioimpedance Patterns and Body Composition in Male Elite Youth Soccer Players. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2019, 16, 4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Mascio, M.; Ade, J.; Musham, C.; Girard, O.; Bradley, P.S. Soccer-Specific Reactive Repeated-Sprint Ability in Elite Youth Soccer Players: Maturation Trends and Association With Various Physical Performance Tests. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2020, 34, 3538–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toselli, S.; Marini, E.; Maietta Latessa, P.; Benedetti, L.; Campa, F. Maturity Related Differences in Body Composition Assessed by Classic and Specific Bioimpedance Vector Analysis among Male Elite Youth Soccer Players. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2020, 17, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barnes, C.; Archer, D.T.; Hogg, B.; Bush, M.; Bradley, P.S. The Evolution of Physical and Technical Performance Parameters in the English Premier League. Int. J. Sports Med. 2014, 35, 1095–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, A.; Farooq, A.; Whiteley, R. Skeletal Maturation Status Is More Strongly Associated with Academy Selection than Birth Quarter. Sci. Med. Footb. 2017, 1, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towlson, C.; Cobley, S.; Midgley, A.W.; Garrett, A.; Parkin, G.; Lovell, R. Relative Age, Maturation and Physical Biases on Position Allocation in Elite-Youth Soccer. Int. J. Sports Med. 2017, 38, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Toselli, S.; Mauro, M.; Grigoletto, A.; Cataldi, S.; Benedetti, L.; Nanni, G.; Di Miceli, R.; Aiello, P.; Gallamini, D.; Fischetti, F.; et al. Assessment of Body Composition and Physical Performance of Young Soccer Players: Differences According to the Competitive Level. Biology 2022, 11, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohman, T.G.; Roche, A.F.; Martorell, R. Anthropometric Standardization Reference Manual; Human Kinetics Books: Champaign, IL, USA, 1988; ISBN 978-0-87322-121-4. [Google Scholar]
- Slaughter, M.H.; Lohman, T.G.; Boileau, R.A.; Horswill, C.A.; Stillman, R.J.; Van Loan, M.D.; Bemben, D.A. Skinfold Equations for Estimation of Body Fatness in Children and Youth. Hum. Biol. 1988, 60, 709–723. [Google Scholar]
- Frisancho, A.R. Anthropometric Standards: An Interactive Nutritional Reference of Body Size and Body Composition for Children and Adults; University of Michigan Press: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2008; ISBN 978-0-472-11591-4. [Google Scholar]
- Lukaski, H.; Piccoli, A. Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis for Assessment of Hydration in Physiological States and Clinical Conditions. In Handbook of Anthropometry: Physical Measures of Human Form in Health and Disease; Preedy, V.R., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 287–305. ISBN 978-1-4419-1787-4. [Google Scholar]
- Piccoli, A.; Rossi, B.; Pillon, L.; Bucciante, G. A New Method for Monitoring Body Fluid Variation by Bioimpedance Analysis: The RXc Graph. Kidney Int. 1994, 46, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Micheli, M.L.; Pagani, L.; Marella, M.; Gulisano, M.; Piccoli, A.; Angelini, F.; Burtscher, M.; Gatterer, H. Bioimpedance and Impedance Vector Patterns as Predictors of League Level in Male Soccer Players. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2014, 9, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campa, F.; Toselli, S.; Mazzilli, M.; Gobbo, L.A.; Coratella, G. Assessment of Body Composition in Athletes: A Narrative Review of Available Methods with Special Reference to Quantitative and Qualitative Bioimpedance Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirwald, R.L.; Baxter-Jones, A.D.G.; Bailey, D.A.; Beunen, G.P. An Assessment of Maturity from Anthropometric Measurements. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2002, 34, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malina, R.M.; Kozieł, S.M. Validation of Maturity Offset in a Longitudinal Sample of Polish Boys. J. Sports Sci. 2014, 32, 424–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drenowatz, C.; Wartha, O.; Klenk, J.; Brandstetter, S.; Wabitsch, M.; Steinacker, J. Differences in Health Behavior, Physical Fitness, and Cardiovascular Risk in Early, Average, and Late Mature Children. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 2013, 25, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingebrigtsen, J.; Brochmann, M.; Castagna, C.; Bradley, P.S.; Ade, J.; Krustrup, P.; Holtermann, A. Relationships between Field Performance Tests in High-Level Soccer Players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germano, M.D.; Mattos, R.S.D.; Sindorf, M.A.G.; Marchetti, P.H.; Verlengia, R.; Lopes, C.R.; Mota, G.R.D.; Crisp, A.H. Effects of Pre-Season Short-Term Daily Undulating Periodized Training on Muscle Strength and Sprint Performance of Under-20 Soccer Players. Int. J. Sport Cult. Sci. 2015, 3, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rampinini, E.; Sassi, A.; Morelli, A.; Mazzoni, S.; Fanchini, M.; Coutts, A.J. Repeated-Sprint Ability in Professional and Amateur Soccer Players. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. Physiol. Appl. Nutr. Metab. 2009, 34, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krustrup, P.; Mohr, M.; Amstrup, T.; Rysgaard, T.; Johansen, J.; Steensberg, A.; Pedersen, P.K.; Bangsbo, J. The Yo-Yo Intermittent Recovery Test: Physiological Response, Reliability, and Validity. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2003, 35, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brustio, P.R.; Lupo, C.; Ungureanu, A.N.; Frati, R.; Rainoldi, A.; Boccia, G. The Relative Age Effect Is Larger in Italian Soccer Top-Level Youth Categories and Smaller in Serie A. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cobley, S.P.; Schorer, J.; Baker, J. Relative Age Effects in Professional German Soccer: A Historical Analysis. J. Sports Sci. 2008, 26, 1531–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.R.; Bottomley, P.A. The Relative Age Effect in European Elite Soccer: A Practical Guide to Poisson Regression Modelling. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, P.; Seabra, A.; Brito, M.; Galvão, M.; Brito, J. Are Soccer and Futsal Affected by the Relative Age Effect? The Portuguese Football Association Case. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 679476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Götze, M.; Hoppe, M.W. Relative Age Effect in Elite German Soccer: Influence of Gender and Competition Level. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 587023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helsen, W.F.; Starkes, J.L.; Van Winckel, J. The Influence of Relative Age on Success and Dropout in Male Soccer Players. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 1998, 10, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helsen, W.F.; Baker, J.; Michiels, S.; Schorer, J.; Van Winckel, J.; Williams, A.M. The Relative Age Effect in European Professional Soccer: Did Ten Years of Research Make Any Difference? J. Sports Sci. 2012, 30, 1665–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, I.P.; Pain, M.T.G. Relative Age Effect in Spanish Association Football: Its Extent and Implications for Wasted Potential. J. Sports Sci. 2008, 26, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lupo, C.; Boccia, G.; Ungureanu, A.N.; Frati, R.; Marocco, R.; Brustio, P.R. The Beginning of Senior Career in Team Sport Is Affected by Relative Age Effect. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujika, I.; Vaeyens, R.; Matthys, S.P.J.; Santisteban, J.; Goiriena, J.; Philippaerts, R. The Relative Age Effect in a Professional Football Club Setting. J. Sports Sci. 2009, 27, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musch, J.; Hay, R. The Relative Age Effect in Soccer: Cross-Cultural Evidence for a Systematic Discrimination against Children Born Late in the Competition Year. Sociol. Sport J. 1999, 16, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rađa, A.; Padulo, J.; Jelaska, I.; Ardigò, L.P.; Fumarco, L. Relative Age Effect and Second-Tiers: No Second Chance for Later-Born Players. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinero, J.J.; Pérez, B.; Burillo, P.; Lesma, M.L. Relative Age Effect in European Professional Football: Analysis by Position. J. Hum. Sport Exerc. 2013, 8, 966–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williams, J.H. Relative Age Effect in Youth Soccer: Analysis of the FIFA U17 World Cup Competition. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2010, 20, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña-González, I.; Fernández-Fernández, J.; Moya-Ramón, M.; Cervelló, E. Relative Age Effect, Biological Maturation, and Coaches’ Efficacy Expectations in Young Male Soccer Players. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2018, 89, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobley, S.; Baker, J.; Wattie, N.; McKenna, J. Annual Age-Grouping and Athlete Development: A Meta-Analytical Review of Relative Age Effects in Sport. Sports Med. 2009, 39, 235–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doncaster, G.; Medina, D.; Drobnic, F.; Gómez-Díaz, A.J.; Unnithan, V. Appreciating Factors Beyond the Physical in Talent Identification and Development: Insights From the FC Barcelona Sporting Model. Front. Sports Act. Living 2020, 2, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovell, R.; Towlson, C.; Parkin, G.; Portas, M.; Vaeyens, R.; Cobley, S. Soccer Player Characteristics in English Lower-League Development Programmes: The Relationships between Relative Age, Maturation, Anthropometry and Physical Fitness. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deprez, D.; Coutts, A.J.; Fransen, J.; Deconinck, F.; Lenoir, M.; Vaeyens, R.; Philippaerts, R. Relative Age, Biological Maturation and Anaerobic Characteristics in Elite Youth Soccer Players. Int. J. Sports Med. 2013, 34, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Müller, L.; Gonaus, C.; Perner, C.; Müller, E.; Raschner, C. Maturity Status Influences the Relative Age Effect in National Top Level Youth Alpine Ski Racing and Soccer. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-González, I.; Javaloyes, A.; Sarabia, J.M.; Moya-Ramón, M. Relative Age-Related Differences between Different Competitive Levels and Field Positions in Young Soccer Players. Res. Sports Med. Print 2021, 29, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, D.; Pérez-González, B.; Raya-González, J.; Fernández-Luna, Á.; Burillo, P.; Lago-Rodríguez, Á. Selection and Promotion Processes Are Not Associated by the Relative Age Effect in an Elite Spanish Soccer Academy. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parr, J.; Winwood, K.; Hodson-Tole, E.; Deconinck, F.J.A.; Hill, J.P.; Teunissen, J.W.; Cumming, S.P. The Main and Interactive Effects of Biological Maturity and Relative Age on Physical Performance in Elite Youth Soccer Players. J. Sports Med. 2020, 2020, e1957636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchheit, M.; Mendez-Villanueva, A. Effects of Age, Maturity and Body Dimensions on Match Running Performance in Highly Trained under-15 Soccer Players. J. Sports Sci. 2014, 32, 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malina, R.M.; Rogol, A.D.; Cumming, S.P.; Coelho e Silva, M.J.; Figueiredo, A.J. Biological Maturation of Youth Athletes: Assessment and Implications. Br. J. Sports Med. 2015, 49, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bongiovanni, T.; Genovesi, F.; Nemmer, M.; Carling, C.; Alberti, G.; Howatson, G. Nutritional Interventions for Reducing the Signs and Symptoms of Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage and Accelerate Recovery in Athletes: Current Knowledge, Practical Application and Future Perspectives. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2020, 120, 1965–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




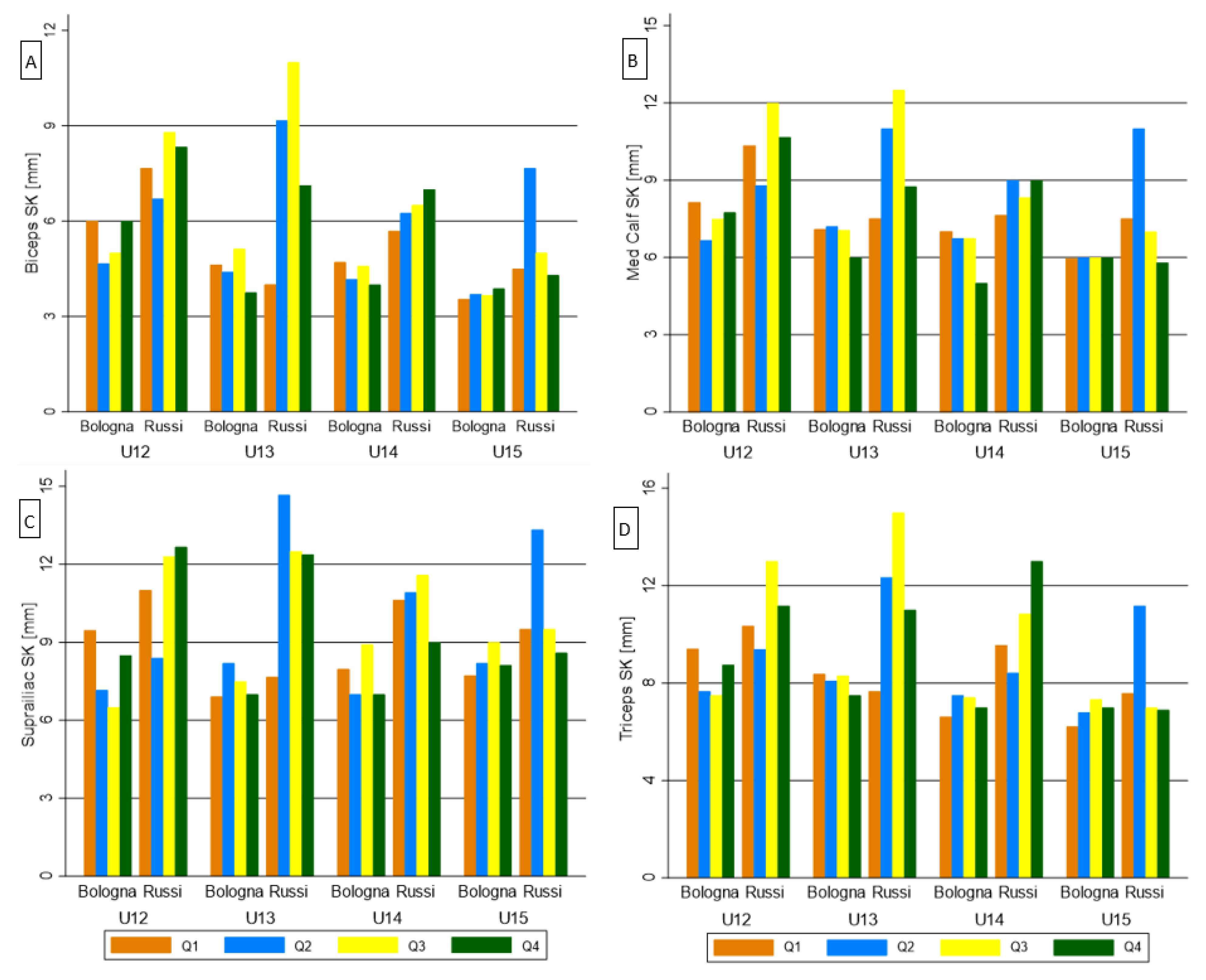



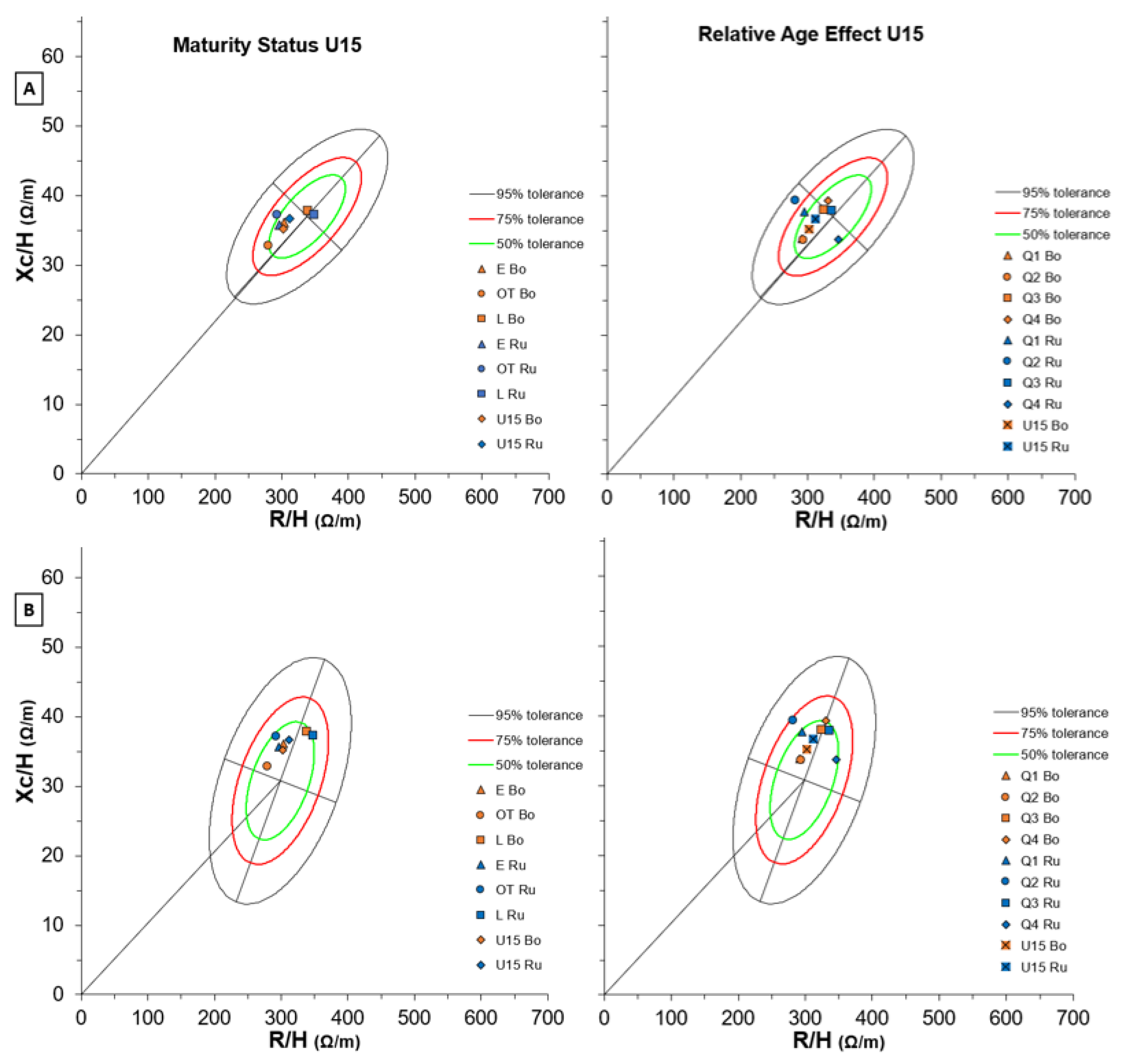
| ∆ Bologna-Russi U12 | ∆ Bologna-Russi U13 | ∆ Bologna-Russi U14 | ∆ Bologna-Russi U15 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maturity | Z or χ2 | p | RR | Z or χ2 | p | RR | Z or χ2 | p | RR | Z or χ2 | p | RR |
| E | 0.232 | 0.817 | 1.067 | 1.065 | 0.287 | 1.556 | −0.423 | 0.6725 | 0.817 | 0.359 | 0.717 | 1.174 |
| L | 0.752 | 0.452 | 1.778 | 1.630 | 0.103 | 2.444 | 0.11 | 0.912 | 1.050 | −0.482 | 0.630 | 0.783 |
| OT | −0.424 | 0.671 | 0.667 | 0.178 | 0.859 | 0.500 | 0.269 | 0.788 | 1.089 | 0.092 | 0.926 | 1.043 |
| Total | 1.263 | 0.532 | 3.871 | 0.144 | 0.181 | 0.913 | 0.2531 | 0.881 | ||||
| RAE | ||||||||||||
| Q1 | 2.505 | 0.012 * | 3.259 | 1.152 | 0.249 | 1.778 | 1.302 | 0.192 | 1.487 | 0.474 | 0.635 | 1.196 |
| Q2 | −1.007 | 0.317 | 0.533 | −0.463 | 0.644 | 0.741 | −0.710 | 0.478 | 0.7 | 0.128 | 0.898 | 1.087 |
| Q3 | −1.449 | 0.147 | 0.355 | 0.856 | 0.392 | 1.778 | −0.710 | 0.478 | 0.7 | 0.626 | 0.531 | 1.956 |
| Q4 | −0.628 | 0.530 | 0.593 | −2.071 | 0.038 * | 0.222 | −0.259 | 0.796 | 0.7 | −1.129 | 0.258 | 0.5 |
| Total | 6.462 | 0.091 | 5.161 | 0.160 | 1.705 | 0.636 | 1.462 | 0.691 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toselli, S.; Mauro, M.; Grigoletto, A.; Cataldi, S.; Benedetti, L.; Nanni, G.; Di Miceli, R.; Aiello, P.; Gallamini, D.; Fischetti, F.; et al. Maturation Selection Biases and Relative Age Effect in Italian Soccer Players of Different Levels. Biology 2022, 11, 1559. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111559
Toselli S, Mauro M, Grigoletto A, Cataldi S, Benedetti L, Nanni G, Di Miceli R, Aiello P, Gallamini D, Fischetti F, et al. Maturation Selection Biases and Relative Age Effect in Italian Soccer Players of Different Levels. Biology. 2022; 11(11):1559. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111559
Chicago/Turabian StyleToselli, Stefania, Mario Mauro, Alessia Grigoletto, Stefania Cataldi, Luca Benedetti, Gianni Nanni, Riccardo Di Miceli, Paolo Aiello, Davide Gallamini, Francesco Fischetti, and et al. 2022. "Maturation Selection Biases and Relative Age Effect in Italian Soccer Players of Different Levels" Biology 11, no. 11: 1559. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111559
APA StyleToselli, S., Mauro, M., Grigoletto, A., Cataldi, S., Benedetti, L., Nanni, G., Di Miceli, R., Aiello, P., Gallamini, D., Fischetti, F., & Greco, G. (2022). Maturation Selection Biases and Relative Age Effect in Italian Soccer Players of Different Levels. Biology, 11(11), 1559. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111559










